TMA for HP OpenView. TMA for HP OpenView. USER and REFERENCE MANUAL. Version:
|
|
|
- Damon Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TMA for HP OpenView USER and REFERENCE MANUAL Version: Telindus Technical Publications Geldenaaksebaan 335 B-3001 Leuven Belgium tel
2 Copyright and safety TMA for HP OpenView Copyright notice The information and descriptions contained in this publication are the property of Telindus. Such information and descriptions must not be copied or reproduced by any means, or disseminated or distributed without the express prior written permission of Telindus. This publication could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors, for which Telindus never can or shall be held liable. Changes are made periodically to the information herein; these changes will be incorporated in new editions of this publication. Telindus may make improvements and/or changes in the product(s) described in this publication at any time, without prior notice. Version September 2002 MRP Telindus ii
3 Preface Preface Organisation of this manual This manual contains three main parts. Part User manual Reference manual Annexes This part introduces TMA for HP OpenView and explains how to install it. completely describes how to configure the Alarm Manager. gives additional information. The following table gives an overview of the chapters in the user manual. Chapter This chapter 1 gives an introduction to TMA for HP OpenView. 2 explains how to install TMA for HP OpenView on a Windows and a UNIX system. 3 briefly describes how to connect the workstation running TMA for HP OpenView with the Orchid 1003 LAN. 4 says something about the HP OpenView network map and the symbols on it. It also says a few words on fault management. 5 shows you how to start a TMA session on a Telindus device. 6 explains how you can manage the Alarm Manager using TMA. 7 describes what the Alarm Manager exactly is and does. It also gives a basic configuration of the Alarm Manager. 8 lists some configuration guidelines for HP OpenView. The following table gives an overview of the chapters in the reference manual. Chapter 9, 10, 11, 12 This chapter lists and explains the configuration, status, performance and alarm attributes, respectively. 13 describes the communication parameters in the Cms2Serv.ini file. 14 helps you when you are unable to open a TMA for HP OpenView session. 15 gives some technical specifications on TMA for HP OpenView. The following table gives an overview of the annexes. Annex Annex A Annex B Annex C This annex gives a list of abbreviations. shows ordering information. tells you how to obtain the required licence key. iii
4 Preface TMA for HP OpenView Conventions used in this manual Typographical conventions The following typographical conventions are used in this manual. The format Normal Italic Computer Computer Bold Narrow Blue Blue underlined is used to indicate normal text. new or emphasised words file names and directory paths, e.g. C:\Program Files\TMA\bin\Tma.exe computer output and code examples, e.g. NOK,1,1,Invalid command. text you have to enter at the prompt, e.g. Get sysname. objects and attributes in the containment tree of a device when they are mentioned in the normal text. I.e. when they are not a part of computer input or output. references to other parts in the manual, e.g. refer to Chapter xx - Technical specifications. a hyperlink to a web site, e.g. Icons The following icons are used throughout the manual. Icon Name Description Remark Useful information or tips. Caution Read the text that follows carefully in order to insure correct operation. Basic TMA attribute Advanced TMA attribute TMA action A basic attribute which can be found in the Telindus Maintenance Application. An advanced attribute which can be found in the Telindus Maintenance Application. An action which can be executed with the Telindus Maintenance Application. iv
5 Preface Software version This manual describes the features of TMA for HP OpenView version S0006/ Your feedback Your satisfaction about this purchase is an extremely important priority to all of us at Telindus. Accordingly, all electronic, functional and cosmetic aspects of this new unit have been carefully and thoroughly tested and inspected. If any fault is found with this unit or should you have any other qualityrelated comment concerning this delivery, please submit the Quality Comment Form on our web page at v
6 Table of contents TMA for HP OpenView Table of contents User manual Introduction to TMA for HP OpenView What is TMA for HP OpenView? Which features has TMA for HP OpenView? What are the building blocks of TMA for HP OpenView? What is a licence key? Installing TMA for HP OpenView System requirements for TMA for HP OpenView System requirements for managing a network Operating systems versus HP OpenView NNM versions Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Windows Installing TMA for HP OpenView on UNIX Installing TMA for HP OpenView on a console station How to obtain and install the licence key How to upgrade the model files Connecting the workstation via the Orchid 1003 LAN What are IP, proxied IP and non-ip devices? The Orchid 1003 LAN as proxy agent Alarm transport protocol The HP OpenView network map and its symbols The HP OpenView network map Fault management The Telindus access device symbol colours Starting TMA on a Telindus access device Starting TMA via the Telindus access device symbol Starting TMA via the command line Starting the sub-system picture via the Telindus access device symbol Starting the sub-system picture via the command line Starting TMA on the Orchid a LAN IP address issue The executable DnsConfigure.exe Defining TMA for HP OpenView users and passwords...64 Continued on next page vi
7 Table of contents Table of contents (continued) 6. Managing the Alarm Manager with TMA Opening a TMA session on the Alarm Manager Containment tree terminology Where can you find an overview of all the attributes? The Alarm Manager containment tree Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager Introducing the Alarm Manager Auto discovery Setting the clock of the Orchid 1003 LAN Configuration and containment tree back-up Model upload Alarm status synchronisation The TMA alarm status of a Telindus device The unknownstate alarm Streaming detection Filtering alarms The alarm log file Conflicting device detection Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView Enabling auto discovery in HP OpenView Making all levels of sub-maps persistent Configuring the polling parameters Setting a sufficiently large poll time-out Cleaning the trapd.conf file Solving possible colour problems on Sun Solaris Continued on next page vii
8 Table of contents TMA for HP OpenView Table of contents (continued) Reference manual Configuration attributes Configuration attribute overview General configuration attributes Objects configuration attributes Inventory configuration attributes Event generation configuration attributes Status attributes Status attribute overview General status attributes Objects status attributes Inventory status attributes Event generation status attributes Performance attributes Performance attribute overview Objects performance attributes Inventory performance attributes Event generation performance attributes Alarm attributes Alarm attribute overview Introducing the alarm attributes General alarms Objects and inventory alarms The Cms2Serv.ini file Parts of the Cms2Serv.ini file Adding parts to the Cms2Serv.ini file TMA error messages TMA start errors Alias errors Reconnect messages Edit errors Export errors Import errors Download errors Subsystem picture errors NACK messages Internal communication errors Continued on next page viii
9 Table of contents Table of contents (continued) 15. Technical specifications System requirements TMA for HP OpenView building blocks Alarm Manager features Alarm notification Management interconnectivity Annexes Annex A: abbreviations Annex B: product information Annex C: licence key request Which information has to be supplied? Licence key request fax ix
10
11 User manual User manual 1
12 2 User manual
13 Introduction to TMA for HP OpenView 1. Introduction to TMA for HP OpenView This chapter gives an introduction to TMA for HP OpenView. The following table gives an overview of this chapter. Section Title Page 1.1 What is TMA for HP OpenView? Which features has TMA for HP OpenView? What are the building blocks of TMA for HP OpenView? What is a licence key? 7 User manual 3
14 Introduction to TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 1.1 What is TMA for HP OpenView? TMA (Telindus Management Application) for HP OpenView is the management application that runs on the widely spread network management platform HP OpenView. It offers the combination of the easy to use graphical interface of the stand-alone version of TMA, together with the advantages and features of HP OpenView. The Telindus access devices are represented in the OpenView map as icons. Double clicking on the icon allows the user to access the management functions of the selected Telindus access device in exactly the same way as with the standalone version of TMA. Alarms are logged into the Event Log of the Node Manager and can change the colour of the icons on the HP OpenView maps. TMA for HP OpenView runs on HP OpenView Network Node Manager versions 5.0X and 6.X. It is available on: Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 Microsoft Windows 2000 Sun Solaris 2.6 / 7. The UNIX workstations are commonly used to manage large networks (more than 1000 modems), whereas the Windows NT / 2000 workstations can be used to manage small and medium sized networks (less than 1000 modems). 4 User manual
15 Introduction to TMA for HP OpenView 1.2 Which features has TMA for HP OpenView? In this manual, the features of TMA for HP OpenView are described (refer to Chapter 7 - Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager). The features of the stand-alone version of TMA, also referred to as standard features, are not repeated in this manual. For more information on those standard features, refer to the TMA manual. The specific features of TMA for HP OpenView are: invoking the TMA user interface via a symbol pop-up menu invoking the TMA user interface via the command line using name resolution auto discovery of Telindus access devices symbol colouring reflecting the global status of the device generation of an OpenView event for every alarm private MIBs (not automatically loaded in HP OpenView). User manual 5
16 Introduction to TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 1.3 What are the building blocks of TMA for HP OpenView? TMA for HP OpenView consists of two main building blocks: the Telindus Maintenance Application or TMA the Alarm Manager. The Telindus Maintenance Application This is the graphical user interface that enables you to manage the Telindus access devices. I.e. you can access the device its configuration attributes and look at the status, performance and alarm information. In order to get acquainted with the TMA user interface, consult the TMA manual. The Alarm Manager Because HP OpenView does not know how to handle non-ip devices and because the usual mechanism of handling IP devices (using SNMP traps) is not optimal, the Alarm Manager was created as part of TMA for HP OpenView. For more information on the Alarm Manager, refer to Chapter 7 - Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager. 6 User manual
17 Introduction to TMA for HP OpenView 1.4 What is a licence key? The number of Telindus access devices that can be managed with TMA for HP OpenView is determined by the installed licence key. This limitation only applies on fault management. It is always possible to start the stand-alone functionality of TMA. TMA for HP OpenView supports three licence types: No licence: this is a demo licence. Maximum 8 access devices can be managed. Entry level licence: a maximum of 250 access devices can be managed. Unlimited licence: there is no limitation on the number of access devices that can be managed. The required licence key can be obtained by sending a fax or an to Telindus. Refer to Annex C: licence key request. User manual 7
18 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 2. Installing TMA for HP OpenView This chapter explains how to install TMA for HP OpenView on the Windows and UNIX platform. First it gives you the system requirements. Read these requirements carefully to make sure your computer will be able to run TMA for HP OpenView. The following table gives an overview of this chapter. Section Title Page 2.1 System requirements for TMA for HP OpenView System requirements for managing a network Operating systems versus HP OpenView NNM versions Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Windows Installing TMA for HP OpenView on UNIX Installing TMA for HP OpenView on a console station How to obtain and install the licence key How to upgrade the model files 28 8 User manual
19 Installing TMA for HP OpenView 2.1 System requirements for TMA for HP OpenView The system requirements are mainly dependent on the HP OpenView configuration. For more information on the HP OpenView configuration refer to the Performance and Configuration Guide for Network Node Manager 5.x. HP Part No. J Therefore, the following system requirements should only be considered as a guideline. The following table gives the system requirements for running TMA for HP OpenView: System Windows NT / 2000 Sun Solaris HP-UX System specification Pentium 150 or more Sun Ultra 10 or more HP or more Operating system version Windows NT 4.0 / Windows 2000 Solaris 2.6 / 7 HP-UX / 11.0 HP OpenView version HP OpenView NNM 5.01 or higher HP OpenView NNM 5.01 or higher HP OpenView NNM 5.01 or higher Available disk space (without HP OpenView) 21 Mb (1) 30 Mb (1) 30 Mb (1) Recommended RAM 256 Mb or more + 64 Mb extra for Windows Mb or more 256 Mb or more Additional hardware CD-ROM CD-ROM CD-ROM mouse mouse mouse networking TCP/IP networking installed and configured TCP/IP networking installed and configured TCP/IP networking installed and configured (1) Because the model files delivered with TMA for HP OpenView evolve as the devices evolve, their size tends to increase with each new release. The figures specified in the table above, is the size of TMA for HP OpenView and the model files as it was when this manual was written. For future releases of TMA for HP OpenView, these figures may be incorrect. The required processing power strongly depends on the amount of alarms that have to be processed. User manual 9
20 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 2.2 System requirements for managing a network Telindus has done tests and simulations to determine the maximum modem network size that can be managed by a single HP OpenView station (HP OpenView + TMA for HP OpenView is installed). The HP OpenView station collects all information and presents it graphically on its console. No other Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) are connected. Managing up to 2500 modems Managing a network of up to 2500 modems requires the following system resources: System Windows NT / 2000 Sun Solaris HP-UX System specification Intel Pentium II or III 500 MHz Sun Ultra 10 HP Operating system version Windows NT 4.0 / Windows 2000 Solaris 2.6 / 7 HP-UX / 11.0 Available disk space 600 Mb 1 Gb 1 Gb Recommended RAM 256 Mb + 64 Mb extra for Windows Mb 256 Mb Managing up to modems Managing a network of up to modems requires the following system resources: System Windows NT / 2000 Sun Solaris HP-UX System specification Intel Pentium II or III 500 MHz Sun Ultra 250 with 2 UltraSparc-II processors HP Operating system version Windows NT 4.0 / Windows 2000 Solaris 2.6 / 7 HP-UX / 11.0 Available disk space 800 Mb 1 Gb 1 Gb Recommended RAM 512 Mb + 64 Mb extra for Windows Mb 512 Mb If all the network units have their own IP address and furthermore polling and auto discovery is active, then the guaranteed number of network units that can be managed per HP OpenView station may drop. 10 User manual
21 Installing TMA for HP OpenView 2.3 Operating systems versus HP OpenView NNM versions The following table indicates which operating supports which version of the HP OpenView Network Node Manager (NNM) and whether it is possible to run TMA for HP OpenView. Possible to run OS NNM 5.x NNM 6.0x NNM 6.1 Possible to run TMA for HP-OV? Solaris yes yes yes no Solaris 2.6 yes yes yes yes Solaris 7 no no yes yes Solaris 8 no no yes no HP-UX yes yes yes yes HP-UX 11 no yes yes yes Windows NT yes yes yes yes Windows 2000 no no yes yes User manual 11
22 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 2.4 Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Windows This section explains how to install TMA for HP OpenView on the Windows NT and Windows 2000 platform. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page The three installation components of TMA for HP OpenView Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Windows NT / Adapting the ovtrapd.lrf file Adapting the netmon.lrf file Location of the TMA for HP OpenView files User manual
23 Installing TMA for HP OpenView The three installation components of TMA for HP OpenView The installation of TMA for HP OpenView comprises three components as listed below: Component TMA executable Model files Licence key Description provides the easy to use graphical interface and the standard TMA features. provide, per access device type, the information TMA needs to connect and exchange information with the access device. restricts the number of Telindus access devices that can be managed. User manual 13
24 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Windows NT / 2000 Important remark If you are going to install TMA for HP OpenView immediately after installation of HP OpenView itself, first reboot your system after the installation of HP OpenView (although this is not asked after the installation procedure of HP OpenView). Else the installation of TMA for HP OpenView will be done incorrect. In order to install TMA for HP OpenView on a Windows NT / 2000 system, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Before commencing the installation of TMA for HP OpenView, make sure HP OpenView and all related services are stopped. On the taskbar select Start! Programs! HP OpenView! Network Node Manager Admin! NNM Services Stop. 2 Insert the installation CD in the CD-ROM drive. 3 Windows automatically starts the set-up procedure for TMA for HP OpenView. If not, select on the taskbar Start! Settings! Control Panel! double click on Add/Remove Programs! Install 4 The InstallShield Wizard guides you through the set-up process. 5 At a certain point, you get the following screen: At this point you can install the TMA executable and the model files and / or the licence key. 6 The InstallShield Wizard guides you through the rest of the set-up process. 14 User manual
25 Installing TMA for HP OpenView Adapting the ovtrapd.lrf file TMA for HP OpenView requires a special configuration of HP OpenView and Windows. Before starting HP OpenView, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Stop the SNMP trap service (permanently). You do this in the Control Panel, under the icon Services. 2 Locate the ovtrapd.lrf file on your system. If you are not sure where this file is located, then select on the taskbar Start! Find! Files or Folders and enter the name of the file. 3 Open the file in a text editor. 4 Locate the following line: ovtrapd:ovtrapd: OVs_YES_START:pmd::OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:: 5 Add W to this line: ovtrapd:ovtrapd: OVs_YES_START:pmd:-W:OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:: 6 Save the ovtrapd.lrf file. 7 Open a DOS window and execute the following command: ovaddobj ovtrapd.lrf 8 In the DOS window execute the following command: ovstop 9 In the DOS window execute the following command: ovstart User manual 15
26 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView Adapting the netmon.lrf file In order to improve the polling performance in big networks, it is recommended to change the netmon.lrf file. Do this as follows: Step Action 1 Locate the netmon.lrf file on your system. If you are not sure where this file is located, then select on the taskbar Start! Find! Files or Folders and enter the name of the file. 2 Open the file in a text editor. 3 Locate the following line: netmon:netmon: OVs_YES_START:ovtopmd,pmd,ovwdb:-P:OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:15:PAUSE 4 Add g 0 to this line: netmon:netmon: OVs_YES_START:ovtopmd,pmd,ovwdb:-P g 0:OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:15:PAUSE 5 Save the netmon.lrf file. 6 Open a DOS window and execute the following command: ovaddobj netmon.lrf 7 In the DOS window execute the following command: ovstop 8 In the DOS window execute the following command: ovstart 16 User manual
