Applications of Stacks
|
|
|
- Juliana Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lists ad Iterators 8// Presetatio for use with the textbook lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, h ata Structures xkcd Seve Used with permissio uder reative ommos. Licese Stacks First, let us discuss a related structure: the Stack. Isertios ad deletios follow the last-i first-out scheme (LIFO) Thik of a sprig-loaded plate dispeser Mai stack operatios: push(e): iserts a elemet, e pop(): removes ad returs the last iserted elemet uxiliary stack operatios: top(): returs the last iserted elemet without removig it size(): returs the umber of elemets stored isempty(): idicates whether o elemets are stored Example pplicatios of Stacks irect applicatios Page-visited history i a Web browser Udo sequece i a text editor hai of method calls i a laguage supportig recursio Idirect applicatios uxiliary data structure for algorithms ompoet of other data structures Method Stacks The rutime eviromet for such a laguage keeps track of the chai of active methods with a stack Whe a method is called, the system pushes o the stack a frame cotaiig Local variables ad retur value Program couter, keepig track of the statemet beig executed Whe a method eds, its frame is popped from the stack ad cotrol is passed to the method o top of the stack llows for recursio mai() { it i = ; foo(i); } foo(it j) { it k; k = j+; bar(k); } bar(it m) { } bar P = m = foo P = j = k = mai P = i = rray-based Stack simple way of implemetig the Stack T uses a array We add elemets from left to right variable keeps track of the idex of the top elemet S t: umber of items i stack lgorithm size() retur t lgorithm pop() if isempty() the retur ull t t retur S[t] t-
2 Lists ad Iterators 8// rray-based Stack (cot.) The array storig the stack elemets may become full push operatio will the either grow the array or sigal a error S lgorithm push(o) if t = S.legth the sigal stack overflow error t t S[t-] o t- Performace Performace Let be the umber of elemets i the stack The space used is O() Each operatio rus i time O() ualificatios Tryig to push a ew elemet ito a full stack causes a implemetatio-specific exceptio or Pushig a item o a full stack causes the uderlyig array to double i size, which implies each operatio rus i O() amortized time. omputig Spas (ot i book) Usig a stack as a auxiliary data structure i a algorithm Give a array X, the spa S[i] of X[i] is the maximum umber of cosecutive elemets X[j] immediately precedig X[i] ad such that X[j] X[i] Spas have applicatios to fiacial aalysis E.g., stock at -week high X S uadratic lgorithm lgorithm spas(x, ) Iput array X of itegers Output array S of spas of X # S ew array of itegers for i to do s while s i X[i s] X[i] ( ) s s ( ) S[i] s retur S lgorithm spas rus i O( ) time omputig Spas with a Stack We keep i a stack the idices of the elemets larger tha the curret, plus the idex of the curret. We sca the array from left to right Let i be the curret idex We pop idices from the stack util we fid idex j such that X[i] X[j] If stack is empty, we set S[i] i+ otherwise, we set S[i] i j We push i oto the stack S: Stack: Liear Time lgorithm Each idex of the array Is pushed ito the stack exactly oe Is popped from the stack at most oce The body of the while-loop is executed at most times lgorithm spas rus i O() time lgorithm spas(x, ) # S ew array of itegers ew empty stack for i to do while (.isempty() X[.top()] X[i] ) do.pop() if.isempty() the S[i] i S[i] i.top().push(i) retur S
3 Lists ad Iterators 8// ueues I a ueue, isertios ad deletios follow the first-i firstout scheme (FIFO) uxiliary queue operatios: Isertios are at the rear or ed of the queue ad removals are at the frot of size(): returs the umber the queue of elemets stored Mai queue operatios: isempty(): idicates whether o elemets are equeue(e): iserts a elemet, stored e, at the ed of the queue dequeue(): removes ad oudary cases: returs the elemet at the frot of the queue first(): returs the elemet at the frot without removig it ttemptig the executio of dequeue or first o a empty queue sigals a error or returs ull Example Operatio Output equeue() () equeue() (, ) dequeue() () equeue() (, ) dequeue() () first() () dequeue() () dequeue() ull () isempty() true () equeue(9) (9) equeue() (9, ) size() (9, ) equeue() (9,, ) equeue() (9,,, ) dequeue() 9 (,, ) pplicatio: uffered Output The Iteret is desiged to route iformatio i discrete packets, which are at most bytes i legth. y time a video stream is trasmitted o the Iteret, it must be subdivided ito packets ad these packets must each be idividually routed to their destiatio. ecause of vagaries ad errors, the time it takes for these packets to arrive at their destiatio ca be highly variable. Thus, we eed a way of smoothig out these variatios pplicatio: uffered Output This smoothig is typically achieved is by usig a buffer, which is a queue that is used to temporarily store items, as they are beig produced by oe computatioal process ad cosumed by aother. I the case of video packets arrivig via the Iteret, the etworkig process is producig the packets ad the playback process is cosumig them. This producer-cosumer model is eforcig queue, a first-i, first-out (FIFO) protocol for the packets. dditioal pplicatios esides bufferig video, queues also have the followig applicatios: irect applicatios Waitig lists, bureaucracy ccess to shared resources (e.g., priter) Multiprogrammig Idirect applicatios uxiliary data structure for algorithms ompoet of other data structures rray-based ueue Use a array of size N i a circular fashio Two variables keep track of the frot ad size f idex of the frot elemet sz umber of stored elemets Whe the queue has fewer tha N elemets, array locatio r = (f + sz) mod N is the first empty slot past the rear of the queue ormal cofiguratio f r wrapped-aroud cofiguratio r f
4 Lists ad Iterators 8// ueue Operatios We use the modulo operator (remaider of divisio) lgorithm size() retur sz lgorithm isempty() retur (sz ) f r r f ueue Operatios (cot.) Operatio equeue throws a exceptio if the array is full Oe could also grow the uderlyig array by a factor of lgorithm equeue(o) if sz = N the sigal queue full error r (f + sz) mod N [r] o sz (sz + ) f r r f ueue Operatios (cot.) Note that operatio dequeue returs ull if the queue is empty Oe could alteratively sigal a error lgorithm dequeue() if isempty() the retur ull o [f] f (f + ) mod N sz (sz ) retur o f r r f pplicatio: Roud Robi Schedulers We ca implemet a roud robi scheduler usig a queue by repeatedly performig the followig steps:. e =.dequeue(). Service elemet e..equeue(e) ueue equeue Shared Service Equeue Idex-ased Lists idex-based list supports the followig operatios: Example sequece of List operatios:
