1/27/12. Vectors: Outline and Reading. Chapter 6: Vectors, Lists and Sequences. The Vector ADT. Applications of Vectors. Array based Vector: Insertion
|
|
|
- Ross Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chater 6: ectors, Lists ad Sequeces ectors: Outlie ad Readig The ector ADT ( 6.1.1) Array-based imlemetatio ( 6.1.2) Nacy Amato Parasol Lab, Det. CSE, Texas A&M Uiversity Ackowledgemet: These slides are adated from slides rovided with Data Structures ad Algorithms i C++, Goodrich, Tamassia ad Mout (Wiley ) htt://arasol.tamu.edu ectors 2 The ector ADT The ector ADT exteds the otio of array by storig a sequece of arbitrary objects A elemet ca be accessed, iserted or removed by secifyig its rak (umber of elemets recedig it) A excetio is throw if a icorrect rak is secified (e.g., a egative rak) Mai vector oeratios: elematrak(it r): returs the elemet at rak r without removig it relaceatrak(it r, Object o): relace the elemet at rak r with o isertatrak(it r, Object o): isert a ew elemet o to have rak r removeatrak(it r): removes the elemet at rak r Additioal oeratios size() ad isemty() ectors 3 Alicatios of ectors Direct alicatios Sorted collectio of objects (elemetary database) Idirect alicatios Auxiliary data structure for algorithms Comoet of other data structures ectors 4 Array-based ector Use a array of size N A variable kees track of the size of the vector (umber of elemets stored) Oeratio elematrak(r) is imlemeted i O(1) time by returig [r] 0 N-1 ectors 5 Array based ector: Isertio I oeratio isertatrak(r,o) we eed to make room for the ew elemet by shiftig forward the r elemets [r],, [ 1] I the worst case (r = 0), this takes O() time o ectors 6 1
2 Deletio Performace I oeratio removeatrak(r) we eed to fill the hole left by the removed elemet by shiftig backward the r 1 elemets [r + 1],, [ 1] I the worst case (r = 0), this takes O() time o ectors 7 I the array based imlemetatio of a ector The sace used by the data structure is O() Size(), isemty(), elematrak(r) ad relaceatrak(r,o) ru i O(1) time isertatrak(r,o) ad removeatrak(r) ru i O() time If we use the array i a circular fashio, isertatrak(0,o) ad removeatrak(0) ru i O(1) time I a isertatrak(r,o) oeratio, whe the array is full, istead of throwig a excetio, we ca relace the array with a larger oe ectors 8 Exercise: Imlemet the Deque ADT usig ector fuctios Deque fuctios: first(), last(), isertfirst(e), isertlast(e), removefirst (), removelast(), size(), isemty() ector fuctios: elematrak( r), relaceatrak(r,e), isertatrak (r,e), removeatrak(r ), size(), isemty() ectors 9 Exercise Solutio: Imlemet the Deque ADT usig ector fuctios Deque fuctios: first(), last(), isertfirst(e), isertlast(e), removefirst(), removelast(), size(), isemty() ector fuctios: elematrak( r), relaceatrak(r,e), isertatrak(r,e), removeatrak (r ), size(), isemty() Deque fuctio : Realizatio usig ector Fuctios size() ad isemty() fcs ca simly call ector fcs directly first() => elematrak(0) last() => elematrak(size()-1) isertfirst(e) => isertatrak(0,e) isertlast(e) => isertatrak(size(), e) removefirst() => removeatrak(0) removelast() => removeatrak(size()-1) ectors 10 STL vector class Iterators Fuctios i the STL vector class (icomlete) Size(), caacity() - retur #elts i vector, #elts vector ca hold emty() - boolea Oerator[r] - returs referece to elt at rak r (o idex check) At( r) - returs referece to elt at rak r (idex checked) Frot(), back() - retur refereces to first/last elts ush_back(e) - isert e at ed of vector o_back() - remove last elt vector() - creates a vector of size Similarities & Differeces with book s ector ADT STL assigmet v[r]=e is equivalet to v.relaceatrak(r,e) No direct STL couerarts of isertatrak( r) & removeatrak( r) STL also rovides more geeratl fcs for isertig & removig from arbitrary ositios i the vector - these use iterators ectors 11 A iterator abstracts the rocess of scaig through a collectio of elemets Methods of the ObjectIterator ADT: boolea hasnext() object ext() reset() Exteds the cocet of ositio by addig a traversal caability May be imlemeted with a array or sigly liked list A iterator is tyically associated with a aother data structure We ca augmet the Stack, Queue, ector, ad other cotaier ADTs with method: ObjectIterator elemets() Two otios of iterator: sashot: freezes the cotets of the data structure at a give time dyamic: follows chages to the data structure ectors 12 2
3 Iterators Some fuctios suorted by STL cotaiers Begi(), ed() - retur iterators to begiig or ed of cotaier Isert(I,e) - isert e just before the ositio idicated by iterator I (aalogous to our isertbefore()) Erase(I) - removes the elt at the ositio idicated by I (aalogous to our remove()) The fuctios ca be used to isert/remove elts from arbitrary ositios i the STL vector ad list ector Summary ector Oeratio Comlexity for Differet Imlemetatios RemoveAtRak(r), IsertAtRak(r,o) elematrak(r), RelaceAtRak(r,o) Array Fixed-Size or Exadable O(1) Best Case (r=0,) O() Worst Case O() Average Case O(1)? Size(), isemty() O(1)? List Sigly or Doubly Liked? ectors 13 ectors 14 Outlie ad Readig Lists ad Sequeces Sigly liked list Positio ADT ( 6.2.1) List ADT ( 6.2.2) Doubly liked list ( 6.2.3) Sequece ADT ( 6.3.1) Imlemetatios of the sequece ADT ( ) Iterators ( 6.2.5) ectors 15 1/27/12 04:04 ectors 16 Positio ADT List ADT ( 5.2.2) The Positio ADT models the otio of lace withi a data structure where a sigle object is stored A secial ull ositio refers to o object. Positios rovide a uified view of diverse ways of storig data, such as a cell of a array a ode of a liked list Member fuctios: Object& elemet(): returs the elemet stored at this ositio bool isnull(): returs true if this is a ull ositio ectors 17 The List ADT models a sequece of ositios storig arbitrary objects establishes a before/after relatio betwee ositios It allows for isertio ad removal i the middle Query methods: isfirst(), islast() Geeric methods: size(), isemty() Accessor methods: first(), last() before(), after() Udate methods: relaceelemet(, o), swaelemets(, q) isertbefore(, o), isertafter(, o), isertfirst(o), isertlast(o) remove() 18 3
