Acknowledgement-Aware MPR MAC Protocol for Distributed WLANs: Design and Analysis
|
|
|
- Millicent White
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
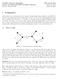
1 Globecom Wireless Commuicatios Symposium Ackowledgemet-Aware MPR MAC Protocol for Distributed WLANs: Desig ad Aalysis Arpa Mukhopadhyay, Neelesh B. Mehta, Seior Member, IEEE, Vikram Sriivasa, Member, IEEE Abstract Multi-packet receptio (MPR, i which a receiver ca decode multiple simultaeous trasmissios, sigificatly improves the uplik throughput of wireless local area etworks (WLANs. However, the medium access cotrol (MAC layer must be redesiged to ecourage, ad ot avoid, simultaeous trasmissios. Asychroous MPR MAC protocols, i which odes idepedetly access the chael so log as the umber of ogoig trasmissios is less tha a threshold, are promisig solutios for eablig MPR i IEEE based WLANs. I this paper, we highlight the problem of ackowledgmet (ACK delays that arises i asychroous MPR whe multiple odes trasmit i successio without the chael becomig idle. We propose a ovel asychroous MAC protocol that reduces the ACK delays, icreases throughput, ad retais the distributed ature of the distributed coordiatio fuctio (DCF. A accurate reewal theoretic fixed-poit aalysis that leads to geeral aalytical expressios for the saturatio throughput is also developed. I. INTRODUCTION IEEE wireless local area etworks (WLANs are very popular, but are facig icreasig demads for higher data rates ad greater spectral efficiecy. These WLANs use the distributed coordiatio fuctio (DCF ad its variats such as ehaced DCF (EDCF for medium access cotrol (MAC [1] [3]. The desig of the DCF is based o the premise that whe multiple statios trasmit simultaeously i a time slot, a collisio occurs ad the receiver caot decode ay trasmissio. Therefore, the DCF uses carrier sese multiple access with collisio avoidace (CSMA/CA to discourage trasmissios by more tha oe user at ay time. This is accomplished by freezig the backoff timer aytime a ode seses a busy chael. However, wireless receivers today are capable of employig sophisticated sigal processig ad multi-user detectio techologies such as successive iterferece cacellatio (SIC, space-time codig, ad multiple ateas [4], ad ca receive multiple packets simultaeously. This capability has bee referred to as multi-packet receptio (MPR i the literature [5] [9]. MPR promises sigificat throughput gais i the uplik, i.e., the lik from the statios to the access poit (AP [10]. However, it also egeders a fudametal redesig of the MAC protocol, which must ow facilitate ad ot discourage simultaeous trasmissios by multiple users. At the same A. Mukhopadhyay is with the Dept. of Electrical ad Computer Eg. at the Uiv. of Waterloo, Caada. N. B. Mehta is with the Dept. of Electrical Commuicatio Eg. at the Idia Istitute of Sciece (IISc, Bagalore, Idia. V. Sriivasa is with Bell Labs Research, Alcatel-Lucet, Bagalore, Idia. A. Mukhopadhyay was at IISc durig the course of this work. s: arpamu@gmail.com, bmehta@ece.iisc.eret.i time, it is desirable that the MAC retais its distributed ature, which is a key reaso for the success of IEEE DCF. While MPR has bee cosidered i the literature, e.g., [7], [10], [11], a sychroous access sceario is ofte assumed. I it, multiple odes ca start trasmittig simultaeously, but o ode ca start a trasmissio if it seses the chael to be busy. This leads to the MPR capability ot beig fully haressed. This problem was firstaddressedbybabichad Comisso i [12], who aalyzed a asychroous protocol usig a Markov chai model. I it, a ode decremets its backoff timer as log as the umber of ogoig trasmissios sesed by it is below a threshold. The umber of receive ateas i the ode determies the umber of trasmissios that it ca sese. However, ackowledgemets (ACKs were ot modeled. It was implicitly assumed that a ode kows whether its trasmissio was successful or ot as soo as its packet trasmissio eds. I fact, i the asychroous MPR setup, ACKs ca get sigificatly delayed. This is because multiple trasmissios to the AP ca ow occur i successio without ay idle period i betwee. Thus, the AP, which is a half-duplex ode, must cotiue to receive these time overlappig trasmissios eve after a particular ode completes its trasmissio. It ca ackowledge all the packets it successfully received oly after the chael becomes idle. However, a ode chooses its backoff timer parameters ad schedules its ext trasmissio oly after it receives its ACK or whe it times out waitig for the ACK. Therefore, this delay ca degrade the protocol s performace. Furthermore, i [12], a memoryless distributio of packet legths was assumed i order to facilitate a Markovia aalysis. This assumptio does ot hold uder heavy traffic situatios whe there are may retrasmissios. I this paper, we first highlight a problem related to ACK delays that is uique to a asychroous MPR MAC protocol. To show that the ACK delays ca degrade the performace of such protocols we compare the performaces of two protocols. The first oe is similar to the oe aalyzed i [12] except that ACKs are ow icorporated i the protocol. The secod protocol, which we propose i this paper, reduces ACK delays by modifyig the rules that gover whe the timer should be decremeted ad froze. We show that the modificatios reduce the ACK delays ad icrease the saturatio throughput, while retaiig the distributed ature of covetioal DCF. Aother importat cotributio of this paper is a fixed-poit aalysis of the proposed asychroous MPR MAC protocol based o reewal theory [13]. Ulike [12], it captures the effect of ACK delays o the protocol s performace ad leads /12/$ IEEE 5087
2 to geeral aalytical expressios for the throughput ad packet collisio probability. It also geeralizes the aalysis i [14], which is applicable oly to covetioal DCF. The packet legths are o loger required to be geometrically distributed i our model. Further, the effect of packet droppig after a fiite umber of retrasmissios is ow explicitly icluded. Thus, our approach provides a more geeral aalysis of the asychroous MPR MAC. The paper is orgaized as follows. Sectio II develops the system model. The proposed protocol is aalyzed i Sectio III. Simulatio results are preseted i Sectio IV, ad are followed by our coclusios i Sectio V. Mathematical derivatios are relegated to the Appedix. II. SYSTEM MODEL AND PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION Cosider a IEEE etwork that cosists of cotedig odes. We assume that the AP ca decode up to two simultaeous trasmissios, ad each ode ca correctly estimate whether there is zero, oe, or more tha oe ogoig trasmissio i the chael, as was also assumed i [12]. 1 This is easily achieved whe each ode is equipped with at least two ateas by meas of directio of arrival (DOA techiques based o eige-decompositio of the received sigal s array correlatio matrix [16] [12, Sec. VI]. All odes follow the biary expoetial backoff scheme, as specified i DCF. Before each packet trasmissio, a ode selects the backoff period i multiples of a slot duratio δ. The multiple is chose uiformly from {0, 1,..., w 1}, where w is called the cotetio widow. It depeds o the umber of failed trasmissios of a packet. I the first attempt, w is set equal to the miimum cotetio widow CW mi. After each usuccessful trasmissio, w is doubled, up to a maximum value of CW max =2 m CW mi. A packet is dropped by a ode after K +1failed trasmissio attempts. A. Protocol 1: Asychroous MPR Protocol i [12] with ACKs I the followig we describe a protocol similar to that i [12] but with ACKs icorporated i it. As metioed earlier, the AP is assumed to be able to decode up to two simultaeous trasmissios. I this protocol, a ode havig a packet to trasmit samples a backoff timer value ad starts decremetig it oce it seses the chael to be idle for a distributed iterframe space (DIFS of duratio T DIFS. The backoff timer is decremeted as log as the ode seses 0 or 1 trasmissios i the chael. Whe the sesed umber of trasmissios becomes greater tha or equal to 2, the ode freezes its backoff timer. It is resumed from the last stored value as soo as the umber of sesed trasmissios agai falls to 1. The ode trasmits its packet whe the backoff timer value becomes zero. 1 We focus o the case with two simultaeous trasmissios sice it is both aalytically rich ad isightful ad practically relevat. As we show, it leads to close to 100% gais i saturatio throughput ad delay over covetioal DCF. Further, it requires odes to have just two ateas, which is feasible today [4], [15]. The aalysis ca be geeralized to hadle more tha two simultaeous trasmissios, though the expressios become more ivolved. Fig. 1. Timig diagram for the proposed scheme showig a system-wide reewal iterval i which two simultaeous asychroous trasmissios to the AP occur. Whe the chael becomes idle after the ed of the overlappig trasmissios, the AP seds a cumulative ACK of duratio T ACK, which ackowledges all the successful trasmissios together [7]. As i covetioal DCF, it