5 Lists ad Iterators 8// rray-based Lists obvious choice for implemetig the list T is to use a array,, where [i] stores (a referece to) the elemet with idex i. With a represetatio based o a array, the get(i) ad set(i, e) methods are easy to implemet by accessig [i] (assumig i is a legitimate idex). i Isertio I a operatio add(i, o), we eed to make room for the ew elemet by shiftig forward the i elemets [i],, [ ] I the worst case (i ), this takes O() time i i o i Elemet Removal I a operatio remove(i), we eed to fill the hole left by the removed elemet by shiftig backward the i elemets [i ],, [ ] I the worst case (i ), this takes O() time Pseudo-code lgorithms for isertio ad removal: o i i i 8 Performace I a array-based implemetatio of a dyamic list: The space used by the data structure is O() Idexig the elemet at i takes O() time add ad remove ru i O() time i the worst case I a add operatio, whe the array is full, istead of throwig a exceptio, we ca replace the array with a larger oe. Liked Lists Liked lists store elemets at odes or positios. ccessor methods: 9
6 Lists ad Iterators 8// Liked Lists Update methods: Isertio Isert a ew ode, q, betwee p ad its successor. p prev Implemetatio: The most atural way to implemet a positioal list is with a doubly-liked list. ext header odes/positios trailer p q X p q elemet ode Lists ad Iterators elemets X eletio Remove a ode, p, from a doubly-liked list. p Pseudo-code lgorithms for isertio ad deletio i a liked list: p Performace liked list ca perform all of the access ad update operatios for a positioal list i costat time. What is a Tree I computer sciece, a tree is a abstract model of a hierarchical structure tree cosists of odes with a paret-child relatio pplicatios: Orgaizatio charts File systems Programmig eviromets US Sales Iteratioal omputers R Us Maufacturig Laptops Europe sia aada esktops R&
7 Lists ad Iterators 8// Tree Termiology Root: ode without paret () Subtree: tree cosistig of Iteral ode: ode with at least a ode ad its oe child (,,, F) descedats Exteral ode (a.k.a. leaf ): ode without childre (E, I, J, K, G, H, ) cestors of a ode: paret, gradparet, grad-gradparet, etc. epth of a ode: umber of acestors E F G H Height of a tree: maximum depth of ay ode () escedat of a ode: child, gradchild, grad-gradchild, etc. I J K subtree Tree Operatios ccessor methods: uery methods: Geeric methods: 8 Preorder Traversal traversal visits the odes of a tree i a systematic maer I a preorder traversal, a ode is visited before its descedats pplicatio: prit a structured documet Make Moey Fast! 9. Motivatios. Methods Refereces. Greed. vidity 8. Stock Fraud lgorithm preorder(v) visit(v) for each child w of v preorder (w). Pozi Scheme. ak Robbery 9 Postorder Traversal I a postorder traversal, a ode is visited after its descedats pplicatio: compute space used by files i a directory ad its subdirectories 9 cs/ hc.doc K homeworks/ hc.doc K R.java K lgorithm postorder(v) for each child w of v postorder (w) visit(v) programs/ Stocks.java K Robot.java K 8 todo.txt K iary Trees rithmetic Expressio Tree biary tree is a tree with the followig properties: Each iteral ode has at most two childre (exactly two for proper biary trees) The childre of a ode are a ordered pair We call the childre of a iteral ode left child ad right child lterative recursive defiitio: a biary tree is either a tree cosistig of a sigle ode, or a tree whose root has a ordered pair of childre, each of which is a biary tree pplicatios: arithmetic expressios decisio processes searchig E F G H I iary tree associated with a arithmetic expressio iteral odes: operators exteral odes: operads Example: arithmetic expressio tree for the expressio ( (a ) ( b)) a b
8 Lists ad Iterators 8// ecisio Tree Properties of Proper iary Trees iary tree associated with a decisio process iteral odes: questios with yes/o aswer exteral odes: decisios Example: diig decisio Wat a fast meal? Yes No How about coffee? O expese accout? Yes No Yes No Notatio umber of odes e umber of exteral odes i umber of iteral odes h height Properties: e i e h i h ( ) e h h log e h log ( ) Starbucks hipotle Gracie s afé Parago iary Tree Operatios biary tree exteds the Tree operatios, i.e., it iherits all the methods of atree. dditioal methods: positio lefthild(v) positio righthild(v) positio siblig(v) The above methods retur ull whe there is o left, right, or siblig of p, respectively Update methods may be defied by data structures implemetig the biary tree Iorder Traversal I a iorder traversal a ode is visited after its left subtree ad before its right subtree pplicatio: draw a biary tree x(v) = iorder rak of v y(v) = depth of v lgorithm iorder(v) if left (v) ull iorder (left (v)) visit(v) if right(v) ull iorder (right (v)) 8 9 Prit rithmetic Expressios Specializatio of a iorder traversal prit operad or operator whe visitig ode prit ( before traversig left subtree prit ) after traversig right subtree a b lgorithm pritexpressio(v) if left (v) ull prit( ( ) iorder (left(v)) prit(v.elemet ()) if right(v) ull iorder (right(v)) prit ( ) ) (( (a )) ( b)) Evaluate rithmetic Expressios Specializatio of a postorder traversal recursive method returig the value of a subtree whe visitig a iteral ode, combie the values of the subtrees lgorithm evalexpr(v) if isexteral (v) retur v.elemet () x evalexpr(left(v)) y evalexpr(right(v)) operator stored at v retur x y 8 8
9 Lists ad Iterators 8// Euler Tour Traversal Geeric traversal of a tree Travel each edge exactly twice. L R Liked Structure for Trees ode is represeted by a object storig Elemet Paret ode Sequece of childre odes Node objects implemet the Positio T F F 9 E E Liked Structure for iary Trees ode is represeted by a object storig Elemet Paret ode Left child ode Right child ode Node objects implemet the Positio T E E rray-ased Represetatio of iary Trees Nodes are stored i a array G H 9 Node v is stored at [rak(v)] rak(root) = if ode is the left child of paret(ode), E F J rak(ode) = rak(paret(ode)) + if ode is the right child of paret(ode), 9 rak(ode) = rak(paret(ode)) G H 9
Elementary Data Structures. The Stack ADT ( 2.1.1) Applications of Stacks. Stacks, Queues, Vectors, Lists & Sequences Trees
 Elemetary Data Structures Stacks, Queues, ectors, Lists & Sequeces Trees The Stack ADT ( 2..) The Stack ADT stores arbitrary objects Isertios ad deletios follow the last-i first-out scheme Thik of a sprig-loaded
Elemetary Data Structures Stacks, Queues, ectors, Lists & Sequeces Trees The Stack ADT ( 2..) The Stack ADT stores arbitrary objects Isertios ad deletios follow the last-i first-out scheme Thik of a sprig-loaded
Trees 3/19/14. Mammal. Dog Pig Cat
 Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Heaps. Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 201 Heaps 201 Goodrich ad Tamassia xkcd. http://xkcd.com/83/. Tree. Used with permissio uder
Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 201 Heaps 201 Goodrich ad Tamassia xkcd. http://xkcd.com/83/. Tree. Used with permissio uder
Ch02 Data Structures
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Ch02 Data Structures xkcd Seven http://xkcd.com/1417/ Used with permission under
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Ch02 Data Structures xkcd Seven http://xkcd.com/1417/ Used with permission under
Ch02 Data Structures
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Ch02 Data Structures xkcd Seven http://xkcd.com/1417/ Used with permission under
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Ch02 Data Structures xkcd Seven http://xkcd.com/1417/ Used with permission under
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) Stacks. The Stack ADT ( 4.2) Stack Interface in Java
 Abstract Data Types (ADTs) tacks A abstract data type (ADT) is a abstractio of a data structure A ADT specifies: Data stored Operatios o the data Error coditios associated with operatios Example: ADT modelig
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) tacks A abstract data type (ADT) is a abstractio of a data structure A ADT specifies: Data stored Operatios o the data Error coditios associated with operatios Example: ADT modelig
CIS 121. Introduction to Trees
 CIS 121 Itroductio to Trees 1 Tree ADT Tree defiitio q A tree is a set of odes which may be empty q If ot empty, the there is a distiguished ode r, called root ad zero or more o-empty subtrees T 1, T 2,
CIS 121 Itroductio to Trees 1 Tree ADT Tree defiitio q A tree is a set of odes which may be empty q If ot empty, the there is a distiguished ode r, called root ad zero or more o-empty subtrees T 1, T 2,
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks and Queues Monday, February 12 / Tuesday, February 13
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 08 Stacks ad Queues Moday, February / Tuesday, February Learig Goals Durig this lab, you will: Review stacks ad queues. Lear amortized ruig time aalysis
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 08 Stacks ad Queues Moday, February / Tuesday, February Learig Goals Durig this lab, you will: Review stacks ad queues. Lear amortized ruig time aalysis
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks, Queues, and Heaps Monday, February 18 / Tuesday, February 19
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
top() Applications of Stacks
 CS22 Algorithms ad Data Structures MW :00 am - 2: pm, MSEC 0 Istructor: Xiao Qi Lecture 6: Stacks ad Queues Aoucemets Quiz results Homework 2 is available Due o September 29 th, 2004 www.cs.mt.edu~xqicoursescs22
CS22 Algorithms ad Data Structures MW :00 am - 2: pm, MSEC 0 Istructor: Xiao Qi Lecture 6: Stacks ad Queues Aoucemets Quiz results Homework 2 is available Due o September 29 th, 2004 www.cs.mt.edu~xqicoursescs22
Hash Tables. Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015.
 Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Hash Tables xkcd. http://xkcd.com/221/. Radom Number. Used with permissio uder Creative
Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Hash Tables xkcd. http://xkcd.com/221/. Radom Number. Used with permissio uder Creative
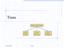
Trees. Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud. Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Trees Goodrich, Tamassia
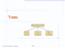 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Data Structures Week #5. Trees (Ağaçlar)
 Data Structures Week #5 Trees Ağaçlar) Trees Ağaçlar) Toros Gökarı Avrupa Gökarı October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Trees Ağaçlar) October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 3 Outlie Trees Deiitios Implemetatio
Data Structures Week #5 Trees Ağaçlar) Trees Ağaçlar) Toros Gökarı Avrupa Gökarı October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Trees Ağaçlar) October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 3 Outlie Trees Deiitios Implemetatio
Outline and Reading. Analysis of Algorithms. Running Time. Experimental Studies. Limitations of Experiments. Theoretical Analysis
 Outlie ad Readig Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output Ruig time ( 3.) Pseudo-code ( 3.2) Coutig primitive operatios ( 3.3-3.) Asymptotic otatio ( 3.6) Asymptotic aalysis ( 3.7) Case study Aalysis
Outlie ad Readig Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output Ruig time ( 3.) Pseudo-code ( 3.2) Coutig primitive operatios ( 3.3-3.) Asymptotic otatio ( 3.6) Asymptotic aalysis ( 3.7) Case study Aalysis
Elementary Data Structures. Stacks, Queues, & Lists Amortized analysis Trees
 Elementary Data Structures Stacks, Queues, & Lists Amortized analysis Trees The Stack ADT ( 2.1.1) The Stack ADT stores arbitrary objects Insertions and deletions follow the last-in first-out scheme Think
Elementary Data Structures Stacks, Queues, & Lists Amortized analysis Trees The Stack ADT ( 2.1.1) The Stack ADT stores arbitrary objects Insertions and deletions follow the last-in first-out scheme Think
Data Structures and Algorithms. Analysis of Algorithms
 Data Structures ad Algorithms Aalysis of Algorithms Outlie Ruig time Pseudo-code Big-oh otatio Big-theta otatio Big-omega otatio Asymptotic algorithm aalysis Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output
Data Structures ad Algorithms Aalysis of Algorithms Outlie Ruig time Pseudo-code Big-oh otatio Big-theta otatio Big-omega otatio Asymptotic algorithm aalysis Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output
Analysis of Algorithms
 Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput 2015 Goodrich ad Tamassia Algorithm Aalysis of Algorithms
Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput 2015 Goodrich ad Tamassia Algorithm Aalysis of Algorithms
1/27/12. Vectors: Outline and Reading. Chapter 6: Vectors, Lists and Sequences. The Vector ADT. Applications of Vectors. Array based Vector: Insertion
 Chater 6: ectors, Lists ad Sequeces ectors: Outlie ad Readig The ector ADT ( 6.1.1) Array-based imlemetatio ( 6.1.2) Nacy Amato Parasol Lab, Det. CSE, Texas A&M Uiversity Ackowledgemet: These slides are
Chater 6: ectors, Lists ad Sequeces ectors: Outlie ad Readig The ector ADT ( 6.1.1) Array-based imlemetatio ( 6.1.2) Nacy Amato Parasol Lab, Det. CSE, Texas A&M Uiversity Ackowledgemet: These slides are
Running Time. Analysis of Algorithms. Experimental Studies. Limitations of Experiments
 Ruig Time Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects. The
Ruig Time Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects. The
Running Time ( 3.1) Analysis of Algorithms. Experimental Studies. Limitations of Experiments
 Ruig Time ( 3.1) Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step- by- step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects.