27 Installing TMA for HP OpenView Location of the TMA for HP OpenView files If you did not change the default file location during the set-up, then the TMA for HP OpenView related directories and files can be found in the directory \Program Files\TMA. This directory has the following sub-directories: Directory This directory contains \bin \config \log \model \picture \snmp \snmp_hpov the executables. the configuration files. the log files. the model files. the subsystem picture files. the Telindus MIB files for non-hp OpenView platforms. the Telindus MIB files for HP OpenView. This directory is not always present on your system. I.e. if the standard MIB files were installed together with HP OpenView, then the content of the \snmp_hpov directory is moved to the HP OpenView directory containing the standard MIB files and the directory itself is removed. Else the \snmp_hpov directory remains on your system. User manual 17
28 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 2.5 Installing TMA for HP OpenView on UNIX This section explains how to install TMA for HP OpenView on the Sun Solaris and HP UNIX platform. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page The three installation components of TMA for HP OpenView Before installing TMA for HP OpenView on UNIX Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Sun Solaris Installing TMA for HP OpenView on HP UNIX Adapting the Dtwm file Adapting the netmon.lrf file Location of the TMA for HP OpenView files User manual
29 Installing TMA for HP OpenView The three installation components of TMA for HP OpenView The installation of TMA for HP OpenView comprises three components as listed below: Component TMA executable Model files Licence key Description provides the easy to use graphical interface and the standard TMA features. provide, per access device type, the information TMA needs to connect and exchange information with the access device. restricts the number of Telindus access devices that can be managed. User manual 19
30 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView Before installing TMA for HP OpenView on UNIX Check available space Before installing HP OpenView and TMA for HP OpenView, you should check whether there is enough space in the partitions on your workstation to insure a correct installation and operation of the applications. In the partition /opt, a minimum of 400 Mb should be available. /var, in case you do data collection, a minimum of 1.5 Gb should be available. Set language In order to avoid problems with unrecognised fonts during the installation of TMA for HP OpenView, set the correct language on your UNIX machine. Do this as follows: Step Action 1 If your UNIX machine is turned off, then boot it and wait until the login window appears. If you are in the Common Desktop Environment of your UNIX machine, then close the CDE so you get the login window. 2 In the login window, press the Options button. 3 Then select the following: Language! C! POSIX 4 Log into your CDE and install TMA for HP OpenView. 20 User manual
31 Installing TMA for HP OpenView Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Sun Solaris In order to install TMA for HP OpenView on a Sun Solaris system, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Before commencing the installation of TMA for HP OpenView, make sure HP OpenView and all related daemons are stopped. Login as root and run ovstop. 2 Insert the installation CD in the CD-ROM drive. 3 Start the install script from the SOL/TMA for HP OpenView directory on the CD-ROM. 4 The script guides you through the set-up process. 5 At a certain point, you get the following screen: At this point you can install the TMA executable and the model files and / or the licence key. 6 The script guides you through the rest of the set-up process. Should you experience problems with the colours when starting the TMA graphical user interface, then refer to Section Solving possible colour problems on Sun Solaris. User manual 21
32 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView Installing TMA for HP OpenView on HP UNIX In order to install TMA for HP OpenView on a HP UNIX system, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Before commencing the installation of TMA for HP OpenView, make sure HP OpenView and all related daemons are stopped. Login as root and run ovstop. 2 Insert the installation CD in the CD-ROM drive. 3 Mount the CD-ROM. Use pfs_mount instead of the standard mount utility. Example: %su - #pfs_mountd& #pfsd 4& #pfs_mount -t rrip /dev/dsk/c0t2d0 /SD_CDROM Install the software... #pfs_umount /SD_CDROM #exit 4 Start the install script from the HPUX/TMA for HP OpenView directory on the CD-ROM. 5 The script guides you through the set-up process. 6 At a certain point, you get the following screen: At this point you can install the TMA executable and the model files and / or the licence key. 7 The script guides you through the rest of the set-up process. 22 User manual
33 Installing TMA for HP OpenView Adapting the Dtwm file For the correct function of the GUI of TMA on a UNIX platform, modify the Dtwm file as follows: Step Action 1 Go to the directory \usr\dt\app-defaults\c. 2 Open the Dtwm file in a text editor. 3 Locate the following: Dtwm*secondariesOnTop 4 Change Dtwm*secondariesOnTop from False to True. 5 Save the Dtwm file. User manual 23
34 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView Adapting the netmon.lrf file In order to improve the polling performance in big networks, it is recommended to change the netmon.lrf file. Do this as follows: Step Action 1 Locate the netmon.lrf file on your system. 2 Open the file in a text editor. 3 Locate the following line: netmon:netmon: OVs_YES_START:ovtopmd,pmd,ovwdb:-P:OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:15:PAUSE 4 Add g 0 to this line: netmon:netmon: OVs_YES_START:ovtopmd,pmd,ovwdb:-P g 0:OVs_WELL_BEHAVED:15:PAUSE 5 Save the netmon.lrf file. 6 Open a terminal window and execute the following command: ovaddobj netmon.lrf 7 In the terminal window execute the following command: ovstop 8 In the terminal window execute the following command: ovstart 24 User manual
35 Installing TMA for HP OpenView Location of the TMA for HP OpenView files The TMA for HP OpenView related directories and files can be found in the directory /opt/tma. This directory has the following sub-directories: Directory This directory contains /bin /config /log /model /picture /snmp /snmp_hpov the executables. the configuration files. the log files. the model files. the subsystem picture files. the Telindus MIB files for non-hp OpenView platforms. the Telindus MIB files for HP OpenView. This directory is not always present on your system. I.e. if the standard MIB files were installed together with HP OpenView, then the content of the /snmp_hpov directory is moved to the HP OpenView directory containing the standard MIB files and the directory itself is removed. Else the /snmp_hpov directory remains on your system. User manual 25
36 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 2.6 Installing TMA for HP OpenView on a console station What is a console station? It is possible to run HP OpenView in a management console station combination. This means that one station runs the full licence version of HP OpenView, called the management station one station runs the view licence version of HP OpenView, called the console station. The latest TMA for HP OpenView version supports this management console station combination. I.e. it is possible to install TMA for HP OpenView on the console station. Installing TMA for HP OpenView on a console station To install TMA for HP OpenView on a console station, just proceed as explained in Section Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Windows NT / 2000 or Section Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Sun Solaris or Section Installing TMA for HP OpenView on HP UNIX However, because you install TMA for HP OpenView on a console station, you do not have to install a licence key. 26 User manual
37 Installing TMA for HP OpenView 2.7 How to obtain and install the licence key The required licence key can be obtained by sending a fax or an to Telindus (Refer to Annex C: licence key request). Once TMA for HP OpenView is installed, you are able to work with the demo version. This manages maximum 8 access devices. If the program satisfies your needs, and you want to use TMA for HP OpenView for managing your entire network, you need to install the licence key. After registration you will receive the licence key and a customer identification. To install the licence key, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Rerun the installation as described in Section Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Windows NT / 2000 or Section Installing TMA for HP OpenView on Sun Solaris or Section Installing TMA for HP OpenView on HP UNIX 2 When you are prompted to select which component you want to install, only select the licence key component. For Windows, the following Licence key window appears: For UNIX, the following Licence key window appears: 3 Enter the customer ID which you received after you submitted your licence key request. 4 Enter the licence key which you received after you submitted your licence key request. User manual 27
38 Installing TMA for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 2.8 How to upgrade the model files The installation of the model files may occur separately from the TMA executable installation. This because the model files evolve as the devices evolve. The model files delivered on the CD-ROM correspond to the latest firmware version of the Telindus access devices at the creation time of the CD- ROM. If, at a later time, you want to add devices with a more recent firmware version, a re-installation of the model files of these devices may be required. Check the most recent model files on the Telindus web site. To download and install the most recent model files, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Go to the Telindus web site at and select Products! Maintenance & Management! TMA for HP OpenView! Download model files upgrade. 2 Carefully read the licence agreement for Telindus software. If you agree with the terms stated in the agreement, select I agree. If you do not agree with the terms stated in the agreement, select I don t agree. 3 Windows For TMA for HP OpenView on Windows, select the following line: TMA part 2: data files rev. xxx [xxxx Kbyte] Save the executable file (e.g. S exe) in a temporary directory on your hard disk. UNIX For TMA for HP OpenView on UNIX, select the following line: TMA part 2: data files UNIX rev. xxx [xxxx Kbyte] Save the tar file xxx.tar.z in a temporary directory on your hard disk. 4 Windows For TMA for HP OpenView on Windows, double click on the executable file. Follow the instructions that appear on your screen. UNIX For TMA for HP OpenView on UNIX, do the following: 1. If you downloaded the tar file on a Windows station, the file name suffix has been changed by the browser into _tar.z. Transfer the file to a temporary directory on your UNIX workstation and change the file extension again into.tar.z. 2. Uncompress the file using the command uncompress xxx.tar.z. 3. Untar the resulting file xxx.tar using the command tar -xvf xxx.tar. 4. Execute the install script from the temporary directory. The device firmware is backwards compatible with the model files. This means that the latest TMA model files support not only the latest firmware version, but also all previous firmware versions of the device. 28 User manual
39 Connecting the workstation via the Orchid 1003 LAN 3. Connecting the workstation via the Orchid 1003 LAN Because the terms IP device, proxied IP device and non-ip device are used in this and the following chapters, they are explained first. Then this chapter briefly describes the Orchid 1003 LAN as proxy agent and how you can connect the HP OpenView workstation to an Orchid 1003 LAN. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page 3.1 What are IP, proxied IP and non-ip devices? The Orchid 1003 LAN as proxy agent Alarm transport protocol 32 User manual 29
40 Connecting the workstation via the Orchid 1003 LAN TMA for HP OpenView 3.1 What are IP, proxied IP and non-ip devices? Because in this and the following chapters the terms IP device, proxied IP device and non-ip device are often used, they are explained in this section. The following table gives a definition of each term together with an example: Term IP device Definition An IP device is a Telindus access device in which you can configure an IP address. that has a dedicated LAN port through which you can connect the device to a LAN. Example The Crocus Inverse Multiplexer is an IP device. You can configure an IP address in the Crocus Inverse Multiplexer using the crocusinvmux/laninterface/ipaddress attribute. The Crocus Inverse Multiplexer can be connected to a LAN through its TPI port located at the back of the device. Other IP devices are for instance: the Orchid 1003 LAN, the Crocus Router Interface, the Crocus Router 2M, etc. non-ip device A non-ip device is a Telindus access device in which you can not configure an IP address. has no dedicated LAN port and therefore can not be connected directly to a LAN. Example The Crocus SDSL F baseband modem is a non-ip device. You can not configure an IP address in the Crocus SDSL F and you can not connect it to a LAN to a dedicated LAN port. Other non-ip devices are for instance: Aster 4 F, Crocus HDSL F, Crocus SDSL F, Crocus FO10M. proxied IP device A proxied IP device is actually a non-ip device. This means it is a Telindus access device in which you can not configure an IP address. However, you can assign an IP address to the device using a proxy IP device also called proxy agent (refer to Section The Orchid 1003 LAN as proxy agent). has no dedicated LAN port and therefore can not be connected directly to a LAN. This is done through the Orchid 1003 LAN which is an IP device and therefore can be connected to a LAN through its dedicated LAN port. Example The Crocus SDSL F baseband modem is a non-ip device. However, by assigning an IP address to the modem in the Orchid 1003 LAN, the modem becomes a proxied IP device. The Orchid 1003 LAN on its turn, is connected through its LAN port to a LAN. I.e. it is as if the Crocus SDSL F modems is connected to the LAN, although not directly. 30 User manual
41 Connecting the workstation via the Orchid 1003 LAN 3.2 The Orchid 1003 LAN as proxy agent Connections to the Telindus IP access devices The connections from the HP OpenView workstation to the Telindus IP access devices are made via an IP network. Connections to the Telindus non-ip access devices The connections from the HP OpenView workstation to the Telindus non-ip access devices are made via an IP network through an Orchid 1003 LAN. In that case the Orchid serves as an IP and SNMP proxy agent and alarm concentrator. The non-ip devices are configured in the o1003/nmsgroup/objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN. In this table you can optionally assign an IP address to a non-ip device connected to the Orchid: If you do not assign an IP address, we speak of a non-ip device. If you do assign an IP address, we speak of a proxied IP device. For more information on the objecttable attribute refer to the section on the NMS group configuration attributes in the manual of the Orchid 1003 LAN. Also a complete overview of all network topologies with the Orchid 1003 LAN can be found in the Orchid 1003 LAN manual. O 1003 LAN Port 1 Port 14 High speed control bus Modem User manual 31
42 Connecting the workstation via the Orchid 1003 LAN TMA for HP OpenView 3.3 Alarm transport protocol CMS2 protocol In previous versions of TMA for HP OpenView, the Orchid 1003 LAN and HP OpenView used SNMP traps to exchange alarm information. Starting from TMA for HP OpenView version S0006/00700 (Windows), S0005/00800 (Sun Solaris) or S0008/00400 (HP UNIX), an Alarm Manager has been implemented in HP OpenView. The communication between this Alarm Manager and the Orchid 1003 LAN uses the proprietary CMS2 protocol. This implies that in case you use HP OpenView with these versions of TMA for HP OpenView as your network manager, you best leave the Orchid 1003 LAN configuration table o1003/snmpproxy/trapdestinations empty. For more information on this attribute refer to the section on SNMP proxy configuration attributes in the manual of the Orchid 1003 LAN. SNMP However, it is still possible to use any SNMP manager as your network manager. In that case, pay attention to the following: Configure the table o1003/snmpproxy/trapdestinations in the Orchid 1003 LAN. For more information on this attribute refer to the section on SNMP proxy configuration attributes in the manual of the Orchid 1003 LAN. Place the *.mib files of the devices you want to manage in the appropriate directory of your SNMP manager application. Refer to the manual of this application for the exact location of this directory. The *.mib files of the Telindus devices can be found on your system in the directory <TMA_path>\TMA\snmp. For proxied IP devices you also have to place the *.mod files of the devices you want to manage on the file system of the Orchid 1003 LAN. For more information, refer to the chapter on proxy management in the manual of the Orchid 1003 LAN. The *.mod files of the Telindus devices can be found on your system in the directory <TMA_path>\TMA\model. For more detailed information on SNMP management of Telindus proxied IP devices, refer to the chapter on proxy management in the manual of the Orchid 1003 LAN. 32 User manual
43 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols 4. The HP OpenView network map and its symbols This chapter explains how you can place symbols on the HP OpenView network map. It shows you how to start TMA. It also gives more information on the fault management in (TMA for) HP OpenView and the symbol colouring. The following table gives an overview of this chapter. Section Title Page 4.1 The HP OpenView network map Fault management The Telindus access device symbol colours 48 User manual 33
44 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView 4.1 The HP OpenView network map This section briefly discusses the HP OpenView network map. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page The Telindus access devices symbols Placing a symbol on the HP OpenView network map Symbol commands User manual
45 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols The Telindus access devices symbols The Telindus access devices are represented on the HP OpenView network map by symbols. Every device has its own symbol. For the Crocus modem range, there is even a different symbol for a Table Top modem and a Card Version symbol. The following table shows the Telindus access device symbols: Symbol This symbol represents a Aster 4 modem Crocus DXC Crocus E3 MUX Crocus FO 10M Table Top Crocus FO10M Card Version Crocus FO 45M Table Top Crocus HDSL Table Top Crocus HDSL Card Version Crocus HS Crocus Inverse Multiplexer Orchid 1003 LAN Continued on next page User manual 35
46 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView The Telindus access devices symbols (continued) Symbol This symbol represents a Crocus Router Crocus SDSL Table Top Crocus SDSL Card Version Crocus SDSL Quad Crocus SDSL Router 36 User manual
47 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols Placing a symbol on the HP OpenView network map The symbols can be placed on the HP OpenView network map in the following ways: The symbols can be placed manually, by means of the Add Object procedure. loadhosts command. For more information, refer to Paragraph a) The Add Object procedure Paragraph b) Running the loadhosts command automatically, auto discovery mechanism. Section Auto discovery Only IP devices can be placed on the HP OpenView network map manually. The following two procedures show how you can place a symbol on the HP OpenView network map manually. a) The Add Object procedure Step Action 1 In the Edit menu, select Add object This brings up the Add Object Palette. 2 In the Add Object Palette, select a Telindus symbol within the symbol class NetDevice. 3 Drag this symbol onto the OpenView network map. The Add Object dialog box appears. 4 In the Add Object dialog box, enter a name in the field Label. 5 Also in the Add Object dialog box, go to the field Object Attributes and double click on IP Map. The Add Object Set Attributes dialog box appears. 6 In the Add Object Set Attributes dialog box, at least enter a valid and unique IP address and press OK. The other fields are optional. 7 The Add Object dialog box reappears. Press OK to finalise the procedure. Continued on next page User manual 37
