Chapter 5. The Network Layer IP
|
|
|
- Scott Arnold
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5 The Netwrk Layer IP These slides are taken frm the bk Cmputer etwrking, A Tp Dwn Apprach Featuring the Internet by Kurse & Rss and frm the bk Cmputer etwrks by Andrew Tanenbaum.
2 The Netwrk Layer in the Internet The IP Prtcl IP Datagram Frmat IP Addresses NAT Internet Cntrl Prtcls ICMP ARP DHCP OSPF The Interir Gateway Ruting Prtcl BGP The Exterir Gateway Ruting Prtcl
3 Netwrk layer transprt segment frm sending t receiving hst n sending side encapsulates segments int datagrams n rcving side, delivers segments t transprt layer netwrk layer prtcls in every hst, ruter Ruter examines header fields in all IP datagrams passing thrugh it applicatin transprt netwrk data link physical netwrk data link physical netwrk data link physical netwrk data link physical netwrk data link physical netwrk data link physical netwrk data link physical netwrk data link physical netwrk data link physical applicatin transprt netwrk data link physical
4 The Internet Netwrk layer Hst, ruter netwrk layer functins: Transprt layer: TCP, UDP Netwrk layer Ruting prtcls path selectin RIP, OSPF, BGP frwarding table IP prtcl addressing cnventins datagram frmat packet handling cnventins ICMP prtcl errr reprting ruter signaling Link layer physical layer
5 IP datagram frmat IP prtcl versin number header length (bytes) type f data max number remaining hps (decremented at each ruter) upper layer prtcl t deliver paylad t hw much verhead with TCP? a)20 bytes f TCP b)20 bytes f IP c)= 40 bytes + app layer verhead ver head. len 16-bit identifier time t live type f service upper layer 32 bits flgs length fragment ffset header checksum 32 bit surce IP address 32 bit destinatin IP address Optins (if any) data (variable length, typically a TCP r UDP segment) ttal datagram length (bytes) fr fragmentatin/ reassembly E.g. timestamp, recrd rute taken, specify list f ruters t visit.
6 The IP Prtcl The IPv4 (Internet Prtcl) header.
7 IP Fragmentatin & Reassembly netwrk links have MTU (max.transfer size) - largest pssible link-level frame. different link types, different MTUs large IP datagram divided ( fragmented ) within net ne datagram becmes several datagrams reassembled nly at final destinatin IP header bits used t identify, rder related fragments reassembly fragmentatin: in: ne large datagram ut: 3 smaller datagrams
8 IP Fragmentatin and Reassembly Example a)4000 byte datagram b)mtu = 1500 bytes length =4000 ID =x fragflag =0 ffset =0 One large datagram becmes several smaller datagrams 1480 bytes in data field ffset = 1480/8 length =1500 length =1500 length =1040 ID =x ID =x ID =x fragflag =1 fragflag =1 fragflag =0 ffset =0 ffset =185 ffset =370
9 IP Addressing: intrductin IP address: 32-bit identifier fr hst, ruter interface interface: cnnectin between hst/ruter and physical link ruter s typically have multiple interfaces hst typically has ne interface IP addresses assciated with each interface =
10 IP Addresses IP address frmats.
11 Subnets What s a subnet? The parts f the netwrk is called subnet device interfaces with same subnet part f IP address can physically reach each ther withut intervening ruter IP address: subnet part (high rder bits) hst part (lw rder bits) subnet netwrk cnsisting f 3 subnets
12 Subnets A campus netwrk cnsisting f LANs fr varius departments.
13 Subnettting Subnetting is the prcess f allcating bits frm the hst prtin as a netwrk prtin A class B netwrk subnetted int 64 subnets.
14 Subnettting Subnet 1: : Subnet 2: : Subnet 3: :
15 IP addressing: CIDR CIDR: Classless InterDmain Ruting subnet prtin f address f arbitrary length address frmat: a.b.c.d/x, where x is # bits in subnet prtin f address subnet part hst part /23
16 IP addresses: hw t get ne? Q: Hw des hst get IP address? a) hard-cded by system admin in a file Wintel: cntrl-panel->netwrk->cnfiguratin- >tcp/ip->prperties UNIX: /etc/rc.cnfig b) DHCP: Dynamic Hst Cnfiguratin Prtcl: dynamically get address frm as server plug-and-play
17 IP addressing: the last wrd... Q: Hw des an ISP get blck f addresses? A: ICANN: Internet Crpratin fr Assigned Names and Numbers allcates addresses manages DNS assigns dmain names, reslves disputes
18 NAT: Netwrk Address Translatin rest f Internet lcal netwrk (e.g., hme netwrk) / All datagrams leaving lcal netwrk have same single surce NAT IP address: , different surce prt numbers Datagrams with surce r destinatin in this netwrk have /24 address fr surce, destinatin (as usual)
19 NAT: Netwrk Address Translatin Mtivatin: lcal netwrk uses just ne IP address as far as utside wrld is cncerned: range f addresses nt needed frm ISP: just ne IP address fr all devices can change addresses f devices in lcal netwrk withut ntifying utside wrld can change ISP withut changing addresses f devices in lcal netwrk devices inside lcal net nt explicitly addressable, visible by utside wrld (a security plus).
