Scenarios and Task Descriptions, Ideation, and Prototyping. Sept 30, 2016
|
|
|
- Emily Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scenarios and Task Descriptions, Ideation, and Prototyping Sept 30, 2016
2 Announcements Milestone I is up Due October 17 (changed from 14) Midterm October 19 (not changed)
3 Questions?
4 Randy Pausch s Tips for Working in a Group Meet people properly. Find things you have in common. Make meeting conditions good. Let everyone talk. Check your egos at the door. Praise each other. Put it in writing. Remember that politics is when you have more than 2 people with that in mind, always CC (carbon copy) any piece of within the group, or to me, to all members of the group. This rule should never be violated; don t try to guess what your group mates might or might not want to hear about. Be open and honest. Avoid conflict at all costs. Phrase alternatives as questions.
5 Overview of Today s Lecture Scenarios & HTA Ideation why some tips Prototyping why what to prototype methods
6 Task Descriptions Task descriptions are structured and organized descriptions of existing or envisioned tasks of a system There are different flavours and they include: Scenarios an informal narrative story, simple, natural, personal, not generalizable Use Cases assume interaction with a system assume detailed understanding of the interaction similar to user stories concept from Agile development Task Decompositions concrete, simple representations of a task to be done. much more explicit and focused than scenarios The focus is on what people want to do, not the technology
7 HTA Plans specify alternatives for how a task might unfold Cleaning a house decomposed into subtasks 0. To vacuum the house 1. get the vacuum cleaner out 2. put on the appropriate attachment 3. vacuum the rooms 3.1 vacuum the hall 3.2 vacuum the living rooms 3.3 vacuum the bedrooms 4. empty the dust bag 5. put the vacuum cleaner and attachments away Plan 0: do in that order when the dust bag gets full do 4 Plan 3: do any of 3.1, 3.2 or 3.3 in any order depending on which rooms need cleaning
8 Task Analysis Stopping Criteria Take a task and break it into subtasks 0. In an emergency 1. read the alarms 2. work out the appropriate corrective action 3. perform corrective action Could go indefinitely, so need to apply a stopping rule When to stop depends on the aim of the system and the importance of the subtask E.g., If aim is to install computer monitoring expand 1 and 3; If aim is to produce on-line manuals expand 2 A general rule is to stop dividing into subtasks when: 1. [Probability (P) of mistake in task] x [Cost (C) of the mistake] < threshold; Or 2. When reaches the level of basic operations (e.g., mouse movement)
9 Scenario-to-Task Scenario 1: George, a regular library visitor approaches Mary at the reference desk and asks if they have the Frankenstein comedy DVD. She asks if he means "Young Frankenstein" by Mel Brooks, and he say yes. She then directs him to the shelf where the DVD is expected to be. George retrieves his library card and brings it to the front desk. Mary checks out the DVD, but reminds George that he has $3.75 in unpaid fees. George says that he will pay the fees at a later date. Mary asks whether George would like a or printed receipt. George says that is fine and leaves with the DVD. Discussion: This task description contains many typical activities, which deal with vague requests about titles, the location of items in the library, as well as reminders about late fees. Most of these tasks are frequently done, and important.
10 Scenario-to-Task Locating a DVD in a library 0. Locate a DVD: 1. Go to the front desk 2. Find the location of DVD on the shelves 2.1 Access the search screen 2.2 Enter the search criteria 2.3 Identify the DVD requested 2.4 Record the location of the movie 3. Go to correct shelf to get the DVD 4. Take the DVD to the front desk Plan 0: do 3-4. If DVD isn t on stacks do Plan 2: do
11 Scenario-to-Task Signing out a DVD 0. Sign out a DVD 1. Enter library care information 2. Decide to sign out video 2.1 Check member s overdue fee status 2.2 Inform member of fees 2.3 Accept to give out DVD 2.4 Decline signing out DVD 3. Get video information 4. Sign out video 5. Give receipt 5.1 Give paper receipt 5.2 receipt Plan 0: do If member not on file do 1-2-[Add member]-3-4 Plan 2: do If member has a large number of late videos Plan 5: If member wants paper do 5.1, otherwise do 5.2.
12 Hierarchical Task Graph (HTG) for Locate DVD Locate DVD 0 Plan 0: do 3-4. If DVD isn t on shelves do Go to front desk 1 Find DVD on shelfs 2 Go to stack to get DVD 3 Take DVD to front desk 4 Plan 2: do Access search screen 2.1 Enter search criteria 2.2 Identify requested DVD 2.3 Record location 2.4
13 Summary: Task Descriptions Scenarios and task descriptions are a great way to solidify and formalize your understanding of your users needs and test cases You can use tasks and scenarios as tests against your ideas, prototypes, and systems
14 Questions?
15 User Centered Design Process Generate lots of ideas Grasp issues and potential solutions
16 Ideation How do we come up with great ideas? How do we come up with lots of ideas? How do we organize ideas? Brief coverage in 3020, more in 4020
17 Inspiring creativity? How can we inspire creativity? Being aware of what works for you is VERY powerful knowledge
18 Creativity. IDEO methods and friends Immerse yourself in the world you are designing for (gathering inspiration) Collect examples from existing systems Collect things that irritate you Collect things that seem really good Sample things that inspire you Brainstorm in groups Chat with others (bounce ideas off of people)
19 Learn from existing systems this isn t plagiarism (but watch those patents ) What s so good about this? (Why is it good?) What is the general problem that this solves? Where else could I use it? Practice articulating what makes something good.
20 Generate Ideas Constantly From Carloyn Snyder s Book: Paper Prototyping (2003) Morgan Kaufmann, p350
21 Sketching Enables you to think through ideas and variations, and convey design ideas to others early in the design phase.
22 What to do with your collection Keep a sketchbook Wallpaper it
23 Group brainstorming keep the results of user research handy during the process (e.g. scenarios, lists of design requirements, etc.) be visual defer judgment encourage wild ideas build on others go for quantity one conversation at a time stay focused on topic
24 Summary: Ideation Find things that x you where x = { inspire, interest, irritate, amuse } Find things that you y where y = {can improve, relate to} Break the rules, and think freely Sketching is a great way to explore and ideate
25 Questions?
26 User Centered Design Process Produce something tangible Identify challenges Uncover subtleties
27 What is a prototype? In other design fields a prototype is a small-scale model: a miniature car a miniature building or town
28 What is a prototype? In interaction design a prototype can be (among other things): a series of screen sketches a storyboard, i.e. a cartoon-like series of scenes a Powerpoint slide show, e.g., simulation a video simulating the use of a system a lump of wood (e.g. PalmPilot) a cardboard mock-up a piece of software with limited functionality written in the target language or in another language
29 From Buxton s Experience Design vs. Interaction Design
30 OrangeX Manual Juicer
31
32
33
34
35 OrangeX Manual Juicer
36 Why Prototype? Prototypes are useful for numerous purposes including: Promoting reflection (Schon 1983) Clarifying requirements Exploring alternatives Initial user testing
37 What to Prototype Screen layouts and information display: placement of different widgets, types of widgets, etc e.g. should edit fields come after/before control buttons Work flow, task design: the sequence of steps required to achieve the task e.g. flow from one screen to another, changes on the screen Difficult, controversial, critical areas: provide alternative solutions to be assessed e.g. business critical reports with specific alignment of fields Technical issues: E.g., will the graphics rendered be fast enough?
