Outline. CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L15. Files. Files
|
|
|
- Robert Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outline CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L15 Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville VHDL What we know (additional topics) Attributes Transport and Inertial Delays Operator Overloading Multivalued Logic and Signal Resolution IEEE 1164 Standard Logic Generics Generate Statements Synthesis of VHDL Code Synthesis Examples What we don t know Files and Text IO Networks for Arithmetic Operations SM Charts 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 2 Files Files File input/output in VHDL Used in test benches Source of test data Storage for test results VHDL provides a standard TEXTIO package read/write lines of text 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 3 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 4 1
2 Standard TEXTIO Package Contains declarations and procedures for working with files composed of lines of text Defines a file type named text: type text is file of string; Contains procedures for reading lines of text from a file of type text and for writing lines of text to a file 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 5 Reading TEXTIO file Readline reads a line of text and places it in a buffer with an associated pointer Pointer to the buffer must be of type line, which is declared in the textio package as: type line is access string; When a variable of type line is declared, it creates a pointer to a string Code variable buff: line;... readline (test_data, buff); reads a line of text from test_data and places it in a buffer which is pointed to by buff 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 6 Extracting Data from the Line Buffer To extract data from the line buffer, call a read procedure one or more times For example, if bv4 is a bit_vector of length four, the call read(buff, bv4) extracts a 4-bit vector from the buffer, sets bv4 equal to this vector, and adjusts the pointer buff to point to the next character in the buffer. Another call to read will then extract the next data object from the line buffer. 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 7 Extracting Data from the Line Buffer (cont d) TEXTIO provides overloaded read procedures to read data of types bit, bit_vector, boolean, character, integer, real, string, and time from buffer Read forms read(pointer, value) read(pointer, value, good) good is boolean that returns TRUE if the read is successful and FALSE if it is not type and size of value determines which of the read procedures is called character, strings, and bit_vectors within files of type text are not delimited by quotes 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 8 2
3 Writing to TEXTIO files Call one or more write procedures to write data to a line buffer and then call writeline to write the line to a file variable buffw : line; variable int1 : integer; variable bv8 : bit_vector(7 downto 0);... write(buffw, int1, right, 6); --right just., 6 ch. wide write(buffw, bv8, right, 10); writeln(buffw, output_file); Write parameters: 1) buffer pointer of type line, 2) a value of any acceptable type, 3) justification (left or right), and 4) field width (number of characters) An Example Procedure to read data from a file and store the data in a memory array Format of the data in the file address N comments byte1 byte2... byten comments address 4 hex digits N indicates the number of bytes of code bytei - 2 hex digits each byte is separated by one space the last byte must be followed by a space anything following the last state will not be read and will be treated as a comment 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 9 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 10 An Example (cont d) Code sequence: an example 12AC 7 (7 hex bytes follow) AE 03 B6 91 C7 00 0C (LDX imm, LDA dir, STA ext) 005B 2 (2 bytes follow) 01 FC_ TEXTIO does not include read procedure for hex numbers we will read each hex value as a string of characters and then convert the string to an integer How to implement conversion? table lookup constant named lookup is an array of integers indexed by characters in the range 0 to F this range includes the 23 ASCII characters: 0, 1,... 9, :, ;, <, =, A,... F corresponding values: 0, 1,... 9, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 11 VHDL Code to Fill Memory Array 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 12 3
4 VHDL Code to Fill Memory Array (cont d) Things to Remember Attributes associated to signals allow checking for setup, hold times, and other timing specifications Attributes associated to arrays allow us to write procedures that do not depend on the manner in which arrays are indexed Inertial and transport delays allow modeling of different delay types that occur in real systems Operator overloading allow us to extend the definition of VHDL operators so that they can be used with different types of operands 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 13 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 14 Things to Remember (cont d) Multivalued logic and the associated resolution functions allow us to model tri -state buses, and systems where a signal is driven by more than one source Generics allow us to specify parameter values for a component when the component is instantiated Generate statements efficient way to describe systems with iterative structure TEXTIO convenient way for file input/output Networks for Arithmetic Operations Case Study: Serial Adder with Accumulator 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 15 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 16 4
5 Networks for Arithmetic Operations Serial Adder with Accumulator State Graphs for Control Networks Use variable names instead of 0s and 1s E.g., XiXj/ZpZq if Xi and Xj inputs are 1, the outputs Zp and Zq are 1 (all other outputs are 0s) E.g., X = X1X2X3X4, Z = Z1Z2Z3Z4 X1X4 /Z2Z3 == / /07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 17 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 18 Constraints on Input Labels Constraints on Input Labels (cont d) Assume: I input expression => we traverse the arc when I=1 Assures that at most one input label can be 1 at any given time Assures that at least one input label will be 1 at any given time 1 + 2: Exactly one label will be 1 => the next state will be uniquely defined for every input combination 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 19 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 20 5
6 Networks for Arithmetic Operations Block Diagram of a Binary Multiplier Case Study: Serial Parallel Multiplier Note: we use unsigned binary numbers 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 21 Ad add signal // adder outputs are stored into the ACC Sh shift signal // shift all 9 bits to right Ld load signal // load multiplier into the 4 lower bits of the ACC and clear the upper 5 bits 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 22 Multiplication Example State Graph for Binary Multiplier 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 23 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 24 6