48 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView Placing a symbol on the HP OpenView network map (continued) b) Running the loadhosts command Step Action 1 Open a DOS window (for Windows) or terminal window (for UNIX). 2 In the DOS or terminal window execute the following command: ovstop netmon 3 Then you can execute the loadhosts command. This is explained with an example. Example Suppose you want to place three IP devices on the HP OpenView network map. They have the following IP addresses: , and The loadhosts command syntax is as follows: loadhosts p m host host host3 <CTRL+D> In this syntax the loadhosts command adds hosts to the IP topology database of HP OpenView. the p parameter executes a ping for each IP address before adding it. the m <mask> parameter is the IP subnet mask. <CTRL+D> is the key CONTROL key / D key combination to terminate the loadhosts command input. For more information on the loadhosts command, refer to the HP OpenView help. 4 In the DOS or terminal window execute the following command: ovstart netmon 38 User manual
49 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols Symbol commands If you position the cursor on a symbol and click the right mouse button, a symbol pop-up menu with commands appears. The commands can only be used when the HP OpenView network map is opened with read-write access. If the commands do not appear in the pop-up menu, double-click the symbol first. The TMA related symbol commands are: Symbol command Start TMA TMA alarm status Short description Opens a Telindus Maintenance Application session on the Telindus access device represented by that particular symbol. Shows all the current, unmasked alarms for the Telindus access device represented by that particular symbol. User manual 39
50 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView 4.2 Fault management This section briefly discusses the fault management. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page Alarms and events Alarm severity level The colour of the symbols on the HP OpenView network map Meaningful symbol colours The sub-map of the Telindus access device symbol Managed and unmanaged sub-map symbols User manual
51 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols Alarms and events When an alarm occurs on a Telindus access device, this alarm is transmitted to the Alarm Manager. The Alarm Manager translates this alarm into an OpenView event. This event is put in an event log. An event contains the following information: date and time that the alarm was received the source of the alarm the severity level a message that describes the alarm that occurred. The severity level of an event determines the colour of that event in the event log. This severity level is defined in the Telindus access device itself. It can be set for each alarm of the device with the attribute alarmlevel. For more information on this attribute, refer to the manual of the Telindus access device. The colouring of an event in the event log does not necessarily affect the colouring of the access device symbol on the HP OpenView map. The following two sections explain more on symbol colouring. User manual 41
52 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView Alarm severity level As said before, an OpenView event contains, among other elements, a severity level. This severity level can be divided into two different levels: Severity level alarm severity level total severity level Description This is the severity of an alarm, as it is defined in the device. This is the severity level of the currently most severe alarm that is active on the device. The total severity level is not necessarily equal to the alarm severity level. The following example explains this. Example On a HDSL modem are, among others, the following alarm levels configured: the LinkDown alarm has severity level 4 the BitError alarm has severity level 2. Now the following happens: Phase Description 1 For some reason the connection to the remote modem is lost. The modem generates a LinkDown alarm. 2 The modem sends this alarm to the Alarm Manager who translates this alarm into an HP OpenView event. This event has an alarm severity level 4 and a total severity level 4. 3 A few moments later, the modem also detects that the bit error threshold is exceeded. The modem generates a BitError alarm. 4 Again, the modem sends this alarm to the Alarm Manager who translates this alarm into an HP OpenView event. This event has an alarm severity level 2 but still a total severity level 4. This because the currently most severe alarm is LinkDown, not BitError. Therefore, it is the total severity level that will determine the colour of the Telindus access device symbol. 42 User manual
53 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols The colour of the symbols on the HP OpenView network map This section explains very briefly how the colour of the Telindus access device symbols on the HP OpenView network map is determined. For a more elaborate discussion of this matter, refer to Section The Telindus access device symbol colours. Colouring of a non-ip device a proxied IP device Description In case of a non-ip device, the total severity level directly determines the colour of the non-ip device symbol on the HP OpenView network map. This because a non-ip device does not have a sub-map. In case of a proxied IP device, the total severity level determines the colour of the AlarmStatus symbol located in the sub-map of the proxied IP device. The AlarmStatus symbol on its turn, determines the colour of the proxied IP device symbol on the HP OpenView network map. This is the case because the other symbols located in the sub-map of the proxied IP device are set to unmanaged by default. For more information on this matter, refer to Section Managed and unmanaged sub-map symbols. an IP device In case of an IP device, the total severity level determines the colour of the AlarmStatus symbol located in the sub-map of the IP device. The AlarmStatus symbol together with the other sub-map symbols (which usually represent an interface) eventually determine the colour of the IP device symbol on the HP OpenView network map. For more information on this matter, refer to Section Managed and unmanaged sub-map symbols. User manual 43
54 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView Meaningful symbol colours In order to get the most meaningful colouring of the Telindus access device symbol, it is recommended to configure HP OpenView so that the most critical status is propagated. Setting meaningful symbol colours in Windows For Windows, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 In the Map menu, select Properties. The Map Properties dialog box appears. 2 In the Map Properties dialog box, select the Status Propagation tab. 3 In the Status Propagation tab, select Propagate Most Critical and press OK. Setting meaningful symbol colours in UNIX For UNIX, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 In the Map menu, pick Maps. 2 Select Describe/Modify. 3 Select Propagate Most Critical. 44 User manual
55 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols The sub-map of the Telindus access device symbol Non-IP devices neither have HP OpenView interfaces nor an AlarmStatus symbol. I.e. they do not have a sub-map. When you double click on a Telindus IP access device or proxied IP access device symbol, a sub-map appears. This sub-map also contains some symbols. The colour of the AlarmStatus symbol together with the other sub-map symbols determine the colour of the Telindus access device symbol on the HP OpenView network map. The other symbols come from the generic SNMP polling in HP OpenView and are the interfaces of the device. Examples An example of a sub-map of a proxied Crocus FO10M modem is: In case of a proxied IP device, as default only the AlarmStatus symbol is set to managed. All other symbols in the sub-map are set to unmanaged. An example of a sub-map of an Orchid 1003 LAN (Card Version) is: In case of an IP device, as default all the symbols in the sub-map are set to managed. User manual 45
56 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView Managed and unmanaged sub-map symbols This section explains why for proxied IP devices only the AlarmStatus symbol is set to managed and all other sub-map symbols are set to unmanaged by default. why for IP devices all sub-map symbols are set to managed by default. There is a difference in the update of the colour information of the AlarmStatus symbol and the other submap symbols (usually these are interfaces), between a proxied IP device and an IP device. This is explained in the following table: The sub-map symbol colour update of a proxied IP device, goes as follows: The AlarmStatus symbol colour is updated every time the access device sends an alarm. The other sub-map symbols are set to unmanaged. I.e. no polling and hence no colour changes occur for these symbols. The reason why the other sub-map symbols are set to unmanaged is explained in the following paragraph. an IP device, The AlarmStatus symbol colour is updated every time the access device sends an alarm (as for a proxied IP device). In case on one of the interface symbols a linkdown alarm (on or off) occurs, a trap is forced in HP OpenView for this particular interface. I.e. the colour of the sub-map symbol is updated immediately, not only when HP OpenView explicitly polls the device. This means that the situation as described in the following paragraph (The sub-map symbols of a proxied IP device), does not apply on an IP device. Therefore, all sub-map symbols of an IP device are set to managed by default. Continued on next page 46 User manual
57 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols Managed and unmanaged sub-map symbols (continued) Why are the other sub-map symbols of a proxied IP device set to unmanaged? Suppose the other sub-map symbols of a proxied IP device are set to managed. In that case, these submap symbols their colour is updated only when HP OpenView explicitly polls the device. You may wish to put this poll interval to a large value, e.g. 24 hours, not to overload the HP OpenView workstation. This is especially true for large networks. This could create the following situation: Phase Description 1 Let us consider the sub-map of a Crocus FO10M as depicted in Section The submap of the Telindus access device symbol. 2 Suppose all is well and therefore the colours of all the sub-map symbols are green. The colour of the Crocus FO10M symbol on the HP OpenView network map is green. 3 HP OpenView polls the Crocus FO10M and finds an alarm situation on the line. The Line interface sub-map symbol turns, for instance, red (1). The colour of the Crocus FO10M symbol on the HP OpenView network map turns, for instance, red (1). (1) The specific colour change depends on your HP OpenView settings (e.g. propagate most critical, ). 4 After a while the alarm situation on the line of the Crocus FO10M is cleared. The Line interface sub-map symbol stays red, because HP OpenView has not yet polled the Crocus FO10M. The colour of the Crocus FO10M symbol on the HP OpenView network map stays red, although all alarm situations are cleared. 5 The next poll session is still, for instance, a couple of hours away from now. The colour of the Crocus FO10M symbol on the HP OpenView network map stays red for a couple of hours. As you can see, this is an incorrect representation of the actual status of the Crocus FO10M. That is why the other symbols in the sub-map are set to unmanaged by default. In that case the colour of the Telindus proxied IP access device symbol is always the same as the AlarmStatus symbol in its sub-map. The Alarm Manager does not allow you to set the other sub-map symbols to managed. If you try to do so anyway, the Alarm Manager automatically resets them to unmanaged. User manual 47
58 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView 4.3 The Telindus access device symbol colours Whereas Section The colour of the symbols on the HP OpenView network map briefly describes the colouring of the Telindus access devices symbols, this section gives a more detailed explanation. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page The status source The status source option Object The status source option Compound The status source option Symbol The Telindus access device symbol colours examples User manual
59 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols The status source What is the status source? In HP OpenView it is possible to set the sources that generate the status for the symbol. I.e. it is possible to configure how the colour of a symbol is determined. The status source of a symbol is automatically set by the application that manages the object. It is recommended not to change the status source of a symbol. Where can I find the status source? To locate the Status Source, proceed as follows: 1. Position the cursor on a symbol. 2. Click the right mouse button. 3. Select the Symbol Properties from the symbol pop-up menu. 4. In the Symbol Property window you find the Status Source field. In the Status Source field you can find three options: Object Compound Symbol For detailed information on the status source and its options, refer to the HP OpenView help. The following three sections explain what these options do and shows on which Telindus access device they are used. The Alarm Manager does not allow you to change the status source of a Telindus access device symbol. If you try to do so anyway, the Alarm Manager automatically resets the status source to its original state. User manual 49
60 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView The status source option Object What does this option do? The device symbol colour is directly related with the status of the corresponding object in the HP OpenView database. On which Telindus access device is it used? This status source option is used on non-ip devices. 50 User manual
61 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols The status source option Compound What does this option do? The total severity level of a device determines the colour of the AlarmStatus symbol located in the submap of the device. The AlarmStatus symbol colour together with the colours of the other sub-map symbols determine the colour of the device symbol. Configuring the Compound option In what way the sub-map symbols determine the colour of the device symbol is also configurable: You can, for instance, only propagate the most critical sub-map symbol status. Suppose you have a device symbol which on its turn contains four sub-map symbols: If three of those symbols are green and one is orange, then the device symbol will be orange. If two of those symbols are green, one is orange and one is red, then the device symbol will be red. You can, for instance, define percentages. Suppose you have a device symbol which on its turn contains four sub-map symbols. Suppose you defined that if 75% of the sub-map symbols are in a critical (red) state, then the device symbol has to reflect this state: If three of those symbols are green and one is orange, then the device symbol will be green. If one of those symbols is green, one is orange and two are red, then the device symbol will be green. If one of those symbols is green and three (i.e. 75%) are red, then the device symbol will be red. On which Telindus access device is it used? This status source option is used on proxied IP devices. However, for proxied IP devices all sub-map symbols other than the AlarmStatus symbol are set to unmanaged. This means that the proxied IP device symbol colour follows the AlarmStatus symbol colour. For more information, refer to Section Managed and unmanaged sub-map symbols. IP devices that have no router functionality. I.e. IP devices that are only present in one segment (e.g. a Crocus Inverse Multiplexer, an Orchid 1003 LAN provided the router functionality is not used, ). This opposed to a router, who has two interfaces with two different IP address. This means the router symbol is present in two different segments in the HP OpenView network map. IP devices that have router functionality but are located in the top network level (also called Internet level). User manual 51
62 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView The status source option Symbol What does this option do? The colour of the device symbol is determined by the status of a specific sub-map symbol. This gives HP OpenView the ability to show a different status for a device depending on where in the network map hierarchy the device symbol is found. On which Telindus access device is it used? This status source option is used on IP devices that have router functionality. E.g. a Crocus Router Interface, a Crocus Router 2M, an Orchid 1003 LAN provided the router functionality is used, However, there is one exception. IP devices that have router functionality and that are located in the top network level (also called Internet level) use the Compound option instead of the Symbol option. How exactly does the Symbol option work? The sub-map of such router IP devices contains (in its most basic form) an AlarmStatus symbol, a LAN interface symbol and a WAN interface symbol. The LAN and WAN interface sub-map symbols each belong to a different IP segment. In each of these IP segments a router IP device symbol is present. Also on the top network level, a router IP device symbol is present. However, the colours of these different router IP device symbols are not determined in the same way: The router IP device symbol located in the LAN IP segment is solely determined by the LAN interface sub-map symbol. The router IP device symbol located in the WAN IP segment is solely determined by the WAN interface sub-map symbol. The router IP device symbol located in the top network level is determined by all the sub-map symbols. I.e. whereas the router IP device symbol located in the LAN or WAN IP segment uses the Symbol option, the router IP device symbol located in the top network level (also called Internet level) uses the Compound option. The two examples in the following section try to clarify the situation as described above. 52 User manual
63 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols The Telindus access device symbol colours examples Example 1 Suppose an Orchid 1003 LAN its router functionality is used: the LAN interface has IP address the WAN interface has IP address The sub-map of the Orchid 1003 LAN contains (in its most basic form): a LAN sub-map symbol a WAN sub-map symbol an AlarmStatus sub-map symbol. The Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol is present in: the LAN IP segment Here, the device symbol colour is determined by the LAN sub-map symbol colour. I.e. in this case, the status source option Symbol is used. the WAN IP segment Here, the device symbol colour is determined by the WAN sub-map symbol colour. I.e. in this case, the status source option Symbol is used. the top network level. Here, the device symbol colour is determined by all the sub-map symbol colours. I.e. in this case, the status source option Compound is used. Suppose the colour of the LAN sub-map symbol is green WAN sub-map symbol is red AlarmStatus sub-map symbol is green. In that case the different Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol colours are: green for the Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol located in the LAN IP segment red for the Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol located in the WAN IP segment red for the Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol located in the top network level. Provided the Compound status propagation option has been set to Propagate most critical. The situation as described above is depicted on the following page. Continued on next page User manual 53
64 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView Example 1 (continued) compound compound symbol compound symbol symbol symbol 54 User manual
65 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols Example 2 Reconsider the situation as described in example 1. The only difference is the colour of the Orchid 1003 LAN sub-map symbols. Suppose the colour of the LAN sub-map symbol is green WAN sub-map symbol is green AlarmStatus sub-map symbol is red. In that case the different Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol colours are: green for the Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol located in the LAN IP segment green for the Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol located in the WAN IP segment red for the Orchid 1003 LAN device symbol located in the top network level. Provided the Compound option has been set to Propagate most critical. The situation as described above is depicted on the following page. Continued on next page User manual 55
66 The HP OpenView network map and its symbols TMA for HP OpenView Example 2 (continued) compound compound symbol compound symbol symbol symbol 56 User manual