waits for the chael to remai idle for a short iter-frame space (SIFS of duratio T SIFS before commecig its trasmissio of the ACK. By settig T DIFS >T SIFS, the ACK gets priority over other trasmissios whe the chael is idle. However, ulike covetioal DCF, a ode expects its ACK to arrive withi a duratio T OUT = T DIFS after the chael becomes idle, ad ot after it has completed its packet trasmissio. I case the ACK does ot arrive, the ode times out, updates its cotetio widow, chooses a ew backoff timer value, ad starts decremetig it. B. Protocol 2: Proposed Protocol We ow propose a asychroous MPR MAC protocol that reduces the ACK delays. As i the previous protocol, a ode with a packet samples a backoff timer ad starts decremetig it whe it fids the chael to be idle for T DIFS duratio. It trasmits its packet whe the timer reaches zero. However, the proposed protocol differs with respect to the coditios uder which the backoff timer is froze ad remais froze. The rule is as follows: Durig the backoff phase, a ode freezes its timer oce the umber of ogoig trasmissios exceeds two or oce it decreases. Thereafter, the ode resumes decremetig its timer oly whe the chael has remaied idle for a duratio T DIFS. The operatio of the AP remais the same as before. The above protocol is illustrated i Figure 1 for three odes A, B, adc. I it, A trasmits first. While A is trasmittig, B ad C cotiue decremetig their timers sice there is oly oe ogoig trasmissio i the chael. Oce B starts trasmittig, C freezes its timer. The timer of C remais froze eve after A s trasmissio eds. Oly after a idle period of duratio T DIFS, do all the odes resume decremetig their timers. I Protocol 1 istead, C will start decremetig its timer as soo as A s trasmissio eds. As a result, its timer may become zero while B is trasmittig. 5088
3 III. ANALYSIS We ow aalyze the proposed MPR scheme i saturated traffic coditios i which trasmissio queue of each ode is assumed to be always o-empty. This gives a limit o the system throughput i heavy traffic loads, ad has bee extesively aalyzed for covetioal DCF; see, for example, [1], [14]. To simplify the aalysis, the odes are assumed to be statistically idetical ad the trasmissio rate is fixed at Ω [1], [14]. A trasmitted packet is received successfully uless it is ivolved i a collisio. To get compact aalytical results, we assume that a data packet trasmissio lasts for a duratio of λ slots. This also illustrates that a o-memoryless packet legth distributio ca be aalyzed, ulike the Markov chai approach of [1], [12]. We also assume that ACKs are successfully received by all the odes. As all the odes use the same backoff parameters, we make the followig two classical decouplig approximatios, which eable a fixed-poit aalysis [1], [14]: 1 Each trasmitted packet suffers a collisio with a probability γ, regardless of the umber of its retrasmissios ad idepedet of all other odes. We shall call γ as the coditioal packet collisio probability. 2 Each ode attempts a trasmissio i a slot where it is allowed to trasmit with a probability β that is idepedet of all other odes. The parameter β will be referred to as the attempt rate. Note that over a sufficietly log time, γ ca be iterpreted as the ratio of the total umber of collisios occurrig i the etwork to the total umber of trasmissio attempts by all odes uder saturated traffic coditios. Similarly, β, ithe log ru, is the average (take over all odes of the ratio of the total umber of trasmissio attempts by a ode to the total umber of slots i which the ode is i its backoff phase. Based o these decouplig approximatios, the followig two reewal processes ca be costructed. Node-specific reewal process: Cosider a give ode, which we heceforth call the tagged ode. Let A j ad B j respectively deote the umber of attempts ad total backoff duratio (i slots eeded by the tagged ode to trasmit its j th packet. From the first approximatio it follows that the backoff process of a tagged ode is a reewal process with reewal lifetimes B j, j 1, ad with the time istats at which the ode starts the fial trasmissio of its j th packet as reewal epochs. If we treat A j, j 1, as the reward gaied i each reewal cycle, the from the reewal reward theorem [13], we have β = E[Aj] E[B j ],wheree[ ] deotes expectatio. It ca be show that the attempt rate β as a fuctio of γ is give by 1+γ + + γ K β G(γ = b 0 + γb γ K, (1 b K ( where b k = k CW mi 1,for0 k K, is the mea backoff duratio (i slots before the (k +1 th trasmissio attempt of a packet. The proof is similar to that i [14], ad is ot show here to coserve space. System-wide reewal process: Cosider the aggregate attempt process by all the odes o the chael. Due to the decouplig approximatios, the aggregate process is aother reewal process. As show i Figure 1, a reewal iterval starts whe all the odes start decremetig their backoff timers ad eds with either a ACK timeout (i case of a collisio or the trasmissio of a cumulative ACK by the AP (i case of a success followed by a idle of duratio T DIFS. Ulike covetioal DCF, more tha oe packet ca get trasmitted i a reewal iterval. We, therefore, defie the first packet ad secod packet of a reewal iterval as follows. A packet is called the first packet i a reewal iterval if the chael is idle whe its trasmissio commeces. A packet is called the secod packet if there is already oe ogoig trasmissio i the chael whe its trasmissio commeces. Give that a tagged ode has trasmitted a packet, let α deote the probability that the packet is the first packet i the reewal iterval. Lemma 1: Give that a tagged ode trasmits i a reewal iterval, the probability α that it is the first packet i the iterval is give by K 1 (β α = K 1 (β+k 2 (β, (2 where K i (β is the probability that the i th packet i a reewal iterval is the tagged ode s packet. Further, K 1 (β = β ad K 2 (β = ( 1β2 (1 β 1 ( (λ 1( 1 ( ( 1. Proof: The proof is relegated to Appedix A. Theorem 1: The coditioal packet collisio probability, γ, as a fuctio of β is give by γ Γ(β =αp 1 (β+(1 αp 2 (β, (3 where P i (β, fori =1, 2, deotes the probability of collisio of the i th trasmitted packet i a reewal iterval. Further, ( 1 (1 β 1 ( 1β(1 β 2 P 1 (β = 1 (1 β ( 1 1 (1 β λ( 1, (4 P 2 (β =1 (1 β 2. (5 Proof: The proof is relegated to Appedix B. Hece, by combiig (1, (2, ad (3, we get the followig fixed-poit equatio: γ = Γ(G(γ. SiceΓ(G(γ is a cotiuous mappig from the closed set [0, 1] to itself, Brouwer s fixed-poit theorem implies that there exists a fixed poit i [0, 1] [14]. Solvig this equatio umerically yields γ. The, (1 directly yields β. 2 A. Saturatio Throughput Let ζ deote the amout of successfully trasmitted data i a reewal iterval of duratio T. From the reewal reward theorem [13], the saturatio throughput, S, isgiveby S = E [ζ] E [T ], (6 2 We have observed that the fixed poit is uique for the parameters of iterest. However, provig uiqueess remais a challegig problem. 5089
4 We ow develop expressios for E [ζ] ad E [T ]. Asshow i Figure 1, a reewal iterval of legth T starts with a idle period of duratio T idle. It is followed by a busy period of duratio T busy, which icludes packet trasmissio(s, a cumulative ACK (if success occurs, ad a idle duratio of legth T DIFS. Depedig o whether a success or collisio has occurred, we refer to the busy period that occurs after the idle period as a success period (of duratio T suc or a collisio period (of duratio T col. Further, let Tcol mi ad Tsuc mi deote the miimum values of T col ad T suc, respectively. It ca be see that Tcol mi = λδ +T DIFS ad Tsuc mi = λδ +T SIFS +T ACK +T DIFS. Lemma 2: The expected legth of the reewal iterval is E [T ]=E [T idle ]+D col + D suc, (7 where D col ad D suc are the cotributios to the average busy period duratio from the collisio ad success evets, respectively. Further, E [T idle ]= 1, [ 1 (1 β β(1 β 1 D col = 1 (1 β ( 1β2 (1 β 2 2(1 (1 β ] T mi col + β (1 ( β 1 1 (1 β 1 ( 1β(1 β 2 (1 (1 β (1 (1 β 1 [ ( 1 (1 β (λ 1( 1 Tcol mi + 1 (1 ( β(λ 1( 1 λ (λ 1(1 β 1 ] (1 (1 β 1 δ, (8 ad D suc = ( 1β2 (1 β 2 +2β(1 β λ( 1 2(1 (1 β Tsuc mi + ( 1β2 (1 β 1 (1 β 2 (1 (1 β (1 (1 β 1 Fig. 2. Proposed protocol: Fiite state machie for the access poit If the umber of sesed trasmissios becomes greater tha or equal to 2 or decreases [ ( 1 (1 β (λ 1( 1 T mi suc + 1 (1 ( β(λ 1( 1 λ (λ 1(1 β 1 (1 (1 β 1 δ. (9 Proof: The proof is relegated to Appedix C. Lemma 3: The expected amout of data trasmitted i a reewal iterval, with a trasmissio rate of Ω, isgiveby ( ( 1β 2 (1 β 2 E [ζ] =2λδΩ 2(1 (1 β + ( 1β2 (1 β [ 2 (1 β 1 (1 β λ( 1] (1 (1 β 1 (1 (1 β β(1 βλ( 1 + λδω 1 (1 β. (10 Proof: The proof is relegated to Appedix D. The expressio for the ormalized saturatio throughput the follows directly from Lemmas 2 ad 3. ] Fig. 3. Proposed protocol: Fiite state machie for a ode IV. NUMERICAL RESULTS We ow preset the results obtaied from Mote Carlo simulatios that use 50,000 samples for differet MAC protocols, ad compare them with aalytical results. A evet-drive simulatio platform writte i C programmig laguage was used to implemet the MPR protocols described i Sectio II. This provides idepedet verificatio of the aalytical results. I it, each ode is modeled as a fiite state machie (FSM havig several states as per the protocols. The FSMs that model the AP ad the odes for the proposed protocol are show i Figures 2 ad 3, respectively. The parameter values used i the simulatios are: δ =20μs, T DIFS = T OUT =50μs, T SIFS =10μs, T ACK = 304 μs, CW mi =32, CW max = 1024, K =7,adλ = 400 slots. Figure 4 plots the ormalized saturatio throughput, S/Ω, 5090