7 Behavioral VHDL Model Behavioral VHDL Model (cont d) 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 25 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 26 Multiplier Control with Counter Multiplier Control with Counter (cont d) Current design: control part generates the control signals (shift/add) and counts the number of steps If the number of bits is large (e.g., 64), the control network can be divided into a counter and a shift/add control Add-shifts control: tests St and M and generates the proper sequence of add and shift signals Counter control: counter generates a completion signal K that stops the multiplier after the proper number of shifts have been completed 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 27 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 28 7
8 Multiplier Control with Counter (cont d) Operation of a Multiplier Using Counter Increment counter each time a shift signal is generated Generate K after n-1 shifts occured 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 29 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 30 Array Multiplier Array Multiplier (cont d) What do we need to realize Array Multiplier? AND gates =? FA =? HA =? 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 31 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 32 8
9 Array Multiplier (cont d) Complexity of the N-bit array multiplier number of AND gates =? number of HA =? number of FA =? Delay tg longest AND gate delay tad longest possible delay through an adder Multiplication of Signed Binary Numbers How to multiply signed binary numbers? Procedure Complement the multiplier if negative Complement the multiplicand if negative Multiply two positive binary numbers Complement the product if it should be negative Simple but requires more hardware and time than other available methods 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 33 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 34 Multiplication of Signed Binary Numbers 2 s Complement Multiplier Four cases Multiplicand is positive, multiplier is positive Multiplicand is negative, multiplier is positive Multiplicand is positive, multiplier is negative Multiplier is negative, multiplicand is negative Examples 0111 x 0101 =? 1101 x 0101 =? 0101 x 1101 =? 1011 x 1101 =? Preserve the sign of the partial product at each step If multiplier is negative, complement the multiplicand before adding it in at the last step 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 35 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 36 9
10 State Graph for 2 s Complement Multiplier Faster Multiplier Move wires from the adder outputs one position to the right => add and shift can occur at the same clock cycle 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 37 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 38 State Graph for Faster Multiplier Behavioral Model for Faster Multiplier 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 39 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 40 10
11 Behavioral Model for Faster Multiplier Command File and Simulation 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 41 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 42 Test Bench for Signed Multiplier Digital design with SM Charts State graphs used to describe state machines controlling a digital system Alternative: use state machine flowchart 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 43 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 44 11
12 State Machine Charts Components of SM charts SM chart or ASM (Algorithmic State Machine) chart Easier to understand the operation of digital system by examining of the SM chart instead of equivalent state graph SM chart leads directly to hardware realization 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 45 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 46 SM Blocks Equivalent SM Blocks SM chart is constructed from SM blocks State S1 is entered => Z1 and Z2 become 1 if X1=0 Z3 and Z4 become 1 if X1=1 and X3=0 Z5 become 1 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 47 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 48 12
13 Equivalent SM Charts for Comb Networks Block with Feedback 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 49 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 50 Equivalent SM Blocks Converting a State Graph to an SM Chart 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 51 16/07/2003 UAH-CPE/EE 422/522 AM 52 13
CPE/EE 422/522. Chapter 8 - Additional Topics in VHDL. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. 8.1 Attributes - Signal Attributes that return a value
 CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter 8 - Additional Topics in VHDL Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH 1 8.1 Attributes - Signal Attributes that return a value A event true if a has just occurred A active true if A has, even if
CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter 8 - Additional Topics in VHDL Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH 1 8.1 Attributes - Signal Attributes that return a value A event true if a has just occurred A active true if A has, even if
Outline CPE 626. Advanced VLSI Design. Lecture 4: VHDL Recapitulation (Part 2) Signals. Variables. Constants. Variables vs.
 CPE 626 Lecture 4: VHDL Recapitulation (Part 2) Aleksandar Milenkovic http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka/cpe626-04f/ milenka@ece.uah.edu Assistant Professor Electrical and
CPE 626 Lecture 4: VHDL Recapitulation (Part 2) Aleksandar Milenkovic http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka/cpe626-04f/ milenka@ece.uah.edu Assistant Professor Electrical and
Outline CPE 626. Advanced VLSI Design. Lecture 3: VHDL Recapitulation. Intro to VHDL. Intro to VHDL. Entity-Architecture Pair
 Outline CPE 626 Lecture 3: VHDL Recapitulation Aleksandar Milenkovic http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka/cpe626-04f/ milenka@ece.uah.edu Assistant Professor Electrical and Computer
Outline CPE 626 Lecture 3: VHDL Recapitulation Aleksandar Milenkovic http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka/cpe626-04f/ milenka@ece.uah.edu Assistant Professor Electrical and Computer
Outline. CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L07. Review: JK Flip-Flop Model. Review: VHDL Program Structure. Review: VHDL Models for a MUX
 Outline CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L07 Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville What we know How to model Combinational Networks in VHDL Structural, Dataflow, Behavioral
Outline CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L07 Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville What we know How to model Combinational Networks in VHDL Structural, Dataflow, Behavioral
In this section we cover the following: State graphs introduction Serial Adder Multiplier Divider STATE GRAPHS FOR CONTROL NETWORKS What are the
 In this section we cover the following: State graphs introduction Serial Adder Multiplier Divider STATE GRAPHS FOR CONTROL NETWORKS What are the conditions for having a proper state graph? If an arc is
In this section we cover the following: State graphs introduction Serial Adder Multiplier Divider STATE GRAPHS FOR CONTROL NETWORKS What are the conditions for having a proper state graph? If an arc is
Outline. CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L05. Review: General Model of Moore Sequential Machine. Review: Mealy Sequential Networks.