67 Starting TMA on a Telindus access device 5. Starting TMA on a Telindus access device This section explains how to start a TMA session on a Telindus access device. The following table gives an overview of this chapter. Section Title Page 5.1 Starting TMA via the Telindus access device symbol Starting TMA via the command line Starting TMA on the Orchid a LAN IP address issue The executable DnsConfigure.exe Defining TMA for HP OpenView users and passwords 64 User manual 57
68 Starting TMA on a Telindus access device TMA for HP OpenView 5.1 Starting TMA via the Telindus access device symbol You are able to start a TMA session on a Telindus access device via the symbol on the HP OpenView network map. Proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Position the cursor on a Telindus access device symbol. 2 Click on the right mouse button. A symbol pop-up menu with commands appears. 3 From the symbol pop-up menu, select the Start TMA command. The TMA window opens, displaying the Telindus access device containment tree. Should you experience problems with the colours when starting the TMA graphical user interface on Sun Solaris, then refer to Section Solving possible colour problems on Sun Solaris. 58 User manual
69 Starting TMA on a Telindus access device 5.2 Starting TMA via the command line As an alternative to the symbol pop-up command, you can also start a TMA session on a Telindus access device via the command line. This uses the name resolution feature offered by the Alarm Manager. The command line syntax depends whether you want to start a TMA session on an IP device or a proxied IP device. Command line syntax for an IP device To start a TMA session via the command line on an IP device, use the following syntax: TMAOV <sysname> Examples: Suppose you have a Crocus E3 MUX connected to a LAN, with an IP address and with sysname = e3mux. In that case, type the following: TMAOV e3mux Suppose you have an Orchid 1003 LAN connected to a LAN, with an IP address and with sysname = Orchid_1003_LAN. In that case, type the following: TMAOV Orchid_1003_LAN Command line syntax for a proxied IP device TMAOV <proxy_sysname>_<objecttable_name> Examples: Suppose you have a Crocus HDSL connected to an Orchid 1003 LAN. The name for the Crocus HDSL in the Orchid its objecttable is hdsltt. The Orchid 1003 LAN on its turn is connected to a LAN, has an IP address and its sysname = o1003. In that case, type the following: TMAOV o1003_hdsltt Suppose you have a Crocus DXC connected to an Orchid 1003 LAN. The name for the Crocus DXC in the Orchid its objecttable is Crocus_DXC. The Orchid 1003 LAN on its turn is connected to a LAN, has an IP address and its sysname = Orchid_1003_LAN. In that case, type the following: TMAOV Orchid_1003_LAN_Crocus_DXC Important remarks The sysname or objecttable name may not contain white spaces. Use, for example, an underscore character instead. Refer to the examples above. Also the filter in the HP OpenView alarm browser does not allow white spaces in the sysname or objecttable name. Refer to Section The logged event. As explained in the table above, it is not possible to use the sysname of a proxied IP device. Instead use <proxy_sysname>_<objecttable_name>. If the Alarm Manager resides on a remote system, it is still possible to use its name resolution feature on your local system. You only have to define the remote system its IP address on your local system. Use the executable DnsConfigure.exe for this purpose. Refer to Section The executable DnsConfigure.exe. User manual 59
70 Starting TMA on a Telindus access device TMA for HP OpenView 5.3 Starting the sub-system picture via the Telindus access device symbol You are able to start the TMA sub-system picture of a Telindus access device via the symbol on the HP OpenView network map without having to open the TMA GUI. Proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Position the cursor on a Telindus access device symbol. 2 Click on the right mouse button. A symbol pop-up menu with commands appears. 3 From the symbol pop-up menu, select the Start TmaPicture command. A TMA window opens, displaying the Telindus access device sub-system picture. Should you experience problems with the colours when starting the TMA graphical user interface on Sun Solaris, then refer to Section Solving possible colour problems on Sun Solaris. 60 User manual
71 Starting TMA on a Telindus access device 5.4 Starting the sub-system picture via the command line As an alternative to the symbol pop-up command, you can also start the TMA sub-system picture of a Telindus access device via the command line. The syntax is the same as described in Section Starting TMA via the command line, except that the string TMAOV has to be replaced by TmaSsp: TmaSsp <sysname> For example: TmaSsp e3mux TmaSsp Orchid_1003_LAN TmaSsp <proxy_sysname>_<objecttable_name> For example: TmaSsp o1003_hdsltt TmaSsp Orchid_1003_LAN_Crocus_DXC User manual 61
72 Starting TMA on a Telindus access device TMA for HP OpenView 5.5 Starting TMA on the Orchid a LAN IP address issue Problem Suppose you have the following set-up: An Orchid 1003 LAN with an IP address on port A and on the LAN interface. Port A is connected to a Frame Relay network. The LAN interface is not connected (although it has an IP address). When the Orchid is discovered by HP OpenView, the IP address that is displayed in the objecttable of the AlarmManager is the IP address of the Orchid its LAN interface. What is more, when you start a TMA session on the Orchid (as explained in Section Starting TMA via the Telindus access device symbol), then TMA tries to start a TMA session using the IP address of the Orchid its LAN interface. Because this is not connected, you get a No response error after a while. Solution Do not define an IP address on the Orchid 1003 LAN its LAN interface if you are not using it. 62 User manual
73 Starting TMA on a Telindus access device 5.6 The executable DnsConfigure.exe What does this executable do? It is possible that the Alarm Manager resides on a remote system. Even in that case it is possible to use its name resolution feature on your local system. Enable this by configuring the IP address of the remote system on your local system. Use the executable DnsConfigure.exe for this purpose. The DnsConfigure.exe syntax The DnsConfigure.exe syntax is as follows: DnsConfigure <remote_system_ip_address> or DnsConfigure <remote_system_name> In order to remove the path to the remote system, then type: DnsConfigure -undo The DnsConfig file When you execute DnsConfigure.exe, a DnsConfig file is created in the directory <TMA_path>\TMA\config. This file contains the IP address or name of the remote system. Typing the DnsConfigure -undo command removes the DnsConfig file from your system. Example Suppose the Alarm Manager runs on a machine called MainSystem which has IP address Then type at the command prompt of your local system: DnsConfigure or DnsConfigure MainSystem User manual 63
74 Starting TMA on a Telindus access device TMA for HP OpenView 5.7 Defining TMA for HP OpenView users and passwords If a password has been configured in the Telindus access device, this password has to be transmitted before a TMA session can be opened on this device. The TMA for HP OpenView password configuration tool TmaUserConf.exe allows you to create TMA users and assign a password to these users. The TMA users are related to the accounts that are defined on the management station. Example Suppose user Y logs on to a Windows NT management station and starts a TMA session on a Telindus access device. Phase Description 1 TMA for HP OpenView checks which TMA user is related with the account of user Y. 2 TMA for HP OpenView checks which password is assigned to this user. 3 TMA for HP OpenView sends this password to the Telindus access device. 4 If this password corresponds with the password defined in the Telindus access device, then a TMA session opens on the device. does not correspond with the password defined in the Telindus access device, then no TMA session opens. If no passwords are defined in the Telindus access devices, then you do not have to create TMA users and corresponding passwords. However, every time you start a TMA session on a device, the following warning will appear: Warning: Could not read the user configuration file. You can stop this warning from appearing by executing the TmaUserConf.exe application and closing it without entering any data. 64 User manual
75 Managing the Alarm Manager with TMA 6. Managing the Alarm Manager with TMA As the Telindus access devices, the Alarm Manager can be configured using the Telindus Maintenance Application (TMA). This chapter explains how to start TMA on the Alarm Manager and how to browse the containment tree. It also gives an introduction to the attributes of the Alarm Manager. It introduces terms such as containment tree, group, object, attribute, value and action. The following chapter, Chapter 7 - Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager, explains the basic configuration of the Alarm Manager. For a complete overview of all configuration, status and performance attributes, refer to the reference manual. The following table gives an overview of this chapter. Section Title Page 6.1 Opening a TMA session on the Alarm Manager Containment tree terminology Where can you find an overview of all the attributes? The Alarm Manager containment tree 70 User manual 65
76 Managing the Alarm Manager with TMA TMA for HP OpenView 6.1 Opening a TMA session on the Alarm Manager In order to start a TMA session on the Alarm Manager, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Locate the Alarm Manager symbol on the HP OpenView network map. You can find this symbol in the map of the workstation on which HP OpenView is installed. I.e. the management station map. 2 Position the cursor on the Alarm Manager symbol. 3 Click on the right mouse button. A symbol pop-up menu with commands appears. 4 From the symbol pop-up menu, select the Start TMA command. The TMA window opens, displaying the Alarm Manager containment tree. 66 User manual
77 Managing the Alarm Manager with TMA 6.2 Containment tree terminology The following figure depicts the TMA window containing the Alarm Manager containment tree. Containment tree Objects Groups Attributes Attribute values Actions Structured values Continued on next page User manual 67
78 Managing the Alarm Manager with TMA TMA for HP OpenView Containment tree terminology (continued) The following table explains the terminology associated with the containment tree. Term containment tree Description The containment tree represents the hierarchical structure of the Alarm Manager. It is composed of a number of objects that are ordered in a tree. This tree resembles a Windows directory structure: it is also a levelled structure, with nodes which can be expanded or reduced the containment tree objects can be compared with file folders the objects contain attributes like file folders contain files. object An object represents a physical interface, an application or a combination of both. Each object has its own set of attributes. Example: The top object alarmman contains the sub object objects. attribute An attribute is a parameter related to a certain object. It has a certain value. Example: The object objects contains the configuration attribute maxpolltime, which can have a value ranging from 1 up to 20. value An attribute has a certain value which is changeable in case of a configuration attribute (provided you have write access) read only in case of a status, performance and alarm attribute. Example: The configuration attribute maxpolltime can have a value ranging from 1 up to 20. structured value Some attribute values contain underlying values: a structured value. These values are displayed in the structured value window. If an attribute contains structured values then a bit string, <Table> or <Struct> is displayed after the attribute. Example: The debugmask configuration attribute contains a structured value which displays debug messages that can be enabled or disabled. group Groups assemble a set of attributes related by functionality. The Alarm Manager uses three of the four groups in TMA: configuration status performance. action A group in combination with an object may have actions assigned to them. These actions are displayed in the action window. Example: The Clear UnMngtObjectTable action only appears when the object objects is selected in combination with the group Status. 68 User manual
79 Managing the Alarm Manager with TMA 6.3 Where can you find an overview of all the attributes? The reference part of this manual explains all the attributes of the Alarm Manager. One chapter describes one group of attributes: chapter 9 describes the configuration attributes. chapter 10 describes the status attributes. chapter 11 describes the performance attributes. chapter 12 describes the alarm attributes. Within a chapter, the objects and their underlying attributes are discussed in a sequential manner. I.e. from top to bottom, as they appear in the attribute window. User manual 69
80 Managing the Alarm Manager with TMA TMA for HP OpenView 6.4 The Alarm Manager containment tree The following table lists the different objects of the Alarm Manager containment tree. Object This object contains > alarmman the general system attributes. It is the top object in the containment tree. E.g. the configuration attributes sysname, syscontact and syslocation. >> objects the attributes associated with the polling of and synchronising with the Telindus access devices managed by TMA for HP OpenView and HP OpenView. E.g. the configuration attribute maxpolltime. >> inventory the attributes associated with inventory information of the devices that are managed by the Alarm Manager. E.g. the status attribute inventorytable. >> eventgeneration the attributes associated with the streaming of alarms, the alarm log file and the filtering of alarms. E.g. the configuration attribute logfile. 70 User manual
81 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager 7. Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager This chapter explains why the Alarm Manager was introduced in TMA for HP OpenView. It also explains the main features of the Alarm Manager. For a complete overview of all configuration, status and performance attributes, refer to the reference manual. The following table gives an overview of this chapter. Section Title Page 7.1 Introducing the Alarm Manager Auto discovery Setting the clock of the Orchid 1003 LAN Configuration and containment tree back-up Model upload Alarm status synchronisation The TMA alarm status of a Telindus device The unknownstate alarm Streaming detection Filtering alarms The alarm log file Conflicting device detection 96 Because the terms IP device, proxied IP device and non-ip device are often used in this chapter, it is important you understand what they mean. For a detailed description of these terms, refer to Section What are IP, proxied IP and non-ip devices?. User manual 71
82 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView 7.1 Introducing the Alarm Manager Because HP OpenView does not know how to handle non-ip devices and because the usual mechanism of handling IP devices (using SNMP traps) is not optimal, the Alarm Manager was created as part of TMA for HP OpenView. The main features of the Alarm Manager are: Automatically detect all Telindus non-ip devices configured in the Orchid 1003 LAN and create (or delete) them in HP OpenView. Synchronise with the status of all Telindus IP devices in the network. Synchronise with the status of all the Telindus devices managed by the Orchid 1003 LAN. Backing up the configuration of Telindus IP devices. For all the received alarms, generate an event in HP OpenView. Update the colour (representing the total alarm level) of all Telindus devices. Alarm filtering on different levels. Generate an alarm log file. 72 User manual
83 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager 7.2 Auto discovery This section deals with the auto discovery feature. It explains how the IP devices are discovered by HP OpenView and how the non-ip devices are discovered by the Alarm Manager. It also tells you more about the placement of the non-ip devices on the HP OpenView network map. The following table gives an overview of this chapter. Section Title Page Auto discovery of IP devices Auto discovery of non-ip and proxied IP devices Placement of non-ip devices on the network map Placement of non-ip devices on the network map an example 77 User manual 73
84 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView Auto discovery of IP devices HP OpenView features auto discovery of IP devices. Auto discovery uses ping and SNMP messages. When HP OpenView and TMA for HP OpenView are started, all the Telindus IP devices are passed to the Alarm Manager. The Alarm Manager starts polling the IP devices at regular time intervals. This time interval can be configured with the attribute maxpolltime (refer to Section Objects configuration attributes). As soon as the device answers to the poll, supplementary information is asked from the device (refer to Section Alarm status synchronisation). If at a certain moment a new Telindus IP device is auto-detected or created by the user in OpenView, this IP device is also passed to the Alarm Manager, who starts polling the IP device. A list of all the IP devices polled by the Alarm Manager and their corresponding state can be found in the status attribute objecttable (refer to Section Objects status attributes). Orchid 1003 LANs are polled twice by the Alarm Manager: the first poll is to the Orchid itself, the second poll is to the NMS group of the Orchid. 74 User manual
85 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager Auto discovery of non-ip and proxied IP devices Auto discovery of non-ip devices When an Orchid 1003 LAN is discovered by HP OpenView and passed to the Alarm Manager, the objecttable of the Orchid is retrieved and analysed. This is a table where all access devices connected to the Orchid are defined with their NMS address. For more information on this attribute refer to the section on NMS group configuration attributes in the manual of the Orchid 1003 LAN. When a non-ip device is found which is not yet known to HP OpenView, the Alarm Manager passes this device to HP OpenView who adds it to the network map. Auto discovery of proxied IP devices Devices for which an IP address is configured in the objecttable of the Orchid (i.e. proxied IP devices) are treated different from non-ip devices. When a proxied IP device is found by the Alarm Manager, it is not immediately passed to HP OpenView. HP OpenView has to auto-detect the device itself first. Only then the Alarm Manager passes additional information on the device to HP OpenView who adds it to the network map. As long as HP OpenView does not detect the proxied IP device, the nmsobjectstate value in the telindusobjecttable attribute remains unlicensed for the corresponding proxied IP device. Refer to Section Objects status attributes. If a device (non-ip or proxied IP) is no longer configured in the objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN, then the Alarm Manager deletes it from the HP OpenView network map. User manual 75
86 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView Placement of non-ip devices on the network map HP OpenView is a platform designed for IP devices. Therefore, the Alarm Manager must specify in which map the non-ip devices must be placed. The map is chosen on basis of the configured mapnumber in the objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN. This mapnumber corresponds to an IP network configured in the managednetworks attribute of the Orchid 1003 LAN. For more information on these attributes attribute refer to the section on NMS group configuration attributes in the manual of the Orchid 1003 LAN. In case the mapnumber in the objecttable is not filled in, one of the IP segments of the Orchid 1003 LAN is taken as default. This is determined in the following order: 1. If filled in, the value of the attribute o1003/nmsgroup/mainnmsipaddress is taken. This value must be a configured IP address of the Orchid 1003 LAN. 2. The first non-zero LAN IP address is taken. 3. The first non-zero IP address of port A is taken. 4. The first non-zero IP address of port B is taken. 5. The first non-zero IP address configured in the attribute o1003/nmsgroup/ipnmsgateway/managednetworks is taken. The following section gives an example on how non-ip devices are placed on the network map using the mapnumber attribute of the Orchid 1003 LAN. 76 User manual