5 Normalized saturatio throughput, S/Ω % 28.3% 18.1% 14.2% 0.5 Proposed protocol Protocol DCF basic access Sychroous MPR MAC Number of odes, Coditioal collisio probability, γ Covetioal o MPR DCF Proposed protocol Aalysis (Proposed protocol Simulatio (Proposed protocol Aalysis ( DCF basic access Simulatio ( DCF basic access Number of odes, Fig. 4. Saturatio throughput as a fuctio of the umber of odes Fig. 6. Coditioal packet collisio probability as a fuctio of the umber of odes Average head of lie packet delay (ms Proposed protocol Protocol DCF basic access Number of odes, Fig. 5. Saturatio delay as a fuctio of the umber of odes as a fuctio of the umber of cotedig odes,, for covetioal DCF, Protocol 1, ad the proposed Protocol 2. Also plotted is the throughput of a sychroous MPR protocol i which the odes freeze their backoff timers if they sese the chael to be busy regardless of the umber of ogoig trasmissios i the chael. However, if oe or two odes trasmit simultaeously, their packets will be received successfully by the AP. The ACKs are icorporated i all the protocols i order to esure a fair compariso. We see that the throughput of the proposed protocol is twice that of covetioal DCF, 10-15% more tha Protocol 1, ad 16-38% more tha the sychroous MPR versio. 3 Figure 5 plots the average head-of lie packet delay, i.e., the average time spet by a packet at the head of a ode s queue util the ode receives a ACK cofirmig successful trasmissio or the ode drops the packet. Agai, the proposed protocol outperforms the two bechmark protocols. The headof-lie delay is a importat performace metric that affects the performace of higher layers of the protocol stack [17]. The coditioal packet collisio probability as a fuctio of 3 For the geeral case where the AP ca decode up to L 2 overlappig trasmissios, Protocol 2 ca be geeralized as follows. A ode freezes its timer whe the umber of trasmissios i the chael exceeds L 1 or whe the umber of trasmissios starts decreasig. For L =3, 4, ad 5, the throughput of Protocol 2 is 2.96, 3.95, ad 4.98 times, respectively, more tha the throughput of covetioal DCF. It is at least 10% more tha the that of Protocol 1. is show i Figure 6. Notice that the aalysis ad simulatio results match each other well. Further, as icreases, the percetage error decreases. This is i cosoace with the results i mea field iteractio theory, which provides a mathematical justificatio for this behavior [18]. V. CONCLUSIONS We saw that makig the odes freeze their backoff timers oce the umber of ogoig trasmissios i the chael has crossed a threshold value or decreased from its previous value reduces the ACK delays i the asychroous MPR setup. It restricts the umber of ovelappig trasmissios i a reewal iterval, ad leads to saturatio throughput gais over the asychroous MPR MAC protocol cosidered i the literature ad over covetioal DCF. We saw that our reewal-theoretic fixed-poit aalysis is accurate ad geeral. It eables the modelig of packet droppig after K retrasmissios. Also, ulike the Markovia aalysis, it does ot eed to assume a memoryless packet legth distributio. Future work icludes evaluatig the effect of adaptive modulatio ad codig ad imperfect estimatio of the umber of ogoig trasmissios i the chael, ad determiig the o-saturated throughput. Correspodig throughput improvemets i the dowlik, which ca be achieved usig trasmissios techiques such as superpositio codig or spatial multiplexig at the AP, are also worth ivestigatig. APPENDIX A. Proof of Lemma 1 Expressio for K 1 (β: Let the tagged ode trasmit i slot t (t 1 of the reewal iterval. This occurs with probability (1 β (t 1 β, sice oe of the odes should have trasmitted i the slots 1,...,t 1 ad the tagged ode must trasmit i slot t. Hece, K 1 (β = β(1 β (t 1 β β = 1 (1 β. t=1 Expressio for K 2 (β: Let the first trasmissio from exactly oe ode other tha the tagged ode begi i slot t 1 of the reewal iterval, where t 1 1, ad let the tagged ode 5091
6 trasmit i slot t 1 + t Clearly, 0 t 2 λ 2, sice the proposed protocol does ot permit the tagged ode to trasmit oce the chael becomes idle. The probability of this evet is (1 β (t1 1 ( 1β(1 β 2 (1 β(1 β ( 1t2 β. Summig the probabilities over t 1 ad t 2 yields the desired expressio for K 2 (β. The expressio i (2 for α i terms of K 1 (β ad K 2 (β follows directly from Baye s rule. B. Proof of Theorem 1 A packet trasmitted by the tagged ode suffers a collisio uder the followig two scearios. 1 It is the first packet i the iterval: I this case, the packet suffers a collisio oly if, i ay of its λ slots, at least two amog the other 1 odes trasmit. The probability that the first i slots (0 i λ 1 of the trasmitted packet are free from collisios is (1 β i( 1. Ad, the probability that two or more odes trasmit i the (i+1 th slot is 1 (1 β 1 ( ( 1β(1 β 2. Thus, we have P 1 = λ 1 i=0 (1 βi( 1 1 (1 β 1 ( 1β(1 β 2, which simplifies to (5. 2 It is the secod packet i the iterval: I this case, a collisio ca occur oly i the first slot of the packet. This happes whe at least oe amog the remaiig 2 odes trasmits i the slot, which occurs with probability 1 (1 β 2. C. Proof of Lemma 2 Let P [ ] deote probability. Expressio for E [T idle ]: Clearly, P [T idle >x]=(1 β x, for x =0, 1,..., because o ode must trasmit for at least x slots. Hece, we get E [T idle ] = x=0 P [T idle > x] = x=0 (1 βx 1 =. Expressio for D col : Whe two or more odes start trasmittig simultaeously just after the idle period eds, we have T col = Tcol mi. This occurs with probability β(1 β 1 ( 1 2 β 2 (1 β 2. The deomiator term of 1 (1 β arises due to coditioig o the evet that the idle period has eded. Now, T col = Tcol mi + xδ, for 1 x λ 1, whe exactly oe amog the odes starts trasmittig after the idle period is over, oe of the remaiig 1 odes trasmit i the ext x 1 slots, ad at least two of the remaiig 1 odes trasmit i the followig slot. This happes with probability β(1 β 1 (1 β (x 1( 1 ( 1 ( 1β(1 β 2.Summig over x results i (8. Expressio for D suc : If just after the idle period, oly oe ode trasmits i the whole reewal iterval or exactly two odes start trasmittig simultaeously the a success occurs ad T suc = Tsuc mi. Its probability of occurrece is ( 1 2 β 2 (1 β 2 +β(1 β 1 (1 β (λ 1( 1.Similarly, it ca be show that P [T suc = Tsuc mi + xδ] = β(1 β 1 (1 β (x 1( 1 ( 1β(1 β 2,for1 x λ 1. Summig over x yields the desired expressio i (9. D. Brief Proof of Lemma 3 If a collisio occurs i a reewal iterval, the the AP caot decode ay of the trasmitted packets. Hece, i this case ζ =0.Otherwise,ζ equals iλδω if i {1, 2} odes trasmit i the reewal iterval. The probabilities of these evets have bee derived i Appedix C. Therefore, (( β(1 βλ( 1 E [ζ] = 1 (1 β λδω+ 2 β 2 (1 β 2 1 (1 β λ 1 ( 1β 2 (1 β 2 (1 β x( (1 β 2λδΩ. (11 x=1 The expressio above simplifies to (10. REFERENCES [1] G. Biachi, Performace aalysis of the IEEE distributed coordiatio fuctio, IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commu., vol. 18, pp , Mar [2] K. Medepalli ad F. A. Tobagi, Towards performace modelig of IEEE based wireless etworks: a uified framework ad its applicatios, i Proc. INFOCOM, pp. 1 12, Apr [3] F. Cal, M. Coti, ad E. Gregori, IEEE protocol: desig ad performace evaluatio of a adaptive backoff mechaism, IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commu., vol. 18, pp , Sep [4] M. Z. Siam ad M. Kruz, A overview of MIMO-orieted chael access i wireless etworks, IEEE Wireless Commu., vol. 15, pp , Feb [5] L. Tog, Q. Zhao, ad G. Merge, Multipacket receptio i radom access wireless etworks: from sigal processig to optimal medium access cotrol, IEEE Commu. Mag., vol. 39, pp , Nov [6] G. D. Celik, G. Zussma, W. F. Kha, ad E. Modiao, MAC for etworks with multipacket receptio capability ad spatially distributed odes, i Proc. INFOCOM, pp , Apr [7] W. L. Huag, K. B. Letaief, ad Y. J. Zhag, Joit chael state based radom access ad adaptive modulatio i wireless LANs with multipacket receptio, IEEE Tras. Wireless Commu., vol. 7, pp , Nov [8] F. Shad, T. D. Todd, V. Kezys, ad J. Litva, Dyamic slot allocatio (DSA i idoor SDMA/TDMA usig a smart atea basestatio, IEEE/ACM Tras. Networkig, vol. 9, pp , Feb [9] D. Truhachev, S. Nagaraj, ad C. Schlegel, Throughput/reliability tradeoffs i spread spectrum multi-hop ad hoc wireless etworks with multi-packet detectio, i Proc. ICC, Ju [10] S. Ghez, S. Verdu, ad S. C. Schwartz, Stability properties of slotted ALOHA with multipacket receptio capability, IEEE Tras. Automat. Cotr., vol. 33, pp , Jul [11] P. X. Zheg, Y. J. Zhag, ad S. C. Liew, Multipacket receptio i wireless local area etworks, i Proc. ICC, pp , Ju [12] F. Babich ad M. Comisso, Theoretical aalysis of asychroous multipacket receptio i etworks, IEEE Tras. Commu., vol. 58, pp , Ju [13] R. W. Wolff, Stochastic Modelig ad the Theory of Queues. Pretice Hall, [14] A. Kumar, E. Altma, D. Mioradi, ad M. Goyal, New isights from a fixed poit aalysis of sigle cell IEEE WLANs, IEEE/ACM Tras. Networkig, vol. 15, pp , Ju [15] T. Kaiser, Whe will smart ateas be ready for the market? part I, IEEE Sig. Proc. Mag., vol. 22, pp , Mar [16] L. C. Godara, Applicatio of atea arrays to mobile commuicatios part II: beam formig ad directio-of-arrival cosideratios, Proc. IEEE, vol. 85, pp , Aug [17] M. M. Carvalho ad J. J. Garcia-Lua-Aceves, Delay aalysis of IEEE i sigle-hop etworks, i Proc. IEEE Itl. Cof. Network Protocols, pp , Nov [18] M. Beaim ad J.-Y. L. Boudec, A class of mea field iteractio models for computer ad commuicatio systems, Perform. Eval., vol. 20, pp , Nov
Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems. Chapter 6. Multiple Radio Access Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Itroductio to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 6 Multiple Radio Access 1 Outlie Itroductio Multiple Radio Access Protocols Cotetio-based Protocols Pure ALOHA Slotted ALOHA CSMA (Carrier Sese Multiple
Itroductio to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 6 Multiple Radio Access 1 Outlie Itroductio Multiple Radio Access Protocols Cotetio-based Protocols Pure ALOHA Slotted ALOHA CSMA (Carrier Sese Multiple
Lecture 28: Data Link Layer
 Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) 2. Go ack N ARQ Although the Stop ad Wait ARQ is very simple, you ca easily show that it has very the low efficiecy. The low efficiecy comes from the fact that the trasmittig
Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) 2. Go ack N ARQ Although the Stop ad Wait ARQ is very simple, you ca easily show that it has very the low efficiecy. The low efficiecy comes from the fact that the trasmittig
Announcements. Reading. Project #4 is on the web. Homework #1. Midterm #2. Chapter 4 ( ) Note policy about project #3 missing components
 Aoucemets Readig Chapter 4 (4.1-4.2) Project #4 is o the web ote policy about project #3 missig compoets Homework #1 Due 11/6/01 Chapter 6: 4, 12, 24, 37 Midterm #2 11/8/01 i class 1 Project #4 otes IPv6Iit,
Aoucemets Readig Chapter 4 (4.1-4.2) Project #4 is o the web ote policy about project #3 missig compoets Homework #1 Due 11/6/01 Chapter 6: 4, 12, 24, 37 Midterm #2 11/8/01 i class 1 Project #4 otes IPv6Iit,
Markov Chain Model of HomePlug CSMA MAC for Determining Optimal Fixed Contention Window Size
 Markov Chai Model of HomePlug CSMA MAC for Determiig Optimal Fixed Cotetio Widow Size Eva Krimiger * ad Haiph Latchma Dept. of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig, Uiversity of Florida, Gaiesville, FL, USA
Markov Chai Model of HomePlug CSMA MAC for Determiig Optimal Fixed Cotetio Widow Size Eva Krimiger * ad Haiph Latchma Dept. of Electrical ad Computer Egieerig, Uiversity of Florida, Gaiesville, FL, USA
History Based Probabilistic Backoff Algorithm
 America Joural of Egieerig ad Applied Scieces, 2012, 5 (3), 230-236 ISSN: 1941-7020 2014 Rajagopala ad Mala, This ope access article is distributed uder a Creative Commos Attributio (CC-BY) 3.0 licese
America Joural of Egieerig ad Applied Scieces, 2012, 5 (3), 230-236 ISSN: 1941-7020 2014 Rajagopala ad Mala, This ope access article is distributed uder a Creative Commos Attributio (CC-BY) 3.0 licese
Improvement of the Orthogonal Code Convolution Capabilities Using FPGA Implementation
 Improvemet of the Orthogoal Code Covolutio Capabilities Usig FPGA Implemetatio Naima Kaabouch, Member, IEEE, Apara Dhirde, Member, IEEE, Saleh Faruque, Member, IEEE Departmet of Electrical Egieerig, Uiversity
Improvemet of the Orthogoal Code Covolutio Capabilities Usig FPGA Implemetatio Naima Kaabouch, Member, IEEE, Apara Dhirde, Member, IEEE, Saleh Faruque, Member, IEEE Departmet of Electrical Egieerig, Uiversity
Lecture 10 Collision resolution. Collision resolution
 Lecture 10 Collisio resolutio Collisio resolutio May applicatios ivolve a iquiry over a shared chael, which ca be ivoked for: discovery of eighborig devices i ad hoc etworks, coutig the umber of RFID tags
Lecture 10 Collisio resolutio Collisio resolutio May applicatios ivolve a iquiry over a shared chael, which ca be ivoked for: discovery of eighborig devices i ad hoc etworks, coutig the umber of RFID tags
Media Access Protocols. Spring 2018 CS 438 Staff, University of Illinois 1
 Media Access Protocols Sprig 2018 CS 438 Staff, Uiversity of Illiois 1 Where are We? you are here 00010001 11001001 00011101 A midterm is here Sprig 2018 CS 438 Staff, Uiversity of Illiois 2 Multiple Access
Media Access Protocols Sprig 2018 CS 438 Staff, Uiversity of Illiois 1 Where are We? you are here 00010001 11001001 00011101 A midterm is here Sprig 2018 CS 438 Staff, Uiversity of Illiois 2 Multiple Access
Data diverse software fault tolerance techniques
 Data diverse software fault tolerace techiques Complemets desig diversity by compesatig for desig diversity s s limitatios Ivolves obtaiig a related set of poits i the program data space, executig the
Data diverse software fault tolerace techiques Complemets desig diversity by compesatig for desig diversity s s limitatios Ivolves obtaiig a related set of poits i the program data space, executig the
Throughput-Delay Scaling in Wireless Networks with Constant-Size Packets
 Throughput-Delay Scalig i Wireless Networks with Costat-Size Packets Abbas El Gamal, James Mamme, Balaji Prabhakar, Devavrat Shah Departmets of EE ad CS Staford Uiversity, CA 94305 Email: {abbas, jmamme,
Throughput-Delay Scalig i Wireless Networks with Costat-Size Packets Abbas El Gamal, James Mamme, Balaji Prabhakar, Devavrat Shah Departmets of EE ad CS Staford Uiversity, CA 94305 Email: {abbas, jmamme,
1. SWITCHING FUNDAMENTALS
 . SWITCING FUNDMENTLS Switchig is the provisio of a o-demad coectio betwee two ed poits. Two distict switchig techiques are employed i commuicatio etwors-- circuit switchig ad pacet switchig. Circuit switchig
. SWITCING FUNDMENTLS Switchig is the provisio of a o-demad coectio betwee two ed poits. Two distict switchig techiques are employed i commuicatio etwors-- circuit switchig ad pacet switchig. Circuit switchig
Adaptive Resource Allocation for Electric Environmental Pollution through the Control Network
 Available olie at www.sciecedirect.com Eergy Procedia 6 (202) 60 64 202 Iteratioal Coferece o Future Eergy, Eviromet, ad Materials Adaptive Resource Allocatio for Electric Evirometal Pollutio through the
Available olie at www.sciecedirect.com Eergy Procedia 6 (202) 60 64 202 Iteratioal Coferece o Future Eergy, Eviromet, ad Materials Adaptive Resource Allocatio for Electric Evirometal Pollutio through the
Recursive Estimation
 Recursive Estimatio Raffaello D Adrea Sprig 2 Problem Set: Probability Review Last updated: February 28, 2 Notes: Notatio: Uless otherwise oted, x, y, ad z deote radom variables, f x (x) (or the short
Recursive Estimatio Raffaello D Adrea Sprig 2 Problem Set: Probability Review Last updated: February 28, 2 Notes: Notatio: Uless otherwise oted, x, y, ad z deote radom variables, f x (x) (or the short
3D Model Retrieval Method Based on Sample Prediction
 20 Iteratioal Coferece o Computer Commuicatio ad Maagemet Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (20) (20) IACSIT Press, Sigapore 3D Model Retrieval Method Based o Sample Predictio Qigche Zhag, Ya Tag* School of Computer
20 Iteratioal Coferece o Computer Commuicatio ad Maagemet Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (20) (20) IACSIT Press, Sigapore 3D Model Retrieval Method Based o Sample Predictio Qigche Zhag, Ya Tag* School of Computer
. Written in factored form it is easy to see that the roots are 2, 2, i,
 CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
A Generalized Markov Chain Model for Effective Analysis of Slotted IEEE
 A Geeralized Markov Chai Model for Effective Aalysis of Slotted IEEE 8..4 Pagu Park, Piergiuseppe Di Marco, Pablo Soldati, Carlo Fischioe, Karl Herik Johasso Abstract A geeralized aalysis of the IEEE 8..4
A Geeralized Markov Chai Model for Effective Aalysis of Slotted IEEE 8..4 Pagu Park, Piergiuseppe Di Marco, Pablo Soldati, Carlo Fischioe, Karl Herik Johasso Abstract A geeralized aalysis of the IEEE 8..4
Ones Assignment Method for Solving Traveling Salesman Problem
 Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
6.854J / J Advanced Algorithms Fall 2008
 MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
Pattern Recognition Systems Lab 1 Least Mean Squares
 Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
MAC Throughput Improvement Using Adaptive Contention Window