4 List ADT List ADT Query methods: isfirst(), islast() : retur boolea idicatig if the give ositio is the first or last, res. Accessor methods first(), last(): retur the ositio of the first or last, res., elemet of S a error occurs if S is emty before(), after(): retur the ositio of the elemet of S recedig or followig, res, the oe at ositio a error occurs if S is emty, or is the first or last, res., ositio ectors 19 Udate Methods relaceelemet(, o) Relace the elemet at ositio with e swaelemets(, q) Swa the elemets stored at ositios & q isertbefore(, o), isertafter(, o), Isert a ew elemet o ito S before or after, res., ositio Outut: ositio of the ewly iserted elemet isertfirst(o), isertlast(o) Isert a ew elemet o ito S as the first or last, res., elemet Outut: ositio of the ewly iserted elemet remove() Remove the elemet at ositio from S ectors 20 Exercise: Describe how to imlemet the followig list ADT oeratios usig a sigly-liked list list ADT oeratios: first(), last(), before(), after() For each oeratio, exlai how it is imlemeted ad rovide the ruig time A sigly liked list cocrete data structure cosists of a sequece of odes Each ode stores elemet lik to the ext ode elem ext ode A B C D ectors 1/27/ :58 Exercise: Describe how to imlemet the followig list ADT oeratios usig a doubly-liked list list ADT oeratios: first(), last(), before(), after() For each oeratio, exlai how it is imlemeted ad rovide the ruig time Doubly-Liked List Nodes imlemet Positio ad store: elemet header lik to revious ode lik to ext ode Secial trailer ad header odes rev elem ext ode trailer elemets ectors 1/27/ :58 Isertio Deletio We visualize oeratio isertafter(, X) which returs ositio q We visualize remove(), where = last() A B C A B C D A B q C A B C q X D A B X C ectors 23 A B C ectors 24 4
5 Performace I the imlemetatio of the List ADT by meas of a doubly liked list The sace used by a list with elemets is O() The sace used by each ositio of the list is O(1) All the oeratios of the List ADT ru i O(1) time Oeratio elemet() of the Positio ADT rus i O(1) time STL list class Fuctios i the STL list class Size() - retur #elts i list, emty() - boolea Frot(), back() - retur refereces to first/last elts Push_frot(e), ush_back(e) - isert e at frot/ed Po_frot(), o_back() - remove first/last elt List() - creates a emty list Similarities & Differeces with book s List ADT STL frot() & back() corresod to first() & last() excet the STL fuctios retur the elemet & ot its ositio STL ush() & o() are equiv to List ADT isert ad remove whe alied to the begiig & ed of the list STL also rovides fcs for isertig & removig from arbitrary ositios i the list - these use iterators ectors 25 ectors 26 List Summary List Oeratio Comlexity for differet imlemetatios first(), last(), after() isertafter(,o), relaceelemet(,o), swaelemets(,q) before(), isertbefore(,o), remove() List Sigly-Liked O(1) O() WC & AC O(1) BC List Doubly- Liked O(1) O(1) Size(), isemty() O(1) O(1) ectors 27 Sequece ADT The Sequece ADT is the uio of the ector ad List ADTs Elemets accessed by Rak, or Positio Geeric methods: size(), isemty() ector-based methods: elematrak(r), relaceatrak(r, o), isertatrak(r, o), removeatrak(r) List-based methods: first(), last(), before(), after(), relaceelemet(, o), swaelemets(, q), isertbefore(, o), isertafter(, o), isertfirst(o), isertlast (o), remove() Bridge methods: atrak(r), rakof() ectors 28 Alicatios of Sequeces Array-based Imlemetatio The Sequece ADT is a basic, geeralurose, data structure for storig a ordered collectio of elemets Direct alicatios: Geeric relacemet for stack, queue, vector, or list small database (e.g., address book) Idirect alicatios: Buildig block of more comlex data structures ectors 29 We use a circular array storig ositios A ositio object stores: Elemet Rak Idices f ad l kee track of first ad last ositios S f elemets ositios ectors 30 l 5
6 Sequece Imlemetatios Oeratio Array List size, isemty 1 1 atrak, rakof, elematrak 1 first, last, before, after 1 1 relaceelemet, swaelemets 1 1 relaceatrak 1 isertatrak, removeatrak isertfirst, isertlast 1 1 isertafter, isertbefore 1 remove 1 ectors 31 6
Elementary Data Structures. The Stack ADT ( 2.1.1) Applications of Stacks. Stacks, Queues, Vectors, Lists & Sequences Trees
 Elemetary Data Structures Stacks, Queues, ectors, Lists & Sequeces Trees The Stack ADT ( 2..) The Stack ADT stores arbitrary objects Isertios ad deletios follow the last-i first-out scheme Thik of a sprig-loaded
Elemetary Data Structures Stacks, Queues, ectors, Lists & Sequeces Trees The Stack ADT ( 2..) The Stack ADT stores arbitrary objects Isertios ad deletios follow the last-i first-out scheme Thik of a sprig-loaded
! Given the following Structure: ! We can define a pointer to a structure. ! Now studentptr points to the s1 structure.
 Liked Lists Uit 5 Sectios 11.9 & 18.1-2 CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seama 11.9: Poiters to Structures! Give the followig Structure: struct Studet { strig ame; // Studet s ame it idnum; // Studet ID umber it
Liked Lists Uit 5 Sectios 11.9 & 18.1-2 CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seama 11.9: Poiters to Structures! Give the followig Structure: struct Studet { strig ame; // Studet s ame it idnum; // Studet ID umber it
Heaps. Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 201 Heaps 201 Goodrich ad Tamassia xkcd. http://xkcd.com/83/. Tree. Used with permissio uder
Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 201 Heaps 201 Goodrich ad Tamassia xkcd. http://xkcd.com/83/. Tree. Used with permissio uder
CH 6 : VECTORS, LISTS AND SEQUENCES
 CH 6 : VECTORS, LISTS AND SEQUENCES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM
CH 6 : VECTORS, LISTS AND SEQUENCES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM
CH 6. VECTORS, LISTS, AND SEQUENCES
 CH 6. VECTORS, LISTS, AND SEQUENCES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM
CH 6. VECTORS, LISTS, AND SEQUENCES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM
Linked Lists 11/16/18. Preliminaries. Java References. Objects and references. Self references. Linking self-referential nodes
 Prelimiaries Liked Lists public class StrageObject { Strig ame; StrageObject other; Arrays are ot always the optimal data structure: A array has fixed size eeds to be copied to expad its capacity Addig
Prelimiaries Liked Lists public class StrageObject { Strig ame; StrageObject other; Arrays are ot always the optimal data structure: A array has fixed size eeds to be copied to expad its capacity Addig
CH 6 : VECTORS, LISTS AND SEQUENCES
 CH 6 : VECTORS, LISTS AND SEQUENCES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM
CH 6 : VECTORS, LISTS AND SEQUENCES ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM
Priority Queues. Binary Heaps
 Priority Queues Biary Heaps Priority Queues Priority: some property of a object that allows it to be prioritized with respect to other objects of the same type Mi Priority Queue: homogeeous collectio of
Priority Queues Biary Heaps Priority Queues Priority: some property of a object that allows it to be prioritized with respect to other objects of the same type Mi Priority Queue: homogeeous collectio of
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks, Queues, and Heaps Monday, February 18 / Tuesday, February 19
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
Hash Tables. Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015.
 Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Hash Tables xkcd. http://xkcd.com/221/. Radom Number. Used with permissio uder Creative
Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Hash Tables xkcd. http://xkcd.com/221/. Radom Number. Used with permissio uder Creative
Computers and Scientific Thinking
 Computers ad Scietific Thikig David Reed, Creighto Uiversity Chapter 15 JavaScript Strigs 1 Strigs as Objects so far, your iteractive Web pages have maipulated strigs i simple ways use text box to iput
Computers ad Scietific Thikig David Reed, Creighto Uiversity Chapter 15 JavaScript Strigs 1 Strigs as Objects so far, your iteractive Web pages have maipulated strigs i simple ways use text box to iput
Homework 1 Solutions MA 522 Fall 2017
 Homework 1 Solutios MA 5 Fall 017 1. Cosider the searchig problem: Iput A sequece of umbers A = [a 1,..., a ] ad a value v. Output A idex i such that v = A[i] or the special value NIL if v does ot appear
Homework 1 Solutios MA 5 Fall 017 1. Cosider the searchig problem: Iput A sequece of umbers A = [a 1,..., a ] ad a value v. Output A idex i such that v = A[i] or the special value NIL if v does ot appear
Computer Science Foundation Exam. August 12, Computer Science. Section 1A. No Calculators! KEY. Solutions and Grading Criteria.
 Computer Sciece Foudatio Exam August, 005 Computer Sciece Sectio A No Calculators! Name: SSN: KEY Solutios ad Gradig Criteria Score: 50 I this sectio of the exam, there are four (4) problems. You must
Computer Sciece Foudatio Exam August, 005 Computer Sciece Sectio A No Calculators! Name: SSN: KEY Solutios ad Gradig Criteria Score: 50 I this sectio of the exam, there are four (4) problems. You must
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Miimum Spaig Trees Miimum Spaig Trees Spaig subgraph Subgraph of a graph G cotaiig all the vertices of G Spaig tree Spaig subgraph that is itself a (free) tree Miimum spaig tree (MST) Spaig tree of a weighted
Miimum Spaig Trees Miimum Spaig Trees Spaig subgraph Subgraph of a graph G cotaiig all the vertices of G Spaig tree Spaig subgraph that is itself a (free) tree Miimum spaig tree (MST) Spaig tree of a weighted
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks and Queues Monday, February 12 / Tuesday, February 13
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 08 Stacks ad Queues Moday, February / Tuesday, February Learig Goals Durig this lab, you will: Review stacks ad queues. Lear amortized ruig time aalysis
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 08 Stacks ad Queues Moday, February / Tuesday, February Learig Goals Durig this lab, you will: Review stacks ad queues. Lear amortized ruig time aalysis
1/18/12. Chapter 5: Stacks, Queues and Deques. Stacks. Outline and Reading. Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University
 Chapter 5: Stacks, ueues and Deques Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, Goodrich,
Chapter 5: Stacks, ueues and Deques Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, Goodrich,
A NOTE ON COARSE GRAINED PARALLEL INTEGER SORTING
 Chater 26 A NOTE ON COARSE GRAINED PARALLEL INTEGER SORTING A. Cha ad F. Dehe School of Comuter Sciece Carleto Uiversity Ottawa, Caada K1S 5B6 æ {acha,dehe}@scs.carleto.ca Abstract Keywords: We observe
Chater 26 A NOTE ON COARSE GRAINED PARALLEL INTEGER SORTING A. Cha ad F. Dehe School of Comuter Sciece Carleto Uiversity Ottawa, Caada K1S 5B6 æ {acha,dehe}@scs.carleto.ca Abstract Keywords: We observe
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Miimum Spaig Trees 0 Goodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig a Network Suppose
Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Miimum Spaig Trees 0 Goodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig a Network Suppose
CIS 121. Introduction to Trees
 CIS 121 Itroductio to Trees 1 Tree ADT Tree defiitio q A tree is a set of odes which may be empty q If ot empty, the there is a distiguished ode r, called root ad zero or more o-empty subtrees T 1, T 2,
CIS 121 Itroductio to Trees 1 Tree ADT Tree defiitio q A tree is a set of odes which may be empty q If ot empty, the there is a distiguished ode r, called root ad zero or more o-empty subtrees T 1, T 2,
Chapter 8. Strings and Vectors. Copyright 2014 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 8 Strigs ad Vectors Overview 8.1 A Array Type for Strigs 8.2 The Stadard strig Class 8.3 Vectors Slide 8-3 8.1 A Array Type for Strigs A Array Type for Strigs C-strigs ca be used to represet strigs
Chapter 8 Strigs ad Vectors Overview 8.1 A Array Type for Strigs 8.2 The Stadard strig Class 8.3 Vectors Slide 8-3 8.1 A Array Type for Strigs A Array Type for Strigs C-strigs ca be used to represet strigs
University of Waterloo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 250 Algorithms and Data Structures
 Uiversity of Waterloo Departmet of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig ECE 250 Algorithms ad Data Structures Midterm Examiatio ( pages) Istructor: Douglas Harder February 7, 2004 7:30-9:00 Name (last, first)
Uiversity of Waterloo Departmet of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig ECE 250 Algorithms ad Data Structures Midterm Examiatio ( pages) Istructor: Douglas Harder February 7, 2004 7:30-9:00 Name (last, first)
top() Applications of Stacks
 CS22 Algorithms ad Data Structures MW :00 am - 2: pm, MSEC 0 Istructor: Xiao Qi Lecture 6: Stacks ad Queues Aoucemets Quiz results Homework 2 is available Due o September 29 th, 2004 www.cs.mt.edu~xqicoursescs22
CS22 Algorithms ad Data Structures MW :00 am - 2: pm, MSEC 0 Istructor: Xiao Qi Lecture 6: Stacks ad Queues Aoucemets Quiz results Homework 2 is available Due o September 29 th, 2004 www.cs.mt.edu~xqicoursescs22
Chapter 11. Friends, Overloaded Operators, and Arrays in Classes. Copyright 2014 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 11 Frieds, Overloaded Operators, ad Arrays i Classes Copyright 2014 Pearso Addiso-Wesley. All rights reserved. Overview 11.1 Fried Fuctios 11.2 Overloadig Operators 11.3 Arrays ad Classes 11.4
Chapter 11 Frieds, Overloaded Operators, ad Arrays i Classes Copyright 2014 Pearso Addiso-Wesley. All rights reserved. Overview 11.1 Fried Fuctios 11.2 Overloadig Operators 11.3 Arrays ad Classes 11.4
Data Structures Week #9. Sorting
 Data Structures Week #9 Sortig Outlie Motivatio Types of Sortig Elemetary (O( 2 )) Sortig Techiques Other (O(*log())) Sortig Techiques 21.Aralık.2010 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Sortig 21.Aralık.2010 Boraha
Data Structures Week #9 Sortig Outlie Motivatio Types of Sortig Elemetary (O( 2 )) Sortig Techiques Other (O(*log())) Sortig Techiques 21.Aralık.2010 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Sortig 21.Aralık.2010 Boraha
Chapter 8. Strings and Vectors. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 8 Strigs ad Vectors Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 8.1 A Array Type for Strigs 8.2 The Stadard strig Class 8.3 Vectors Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd..