20 NAT: Netwrk Address Translatin Implementatin: NAT ruter must: utging datagrams: replace (surce IP address, prt #) f every utging datagram t (NAT IP address, new prt #)... remte clients/servers will respnd using (NAT IP address, new prt #) as destinatin addr. remember (in AT translatin table) every (surce IP address, prt #) t (NAT IP address, new prt #) translatin pair incming datagrams: replace (NAT IP address, new prt #) in dest fields f every incming datagram with crrespnding (surce IP address, prt #) stred in NAT table
21 NAT: Netwrk Address Translatin 2: NAT ruter changes datagram surce addr frm , 3345 t , 5001, updates table 2 NAT translatin table WAN side addr LAN side addr , , 3345 S: , 5001 D: , S: , 3345 D: , : hst sends datagram t , S: , 80 D: , : Reply arrives dest. address: , 5001 S: , 80 D: , : NAT ruter changes datagram dest addr frm , 5001 t , 3345
22 NAT: Netwrk Address Translatin 16-bit prt-number field: 60,000 simultaneus cnnectins with a single LANside address! NAT is cntrversial: ruters shuld nly prcess up t layer 3 (mdifies TCP lad. Layer 4) vilates end-t-end argument cnnectinless -> cnectin riented (if the NAT table crashes all TCP cnectins get lst. Prcesses d nt require TCP (prt # is nt avail.)
23 ICMP: Internet Cntrl Message Prtcl used by hsts & ruters t cmmunicate netwrk-level infrmatin errr reprting: unreachable hst, netwrk, prt, prtcl ech request/reply (used by ping) netwrk-layer abve IP: ICMP msgs carried in IP datagrams ICMP message: type, cde plus first 8 bytes f IP datagram causing errr
24 Internet Cntrl Message Prtcl 5-61 The principal ICMP message types.
25 Tracerute and ICMP a)surce sends series f UDP segments t dest First has TTL =1 Secnd has TTL=2, etc. Unlikely prt number b)when nth datagram arrives t nth ruter: Ruter discards datagram And sends t surce an ICMP message (type 11, cde 0, TTL expired ) Message includes name f ruter& IP address a)when ICMP message arrives, surce calculates RTT b)tracerute des this 3 times Stpping criterin a)udp segment eventually arrives at destinatin hst b)destinatin returns ICMP hst unreachable packet (type 3, cde 3, destinatin prt unreachable ) c)when surce gets this ICMP, stps.
Network layer: Overview. Network layer functions IP Routing and forwarding NAT ARP IPv6 Routing
 Network layer: Overview Network layer functions IP Routing and forwarding NAT ARP IPv6 Routing 1 Network Layer Functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every
Network layer: Overview Network layer functions IP Routing and forwarding NAT ARP IPv6 Routing 1 Network Layer Functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every
Network layer: Overview. Network Layer Functions
 Network layer: Overview Network layer functions IP Routing and forwarding NAT ARP IPv6 Routing 1 Network Layer Functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every
Network layer: Overview Network layer functions IP Routing and forwarding NAT ARP IPv6 Routing 1 Network Layer Functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every
Master Course Computer Networks IN2097
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department for Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Chair for
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department for Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Chair for
Subnets. IP datagram format. The Internet Network layer. IP Fragmentation and Reassembly. IP Fragmentation & Reassembly. IP Addressing: introduction
 The Network layer Host, network layer functions: Network layer Routing protocols path selection R, OSPF, BGP Transport layer: TCP, forwarding table Link layer physical layer protocol addressing conventions
The Network layer Host, network layer functions: Network layer Routing protocols path selection R, OSPF, BGP Transport layer: TCP, forwarding table Link layer physical layer protocol addressing conventions
Router Architecture Overview
 Chapter 4: r Introduction (forwarding and routing) r Review of queueing theory r Router design and operation r IP: Internet Protocol m IPv4 (datagram format, addressing, ICMP, NAT) m Ipv6 r Generalized
Chapter 4: r Introduction (forwarding and routing) r Review of queueing theory r Router design and operation r IP: Internet Protocol m IPv4 (datagram format, addressing, ICMP, NAT) m Ipv6 r Generalized
Chapter 4: Network Layer
 Chapter 4: Introduction (forwarding and routing) Review of queueing theory Routing algorithms Link state, Distance Vector Router design and operation IP: Internet Protocol IPv4 (datagram format, addressing,
Chapter 4: Introduction (forwarding and routing) Review of queueing theory Routing algorithms Link state, Distance Vector Router design and operation IP: Internet Protocol IPv4 (datagram format, addressing,
Network Layer. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