 Outline CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L05 Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville What we know Combinational Networks Sequential Networks: Basic Building Blocks,
Outline CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L05 Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville What we know Combinational Networks Sequential Networks: Basic Building Blocks,
VHDL for Complex Designs
 ELEC 379 : DESIGN OF DIGITAL AND MICROCOMPUTER SYSTEMS 1998/99 WINTER SESSION, TERM 2 VHDL for Complex Designs This lecture covers VHDL features that are useful when designing complex logic circuits. After
ELEC 379 : DESIGN OF DIGITAL AND MICROCOMPUTER SYSTEMS 1998/99 WINTER SESSION, TERM 2 VHDL for Complex Designs This lecture covers VHDL features that are useful when designing complex logic circuits. After
The Designer's Guide to VHDL Second Edition
 The Designer's Guide to VHDL Second Edition Peter J. Ashenden EDA CONSULTANT, ASHENDEN DESIGNS PTY. VISITING RESEARCH FELLOW, ADELAIDE UNIVERSITY Cl MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS An Imprint of Elsevier SAN
The Designer's Guide to VHDL Second Edition Peter J. Ashenden EDA CONSULTANT, ASHENDEN DESIGNS PTY. VISITING RESEARCH FELLOW, ADELAIDE UNIVERSITY Cl MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS An Imprint of Elsevier SAN
Timing for Ripple Carry Adder
 Timing for Ripple Carry Adder 1 2 3 Look Ahead Method 5 6 7 8 9 Look-Ahead, bits wide 10 11 Multiplication Simple Gradeschool Algorithm for 32 Bits (6 Bit Result) Multiplier Multiplicand AND gates 32
Timing for Ripple Carry Adder 1 2 3 Look Ahead Method 5 6 7 8 9 Look-Ahead, bits wide 10 11 Multiplication Simple Gradeschool Algorithm for 32 Bits (6 Bit Result) Multiplier Multiplicand AND gates 32
Microcontroller Systems
 µcontroller systems 1 / 43 Microcontroller Systems Engineering Science 2nd year A2 Lectures Prof David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2co Michaelmas 2014 µcontroller
µcontroller systems 1 / 43 Microcontroller Systems Engineering Science 2nd year A2 Lectures Prof David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2co Michaelmas 2014 µcontroller
ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL. Chapter 7
 ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL Chapter 7 Introduction A design s functionality should be verified before its description is synthesized. A testbench is a program used to verify a design s functionality
ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL Chapter 7 Introduction A design s functionality should be verified before its description is synthesized. A testbench is a program used to verify a design s functionality
ECE 4514 Digital Design II. Spring Lecture 7: Dataflow Modeling
 ECE 4514 Digital Design II Lecture 7: Dataflow Modeling A language Lecture Today's topic Dataflow Modeling input input input module output output Model with submodules and gates = Structural Model with
ECE 4514 Digital Design II Lecture 7: Dataflow Modeling A language Lecture Today's topic Dataflow Modeling input input input module output output Model with submodules and gates = Structural Model with
Microcomputers. Outline. Number Systems and Digital Logic Review
 Microcomputers Number Systems and Digital Logic Review Lecture 1-1 Outline Number systems and formats Common number systems Base Conversion Integer representation Signed integer representation Binary coded
Microcomputers Number Systems and Digital Logic Review Lecture 1-1 Outline Number systems and formats Common number systems Base Conversion Integer representation Signed integer representation Binary coded
Kinds Of Data CHAPTER 3 DATA REPRESENTATION. Numbers Are Different! Positional Number Systems. Text. Numbers. Other
 Kinds Of Data CHAPTER 3 DATA REPRESENTATION Numbers Integers Unsigned Signed Reals Fixed-Point Floating-Point Binary-Coded Decimal Text ASCII Characters Strings Other Graphics Images Video Audio Numbers
Kinds Of Data CHAPTER 3 DATA REPRESENTATION Numbers Integers Unsigned Signed Reals Fixed-Point Floating-Point Binary-Coded Decimal Text ASCII Characters Strings Other Graphics Images Video Audio Numbers
Dec Hex Bin ORG ; ZERO. Introduction To Computing
 Dec Hex Bin 0 0 00000000 ORG ; ZERO Introduction To Computing OBJECTIVES this chapter enables the student to: Convert any number from base 2, base 10, or base 16 to any of the other two bases. Add and
Dec Hex Bin 0 0 00000000 ORG ; ZERO Introduction To Computing OBJECTIVES this chapter enables the student to: Convert any number from base 2, base 10, or base 16 to any of the other two bases. Add and
Lecture 8: Addition, Multiplication & Division
 Lecture 8: Addition, Multiplication & Division Today s topics: Signed/Unsigned Addition Multiplication Division 1 Signed / Unsigned The hardware recognizes two formats: unsigned (corresponding to the C
Lecture 8: Addition, Multiplication & Division Today s topics: Signed/Unsigned Addition Multiplication Division 1 Signed / Unsigned The hardware recognizes two formats: unsigned (corresponding to the C
Register Transfer and Micro-operations
 Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Introduction to VHDL. Main language concepts
 Introduction to VHDL VHSIC (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit) Hardware Description Language Current standard is IEEE 1076-1993 (VHDL-93). Some tools still only support VHDL-87. Tools used in the lab
Introduction to VHDL VHSIC (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit) Hardware Description Language Current standard is IEEE 1076-1993 (VHDL-93). Some tools still only support VHDL-87. Tools used in the lab
Computer Organization
 Register Transfer Logic Department of Computer Science Missouri University of Science & Technology hurson@mst.edu 1 Note, this unit will be covered in three lectures. In case you finish it earlier, then
Register Transfer Logic Department of Computer Science Missouri University of Science & Technology hurson@mst.edu 1 Note, this unit will be covered in three lectures. In case you finish it earlier, then
Le L c e t c ur u e e 2 To T p o i p c i s c t o o b e b e co c v o e v r e ed e Variables Operators
 Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 2 Topics to be covered Variables Operators Variables -Introduction A variables can be considered as a name given to the location in memory where values are stored. One
Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 2 Topics to be covered Variables Operators Variables -Introduction A variables can be considered as a name given to the location in memory where values are stored. One
A flow chart is a graphical or symbolic representation of a process.
 Q1. Define Algorithm with example? Answer:- A sequential solution of any program that written in human language, called algorithm. Algorithm is first step of the solution process, after the analysis of
Q1. Define Algorithm with example? Answer:- A sequential solution of any program that written in human language, called algorithm. Algorithm is first step of the solution process, after the analysis of
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
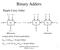 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic
 Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic 1 / 126 1 Motivation 2 Arithmetic and Logic Unit 3 Integer representation
Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic 1 / 126 1 Motivation 2 Arithmetic and Logic Unit 3 Integer representation
Note that none of the above MAY be a VALID ANSWER.