Chapter 8 Strigs ad Vectors Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 8.1 A Array Type for Strigs 8.2 The Stadard strig Class 8.3 Vectors Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd..
Overview. Common tasks. Observation. Chapter 20 The STL (containers, iterators, and algorithms) 8/13/18. Bjarne Stroustrup
 Overview Chapter 20 The STL (cotaiers, iterators, ad algorithms) Bjare Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programmig Commo tasks ad ideals Geeric programmig Cotaiers, algorithms, ad iterators The simplest algorithm:
Overview Chapter 20 The STL (cotaiers, iterators, ad algorithms) Bjare Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programmig Commo tasks ad ideals Geeric programmig Cotaiers, algorithms, ad iterators The simplest algorithm:
Minimum Spanning Trees. Application: Connecting a Network
 Miimum Spaig Tree // : Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. oodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, Miimum Spaig Trees oodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig
Miimum Spaig Tree // : Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. oodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, Miimum Spaig Trees oodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig
The Magma Database file formats
 The Magma Database file formats Adrew Gaylard, Bret Pikey, ad Mart-Mari Breedt Johaesburg, South Africa 15th May 2006 1 Summary Magma is a ope-source object database created by Chris Muller, of Kasas City,
The Magma Database file formats Adrew Gaylard, Bret Pikey, ad Mart-Mari Breedt Johaesburg, South Africa 15th May 2006 1 Summary Magma is a ope-source object database created by Chris Muller, of Kasas City,
Lecture 28: Data Link Layer
 Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) 2. Go ack N ARQ Although the Stop ad Wait ARQ is very simple, you ca easily show that it has very the low efficiecy. The low efficiecy comes from the fact that the trasmittig
Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) 2. Go ack N ARQ Although the Stop ad Wait ARQ is very simple, you ca easily show that it has very the low efficiecy. The low efficiecy comes from the fact that the trasmittig
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity
 Time CSE 47: Algorithms ad Computatioal Readig assigmet Read Chapter of The ALGORITHM Desig Maual Aalysis & Sortig Autum 00 Paul Beame aalysis Problem size Worst-case complexity: max # steps algorithm
Time CSE 47: Algorithms ad Computatioal Readig assigmet Read Chapter of The ALGORITHM Desig Maual Aalysis & Sortig Autum 00 Paul Beame aalysis Problem size Worst-case complexity: max # steps algorithm
Chapter 10. Defining Classes. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Defiig Classes Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 10.1 Structures 10.2 Classes 10.3 Abstract Data Types 10.4 Itroductio to Iheritace Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio,
Chapter 10 Defiig Classes Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 10.1 Structures 10.2 Classes 10.3 Abstract Data Types 10.4 Itroductio to Iheritace Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio,
DATA STRUCTURES. amortized analysis binomial heaps Fibonacci heaps union-find. Data structures. Appetizer. Appetizer
 Data structures DATA STRUCTURES Static problems. Give a iput, produce a output. Ex. Sortig, FFT, edit distace, shortest paths, MST, max-flow,... amortized aalysis biomial heaps Fiboacci heaps uio-fid Dyamic
Data structures DATA STRUCTURES Static problems. Give a iput, produce a output. Ex. Sortig, FFT, edit distace, shortest paths, MST, max-flow,... amortized aalysis biomial heaps Fiboacci heaps uio-fid Dyamic
Lists and Sequences. 1/18/2005 4:12 AM Sequences 1
 Lists and Sequences /8/2005 4:2 AM Sequences Outline and Reading Singly linked list Position ADT and List ADT ( 2.2.2) Doubly linked list ( 2.2.2) Sequence ADT ( 2.2.3) Implementations of the sequence
Lists and Sequences /8/2005 4:2 AM Sequences Outline and Reading Singly linked list Position ADT and List ADT ( 2.2.2) Doubly linked list ( 2.2.2) Sequence ADT ( 2.2.3) Implementations of the sequence
Chapter 9. Pointers and Dynamic Arrays. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Poiters ad Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 9.1 Poiters 9.2 Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Slide 9-3
Chapter 9 Poiters ad Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 9.1 Poiters 9.2 Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Slide 9-3
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) Stacks. The Stack ADT ( 4.2) Stack Interface in Java
 Abstract Data Types (ADTs) tacks A abstract data type (ADT) is a abstractio of a data structure A ADT specifies: Data stored Operatios o the data Error coditios associated with operatios Example: ADT modelig
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) tacks A abstract data type (ADT) is a abstractio of a data structure A ADT specifies: Data stored Operatios o the data Error coditios associated with operatios Example: ADT modelig
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science
 Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 6 Defiig Fuctios Pytho Programmig, 2/e 1 Objectives To uderstad why programmers divide programs up ito sets of cooperatig fuctios. To be able to
Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 6 Defiig Fuctios Pytho Programmig, 2/e 1 Objectives To uderstad why programmers divide programs up ito sets of cooperatig fuctios. To be able to
CH7. LIST AND ITERATOR ADTS
 CH7. LIST AND ITERATOR ADTS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) LIST ADT EXAMPLE A
CH7. LIST AND ITERATOR ADTS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) LIST ADT EXAMPLE A
Solution printed. Do not start the test until instructed to do so! CS 2604 Data Structures Midterm Spring, Instructions:
 CS 604 Data Structures Midterm Sprig, 00 VIRG INIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE U T PROSI M UNI VERSI TY Istructios: Prit your ame i the space provided below. This examiatio is closed book ad closed