87 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager Placement of non-ip devices on the network map an example The following is an example of how the non-ip devices are placed on the network map using the mapnumber attribute of the Orchid 1003 LAN. The o1003/nmsgroup/objecttable attribute Suppose the following is configured in the objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN: As you can see in the screenshot above, the mainnmsipaddress is set to This is, for instance, the IP address of the LAN interface of the Orchid 1003 LAN. Modem4 in the objecttable configuration, is a Card Version modem. Hence it is inserted in a card nest CN4. Therefore, its exitport attribute is defined as follows: The o1003/nmsgroup/ipnmsgateway/managednetworks attribute The managednetworks attribute is configured as follows: Continued on next page User manual 77
88 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView Placement of non-ip devices on the network map an example (continued) The Orchid 1003 LAN map Suppose the IP address of the LAN interface of the Orchid 1003 LAN is: with mask In that case the map for this Orchid looks like: The modem1 map In the objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN, no mapnumber is defined for modem1 (<OPT>). Therefore, the mainnmsipaddress value is taken to define in which map modem1 is placed. In our example, the mainnmsipaddress value is the IP address of the LAN interface of the Orchid. Therefore, modem1 is placed in the sub-map of the LAN interface (i.e. sub-map ). Continued on next page 78 User manual
89 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager Placement of non-ip devices on the network map an example (continued) The modem2 map In the objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN, mapnumber 0 is defined for modem2. This mapnumber corresponds with the mapnumber 0 defined in the managednetworks attribute. In this attribute, mapnumber 0 is assigned IP address Therefore, modem2 is placed in the sub-map The modem3 map In the objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN, mapnumber 1 is defined for modem3. This mapnumber corresponds with the mapnumber 1 defined in the managednetworks attribute. In this attribute, mapnumber 1 is assigned IP address Therefore, modem3 is placed in the sub-map The modem4 map In the objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN, mapnumber cardnest is defined for modem4. This means that in the managednetworks attribute, a mapnumber is searched for which the value corresponds with the cardnestaddress value of modem4. In our example, the cardnestaddress for modem4 is 2. In the managednetworks attribute, a mapnumber is defined with value 2. The IP address assigned to this mapnumber 2 is Therefore, modem4 is placed in the sub-map User manual 79
90 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView 7.3 Setting the clock of the Orchid 1003 LAN Because alarms coming from an Orchid 1003 LAN contain a timestamp, it is important that the real-time clock of all the Orchids are synchronised. Therefore, the Alarm Manager sets the clock of all the Orchids: the first time when the Alarm Manager successfully polls the Orchid 1003 LAN from then on, every day at midnight. 80 User manual
91 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager 7.4 Configuration and containment tree back-up How does configuration and containment tree back-up work? The Alarm Manager can back-up up to ten configurations and containment trees of a Telindus device. As soon as the Alarm Manager successfully polled a device, it verifies whether the configuration and/or the containment tree of this device has changed. If so, the Alarm Manager retrieves the full configuration and/or containment tree and saves it to the hard disk. Using the maxcfgfilessaved attribute you can configure how many configurations and containment trees the Alarm Manager has to back-up for each device. Older files are deleted. For more information, refer to Section Objects configuration attributes. Where are the files stored? The configuration and containment tree files are stored in the following directories: <TMA_path>\TMA\config\ipcfg : contains the configuration files of the IP devices. The file name is formatted as follows: c<ip>_<n>.cms. <TMA_path>\TMA\config\ipinv : contains the containment tree files of the IP devices. The file name is formatted as follows: t<ip>_<n>.cms. <TMA_path>\TMA\config\nmscfg : contains the configuration files of the non-ip and proxied IP devices. The file name is formatted as follows: c<ip>_<address>_<n>.cms. <TMA_path>\TMA\config\nmsinv : contains the containment tree files of the non-ip and proxied IP devices. The file name is formatted as follows: t<ip>_<address>_<n>.cms. Also the Alarm Manager its own configuration is kept on the hard disk: <TMA_path>\TMA\config\alarmman.cms. How is the file name formatted? As you can see in the paragraph above, the file name contains the following strings: c: indicates it is a configuration file. t: indicates it is a containment tree file. <ip>: is the IP address of the IP device (in case of an IP device). proxy device, e.g. the Orchid 1003 LAN (in case of a non-ip or proxied IP device). <address>: is the absolute or relative address of the non-ip or proxied IP device. It can have the following format: A<a> is the absolute address of the device, where <a> is the address value. R<r>R<x-yy-z> is the relative address of the device when connected through the high-speed bus, where <r> is the address value, <x> is the rack number, <yy> is the slot number and <z> is the device number (i.e. A, B, C or D). R<r>P<p> is the relative address of the device when connected through a serial port, where <r> is the address value and <p> is the serial port number. <n> is the serial number of the file name. This number increments each time a new file is saved. The number ranges from 0 up to 9. I.e. when 10 is reached, the number wraps to 0. What is the format of the files? The format of the configuration and containment tree files is CMS. This is the same format as if you performed a Export - Full configuration command in TMA. User manual 81
92 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView 7.5 Model upload What is a model file? A model file provides, for each Telindus device, the information TMA needs to connect and exchange information with the device. The installation of the model files may occur separately from the TMA executable installation. This because the model files evolve as the devices evolve. The model files delivered on the CD-ROM correspond to the latest firmware version of the Telindus devices at the creation time of the CD-ROM. If, at a later time, you want to add devices with a more recent firmware version, a re-installation of the model files of these devices may be required. Auto upload automates this process. What is the location of the model files? The model files are located in the directory <TMA_path>\TMA\model and have the extension *.mod. What is model upload? The Alarm Manager is capable of retrieving (uploading) the model file from the device. This means that as soon as the Alarm Manager is able to poll the device, it asks the device for its model file and places it in the directory <TMA_path>\TMA\model. These uploaded model files can be identified because they have the extension *.smo. They are present alongside the normal model file (*.mod). They are, as it were, an addition to the normal model file. If for some reason the auto upload feature does not work, you will still need to do the model upgrade manually. Refer to Section How to upgrade the model files. 82 User manual
93 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager 7.6 Alarm status synchronisation This section explains how the Alarm Manager synchronises with the alarm status of the Telindus access devices. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page Synchronising with the alarm status of IP devices Synchronising with the alarm status of non-ip and proxied IP devices The logged event 86 User manual 83
94 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView Synchronising with the alarm status of IP devices First time synchronisation As soon as the Alarm Manager successfully polled an IP device, it asks the current alarm status of that device. The first time the status is retrieved, all the currently active alarms of the device are translated by the Alarm Manager into HP OpenView events. Also the total alarm level of the device is passed to HP OpenView. This total alarm level then determines the colour of the device symbol on the HP OpenView network map. For more information on symbol colouring refer to Section The colour of the symbols on the HP OpenView network map and Section The Telindus access device symbol colours. Continuous synchronisation When the Alarm Manager is synchronised with the alarm status of the IP device, the alarms of the device are translated into events as they come in. I.e. each alarm received from the device is translated by the Alarm Manager into an HP OpenView event. If necessary, the colour of the device symbol is adjusted. Resynchronisation If the Alarm Manager has to resynchronise with the alarm status of an IP device (i.e. the status has to be re-read), then it activates the AlarmSyncLoss alarm. After that, all the changed alarms of the device are passed by the Alarm Manager to HP OpenView. Then the Alarm Manager deactivates the AlarmSyncLoss alarm. 84 User manual
95 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager Synchronising with the alarm status of non-ip and proxied IP devices For non-ip and proxied IP devices, it is the Orchid 1003 LAN that synchronises with the alarm status of these devices. This status information is then passed on to the Alarm Manager. I.e. the Alarm Manager indirectly synchronises with the non-ip and proxied IP devices through the NMS group of the Orchid 1003 LAN. First time synchronisation When an Orchid 1003 LAN boots, it synchronises with the devices configured in the objecttable. During such a start-up phase, a lot of alarms are generated. Because these particular alarms are not very useful, it is best that they are not passed on to the Alarm Manager. Therefore, the Alarm Manager waits a certain time before it synchronises with the NMS group of the Orchid 1003 LAN. This delay time can be set with the statusdelay attribute (refer to Section Objects configuration attributes). The statusdelay is the sysuptime of the Orchid 1003 LAN before the Alarm Manager starts synchronising. Continuous synchronisation When the Alarm Manager is synchronised with the alarm status of the non-ip or proxied IP device, the alarms of the device are translated into events as they come in. I.e. each alarm received from the device by the Orchid 1003 LAN, is passed to the Alarm Manager who translates this alarm into an HP OpenView event. If necessary, the colour of the device symbol is adjusted. Resynchronisation If the Alarm Manager, or more particular the Orchid 1003 LAN, has to resynchronise with the alarm status of a device (i.e. the status has to be re-read), then it activates the AlarmSyncLoss alarm. After that, all the changed alarms of the device are passed through the Orchid to the Alarm Manager and eventually to HP OpenView. Then the Orchid 1003 LAN deactivates the AlarmSyncLoss alarm. User manual 85
96 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView The logged event The event (or alarm message) that is logged in the HP OpenView alarm browser has the following format: <topobject>\ \<objectx>.<alarmname> on/off (duration = <number> seconds) The duration is the time difference between the current state change of the alarm and the previous state change of that alarm. A state change is when the alarm goes from off to on or vice versa. Example Suppose a linkdown alarm becomes active on the waninterface of a Crocus Router Interface. The last time the state of this linkdown alarm changed from on to off was 5 minutes ago. This results in the following alarm message: crocusrouter\waninterface.linkdown on (offduration = 300 seconds) Important remark The HP OpenView alarm browser allows you to filter out alarms of certain devices. For proxied devices you define the filter based on the sysname of the proxy device and the objecttable name of the proxied device: <proxy_sysname>_<objecttable_name> However, it is not allowed that the sysname or the objecttable name contains white spaces. If it does, you get the following message when trying to define the filter: Warning! Invalid white space in the node name Solve this problem by removing the white spaces in the sysname and / or objecttable name (e.g. use the underscore character instead). 86 User manual
97 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager 7.7 The TMA alarm status of a Telindus device This section explains how you can quickly get an overview of the alarm status of a Telindus device. It also shows you how you can acknowledge individual alarms. It discusses the relation between the TMA alarm status window and the HP OpenView alarm browser. Finally, a short word is said on how acknowledged and unacknowledged alarms can influence the colour of the Telindus device symbol. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page Displaying the TMA alarm status window The TMA alarm status window elements The TMA alarm status window alarm browser relation (Un)acknowledged alarms and the symbol colour 91 User manual 87
98 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView Displaying the TMA alarm status window What is the TMA alarm status window? The TMA alarm status window of a Telindus access device contains all the unmasked alarms that are currently active on the device. Displaying the TMA alarm status window In order to display the TMA alarm status window, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Position the cursor on a Telindus access device symbol. 2 Click on the right mouse button. A symbol pop-up menu with commands appears. 3 From the symbol pop-up menu, select the TMA alarm status command. The TMA alarm status window opens, displaying the current, unmasked Telindus access device alarms. 88 User manual
99 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager The TMA alarm status window elements The following figure shows an example of an TMA alarm status window: The elements of the TMA alarm status window are the following: Element Description This is the refresh button. Use this button to refresh the TMA alarm status window so that it displays the latest information. This is the acknowledge button. Use this button to acknowledge an alarm. Do this by selecting an entire line and pressing the button. Alternatively you can immediately tick the acknowledge field (first field). <Ack field> By ticking the first field of a line, you acknowledge the alarm. This has an impact on the HP OpenView alarm browser and possibly on the colour of the Telindus access device symbol. For more information refer to Section The TMA alarm status window alarm browser relation and Section (Un)acknowledged alarms and the symbol colour. Path Displays the Telindus access device containment tree path of the current alarm. The path is of the form <top_object>/<sub_object>.<alarm>. Example Suppose the following is displayed: crocusfocv/quade1/g703[3].linkdown. This means the linkdown alarm is active. This alarm is located in the sub-object g703[3], which is located in the sub-object quade1 which is located in the top-object crocusfocv. Timestamp Displays the date and time the Orchid 1003 LAN (in case of a non- or poxied IP device) or the Alarm Manager (in case of a true IP device) received the alarm. The timestamp is of the form mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss AM/PM Duration Level Acked by Ack time Displays the time the alarm is active. Displays the alarm level of the current alarm. In case the alarm is acknowledged, this field displays the login name of the person who acknowledged the alarm. In case the alarm is acknowledged, this field displays the time when this alarm was acknowledged. The ack time is of the form mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss AM/PM Streaming Displays whether the alarm is streaming (on) or not (off). User manual 89
100 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView The TMA alarm status window alarm browser relation Starting from HP OpenView version 6.0 the TMA alarm status window and the HP OpenView alarm browser are linked. This explained in the following table: alarm browser TMA alarm status window Description acknowledge acknowledge If you acknowledge an alarm in the alarm browser then this alarm is also acknowledged in the TMA alarm status window, and vice versa. unacknowledge unacknowledge If you unacknowledge an alarm in the alarm browser then this alarm is also unacknowledged in the TMA alarm status window. It is not possible to unacknowledge alarms in the TMA alarm status window. delete acknowledge no action If you delete an alarm in the alarm browser then this alarm is acknowledged left unchanged in the TMA alarm status window, depending on the value of the attribute deleteeventaction. See below. alarmman/eventgeneration/deleteeventaction default: ack event Use the deleteeventaction attribute to determine what is done with an alarm in the TMA alarm status window when this alarm is deleted in the HP OpenView alarm browser. The following table clarifies this: If you delete an alarm in the alarm browser then in the TMA alarm status window this alarm is acknowledged left unchanged when the deleteeventaction attribute is set to ack event none 90 User manual
101 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager (Un)acknowledged alarms and the symbol colour alarmman/eventgeneration/statussource default: all events Use the statussource attribute to determine how the (un)acknowledged alarms influence the colour of the Telindus access device symbol. The following table clarifies this: If the statussource attribute is set to all events, unacked events, then the device status corresponds with the total alarm level of all alarms, both acknowledged and unacknowledged. the unacknowledged alarms only. I.e. the acknowledged alarms are ignored. User manual 91
102 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView 7.8 The unknownstate alarm If an IP device does not respond to the polling of the Alarm Manager, then a notresponding alarm is generated for this device. If this device is an Orchid 1003 LAN, then it is also impossible to synchronise with the non-ip or proxied IP devices that are connected to this Orchid. For these devices, an unknownstate alarm is generated. In case such an unknownstate alarm occurs, you can configure what action has to be taken. For more information, refer to the unknownalarmconfig attribute in Section Event generation configuration attributes. 92 User manual
103 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager 7.9 Streaming detection What is streaming? Under certain circumstances, it is possible that an alarm continuously toggles between on and off. This is called streaming. Streaming results in a very long alarm list in HP OpenView which eventually could overload the system. To prevent this from happening, the Alarm Manager is able to detect streaming and to stop that the streaming alarm is passed on to HP OpenView. How does the Alarm Manager detect streaming? If the number of times a certain alarm comes on during a certain period (i.e. the streaminginterval attribute) equals or exceeds the value configured in the attribute streamingonlimit, then the Alarm Manager considers that this particular alarm is streaming. The Alarm Manager passes the particular alarm on to HP OpenView once, and adds the string Streaming Activated at the end of the alarm message. From that moment forward, the Alarm Manager stops passing on the streaming alarm to HP OpenView. When is streaming deactivated? If the number of times a certain alarm comes on during the streaminginterval equals or drops below the value configured in the attribute streamingofflimit, then the Alarm Manager no longer considers that this particular alarm is streaming. The Alarm Manager passes an alarm on to HP OpenView which contains the string Streaming Deactivated at the end of the alarm message. From that moment forward, the passing of alarms to HP OpenView is normalised again. User manual 93
104 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView 7.10 Filtering alarms Using the filter attribute in the objecttable of the Orchid 1003 LAN, you can define a filter number for each non-ip and proxied IP device entered in this table. For IP devices, you can define this filter number using the alarmfilter attribute located in the management object. These filter numbers correspond to the filter numbers as they can be defined using the filters attribute in the eventgeneration object of the Alarm Manager. Using these filter numbers, you can determine which is the minimum required alarm level in order to log an alarm in the log file pass the alarm to HP OpenView. For more information on the filters attribute, refer to Section Event generation configuration attributes. In older firmware versions of Telindus IP access devices it is possible that the alarmfilter attribute is not present yet. In that case, a value of 0 is assumed. 94 User manual