 ECE 270 Learning Outcome 4-1 - Practice Exam / Solution OUTCOME #4: An ability to design and implement computer logic circuits. Multiple Choice select the single most appropriate response for each question.
ECE 270 Learning Outcome 4-1 - Practice Exam / Solution OUTCOME #4: An ability to design and implement computer logic circuits. Multiple Choice select the single most appropriate response for each question.
Lecture 14 Test Bench Design
 CPE 487: Digital System Design Spring 2018 Lecture 14 Test Bench Design Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken, NJ 07030 1 Testing Digital
CPE 487: Digital System Design Spring 2018 Lecture 14 Test Bench Design Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken, NJ 07030 1 Testing Digital
3 Designing Digital Systems with Algorithmic State Machine Charts
 3 Designing with Algorithmic State Machine Charts An ASM chart is a method of describing the sequential operations of a digital system which has to implement an algorithm. An algorithm is a well defined
3 Designing with Algorithmic State Machine Charts An ASM chart is a method of describing the sequential operations of a digital system which has to implement an algorithm. An algorithm is a well defined
(+A) + ( B) + (A B) (B A) + (A B) ( A) + (+ B) (A B) + (B A) + (A B) (+ A) (+ B) + (A - B) (B A) + (A B) ( A) ( B) (A B) + (B A) + (A B)
 COMPUTER ARITHMETIC 1. Addition and Subtraction of Unsigned Numbers The direct method of subtraction taught in elementary schools uses the borrowconcept. In this method we borrow a 1 from a higher significant
COMPUTER ARITHMETIC 1. Addition and Subtraction of Unsigned Numbers The direct method of subtraction taught in elementary schools uses the borrowconcept. In this method we borrow a 1 from a higher significant
HIERARCHICAL DESIGN. RTL Hardware Design by P. Chu. Chapter 13 1
 HIERARCHICAL DESIGN Chapter 13 1 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Components 3. Generics 4. Configuration 5. Other supporting constructs Chapter 13 2 1. Introduction How to deal with 1M gates or more? Hierarchical
HIERARCHICAL DESIGN Chapter 13 1 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Components 3. Generics 4. Configuration 5. Other supporting constructs Chapter 13 2 1. Introduction How to deal with 1M gates or more? Hierarchical
Outline HIERARCHICAL DESIGN. 1. Introduction. Benefits of hierarchical design
 Outline HIERARCHICAL DESIGN 1. Introduction 2. Components 3. Generics 4. Configuration 5. Other supporting constructs Chapter 13 1 Chapter 13 2 1. Introduction How to deal with 1M gates or more? Hierarchical
Outline HIERARCHICAL DESIGN 1. Introduction 2. Components 3. Generics 4. Configuration 5. Other supporting constructs Chapter 13 1 Chapter 13 2 1. Introduction How to deal with 1M gates or more? Hierarchical
Register Transfer Level in Verilog: Part I
 Source: M. Morris Mano and Michael D. Ciletti, Digital Design, 4rd Edition, 2007, Prentice Hall. Register Transfer Level in Verilog: Part I Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National
Source: M. Morris Mano and Michael D. Ciletti, Digital Design, 4rd Edition, 2007, Prentice Hall. Register Transfer Level in Verilog: Part I Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National
Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction
 Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction Iterative combinational circuits Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple carry and carry lookahead adders Binary subtraction Binary adder-subtractors Signed binary
Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction Iterative combinational circuits Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple carry and carry lookahead adders Binary subtraction Binary adder-subtractors Signed binary
Register Transfer Level
 Register Transfer Level Something between the logic level and the architecture level A convenient way to describe synchronous sequential systems State diagrams for pros Hierarchy of Designs The design
Register Transfer Level Something between the logic level and the architecture level A convenient way to describe synchronous sequential systems State diagrams for pros Hierarchy of Designs The design
Operations On Data CHAPTER 4. (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions
 CHAPTER 4 Operations On Data (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions 1. Arithmetic operations interpret bit patterns as numbers. Logical operations interpret each bit as a logical values
CHAPTER 4 Operations On Data (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions 1. Arithmetic operations interpret bit patterns as numbers. Logical operations interpret each bit as a logical values
Hardware Description Languages (HDLs) Verilog
 Hardware Description Languages (HDLs) Verilog Material from Mano & Ciletti book By Kurtulus KULLU Ankara University What are HDLs? A Hardware Description Language resembles a programming language specifically
Hardware Description Languages (HDLs) Verilog Material from Mano & Ciletti book By Kurtulus KULLU Ankara University What are HDLs? A Hardware Description Language resembles a programming language specifically
Lecture 7. Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits. Hardware Description Language)
 Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits Hardware Description Language) 1 Standard ICs PLD: Programmable Logic Device CPLD: Complex PLD FPGA: Field Programmable
Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits Hardware Description Language) 1 Standard ICs PLD: Programmable Logic Device CPLD: Complex PLD FPGA: Field Programmable
LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS
 Goals To Do LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS Learn how the performance of the processor is determined. Improve the processor performance by adding new instructions. Determine the speed of the processor in
Goals To Do LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS Learn how the performance of the processor is determined. Improve the processor performance by adding new instructions. Determine the speed of the processor in
ECE 3401 Lecture 10. More on VHDL
 ECE 3401 Lecture 10 More on VHDL Outline More on VHDL Some VHDL Basics Data Types Operators Delay Models VHDL for Simulation VHDL for Synthesis 1 Data Types Every signal has a type, type specifies possible
ECE 3401 Lecture 10 More on VHDL Outline More on VHDL Some VHDL Basics Data Types Operators Delay Models VHDL for Simulation VHDL for Synthesis 1 Data Types Every signal has a type, type specifies possible
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 90 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a)
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 90 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a)
Manipulating Integers
 Manipulating Integers Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE2030: Introduction to Computer Systems, Spring 2018, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu)
Manipulating Integers Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE2030: Introduction to Computer Systems, Spring 2018, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu)
MOXSYN. General Description. Features. Symbol
 MOXSYN C68MX11 CPU General Description The C68MX11 CPU core is based on the Motorola M68HC11 microcontroller controller, but has an enhanced full 16 bit architecture, thus requiring less clock cycles for
MOXSYN C68MX11 CPU General Description The C68MX11 CPU core is based on the Motorola M68HC11 microcontroller controller, but has an enhanced full 16 bit architecture, thus requiring less clock cycles for
VHDL Structural Modeling II
 VHDL Structural Modeling II ECE-331, Digital Design Prof. Hintz Electrical and Computer Engineering 5/7/2001 331_13 1 Ports and Their Usage Port Modes in reads a signal out writes a signal inout reads
VHDL Structural Modeling II ECE-331, Digital Design Prof. Hintz Electrical and Computer Engineering 5/7/2001 331_13 1 Ports and Their Usage Port Modes in reads a signal out writes a signal inout reads
Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators. JAVA Standard Edition
 Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators JAVA Standard Edition Java - Basic Operators Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables.
Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators JAVA Standard Edition Java - Basic Operators Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables.
CS 121 Digital Logic Design. Chapter 1. Teacher Assistant. Hadeel Al-Ateeq
 CS 121 Digital Logic Design Chapter 1 Teacher Assistant Hadeel Al-Ateeq Announcement DON T forgot to SIGN your schedule OR you will not be allowed to attend next lecture. Communication Office hours (8
CS 121 Digital Logic Design Chapter 1 Teacher Assistant Hadeel Al-Ateeq Announcement DON T forgot to SIGN your schedule OR you will not be allowed to attend next lecture. Communication Office hours (8
ECE Digital System Design & Synthesis Exercise 1 - Logic Values, Data Types & Operators - With Answers
 ECE 601 - Digital System Design & Synthesis Exercise 1 - Logic Values, Data Types & Operators - With Answers Fall 2001 Final Version (Important changes from original posted Exercise 1 shown in color) Variables
ECE 601 - Digital System Design & Synthesis Exercise 1 - Logic Values, Data Types & Operators - With Answers Fall 2001 Final Version (Important changes from original posted Exercise 1 shown in color) Variables
Review Topics. Midterm Exam Review Slides
 Review Topics Midterm Exam Review Slides Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University!! Computer Arithmetic!! Combinational
Review Topics Midterm Exam Review Slides Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University!! Computer Arithmetic!! Combinational
Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Page 1. Where Have We Been? Chapter 2 Representing and Manipulating Information. Why Don t Computers Use Base 10?
 Where Have We Been? Class Introduction Great Realities of Computing Int s are not Integers, Float s are not Reals You must know assembly Memory Matters Performance! Asymptotic Complexity It s more than
Where Have We Been? Class Introduction Great Realities of Computing Int s are not Integers, Float s are not Reals You must know assembly Memory Matters Performance! Asymptotic Complexity It s more than
Bits, Bytes, and Integers Part 2
 Bits, Bytes, and Integers Part 2 15-213: Introduction to Computer Systems 3 rd Lecture, Jan. 23, 2018 Instructors: Franz Franchetti, Seth Copen Goldstein, Brian Railing 1 First Assignment: Data Lab Due:
Bits, Bytes, and Integers Part 2 15-213: Introduction to Computer Systems 3 rd Lecture, Jan. 23, 2018 Instructors: Franz Franchetti, Seth Copen Goldstein, Brian Railing 1 First Assignment: Data Lab Due:
Inthis lecture we will cover the following material:
 Lecture #8 Inthis lecture we will cover the following material: The standard package, The std_logic_1164 Concordia Objects & data Types (Signals, Variables, Constants, Literals, Character) Types and Subtypes
Lecture #8 Inthis lecture we will cover the following material: The standard package, The std_logic_1164 Concordia Objects & data Types (Signals, Variables, Constants, Literals, Character) Types and Subtypes
Corrections for Digital Systems Design Using VHDL, 3rd printing
 Corrections for Digital Systems Design Using VHDL, 3rd printing Corrected VHDL code can be found on the web page: http://www.brookscole.com/engineering/ee/roth.html line 7 means 7th line from bottom, etc.
Corrections for Digital Systems Design Using VHDL, 3rd printing Corrected VHDL code can be found on the web page: http://www.brookscole.com/engineering/ee/roth.html line 7 means 7th line from bottom, etc.
csitnepal Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design
 Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design Introduction We introduce here a basic computer whose operation can be specified by the resister transfer statements. Internal organization of the computer
Unit 3 Basic Computer Organization and Design Introduction We introduce here a basic computer whose operation can be specified by the resister transfer statements. Internal organization of the computer
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design
 CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10122011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Fixed Point Arithmetic Addition/Subtraction
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10122011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Fixed Point Arithmetic Addition/Subtraction