CS 604 Data Structures Midterm Sprig, 00 VIRG INIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE U T PROSI M UNI VERSI TY Istructios: Prit your ame i the space provided below. This examiatio is closed book ad closed
Pseudocode ( 1.1) Analysis of Algorithms. Primitive Operations. Pseudocode Details. Running Time ( 1.1) Estimating performance
 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
n The C++ template facility provides the ability to define n A generic facility allows code to be written once then
 UCLA PIC 10 B Problem Solvig usig C++ Programmig Ivo Diov, Asst. Prof. i Mathematics, Neurology, Statistics Istructor: Teachig Assistat: Suzae Nezzar, Mathematics Chapter 13 Templates for More Abstractio
UCLA PIC 10 B Problem Solvig usig C++ Programmig Ivo Diov, Asst. Prof. i Mathematics, Neurology, Statistics Istructor: Teachig Assistat: Suzae Nezzar, Mathematics Chapter 13 Templates for More Abstractio
CS 11 C track: lecture 1
 CS 11 C track: lecture 1 Prelimiaries Need a CMS cluster accout http://acctreq.cms.caltech.edu/cgi-bi/request.cgi Need to kow UNIX IMSS tutorial liked from track home page Track home page: http://courses.cms.caltech.edu/courses/cs11/material
CS 11 C track: lecture 1 Prelimiaries Need a CMS cluster accout http://acctreq.cms.caltech.edu/cgi-bi/request.cgi Need to kow UNIX IMSS tutorial liked from track home page Track home page: http://courses.cms.caltech.edu/courses/cs11/material
islerp: An Incremental Approach to Slerp
 isler: A Icremetal Aroach to Sler Xi Li Comuter Sciece Deartmet Digie Istitute of Techology xli@digie.edu Abstract I this aer, a icremetal uaterio iterolatio algorithm is itroduced. With the assumtio of
isler: A Icremetal Aroach to Sler Xi Li Comuter Sciece Deartmet Digie Istitute of Techology xli@digie.edu Abstract I this aer, a icremetal uaterio iterolatio algorithm is itroduced. With the assumtio of
Exercise Set: Implementing an Object-Oriented Design
 Exercise Set: Implemetig a Object-Orieted Desig I this exercise set, we have marked questios we thik are harder tha others with a [ ]. We have also marked questios for which solutios are provided at the
Exercise Set: Implemetig a Object-Orieted Desig I this exercise set, we have marked questios we thik are harder tha others with a [ ]. We have also marked questios for which solutios are provided at the
Applications of Stacks
 Lists ad Iterators 8// Presetatio for use with the textbook lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, h ata Structures xkcd Seve http://xkcd.com// Used with permissio uder reative
Lists ad Iterators 8// Presetatio for use with the textbook lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, h ata Structures xkcd Seve http://xkcd.com// Used with permissio uder reative
Chapter 24. Sorting. Objectives. 1. To study and analyze time efficiency of various sorting algorithms
 Chapter 4 Sortig 1 Objectives 1. o study ad aalyze time efficiecy of various sortig algorithms 4. 4.7.. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze bubble sort 4.. 3. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze merge sort 4.3. 4. o
Chapter 4 Sortig 1 Objectives 1. o study ad aalyze time efficiecy of various sortig algorithms 4. 4.7.. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze bubble sort 4.. 3. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze merge sort 4.3. 4. o
Lists and Sequences. 1/22/ :32 PM Sequences 1
 Lists and Sequences 1/22/2018 10:32 PM Sequences 1 Outline Singly linked list Position ADT and List ADT Doubly linked list Sequence ADT Implementations of the sequence ADT Iterators 1/22/2018 10:32 PM
Lists and Sequences 1/22/2018 10:32 PM Sequences 1 Outline Singly linked list Position ADT and List ADT Doubly linked list Sequence ADT Implementations of the sequence ADT Iterators 1/22/2018 10:32 PM
Vectors. 9/14/2007 2:55 PM Vectors 1
 Vectors 9/4/2007 2:55 PM Vectors Outline and Reading The Vector ADT ( 5..) Array-based implementation ( 5..2) 9/4/2007 2:55 PM Vectors 2 The Vector ADT The Vector ADT stores objects to which it provides
Vectors 9/4/2007 2:55 PM Vectors Outline and Reading The Vector ADT ( 5..) Array-based implementation ( 5..2) 9/4/2007 2:55 PM Vectors 2 The Vector ADT The Vector ADT stores objects to which it provides
Sorting in Linear Time. Data Structures and Algorithms Andrei Bulatov
 Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Graphs. Minimum Spanning Trees. Slides by Rose Hoberman (CMU)
 Graphs Miimum Spaig Trees Slides by Rose Hoberma (CMU) Problem: Layig Telephoe Wire Cetral office 2 Wirig: Naïve Approach Cetral office Expesive! 3 Wirig: Better Approach Cetral office Miimize the total
Graphs Miimum Spaig Trees Slides by Rose Hoberma (CMU) Problem: Layig Telephoe Wire Cetral office 2 Wirig: Naïve Approach Cetral office Expesive! 3 Wirig: Better Approach Cetral office Miimize the total
Lower Bounds for Sorting
 Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
Examples and Applications of Binary Search
 Toy Gog ITEE Uiersity of Queeslad I the secod lecture last week we studied the biary search algorithm that soles the problem of determiig if a particular alue appears i a sorted list of iteger or ot. We
Toy Gog ITEE Uiersity of Queeslad I the secod lecture last week we studied the biary search algorithm that soles the problem of determiig if a particular alue appears i a sorted list of iteger or ot. We
CMPT 125 Assignment 2 Solutions
 CMPT 25 Assigmet 2 Solutios Questio (20 marks total) a) Let s cosider a iteger array of size 0. (0 marks, each part is 2 marks) it a[0]; I. How would you assig a poiter, called pa, to store the address
CMPT 25 Assigmet 2 Solutios Questio (20 marks total) a) Let s cosider a iteger array of size 0. (0 marks, each part is 2 marks) it a[0]; I. How would you assig a poiter, called pa, to store the address
why study sorting? Sorting is a classic subject in computer science. There are three reasons for studying sorting algorithms.