 Joural of Computer ad Commuicatios, 2015, 3, 1 14 Published Olie Jauary 2015 i SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/joural/jcc http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jcc.2015.31001 MAC Throughput Improvemet Usig Adaptive Cotetio
Joural of Computer ad Commuicatios, 2015, 3, 1 14 Published Olie Jauary 2015 i SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/joural/jcc http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jcc.2015.31001 MAC Throughput Improvemet Usig Adaptive Cotetio
Admission control issues in sensor clusters
 Admissio cotrol issues i 802.15.4 sesor clusters Jelea Mišić, Shairmia Shafi, ad Vojislav B. Mišić Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Maitoba Wiipeg, Maitoba, Caada PACS umbers: Valid PACS appear
Admissio cotrol issues i 802.15.4 sesor clusters Jelea Mišić, Shairmia Shafi, ad Vojislav B. Mišić Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Maitoba Wiipeg, Maitoba, Caada PACS umbers: Valid PACS appear
1 Graph Sparsfication
 CME 305: Discrete Mathematics ad Algorithms 1 Graph Sparsficatio I this sectio we discuss the approximatio of a graph G(V, E) by a sparse graph H(V, F ) o the same vertex set. I particular, we cosider
CME 305: Discrete Mathematics ad Algorithms 1 Graph Sparsficatio I this sectio we discuss the approximatio of a graph G(V, E) by a sparse graph H(V, F ) o the same vertex set. I particular, we cosider
A New per-class Flow Fixed Proportional Differentiated Service for Multi-service Wireless LAN*
 A New per-class Flow Fixed Proportioal Differetiated Service for Multi-service Wireless LAN* Meg Chag Che, Li-Pig Tug 2, Yeali S. Su 3, ad Wei-Kua Shih 2 Istitute of Iformatio Sciece, Academia Siica, Taipei,
A New per-class Flow Fixed Proportioal Differetiated Service for Multi-service Wireless LAN* Meg Chag Che, Li-Pig Tug 2, Yeali S. Su 3, ad Wei-Kua Shih 2 Istitute of Iformatio Sciece, Academia Siica, Taipei,
Research Article Delay Analysis of GTS Bridging between IEEE and IEEE Networks for Healthcare Applications
 Hidawi Publishig Corporatio Iteratioal Joural of Telemedicie ad Applicatios Volume 29, Article ID 98746, 13 pages doi:1.1155/29/98746 Research Article Delay Aalysis of GTS Bridgig betwee IEEE 82.15.4 ad
Hidawi Publishig Corporatio Iteratioal Joural of Telemedicie ad Applicatios Volume 29, Article ID 98746, 13 pages doi:1.1155/29/98746 Research Article Delay Aalysis of GTS Bridgig betwee IEEE 82.15.4 ad
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers 26 February, COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 5
 Morga Kaufma Publishers 26 February, 28 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Iterface 5 th Editio Chapter 5 Set-Associative Cache Architecture Performace Summary Whe CPU performace icreases:
Morga Kaufma Publishers 26 February, 28 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Iterface 5 th Editio Chapter 5 Set-Associative Cache Architecture Performace Summary Whe CPU performace icreases:
ECE4050 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture 6: Searching
 ECE4050 Data Structures ad Algorithms Lecture 6: Searchig 1 Search Give: Distict keys k 1, k 2,, k ad collectio L of records of the form (k 1, I 1 ), (k 2, I 2 ),, (k, I ) where I j is the iformatio associated
ECE4050 Data Structures ad Algorithms Lecture 6: Searchig 1 Search Give: Distict keys k 1, k 2,, k ad collectio L of records of the form (k 1, I 1 ), (k 2, I 2 ),, (k, I ) where I j is the iformatio associated
The isoperimetric problem on the hypercube
 The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks and Queues Monday, February 12 / Tuesday, February 13
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 08 Stacks ad Queues Moday, February / Tuesday, February Learig Goals Durig this lab, you will: Review stacks ad queues. Lear amortized ruig time aalysis
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 08 Stacks ad Queues Moday, February / Tuesday, February Learig Goals Durig this lab, you will: Review stacks ad queues. Lear amortized ruig time aalysis
Reliable Transmission. Spring 2018 CS 438 Staff - University of Illinois 1
 Reliable Trasmissio Sprig 2018 CS 438 Staff - Uiversity of Illiois 1 Reliable Trasmissio Hello! My computer s ame is Alice. Alice Bob Hello! Alice. Sprig 2018 CS 438 Staff - Uiversity of Illiois 2 Reliable
Reliable Trasmissio Sprig 2018 CS 438 Staff - Uiversity of Illiois 1 Reliable Trasmissio Hello! My computer s ame is Alice. Alice Bob Hello! Alice. Sprig 2018 CS 438 Staff - Uiversity of Illiois 2 Reliable
Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs
 Spectral Graph Theory ad Applicatios WS 20/202 Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Su Our goal is to use the properties of the adjacecy/laplacia matrix of graphs to first uderstad
Spectral Graph Theory ad Applicatios WS 20/202 Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Su Our goal is to use the properties of the adjacecy/laplacia matrix of graphs to first uderstad
Bayesian approach to reliability modelling for a probability of failure on demand parameter
 Bayesia approach to reliability modellig for a probability of failure o demad parameter BÖRCSÖK J., SCHAEFER S. Departmet of Computer Architecture ad System Programmig Uiversity Kassel, Wilhelmshöher Allee
Bayesia approach to reliability modellig for a probability of failure o demad parameter BÖRCSÖK J., SCHAEFER S. Departmet of Computer Architecture ad System Programmig Uiversity Kassel, Wilhelmshöher Allee
Performance Analysis of Multiclass FIFO: Motivation, Difficulty and a Network Calculus Approach
 Performace Aalysis of Multiclass FIFO: Motivatio, Difficulty ad a Network alculus Approach Yumig Jiag Norwegia Uiversity of Sciece ad Techology (NTNU) 1 19 March 2014, 2d Workshop o Network alculus, Bamberg,
Performace Aalysis of Multiclass FIFO: Motivatio, Difficulty ad a Network alculus Approach Yumig Jiag Norwegia Uiversity of Sciece ad Techology (NTNU) 1 19 March 2014, 2d Workshop o Network alculus, Bamberg,
Price-based Congestion-Control in Wi-Fi Hot Spots
 Price-based Cogestio-Cotrol i Wi-Fi Hot Spots Roberto Battiti, Marco Coti, Erico Gregori, Mikalai Sabel To cite this versio: Roberto Battiti, Marco Coti, Erico Gregori, Mikalai Sabel. Price-based Cogestio-Cotrol
Price-based Cogestio-Cotrol i Wi-Fi Hot Spots Roberto Battiti, Marco Coti, Erico Gregori, Mikalai Sabel To cite this versio: Roberto Battiti, Marco Coti, Erico Gregori, Mikalai Sabel. Price-based Cogestio-Cotrol
Examples and Applications of Binary Search
 Toy Gog ITEE Uiersity of Queeslad I the secod lecture last week we studied the biary search algorithm that soles the problem of determiig if a particular alue appears i a sorted list of iteger or ot. We
Toy Gog ITEE Uiersity of Queeslad I the secod lecture last week we studied the biary search algorithm that soles the problem of determiig if a particular alue appears i a sorted list of iteger or ot. We
BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY
 CHAPTER 3 BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY 3.1 ISOMORPHIC PROPERTIES The ame Boolea Arithmetic was chose because it was discovered that literal Boolea Algebra could have a isomorphic umerical aspect.
CHAPTER 3 BOOLEAN MATHEMATICS: GENERAL THEORY 3.1 ISOMORPHIC PROPERTIES The ame Boolea Arithmetic was chose because it was discovered that literal Boolea Algebra could have a isomorphic umerical aspect.
IMP: Superposer Integrated Morphometrics Package Superposition Tool
 IMP: Superposer Itegrated Morphometrics Package Superpositio Tool Programmig by: David Lieber ( 03) Caisius College 200 Mai St. Buffalo, NY 4208 Cocept by: H. David Sheets, Dept. of Physics, Caisius College
IMP: Superposer Itegrated Morphometrics Package Superpositio Tool Programmig by: David Lieber ( 03) Caisius College 200 Mai St. Buffalo, NY 4208 Cocept by: H. David Sheets, Dept. of Physics, Caisius College
Algorithms for Disk Covering Problems with the Most Points
 Algorithms for Disk Coverig Problems with the Most Poits Bi Xiao Departmet of Computig Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog csbxiao@comp.polyu.edu.hk Qigfeg Zhuge, Yi He, Zili Shao, Edwi
Algorithms for Disk Coverig Problems with the Most Poits Bi Xiao Departmet of Computig Hog Kog Polytechic Uiversity Hug Hom, Kowloo, Hog Kog csbxiao@comp.polyu.edu.hk Qigfeg Zhuge, Yi He, Zili Shao, Edwi
Elementary Educational Computer
 Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
Chapter 5 Elemetary Educatioal Computer. Geeral structure of the Elemetary Educatioal Computer (EEC) The EEC coforms to the 5 uits structure defied by vo Neuma's model (.) All uits are preseted i a simplified
Pseudocode ( 1.1) Analysis of Algorithms. Primitive Operations. Pseudocode Details. Running Time ( 1.1) Estimating performance
 Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Pseudocode ( 1.1) High-level descriptio of a algorithm More structured
Basic allocator mechanisms The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory Management II: Dynamic Storage Allocation Mar 6, 2000.