 Handut 5 CAN1102 Netwrk Layer Internet Cntrl Message Prtcl (ICMP) Netwrks Netwrk Layer Services Ruting principles: path selectin Hierarchal ruting IP Internet Ruting Prtcls: Reliable Transfer a. Intra
Handut 5 CAN1102 Netwrk Layer Internet Cntrl Message Prtcl (ICMP) Netwrks Netwrk Layer Services Ruting principles: path selectin Hierarchal ruting IP Internet Ruting Prtcls: Reliable Transfer a. Intra
Chapter 2. The OSI Model and TCP/IP Protocol Suite. PDF created with FinePrint pdffactory Pro trial version
 Chapter 2 The OSI Mdel and TCP/IP Prtcl Suite PDF created with FinePrint pdffactry Pr trial versin www.pdffactry.cm Outline THE OSI MODEL LAYERS IN THE OSI MODEL TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE ADDRESSING TCP/IP
Chapter 2 The OSI Mdel and TCP/IP Prtcl Suite PDF created with FinePrint pdffactry Pr trial versin www.pdffactry.cm Outline THE OSI MODEL LAYERS IN THE OSI MODEL TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE ADDRESSING TCP/IP
internet technologies and standards
 Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology 2017 internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek Andrzej Bąk Michał Jarociński Network Layer The majority of slides presented in
Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology 2017 internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek Andrzej Bąk Michał Jarociński Network Layer The majority of slides presented in
Network Layer: Internet Protocol
 Network Layer: Internet Protocol Motivation Heterogeneity Scale Intering IP is the glue that connects heterogeneous s giving the illusion of a homogenous one. Salient Features Each host is identified by
Network Layer: Internet Protocol Motivation Heterogeneity Scale Intering IP is the glue that connects heterogeneous s giving the illusion of a homogenous one. Salient Features Each host is identified by
CMPE 80N: Introduction to Networking and the Internet
 CMPE 80N: Introduction to Networking and the Internet Katia Obraczka Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 17 CMPE 80N Spring'10 1 Announcements Next class: Presentation of fun projects
CMPE 80N: Introduction to Networking and the Internet Katia Obraczka Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 17 CMPE 80N Spring'10 1 Announcements Next class: Presentation of fun projects
Lecture 8. Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1
 Lecture 8 Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets Network
Lecture 8 Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets Network
CMPE 150/L : Introduction to Computer Networks. Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 12
 CMPE 150/L : Introduction to Computer Networks Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 12 1 Chapter 4: outline 4.1 introduction 4.2 virtual circuit and datagram networks 4.3 what
CMPE 150/L : Introduction to Computer Networks Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 12 1 Chapter 4: outline 4.1 introduction 4.2 virtual circuit and datagram networks 4.3 what
Chapter 6 Delivery and Routing of IP Packets. PDF created with FinePrint pdffactory Pro trial version
 Chapter 6 Delivery and Ruting f IP Packets PDF created with FinePrint pdffactry Pr trial versin www.pdffactry.cm Outline Cnnectin Delivery Ruting methds Static and dynamic ruting Ruting table and mdule
Chapter 6 Delivery and Ruting f IP Packets PDF created with FinePrint pdffactry Pr trial versin www.pdffactry.cm Outline Cnnectin Delivery Ruting methds Static and dynamic ruting Ruting table and mdule
The Internet protocol
 The Internet prtcl Party time! IPv4 datagram frmat IPv4 2 bytes n ptins delue r ecnmy? header + data mre later CS242 Cmputer Netwrks Department f Cmputer Science Wellesley Cllege decremented by each ruter;
The Internet prtcl Party time! IPv4 datagram frmat IPv4 2 bytes n ptins delue r ecnmy? header + data mre later CS242 Cmputer Netwrks Department f Cmputer Science Wellesley Cllege decremented by each ruter;
Quiz. Segment structure and fields Flow control (rwnd) Timeout interval. Phases transition ssthresh setting Cwnd setting
 Quiz v 10/30/2013 (Wednesday), 20 mins v Midterm question (available on website) v TCP basics Segment structure and fields Flow control (rwnd) Timeout interval v TCP Congestion control Phases transition
Quiz v 10/30/2013 (Wednesday), 20 mins v Midterm question (available on website) v TCP basics Segment structure and fields Flow control (rwnd) Timeout interval v TCP Congestion control Phases transition
The transport layer. Transport-layer services. Transport layer runs on top of network layer. In other words,
 The transprt layer An intrductin t prcess t prcess cmmunicatin CS242 Cmputer Netwrks Department f Cmputer Science Wellesley Cllege Transprt-layer services Prvides fr lgical cmmunicatin* between applicatin