2. MACHINE REPRESENTATION OF TYPICAL ARITHMETIC DATA FORMATS (NATURAL AND INTEGER NUMBERS).
 2. MACHINE REPRESENTATION OF TYPICAL ARITHMETIC DATA FORMATS (NATURAL AND INTEGER NUMBERS). 2.. Natural Binary Code (NBC). The positional code with base 2 (B=2), introduced in Exercise, is used to encode
2. MACHINE REPRESENTATION OF TYPICAL ARITHMETIC DATA FORMATS (NATURAL AND INTEGER NUMBERS). 2.. Natural Binary Code (NBC). The positional code with base 2 (B=2), introduced in Exercise, is used to encode
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 2 Data Representation
 Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 2 Data Representation Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Last lecture Moore s law Types of computer systems Computer components Computer system stack
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 2 Data Representation Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Last lecture Moore s law Types of computer systems Computer components Computer system stack
Review Topics. Midterm Exam Review Slides
 Review Topics Midterm Exam Review Slides Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Computer Arithmetic Combinational
Review Topics Midterm Exam Review Slides Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Computer Arithmetic Combinational
Course Topics - Outline
 Course Topics - Outline Lecture 1 - Introduction Lecture 2 - Lexical conventions Lecture 3 - Data types Lecture 4 - Operators Lecture 5 - Behavioral modeling A Lecture 6 Behavioral modeling B Lecture 7
Course Topics - Outline Lecture 1 - Introduction Lecture 2 - Lexical conventions Lecture 3 - Data types Lecture 4 - Operators Lecture 5 - Behavioral modeling A Lecture 6 Behavioral modeling B Lecture 7
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION. Operation Add Magnitudes Subtract Magnitudes (+A) + ( B) + (A B) (B A) + (A B)
 Computer Arithmetic Data is manipulated by using the arithmetic instructions in digital computers. Data is manipulated to produce results necessary to give solution for the computation problems. The Addition,
Computer Arithmetic Data is manipulated by using the arithmetic instructions in digital computers. Data is manipulated to produce results necessary to give solution for the computation problems. The Addition,
Lecture 12 Integers. Computer and Network Security 19th of December Computer Science and Engineering Department
 Lecture 12 Integers Computer and Network Security 19th of December 2016 Computer Science and Engineering Department CSE Dep, ACS, UPB Lecture 12, Integers 1/40 Outline Data Types Representation Conversions
Lecture 12 Integers Computer and Network Security 19th of December 2016 Computer Science and Engineering Department CSE Dep, ACS, UPB Lecture 12, Integers 1/40 Outline Data Types Representation Conversions
COE 405 Design Methodology Based on VHDL
 COE 405 Design Methodology Based on VHDL Dr. Aiman H. El-Maleh Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Outline Elements of VHDL Top-Down Design Top-Down Design with
COE 405 Design Methodology Based on VHDL Dr. Aiman H. El-Maleh Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Outline Elements of VHDL Top-Down Design Top-Down Design with
NUMBER OPERATIONS. Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi. CS/ECE 3810: Computer Organization. Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah
 NUMBER OPERATIONS Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 3810: Computer Organization Overview Homework 4 is due tonight Verify your uploaded file before the
NUMBER OPERATIONS Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 3810: Computer Organization Overview Homework 4 is due tonight Verify your uploaded file before the
The type of all data used in a C++ program must be specified
 The type of all data used in a C++ program must be specified A data type is a description of the data being represented That is, a set of possible values and a set of operations on those values There are
The type of all data used in a C++ program must be specified A data type is a description of the data being represented That is, a set of possible values and a set of operations on those values There are
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 24, 2018 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 8: A C++ Introduction For Python Programmers Expressions and Operator Precedence
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 24, 2018 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 8: A C++ Introduction For Python Programmers Expressions and Operator Precedence
Control and Datapath 8
 Control and Datapath 8 Engineering attempts to develop design methods that break a problem up into separate steps to simplify the design and increase the likelihood of a correct solution. Digital system
Control and Datapath 8 Engineering attempts to develop design methods that break a problem up into separate steps to simplify the design and increase the likelihood of a correct solution. Digital system
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals VHDL. Part 1 Chapter 4 Basics and Constructs
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals VHDL Part Chapter 4 Basics and Constructs Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 24 Pearson Education, Inc. Terms of Use (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals VHDL Part Chapter 4 Basics and Constructs Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 24 Pearson Education, Inc. Terms of Use (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data
 Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
The x86 Microprocessors. Introduction. The 80x86 Microprocessors. 1.1 Assembly Language
 The x86 Microprocessors Introduction 1.1 Assembly Language Numbering and Coding Systems Human beings use the decimal system (base 10) Decimal digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Computer systems use the
The x86 Microprocessors Introduction 1.1 Assembly Language Numbering and Coding Systems Human beings use the decimal system (base 10) Decimal digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Computer systems use the
VHDL: RTL Synthesis Basics. 1 of 59
 VHDL: RTL Synthesis Basics 1 of 59 Goals To learn the basics of RTL synthesis. To be able to synthesize a digital system, given its VHDL model. To be able to relate VHDL code to its synthesized output.
VHDL: RTL Synthesis Basics 1 of 59 Goals To learn the basics of RTL synthesis. To be able to synthesize a digital system, given its VHDL model. To be able to relate VHDL code to its synthesized output.
1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4]
![1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4] 1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4]](/thumbs/81/83055464.jpg) HW 3 Answer Key 1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4] You can build a NAND gate from tri-state buffers and inverters and thus you