38 Low-Fidelity Prototyping Fidelity refers to level of detail High fidelity implies finished or detailed Low fidelity implies incomplete or lacking some detail Why low-fidelity? Cheaper, faster to create Can explore multiple alternative design without getting stuck on technical details Users often more inclined to comment on designs that appear less finished
39 Phases of Prototyping Early design Brainstorm different representations Choose a representation Sketch out interface style Task centered walkthrough and redesign Fine tune interface, screen design Heuristic evaluation and redesign Usability testing and redesign Low fidelity paper prototypes Medium-fidelity prototypes High-fidelity prototypes / restricted systems Limited field testing Alpha/Beta tests Working systems Late design
40 Low-Fidelity Prototyping How: Paper-based sketches Physical mock-ups using paper, cardboard
41 Sketching Sketching is important to low-fidelity prototyping Benefits: Convenient Doesn t look finished Can abstract away details Don t be inhibited about drawing ability. Practice using and building your repertoire of simple symbols Can also trace from images If you have a tablet, you can store and re-use a set of frequently used elements
42 Paper Prototyping Two common types: Index cards Storyboards
43 Index Cards Index cards (3 X 5 inches) Each card represents one screen Often used in website development As user interacts with the screen, the designer switches the card Any missing/unclear functionality can be fixed on the spot
44 Paper + Video Xq3XHSc effective-video-examples-of-paperprototyping/
45 Storyboards comic book approach, a series of keyframes as sketches illustrates a sequence originally from film; used to get the idea of a scene snapshots of the interface at particular key points in the interaction users can evaluate quickly the direction the interface is heading use with your personas and tasks
46 Storyboards
47 Storyboards Poor example This is the main screen. The user can move songs back and forth from the Song List to the Play List. The time left on the tape is shown at the bottom.
48 Storyboards -- Better example Even though the "poor example" above may superficially appear more polished because of the realistic screen shot, the example below is better because it shows the detailed steps needed to manipulate the interface. File Song Options Song Pool 3:28 Little Green 3:51 California 4:05 River 3:34 All I Want 4:23 A Case of You 2:52 This Flight Tonight Time Used: 0:00 Remaining: 45:00 Play List (1) This is the main screen after a file has been opened. The song title and duration of each song in the file appears in the Song Pool. The Time Used is initially zero, and the Remaining time shows the available time on the tape.
49 Storyboards -- Better example File Song Options Song Pool 3:28 Little Green 3:51 California 4:05 River 3:34 All I Want 4:23 A Case of You 2:52 This Flight Tonight Play List Time Used: 0:00 Remaining: 45:00 (2) The user wants to add a song to the Play List so she has clicked on the song "River" to select it.
50 Storyboards -- Better example File Song Options Song Pool 3:28 Little Green 3:51 California 3:34 All I Want 4:23 A Case of You 2:52 This Flight Tonight 4:05 River Play List Time Used: 4:05 Remaining: 40:55 (3) The user has clicked on the ">>" button to move the selected song to the Play List. The time used and time remaining are automatically computed and updated beneath the playlist
51 Storyboards -- Better example File Song Options Song Pool 3:28 Little Green 3:34 All I Want 4:23 A Case of You 2:52 This Flight Tonight 4:05 River Play List 3:51 California Time Used: 7:56 Remaining: 32:04 (4) In a similar fashion the user has moved the song "California" to the Play List.
52 Storyboards -- Better example File Song Options Song Pool 3:28 Little Green 3:34 All I Want 4:23 A Case of You 2:52 This Flight Tonight 4:05 River Play List 3:51 California Time Used: 7:56 Remaining: 32:04 (5) Now the user has changed her mind and doesn't want "River" in the Play List. She selects "River" by clicking on it.
53 Storyboards -- Better example File Song Options Song Pool 3:28 Little Green 3:34 All I Want 4:23 A Case of You 2:52 This Flight Tonight 4:05 River Play List 3:51 California Time Used: 3:51 Remaining: 41:09 (6) The user has clicked on the "<<" button to return the selected song to the Song Pool. The time used and time remaining are automatically computed and updated beneath the playlist.
54 Tangible Prototypes
55 Low-Fidelity Prototyping Some issues Sometimes difficult to fake/simulate behaviour Client (i.e., the person paying you) might be confused by the lack of programming Can give a mistaken impression of how hard stuff is User/client feedback might involve requests for things that are extremely difficult to implement (e.g., speech recognition)
User Centered Design Process. Prototyping II. What is a prototype? Prototyping phases Oct 11, 2017
 User Centered Design Process Prototyping II Oct 11, 2017 Produce something tangible Identify challenges Uncover subtleties 2 What is a prototype? A prototype is defined less by form, and more by its function:
User Centered Design Process Prototyping II Oct 11, 2017 Produce something tangible Identify challenges Uncover subtleties 2 What is a prototype? A prototype is defined less by form, and more by its function:
Prototyping. Oct 3, 2016
 Prototyping Oct 3, 2016 Announcements A1 marks available A2 due Wednesday Questions? What is a prototype? In interaction design a prototype can be (among other things): a series of screen sketches a storyboard,
Prototyping Oct 3, 2016 Announcements A1 marks available A2 due Wednesday Questions? What is a prototype? In interaction design a prototype can be (among other things): a series of screen sketches a storyboard,
Design, prototyping and construction
 Chapter 11 Design, prototyping and construction 1 Overview Prototyping and construction Conceptual design Physical design Generating prototypes Support for design 2 Prototyping and construction What is
Chapter 11 Design, prototyping and construction 1 Overview Prototyping and construction Conceptual design Physical design Generating prototypes Support for design 2 Prototyping and construction What is
The process of interaction design and Prototyping
 Chapter 6 edited The process of interaction design and Prototyping 1 Overview What is involved in Interaction Design? Importance of involving users Degrees of user involvement What is a user-centered approach?
Chapter 6 edited The process of interaction design and Prototyping 1 Overview What is involved in Interaction Design? Importance of involving users Degrees of user involvement What is a user-centered approach?
Chapter 11 DESIGN, PROTOTYPING and CONSTRUCTION
 Chapter 11 DESIGN, PROTOTYPING and CONSTRUCTION Overview Prototyping Conceptual design Concrete design Using scenarios Generating prototypes Construction 2 Prototyping What is a prototype? Why prototype?