105 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager 7.11 The alarm log file What is the alarm log file? The Alarm Manager not only passes alarms to HP OpenView, it also writes them to a log file. This file is located in the sub-directory <TMA_path>\TMA\log. You can set the properties of this log file using the logfile attribute in the eventgeneration object of the Alarm Manager. For more information, refer to Section Event generation configuration attributes. The alarm log file name The name of the alarm log file looks as follows: am<dd>_<mm>_<yyyy>_<hh>h<mm>m<ss>s.log Where dd/mm/yyyy and hh:mm:ss is the date and hour when the first alarm was logged in the file. Example: am03_07_2000_18h34m46s.log What is logged in the alarm log file? The following elements are logged in the file (they are separated by tabs): The timestamp of the alarm followed by the duration. The duration is the time difference between the current state change of the alarm and the previous state change of that alarm. A state change is when the alarm goes from off to on or vice versa. E.g. 24 march :44:12 (445 seconds) The alarm level of this alarm. This can range from 0 up to 254. The name of the device that has sent the alarm. In case of an IP device, this is the sysname. If the sysname is empty, it is the IP address of the device. In case of non-ip and proxied IP devices, this is the sysname of the Orchid 1003 LAN followed by a _ character and the name by which the device is configured in the objecttable of the Orchid. The alarm message. This includes the object path of the alarm separated by a /. The last object is followed by a. and the name of the alarm. Then the string on or off is printed. This results in the following: <topobject>\ \<objectx>.<alarmname> on/off. E.g. crocusrouter\waninterface.linkdown on User manual 95
106 Basic configuration of the Alarm Manager TMA for HP OpenView 7.12 Conflicting device detection When are devices conflicting? Devices can conflict, for instance, due to an incorrect configuration (e.g. two devices with the same IP address). How are conflicting devices indicated? The Alarm Manager is able to detect conflicting devices. It indicates a conflicting device as follows: When the conflicting device is an IP device, a proxied IP device, a non-ip device, then its symbol is coloured blue on the HP OpenView map, the ctrlpollstate indicates Conflicting and a message is shown in the messages table. its symbol is coloured blue on the HP OpenView map, the nmspollstate indicates Conflicting and a message is shown in the messages table. its symbol is deleted from the HP OpenView map, the nmspollstate indicates Conflicting and a message is shown in the messages table. A device conflicting with itself When two devices are in conflict with each other due to an erroneous configuration, we can speak of a true conflict. However, a device can be in conflict with itself when HP OpenView does not see it as being one and the same device. Example: Suppose an IP device has a certain IP address and HP OpenView uses this address to poll the device. Phase Description 1 Suppose you change the IP address of the device. The device gets the status Not Responding in HP OpenView. 2 HP OpenView then auto-discovers the new IP address, it does not know that the nonresponding device and the device with the new IP address is one and the same device. It creates a new devices and sends it to the Alarm Manager. 3 The Alarm Manager detects that these two devices are in conflict with each other. It colours both symbols blue. 4 The situation stays like this until one of the two devices is deleted in HP OpenView (by the user or HP OpenView itself) after which the situation normalises and the remaining device contains the latest status information. 96 User manual
107 Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView 8. Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView This chapter gives some useful configuration guidelines for HP OpenView. The following table gives an overview of this chapter. Section Title Page 8.1 Enabling auto discovery in HP OpenView Making all levels of sub-maps persistent Configuring the polling parameters Setting a sufficiently large poll time-out Cleaning the trapd.conf file Solving possible colour problems on Sun Solaris 105 User manual 97
108 Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 8.1 Enabling auto discovery in HP OpenView To enable auto discovery in HP OpenView, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 In the Options menu, select Network Polling Configuration: IP/IPX. 2 In the IP Discovery tab, select Discover new IP nodes and press OK. 98 User manual
109 Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView 8.2 Making all levels of sub-maps persistent All levels of sub-maps should be made persistent in order to prevent problems with the auto discovery of the Telindus access devices. For Windows, the levels of sub-maps are not persistent by default. To make all levels of sub-maps persistent for Windows, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 In the Map menu, select Properties. 2 In the Applications tab, select IP Map and press Configure For This Map. 3 Double click on the field To what level should sub-maps be persistent, select All levels and press OK. To make all levels of sub-maps persistent for UNIX, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 In the Map menu, pick Maps. 2 Select Describe/Modify. 3 For the field To what level should sub-maps be persistent, select All levels. User manual 99
110 Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 8.3 Configuring the polling parameters For the true IP device (i.e. not for the proxied IP devices) such as Orchid 1003 LAN, Crocus Router 2M, etc., the configuration of the polling parameters is very critical for the well behaviour and performance of HP OpenView. For the well configuration of the polling parameters, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 In the Performance menu, select Network Polling Statistics. 2 In the Options menu, select SNMP configuration. 3 Change the polling parameters so that every single line in the statistics graph stays in the positive region. 100 User manual
111 Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView 8.4 Setting a sufficiently large poll time-out Modems without flash memory (1) need a sufficiently large poll timeout configured on HP OpenView for proper operation. Especially if statistical information is assembled via SNMP, a minimum time-out value of 20 seconds is recommended. Either you can set the polling timeout for all devices Step Action 1 In the Options menu, select SNMP configuration. 2 Change the Status Polling value to e.g. 60 seconds. or you can change the poll timeout selectively Step Action 1 In the Options menu, select SNMP configuration. 2 Select the Specific nodes tab. 3 Change the Status Polling value to e.g. 60 seconds for a specific device. (1) Usually these are older devices, such as the Crocus HS or Crocus HDSL (not the Crocus HDSL F). More recent devices all have flash memory. User manual 101
112 Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView 8.5 Cleaning the trapd.conf file This section explains what the HP OpenView file trapd.conf is. It also explains when and how to clean this file. The following table gives an overview of this section. Section Title Page What is the trapd.conf file? When to clean the trapd.conf file? Cleaning the trapd.conf file User manual
113 Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView What is the trapd.conf file? The HP OpenView file trapd.conf contains trap definitions. TMA for HP OpenView before the Alarm Manager In previous versions of TMA for HP OpenView, the Orchid 1003 LAN and HP OpenView used SNMP traps to exchange alarm information. When such a version of TMA for HP OpenView was installed, it created a directory <TMA_path>\TMA\TMAOV where the trap files (*.trp) of all the Telindus devices were placed. What is more, the information contained in these files was copied to the HP OpenView file trapd.conf. TMA for HP OpenView and the Alarm Manager Starting from TMA for HP OpenView version S0006/00700 (Windows), S0005/00800 (Sun Solaris) or S0008/00400 (HP UNIX) and the TMA data files version S0011/03100, an Alarm Manager has been implemented in HP OpenView. The communication between this Alarm Manager and the Orchid 1003 LAN now uses the proprietary CMS2 protocol. This means that the trap files are no longer necessary. Therefore, the directory <TMA_path>\TMA\TMAOV is removed when a newer version of TMA for HP OpenView is installed. However, the data in the trapd.conf file is not removed. Because the performance of HP OpenView is inversely proportional with the length of the trapd.conf file, it might be best to clean this file. I.e. to remove the (unnecessary) trap information of the Telindus devices When to clean the trapd.conf file? You have to clean the trapd.conf file when you upgrade from a TMA for HP OpenView version lower than S0006/00700 (Windows), S0005/00800 (Sun Solaris) or S0008/00400 (HP UNIX) to a higher version. User manual 103
114 Configuration guidelines for HP OpenView TMA for HP OpenView Cleaning the trapd.conf file In order to clean the trapd.conf file, proceed as follows: Step Action 1 Locate the trapd.conf file on your system. 2 Open the trapd.conf file in a text editor. 3 Search for the following Telindus identification string: Remove every entry from the word EVENT up to the word EDESC where this string appears. However, do not remove the entries of the Alarm Manager. The following figure clarifies this: REMOVE: DO NOT REMOVE: 5 Save the trapd.conf file. 104 User manual
TMA CLI TMA CLI. USER and REFERENCE MANUAL. Version:
 TMA CLI USER and REFERENCE MANUAL Version: 1.5 182085 Telindus Technical Publications Geldenaaksebaan 335 B-3001 Leuven Belgium tel. +32 16 382011 Copyright TMA CLI Copyright notice The information and
TMA CLI USER and REFERENCE MANUAL Version: 1.5 182085 Telindus Technical Publications Geldenaaksebaan 335 B-3001 Leuven Belgium tel. +32 16 382011 Copyright TMA CLI Copyright notice The information and
TMA TMA. USER and REFERENCE MANUAL. Version:
 USER and REFERENCE MANUAL Version: 5.6 182086 Telindus Technical Publications Geldenaaksebaan 335 B-3001 Leuven Belgium tel. +32 16 382011 Copyright notice Copyright notice The information and descriptions
USER and REFERENCE MANUAL Version: 5.6 182086 Telindus Technical Publications Geldenaaksebaan 335 B-3001 Leuven Belgium tel. +32 16 382011 Copyright notice Copyright notice The information and descriptions
Xerox CentreWare for HP OpenView NNM Users Guide Version 1.5
 Xerox CentreWare for HP OpenView NNM Users Guide Version 1.5 2002 by Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Copyright protection claimed includes all forms and matters of copyright material and information
Xerox CentreWare for HP OpenView NNM Users Guide Version 1.5 2002 by Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Copyright protection claimed includes all forms and matters of copyright material and information
INSTALLATION and OPERATION MANUAL
 INSTALLATION and OPERATION MANUAL TMA User Manual Fourth Edition MRP : 160791 Telindus Technical Publications Geldenaaksebaan 335 B-3001 Leuven Belgium +32 16 382 011 PROPRIETARY MATERIAL The information
INSTALLATION and OPERATION MANUAL TMA User Manual Fourth Edition MRP : 160791 Telindus Technical Publications Geldenaaksebaan 335 B-3001 Leuven Belgium +32 16 382 011 PROPRIETARY MATERIAL The information
Xerox CentreWare for Tivoli NetView Users Guide Version 1.1.8
 Xerox CentreWare for Tivoli NetView Users Guide Version 1.1.8 2009 by Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Copyright protection claimed includes all forms and matters of copyright material and information
Xerox CentreWare for Tivoli NetView Users Guide Version 1.1.8 2009 by Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Copyright protection claimed includes all forms and matters of copyright material and information
ehealth Integration for HP OpenView User Guide
 ehealth Integration for HP OpenView User Guide MN-NHHPOV-003 July 2005 Important Notice Concord Communications, Inc., ehealth, ehealth Suite, the Concord Logo, eroi, AdvantEDGE, SystemEDGE, Live Health,
ehealth Integration for HP OpenView User Guide MN-NHHPOV-003 July 2005 Important Notice Concord Communications, Inc., ehealth, ehealth Suite, the Concord Logo, eroi, AdvantEDGE, SystemEDGE, Live Health,
HP StorageWorks Performance Advisor. Installation Guide. Version 1.7A
 HP StorageWorks Performance Advisor Installation Guide Version 1.7A notice Copyright 2002-2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Edition 0402 Part Number B9369-96068 Hewlett-Packard Company makes
HP StorageWorks Performance Advisor Installation Guide Version 1.7A notice Copyright 2002-2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Edition 0402 Part Number B9369-96068 Hewlett-Packard Company makes
Xerox CentreWare for HP OpenView NNM User Guide. Version 1.1
 Xerox CentreWare for HP OpenView NNM User Guide Version 1.1 2000 by Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Copyright protection claimed includes all forms and matters of copyright material and information
Xerox CentreWare for HP OpenView NNM User Guide Version 1.1 2000 by Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. Copyright protection claimed includes all forms and matters of copyright material and information
AlliedView -EMS 4.0 INSTALLATION GUIDE
 AlliedView -EMS 4.0 INSTALLATION GUIDE AlliedView -EMS 4.0 INSTALLATION GUIDE Page 1 of 29 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION...3 2 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS...3 2.1 WINDOWS... 3 2.2 SOLARIS... 3 2.3 HP-UX...
AlliedView -EMS 4.0 INSTALLATION GUIDE AlliedView -EMS 4.0 INSTALLATION GUIDE Page 1 of 29 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION...3 2 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS...3 2.1 WINDOWS... 3 2.2 SOLARIS... 3 2.3 HP-UX...
User s Guide. Duralink Server Manager
 R User s Guide Duralink Server Manager R Adaptec, Inc. 691 South Milpitas Boulevard Milpitas, CA 95035 1997 Adaptec, Inc. All rights reserved. Adaptec, and the Adaptec logo are trademarks of Adaptec, Inc.
R User s Guide Duralink Server Manager R Adaptec, Inc. 691 South Milpitas Boulevard Milpitas, CA 95035 1997 Adaptec, Inc. All rights reserved. Adaptec, and the Adaptec logo are trademarks of Adaptec, Inc.
Installation Guide V1.1
 Installation Guide V1.1 The information contained in this manual is the licensed property of Fujitsu Software Technology Corporation. Use of the information contained herein is restricted to the terms
Installation Guide V1.1 The information contained in this manual is the licensed property of Fujitsu Software Technology Corporation. Use of the information contained herein is restricted to the terms
ChromQuest 4.2 Chromatography Data System
 ChromQuest 4.2 Chromatography Data System Installation Guide CHROM-97200 Revision A April 2005 2006 Thermo Electron Corporation. All rights reserved. Surveyor is a registered trademark and ChromQuest is
ChromQuest 4.2 Chromatography Data System Installation Guide CHROM-97200 Revision A April 2005 2006 Thermo Electron Corporation. All rights reserved. Surveyor is a registered trademark and ChromQuest is
LifeSize Gatekeeper Installation Guide
 LifeSize Gatekeeper Installation Guide July 2008 Copyright Notice 2008 LifeSize Communications Inc, and its licensors. All rights reserved. LifeSize Communications has made every effort to ensure that
LifeSize Gatekeeper Installation Guide July 2008 Copyright Notice 2008 LifeSize Communications Inc, and its licensors. All rights reserved. LifeSize Communications has made every effort to ensure that
Network Management Utility
 4343-7705-02 Network Management Utility Foreword Welcome Network Management Utility is utility software that provides central control over printers, copiers, and other devices on a network. With Network
4343-7705-02 Network Management Utility Foreword Welcome Network Management Utility is utility software that provides central control over printers, copiers, and other devices on a network. With Network
Installing Essentials
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes installing Resource Manager Essentials 3.2 on a Windows system. It consists of: Product Overview Installation Overview Preparing to Install Essentials Importing Data Manually
CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes installing Resource Manager Essentials 3.2 on a Windows system. It consists of: Product Overview Installation Overview Preparing to Install Essentials Importing Data Manually
Installing Essentials
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to install and uninstall Essentials, including upgrades and reinstallation. You must install CiscoWorks2000 CD One before you can install Resource Manager Essentials.
CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to install and uninstall Essentials, including upgrades and reinstallation. You must install CiscoWorks2000 CD One before you can install Resource Manager Essentials.
EMS Installation. Workstation Requirements CHAPTER. EMS Lite (Windows 95/98) EMS NT (Windows NT 4.0)
 CHAPTER 2 EMS Installation This chapter provides instructions for installing the Element Management System (EMS) software on a user workstation. Workstation Requirements The following sections list the
CHAPTER 2 EMS Installation This chapter provides instructions for installing the Element Management System (EMS) software on a user workstation. Workstation Requirements The following sections list the
9936A LogWare III. User s Guide. Revision
 9936A LogWare III User s Guide Revision 850701 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...1 1.1 Symbols Used... 1 1.2 Conventions... 1 1.3 What is LogWare?... 1 1.4 License Agreement... 2 1.5 Requirements...
9936A LogWare III User s Guide Revision 850701 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...1 1.1 Symbols Used... 1 1.2 Conventions... 1 1.3 What is LogWare?... 1 1.4 License Agreement... 2 1.5 Requirements...
LABEL ARCHIVE Administrator s Guide
 LABEL ARCHIVE Administrator s Guide DOC-LAS2015_25/05/2015 The information in this manual is not binding and may be modified without prior notice. Supply of the software described in this manual is subject
LABEL ARCHIVE Administrator s Guide DOC-LAS2015_25/05/2015 The information in this manual is not binding and may be modified without prior notice. Supply of the software described in this manual is subject
HP ProCurve Manager Plus
 HP ProCurve Manager Plus Getting Started Guide The all-in-one solution for managing HP ProCurve networks HP ProCurve Manager Plus Getting Started Guide Copyright 2003-2004 Hewlett-Packard Development
HP ProCurve Manager Plus Getting Started Guide The all-in-one solution for managing HP ProCurve networks HP ProCurve Manager Plus Getting Started Guide Copyright 2003-2004 Hewlett-Packard Development
Laser Beam Printer. Network Guide. IMPORTANT: Read this manual carefully before using your printer. Save this manual for future reference.
 Laser Beam Printer Network Guide IMPORTANT: Read this manual carefully before using your printer. Save this manual for future reference. ENG Network Guide How This Manual Is Organized Chapter 1 Before
Laser Beam Printer Network Guide IMPORTANT: Read this manual carefully before using your printer. Save this manual for future reference. ENG Network Guide How This Manual Is Organized Chapter 1 Before
Table of Contents. 1 Introduction. 2 Wireless Configurations. 3 Setting Up your LAN Administrator Station
 Table of Contents 1 Introduction About Avaya Wireless 1-1 About Avaya Wireless Tools 1-2 About Avaya Wireless Access Points 1-5 About This User s Guide 1-6 About Icons used in this Document 1-7 On-line
Table of Contents 1 Introduction About Avaya Wireless 1-1 About Avaya Wireless Tools 1-2 About Avaya Wireless Access Points 1-5 About This User s Guide 1-6 About Icons used in this Document 1-7 On-line
CA ehealth Integration for HP OpenView
 CA ehealth Integration for HP OpenView User Guide r6.1 This documentation and any related computer software help programs (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for the end user s informational
CA ehealth Integration for HP OpenView User Guide r6.1 This documentation and any related computer software help programs (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for the end user s informational
AVWorks. Installer/User Guide
 AVWorks Installer/User Guide INSTRUCTIONS This symbol is intended to alert the user to the presence of important operating and maintenance (servicing) instructions in the literature accompanying the appliance.