HW 3 Answer Key 1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4] You can build a NAND gate from tri-state buffers and inverters and thus you
CHAPTER SIX BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 CHAPTER SIX BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 6.1. Instruction Codes The organization of a digital computer defined by: 1. The set of registers it contains and their function. 2. The set of instructions
CHAPTER SIX BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 6.1. Instruction Codes The organization of a digital computer defined by: 1. The set of registers it contains and their function. 2. The set of instructions
Integer Multiplication and Division
 Integer Multiplication and Division COE 301 Computer Organization Prof. Muhamed Mudawar College of Computer Sciences and Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline
Integer Multiplication and Division COE 301 Computer Organization Prof. Muhamed Mudawar College of Computer Sciences and Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline
Number Systems, Scalar Types, and Input and Output
 Number Systems, Scalar Types, and Input and Output Outline: Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal, and Decimal Numbers Character Set Comments Declaration Data Types and Constants Integral Data Types Floating-Point
Number Systems, Scalar Types, and Input and Output Outline: Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal, and Decimal Numbers Character Set Comments Declaration Data Types and Constants Integral Data Types Floating-Point
COMP2611: Computer Organization. Data Representation
 COMP2611: Computer Organization Comp2611 Fall 2015 2 1. Binary numbers and 2 s Complement Numbers 3 Bits: are the basis for binary number representation in digital computers What you will learn here: How
COMP2611: Computer Organization Comp2611 Fall 2015 2 1. Binary numbers and 2 s Complement Numbers 3 Bits: are the basis for binary number representation in digital computers What you will learn here: How
BASIC VHDL LANGUAGE ELEMENTS AND SEMANTICS. Lecture 7 & 8 Dr. Tayab Din Memon
 BASIC VHDL LANGUAGE ELEMENTS AND SEMANTICS Lecture 7 & 8 Dr. Tayab Din Memon Outline Data Objects Data Types Operators Attributes VHDL Data Types VHDL Data Objects Signal Constant Variable File VHDL Data
BASIC VHDL LANGUAGE ELEMENTS AND SEMANTICS Lecture 7 & 8 Dr. Tayab Din Memon Outline Data Objects Data Types Operators Attributes VHDL Data Types VHDL Data Objects Signal Constant Variable File VHDL Data
Introduction to VHDL #1
 ECE 3220 Digital Design with VHDL Introduction to VHDL #1 Lecture 3 Introduction to VHDL The two Hardware Description Languages that are most often used in industry are: n VHDL n Verilog you will learn
ECE 3220 Digital Design with VHDL Introduction to VHDL #1 Lecture 3 Introduction to VHDL The two Hardware Description Languages that are most often used in industry are: n VHDL n Verilog you will learn
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 15: Midterm 1 Review Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Basics Midterm to cover Book Sections (inclusive) 1.1 1.5
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 15: Midterm 1 Review Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Basics Midterm to cover Book Sections (inclusive) 1.1 1.5
CC411: Introduction To Microprocessors
 CC411: Introduction To Microprocessors OBJECTIVES this chapter enables the student to: Use number { base 2, base 10, or base 16 }. Add and subtract binary/hex numbers. Represent any binary number in 2
CC411: Introduction To Microprocessors OBJECTIVES this chapter enables the student to: Use number { base 2, base 10, or base 16 }. Add and subtract binary/hex numbers. Represent any binary number in 2
JUNE, JULY 2013 Fundamentals of HDL (10EC45) PART A
 JUNE, JULY 2013 Fundamentals of HDL (10EC45) Time: 3hrs Max Marks:100 Note: Answer FIVE full questions, selecting at least TWO questions from each part. PART A Q1.a. Describe VHDL scalar data types with
JUNE, JULY 2013 Fundamentals of HDL (10EC45) Time: 3hrs Max Marks:100 Note: Answer FIVE full questions, selecting at least TWO questions from each part. PART A Q1.a. Describe VHDL scalar data types with
LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS
 LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS Goals Learn how to determine the performance of a processor. Improve the processor performance by adding new instructions. To Do Determine the speed of the processor in Lab
LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS Goals Learn how to determine the performance of a processor. Improve the processor performance by adding new instructions. To Do Determine the speed of the processor in Lab
srl - shift right logical - 0 enters from left, bit drops off right end note: little-endian bit notation msb lsb "b" for bit
 Clemson University -- CPSC 231 Shifts (p. 123) srl - shift right logical - 0 enters from left, bit drops off right end 0 b 31 b 30 b 2 b 1 b 0 note: little-endian bit notation msb lsb "b" for bit a f 5
Clemson University -- CPSC 231 Shifts (p. 123) srl - shift right logical - 0 enters from left, bit drops off right end 0 b 31 b 30 b 2 b 1 b 0 note: little-endian bit notation msb lsb "b" for bit a f 5
ECOM4311 Digital Systems Design
 ECOM 4311 Digital Systems Design Eng. Monther Abusultan Computer Engineering Dept. Islamic University of Gaza Page 1 Agenda 1. VHDL : Data Types Cont d 2. VHDL : Operators 3. VHDL : Signal Assignments
ECOM 4311 Digital Systems Design Eng. Monther Abusultan Computer Engineering Dept. Islamic University of Gaza Page 1 Agenda 1. VHDL : Data Types Cont d 2. VHDL : Operators 3. VHDL : Signal Assignments
Partial product generation. Multiplication. TSTE18 Digital Arithmetic. Seminar 4. Multiplication. yj2 j = xi2 i M
 TSTE8 igital Arithmetic Seminar 4 Oscar Gustafsson Multiplication Multiplication can typically be separated into three sub-problems Generating partial products Adding the partial products using a redundant
TSTE8 igital Arithmetic Seminar 4 Oscar Gustafsson Multiplication Multiplication can typically be separated into three sub-problems Generating partial products Adding the partial products using a redundant
14:332:231 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN. Hardware Description Languages
 14:332:231 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & Computer Engineering Fall 2013 Lecture #22: Introduction to Verilog Hardware Description Languages Basic idea: Language constructs
14:332:231 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & Computer Engineering Fall 2013 Lecture #22: Introduction to Verilog Hardware Description Languages Basic idea: Language constructs
EE 8351 Digital Logic Circuits Ms.J.Jayaudhaya, ASP/EEE
 EE 8351 Digital Logic Circuits Ms.J.Jayaudhaya, ASP/EEE 1 Logic circuits for digital systems may be combinational or sequential. A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output
EE 8351 Digital Logic Circuits Ms.J.Jayaudhaya, ASP/EEE 1 Logic circuits for digital systems may be combinational or sequential. A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