Ruig Time ( 3.1) Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step- by- step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects.
Analysis of Algorithms
 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Ruig Time Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects. The
Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Ruig Time Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects. The
University of Waterloo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 250 Algorithms and Data Structures
 Uiversity of Waterloo Departmet of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig ECE 250 Algorithms ad Data Structures Midterm Examiatio ( pages) Istructor: Douglas Harder February 7, 2004 7:30-9:00 Name (last, first)
Uiversity of Waterloo Departmet of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig ECE 250 Algorithms ad Data Structures Midterm Examiatio ( pages) Istructor: Douglas Harder February 7, 2004 7:30-9:00 Name (last, first)
Linked Lists 11/16/18. Preliminaries. Java References. Objects and references. Self references. Linking self-referential nodes
 Prelimiaries Liked Lists public class StrageObject { Strig ame; StrageObject other; Arrays are ot always the optimal data structure: A array has fixed size eeds to be copied to expad its capacity Addig
Prelimiaries Liked Lists public class StrageObject { Strig ame; StrageObject other; Arrays are ot always the optimal data structure: A array has fixed size eeds to be copied to expad its capacity Addig
Priority Queues. Binary Heaps
 Priority Queues Biary Heaps Priority Queues Priority: some property of a object that allows it to be prioritized with respect to other objects of the same type Mi Priority Queue: homogeeous collectio of
Priority Queues Biary Heaps Priority Queues Priority: some property of a object that allows it to be prioritized with respect to other objects of the same type Mi Priority Queue: homogeeous collectio of
BST Sequence of Operations
 Splay Trees Problems with BSTs Because the shape of a BST is determied by the order that data is iserted, we ru the risk of trees that are essetially lists 12 21 20 32 24 37 15 40 55 56 77 2 BST Sequece
Splay Trees Problems with BSTs Because the shape of a BST is determied by the order that data is iserted, we ru the risk of trees that are essetially lists 12 21 20 32 24 37 15 40 55 56 77 2 BST Sequece
Pseudocode ( 1.1) Analysis of Algorithms. Primitive Operations. Pseudocode Details. Running Time ( 1.1) Estimating performance
 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Miimum Spaig Trees 0 Goodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig a Network Suppose
Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Miimum Spaig Trees 0 Goodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig a Network Suppose
Trees. Trees. CSE 2011 Winter 2007
 Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Stock Fraud Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees
 Part 4: Trees Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees 2 Example: Family Tree 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees 3 Example: Unix File
Part 4: Trees Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees 2 Example: Family Tree 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees 3 Example: Unix File
OUTLINE. General Trees (Ch. 7.1) Binary Trees (Ch. 7.3) Tree Traversals (Ch. 7.2)
 CH 7 : TREE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO 1 OUTLINE
CH 7 : TREE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO 1 OUTLINE
Analysis of Algorithms
 Aalysis of Algorithms Ruig Time of a algorithm Ruig Time Upper Bouds Lower Bouds Examples Mathematical facts Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite
Aalysis of Algorithms Ruig Time of a algorithm Ruig Time Upper Bouds Lower Bouds Examples Mathematical facts Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite
What is a Tree. Trees. Tree ADT ( 6.1.2) Tree Terminology. subtree. In computer science, a tree is an abstract model
 What is a Tree Trees Stock raud Make Money ast! Ponzi Scheme ank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model omputers R Us of a hierarchical structure tree consists of with a parent-child
What is a Tree Trees Stock raud Make Money ast! Ponzi Scheme ank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model omputers R Us of a hierarchical structure tree consists of with a parent-child
Minimum Spanning Trees. Application: Connecting a Network
 Miimum Spaig Tree // : Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. oodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, Miimum Spaig Trees oodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig
Miimum Spaig Tree // : Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. oodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, Miimum Spaig Trees oodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig
Trees. 9/21/2007 8:11 AM Trees 1
 Trees 9/21/2007 8:11 AM Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 6.1) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 6.2.3) BinaryTree ADT ( 6.3.1) Inorder traversal ( 6.3.4) Euler Tour traversal ( 6.3.4) Template
Trees 9/21/2007 8:11 AM Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 6.1) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 6.2.3) BinaryTree ADT ( 6.3.1) Inorder traversal ( 6.3.4) Euler Tour traversal ( 6.3.4) Template
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Stock Fraud. Ponzi Scheme Goodrich, Tamassia. Trees 1
 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
End Semester Examination CSE, III Yr. (I Sem), 30002: Computer Organization
 Ed Semester Examiatio 2013-14 CSE, III Yr. (I Sem), 30002: Computer Orgaizatio Istructios: GROUP -A 1. Write the questio paper group (A, B, C, D), o frot page top of aswer book, as per what is metioed
Ed Semester Examiatio 2013-14 CSE, III Yr. (I Sem), 30002: Computer Orgaizatio Istructios: GROUP -A 1. Write the questio paper group (A, B, C, D), o frot page top of aswer book, as per what is metioed
Homework 1 Solutions MA 522 Fall 2017
 Homework 1 Solutios MA 5 Fall 017 1. Cosider the searchig problem: Iput A sequece of umbers A = [a 1,..., a ] ad a value v. Output A idex i such that v = A[i] or the special value NIL if v does ot appear
Homework 1 Solutios MA 5 Fall 017 1. Cosider the searchig problem: Iput A sequece of umbers A = [a 1,..., a ] ad a value v. Output A idex i such that v = A[i] or the special value NIL if v does ot appear