 5-23 The course that gives CM its Zip Memory Maagemet II: Dyamic Storage Allocatio Mar 6, 2000 Topics Segregated lists Buddy system Garbage collectio Mark ad Sweep Copyig eferece coutig Basic allocator
5-23 The course that gives CM its Zip Memory Maagemet II: Dyamic Storage Allocatio Mar 6, 2000 Topics Segregated lists Buddy system Garbage collectio Mark ad Sweep Copyig eferece coutig Basic allocator
Improved Random Graph Isomorphism
 Improved Radom Graph Isomorphism Tomek Czajka Gopal Paduraga Abstract Caoical labelig of a graph cosists of assigig a uique label to each vertex such that the labels are ivariat uder isomorphism. Such
Improved Radom Graph Isomorphism Tomek Czajka Gopal Paduraga Abstract Caoical labelig of a graph cosists of assigig a uique label to each vertex such that the labels are ivariat uder isomorphism. Such
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic. Lecture 13 Control and Sequencing: Hardwired and Microprogrammed Control
 EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Desig with Programmable Logic Lecture 13 Cotrol ad Sequecig: Hardwired ad Microprogrammed Cotrol Refereces: Chapter s 4,5 from textbook Chapter 7 of M.M. Mao ad C.R. Kime,
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Desig with Programmable Logic Lecture 13 Cotrol ad Sequecig: Hardwired ad Microprogrammed Cotrol Refereces: Chapter s 4,5 from textbook Chapter 7 of M.M. Mao ad C.R. Kime,
Appendix D. Controller Implementation
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Iterface 5 th Editio Appedix D Cotroller Implemetatio Cotroller Implemetatios Combiatioal logic (sigle-cycle); Fiite state machie (multi-cycle, pipelied);
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Iterface 5 th Editio Appedix D Cotroller Implemetatio Cotroller Implemetatios Combiatioal logic (sigle-cycle); Fiite state machie (multi-cycle, pipelied);
Lecture Notes 6 Introduction to algorithm analysis CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming
 Lecture Notes 6 Itroductio to algorithm aalysis CSS 501 Data Structures ad Object-Orieted Programmig Readig for this lecture: Carrao, Chapter 10 To be covered i this lecture: Itroductio to algorithm aalysis
Lecture Notes 6 Itroductio to algorithm aalysis CSS 501 Data Structures ad Object-Orieted Programmig Readig for this lecture: Carrao, Chapter 10 To be covered i this lecture: Itroductio to algorithm aalysis
Optimal Mapped Mesh on the Circle
 Koferece ANSYS 009 Optimal Mapped Mesh o the Circle doc. Ig. Jaroslav Štigler, Ph.D. Bro Uiversity of Techology, aculty of Mechaical gieerig, ergy Istitut, Abstract: This paper brigs out some ideas ad
Koferece ANSYS 009 Optimal Mapped Mesh o the Circle doc. Ig. Jaroslav Štigler, Ph.D. Bro Uiversity of Techology, aculty of Mechaical gieerig, ergy Istitut, Abstract: This paper brigs out some ideas ad
Guaranteeing Hard Real Time End-to-End Communications Deadlines
 Guarateeig Hard Real Time Ed-to-Ed Commuicatios Deadlies K. W. Tidell A. Burs A. J. Welligs Real Time Systems Research Group Departmet of Computer Sciece Uiversity of York e-mail: ke@mister.york.ac.uk
Guarateeig Hard Real Time Ed-to-Ed Commuicatios Deadlies K. W. Tidell A. Burs A. J. Welligs Real Time Systems Research Group Departmet of Computer Sciece Uiversity of York e-mail: ke@mister.york.ac.uk
Evaluation scheme for Tracking in AMI
 A M I C o m m u i c a t i o A U G M E N T E D M U L T I - P A R T Y I N T E R A C T I O N http://www.amiproject.org/ Evaluatio scheme for Trackig i AMI S. Schreiber a D. Gatica-Perez b AMI WP4 Trackig:
A M I C o m m u i c a t i o A U G M E N T E D M U L T I - P A R T Y I N T E R A C T I O N http://www.amiproject.org/ Evaluatio scheme for Trackig i AMI S. Schreiber a D. Gatica-Perez b AMI WP4 Trackig:
On (K t e)-saturated Graphs
 Noame mauscript No. (will be iserted by the editor O (K t e-saturated Graphs Jessica Fuller Roald J. Gould the date of receipt ad acceptace should be iserted later Abstract Give a graph H, we say a graph
Noame mauscript No. (will be iserted by the editor O (K t e-saturated Graphs Jessica Fuller Roald J. Gould the date of receipt ad acceptace should be iserted later Abstract Give a graph H, we say a graph
A General Framework for Accurate Statistical Timing Analysis Considering Correlations
 A Geeral Framework for Accurate Statistical Timig Aalysis Cosiderig Correlatios 7.4 Vishal Khadelwal Departmet of ECE Uiversity of Marylad-College Park vishalk@glue.umd.edu Akur Srivastava Departmet of
A Geeral Framework for Accurate Statistical Timig Aalysis Cosiderig Correlatios 7.4 Vishal Khadelwal Departmet of ECE Uiversity of Marylad-College Park vishalk@glue.umd.edu Akur Srivastava Departmet of
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science
 Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 6 Defiig Fuctios Pytho Programmig, 2/e 1 Objectives To uderstad why programmers divide programs up ito sets of cooperatig fuctios. To be able to
Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 6 Defiig Fuctios Pytho Programmig, 2/e 1 Objectives To uderstad why programmers divide programs up ito sets of cooperatig fuctios. To be able to
Adaptive Graph Partitioning Wireless Protocol S. L. Ng 1, P. M. Geethakumari 1, S. Zhou 2, and W. J. Dewar 1 1
 Adaptive Graph Partitioig Wireless Protocol S. L. Ng 1, P. M. Geethakumari 1, S. Zhou 2, ad W. J. Dewar 1 1 School of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of New South Wales, Australia 2 Divisio of Radiophysics
Adaptive Graph Partitioig Wireless Protocol S. L. Ng 1, P. M. Geethakumari 1, S. Zhou 2, ad W. J. Dewar 1 1 School of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of New South Wales, Australia 2 Divisio of Radiophysics
Fundamentals of Media Processing. Shin'ichi Satoh Kazuya Kodama Hiroshi Mo Duy-Dinh Le
 Fudametals of Media Processig Shi'ichi Satoh Kazuya Kodama Hiroshi Mo Duy-Dih Le Today's topics Noparametric Methods Parze Widow k-nearest Neighbor Estimatio Clusterig Techiques k-meas Agglomerative Hierarchical
Fudametals of Media Processig Shi'ichi Satoh Kazuya Kodama Hiroshi Mo Duy-Dih Le Today's topics Noparametric Methods Parze Widow k-nearest Neighbor Estimatio Clusterig Techiques k-meas Agglomerative Hierarchical
Achieving Fairness in Wireless LANs by Enhanced IEEE DCF *
 Achievig Fairess i Wireless LANs by Ehaced IEEE 802.11 DCF * Nagesh S. P. Nadiraju, Hrishikesh Gossai, Dave Cavalcati, Kaushik R. Chowdhury, Dharma P. Agrawal Ceter for Distributed ad Mobile Computig,
Achievig Fairess i Wireless LANs by Ehaced IEEE 802.11 DCF * Nagesh S. P. Nadiraju, Hrishikesh Gossai, Dave Cavalcati, Kaushik R. Chowdhury, Dharma P. Agrawal Ceter for Distributed ad Mobile Computig,
Switching Hardware. Spring 2018 CS 438 Staff, University of Illinois 1
 Switchig Hardware Sprig 208 CS 438 Staff, Uiversity of Illiois Where are we? Uderstad Differet ways to move through a etwork (forwardig) Read sigs at each switch (datagram) Follow a kow path (virtual circuit)
Switchig Hardware Sprig 208 CS 438 Staff, Uiversity of Illiois Where are we? Uderstad Differet ways to move through a etwork (forwardig) Read sigs at each switch (datagram) Follow a kow path (virtual circuit)
CS 683: Advanced Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CS 683: Advaced Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Lecture 6, February 1, 2008 Lecturer: Joh Hopcroft Scribes: Shaomei Wu, Etha Feldma February 7, 2008 1 Threshold for k CNF Satisfiability I the previous lecture,
CS 683: Advaced Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Lecture 6, February 1, 2008 Lecturer: Joh Hopcroft Scribes: Shaomei Wu, Etha Feldma February 7, 2008 1 Threshold for k CNF Satisfiability I the previous lecture,
GTS Scheduling Scheme for Real-Time Communication in IEEE Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks
 Idia Joural of Sciece ad Techology, Vol 9(7), DOI:.7485/ijst/6/v9i7/87734, February 6 ISSN (Prit) : 974-6846 ISSN (Olie) : 974-5645 GTS Schedulig Scheme for Real-Time Commuicatio i IEEE8.5.4 Idustrial
Idia Joural of Sciece ad Techology, Vol 9(7), DOI:.7485/ijst/6/v9i7/87734, February 6 ISSN (Prit) : 974-6846 ISSN (Olie) : 974-5645 GTS Schedulig Scheme for Real-Time Commuicatio i IEEE8.5.4 Idustrial
Structuring Redundancy for Fault Tolerance. CSE 598D: Fault Tolerant Software
 Structurig Redudacy for Fault Tolerace CSE 598D: Fault Tolerat Software What do we wat to achieve? Versios Damage Assessmet Versio 1 Error Detectio Iputs Versio 2 Voter Outputs State Restoratio Cotiued
Structurig Redudacy for Fault Tolerace CSE 598D: Fault Tolerat Software What do we wat to achieve? Versios Damage Assessmet Versio 1 Error Detectio Iputs Versio 2 Voter Outputs State Restoratio Cotiued
Computer Science Foundation Exam. August 12, Computer Science. Section 1A. No Calculators! KEY. Solutions and Grading Criteria.
 Computer Sciece Foudatio Exam August, 005 Computer Sciece Sectio A No Calculators! Name: SSN: KEY Solutios ad Gradig Criteria Score: 50 I this sectio of the exam, there are four (4) problems. You must
Computer Sciece Foudatio Exam August, 005 Computer Sciece Sectio A No Calculators! Name: SSN: KEY Solutios ad Gradig Criteria Score: 50 I this sectio of the exam, there are four (4) problems. You must
Chapter 3 Classification of FFT Processor Algorithms
 Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
Chapter Classificatio of FFT Processor Algorithms The computatioal complexity of the Discrete Fourier trasform (DFT) is very high. It requires () 2 complex multiplicatios ad () complex additios [5]. As
Probability of collisions in Soft Input Decryption
 Issue 1, Volume 1, 007 1 Probability of collisios i Soft Iput Decryptio Nataša Živić, Christoph Rulad Abstract I this work, probability of collisio i Soft Iput Decryptio has bee aalyzed ad calculated.
Issue 1, Volume 1, 007 1 Probability of collisios i Soft Iput Decryptio Nataša Živić, Christoph Rulad Abstract I this work, probability of collisio i Soft Iput Decryptio has bee aalyzed ad calculated.