Approaches to Digital System Design
 Approaches to Digital System Design In Digital Devices, you learned how to create a logic network (Flip-flops + combinational gates) to solve a problem The logic network was SPECIFIC to the problem. To
Approaches to Digital System Design In Digital Devices, you learned how to create a logic network (Flip-flops + combinational gates) to solve a problem The logic network was SPECIFIC to the problem. To
Design Example: 4-bit Multiplier
 Design Example: 4-bit Multiplier Consider how we normally multiply numbers: 123 x 264 492 7380 24600 32472 Binary multiplication is similar. (Note that the product of two 4-bit numbers is potentially an
Design Example: 4-bit Multiplier Consider how we normally multiply numbers: 123 x 264 492 7380 24600 32472 Binary multiplication is similar. (Note that the product of two 4-bit numbers is potentially an
CT 229. Java Syntax 26/09/2006 CT229
 CT 229 Java Syntax 26/09/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Assignment Due Date: Oct 1 st Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given in the assignment sheet!!!! Remember:
CT 229 Java Syntax 26/09/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Assignment Due Date: Oct 1 st Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given in the assignment sheet!!!! Remember:
Exam I Review February 2017
 Exam I Review February 2017 Binary Number Representations Conversion of binary to hexadecimal and decimal. Convert binary number 1000 1101 to hexadecimal: Make groups of 4 bits to convert to hexadecimal,
Exam I Review February 2017 Binary Number Representations Conversion of binary to hexadecimal and decimal. Convert binary number 1000 1101 to hexadecimal: Make groups of 4 bits to convert to hexadecimal,
Contents. Appendix D VHDL Summary Page 1 of 23
 Appendix D VHDL Summary Page 1 of 23 Contents Appendix D VHDL Summary...2 D.1 Basic Language Elements...2 D.1.1 Comments...2 D.1.2 Identifiers...2 D.1.3 Data Objects...2 D.1.4 Data Types...2 D.1.5 Data
Appendix D VHDL Summary Page 1 of 23 Contents Appendix D VHDL Summary...2 D.1 Basic Language Elements...2 D.1.1 Comments...2 D.1.2 Identifiers...2 D.1.3 Data Objects...2 D.1.4 Data Types...2 D.1.5 Data
ECE 341. Lecture # 6
 ECE 34 Lecture # 6 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@pdx.edu October 5, 24 Portland State University Lecture Topics Design of Fast Adders Carry Looakahead Adders (CLA) Blocked Carry-Lookahead Adders Multiplication
ECE 34 Lecture # 6 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@pdx.edu October 5, 24 Portland State University Lecture Topics Design of Fast Adders Carry Looakahead Adders (CLA) Blocked Carry-Lookahead Adders Multiplication
HC11 Instruction Set Architecture
 HC11 Instruction Set Architecture High-level HC11 architecture Interrupt logic MEMORY Timer and counter M8601 CPU core Serial I/O A/D converter Port A Port B Port C Port D Port E CMPE12 Summer 2009 16-2
HC11 Instruction Set Architecture High-level HC11 architecture Interrupt logic MEMORY Timer and counter M8601 CPU core Serial I/O A/D converter Port A Port B Port C Port D Port E CMPE12 Summer 2009 16-2
Chapter 2 Basic Logic Circuits and VHDL Description
 Chapter 2 Basic Logic Circuits and VHDL Description We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them. ----- Albert Einstein Like a C or C++ programmer don t apply the logic.
Chapter 2 Basic Logic Circuits and VHDL Description We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them. ----- Albert Einstein Like a C or C++ programmer don t apply the logic.
HC11 Instruction Set Architecture
 HC11 Instruction Set Architecture Summer 2008 High-level HC11 architecture Interrupt logic MEMORY Timer and counter M8601 CPU core Serial I/O A/D converter Port A Port B Port C Port D Port E CMPE12 Summer
HC11 Instruction Set Architecture Summer 2008 High-level HC11 architecture Interrupt logic MEMORY Timer and counter M8601 CPU core Serial I/O A/D converter Port A Port B Port C Port D Port E CMPE12 Summer
Verilog Design Principles
 16 h7fex // 16-bit value, low order 4 bits unknown 8 bxx001100 // 8-bit value, most significant 2 bits unknown. 8 hzz // 8-bit value, all bits high impedance. Verilog Design Principles ECGR2181 Extra Notes
16 h7fex // 16-bit value, low order 4 bits unknown 8 bxx001100 // 8-bit value, most significant 2 bits unknown. 8 hzz // 8-bit value, all bits high impedance. Verilog Design Principles ECGR2181 Extra Notes
EXPERIMENT NO. 1 THE MKT 8085 MICROPROCESSOR TRAINER
 OBJECT: EXPERIMENT NO. 1 THE MKT 8085 MICROPROCESSOR TRAINER To understand the structure and operating instruction of the microprocessor trainer. INTRODUCTION: The MKT 8085 is a single-board microcomputer,
OBJECT: EXPERIMENT NO. 1 THE MKT 8085 MICROPROCESSOR TRAINER To understand the structure and operating instruction of the microprocessor trainer. INTRODUCTION: The MKT 8085 is a single-board microcomputer,
The type of all data used in a C (or C++) program must be specified
 The type of all data used in a C (or C++) program must be specified A data type is a description of the data being represented That is, a set of possible values and a set of operations on those values
The type of all data used in a C (or C++) program must be specified A data type is a description of the data being represented That is, a set of possible values and a set of operations on those values
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
 Least Common Multiple (LCM) Task: Implement an LCM algorithm that is able to handle any combination of 8-bit (sign bit included) numbers. Use two's complement format to represent negative values. Provide
Least Common Multiple (LCM) Task: Implement an LCM algorithm that is able to handle any combination of 8-bit (sign bit included) numbers. Use two's complement format to represent negative values. Provide
COSC 243. Data Representation 3. Lecture 3 - Data Representation 3 1. COSC 243 (Computer Architecture)
 COSC 243 Data Representation 3 Lecture 3 - Data Representation 3 1 Data Representation Test Material Lectures 1, 2, and 3 Tutorials 1b, 2a, and 2b During Tutorial a Next Week 12 th and 13 th March If you
COSC 243 Data Representation 3 Lecture 3 - Data Representation 3 1 Data Representation Test Material Lectures 1, 2, and 3 Tutorials 1b, 2a, and 2b During Tutorial a Next Week 12 th and 13 th March If you
CSCI2467: Systems Programming Concepts
 CSCI2467: Systems Programming Concepts Slideset 2: Information as Data (CS:APP Chap. 2) Instructor: M. Toups Spring 2018 Course updates datalab out today! - due after Mardi gras... - do not wait until
CSCI2467: Systems Programming Concepts Slideset 2: Information as Data (CS:APP Chap. 2) Instructor: M. Toups Spring 2018 Course updates datalab out today! - due after Mardi gras... - do not wait until
CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 5 Basic Organization and Design Outline Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions