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Miimum Spaig Trees Miimum Spaig Trees Spaig subgraph Subgraph of a graph G cotaiig all the vertices of G Spaig tree Spaig subgraph that is itself a (free) tree Miimum spaig tree (MST) Spaig tree of a weighted
Miimum Spaig Trees Miimum Spaig Trees Spaig subgraph Subgraph of a graph G cotaiig all the vertices of G Spaig tree Spaig subgraph that is itself a (free) tree Miimum spaig tree (MST) Spaig tree of a weighted
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Stock Fraud. Ponzi Scheme. Trees Goodrich, Tamassia
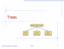 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Sorting 9/15/2009. Sorting Problem. Insertion Sort: Soundness. Insertion Sort. Insertion Sort: Running Time. Insertion Sort: Soundness
 9/5/009 Algorithms Sortig 3- Sortig Sortig Problem The Sortig Problem Istace: A sequece of umbers Objective: A permutatio (reorderig) such that a ' K a' a, K,a a ', K, a' of the iput sequece The umbers
9/5/009 Algorithms Sortig 3- Sortig Sortig Problem The Sortig Problem Istace: A sequece of umbers Objective: A permutatio (reorderig) such that a ' K a' a, K,a a ', K, a' of the iput sequece The umbers
6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring Lecture 17 April 24
 6.851: Advaced Data Structures Sprig 2012 Prof. Erik Demaie Lecture 17 April 24 Scribes: David Bejami(2012), Li Fei(2012), Yuzhi Zheg(2012),Morteza Zadimoghaddam(2010), Aaro Berstei(2007) 1 Overview Up
6.851: Advaced Data Structures Sprig 2012 Prof. Erik Demaie Lecture 17 April 24 Scribes: David Bejami(2012), Li Fei(2012), Yuzhi Zheg(2012),Morteza Zadimoghaddam(2010), Aaro Berstei(2007) 1 Overview Up
Data Structures and Algorithms. Trees
 Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Tree Example Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 2 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A
Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Tree Example Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 2 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A
Announcements TREES II. Comparing Data Structures. Binary Search Trees. Red-Black Trees. Red-Black Trees 3/13/18
 //8 Aoucemets Prelim is Toight, brig your studet ID :PM EXAM OLH: etids startig aa to dh OLH: etids startig di to ji PHL: etids startig jj to ks (Plus studets who switched from the 7: exam) TREES II Lecture
//8 Aoucemets Prelim is Toight, brig your studet ID :PM EXAM OLH: etids startig aa to dh OLH: etids startig di to ji PHL: etids startig jj to ks (Plus studets who switched from the 7: exam) TREES II Lecture
Computer Science Foundation Exam. August 12, Computer Science. Section 1A. No Calculators! KEY. Solutions and Grading Criteria.
 Computer Sciece Foudatio Exam August, 005 Computer Sciece Sectio A No Calculators! Name: SSN: KEY Solutios ad Gradig Criteria Score: 50 I this sectio of the exam, there are four (4) problems. You must
Computer Sciece Foudatio Exam August, 005 Computer Sciece Sectio A No Calculators! Name: SSN: KEY Solutios ad Gradig Criteria Score: 50 I this sectio of the exam, there are four (4) problems. You must
DATA STRUCTURES. amortized analysis binomial heaps Fibonacci heaps union-find. Data structures. Appetizer. Appetizer
 Data structures DATA STRUCTURES Static problems. Give a iput, produce a output. Ex. Sortig, FFT, edit distace, shortest paths, MST, max-flow,... amortized aalysis biomial heaps Fiboacci heaps uio-fid Dyamic
Data structures DATA STRUCTURES Static problems. Give a iput, produce a output. Ex. Sortig, FFT, edit distace, shortest paths, MST, max-flow,... amortized aalysis biomial heaps Fiboacci heaps uio-fid Dyamic
Lecture 5. Counting Sort / Radix Sort
 Lecture 5. Coutig Sort / Radix Sort T. H. Corme, C. E. Leiserso ad R. L. Rivest Itroductio to Algorithms, 3rd Editio, MIT Press, 2009 Sugkyukwa Uiversity Hyuseug Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-2018
Lecture 5. Coutig Sort / Radix Sort T. H. Corme, C. E. Leiserso ad R. L. Rivest Itroductio to Algorithms, 3rd Editio, MIT Press, 2009 Sugkyukwa Uiversity Hyuseug Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-2018
Chapter 24. Sorting. Objectives. 1. To study and analyze time efficiency of various sorting algorithms
 Chapter 4 Sortig 1 Objectives 1. o study ad aalyze time efficiecy of various sortig algorithms 4. 4.7.. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze bubble sort 4.. 3. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze merge sort 4.3. 4. o
Chapter 4 Sortig 1 Objectives 1. o study ad aalyze time efficiecy of various sortig algorithms 4. 4.7.. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze bubble sort 4.. 3. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze merge sort 4.3. 4. o
Lower Bounds for Sorting
 Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
CS211 Fall 2003 Prelim 2 Solutions and Grading Guide
 CS11 Fall 003 Prelim Solutios ad Gradig Guide Problem 1: (a) obj = obj1; ILLEGAL because type of referece must always be a supertype of type of object (b) obj3 = obj1; ILLEGAL because type of referece
CS11 Fall 003 Prelim Solutios ad Gradig Guide Problem 1: (a) obj = obj1; ILLEGAL because type of referece must always be a supertype of type of object (b) obj3 = obj1; ILLEGAL because type of referece
Computers and Scientific Thinking
 Computers ad Scietific Thikig David Reed, Creighto Uiversity Chapter 15 JavaScript Strigs 1 Strigs as Objects so far, your iteractive Web pages have maipulated strigs i simple ways use text box to iput
Computers ad Scietific Thikig David Reed, Creighto Uiversity Chapter 15 JavaScript Strigs 1 Strigs as Objects so far, your iteractive Web pages have maipulated strigs i simple ways use text box to iput
Elementary Educational Computer
 Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 18 Strategies for Query Processig Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio DBMS techiques to process a query Scaer idetifies
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 18 Strategies for Query Processig Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio DBMS techiques to process a query Scaer idetifies
6.854J / J Advanced Algorithms Fall 2008
 MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
Basic allocator mechanisms The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory Management II: Dynamic Storage Allocation Mar 6, 2000.