The transprt layer An intrductin t prcess t prcess cmmunicatin CS242 Cmputer Netwrks Department f Cmputer Science Wellesley Cllege Transprt-layer services Prvides fr lgical cmmunicatin* between applicatin
CCNA 1 Chapter v5.1 Answers 100%
 CCNA 1 Chapter 6 2016 v5.1 Answers 100% 1. Which characteristic f the netwrk layer in the OSI mdel allws carrying packets fr multiple types f cmmunicatins amng many hsts? the de-encapsulatin f headers
CCNA 1 Chapter 6 2016 v5.1 Answers 100% 1. Which characteristic f the netwrk layer in the OSI mdel allws carrying packets fr multiple types f cmmunicatins amng many hsts? the de-encapsulatin f headers
CPSC 826 Internetworking. The Network Layer: Routing & Addressing Outline. The Network Layer
 1 CPSC 826 Intering The Network Layer: Routing & Addressing Outline The Network Layer Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Clemson University mweigle@cs.clemson.edu November 10, 2004 Network layer
1 CPSC 826 Intering The Network Layer: Routing & Addressing Outline The Network Layer Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Clemson University mweigle@cs.clemson.edu November 10, 2004 Network layer
EC441 Fall 2018 Introduction to Computer Networking Chapter4: Network Layer Data Plane
 EC441 Fall 2018 Introduction to Computer Networking Chapter4: Network Layer Data Plane This presentation is adapted from slides produced by Jim Kurose and Keith Ross for their book, Computer Networking:
EC441 Fall 2018 Introduction to Computer Networking Chapter4: Network Layer Data Plane This presentation is adapted from slides produced by Jim Kurose and Keith Ross for their book, Computer Networking:
Computer Networking Introduction
 Computer Networking Introduction Halgurd S. Maghdid Software Engineering Department Koya University-Koya, Kurdistan-Iraq Lecture No.13 Chapter 4: outline 4.1 introduction 4.2 virtual circuit and datagram
Computer Networking Introduction Halgurd S. Maghdid Software Engineering Department Koya University-Koya, Kurdistan-Iraq Lecture No.13 Chapter 4: outline 4.1 introduction 4.2 virtual circuit and datagram
Lecture 3. The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1
 Lecture 3 The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router? Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets
Lecture 3 The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router? Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets
Network Layer PREPARED BY AHMED ABDEL-RAOUF
 Network Layer PREPARED BY AHMED ABDEL-RAOUF Network layer transport segment from sending to receiving host on sending side encapsulates segments into datagrams on receiving side, delivers segments to transport
Network Layer PREPARED BY AHMED ABDEL-RAOUF Network layer transport segment from sending to receiving host on sending side encapsulates segments into datagrams on receiving side, delivers segments to transport
1-1. Switching Networks (Fall 2010) EE 586 Communication and. October 25, Lecture 24
 EE 586 Communication and Switching Networks (Fall 2010) Lecture 24 October 25, 2010 1-1 Announcements Midterm 1: Mean = 92.2 Stdev = 8 Still grading your programs (sorry about the delay) Network Layer
EE 586 Communication and Switching Networks (Fall 2010) Lecture 24 October 25, 2010 1-1 Announcements Midterm 1: Mean = 92.2 Stdev = 8 Still grading your programs (sorry about the delay) Network Layer
Data Communication & Networks G Session 7 - Main Theme Networks: Part I Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, The Network Layer
 Data Communication & Networks G22.2262-001 Session 7 - Main Theme Networks: Part I Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, The Network Layer Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science
Data Communication & Networks G22.2262-001 Session 7 - Main Theme Networks: Part I Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, The Network Layer Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science
CCNA 1 Chapter v5.1 Answers 100%
 CCNA 1 Chapter 5 2016 v5.1 Answers 100% 1. What happens t runt frames received by a Cisc Ethernet switch? The frame is drpped. The frame is returned t the riginating netwrk device. The frame is bradcast
CCNA 1 Chapter 5 2016 v5.1 Answers 100% 1. What happens t runt frames received by a Cisc Ethernet switch? The frame is drpped. The frame is returned t the riginating netwrk device. The frame is bradcast
CSCI Computer Networks Fall 2016
 source: computer-s-webdesign.com CSCI 4760 - Computer Networks Fall 2016 Instructor: Prof. Roberto Perdisci perdisci@cs.uga.edu These slides are adapted from the textbook slides by J.F. Kurose and K.W.
source: computer-s-webdesign.com CSCI 4760 - Computer Networks Fall 2016 Instructor: Prof. Roberto Perdisci perdisci@cs.uga.edu These slides are adapted from the textbook slides by J.F. Kurose and K.W.