Chapter 11 DESIGN, PROTOTYPING and CONSTRUCTION Overview Prototyping Conceptual design Concrete design Using scenarios Generating prototypes Construction 2 Prototyping What is a prototype? Why prototype?
Human-Computer Interaction. CA357 Lecture 7 More on Prototyping
 Human-Computer Interaction CA357 Lecture 7 More on Prototyping Overview By the end of the session, you should be aware of: Design Importance of prototyping Low fidelity vs High fidelity prototyping Why
Human-Computer Interaction CA357 Lecture 7 More on Prototyping Overview By the end of the session, you should be aware of: Design Importance of prototyping Low fidelity vs High fidelity prototyping Why
Projects. Quiz #2. Projects. Projects. Reading Assignment #3. Projects. What is the purpose of Marissa s Gravity Project?
 Quiz #2 What is the purpose of Marissa s Gravity Project? Write one tradeoff in usability engineering. Projects Project Phase 1 reports due on Oct. 25 Phase 1: team formation & topic choice, understanding
Quiz #2 What is the purpose of Marissa s Gravity Project? Write one tradeoff in usability engineering. Projects Project Phase 1 reports due on Oct. 25 Phase 1: team formation & topic choice, understanding
CS3205: Task Analysis and Techniques
 CS3205: Task Analysis and Techniques CS3205: Task Analysis and Techniques Readings (same as before): 1) ID-Book Chapter Establishing Requirements, Ch. 10 (Ch. 9 in course ebook) 2) Chapter 2 from Task-Centered
CS3205: Task Analysis and Techniques CS3205: Task Analysis and Techniques Readings (same as before): 1) ID-Book Chapter Establishing Requirements, Ch. 10 (Ch. 9 in course ebook) 2) Chapter 2 from Task-Centered
Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping
 Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping Course announcements Deadlines Individual assignment (extended) deadline: today (June 7) 8:00 am by email User testing summary for paper prototype testing- Thursday June
Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping Course announcements Deadlines Individual assignment (extended) deadline: today (June 7) 8:00 am by email User testing summary for paper prototype testing- Thursday June
User Centered Design And Prototyping
 User Centered Design And Prototyping Why User Centered Design is important Approaches to User Centered Design Rapid prototype techniques The Design Of Well Crafted Tools The All Too Common Approach In
User Centered Design And Prototyping Why User Centered Design is important Approaches to User Centered Design Rapid prototype techniques The Design Of Well Crafted Tools The All Too Common Approach In
UE&UX Lecture 6: Handbook Chapters 10, 11, and 12. Egon L. van den Broek
 UE&UX Lecture 6: Handbook Chapters 10, 11, and 12 Egon L. van den Broek Chapter 10 ESTABLISHING REQUIREMENTS Notes (1) How to read the book? Important: main text objectives and summaries figures and tables
UE&UX Lecture 6: Handbook Chapters 10, 11, and 12 Egon L. van den Broek Chapter 10 ESTABLISHING REQUIREMENTS Notes (1) How to read the book? Important: main text objectives and summaries figures and tables
IPM 15/16 T2.1 Prototyping
 IPM 15/16 T2.1 Prototyping Miguel Tavares Coimbra Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by Prof. Kellogg Booth at the British Columbia University, Vancouver, Canada.
IPM 15/16 T2.1 Prototyping Miguel Tavares Coimbra Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by Prof. Kellogg Booth at the British Columbia University, Vancouver, Canada.
Design Exploration! CS HCID: User Interface Design, Prototyping, Evaluation, Autumn 2014 Prof. James A. Landay Stanford University
 HCI+D: USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Design Exploration Computer Science Department THINQ Smart Fridge By LG October 2, 2014 * slides marked Buxton are courtesy
HCI+D: USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Design Exploration Computer Science Department THINQ Smart Fridge By LG October 2, 2014 * slides marked Buxton are courtesy
Design, prototyping and construction
 Overview Design, prototyping and construction Prototyping and construction Conceptual design Physical design Generating prototypes Tool support What is a prototype? Why prototype? A prototype is a small-scale
Overview Design, prototyping and construction Prototyping and construction Conceptual design Physical design Generating prototypes Tool support What is a prototype? Why prototype? A prototype is a small-scale
Software Quality. Martin Glinz. Thomas Fritz. Lecture 7 UI Design, Usability & Testing. Many thanks to Meghan Allen and Daniel Greenblatt.
 Institut für Informatik Software Quality Lecture 7 UI Design, Usability & Testing Thomas Fritz Martin Glinz Many thanks to Meghan Allen and Daniel Greenblatt. Overview Introduction to UI design User-centered
Institut für Informatik Software Quality Lecture 7 UI Design, Usability & Testing Thomas Fritz Martin Glinz Many thanks to Meghan Allen and Daniel Greenblatt. Overview Introduction to UI design User-centered
Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique. Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design
 Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design Scenarios Creating a written story that explains how a person will use a product, service, or system to achieve
Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design Scenarios Creating a written story that explains how a person will use a product, service, or system to achieve
dt+ux Design Thinking for User Experience Design, Prototyping & Evaluation Autumn 2015 Prof. James A. Landay, Stanford University
 DESIGN THINKING FOR USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Concept Videos Podcasts App Apple Inc. Prof. James A. Landay Computer Science Department Stanford University
DESIGN THINKING FOR USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Concept Videos Podcasts App Apple Inc. Prof. James A. Landay Computer Science Department Stanford University
Design, Ideation, and Prototyping
 Design, Ideation, and Prototyping Why User Centered Design is important How Prototyping helps User Centered Design System Centered Design System Centered Design What can be built easily on this platform?
Design, Ideation, and Prototyping Why User Centered Design is important How Prototyping helps User Centered Design System Centered Design System Centered Design What can be built easily on this platform?