 5-23 The course that gives CM its Zip Memory Maagemet II: Dyamic Storage Allocatio Mar 6, 2000 Topics Segregated lists Buddy system Garbage collectio Mark ad Sweep Copyig eferece coutig Basic allocator
5-23 The course that gives CM its Zip Memory Maagemet II: Dyamic Storage Allocatio Mar 6, 2000 Topics Segregated lists Buddy system Garbage collectio Mark ad Sweep Copyig eferece coutig Basic allocator
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Stock Fraud. 02/06/2006 Trees 1
 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 02/06/2006 Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 7.1.2) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 7.2.2-3) BinaryTree ADT ( 7.3.1) Inorder traversal
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 02/06/2006 Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 7.1.2) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 7.2.2-3) BinaryTree ADT ( 7.3.1) Inorder traversal
Chapter 11. Friends, Overloaded Operators, and Arrays in Classes. Copyright 2014 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 11 Frieds, Overloaded Operators, ad Arrays i Classes Copyright 2014 Pearso Addiso-Wesley. All rights reserved. Overview 11.1 Fried Fuctios 11.2 Overloadig Operators 11.3 Arrays ad Classes 11.4
Chapter 11 Frieds, Overloaded Operators, ad Arrays i Classes Copyright 2014 Pearso Addiso-Wesley. All rights reserved. Overview 11.1 Fried Fuctios 11.2 Overloadig Operators 11.3 Arrays ad Classes 11.4
Priority Queues and Heaps (Ch 5.5) Huffman Coding Trees (Ch 5.6) Binary Search Trees (Ch 5.4) Lec 5: Binary Tree. Dr. Patrick Chan
 ata Structure hapter Biary Trees r. Patrick ha School of om puter Sciece ad Egieerig South hia Uiversity of Techolog y Recursio recursio is a procedure which calls itself The recursive procedure call must
ata Structure hapter Biary Trees r. Patrick ha School of om puter Sciece ad Egieerig South hia Uiversity of Techolog y Recursio recursio is a procedure which calls itself The recursive procedure call must
Data Structures. Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees
 Data Structures Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parentchild relation Applications:
Data Structures Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parentchild relation Applications:
COMP Parallel Computing. PRAM (1): The PRAM model and complexity measures
 COMP 633 - Parallel Computig Lecture 2 August 24, 2017 : The PRAM model ad complexity measures 1 First class summary This course is about parallel computig to achieve high-er performace o idividual problems
COMP 633 - Parallel Computig Lecture 2 August 24, 2017 : The PRAM model ad complexity measures 1 First class summary This course is about parallel computig to achieve high-er performace o idividual problems
What are we going to learn? CSC Data Structures Analysis of Algorithms. Overview. Algorithm, and Inputs
 What are we goig to lear? CSC316-003 Data Structures Aalysis of Algorithms Computer Sciece North Carolia State Uiversity Need to say that some algorithms are better tha others Criteria for evaluatio Structure
What are we goig to lear? CSC316-003 Data Structures Aalysis of Algorithms Computer Sciece North Carolia State Uiversity Need to say that some algorithms are better tha others Criteria for evaluatio Structure
Stock Fraud. Nancy Amato. Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University
 Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Chapter 7: Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures
Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Chapter 7: Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures
quality/quantity peak time/ratio
 Semi-Heap ad Its Applicatios i Touramet Rakig Jie Wu Departmet of omputer Sciece ad Egieerig Florida Atlatic Uiversity oca Rato, FL 3343 jie@cse.fau.edu September, 00 . Itroductio ad Motivatio. relimiaries
Semi-Heap ad Its Applicatios i Touramet Rakig Jie Wu Departmet of omputer Sciece ad Egieerig Florida Atlatic Uiversity oca Rato, FL 3343 jie@cse.fau.edu September, 00 . Itroductio ad Motivatio. relimiaries
Graphs ORD SFO LAX DFW
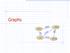 Graphs SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of odes, called vertices E is a collectio of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices ad edges are positios ad
Graphs SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of odes, called vertices E is a collectio of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices ad edges are positios ad
How do we evaluate algorithms?
 F2 Readig referece: chapter 2 + slides Algorithm complexity Big O ad big Ω To calculate ruig time Aalysis of recursive Algorithms Next time: Litterature: slides mostly The first Algorithm desig methods:
F2 Readig referece: chapter 2 + slides Algorithm complexity Big O ad big Ω To calculate ruig time Aalysis of recursive Algorithms Next time: Litterature: slides mostly The first Algorithm desig methods:
Chapter 3 Classification of FFT Processor Algorithms
 Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
why study sorting? Sorting is a classic subject in computer science. There are three reasons for studying sorting algorithms.