 Chapter 5 Sortig IST311 - CIS65/506 Clevelad State Uiversity Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Itroductio to Java Programmig: Comprehesive Versio, Eighth Editio by Y. Daiel Liag why study sortig? Sortig
Chapter 5 Sortig IST311 - CIS65/506 Clevelad State Uiversity Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Itroductio to Java Programmig: Comprehesive Versio, Eighth Editio by Y. Daiel Liag why study sortig? Sortig
. Written in factored form it is easy to see that the roots are 2, 2, i,
 CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
Sorting 9/15/2009. Sorting Problem. Insertion Sort: Soundness. Insertion Sort. Insertion Sort: Running Time. Insertion Sort: Soundness
 9/5/009 Algorithms Sortig 3- Sortig Sortig Problem The Sortig Problem Istace: A sequece of umbers Objective: A permutatio (reorderig) such that a ' K a' a, K,a a ', K, a' of the iput sequece The umbers
9/5/009 Algorithms Sortig 3- Sortig Sortig Problem The Sortig Problem Istace: A sequece of umbers Objective: A permutatio (reorderig) such that a ' K a' a, K,a a ', K, a' of the iput sequece The umbers
Analysis of Algorithms
 Aalysis of Algorithms Ruig Time of a algorithm Ruig Time Upper Bouds Lower Bouds Examples Mathematical facts Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite
Aalysis of Algorithms Ruig Time of a algorithm Ruig Time Upper Bouds Lower Bouds Examples Mathematical facts Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite
CS211 Fall 2003 Prelim 2 Solutions and Grading Guide
 CS11 Fall 003 Prelim Solutios ad Gradig Guide Problem 1: (a) obj = obj1; ILLEGAL because type of referece must always be a supertype of type of object (b) obj3 = obj1; ILLEGAL because type of referece
CS11 Fall 003 Prelim Solutios ad Gradig Guide Problem 1: (a) obj = obj1; ILLEGAL because type of referece must always be a supertype of type of object (b) obj3 = obj1; ILLEGAL because type of referece
Lecture Notes 6 Introduction to algorithm analysis CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming
 Lecture Notes 6 Itroductio to algorithm aalysis CSS 501 Data Structures ad Object-Orieted Programmig Readig for this lecture: Carrao, Chapter 10 To be covered i this lecture: Itroductio to algorithm aalysis
Lecture Notes 6 Itroductio to algorithm aalysis CSS 501 Data Structures ad Object-Orieted Programmig Readig for this lecture: Carrao, Chapter 10 To be covered i this lecture: Itroductio to algorithm aalysis
Classes and Objects. Again: Distance between points within the first quadrant. José Valente de Oliveira 4-1
 Classes ad Objects jvo@ualg.pt José Valete de Oliveira 4-1 Agai: Distace betwee poits withi the first quadrat Sample iput Sample output 1 1 3 4 2 jvo@ualg.pt José Valete de Oliveira 4-2 1 The simplest
Classes ad Objects jvo@ualg.pt José Valete de Oliveira 4-1 Agai: Distace betwee poits withi the first quadrat Sample iput Sample output 1 1 3 4 2 jvo@ualg.pt José Valete de Oliveira 4-2 1 The simplest
Data Structures and Algorithms Part 1.4
 1 Data Structures ad Algorithms Part 1.4 Werer Nutt 2 DSA, Part 1: Itroductio, syllabus, orgaisatio Algorithms Recursio (priciple, trace, factorial, Fiboacci) Sortig (bubble, isertio, selectio) 3 Sortig
1 Data Structures ad Algorithms Part 1.4 Werer Nutt 2 DSA, Part 1: Itroductio, syllabus, orgaisatio Algorithms Recursio (priciple, trace, factorial, Fiboacci) Sortig (bubble, isertio, selectio) 3 Sortig
Data Structures and Algorithms. Analysis of Algorithms
 Data Structures ad Algorithms Aalysis of Algorithms Outlie Ruig time Pseudo-code Big-oh otatio Big-theta otatio Big-omega otatio Asymptotic algorithm aalysis Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output
Data Structures ad Algorithms Aalysis of Algorithms Outlie Ruig time Pseudo-code Big-oh otatio Big-theta otatio Big-omega otatio Asymptotic algorithm aalysis Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output
Solutions to Final COMS W4115 Programming Languages and Translators Monday, May 4, :10-5:25pm, 309 Havemeyer
 Departmet of Computer ciece Columbia Uiversity olutios to Fial COM W45 Programmig Laguages ad Traslators Moday, May 4, 2009 4:0-5:25pm, 309 Havemeyer Closed book, o aids. Do questios 5. Each questio is
Departmet of Computer ciece Columbia Uiversity olutios to Fial COM W45 Programmig Laguages ad Traslators Moday, May 4, 2009 4:0-5:25pm, 309 Havemeyer Closed book, o aids. Do questios 5. Each questio is
Graph Terminology and Representations
 Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Graph Termiology ad Represetatios 2015 Goodrich ad Tamassia Graphs 1 Graphs A graph is
Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Graph Termiology ad Represetatios 2015 Goodrich ad Tamassia Graphs 1 Graphs A graph is
Basic allocator mechanisms The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory Management II: Dynamic Storage Allocation Mar 6, 2000.
 5-23 The course that gives CM its Zip Memory Maagemet II: Dyamic Storage Allocatio Mar 6, 2000 Topics Segregated lists Buddy system Garbage collectio Mark ad Sweep Copyig eferece coutig Basic allocator
5-23 The course that gives CM its Zip Memory Maagemet II: Dyamic Storage Allocatio Mar 6, 2000 Topics Segregated lists Buddy system Garbage collectio Mark ad Sweep Copyig eferece coutig Basic allocator
n n B. How many subsets of C are there of cardinality n. We are selecting elements for such a
 4. [10] Usig a combiatorial argumet, prove that for 1: = 0 = Let A ad B be disjoit sets of cardiality each ad C = A B. How may subsets of C are there of cardiality. We are selectig elemets for such a subset
4. [10] Usig a combiatorial argumet, prove that for 1: = 0 = Let A ad B be disjoit sets of cardiality each ad C = A B. How may subsets of C are there of cardiality. We are selectig elemets for such a subset
Chapter 2. C++ Basics. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 2 C++ Basics Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 2.1 Variables ad Assigmets 2.2 Iput ad Output 2.3 Data Types ad Expressios 2.4 Simple Flow of Cotrol 2.5 Program
Chapter 2 C++ Basics Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 2.1 Variables ad Assigmets 2.2 Iput ad Output 2.3 Data Types ad Expressios 2.4 Simple Flow of Cotrol 2.5 Program
Analysis of Algorithms
 Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput 2015 Goodrich ad Tamassia Algorithm Aalysis of Algorithms
Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput 2015 Goodrich ad Tamassia Algorithm Aalysis of Algorithms
Lists ADT and Iterators
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Lists ADT and Iterators 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia,
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Lists ADT and Iterators 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia,
quality/quantity peak time/ratio
 Semi-Heap ad Its Applicatios i Touramet Rakig Jie Wu Departmet of omputer Sciece ad Egieerig Florida Atlatic Uiversity oca Rato, FL 3343 jie@cse.fau.edu September, 00 . Itroductio ad Motivatio. relimiaries
Semi-Heap ad Its Applicatios i Touramet Rakig Jie Wu Departmet of omputer Sciece ad Egieerig Florida Atlatic Uiversity oca Rato, FL 3343 jie@cse.fau.edu September, 00 . Itroductio ad Motivatio. relimiaries
Contrace: Traceroute Facility for Content- Centric Network
 Cotrace: Traceroute Facility for Cotet- Cetric Network htts://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-asaeda-icrg-cotrace-01 Hitoshi Asaeda (NICT) Xu Shao (NICT) Thierry Turletti (Iria) 1 Outlie Motivatio Desig cocet
Cotrace: Traceroute Facility for Cotet- Cetric Network htts://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-asaeda-icrg-cotrace-01 Hitoshi Asaeda (NICT) Xu Shao (NICT) Thierry Turletti (Iria) 1 Outlie Motivatio Desig cocet
Last Class. Announcements. Lecture Outline. Types. Structural Equivalence. Type Equivalence. Read: Scott, Chapters 7 and 8. T2 y; x = y; n Types
 Aoucemets HW9 due today HW10 comig up, will post after class Team assigmet Data abstractio (types) ad cotrol abstractio (parameter passig) Due o Tuesday, November 27 th Last Class Types Type systems Type
Aoucemets HW9 due today HW10 comig up, will post after class Team assigmet Data abstractio (types) ad cotrol abstractio (parameter passig) Due o Tuesday, November 27 th Last Class Types Type systems Type
Major CSL Write your name and entry no on every sheet of the answer script. Time 2 Hrs Max Marks 70
 NOTE:. Attempt all seve questios. Major CSL 02 2. Write your ame ad etry o o every sheet of the aswer script. Time 2 Hrs Max Marks 70 Q No Q Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Q 5 Q 6 Q 7 Total MM 6 2 4 0 8 4 6 70 Q. Write a
NOTE:. Attempt all seve questios. Major CSL 02 2. Write your ame ad etry o o every sheet of the aswer script. Time 2 Hrs Max Marks 70 Q No Q Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Q 5 Q 6 Q 7 Total MM 6 2 4 0 8 4 6 70 Q. Write a
Elementary Educational Computer
 Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
BST Sequence of Operations
 Splay Trees Problems with BSTs Because the shape of a BST is determied by the order that data is iserted, we ru the risk of trees that are essetially lists 12 21 20 32 24 37 15 40 55 56 77 2 BST Sequece
Splay Trees Problems with BSTs Because the shape of a BST is determied by the order that data is iserted, we ru the risk of trees that are essetially lists 12 21 20 32 24 37 15 40 55 56 77 2 BST Sequece
How do we evaluate algorithms?