dt+ux Design Thinking for User Experience Design, Prototyping & Evaluation Autumn 2016 Prof. James A. Landay Stanford University
 DESIGN THINKING FOR USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Early Stage Prototyping Computer Science Department October 20, 2016 Paper ipad App By 53 2 Hall of Fame or
DESIGN THINKING FOR USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Early Stage Prototyping Computer Science Department October 20, 2016 Paper ipad App By 53 2 Hall of Fame or
Page 1. Ideas to windows. Lecture 7: Prototyping & Evaluation. Levels of prototyping. Progressive refinement
 Ideas to windows Lecture 7: Prototyping & Evaluation How do we go from ideas to windows? Prototyping... rapid initial development, sketching & testing many designs to determine the best (few?) to continue
Ideas to windows Lecture 7: Prototyping & Evaluation How do we go from ideas to windows? Prototyping... rapid initial development, sketching & testing many designs to determine the best (few?) to continue
CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INTRODUCTION TO PROTOTYPING. Tom Horton. * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford)
 CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INTRODUCTION TO PROTOTYPING Tom Horton * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford) READINGS ID Book. Chapter 11 in published book, Design, Prototyping,
CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INTRODUCTION TO PROTOTYPING Tom Horton * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford) READINGS ID Book. Chapter 11 in published book, Design, Prototyping,
A Digital Talking Storybook
 Using ICT Levels 1, 2 & 3 A Digital Talking Storybook Desirable Features: Presenting Music and Sound Assessment Focus Film and Animation Express Evaluate Exhibit Pupil Notes Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Part
Using ICT Levels 1, 2 & 3 A Digital Talking Storybook Desirable Features: Presenting Music and Sound Assessment Focus Film and Animation Express Evaluate Exhibit Pupil Notes Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Part
CS -213 Human Computer Interaction Spring Prototyping. Imran Ihsan. Assistant Professor (CS) Air University, Islamabad
 CS -213 Human Computer Interaction Spring 2015 07 Prototyping Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor (CS) Air University, Islamabad www.imranihsan.com www.opuseven.com opuseven iimranihsan imranihsan iimranihsan
CS -213 Human Computer Interaction Spring 2015 07 Prototyping Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor (CS) Air University, Islamabad www.imranihsan.com www.opuseven.com opuseven iimranihsan imranihsan iimranihsan
Interaction Design. Heuristic Evaluation & Cognitive Walkthrough
 Interaction Design Heuristic Evaluation & Cognitive Walkthrough Interaction Design Iterative user centered design and development Requirements gathering Quick design Build prototype Evaluate and refine
Interaction Design Heuristic Evaluation & Cognitive Walkthrough Interaction Design Iterative user centered design and development Requirements gathering Quick design Build prototype Evaluate and refine
iflix is246 Multimedia Metadata Final Project Supplement on User Feedback Sessions Cecilia Kim, Nick Reid, Rebecca Shapley
 iflix is246 Multimedia Metadata Final Project Supplement on User Feedback Sessions Cecilia Kim, Nick Reid, Rebecca Shapley Table of Contents Table of Contents 2 Interviews with Users 2 Conclusions 2 Transcripts
iflix is246 Multimedia Metadata Final Project Supplement on User Feedback Sessions Cecilia Kim, Nick Reid, Rebecca Shapley Table of Contents Table of Contents 2 Interviews with Users 2 Conclusions 2 Transcripts
Unit 9 Tech savvy? Tech support. 1 I have no idea why... Lesson A. A Unscramble the questions. Do you know which battery I should buy?
 Unit 9 Tech savvy? Lesson A Tech support 1 I have no idea why... A Unscramble the questions. 1. which battery / Do you know / should / buy / I? Do you know which battery I should buy? 2. they / where /
Unit 9 Tech savvy? Lesson A Tech support 1 I have no idea why... A Unscramble the questions. 1. which battery / Do you know / should / buy / I? Do you know which battery I should buy? 2. they / where /
Analysis, Dekalb Roofing Company Web Site
 Analysis, Dekalb Roofing Company Web Site Client: Dekalb Roofing Company Site: dekalbroofingcompanyinc.com Overall Look & Design This is a very good-looking site. It s clean, tasteful, has well-coordinated
Analysis, Dekalb Roofing Company Web Site Client: Dekalb Roofing Company Site: dekalbroofingcompanyinc.com Overall Look & Design This is a very good-looking site. It s clean, tasteful, has well-coordinated
Rapid Prototyping. Sketches, storyboards, mock-ups and scenarios
 Rapid Prototyping Sketches, storyboards, mock-ups and scenarios Agenda Dimensions and terminology Non-computer methods Computer methods 2 Your Project Group 3 An Essential Concept of UCD Requirements for
Rapid Prototyping Sketches, storyboards, mock-ups and scenarios Agenda Dimensions and terminology Non-computer methods Computer methods 2 Your Project Group 3 An Essential Concept of UCD Requirements for
Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique. Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design
 Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design Scenarios Creating a written story that explains how a person will use a product, service, or system to achieve
Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design Scenarios Creating a written story that explains how a person will use a product, service, or system to achieve
Videos and Animations:
 Videos and Animations: Textbook images limit the ability to describe spatial and temporal interactions of macromolecules in the context of the cell. These limitations are typically overcome by depicting
Videos and Animations: Textbook images limit the ability to describe spatial and temporal interactions of macromolecules in the context of the cell. These limitations are typically overcome by depicting
13/9/10 PROTOTYPING. Cris3an Bogdan
 PROTOTYPING Cris3an Bogdan cris3@kth.se 1 What is a prototype? Concrete representation of an interactive system/service, or relevant part of it Tangible artifact Relevance depends on what is being explored
PROTOTYPING Cris3an Bogdan cris3@kth.se 1 What is a prototype? Concrete representation of an interactive system/service, or relevant part of it Tangible artifact Relevance depends on what is being explored
..in a nutshell. credit: Chris Hundhausen Associate Professor, EECS Director, HELP Lab
 ..in a nutshell credit: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6mczkwhjr9o Chris Hundhausen Associate Professor, EECS Director, HELP Lab Human-Centered Design in a Nutshell Key topics for this talk 1. User-centered
..in a nutshell credit: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6mczkwhjr9o Chris Hundhausen Associate Professor, EECS Director, HELP Lab Human-Centered Design in a Nutshell Key topics for this talk 1. User-centered
stanford hci group / cs376 Design Tools Ron B. Yeh 26 October 2004 Research Topics in Human-Computer Interaction
 stanford hci group / cs376 Design Tools Ron B. Yeh 26 October 2004 Research Topics in Human-Computer Interaction http://cs376.stanford.edu Reading Research Papers Selective Attention =) Or alternatively,
stanford hci group / cs376 Design Tools Ron B. Yeh 26 October 2004 Research Topics in Human-Computer Interaction http://cs376.stanford.edu Reading Research Papers Selective Attention =) Or alternatively,
NUR- Formal description/models of user interfaces. Scenarios, Storyboards, Task models
 NUR- Formal description/models of user interfaces Scenarios, Storyboards, Task models System modeling Analysis of user activities Description of the course of the dialogue Application Domain step 0 User
NUR- Formal description/models of user interfaces Scenarios, Storyboards, Task models System modeling Analysis of user activities Description of the course of the dialogue Application Domain step 0 User
CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROTOTYPING STRATEGIES. Tom Horton. * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford)
 CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROTOTYPING STRATEGIES Tom Horton * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford) WHAT WILL WE BE TALKING ABOUT? Specific Prototyping Strategies! Low-Fidelity
CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROTOTYPING STRATEGIES Tom Horton * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford) WHAT WILL WE BE TALKING ABOUT? Specific Prototyping Strategies! Low-Fidelity
Midterm Exam, October 24th, 2000 Tuesday, October 24th, Human-Computer Interaction IT 113, 2 credits First trimester, both modules 2000/2001
 257 Midterm Exam, October 24th, 2000 258 257 Midterm Exam, October 24th, 2000 Tuesday, October 24th, 2000 Course Web page: http://www.cs.uni sb.de/users/jameson/hci Human-Computer Interaction IT 113, 2
257 Midterm Exam, October 24th, 2000 258 257 Midterm Exam, October 24th, 2000 Tuesday, October 24th, 2000 Course Web page: http://www.cs.uni sb.de/users/jameson/hci Human-Computer Interaction IT 113, 2
Human-Computer Interaction Design
 Human-Computer Interaction Design COGS120/CSE170 - Intro. HCI Instructor: Philip Guo Week 2 - Prototyping (2016-10-04) some slides adapted from Scott Klemmer s Intro. HCI course Grading policy: aim for
Human-Computer Interaction Design COGS120/CSE170 - Intro. HCI Instructor: Philip Guo Week 2 - Prototyping (2016-10-04) some slides adapted from Scott Klemmer s Intro. HCI course Grading policy: aim for
What is a prototype?