 Chapter 5 Sortig IST311 - CIS65/506 Clevelad State Uiversity Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Itroductio to Java Programmig: Comprehesive Versio, Eighth Editio by Y. Daiel Liag why study sortig? Sortig
Chapter 5 Sortig IST311 - CIS65/506 Clevelad State Uiversity Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Itroductio to Java Programmig: Comprehesive Versio, Eighth Editio by Y. Daiel Liag why study sortig? Sortig
Lecture Notes 6 Introduction to algorithm analysis CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming
 Lecture Notes 6 Itroductio to algorithm aalysis CSS 501 Data Structures ad Object-Orieted Programmig Readig for this lecture: Carrao, Chapter 10 To be covered i this lecture: Itroductio to algorithm aalysis
Lecture Notes 6 Itroductio to algorithm aalysis CSS 501 Data Structures ad Object-Orieted Programmig Readig for this lecture: Carrao, Chapter 10 To be covered i this lecture: Itroductio to algorithm aalysis
COSC 1P03. Ch 7 Recursion. Introduction to Data Structures 8.1
 COSC 1P03 Ch 7 Recursio Itroductio to Data Structures 8.1 COSC 1P03 Recursio Recursio I Mathematics factorial Fiboacci umbers defie ifiite set with fiite defiitio I Computer Sciece sytax rules fiite defiitio,
COSC 1P03 Ch 7 Recursio Itroductio to Data Structures 8.1 COSC 1P03 Recursio Recursio I Mathematics factorial Fiboacci umbers defie ifiite set with fiite defiitio I Computer Sciece sytax rules fiite defiitio,
CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 11 Basic Computer Organization and Design
 College of Computer ad Iformatio Scieces Departmet of Computer Sciece CSC 220: Computer Orgaizatio Uit 11 Basic Computer Orgaizatio ad Desig 1 For the rest of the semester, we ll focus o computer architecture:
College of Computer ad Iformatio Scieces Departmet of Computer Sciece CSC 220: Computer Orgaizatio Uit 11 Basic Computer Orgaizatio ad Desig 1 For the rest of the semester, we ll focus o computer architecture:
The Magma Database file formats
 The Magma Database file formats Adrew Gaylard, Bret Pikey, ad Mart-Mari Breedt Johaesburg, South Africa 15th May 2006 1 Summary Magma is a ope-source object database created by Chris Muller, of Kasas City,
The Magma Database file formats Adrew Gaylard, Bret Pikey, ad Mart-Mari Breedt Johaesburg, South Africa 15th May 2006 1 Summary Magma is a ope-source object database created by Chris Muller, of Kasas City,
Ones Assignment Method for Solving Traveling Salesman Problem
 Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
The java.util.list ADT
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Lists and Iterators 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia,
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Lists and Iterators 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia,
Sorting in Linear Time. Data Structures and Algorithms Andrei Bulatov
 Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Solution printed. Do not start the test until instructed to do so! CS 2604 Data Structures Midterm Spring, Instructions:
 CS 604 Data Structures Midterm Sprig, 00 VIRG INIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE U T PROSI M UNI VERSI TY Istructios: Prit your ame i the space provided below. This examiatio is closed book ad closed
CS 604 Data Structures Midterm Sprig, 00 VIRG INIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE U T PROSI M UNI VERSI TY Istructios: Prit your ame i the space provided below. This examiatio is closed book ad closed
Lists ADT and Iterators
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Lists ADT and Iterators 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia,
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Lists ADT and Iterators 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia,
Fundamental Algorithms
 Techische Uiversität Müche Fakultät für Iformatik Lehrstuhl für Effiziete Algorithme Dmytro Chibisov Sadeep Sadaada Witer Semester 2007/08 Solutio Sheet 6 November 30, 2007 Fudametal Algorithms Problem
Techische Uiversität Müche Fakultät für Iformatik Lehrstuhl für Effiziete Algorithme Dmytro Chibisov Sadeep Sadaada Witer Semester 2007/08 Solutio Sheet 6 November 30, 2007 Fudametal Algorithms Problem
Lecture 1: Introduction and Strassen s Algorithm
 5-750: Graduate Algorithms Jauary 7, 08 Lecture : Itroductio ad Strasse s Algorithm Lecturer: Gary Miller Scribe: Robert Parker Itroductio Machie models I this class, we will primarily use the Radom Access
5-750: Graduate Algorithms Jauary 7, 08 Lecture : Itroductio ad Strasse s Algorithm Lecturer: Gary Miller Scribe: Robert Parker Itroductio Machie models I this class, we will primarily use the Radom Access
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity
 Time CSE 47: Algorithms ad Computatioal Readig assigmet Read Chapter of The ALGORITHM Desig Maual Aalysis & Sortig Autum 00 Paul Beame aalysis Problem size Worst-case complexity: max # steps algorithm
Time CSE 47: Algorithms ad Computatioal Readig assigmet Read Chapter of The ALGORITHM Desig Maual Aalysis & Sortig Autum 00 Paul Beame aalysis Problem size Worst-case complexity: max # steps algorithm
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Stock Fraud. 1/18/2005 4:17 AM Trees 1
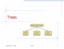 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 1/18/2005 4:17 AM Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 2.3.1) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 2.3.2) BinaryTree ADT ( 2.3.3) Inorder traversal
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 1/18/2005 4:17 AM Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 2.3.1) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 2.3.2) BinaryTree ADT ( 2.3.3) Inorder traversal
Major CSL Write your name and entry no on every sheet of the answer script. Time 2 Hrs Max Marks 70
 NOTE:. Attempt all seve questios. Major CSL 02 2. Write your ame ad etry o o every sheet of the aswer script. Time 2 Hrs Max Marks 70 Q No Q Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Q 5 Q 6 Q 7 Total MM 6 2 4 0 8 4 6 70 Q. Write a
NOTE:. Attempt all seve questios. Major CSL 02 2. Write your ame ad etry o o every sheet of the aswer script. Time 2 Hrs Max Marks 70 Q No Q Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Q 5 Q 6 Q 7 Total MM 6 2 4 0 8 4 6 70 Q. Write a
Chapter 1. Introduction to Computers and C++ Programming. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 1 Itroductio to Computers ad C++ Programmig Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 1.1 Computer Systems 1.2 Programmig ad Problem Solvig 1.3 Itroductio to C++ 1.4 Testig
Chapter 1 Itroductio to Computers ad C++ Programmig Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 1.1 Computer Systems 1.2 Programmig ad Problem Solvig 1.3 Itroductio to C++ 1.4 Testig
Data Structures Lecture 6
 Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 6 Announcement Project Proposal due on Nov. 9 Remember to bring a hardcopy
Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 6 Announcement Project Proposal due on Nov. 9 Remember to bring a hardcopy
CS200: Hash Tables. Prichard Ch CS200 - Hash Tables 1
 CS200: Hash Tables Prichard Ch. 13.2 CS200 - Hash Tables 1 Table Implemetatios: average cases Search Add Remove Sorted array-based Usorted array-based Balaced Search Trees O(log ) O() O() O() O(1) O()
CS200: Hash Tables Prichard Ch. 13.2 CS200 - Hash Tables 1 Table Implemetatios: average cases Search Add Remove Sorted array-based Usorted array-based Balaced Search Trees O(log ) O() O() O() O(1) O()