 F2 Readig referece: chapter 2 + slides Algorithm complexity Big O ad big Ω To calculate ruig time Aalysis of recursive Algorithms Next time: Litterature: slides mostly The first Algorithm desig methods:
F2 Readig referece: chapter 2 + slides Algorithm complexity Big O ad big Ω To calculate ruig time Aalysis of recursive Algorithms Next time: Litterature: slides mostly The first Algorithm desig methods:
CS200: Hash Tables. Prichard Ch CS200 - Hash Tables 1
 CS200: Hash Tables Prichard Ch. 13.2 CS200 - Hash Tables 1 Table Implemetatios: average cases Search Add Remove Sorted array-based Usorted array-based Balaced Search Trees O(log ) O() O() O() O(1) O()
CS200: Hash Tables Prichard Ch. 13.2 CS200 - Hash Tables 1 Table Implemetatios: average cases Search Add Remove Sorted array-based Usorted array-based Balaced Search Trees O(log ) O() O() O() O(1) O()
Data Structures Week #5. Trees (Ağaçlar)
 Data Structures Week #5 Trees Ağaçlar) Trees Ağaçlar) Toros Gökarı Avrupa Gökarı October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Trees Ağaçlar) October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 3 Outlie Trees Deiitios Implemetatio
Data Structures Week #5 Trees Ağaçlar) Trees Ağaçlar) Toros Gökarı Avrupa Gökarı October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Trees Ağaçlar) October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 3 Outlie Trees Deiitios Implemetatio
Analysis Metrics. Intro to Algorithm Analysis. Slides. 12. Alg Analysis. 12. Alg Analysis
 Itro to Algorithm Aalysis Aalysis Metrics Slides. Table of Cotets. Aalysis Metrics 3. Exact Aalysis Rules 4. Simple Summatio 5. Summatio Formulas 6. Order of Magitude 7. Big-O otatio 8. Big-O Theorems
Itro to Algorithm Aalysis Aalysis Metrics Slides. Table of Cotets. Aalysis Metrics 3. Exact Aalysis Rules 4. Simple Summatio 5. Summatio Formulas 6. Order of Magitude 7. Big-O otatio 8. Big-O Theorems
Algorithm Design Techniques. Divide and conquer Problem
 Algorithm Desig Techiques Divide ad coquer Problem Divide ad Coquer Algorithms Divide ad Coquer algorithm desig works o the priciple of dividig the give problem ito smaller sub problems which are similar
Algorithm Desig Techiques Divide ad coquer Problem Divide ad Coquer Algorithms Divide ad Coquer algorithm desig works o the priciple of dividig the give problem ito smaller sub problems which are similar
Outline and Reading. Analysis of Algorithms. Running Time. Experimental Studies. Limitations of Experiments. Theoretical Analysis
 Outlie ad Readig Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output Ruig time ( 3.) Pseudo-code ( 3.2) Coutig primitive operatios ( 3.3-3.) Asymptotic otatio ( 3.6) Asymptotic aalysis ( 3.7) Case study Aalysis
Outlie ad Readig Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output Ruig time ( 3.) Pseudo-code ( 3.2) Coutig primitive operatios ( 3.3-3.) Asymptotic otatio ( 3.6) Asymptotic aalysis ( 3.7) Case study Aalysis
Exercise 6 (Week 42) For the foreign students only.
 These are the last exercises of the course. Please, remember that to pass exercises, the sum of the poits gathered by solvig the questios ad attedig the exercise groups must be at least 4% ( poits) of
These are the last exercises of the course. Please, remember that to pass exercises, the sum of the poits gathered by solvig the questios ad attedig the exercise groups must be at least 4% ( poits) of
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 20 Itroductio to Trasactio Processig Cocepts ad Theory Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio Trasactio Describes local
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 20 Itroductio to Trasactio Processig Cocepts ad Theory Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio Trasactio Describes local
One advantage that SONAR has over any other music-sequencing product I ve worked
 *gajedra* D:/Thomso_Learig_Projects/Garrigus_163132/z_productio/z_3B2_3D_files/Garrigus_163132_ch17.3d, 14/11/08/16:26:39, 16:26, page: 647 17 CAL 101 Oe advatage that SONAR has over ay other music-sequecig
*gajedra* D:/Thomso_Learig_Projects/Garrigus_163132/z_productio/z_3B2_3D_files/Garrigus_163132_ch17.3d, 14/11/08/16:26:39, 16:26, page: 647 17 CAL 101 Oe advatage that SONAR has over ay other music-sequecig
CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 11 Basic Computer Organization and Design
 College of Computer ad Iformatio Scieces Departmet of Computer Sciece CSC 220: Computer Orgaizatio Uit 11 Basic Computer Orgaizatio ad Desig 1 For the rest of the semester, we ll focus o computer architecture:
College of Computer ad Iformatio Scieces Departmet of Computer Sciece CSC 220: Computer Orgaizatio Uit 11 Basic Computer Orgaizatio ad Desig 1 For the rest of the semester, we ll focus o computer architecture:
Mini Hi-Fi Component System
 3-864--11 (1 Mii Hi-Fi Comoet System Oeratig Istructios T DHC-EX88MD DHC-MD717 1998 by Soy Cororatio WARIG To revet fire or shock hazard, do ot exose the uit to rai or moisture. To avoid electrical shock,
3-864--11 (1 Mii Hi-Fi Comoet System Oeratig Istructios T DHC-EX88MD DHC-MD717 1998 by Soy Cororatio WARIG To revet fire or shock hazard, do ot exose the uit to rai or moisture. To avoid electrical shock,
Software development of components for complex signal analysis on the example of adaptive recursive estimation methods.