 Prototyping Unit 4 Learning outcomes Understand the uses of different types of prototypes for different kinds/stages of design and be able to choose appropriately Know the basic techniques for low-fidelity
Prototyping Unit 4 Learning outcomes Understand the uses of different types of prototypes for different kinds/stages of design and be able to choose appropriately Know the basic techniques for low-fidelity
Welcome to Python! If you re the type of person who wants to know
 In This Chapter The history of Python What people use Python for Chapter 1 Introducing Python Useful concepts for Python programming Welcome to Python! If you re the type of person who wants to know what
In This Chapter The history of Python What people use Python for Chapter 1 Introducing Python Useful concepts for Python programming Welcome to Python! If you re the type of person who wants to know what
Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a
 Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a heuristic evaluation and ending with How to rate severity.
Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a heuristic evaluation and ending with How to rate severity.
Telling a Story Visually. Copyright 2012, Oracle. All rights reserved.
 What Will I Learn? Objectives In this lesson, you will learn how to: Compare and define an animation and a scenario Demonstrate how to use the four problem solving steps to storyboard your animation Use
What Will I Learn? Objectives In this lesson, you will learn how to: Compare and define an animation and a scenario Demonstrate how to use the four problem solving steps to storyboard your animation Use
Up and Running Software The Development Process
 Up and Running Software The Development Process Success Determination, Adaptative Processes, and a Baseline Approach About This Document: Thank you for requesting more information about Up and Running
Up and Running Software The Development Process Success Determination, Adaptative Processes, and a Baseline Approach About This Document: Thank you for requesting more information about Up and Running
GUI Design Principles
 GUI Design Principles User Interfaces Are Hard to Design You are not the user Most software engineering is about communicating with other programmers UI is about communicating with users The user is always
GUI Design Principles User Interfaces Are Hard to Design You are not the user Most software engineering is about communicating with other programmers UI is about communicating with users The user is always
The Experience of Prototyping. Jennifer Kalz, CBAP, CUA, CSM March 28, 2017
 The Experience of Prototyping Jennifer Kalz, CBAP, CUA, CSM March 28, 2017 Agenda Core Concept Model Overview and Benefits of the Technique Fidelity of a Prototype Best Practices with the Technique Usability
The Experience of Prototyping Jennifer Kalz, CBAP, CUA, CSM March 28, 2017 Agenda Core Concept Model Overview and Benefits of the Technique Fidelity of a Prototype Best Practices with the Technique Usability
Administrative Stuff. Examples of project processbooks and link to a project prototype on the website Next Week: Evaluation methods, cultural probes
 Administrative Stuff Examples of project processbooks and link to a project prototype on the website Next Week: Evaluation methods, cultural probes Prototyping Irene Rae Computer Sciences CS-570 Introduction
Administrative Stuff Examples of project processbooks and link to a project prototype on the website Next Week: Evaluation methods, cultural probes Prototyping Irene Rae Computer Sciences CS-570 Introduction
How Pixar Tells a Story By Rachel Slivnick 2018
 Name: Class: How Pixar Tells a Story By Rachel Slivnick 2018 Pixar is an animation studio that uses computer images to create movies. You ve likely seen several of Pixar s films, which include Toy Story,
Name: Class: How Pixar Tells a Story By Rachel Slivnick 2018 Pixar is an animation studio that uses computer images to create movies. You ve likely seen several of Pixar s films, which include Toy Story,
10/1/2015. dt+ux Design Thinking for User Experience Design, Prototyping & Evaluation, Autumn 2015 Prof. James A. Landay Stanford University
 dt+ux: DESIGN THINKING FOR USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy
dt+ux: DESIGN THINKING FOR USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy
What is a prototype?
 Prototyping Unit 4 Learning outcomes Understand the uses of different types of prototypes for different kinds/stages of design and be able to choose appropriately Know the basic techniques for low-fidelity
Prototyping Unit 4 Learning outcomes Understand the uses of different types of prototypes for different kinds/stages of design and be able to choose appropriately Know the basic techniques for low-fidelity
CS 160: Evaluation. Professor John Canny Spring /15/2006 1
 CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 Outline User testing process Severity and Cost ratings Discount usability methods Heuristic evaluation HE vs. user testing 2/15/2006 2 Outline
CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 Outline User testing process Severity and Cost ratings Discount usability methods Heuristic evaluation HE vs. user testing 2/15/2006 2 Outline
CS 160: Evaluation. Outline. Outline. Iterative Design. Preparing for a User Test. User Test
 CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 2/15/2006 2 Iterative Design Prototype low-fi paper, DENIM Design task analysis contextual inquiry scenarios sketching 2/15/2006 3 Evaluate
CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 2/15/2006 2 Iterative Design Prototype low-fi paper, DENIM Design task analysis contextual inquiry scenarios sketching 2/15/2006 3 Evaluate
NUR- Formal description/models of user interfaces. Task models
 NUR- Formal description/models of user interfaces Task models User requirements Analysis of user activities (task analysis) Description of the course of the dialogue. The description will be used to the
NUR- Formal description/models of user interfaces Task models User requirements Analysis of user activities (task analysis) Description of the course of the dialogue. The description will be used to the
Usability. CSE 331 Spring Slides originally from Robert Miller
 Usability CSE 331 Spring 2010 Slides originally from Robert Miller 1 User Interface Hall of Shame Source: Interface Hall of Shame 2 User Interface Hall of Shame Source: Interface Hall of Shame 3 Redesigning
Usability CSE 331 Spring 2010 Slides originally from Robert Miller 1 User Interface Hall of Shame Source: Interface Hall of Shame 2 User Interface Hall of Shame Source: Interface Hall of Shame 3 Redesigning
Interactive (High-fi) Prototype (Group)
 Interactive (High-fi) Prototype (Group) Midway Milestone due at the start of your studio (Thursday/Friday Dec 1-2) Final Prototype due at the start of your studio (Thursday/Friday Dec 8-9) Writeup due
Interactive (High-fi) Prototype (Group) Midway Milestone due at the start of your studio (Thursday/Friday Dec 1-2) Final Prototype due at the start of your studio (Thursday/Friday Dec 8-9) Writeup due
CS/ISE 5714 Spring 2013
 CS/ISE 5714 Spring 2013 Chapter 11. Prototyping Chapter 10. UX Goals, Metrics, Targets Introduction A way to evaluate design before it s too late and too expensive Copyright MKP. All rights reserved. 2