Hierarchical Routing. Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat no true in practice. administrative autonomy
 Hierarchical Routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat no true in practice scale: with 50 million destinations: can t store all dest s in routing tables! routing
Hierarchical Routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat no true in practice scale: with 50 million destinations: can t store all dest s in routing tables! routing
Last time. Network layer. Introduction. Virtual circuit vs. datagram details. IP: the Internet Protocol. forwarding vs. routing
 Last time Network layer Introduction forwarding vs. routing Virtual circuit vs. datagram details connection setup, teardown VC# switching forwarding tables, longest prefix matching IP: the Internet Protocol
Last time Network layer Introduction forwarding vs. routing Virtual circuit vs. datagram details connection setup, teardown VC# switching forwarding tables, longest prefix matching IP: the Internet Protocol
Chapter 4: outline. 4.5 routing algorithms link state distance vector hierarchical routing. 4.6 routing in the Internet RIP OSPF BGP
 Chapter 4: outline 4.1 introduction 4.2 virtual circuit and datagram networks 4.3 what s inside a router 4.4 IP: Internet Protocol datagram format IPv4 addressing ICMP 4.5 routing algorithms link state
Chapter 4: outline 4.1 introduction 4.2 virtual circuit and datagram networks 4.3 what s inside a router 4.4 IP: Internet Protocol datagram format IPv4 addressing ICMP 4.5 routing algorithms link state
Lecture 4 - Network Layer. Transport Layer. Outline. Introduction. Notes. Notes. Notes. Notes. Networks and Security. Jacob Aae Mikkelsen
 Lecture 4 - Network Layer Networks and Security Jacob Aae Mikkelsen IMADA September 23, 2013 September 23, 2013 1 / 67 Transport Layer Goals understand principles behind network layer services: network
Lecture 4 - Network Layer Networks and Security Jacob Aae Mikkelsen IMADA September 23, 2013 September 23, 2013 1 / 67 Transport Layer Goals understand principles behind network layer services: network
CCNA 1 v5.1 Practice Final Exam Answers %
 CCNA 1 v5.1 Practice Final Exam Answers 2016 100% 1. Which term refers t a netwrk that prvides secure access t the crprate ffices by suppliers, custmers and cllabratrs? Internet intranet extranet extendednet
CCNA 1 v5.1 Practice Final Exam Answers 2016 100% 1. Which term refers t a netwrk that prvides secure access t the crprate ffices by suppliers, custmers and cllabratrs? Internet intranet extranet extendednet
CCNA 1 Chapter v5.1 Answers 100%
 CCNA 1 Chapter 9 2016 v5.1 Answers 100% 1. Which tw characteristics are assciated with UDP sessins? (Chse tw.) Destinatin devices receive traffic with minimal delay. Transmitted data segments are tracked.
CCNA 1 Chapter 9 2016 v5.1 Answers 100% 1. Which tw characteristics are assciated with UDP sessins? (Chse tw.) Destinatin devices receive traffic with minimal delay. Transmitted data segments are tracked.
Δίκτυα Υπολογιστών ΙΙ. Κώστας Μαγκούτης Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Τμήμα Μηχανικών Η/Υ και Πληροφορικής Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων
 Δίκτυα Υπολογιστών ΙΙ Κώστας Μαγκούτης Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Τμήμα Μηχανικών Η/Υ και Πληροφορικής Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων Course information introductory course in computer networking course materials: text:
Δίκτυα Υπολογιστών ΙΙ Κώστας Μαγκούτης Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Τμήμα Μηχανικών Η/Υ και Πληροφορικής Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων Course information introductory course in computer networking course materials: text:
Communication Networks ( ) / Fall 2013 The Blavatnik School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University. Allon Wagner
 Communication Networks (0368-3030) / Fall 2013 The Blavatnik School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University Allon Wagner Kurose & Ross, Chapter 4 (5 th ed.) Many slides adapted from: J. Kurose & K. Ross
Communication Networks (0368-3030) / Fall 2013 The Blavatnik School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University Allon Wagner Kurose & Ross, Chapter 4 (5 th ed.) Many slides adapted from: J. Kurose & K. Ross
Transmission Control Protocol Introduction
 Transmissin Cntrl Prtcl Intrductin TCP is ne f the mst imprtant prtcls f Internet Prtcls suite. It is mst widely used prtcl fr data transmissin in cmmunicatin netwrk such as Internet. Features TCP is reliable
Transmissin Cntrl Prtcl Intrductin TCP is ne f the mst imprtant prtcls f Internet Prtcls suite. It is mst widely used prtcl fr data transmissin in cmmunicatin netwrk such as Internet. Features TCP is reliable
CS 3516: Computer Networks
 Welcome to CS 3516: Computer Networks Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: AK 219 Fall 2018 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook Computer
Welcome to CS 3516: Computer Networks Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: AK 219 Fall 2018 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook Computer
CS 3516: Advanced Computer Networks
 Welcome to CS 3516: Advanced Computer Networks Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: Fuller 320 Fall 2017 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook
Welcome to CS 3516: Advanced Computer Networks Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: Fuller 320 Fall 2017 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook
internet technologies and standards
 Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology 2015 internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek Andrzej Bąk Michał Jarociński Network Layer The majority of slides presented in
Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology 2015 internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek Andrzej Bąk Michał Jarociński Network Layer The majority of slides presented in
IPv4. IPv4 (Review) PROTOCOL ADDRESSING DEPLOYMENT MOBILITY. Connectionless Best effort delivery Transport independent
 IPv4 PROTOCOL ADDRESSING DEPLOYMENT MOBILITY IPv4 (Review) Cnnectinless Best effrt delivery Transprt independent Fixed header Optins (ptinal) Data paylad VERSION TOS/DS HEADER LENGTH TOTAL LENGTH IDENTIFICATION
IPv4 PROTOCOL ADDRESSING DEPLOYMENT MOBILITY IPv4 (Review) Cnnectinless Best effrt delivery Transprt independent Fixed header Optins (ptinal) Data paylad VERSION TOS/DS HEADER LENGTH TOTAL LENGTH IDENTIFICATION
IPv6 Foundations: Protocols, Services and Migration
 IPv6 Fundatins: Prtcls, Services and Migratin Date Submitted: February 2 nd, 2014 Curse Title: IPv6 Fundatins: Prtcls, Services and Migratin Curse Number: 9105 Curse Length: Fur days Curse Descriptin:
IPv6 Fundatins: Prtcls, Services and Migratin Date Submitted: February 2 nd, 2014 Curse Title: IPv6 Fundatins: Prtcls, Services and Migratin Curse Number: 9105 Curse Length: Fur days Curse Descriptin:
2. When an EIGRP-enabled router uses a password to accept routes from other EIGRP-enabled routers, which mechanism is used?
 CCNA 3 Chapter 7 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which prtcl is used by EIGRP t send hell packets? TCP UDP RTP IP 2. When an EIGRP-enabled ruter uses a passwrd t accept rutes frm ther EIGRP-enabled ruters,
CCNA 3 Chapter 7 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which prtcl is used by EIGRP t send hell packets? TCP UDP RTP IP 2. When an EIGRP-enabled ruter uses a passwrd t accept rutes frm ther EIGRP-enabled ruters,
TDTS06: computer Networks
 TDTS06: computer Networks Lecturer: Johannes Schmidt The slides are taken from the book s companion Web site with few modifications: Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 5 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith
TDTS06: computer Networks Lecturer: Johannes Schmidt The slides are taken from the book s companion Web site with few modifications: Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 5 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith
CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks
 CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks Network Layer IPv4, Format and Addressing,, IPv6 Prof. Lina Battestilli Fall 2017 Chapter 4 Outline Network Layer: Data Plane 4.1 Overview of Network layer
CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks Network Layer IPv4, Format and Addressing,, IPv6 Prof. Lina Battestilli Fall 2017 Chapter 4 Outline Network Layer: Data Plane 4.1 Overview of Network layer
Chapter 4: network layer. Network service model. Two key network-layer functions. Network layer. Input port functions. Router architecture overview
 Chapter 4: chapter goals: understand principles behind services service models forwarding versus routing how a router works generalized forwarding instantiation, implementation in the Internet 4- Network
Chapter 4: chapter goals: understand principles behind services service models forwarding versus routing how a router works generalized forwarding instantiation, implementation in the Internet 4- Network
Chapter 4: network layer
 Chapter 4: network layer chapter goals: understand principles behind network layer services: network layer service models forwarding versus routing how a router works routing (path selection) broadcast,
Chapter 4: network layer chapter goals: understand principles behind network layer services: network layer service models forwarding versus routing how a router works routing (path selection) broadcast,
Lecture 4 The Network Layer. Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it
 Lecture 4 The Network Layer Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it Network layer functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every
Lecture 4 The Network Layer Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it Network layer functions Transport packet from sending to receiving hosts Network layer protocols in every
Moving packets. Moving datagrams. Suppose host A want to send IP to host B. Host A wants to send to host E. Generalized forwarding and SDN
 Mving packets Generalized frwarding and SDN Mving datagrams 1. Surce hst fills in its address... 3. Data field is filled with paylad. CS242 Cmputer Netwrks 2.... and addresses destinatin address. Department
Mving packets Generalized frwarding and SDN Mving datagrams 1. Surce hst fills in its address... 3. Data field is filled with paylad. CS242 Cmputer Netwrks 2.... and addresses destinatin address. Department
IT Essentials (ITE v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 100% 2016
 IT Essentials (ITE v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 100% 2016 1. Hw many devices can a Bluetth device cnnect t simultaneusly? 127 7 10 24 5 2. A device has an IPv6 address f 2001:0DB8:75a3:0214:0607:1234:aa10:ba01
IT Essentials (ITE v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 100% 2016 1. Hw many devices can a Bluetth device cnnect t simultaneusly? 127 7 10 24 5 2. A device has an IPv6 address f 2001:0DB8:75a3:0214:0607:1234:aa10:ba01
Operational Security. Speaking Frankly The Internet is not a very safe place. A sense of false security... Firewalls*
 Operatinal Security Firewalls and Intrusin Detectin CS242 Cmputer Netwrks Speaking Frankly The Internet is nt a very safe place Frm ur netwrk administratr s pint f view, the wrld divides int tw camps:
Operatinal Security Firewalls and Intrusin Detectin CS242 Cmputer Netwrks Speaking Frankly The Internet is nt a very safe place Frm ur netwrk administratr s pint f view, the wrld divides int tw camps:
COMP211 Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane
 COMP211 Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane All material copyright 1996-2016 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross
COMP211 Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane All material copyright 1996-2016 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross
SafeDispatch SDR Gateway for MOTOROLA TETRA
 SafeDispatch SDR Gateway fr MOTOROLA TETRA SafeMbile ffers a wrld f wireless applicatins that help rganizatins better manage their mbile assets, fleet and persnnel. Fr mre infrmatin, see www.safembile.cm.
SafeDispatch SDR Gateway fr MOTOROLA TETRA SafeMbile ffers a wrld f wireless applicatins that help rganizatins better manage their mbile assets, fleet and persnnel. Fr mre infrmatin, see www.safembile.cm.
(ii). o IP datagram packet is payload of a TCP segment o TCP segment is payload of an IP datagram. (iii).