Counting the Number of Minimum Roman Dominating Functions of a Graph
 Coutig the Number of Miimum Roma Domiatig Fuctios of a Graph SHI ZHENG ad KOH KHEE MENG, Natioal Uiversity of Sigapore We provide two algorithms coutig the umber of miimum Roma domiatig fuctios of a graph
Coutig the Number of Miimum Roma Domiatig Fuctios of a Graph SHI ZHENG ad KOH KHEE MENG, Natioal Uiversity of Sigapore We provide two algorithms coutig the umber of miimum Roma domiatig fuctios of a graph
Data Structures and Algorithms. Analysis of Algorithms
 Data Structures ad Algorithms Aalysis of Algorithms Outlie Ruig time Pseudo-code Big-oh otatio Big-theta otatio Big-omega otatio Asymptotic algorithm aalysis Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output
Data Structures ad Algorithms Aalysis of Algorithms Outlie Ruig time Pseudo-code Big-oh otatio Big-theta otatio Big-omega otatio Asymptotic algorithm aalysis Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output
One advantage that SONAR has over any other music-sequencing product I ve worked
 *gajedra* D:/Thomso_Learig_Projects/Garrigus_163132/z_productio/z_3B2_3D_files/Garrigus_163132_ch17.3d, 14/11/08/16:26:39, 16:26, page: 647 17 CAL 101 Oe advatage that SONAR has over ay other music-sequecig
*gajedra* D:/Thomso_Learig_Projects/Garrigus_163132/z_productio/z_3B2_3D_files/Garrigus_163132_ch17.3d, 14/11/08/16:26:39, 16:26, page: 647 17 CAL 101 Oe advatage that SONAR has over ay other music-sequecig
Exact Minimum Lower Bound Algorithm for Traveling Salesman Problem
 Exact Miimum Lower Boud Algorithm for Travelig Salesma Problem Mohamed Eleiche GeoTiba Systems mohamed.eleiche@gmail.com Abstract The miimum-travel-cost algorithm is a dyamic programmig algorithm to compute
Exact Miimum Lower Boud Algorithm for Travelig Salesma Problem Mohamed Eleiche GeoTiba Systems mohamed.eleiche@gmail.com Abstract The miimum-travel-cost algorithm is a dyamic programmig algorithm to compute
Convergence results for conditional expectations
 Beroulli 11(4), 2005, 737 745 Covergece results for coditioal expectatios IRENE CRIMALDI 1 ad LUCA PRATELLI 2 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Bologa, Piazza di Porta Sa Doato 5, 40126 Bologa,
Beroulli 11(4), 2005, 737 745 Covergece results for coditioal expectatios IRENE CRIMALDI 1 ad LUCA PRATELLI 2 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Bologa, Piazza di Porta Sa Doato 5, 40126 Bologa,
Protected points in ordered trees
 Applied Mathematics Letters 008 56 50 www.elsevier.com/locate/aml Protected poits i ordered trees Gi-Sag Cheo a, Louis W. Shapiro b, a Departmet of Mathematics, Sugkyukwa Uiversity, Suwo 440-746, Republic
Applied Mathematics Letters 008 56 50 www.elsevier.com/locate/aml Protected poits i ordered trees Gi-Sag Cheo a, Louis W. Shapiro b, a Departmet of Mathematics, Sugkyukwa Uiversity, Suwo 440-746, Republic
Lecture 1: Introduction and Strassen s Algorithm
 5-750: Graduate Algorithms Jauary 7, 08 Lecture : Itroductio ad Strasse s Algorithm Lecturer: Gary Miller Scribe: Robert Parker Itroductio Machie models I this class, we will primarily use the Radom Access
5-750: Graduate Algorithms Jauary 7, 08 Lecture : Itroductio ad Strasse s Algorithm Lecturer: Gary Miller Scribe: Robert Parker Itroductio Machie models I this class, we will primarily use the Radom Access
Sorting in Linear Time. Data Structures and Algorithms Andrei Bulatov
 Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
The Magma Database file formats
 The Magma Database file formats Adrew Gaylard, Bret Pikey, ad Mart-Mari Breedt Johaesburg, South Africa 15th May 2006 1 Summary Magma is a ope-source object database created by Chris Muller, of Kasas City,
The Magma Database file formats Adrew Gaylard, Bret Pikey, ad Mart-Mari Breedt Johaesburg, South Africa 15th May 2006 1 Summary Magma is a ope-source object database created by Chris Muller, of Kasas City,
MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fitting)
 MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fittig) I this chapter, we will eamie some methods of aalysis ad data processig; data obtaied as a result of a give
MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENTAL DATA PROCESSING (Or Methods of Curve Fittig) I this chapter, we will eamie some methods of aalysis ad data processig; data obtaied as a result of a give
The Adjacency Matrix and The nth Eigenvalue
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 3 The Adjacecy Matrix ad The th Eigevalue Daiel A. Spielma September 5, 2012 3.1 About these otes These otes are ot ecessarily a accurate represetatio of what happeed i class.
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 3 The Adjacecy Matrix ad The th Eigevalue Daiel A. Spielma September 5, 2012 3.1 About these otes These otes are ot ecessarily a accurate represetatio of what happeed i class.
FREQUENCY ESTIMATION OF INTERNET PACKET STREAMS WITH LIMITED SPACE: UPPER AND LOWER BOUNDS
 FREQUENCY ESTIMATION OF INTERNET PACKET STREAMS WITH LIMITED SPACE: UPPER AND LOWER BOUNDS Prosejit Bose Evagelos Kraakis Pat Mori Yihui Tag School of Computer Sciece, Carleto Uiversity {jit,kraakis,mori,y
FREQUENCY ESTIMATION OF INTERNET PACKET STREAMS WITH LIMITED SPACE: UPPER AND LOWER BOUNDS Prosejit Bose Evagelos Kraakis Pat Mori Yihui Tag School of Computer Sciece, Carleto Uiversity {jit,kraakis,mori,y
Lecture 18. Optimization in n dimensions
 Lecture 8 Optimizatio i dimesios Itroductio We ow cosider the problem of miimizig a sigle scalar fuctio of variables, f x, where x=[ x, x,, x ]T. The D case ca be visualized as fidig the lowest poit of
Lecture 8 Optimizatio i dimesios Itroductio We ow cosider the problem of miimizig a sigle scalar fuctio of variables, f x, where x=[ x, x,, x ]T. The D case ca be visualized as fidig the lowest poit of
performance to the performance they can experience when they use the services from a xed location.
 I the Proceedigs of The First Aual Iteratioal Coferece o Mobile Computig ad Networkig (MobiCom 9) November -, 99, Berkeley, Califoria USA Performace Compariso of Mobile Support Strategies Rieko Kadobayashi
I the Proceedigs of The First Aual Iteratioal Coferece o Mobile Computig ad Networkig (MobiCom 9) November -, 99, Berkeley, Califoria USA Performace Compariso of Mobile Support Strategies Rieko Kadobayashi
Redundancy Allocation for Series Parallel Systems with Multiple Constraints and Sensitivity Analysis
 IOSR Joural of Egieerig Redudacy Allocatio for Series Parallel Systems with Multiple Costraits ad Sesitivity Aalysis S. V. Suresh Babu, D.Maheswar 2, G. Ragaath 3 Y.Viaya Kumar d G.Sakaraiah e (Mechaical
IOSR Joural of Egieerig Redudacy Allocatio for Series Parallel Systems with Multiple Costraits ad Sesitivity Aalysis S. V. Suresh Babu, D.Maheswar 2, G. Ragaath 3 Y.Viaya Kumar d G.Sakaraiah e (Mechaical
Lecture 6. Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribes: Chen Ziv, Eliav Buchnik, Ophir Arie, Jonathan Gradstein
 068.670 Subliear Time Algorithms November, 0 Lecture 6 Lecturer: Roitt Rubifeld Scribes: Che Ziv, Eliav Buchik, Ophir Arie, Joatha Gradstei Lesso overview. Usig the oracle reductio framework for approximatig
068.670 Subliear Time Algorithms November, 0 Lecture 6 Lecturer: Roitt Rubifeld Scribes: Che Ziv, Eliav Buchik, Ophir Arie, Joatha Gradstei Lesso overview. Usig the oracle reductio framework for approximatig
9.1. Sequences and Series. Sequences. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. Definition of Sequence
 _9.qxd // : AM Page Chapter 9 Sequeces, Series, ad Probability 9. Sequeces ad Series What you should lear Use sequece otatio to write the terms of sequeces. Use factorial otatio. Use summatio otatio to
_9.qxd // : AM Page Chapter 9 Sequeces, Series, ad Probability 9. Sequeces ad Series What you should lear Use sequece otatio to write the terms of sequeces. Use factorial otatio. Use summatio otatio to
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks, Queues, and Heaps Monday, February 18 / Tuesday, February 19
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
n Learn how resiliency strategies reduce risk n Discover automation strategies to reduce risk
 Chapter Objectives Lear how resiliecy strategies reduce risk Discover automatio strategies to reduce risk Chapter #16: Architecture ad Desig Resiliecy ad Automatio Strategies 2 Automatio/Scriptig Resiliet
Chapter Objectives Lear how resiliecy strategies reduce risk Discover automatio strategies to reduce risk Chapter #16: Architecture ad Desig Resiliecy ad Automatio Strategies 2 Automatio/Scriptig Resiliet
EE123 Digital Signal Processing
 Last Time EE Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 7 Block Covolutio, Overlap ad Add, FFT Discrete Fourier Trasform Properties of the Liear covolutio through circular Today Liear covolutio with Overlap ad add
Last Time EE Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 7 Block Covolutio, Overlap ad Add, FFT Discrete Fourier Trasform Properties of the Liear covolutio through circular Today Liear covolutio with Overlap ad add