CS/ISE 5714 Spring 2013 Chapter 11. Prototyping Chapter 10. UX Goals, Metrics, Targets Introduction A way to evaluate design before it s too late and too expensive Copyright MKP. All rights reserved. 2
Exemplar candidate work. Introduction
 Exemplar candidate work Introduction OCR has produced these simulated candidate style answers to support teachers in interpreting the assessment criteria for the new Creative imedia specifications and
Exemplar candidate work Introduction OCR has produced these simulated candidate style answers to support teachers in interpreting the assessment criteria for the new Creative imedia specifications and
Prototyping. Unit 5. Zeno Menestrina, MSc Prof. Antonella De Angeli, PhD
 Prototyping Unit 5 Zeno Menestrina, MSc zeno.menestrina@unitn.it Prof. Antonella De Angeli, PhD antonella.deangeli@unitn.it Assessment Pervasive game to support social life in/from the campus 2 Assessment
Prototyping Unit 5 Zeno Menestrina, MSc zeno.menestrina@unitn.it Prof. Antonella De Angeli, PhD antonella.deangeli@unitn.it Assessment Pervasive game to support social life in/from the campus 2 Assessment
Interaction Design. Task Analysis & Modelling
 Interaction Design Task Analysis & Modelling This Lecture Conducting task analysis Constructing task models Understanding the shortcomings of task analysis Task Analysis for Interaction Design Find out
Interaction Design Task Analysis & Modelling This Lecture Conducting task analysis Constructing task models Understanding the shortcomings of task analysis Task Analysis for Interaction Design Find out
Introduction to User Stories. CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014
 Introduction to User Stories CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014 1 Goals Present an introduction to the topic of user stories concepts and terminology benefits and limitations
Introduction to User Stories CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014 1 Goals Present an introduction to the topic of user stories concepts and terminology benefits and limitations
Strong signs your website needs a professional redesign
 Strong signs your website needs a professional redesign Think - when was the last time that your business website was updated? Better yet, when was the last time you looked at your website? When the Internet
Strong signs your website needs a professional redesign Think - when was the last time that your business website was updated? Better yet, when was the last time you looked at your website? When the Internet
What is a prototype?
 Prototyping Unit 4 Learning outcomes Understand the uses of different types of prototypes for different kinds/stages of design and be able to choose appropriately Know the basic techniques for low-fidelity
Prototyping Unit 4 Learning outcomes Understand the uses of different types of prototypes for different kinds/stages of design and be able to choose appropriately Know the basic techniques for low-fidelity
Lecture 6. Design (3) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 6. Design (3) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 28 2009 1 Outline Prototyping techniques: - Paper prototype - Computer prototype - Wizard of Oz Reading: Wickens pp. 50-57 Marc Rettig: Prototyping
Lecture 6. Design (3) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 28 2009 1 Outline Prototyping techniques: - Paper prototype - Computer prototype - Wizard of Oz Reading: Wickens pp. 50-57 Marc Rettig: Prototyping
Sketching and Prototyping
 Sketching and Prototyping SWE 632 Spring 2018 Thomas LaToza Administrivia HW 3 due in 1 week In-class midterm exam in two weeks 2 Expectations for midterm exam Multiple choice questions, free response,
Sketching and Prototyping SWE 632 Spring 2018 Thomas LaToza Administrivia HW 3 due in 1 week In-class midterm exam in two weeks 2 Expectations for midterm exam Multiple choice questions, free response,
Human-Centred Interaction Design
 Human-Centred Interaction Design Scoping a problem with PACT The aim of human-centred interaction design is to harmonise the PACT elements in a particular domain. Designers want to get the right mix of
Human-Centred Interaction Design Scoping a problem with PACT The aim of human-centred interaction design is to harmonise the PACT elements in a particular domain. Designers want to get the right mix of
Quick Reference Design Guide
 Presentation is everything. At one time or another, you have probably heard the phrase a book is judged by its cover. That s still true and probably even more so today because we live in a very distracted,
Presentation is everything. At one time or another, you have probably heard the phrase a book is judged by its cover. That s still true and probably even more so today because we live in a very distracted,
Heuristic Evaluation of Math Out of the Box
 Heuristic Evaluation of Math Out of the Box Evaluator #A: Joanie Hollberg Evaluator #B: Rassan Walker Evaluator #C: Alex Wang Evaluator #D: Carlos Araujo 1. Problem Math Out of The Box is a mobile application
Heuristic Evaluation of Math Out of the Box Evaluator #A: Joanie Hollberg Evaluator #B: Rassan Walker Evaluator #C: Alex Wang Evaluator #D: Carlos Araujo 1. Problem Math Out of The Box is a mobile application
Assignments. Assignment 2 is due TODAY, 11:59pm! Submit one per pair on Blackboard.
 HCI and Design Assignments Assignment 2 is due TODAY, 11:59pm! Submit one per pair on Blackboard. Today Paper prototyping An essential tool in your design toolbox! How do we design things that actually
HCI and Design Assignments Assignment 2 is due TODAY, 11:59pm! Submit one per pair on Blackboard. Today Paper prototyping An essential tool in your design toolbox! How do we design things that actually
 User Interfaces Assignment 3: Heuristic Re-Design of Craigslist (English) Completed by Group 5 November 10, 2015 Phase 1: Analysis of Usability Issues Homepage Error 1: Overall the page is overwhelming
User Interfaces Assignment 3: Heuristic Re-Design of Craigslist (English) Completed by Group 5 November 10, 2015 Phase 1: Analysis of Usability Issues Homepage Error 1: Overall the page is overwhelming
Final Cut Pro Trimming: The Fine Points
 Final Cut Pro Trimming: The Fine Points Part 1: Trimming Two Edit Points upart 2: Slipping One Clipo Part 3: Rolling Two Edit Points Part 4: Sliding Clips to Refine Position Part 5: Shuffling Clips to
Final Cut Pro Trimming: The Fine Points Part 1: Trimming Two Edit Points upart 2: Slipping One Clipo Part 3: Rolling Two Edit Points Part 4: Sliding Clips to Refine Position Part 5: Shuffling Clips to
Usable Privacy and Security Introduction to HCI Methods January 19, 2006 Jason Hong Notes By: Kami Vaniea
 Usable Privacy and Security Introduction to HCI Methods January 19, 2006 Jason Hong Notes By: Kami Vaniea Due Today: List of preferred lectures to present Due Next Week: IRB training completion certificate
Usable Privacy and Security Introduction to HCI Methods January 19, 2006 Jason Hong Notes By: Kami Vaniea Due Today: List of preferred lectures to present Due Next Week: IRB training completion certificate
Key questions to ask before commissioning any web designer to build your website.