AVWorks Installer/User Guide INSTRUCTIONS This symbol is intended to alert the user to the presence of important operating and maintenance (servicing) instructions in the literature accompanying the appliance.
ARM Firmware Suite v1.4 Installation Guide
 ARM Firmware Suite v1.4 Installation Guide Copyright 2000-2002 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. Release Information Date Issue Change 16 February 2000 A First Release 1 June 2000 B P720 Release 1 October
ARM Firmware Suite v1.4 Installation Guide Copyright 2000-2002 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. Release Information Date Issue Change 16 February 2000 A First Release 1 June 2000 B P720 Release 1 October
OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for AT&T OneVision
 585-229-109 Issue 1 October, 1995 Table of Contents OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for AT&T OneVision Graphics AT&T 1988 Contents About This Book vii Intended Audiences
585-229-109 Issue 1 October, 1995 Table of Contents OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for AT&T OneVision Graphics AT&T 1988 Contents About This Book vii Intended Audiences
Installation Guide. EventTracker Enterprise. Install Guide Centre Park Drive Publication Date: Aug 03, U.S. Toll Free:
 EventTracker Enterprise Install Guide 8815 Centre Park Drive Publication Date: Aug 03, 2010 Columbia MD 21045 U.S. Toll Free: 877.333.1433 Abstract The purpose of this document is to help users install
EventTracker Enterprise Install Guide 8815 Centre Park Drive Publication Date: Aug 03, 2010 Columbia MD 21045 U.S. Toll Free: 877.333.1433 Abstract The purpose of this document is to help users install
CiscoView CD Installation Instructions for Solaris and HP-UX
 CiscoView CD Installation Instructions for Solaris and HP-UX This instruction book provides information about installing and running CiscoView on your network management station. You can install CiscoView
CiscoView CD Installation Instructions for Solaris and HP-UX This instruction book provides information about installing and running CiscoView on your network management station. You can install CiscoView
Mailbox Manager Getting Started Guide. Licensing Installation Options System Requirements Installation Instructions
 Mailbox Manager Getting Started Guide Licensing Installation Options System Requirements Installation Instructions Mailbox Manager Release 5.4 December 2006 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Licenses...
Mailbox Manager Getting Started Guide Licensing Installation Options System Requirements Installation Instructions Mailbox Manager Release 5.4 December 2006 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Licenses...
2008 Elluminate, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Installation Guide
 2008 Elluminate, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Installation Guide No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording
2008 Elluminate, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Installation Guide No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording
Batch Eligibility Long Term Care claims
 DXC Technology Provider Electronic Solutions software lets Connecticut Medical Assistance Program providers verify patient s eligibility and submit and correct claims for services all electronically. The
DXC Technology Provider Electronic Solutions software lets Connecticut Medical Assistance Program providers verify patient s eligibility and submit and correct claims for services all electronically. The
Avigilon Control Center Server User Guide
 Avigilon Control Center Server User Guide Version 4.12 PDF-SERVER-E-Rev1 Copyright 2012 Avigilon. All rights reserved. The information presented is subject to change without notice. No copying, distribution,
Avigilon Control Center Server User Guide Version 4.12 PDF-SERVER-E-Rev1 Copyright 2012 Avigilon. All rights reserved. The information presented is subject to change without notice. No copying, distribution,
Configuration Guide for Microsoft Internet Connection Sharing
 Configuration Guide for Microsoft Internet Connection Sharing HUB INTERNET HOST CLIENTS Copyright 2002 Hughes Network Systems, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Hughes Electronics Corporation. All rights
Configuration Guide for Microsoft Internet Connection Sharing HUB INTERNET HOST CLIENTS Copyright 2002 Hughes Network Systems, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Hughes Electronics Corporation. All rights
HP LeftHand SAN Solutions
 HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document Installation Manuals VSA 8.0 Quick Start - Demo Version Legal Notices Warranty The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty
HP LeftHand SAN Solutions Support Document Installation Manuals VSA 8.0 Quick Start - Demo Version Legal Notices Warranty The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty
Lesson 1: Preparing for Installation
 2-2 Chapter 2 Installing Windows XP Professional Lesson 1: Preparing for Installation When you install Windows XP Professional, the Windows XP Professional Setup program allows you to specify how to install
2-2 Chapter 2 Installing Windows XP Professional Lesson 1: Preparing for Installation When you install Windows XP Professional, the Windows XP Professional Setup program allows you to specify how to install
PD-SATA USB/LAN Network Attached Storage Enclosure for 3.5 SATA Hard Drives
 Network Attached Storage Enclosure for 3.5 SATA Hard Drives User Manual & Installation Guide March 16, 2008 - v1.0 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...1 1.1 ICON KEY...1 1.2 THE...1 1.3 PACKAGE CONTENTS...1
Network Attached Storage Enclosure for 3.5 SATA Hard Drives User Manual & Installation Guide March 16, 2008 - v1.0 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...1 1.1 ICON KEY...1 1.2 THE...1 1.3 PACKAGE CONTENTS...1
SVA NMP Monitor for Unicenter TNG on Windows NT/2000
 SVA NMP Monitor for Unicenter TNG on Windows NT/2000 Installation Guide Version 3.1.1 First Edition Proprietary Information Statement The information in this document is confidential and proprietary to
SVA NMP Monitor for Unicenter TNG on Windows NT/2000 Installation Guide Version 3.1.1 First Edition Proprietary Information Statement The information in this document is confidential and proprietary to
Appendix A: Metasys Web Access (MWA) Server Installation Guidelines
 Technical Bulletin Issue Date February 26, 2003 Appendix A: Metasys Web Access (MWA) Server Installation Guidelines Appendix A: Metasys Web Access Server Installation Guidelines...2 Introduction... 2 Detailed
Technical Bulletin Issue Date February 26, 2003 Appendix A: Metasys Web Access (MWA) Server Installation Guidelines Appendix A: Metasys Web Access Server Installation Guidelines...2 Introduction... 2 Detailed
TIBCO iprocess Objects (Java) Installation. Software Release 10.4 May 2010
 TIBCO iprocess Objects (Java) Installation Software Release 10.4 May 2010 Important Information SOME TIBCO SOFTWARE EMBEDS OR BUNDLES OTHER TIBCO SOFTWARE. USE OF SUCH EMBEDDED OR BUNDLED TIBCO SOFTWARE
TIBCO iprocess Objects (Java) Installation Software Release 10.4 May 2010 Important Information SOME TIBCO SOFTWARE EMBEDS OR BUNDLES OTHER TIBCO SOFTWARE. USE OF SUCH EMBEDDED OR BUNDLED TIBCO SOFTWARE
OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for AT&T OneVision
 585-229-109 Issue 1 October, 1995 Table of Contents OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for AT&T OneVision Graphics AT&T 1988 Blank Page Contents About This Book vii Intended
585-229-109 Issue 1 October, 1995 Table of Contents OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for AT&T OneVision Graphics AT&T 1988 Blank Page Contents About This Book vii Intended
SANsurfer iscsi HBA Application User s Guide
 Q Simplify SANsurfer iscsi HBA Application User s Guide Management Application for SANsurfer iscsi Host Bus Adapters IS0054602-00 A Page i SANsurfer iscsi HBA Application User s Guide Management Application
Q Simplify SANsurfer iscsi HBA Application User s Guide Management Application for SANsurfer iscsi Host Bus Adapters IS0054602-00 A Page i SANsurfer iscsi HBA Application User s Guide Management Application
PROMISE ARRAY MANAGEMENT ( PAM) USER MANUAL
 PROMISE ARRAY MANAGEMENT ( PAM) USER MANUAL Copyright 2002, Promise Technology, Inc. Copyright by Promise Technology, Inc. (Promise Technology). No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted
PROMISE ARRAY MANAGEMENT ( PAM) USER MANUAL Copyright 2002, Promise Technology, Inc. Copyright by Promise Technology, Inc. (Promise Technology). No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted
X-618 Public Address and Voice
 X-618 Public Address and Voice Alarm System Commissioning Manual M_XXXXXX_CN_0 Copyright 2012 Honeywell International Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced in any form without
X-618 Public Address and Voice Alarm System Commissioning Manual M_XXXXXX_CN_0 Copyright 2012 Honeywell International Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced in any form without
Remote ialarm Center. User s Manual
 Remote ialarm Center User s Manual July 2011 COPYRIGHT 2011 AVer Information Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form, or by any means without the
Remote ialarm Center User s Manual July 2011 COPYRIGHT 2011 AVer Information Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form, or by any means without the
Transport Gateway Installation / Registration / Configuration
 CHAPTER 2 Transport Gateway Installation / Registration / Configuration This chapter covers the following areas: Transport Gateway requirements. Security Considerations When Using a Transport Gateway.
CHAPTER 2 Transport Gateway Installation / Registration / Configuration This chapter covers the following areas: Transport Gateway requirements. Security Considerations When Using a Transport Gateway.
Trace Debug Tools Version 1.2 Installation Guide
 Trace Debug Tools Version 1.2 Installation Guide Copyright 2000-2002 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. Proprietary Notice Words and logos marked with or are registered trademarks or trademarks owned by
Trace Debug Tools Version 1.2 Installation Guide Copyright 2000-2002 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. Proprietary Notice Words and logos marked with or are registered trademarks or trademarks owned by
pcaframe Quick Start Guide
 System Requirements pcaframe Quick Start Guide Operating systems Microsoft Windows 95 Windows 98 Second Edition Windows ME Windows NT4 Windows 2000 Windows XP Minimum Requirements 100 MHz processor 32
System Requirements pcaframe Quick Start Guide Operating systems Microsoft Windows 95 Windows 98 Second Edition Windows ME Windows NT4 Windows 2000 Windows XP Minimum Requirements 100 MHz processor 32
OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for Cabletron SPECTRUM on a SunOS
 585-229-110 Issue 1 April, 1996 Table of Contents OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for Cabletron SPECTRUM on a SunOS Graphics AT&T 1988 Blank Page Contents About This
585-229-110 Issue 1 April, 1996 Table of Contents OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for Cabletron SPECTRUM on a SunOS Graphics AT&T 1988 Blank Page Contents About This
LAN-505 Ethernet Communication
 Ethernet Communication 1.0 Purpose of this Document This document discusses how to setup, configure, and use the Universal Device Server to provide LAN/WAN Ethernet connectivity between Doors and one or
Ethernet Communication 1.0 Purpose of this Document This document discusses how to setup, configure, and use the Universal Device Server to provide LAN/WAN Ethernet connectivity between Doors and one or
OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for HP OpenView on an HP9000
 585-229-104 Issue 2 April 1996 Table of Contents OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for HP OpenView on an HP9000 Graphics Contents About This Book vii Audience vii Prerequisites
585-229-104 Issue 2 April 1996 Table of Contents OneVision DEFINITY G3 Fault Management Installation and Integration for HP OpenView on an HP9000 Graphics Contents About This Book vii Audience vii Prerequisites
Topcat. Installation Guide. Version 1.03
 Microlynx Software Engineering Topcat Installation Guide Version 1.03 1998 Microlynx Software Engineering ii Copyright 1998 Microlynx Software Engineering Neither the whole nor any part of the information
Microlynx Software Engineering Topcat Installation Guide Version 1.03 1998 Microlynx Software Engineering ii Copyright 1998 Microlynx Software Engineering Neither the whole nor any part of the information
OneClick. Installation Guide. Document 5142
 OneClick Installation Guide Document 5142 Notice This documentation (the "Documentation") and related computer software program (the "Software") (hereinafter collectively referred to as the "Product")
OneClick Installation Guide Document 5142 Notice This documentation (the "Documentation") and related computer software program (the "Software") (hereinafter collectively referred to as the "Product")
Relativity Designer Installation Guide
 Liant Software Corporation Relativity Designer Installation Guide Version 5 Copyright 1994-2003 by Liant Software Corporation. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. No part of this publication may be
Liant Software Corporation Relativity Designer Installation Guide Version 5 Copyright 1994-2003 by Liant Software Corporation. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. No part of this publication may be
NDA ISSUE 1 STOCK # MATWorX 32 User s Guide. December, NEC America, Inc.
 NDA-24215 ISSUE 1 STOCK # 151942 MATWorX 32 User s Guide December, 1997 NEC America, Inc. LIABILITY DISCLAIMER NEC America, Inc. reserves the right to change the specifications, functions, or features,
NDA-24215 ISSUE 1 STOCK # 151942 MATWorX 32 User s Guide December, 1997 NEC America, Inc. LIABILITY DISCLAIMER NEC America, Inc. reserves the right to change the specifications, functions, or features,
IBM Networking OS. BBI Quick Guide. for the EN2092 1Gb Ethernet Scalable Switch, Second edition (replaces 88Y7949)
 IBM Networking OS BBI Quick Guide for the EN2092 1Gb Ethernet Scalable Switch, Second edition (replaces 88Y7949) IBM Networking OS BBI Quick Guide for the EN2092 1Gb Ethernet Scalable Switch, Second edition
IBM Networking OS BBI Quick Guide for the EN2092 1Gb Ethernet Scalable Switch, Second edition (replaces 88Y7949) IBM Networking OS BBI Quick Guide for the EN2092 1Gb Ethernet Scalable Switch, Second edition
ODBC. Getting Started OpenLink Server Software Using ODBC
 Getting Started OpenLink Server Software Using The documentation in this publication is provided pursuant to a Sales and Licensing Contract for the Prophet 21 System entered into by and between Prophet
Getting Started OpenLink Server Software Using The documentation in this publication is provided pursuant to a Sales and Licensing Contract for the Prophet 21 System entered into by and between Prophet
Fast Ethernet Print Server 1 Parallel, 2 USB
 Fast Ethernet Print Server 1 Parallel, 2 USB User s Manual Rev. 01 (Nov, 2005) Made In Taiwan TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS GUIDE... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 PACKAGE CONTENTS... 6 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 6 GENERAL
Fast Ethernet Print Server 1 Parallel, 2 USB User s Manual Rev. 01 (Nov, 2005) Made In Taiwan TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS GUIDE... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 PACKAGE CONTENTS... 6 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 6 GENERAL
SiloTrack V3.0. Inventory Management Software. Server & Client Software Demonstration Guideline.
 SiloTrack V3.0 Inventory Management Software Server & Client Software Demonstration Guideline www.monitortech.com PREFACE Thank you for taking the time to examine our SiloTrack V3.0 demonstration software.
SiloTrack V3.0 Inventory Management Software Server & Client Software Demonstration Guideline www.monitortech.com PREFACE Thank you for taking the time to examine our SiloTrack V3.0 demonstration software.
Integration with Network Management Systems. Network Management System (NMS) Integration
 Integration with Network Management Systems Network Management System (NMS) Integration The securityprobe is embedded with full SNMP and can integrate with any SNMP based network management systems, such
Integration with Network Management Systems Network Management System (NMS) Integration The securityprobe is embedded with full SNMP and can integrate with any SNMP based network management systems, such
XLmanage Version 2.4. Installation Guide. ClearCube Technology, Inc.