 Software developmet of compoets for complex sigal aalysis o the example of adaptive recursive estimatio methods. SIMON BOYMANN, RALPH MASCHOTTA, SILKE LEHMANN, DUNJA STEUER Istitute of Biomedical Egieerig
Software developmet of compoets for complex sigal aalysis o the example of adaptive recursive estimatio methods. SIMON BOYMANN, RALPH MASCHOTTA, SILKE LEHMANN, DUNJA STEUER Istitute of Biomedical Egieerig
LU Decomposition Method
 SOLUTION OF SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS LU Decompositio Method Jamie Traha, Autar Kaw, Kevi Marti Uiversity of South Florida Uited States of America kaw@eg.usf.edu http://umericalmethods.eg.usf.edu Itroductio
SOLUTION OF SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS LU Decompositio Method Jamie Traha, Autar Kaw, Kevi Marti Uiversity of South Florida Uited States of America kaw@eg.usf.edu http://umericalmethods.eg.usf.edu Itroductio
Queues COL 106. Slides by Amit Kumar, Shweta Agrawal
 Queues COL 106 Slides by Amit Kumar, Shweta Agrawal The Queue ADT The Queue ADT stores arbitrary objects Insertions and deletions follow the first-in first-out (FIFO) scheme Insertions are at the rear
Queues COL 106 Slides by Amit Kumar, Shweta Agrawal The Queue ADT The Queue ADT stores arbitrary objects Insertions and deletions follow the first-in first-out (FIFO) scheme Insertions are at the rear
CSC165H1 Worksheet: Tutorial 8 Algorithm analysis (SOLUTIONS)
 CSC165H1, Witer 018 Learig Objectives By the ed of this worksheet, you will: Aalyse the ruig time of fuctios cotaiig ested loops. 1. Nested loop variatios. Each of the followig fuctios takes as iput a
CSC165H1, Witer 018 Learig Objectives By the ed of this worksheet, you will: Aalyse the ruig time of fuctios cotaiig ested loops. 1. Nested loop variatios. Each of the followig fuctios takes as iput a
Solutions for Homework 2
 Solutios for Homework 2 IIR Book: Exercise.2 (0.5 ) Cosider these documets: Doc breakthrough drug for schizophreia Doc 2 ew schizophreia drug Doc 3 ew approach for treatmet of schizophreia Doc 4 ew hopes
Solutios for Homework 2 IIR Book: Exercise.2 (0.5 ) Cosider these documets: Doc breakthrough drug for schizophreia Doc 2 ew schizophreia drug Doc 3 ew approach for treatmet of schizophreia Doc 4 ew hopes
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 18 Strategies for Query Processig Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio DBMS techiques to process a query Scaer idetifies
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 18 Strategies for Query Processig Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio DBMS techiques to process a query Scaer idetifies
Graphs ORD SFO LAX DFW
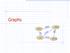 Graphs SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of odes, called vertices E is a collectio of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices ad edges are positios ad
Graphs SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of odes, called vertices E is a collectio of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices ad edges are positios ad
COP4020 Programming Languages. Functional Programming Prof. Robert van Engelen
 COP4020 Programmig Laguages Fuctioal Programmig Prof. Robert va Egele Overview What is fuctioal programmig? Historical origis of fuctioal programmig Fuctioal programmig today Cocepts of fuctioal programmig
COP4020 Programmig Laguages Fuctioal Programmig Prof. Robert va Egele Overview What is fuctioal programmig? Historical origis of fuctioal programmig Fuctioal programmig today Cocepts of fuctioal programmig
Getting Started. Getting Started - 1
 Gettig Started Gettig Started - 1 Issue 1 Overview of Gettig Started Overview of Gettig Started This sectio explais the basic operatios of the AUDIX system. It describes how to: Log i ad log out of the
Gettig Started Gettig Started - 1 Issue 1 Overview of Gettig Started Overview of Gettig Started This sectio explais the basic operatios of the AUDIX system. It describes how to: Log i ad log out of the
K-NET bus. When several turrets are connected to the K-Bus, the structure of the system is as showns
 K-NET bus The K-Net bus is based o the SPI bus but it allows to addressig may differet turrets like the I 2 C bus. The K-Net is 6 a wires bus (4 for SPI wires ad 2 additioal wires for request ad ackowledge
K-NET bus The K-Net bus is based o the SPI bus but it allows to addressig may differet turrets like the I 2 C bus. The K-Net is 6 a wires bus (4 for SPI wires ad 2 additioal wires for request ad ackowledge
Lecture 2. RTL Design Methodology. Transition from Pseudocode & Interface to a Corresponding Block Diagram
 Lecture 2 RTL Desig Methodology Trasitio from Pseudocode & Iterface to a Correspodig Block Diagram Structure of a Typical Digital Data Iputs Datapath (Executio Uit) Data Outputs System Cotrol Sigals Status
Lecture 2 RTL Desig Methodology Trasitio from Pseudocode & Iterface to a Correspodig Block Diagram Structure of a Typical Digital Data Iputs Datapath (Executio Uit) Data Outputs System Cotrol Sigals Status
Greedy Algorithms. Interval Scheduling. Greedy Algorithms. Interval scheduling. Greedy Algorithms. Interval Scheduling
 Greedy Algorithms Greedy Algorithms Witer Paul Beame Hard to defie exactly but ca give geeral properties Solutio is built i small steps Decisios o how to build the solutio are made to maximize some criterio
Greedy Algorithms Greedy Algorithms Witer Paul Beame Hard to defie exactly but ca give geeral properties Solutio is built i small steps Decisios o how to build the solutio are made to maximize some criterio
of types having a total order and a predecessor and a successor function. In the
 J. Fuctioal Programmig 1 (1): 1{000, Jauary 1993 c 1993 Cambridge Uiversity Press 1 F U N C T I O N A L P E A R L S Diets for Fat Sets Marti Erwig FerUiversitat Hage, Praktische Iformatik IV 58084 Hage,
J. Fuctioal Programmig 1 (1): 1{000, Jauary 1993 c 1993 Cambridge Uiversity Press 1 F U N C T I O N A L P E A R L S Diets for Fat Sets Marti Erwig FerUiversitat Hage, Praktische Iformatik IV 58084 Hage,
The Implementation of Data Structures in Version 5 of Icon* Ralph E. Gr is wo Id TR 85-8
 The Implemetatio of Data Structures i Versio 5 of Ico* Ralph E. Gr is wo Id TR 85-8 April 1, 1985 Departmet of Computer Sciece The Uiversity of Arizoa Tucso. Arizoa 85721 This work was supported by the
The Implemetatio of Data Structures i Versio 5 of Ico* Ralph E. Gr is wo Id TR 85-8 April 1, 1985 Departmet of Computer Sciece The Uiversity of Arizoa Tucso. Arizoa 85721 This work was supported by the
From last week. Lecture 5. Outline. Principles of programming languages
 Priciples of programmig laguages From last week Lecture 5 http://few.vu.l/~silvis/ppl/2007 Natalia Silvis-Cividjia e-mail: silvis@few.vu.l ML has o assigmet. Explai how to access a old bidig? Is & for
Priciples of programmig laguages From last week Lecture 5 http://few.vu.l/~silvis/ppl/2007 Natalia Silvis-Cividjia e-mail: silvis@few.vu.l ML has o assigmet. Explai how to access a old bidig? Is & for