 Key questions to ask before commissioning any web designer to build your website. KEY QUESTIONS TO ASK Before commissioning a web designer to build your website. As both an entrepreneur and business owner,
Key questions to ask before commissioning any web designer to build your website. KEY QUESTIONS TO ASK Before commissioning a web designer to build your website. As both an entrepreneur and business owner,
CHAPTER 18: CLIENT COMMUNICATION
 CHAPTER 18: CLIENT COMMUNICATION Chapter outline When to communicate with clients What modes of communication to use How much to communicate How to benefit from client communication Understanding your
CHAPTER 18: CLIENT COMMUNICATION Chapter outline When to communicate with clients What modes of communication to use How much to communicate How to benefit from client communication Understanding your
Understanding prototype fidelity What is Digital Prototyping? Introduction to various digital prototyping tools
 HCI and Design Today Assignment 1 is graded Assignment 3 is posted Understanding prototype fidelity What is Digital Prototyping? Introduction to various digital prototyping tools Reminder: What is a prototype?
HCI and Design Today Assignment 1 is graded Assignment 3 is posted Understanding prototype fidelity What is Digital Prototyping? Introduction to various digital prototyping tools Reminder: What is a prototype?
Prototyping for usability engineering
 analysis of stakeholders, field studies ANALYZE Problem scenarios claims about current practice Prototyping for usability engineering metaphors, information technology, HCI theory, guidelines DESIGN Activity
analysis of stakeholders, field studies ANALYZE Problem scenarios claims about current practice Prototyping for usability engineering metaphors, information technology, HCI theory, guidelines DESIGN Activity
Lecture Notes CPSC 491 (Fall 2018) Topics. Peer evals. UI Sketches. Homework. Quiz 4 next Tues. HW5 out. S. Bowers 1 of 11
 Topics Peer evals UI Sketches Homework Quiz 4 next Tues HW5 out S. Bowers 1 of 11 Context Diagrams Context Diagrams describe the system boundaries what is inside ( in scope ) vs outside ( out of scope
Topics Peer evals UI Sketches Homework Quiz 4 next Tues HW5 out S. Bowers 1 of 11 Context Diagrams Context Diagrams describe the system boundaries what is inside ( in scope ) vs outside ( out of scope
Prototyping. SWE 432, Fall Web Application Development
 Prototyping SWE 432, Fall 2018 Web Application Development Conceptual design Goal: match users mental model Tool: Metaphor - analogies from existing system Offers expectations about what system does &
Prototyping SWE 432, Fall 2018 Web Application Development Conceptual design Goal: match users mental model Tool: Metaphor - analogies from existing system Offers expectations about what system does &
Ideate. Empathize. Prototype. Define. Test. CS:2520 Human-Computer Interaction. Fall 2016.
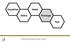 Empathize Ideate Define Prototype Test Designing Prototypes From Preece, Rogers & Sharp s Interaction Design Process Conceptual design What product will do How it will behave Physical design Actual visual
Empathize Ideate Define Prototype Test Designing Prototypes From Preece, Rogers & Sharp s Interaction Design Process Conceptual design What product will do How it will behave Physical design Actual visual
The Stack, Free Store, and Global Namespace
 Pointers This tutorial is my attempt at clarifying pointers for anyone still confused about them. Pointers are notoriously hard to grasp, so I thought I'd take a shot at explaining them. The more information
Pointers This tutorial is my attempt at clarifying pointers for anyone still confused about them. Pointers are notoriously hard to grasp, so I thought I'd take a shot at explaining them. The more information
Prototyping & Building a System
 1 Prototyping & Building a System How Prototyping helps (especially when done with User-Centered Design) Prototyping http://dilbert.com/strip/2009-07-22 2 Designing Your System Decide which users and tasks
1 Prototyping & Building a System How Prototyping helps (especially when done with User-Centered Design) Prototyping http://dilbert.com/strip/2009-07-22 2 Designing Your System Decide which users and tasks
Design Thinking: Design Review Workshop
 Design Thinking: Design Review Workshop Introductions Guliz Sicotte Director of Product Design Magento Commerce @gsicotte Eric Erway Sr. UX Manager Magento Commerce @ericerway Ann Hudspeth UX Manager Magento
Design Thinking: Design Review Workshop Introductions Guliz Sicotte Director of Product Design Magento Commerce @gsicotte Eric Erway Sr. UX Manager Magento Commerce @ericerway Ann Hudspeth UX Manager Magento
HCI and Design SPRING 2016
 HCI and Design SPRING 2016 Topics for today Heuristic Evaluation 10 usability heuristics How to do heuristic evaluation Project planning and proposals Usability Testing Formal usability testing in a lab
HCI and Design SPRING 2016 Topics for today Heuristic Evaluation 10 usability heuristics How to do heuristic evaluation Project planning and proposals Usability Testing Formal usability testing in a lab
It s possible to get your inbox to zero and keep it there, even if you get hundreds of s a day.
 It s possible to get your email inbox to zero and keep it there, even if you get hundreds of emails a day. It s not super complicated, though it does take effort and discipline. Many people simply need
It s possible to get your email inbox to zero and keep it there, even if you get hundreds of emails a day. It s not super complicated, though it does take effort and discipline. Many people simply need
Animator Friendly Rigging Part 1
 Animator Friendly Rigging Part 1 Creating animation rigs which solve problems, are fun to use, and don t cause nervous breakdowns. - http://jasonschleifer.com/ - 1- CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION... 4 What is
Animator Friendly Rigging Part 1 Creating animation rigs which solve problems, are fun to use, and don t cause nervous breakdowns. - http://jasonschleifer.com/ - 1- CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION... 4 What is
Plus 10: Descending the Design Funnel THE 10 PLUS 10 METHOD. developing 10 different ideas and refinements of selected ideas
 10 Plus 10: Descending the Design Funnel developing 10 different ideas and refinements of selected ideas 1.4 The design funnel describes a process that you, as an interaction designer, need to habitually
10 Plus 10: Descending the Design Funnel developing 10 different ideas and refinements of selected ideas 1.4 The design funnel describes a process that you, as an interaction designer, need to habitually
SOLUTIONS GUIDE. I Don t Know What to or
 SOLUTIONS GUIDE I Don t Know What to Email or How to Write My Email, Can I Have Some Ideas? We often hear from new students that one of their biggest challenges creating content for email campaigns. Not
SOLUTIONS GUIDE I Don t Know What to Email or How to Write My Email, Can I Have Some Ideas? We often hear from new students that one of their biggest challenges creating content for email campaigns. Not
Design Heuristics and Evaluation
 Design Heuristics and Evaluation Rapid Evaluation Selected material from The UX Book, Hartson & Pyla Heuristic Evaluation Another method for finding usability problems in a UI design Validation during
Design Heuristics and Evaluation Rapid Evaluation Selected material from The UX Book, Hartson & Pyla Heuristic Evaluation Another method for finding usability problems in a UI design Validation during
facebook a guide to social networking for massage therapists
 facebook a guide to social networking for massage therapists table of contents 2 3 5 6 7 9 10 13 15 get the facts first the importance of social media, facebook and the difference between different facebook
facebook a guide to social networking for massage therapists table of contents 2 3 5 6 7 9 10 13 15 get the facts first the importance of social media, facebook and the difference between different facebook
Mayhem Make a little Mayhem in your world.