Random Graphs and Complex Networks T
 Radom Graphs ad Complex Networks T-79.7003 Charalampos E. Tsourakakis Aalto Uiversity Lecture 3 7 September 013 Aoucemet Homework 1 is out, due i two weeks from ow. Exercises: Probabilistic iequalities
Radom Graphs ad Complex Networks T-79.7003 Charalampos E. Tsourakakis Aalto Uiversity Lecture 3 7 September 013 Aoucemet Homework 1 is out, due i two weeks from ow. Exercises: Probabilistic iequalities
1&1 Next Level Hosting
 1&1 Next Level Hostig Performace Level: Performace that grows with your requiremets Copyright 1&1 Iteret SE 2017 1ad1.com 2 1&1 NEXT LEVEL HOSTING 3 Fast page loadig ad short respose times play importat
1&1 Next Level Hostig Performace Level: Performace that grows with your requiremets Copyright 1&1 Iteret SE 2017 1ad1.com 2 1&1 NEXT LEVEL HOSTING 3 Fast page loadig ad short respose times play importat
condition w i B i S maximum u i
 ecture 10 Dyamic Programmig 10.1 Kapsack Problem November 1, 2004 ecturer: Kamal Jai Notes: Tobias Holgers We are give a set of items U = {a 1, a 2,..., a }. Each item has a weight w i Z + ad a utility
ecture 10 Dyamic Programmig 10.1 Kapsack Problem November 1, 2004 ecturer: Kamal Jai Notes: Tobias Holgers We are give a set of items U = {a 1, a 2,..., a }. Each item has a weight w i Z + ad a utility
Lower Bounds for Sorting
 Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
Improving Template Based Spike Detection
 Improvig Template Based Spike Detectio Kirk Smith, Member - IEEE Portlad State Uiversity petra@ee.pdx.edu Abstract Template matchig algorithms like SSE, Covolutio ad Maximum Likelihood are well kow for
Improvig Template Based Spike Detectio Kirk Smith, Member - IEEE Portlad State Uiversity petra@ee.pdx.edu Abstract Template matchig algorithms like SSE, Covolutio ad Maximum Likelihood are well kow for
Big-O Analysis. Asymptotics
 Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
Big-O Aalysis 1 Defiitio: Suppose that f() ad g() are oegative fuctios of. The we say that f() is O(g()) provided that there are costats C > 0 ad N > 0 such that for all > N, f() Cg(). Big-O expresses
The Penta-S: A Scalable Crossbar Network for Distributed Shared Memory Multiprocessor Systems
 The Peta-S: A Scalable Crossbar Network for Distributed Shared Memory Multiprocessor Systems Abdulkarim Ayyad Departmet of Computer Egieerig, Al-Quds Uiversity, Jerusalem, P.O. Box 20002 Tel: 02-2797024,
The Peta-S: A Scalable Crossbar Network for Distributed Shared Memory Multiprocessor Systems Abdulkarim Ayyad Departmet of Computer Egieerig, Al-Quds Uiversity, Jerusalem, P.O. Box 20002 Tel: 02-2797024,
UNIVERSITY OF MORATUWA
 UNIVERSITY OF MORATUWA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING B.Sc. Egieerig 2014 Itake Semester 2 Examiatio CS2052 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Time allowed: 2 Hours Jauary 2016
UNIVERSITY OF MORATUWA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING B.Sc. Egieerig 2014 Itake Semester 2 Examiatio CS2052 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Time allowed: 2 Hours Jauary 2016
15-859E: Advanced Algorithms CMU, Spring 2015 Lecture #2: Randomized MST and MST Verification January 14, 2015
 15-859E: Advaced Algorithms CMU, Sprig 2015 Lecture #2: Radomized MST ad MST Verificatio Jauary 14, 2015 Lecturer: Aupam Gupta Scribe: Yu Zhao 1 Prelimiaries I this lecture we are talkig about two cotets:
15-859E: Advaced Algorithms CMU, Sprig 2015 Lecture #2: Radomized MST ad MST Verificatio Jauary 14, 2015 Lecturer: Aupam Gupta Scribe: Yu Zhao 1 Prelimiaries I this lecture we are talkig about two cotets:
L6: FSMs and Synchronization
 L6: FSMs ad Sychroizatio Ackowledgemets: Materials i this lecture are courtesy of the followig sources ad are used with permissio. Rex Mi J. Rabaey, A. Chadrakasa, B. Nikolic. igital Itegrated Circuits:
L6: FSMs ad Sychroizatio Ackowledgemets: Materials i this lecture are courtesy of the followig sources ad are used with permissio. Rex Mi J. Rabaey, A. Chadrakasa, B. Nikolic. igital Itegrated Circuits:
The Extended Weibull Geometric Family
 The Exteded Weibull Geometric Family Giovaa Oliveira Silva 1 Gauss M. Cordeiro 2 Edwi M. M. Ortega 3 1 Itroductio The literature o Weibull models is vast, disjoited, ad scattered across may differet jourals.
The Exteded Weibull Geometric Family Giovaa Oliveira Silva 1 Gauss M. Cordeiro 2 Edwi M. M. Ortega 3 1 Itroductio The literature o Weibull models is vast, disjoited, ad scattered across may differet jourals.
Random Network Coding in Wireless Sensor Networks: Energy Efficiency via Cross-Layer Approach
 Radom Network Codig i Wireless Sesor Networks: Eergy Efficiecy via Cross-Layer Approach Daiel Platz, Dereje H. Woldegebreal, ad Holger Karl Uiversity of Paderbor, Paderbor, Germay {platz, dereje.hmr, holger.karl}@upb.de
Radom Network Codig i Wireless Sesor Networks: Eergy Efficiecy via Cross-Layer Approach Daiel Platz, Dereje H. Woldegebreal, ad Holger Karl Uiversity of Paderbor, Paderbor, Germay {platz, dereje.hmr, holger.karl}@upb.de
Chapter 1. Introduction to Computers and C++ Programming. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 1 Itroductio to Computers ad C++ Programmig Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 1.1 Computer Systems 1.2 Programmig ad Problem Solvig 1.3 Itroductio to C++ 1.4 Testig
Chapter 1 Itroductio to Computers ad C++ Programmig Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 1.1 Computer Systems 1.2 Programmig ad Problem Solvig 1.3 Itroductio to C++ 1.4 Testig
A SOFTWARE MODEL FOR THE MULTILAYER PERCEPTRON
 A SOFTWARE MODEL FOR THE MULTILAYER PERCEPTRON Roberto Lopez ad Eugeio Oñate Iteratioal Ceter for Numerical Methods i Egieerig (CIMNE) Edificio C1, Gra Capitá s/, 08034 Barceloa, Spai ABSTRACT I this work
A SOFTWARE MODEL FOR THE MULTILAYER PERCEPTRON Roberto Lopez ad Eugeio Oñate Iteratioal Ceter for Numerical Methods i Egieerig (CIMNE) Edificio C1, Gra Capitá s/, 08034 Barceloa, Spai ABSTRACT I this work
Project 2.5 Improved Euler Implementation
 Project 2.5 Improved Euler Implemetatio Figure 2.5.10 i the text lists TI-85 ad BASIC programs implemetig the improved Euler method to approximate the solutio of the iitial value problem dy dx = x+ y,
Project 2.5 Improved Euler Implemetatio Figure 2.5.10 i the text lists TI-85 ad BASIC programs implemetig the improved Euler method to approximate the solutio of the iitial value problem dy dx = x+ y,
CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 11 Basic Computer Organization and Design
 College of Computer ad Iformatio Scieces Departmet of Computer Sciece CSC 220: Computer Orgaizatio Uit 11 Basic Computer Orgaizatio ad Desig 1 For the rest of the semester, we ll focus o computer architecture:
College of Computer ad Iformatio Scieces Departmet of Computer Sciece CSC 220: Computer Orgaizatio Uit 11 Basic Computer Orgaizatio ad Desig 1 For the rest of the semester, we ll focus o computer architecture:
1.2 Binomial Coefficients and Subsets
 1.2. BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS AND SUBSETS 13 1.2 Biomial Coefficiets ad Subsets 1.2-1 The loop below is part of a program to determie the umber of triagles formed by poits i the plae. for i =1 to for j =
1.2. BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS AND SUBSETS 13 1.2 Biomial Coefficiets ad Subsets 1.2-1 The loop below is part of a program to determie the umber of triagles formed by poits i the plae. for i =1 to for j =
Bezier curves. Figure 2 shows cubic Bezier curves for various control points. In a Bezier curve, only
 Edited: Yeh-Liag Hsu (998--; recommeded: Yeh-Liag Hsu (--9; last updated: Yeh-Liag Hsu (9--7. Note: This is the course material for ME55 Geometric modelig ad computer graphics, Yua Ze Uiversity. art of
Edited: Yeh-Liag Hsu (998--; recommeded: Yeh-Liag Hsu (--9; last updated: Yeh-Liag Hsu (9--7. Note: This is the course material for ME55 Geometric modelig ad computer graphics, Yua Ze Uiversity. art of
Creating Exact Bezier Representations of CST Shapes. David D. Marshall. California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, CA , USA
 Creatig Exact Bezier Represetatios of CST Shapes David D. Marshall Califoria Polytechic State Uiversity, Sa Luis Obispo, CA 93407-035, USA The paper presets a method of expressig CST shapes pioeered by
Creatig Exact Bezier Represetatios of CST Shapes David D. Marshall Califoria Polytechic State Uiversity, Sa Luis Obispo, CA 93407-035, USA The paper presets a method of expressig CST shapes pioeered by
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science
 Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 1 Computers ad Programs 1 Objectives To uderstad the respective roles of hardware ad software i a computig system. To lear what computer scietists
Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 1 Computers ad Programs 1 Objectives To uderstad the respective roles of hardware ad software i a computig system. To lear what computer scietists