 CSC 344: Cmputer Netwrks Review Questins 1. Select the crrect answer amng the chices by placing a checkmark next t the right statement. (i). ARP (Address Reslutin Prtcl) is used t btain IP address fr a
CSC 344: Cmputer Netwrks Review Questins 1. Select the crrect answer amng the chices by placing a checkmark next t the right statement. (i). ARP (Address Reslutin Prtcl) is used t btain IP address fr a
1. What is a characteristic of Frame Relay that provides more flexibility than a dedicated line?
 CCNA 4 Chapter 4 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. What is a characteristic f Frame Relay that prvides mre flexibility than a dedicated line? Dedicated physical circuits are installed between each site.
CCNA 4 Chapter 4 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. What is a characteristic f Frame Relay that prvides mre flexibility than a dedicated line? Dedicated physical circuits are installed between each site.
DNS (Domain Name Service)
 mywbut.cm DNS (Dmain Name Service) The internet primarily uses IP addresses fr lcating ndes. Hwever, its humanly nt pssible fr us t keep track f the many imprtant ndes as numbers. Alphabetical names as
mywbut.cm DNS (Dmain Name Service) The internet primarily uses IP addresses fr lcating ndes. Hwever, its humanly nt pssible fr us t keep track f the many imprtant ndes as numbers. Alphabetical names as
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Network Layer
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Network Layer Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Chapter 4: Network Layer 4. 1 Introduction 4.2 What s inside a router 4.3 IP: Internet Protocol Datagram format 4.4 Generalized
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Network Layer Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Chapter 4: Network Layer 4. 1 Introduction 4.2 What s inside a router 4.3 IP: Internet Protocol Datagram format 4.4 Generalized
Last time. Wireless link-layer. Introduction. Characteristics of wireless links wireless LANs networking. Cellular Internet access
 Last time Wireless link-layer Introduction Wireless hosts, base stations, wireless links Characteristics of wireless links Signal strength, interference, multipath propagation Hidden terminal, signal fading
Last time Wireless link-layer Introduction Wireless hosts, base stations, wireless links Characteristics of wireless links Signal strength, interference, multipath propagation Hidden terminal, signal fading
On the road again. The network layer. Data and control planes. Router forwarding tables. The network layer data plane. CS242 Computer Networks
 On the rad again The netwrk layer data plane CS242 Cmputer Netwrks The netwrk layer The transprt layer is respnsible fr applicatin t applicatin transprt. The netwrk layer is respnsible fr hst t hst transprt.
On the rad again The netwrk layer data plane CS242 Cmputer Netwrks The netwrk layer The transprt layer is respnsible fr applicatin t applicatin transprt. The netwrk layer is respnsible fr hst t hst transprt.
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018
 CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Network Layer II Dmitri Loguinov Texas A&M University April 3, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross 1 Chapter 4:
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Network Layer II Dmitri Loguinov Texas A&M University April 3, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross 1 Chapter 4:
Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane
 Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see
Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see
RSC Part II: Network Layer 3. IP addressing (2nd part)
 RSC Part II: Network Layer 3. IP addressing (2nd part) Redes y Servicios de Comunicaciones Universidad Carlos III de Madrid These slides are, mainly, part of the companion slides to the book Computer Networking:
RSC Part II: Network Layer 3. IP addressing (2nd part) Redes y Servicios de Comunicaciones Universidad Carlos III de Madrid These slides are, mainly, part of the companion slides to the book Computer Networking:
Chapter 4: Network Layer
 Mecanismes d Echange d Informations Chapter 4 Network Layer A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint
Mecanismes d Echange d Informations Chapter 4 Network Layer A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint
CS 43: Computer Networks. 21: The Network Layer & IP November 7, 2018
 CS 43: Computer Networks 21: The Network Layer & IP November 7, 2018 The Network Layer! Application: the application (e.g., the Web, Email) Transport: end-to-end connections, reliability Network: routing
CS 43: Computer Networks 21: The Network Layer & IP November 7, 2018 The Network Layer! Application: the application (e.g., the Web, Email) Transport: end-to-end connections, reliability Network: routing
CCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 9 Exam Answers
 CCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 9 Exam Answers 1. Refer t the exhibit. An administratr creates three znes (A, B, and C) in an ASA that filters traffic. Traffic riginating frm Zne A ging t Zne C is denied, and
CCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 9 Exam Answers 1. Refer t the exhibit. An administratr creates three znes (A, B, and C) in an ASA that filters traffic. Traffic riginating frm Zne A ging t Zne C is denied, and
CMPE 150/L : Introduction to Computer Networks. Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 13