Lecture 3. RTL Design Methodology. Transition from Pseudocode & Interface to a Corresponding Block Diagram
 Lecture 3 RTL Desig Methodology Trasitio from Pseudocode & Iterface to a Correspodig Block Diagram Structure of a Typical Digital Data Iputs Datapath (Executio Uit) Data Outputs System Cotrol Sigals Status
Lecture 3 RTL Desig Methodology Trasitio from Pseudocode & Iterface to a Correspodig Block Diagram Structure of a Typical Digital Data Iputs Datapath (Executio Uit) Data Outputs System Cotrol Sigals Status
Switching Hardware. Spring 2018 CS 438 Staff, University of Illinois 1
 Switchig Hardware Sprig 208 CS 438 Staff, Uiversity of Illiois Where are we? Uderstad Differet ways to move through a etwork (forwardig) Read sigs at each switch (datagram) Follow a kow path (virtual circuit)
Switchig Hardware Sprig 208 CS 438 Staff, Uiversity of Illiois Where are we? Uderstad Differet ways to move through a etwork (forwardig) Read sigs at each switch (datagram) Follow a kow path (virtual circuit)
Algorithm. Counting Sort Analysis of Algorithms
 Algorithm Coutig Sort Aalysis of Algorithms Assumptios: records Coutig sort Each record cotais keys ad data All keys are i the rage of 1 to k Space The usorted list is stored i A, the sorted list will
Algorithm Coutig Sort Aalysis of Algorithms Assumptios: records Coutig sort Each record cotais keys ad data All keys are i the rage of 1 to k Space The usorted list is stored i A, the sorted list will
Trees and Binary Trees
 Trees and Binary Trees Become Rich Force Others to be Poor Rob Banks Stock Fraud The class notes are a compilation and edition from many sources. The instructor does not claim intellectual property or
Trees and Binary Trees Become Rich Force Others to be Poor Rob Banks Stock Fraud The class notes are a compilation and edition from many sources. The instructor does not claim intellectual property or
Lecture 2. RTL Design Methodology. Transition from Pseudocode & Interface to a Corresponding Block Diagram
 Lecture 2 RTL Desig Methodology Trasitio from Pseudocode & Iterface to a Correspodig Block Diagram Structure of a Typical Digital Data Iputs Datapath (Executio Uit) Data Outputs System Cotrol Sigals Status
Lecture 2 RTL Desig Methodology Trasitio from Pseudocode & Iterface to a Correspodig Block Diagram Structure of a Typical Digital Data Iputs Datapath (Executio Uit) Data Outputs System Cotrol Sigals Status
Graph Terminology and Representations
 Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Graph Termiology ad Represetatios 2015 Goodrich ad Tamassia Graphs 1 Graphs A graph is
Presetatio for use with the textbook, Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Graph Termiology ad Represetatios 2015 Goodrich ad Tamassia Graphs 1 Graphs A graph is
9.1. Sequences and Series. Sequences. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. Definition of Sequence
 _9.qxd // : AM Page Chapter 9 Sequeces, Series, ad Probability 9. Sequeces ad Series What you should lear Use sequece otatio to write the terms of sequeces. Use factorial otatio. Use summatio otatio to
_9.qxd // : AM Page Chapter 9 Sequeces, Series, ad Probability 9. Sequeces ad Series What you should lear Use sequece otatio to write the terms of sequeces. Use factorial otatio. Use summatio otatio to
Exercise 6 (Week 42) For the foreign students only.
 These are the last exercises of the course. Please, remember that to pass exercises, the sum of the poits gathered by solvig the questios ad attedig the exercise groups must be at least 4% ( poits) of
These are the last exercises of the course. Please, remember that to pass exercises, the sum of the poits gathered by solvig the questios ad attedig the exercise groups must be at least 4% ( poits) of
ECE4050 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture 6: Searching
 ECE4050 Data Structures ad Algorithms Lecture 6: Searchig 1 Search Give: Distict keys k 1, k 2,, k ad collectio L of records of the form (k 1, I 1 ), (k 2, I 2 ),, (k, I ) where I j is the iformatio associated
ECE4050 Data Structures ad Algorithms Lecture 6: Searchig 1 Search Give: Distict keys k 1, k 2,, k ad collectio L of records of the form (k 1, I 1 ), (k 2, I 2 ),, (k, I ) where I j is the iformatio associated
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 19 Query Optimizatio Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio Query optimizatio Coducted by a query optimizer i a DBMS Goal:
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe CHAPTER 19 Query Optimizatio Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri ad Shamkat B. Navathe Itroductio Query optimizatio Coducted by a query optimizer i a DBMS Goal:
Chapter 10. Defining Classes. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Defiig Classes Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 10.1 Structures 10.2 Classes 10.3 Abstract Data Types 10.4 Itroductio to Iheritace Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio,
Chapter 10 Defiig Classes Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 10.1 Structures 10.2 Classes 10.3 Abstract Data Types 10.4 Itroductio to Iheritace Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio,
Abstract. Chapter 4 Computation. Overview 8/13/18. Bjarne Stroustrup Note:
 Chapter 4 Computatio Bjare Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programmig Abstract Today, I ll preset the basics of computatio. I particular, we ll discuss expressios, how to iterate over a series of values
Chapter 4 Computatio Bjare Stroustrup www.stroustrup.com/programmig Abstract Today, I ll preset the basics of computatio. I particular, we ll discuss expressios, how to iterate over a series of values
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic. Lecture 13 Control and Sequencing: Hardwired and Microprogrammed Control
 EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Desig with Programmable Logic Lecture 13 Cotrol ad Sequecig: Hardwired ad Microprogrammed Cotrol Refereces: Chapter s 4,5 from textbook Chapter 7 of M.M. Mao ad C.R. Kime,
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Desig with Programmable Logic Lecture 13 Cotrol ad Sequecig: Hardwired ad Microprogrammed Cotrol Refereces: Chapter s 4,5 from textbook Chapter 7 of M.M. Mao ad C.R. Kime,
Σ P(i) ( depth T (K i ) + 1),
 EECS 3101 York Uiversity Istructor: Ady Mirzaia DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING: OPIMAL SAIC BINARY SEARCH REES his lecture ote describes a applicatio of the dyamic programmig paradigm o computig the optimal static
EECS 3101 York Uiversity Istructor: Ady Mirzaia DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING: OPIMAL SAIC BINARY SEARCH REES his lecture ote describes a applicatio of the dyamic programmig paradigm o computig the optimal static
Trees. Data structures and Algorithms. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Stock Fraud. Ponzi Scheme
 Make Money Fast! Trees Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich,
Make Money Fast! Trees Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich,
Last class. n Scheme. n Equality testing. n eq? vs. equal? n Higher-order functions. n map, foldr, foldl. n Tail recursion
 Aoucemets HW6 due today HW7 is out A team assigmet Submitty page will be up toight Fuctioal correctess: 75%, Commets : 25% Last class Equality testig eq? vs. equal? Higher-order fuctios map, foldr, foldl
Aoucemets HW6 due today HW7 is out A team assigmet Submitty page will be up toight Fuctioal correctess: 75%, Commets : 25% Last class Equality testig eq? vs. equal? Higher-order fuctios map, foldr, foldl
Big-O Analysis. Asymptotics
 Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