 XLmanage Version 2.4 Installation Guide ClearCube Technology, Inc. www.clearcube.com Copyright and Trademark Notices Copyright 2009 ClearCube Technology, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Information in this document
XLmanage Version 2.4 Installation Guide ClearCube Technology, Inc. www.clearcube.com Copyright and Trademark Notices Copyright 2009 ClearCube Technology, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Information in this document
EMC NetWorker Module for SnapImage Release 2.0 Microsoft Windows Version
 EMC NetWorker Module for SnapImage Release 2.0 Microsoft Windows Version Installation and Administration Guide P/N 300-007-130 REV A01 EMC Corporation Corporate Headquarters: Hopkinton, MA 01748-9103 1-508-435-1000
EMC NetWorker Module for SnapImage Release 2.0 Microsoft Windows Version Installation and Administration Guide P/N 300-007-130 REV A01 EMC Corporation Corporate Headquarters: Hopkinton, MA 01748-9103 1-508-435-1000
Version /20/2012. User Manual. AP Manager II Lite Business Class Networking
 Version 1.0 12/20/2012 User Manual AP Manager II Lite Business Class Networking Table of Contents Table of Contents Product Overview... 1 Minimum System Requirements... 2 Access Point Requirements... 2
Version 1.0 12/20/2012 User Manual AP Manager II Lite Business Class Networking Table of Contents Table of Contents Product Overview... 1 Minimum System Requirements... 2 Access Point Requirements... 2
Using Integration Utility
 CHAPTER 3 CiscoWorks Integration Utility downloads Network Management Integration Data Bundle (NMIDB) and integrates LAN Management Solutions (LMS) applications, icons, MIBs, and traps with third-party
CHAPTER 3 CiscoWorks Integration Utility downloads Network Management Integration Data Bundle (NMIDB) and integrates LAN Management Solutions (LMS) applications, icons, MIBs, and traps with third-party
SPECTRUM. Multicast Manager User Guide (5132) r9.0
 SPECTRUM Multicast Manager User Guide (5132) r9.0 This documentation and any related computer software help programs (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for the end user s informational
SPECTRUM Multicast Manager User Guide (5132) r9.0 This documentation and any related computer software help programs (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for the end user s informational
OmniVista 3.5 Discovery Help
 Using Discovery Open the Discovery application by clicking Discovery in the Task Bar, selecting Discovery from the Applications menu, or by clicking the Discovery icon in the Topology Toolbar. The Discovery
Using Discovery Open the Discovery application by clicking Discovery in the Task Bar, selecting Discovery from the Applications menu, or by clicking the Discovery icon in the Topology Toolbar. The Discovery
Troubleshooting the Installation
 APPENDIX A Troubleshooting the Installation This appendix provides troubleshooting information for Essentials installation and setup, and contains the following sections: If the Installer Window Does Not
APPENDIX A Troubleshooting the Installation This appendix provides troubleshooting information for Essentials installation and setup, and contains the following sections: If the Installer Window Does Not
ProSystem fx Engagement
 ProSystem fx Engagement Guide November 2008 Copyright 2008 CCH INCORPORATED. A Wolters Kluwer Business. All Rights Reserved. Material in this publication may not be reproduced or transmitted, in any form
ProSystem fx Engagement Guide November 2008 Copyright 2008 CCH INCORPORATED. A Wolters Kluwer Business. All Rights Reserved. Material in this publication may not be reproduced or transmitted, in any form
OPERATION MANUAL. MV-410HS Layout Editor. Version higher. Command
 OPERATION MANUAL MV-410HS Layout Editor Version 3.0 - higher Command Command Table of Contents 1. Setup... 1 1-1. Overview... 1 1-2. System Requirements... 1 1-3. Operation Flow... 1 1-4. Installing MV-410HS
OPERATION MANUAL MV-410HS Layout Editor Version 3.0 - higher Command Command Table of Contents 1. Setup... 1 1-1. Overview... 1 1-2. System Requirements... 1 1-3. Operation Flow... 1 1-4. Installing MV-410HS
This guide consists of the following two chapters and an appendix. Chapter 1 Installing ETERNUSmgr This chapter describes how to install ETERNUSmgr.
 Preface This installation guide explains how to install the "ETERNUSmgr for HP-UX" storage system management software on an ETERNUS DX400 series, ETERNUS DX8000 series, ETERNUS2000, ETERNUS4000, ETERNUS8000,
Preface This installation guide explains how to install the "ETERNUSmgr for HP-UX" storage system management software on an ETERNUS DX400 series, ETERNUS DX8000 series, ETERNUS2000, ETERNUS4000, ETERNUS8000,
Create a pfsense router for your private lab network template
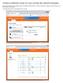 Create a pfsense router for your private lab network template Some labs will require a private network where you can deploy services like DHCP. Here are instructions for setting up an uplink router for
Create a pfsense router for your private lab network template Some labs will require a private network where you can deploy services like DHCP. Here are instructions for setting up an uplink router for
ODBC DOCUMENTATION UPDATES
 DOCUMENTATION UPDATES Date Description Where Changed 5/16/03 New upgrading instructions have been added to upgrade OpenLink to version 4.1. Getting Started chapter, in the Upgrading OpenLink section (page
DOCUMENTATION UPDATES Date Description Where Changed 5/16/03 New upgrading instructions have been added to upgrade OpenLink to version 4.1. Getting Started chapter, in the Upgrading OpenLink section (page
USB 2.0 Print Server. User s Manual. Rev. 01 (Jan, 2004) Made In Taiwan
 USB 2.0 Print Server User s Manual Rev. 01 (Jan, 2004) Made In Taiwan TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS GUIDE... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 PACKAGE CONTENTS... 6 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 6 GENERAL FEATURES... 7 PRODUCT
USB 2.0 Print Server User s Manual Rev. 01 (Jan, 2004) Made In Taiwan TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS GUIDE... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 PACKAGE CONTENTS... 6 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 6 GENERAL FEATURES... 7 PRODUCT
9581SST CONFIGURE OPERATION MANUAL
 9581SST CONFIGURE OPERATION MANUAL Company Profile Trilithic, Inc. was founded in 1986 as an engineering and assembly company providing customized communications and routing systems for business and government
9581SST CONFIGURE OPERATION MANUAL Company Profile Trilithic, Inc. was founded in 1986 as an engineering and assembly company providing customized communications and routing systems for business and government
Chapter. Installing PROKON
 Chapter Installing PROKON This explains the procedures for installing PROKON. step-by-step to help new users avoid pitfalls. The minimum and recommended system requirements are also given. Installing PROKON
Chapter Installing PROKON This explains the procedures for installing PROKON. step-by-step to help new users avoid pitfalls. The minimum and recommended system requirements are also given. Installing PROKON
Galileo Print Manager Installation Guide
 Galileo Print Manager Installation Guide 24 November 2003 Copyright 2003 Galileo International. All rights reserved. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described
Galileo Print Manager Installation Guide 24 November 2003 Copyright 2003 Galileo International. All rights reserved. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described
CiscoView 5.5 CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 2 CiscoView 5.5 CiscoView 5.5 operates in client-server mode. In a client-server mode, the device package and basic management functionality is centrally located on the CiscoView 5.5 server. To
CHAPTER 2 CiscoView 5.5 CiscoView 5.5 operates in client-server mode. In a client-server mode, the device package and basic management functionality is centrally located on the CiscoView 5.5 server. To
Getting Started with ESX Server 3i Installable Update 2 and later for ESX Server 3i version 3.5 Installable and VirtualCenter 2.5
 Getting Started with ESX Server 3i Installable Update 2 and later for ESX Server 3i version 3.5 Installable and VirtualCenter 2.5 Getting Started with ESX Server 3i Installable Revision: 20090313 Item:
Getting Started with ESX Server 3i Installable Update 2 and later for ESX Server 3i version 3.5 Installable and VirtualCenter 2.5 Getting Started with ESX Server 3i Installable Revision: 20090313 Item:
INSTALLATION AND USER GUIDE
 INSTALLATION AND USER GUIDE Introduction 1 Introduction About 6140 Agent Portal Mitel Networks 6140 Agent Portal allows an agent to receive call information via a number of different applications that
INSTALLATION AND USER GUIDE Introduction 1 Introduction About 6140 Agent Portal Mitel Networks 6140 Agent Portal allows an agent to receive call information via a number of different applications that
Avalanche Remote Control User Guide. Version 4.1
 Avalanche Remote Control User Guide Version 4.1 ii Copyright 2012 by Wavelink Corporation. All rights reserved. Wavelink Corporation 10808 South River Front Parkway, Suite 200 South Jordan, Utah 84095
Avalanche Remote Control User Guide Version 4.1 ii Copyright 2012 by Wavelink Corporation. All rights reserved. Wavelink Corporation 10808 South River Front Parkway, Suite 200 South Jordan, Utah 84095
LABVIEW. Contents RELEASE NOTES. Version 6.1
 RELEASE NOTES LABVIEW Version 6.1 These release notes introduce you to LabVIEW, describe the system requirements for the LabVIEW software, and contain installation instructions. The LabVIEW 6.1 Professional
RELEASE NOTES LABVIEW Version 6.1 These release notes introduce you to LabVIEW, describe the system requirements for the LabVIEW software, and contain installation instructions. The LabVIEW 6.1 Professional
CA ehealth. Setting Up Service Availability 2.0. r6.1
 CA ehealth Setting Up Service Availability 2.0 r6.1 This documentation and any related computer software help programs (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for the end user s informational
CA ehealth Setting Up Service Availability 2.0 r6.1 This documentation and any related computer software help programs (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for the end user s informational
EPICenter Installation and Upgrade Note
 EPICenter Installation and Upgrade Note Software Version 5.0 Extreme Networks, Inc. 3585 Monroe Street Santa Clara, California 95051 (888) 257-3000 http://www.extremenetworks.com Published: October 2004
EPICenter Installation and Upgrade Note Software Version 5.0 Extreme Networks, Inc. 3585 Monroe Street Santa Clara, California 95051 (888) 257-3000 http://www.extremenetworks.com Published: October 2004
The Lackner Group. Addendum to the Administrator s Guide for FileMaker Server 5.5 (February 14, 2003)
 The Lackner Group Addendum to the Administrator s Guide for FileMaker Server 5.5 (February 14, 2003) This document will step you through the most common configuration setup for FileMaker Server 5.5 when
The Lackner Group Addendum to the Administrator s Guide for FileMaker Server 5.5 (February 14, 2003) This document will step you through the most common configuration setup for FileMaker Server 5.5 when
Function Point WORKBENCH Release 7.0k INSTALLATION GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Function Point WORKBENCH Release 7.0k GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS FUNCTION POINT WORKBENCH RELEASE 7.0K GUIDE... 1 LICENCE TYPES... 3 Standalone Licence Machine Dependent (Single User)... 3 Network Licence
Function Point WORKBENCH Release 7.0k GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS FUNCTION POINT WORKBENCH RELEASE 7.0K GUIDE... 1 LICENCE TYPES... 3 Standalone Licence Machine Dependent (Single User)... 3 Network Licence
TIBCO ActiveMatrix Adapter for Amdocs CRM Installation. Software Release 5.5 July 2012
 TIBCO ActiveMatrix Adapter for Amdocs CRM Installation Software Release 5.5 July 2012 Important Information SOME TIBCO SOFTWARE EMBEDS OR BUNDLES OTHER TIBCO SOFTWARE. USE OF SUCH EMBEDDED OR BUNDLED TIBCO
TIBCO ActiveMatrix Adapter for Amdocs CRM Installation Software Release 5.5 July 2012 Important Information SOME TIBCO SOFTWARE EMBEDS OR BUNDLES OTHER TIBCO SOFTWARE. USE OF SUCH EMBEDDED OR BUNDLED TIBCO
SPECTRUM Web Operator
 Notice Copyright Notice Copyright 2002-present by Aprisma Management Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved worldwide. Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States government is subject to the
Notice Copyright Notice Copyright 2002-present by Aprisma Management Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved worldwide. Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States government is subject to the
Insight Integration for HP Network Node Manager Revision 3.4 User Guide
 Insight Integration for HP Network Node Manager Revision 3.4 User Guide Part Number 219062-006 August 2007 (Sixth Edition) Copyright 2001, 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
Insight Integration for HP Network Node Manager Revision 3.4 User Guide Part Number 219062-006 August 2007 (Sixth Edition) Copyright 2001, 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
OmniVista 3.5 Quick Start Help
 Quick Start Guide This Quick Start guide will get you up and running OmniVista. It provides instructions for logging into OmniVista and performing automatic discovery of the switches in your network. It
Quick Start Guide This Quick Start guide will get you up and running OmniVista. It provides instructions for logging into OmniVista and performing automatic discovery of the switches in your network. It
Smart Access Control System Software. User Manual. Version 1.0
 Smart Access Control System Software User Manual Version 1.0 Copyright MaCaPS International Ltd. 2002 This manual was produced by MaCaPS International Ltd. MaCaPS International Ltd. http://www.macaps.com.hk
Smart Access Control System Software User Manual Version 1.0 Copyright MaCaPS International Ltd. 2002 This manual was produced by MaCaPS International Ltd. MaCaPS International Ltd. http://www.macaps.com.hk
Kinetica 5.1 Kinetica Installation Guide
 Kinetica 5.1 Kinetica Installation Guide 2012 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. The information in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be construed as a commitment
Kinetica 5.1 Kinetica Installation Guide 2012 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. The information in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be construed as a commitment
TECHNICAL NOTE. Technical Note P/N REV A01
 TECHNICAL NOTE Performing SharePoint Granular Recovery with EMC Avamar for SharePoint VSS and Ontrack PowerControls Technical Notes EMC Avamar v6.0 Technical Note P/N 300-013-036 REV A01 December 7, 2011
TECHNICAL NOTE Performing SharePoint Granular Recovery with EMC Avamar for SharePoint VSS and Ontrack PowerControls Technical Notes EMC Avamar v6.0 Technical Note P/N 300-013-036 REV A01 December 7, 2011
Universal Management Agent Installation Guide G10L
 Universal Management Agent 1.01 Installation Guide IBM G10L-9841-1 IBM Universal Management Agent 1.01 Installation Guide G10L-9841-1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be
Universal Management Agent 1.01 Installation Guide IBM G10L-9841-1 IBM Universal Management Agent 1.01 Installation Guide G10L-9841-1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be
ExpressCluster X Integrated WebManager
 ExpressCluster X Integrated WebManager Administrator s Guide 09/30/2009 Second Edition Revision History Edition Revised Date Description First 06/15/2009 New manual Second 09/30/2009 This manual has been
ExpressCluster X Integrated WebManager Administrator s Guide 09/30/2009 Second Edition Revision History Edition Revised Date Description First 06/15/2009 New manual Second 09/30/2009 This manual has been
BBI Quick Guide Networking OS for 1/10Gb LAN Switch Module. Product Version Getting Help Contents
 Networking OS for 1/10Gb LAN Switch Module FASTFIND LINKS Product Version Getting Help Contents 2014 Hitachi, Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any
Networking OS for 1/10Gb LAN Switch Module FASTFIND LINKS Product Version Getting Help Contents 2014 Hitachi, Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any
Installation Guide for Open VMS
 Installation Guide for Open VMS IDL Version 5.4 September, 2000 Edition Copyright Research Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved Restricted Rights Notice The IDL software program and the accompanying procedures,
Installation Guide for Open VMS IDL Version 5.4 September, 2000 Edition Copyright Research Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved Restricted Rights Notice The IDL software program and the accompanying procedures,
7. copy or distribute the Software, or any part thereof, or any accompanying documentation or part thereof, other than in accordance with 3.
 1 Before You Begin AUSTRALIAN ACCESS SOFTWARE LICENCE AGREEMENT IMPORTANT - READ CAREFULLY 30 DAYS EVALUATION AND FULL LICENSED VERSIONS: A. By agreeing to this licence agreement and/or by installing,
1 Before You Begin AUSTRALIAN ACCESS SOFTWARE LICENCE AGREEMENT IMPORTANT - READ CAREFULLY 30 DAYS EVALUATION AND FULL LICENSED VERSIONS: A. By agreeing to this licence agreement and/or by installing,
Action Request System Gateway Software Release Notice 5.0rev1
 Action Request System Gateway Software Release Notice 5.0rev1 Summary of Changes Version Date Reason/Rational Nature of Changes 9030709 E22 9/4/98 Updated Corrected Anomalies in Chapter 2. Updated Considerations
Action Request System Gateway Software Release Notice 5.0rev1 Summary of Changes Version Date Reason/Rational Nature of Changes 9030709 E22 9/4/98 Updated Corrected Anomalies in Chapter 2. Updated Considerations
CiscoView CD Installation Instructions
 CiscoView CD Installation Instructions This instruction book provides information about installing and running CiscoView on your network management station. You can install CiscoView on a Solaris workstation,
CiscoView CD Installation Instructions This instruction book provides information about installing and running CiscoView on your network management station. You can install CiscoView on a Solaris workstation,
Getting Started with Tally.Developer 9
 Getting Started with Tally.Developer 9 The information contained in this document is current as of the date of publication and subject to change. Because Tally must respond to changing market conditions,
Getting Started with Tally.Developer 9 The information contained in this document is current as of the date of publication and subject to change. Because Tally must respond to changing market conditions,
EXPRESSCLUSTER X Integrated WebManager
 EXPRESSCLUSTER X Integrated WebManager Administrator s Guide 10/02/2017 12th Edition Revision History Edition Revised Date Description 1st 06/15/2009 New manual 2nd 09/30/2009 This manual has been updated
EXPRESSCLUSTER X Integrated WebManager Administrator s Guide 10/02/2017 12th Edition Revision History Edition Revised Date Description 1st 06/15/2009 New manual 2nd 09/30/2009 This manual has been updated