 Mayhem Make a little Mayhem in your world. Team Group Manager - Eli White Documentation - Meaghan Kjelland Design - Jabili Kaza & Jen Smith Testing - Kyle Zemek Problem and Solution Overview Most people
Mayhem Make a little Mayhem in your world. Team Group Manager - Eli White Documentation - Meaghan Kjelland Design - Jabili Kaza & Jen Smith Testing - Kyle Zemek Problem and Solution Overview Most people
Prototyping. Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994.
 Prototyping Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994. 1 What is prototyping? producing cheaper, less accurate renditions of your
Prototyping Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994. 1 What is prototyping? producing cheaper, less accurate renditions of your
Lecture 5: Generating Designs. February 15
 Lecture 5: Generating Designs February 15 1 Recap Five usability attributes: 2 Learnability 3 Efficiency 4 Memory 5 Few errors 6 Satisfaction 7 Recap Two goals of user and task analysis: 1. Understand
Lecture 5: Generating Designs February 15 1 Recap Five usability attributes: 2 Learnability 3 Efficiency 4 Memory 5 Few errors 6 Satisfaction 7 Recap Two goals of user and task analysis: 1. Understand
Virtual Platform Checklist for Adobe Connect 9
 Virtual Platform Checklist for Adobe Connect 9 Adobe Connect is a powerful online meeting tool used to create engaging virtual training. To create an effective learning experience, become familiar with
Virtual Platform Checklist for Adobe Connect 9 Adobe Connect is a powerful online meeting tool used to create engaging virtual training. To create an effective learning experience, become familiar with
Goals PROTOTYPING) Cris%an(Bogdan( (
 PROTOTYPING) Cris%an(Bogdan( cris%@kth.se( ( Goals illustrate(how(we(can((help(designers)( generate(and(share(new(ideas,(get(feedback( from(users(or(customers( choose(among(design(alterna%ves,(and( ar%culate(reasons(for(design(choices.(
PROTOTYPING) Cris%an(Bogdan( cris%@kth.se( ( Goals illustrate(how(we(can((help(designers)( generate(and(share(new(ideas,(get(feedback( from(users(or(customers( choose(among(design(alterna%ves,(and( ar%culate(reasons(for(design(choices.(
Learning more about the internet will help students develop a better understanding of its endless possibilities.
 Title: The Internet Subject Area: Computer Science Grade Level: 2 (suitable for 8 and older) Related Standards of Learning: CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards CPP - Computing Practice & Programming CT
Title: The Internet Subject Area: Computer Science Grade Level: 2 (suitable for 8 and older) Related Standards of Learning: CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards CPP - Computing Practice & Programming CT
Process of Interaction Design and Design Languages
 Process of Interaction Design and Design Languages Process of Interaction Design This week, we will explore how we can design and build interactive products What is different in interaction design compared
Process of Interaction Design and Design Languages Process of Interaction Design This week, we will explore how we can design and build interactive products What is different in interaction design compared
Flow. Streamlining your creative process so you can pursue your passions. Hi-Fidelity Prototype Report
 Flow Streamlining your creative process so you can pursue your passions. Problem and Solution Overview: Hi-Fidelity Prototype Report Genie Hyatt: Team Leader and Documentation Trijeet Mukhopadhyay: Designer
Flow Streamlining your creative process so you can pursue your passions. Problem and Solution Overview: Hi-Fidelity Prototype Report Genie Hyatt: Team Leader and Documentation Trijeet Mukhopadhyay: Designer
Foundation Level Syllabus Usability Tester Sample Exam
 Foundation Level Syllabus Usability Tester Sample Exam Version 2017 Provided by German Testing Board Copyright Notice This document may be copied in its entirety, or extracts made, if the source is acknowledged.
Foundation Level Syllabus Usability Tester Sample Exam Version 2017 Provided by German Testing Board Copyright Notice This document may be copied in its entirety, or extracts made, if the source is acknowledged.
Learn to use the vector and translation tools in GX.
 Learning Objectives Horizontal and Combined Transformations Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 00 50 min. This lesson adds horizontal translations to our previous work with vertical translations and
Learning Objectives Horizontal and Combined Transformations Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 00 50 min. This lesson adds horizontal translations to our previous work with vertical translations and
Media Production in the Junior Writing Program
 Media Production in the Junior Writing Program Phase 1: Teacher Preparation and Planning Establish a team of teachers and identify classes that will collaborate on and participate in a curricular-based
Media Production in the Junior Writing Program Phase 1: Teacher Preparation and Planning Establish a team of teachers and identify classes that will collaborate on and participate in a curricular-based
COSC 341 Human Computer Interaction. Dr. Bowen Hui University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 341 Human Computer Interaction Dr. Bowen Hui University of British Columbia Okanagan 1 Recall: Learning About Your User Common ways to elicit user feedback: Interviews Focus groups Expert reviews
COSC 341 Human Computer Interaction Dr. Bowen Hui University of British Columbia Okanagan 1 Recall: Learning About Your User Common ways to elicit user feedback: Interviews Focus groups Expert reviews
The ClassPass Front Desk Guide. ClassPass Front Desk Guide 1
 The ClassPass Front Desk Guide ClassPass Front Desk Guide 1 Welcome to ClassPass! We re excited to partner with you. In the following guide, we ll share everything you need to know about ClassPass users
The ClassPass Front Desk Guide ClassPass Front Desk Guide 1 Welcome to ClassPass! We re excited to partner with you. In the following guide, we ll share everything you need to know about ClassPass users
EVALUATION OF PROTOTYPES USABILITY TESTING
 EVALUATION OF PROTOTYPES USABILITY TESTING CPSC 544 FUNDAMENTALS IN DESIGNING INTERACTIVE COMPUTATIONAL TECHNOLOGY FOR PEOPLE (HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION) WEEK 9 CLASS 17 Joanna McGrenere and Leila Aflatoony
EVALUATION OF PROTOTYPES USABILITY TESTING CPSC 544 FUNDAMENTALS IN DESIGNING INTERACTIVE COMPUTATIONAL TECHNOLOGY FOR PEOPLE (HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION) WEEK 9 CLASS 17 Joanna McGrenere and Leila Aflatoony