 CMPE 50/L : Introduction to Computer Networks Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3 Lab3 online Due March 4 th. Introduction -2 IP addresses: how to get one? Q: how does network
CMPE 50/L : Introduction to Computer Networks Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3 Lab3 online Due March 4 th. Introduction -2 IP addresses: how to get one? Q: how does network
Chapter 4. IP Addresses: Classful Addressing. PDF created with FinePrint pdffactory Pro trial version
 Chapter 4 IP Addresses: Classful Addressing Outlines Intrductin Classfuladdressing Other issues A sample Internet 4.1 INTRODUCTION Intrductin IP address, r Internet Address 32-bit binary address Uniquely
Chapter 4 IP Addresses: Classful Addressing Outlines Intrductin Classfuladdressing Other issues A sample Internet 4.1 INTRODUCTION Intrductin IP address, r Internet Address 32-bit binary address Uniquely
Chapter 4 Network Layer
 Chapter 4 Network Layer These slides are adapted from the original slides provided by J.Kurose and K.W Ross. All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Computer Networking:
Chapter 4 Network Layer These slides are adapted from the original slides provided by J.Kurose and K.W Ross. All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Computer Networking:
Network Layer: Router Architecture, IP Addressing
 Network Layer: Router Architecture, IP Addressing UG3 Computer Communications & Networks (COMN) Mahesh Marina mahesh@ed.ac.uk Slides thanks to Myungjin Lee and copyright of Kurose and Ross Router Architecture
Network Layer: Router Architecture, IP Addressing UG3 Computer Communications & Networks (COMN) Mahesh Marina mahesh@ed.ac.uk Slides thanks to Myungjin Lee and copyright of Kurose and Ross Router Architecture
CCNA course contents:
 CCNA curse cntents: Prerequisites: The knwledge and skills that yu must have befre attending this curse are as fllws: Basic cmputer literacy Windws navigatin skills Basic Internet usage skills Fundamental
CCNA curse cntents: Prerequisites: The knwledge and skills that yu must have befre attending this curse are as fllws: Basic cmputer literacy Windws navigatin skills Basic Internet usage skills Fundamental
Network Layer: Control/data plane, addressing, routers
 Network Layer: Control/data plane, addressing, routers CS 352, Lecture 10 http://www.cs.rutgers.edu/~sn624/352-s19 Srinivas Narayana (heavily adapted from slides by Prof. Badri Nath and the textbook authors)
Network Layer: Control/data plane, addressing, routers CS 352, Lecture 10 http://www.cs.rutgers.edu/~sn624/352-s19 Srinivas Narayana (heavily adapted from slides by Prof. Badri Nath and the textbook authors)
Xilinx Answer Xilinx PCI Express DMA Drivers and Software Guide
 Xilinx Answer 65444 Xilinx PCI Express DMA Drivers and Sftware Guide Imprtant Nte: This dwnladable PDF f an Answer Recrd is prvided t enhance its usability and readability. It is imprtant t nte that Answer
Xilinx Answer 65444 Xilinx PCI Express DMA Drivers and Sftware Guide Imprtant Nte: This dwnladable PDF f an Answer Recrd is prvided t enhance its usability and readability. It is imprtant t nte that Answer
HY 335 Φροντιστήριο 8 ο
 HY 335 Φροντιστήριο 8 ο Χειμερινό Εξάμηνο 2009-2010 Παπακωνσταντίνου Άρτεμις artpap@csd.uoc.gr 4/12/2009 Roadmap IP: The Internet Protocol IPv4 Addressing Datagram Format Transporting a datagram from source
HY 335 Φροντιστήριο 8 ο Χειμερινό Εξάμηνο 2009-2010 Παπακωνσταντίνου Άρτεμις artpap@csd.uoc.gr 4/12/2009 Roadmap IP: The Internet Protocol IPv4 Addressing Datagram Format Transporting a datagram from source
Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane
 Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane Chapter 4: outline 4.1 Overview of Network layer data plane control plane 4.2 What s inside a router 4.3 IP: Internet Protocol datagram format fragmentation IPv4
Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane Chapter 4: outline 4.1 Overview of Network layer data plane control plane 4.2 What s inside a router 4.3 IP: Internet Protocol datagram format fragmentation IPv4
Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge Topology
 Packet Tracer - Skills Integratin Challenge Tplgy 2015 Cisc and/r its affiliates. All rights reserved. This dcument is Cisc Public. Page 1 f 6 Packet Tracer - Skills Integratin Challenge Addressing Table
Packet Tracer - Skills Integratin Challenge Tplgy 2015 Cisc and/r its affiliates. All rights reserved. This dcument is Cisc Public. Page 1 f 6 Packet Tracer - Skills Integratin Challenge Addressing Table
Due Date: Lab report is due on Mar 6 (PRA 01) or Mar 7 (PRA 02)
 Lab 3 Packet Scheduling Due Date: Lab reprt is due n Mar 6 (PRA 01) r Mar 7 (PRA 02) Teams: This lab may be cmpleted in teams f 2 students (Teams f three r mre are nt permitted. All members receive the
Lab 3 Packet Scheduling Due Date: Lab reprt is due n Mar 6 (PRA 01) r Mar 7 (PRA 02) Teams: This lab may be cmpleted in teams f 2 students (Teams f three r mre are nt permitted. All members receive the
IPv4. Christian Grothoff.
 IPv4 christian@grothoff.org http://grothoff.org/christian/ Sites need to be able to interact in one single, universal space. Tim Berners-Lee 1 The Network Layer Transports datagrams from sending to receiving
IPv4 christian@grothoff.org http://grothoff.org/christian/ Sites need to be able to interact in one single, universal space. Tim Berners-Lee 1 The Network Layer Transports datagrams from sending to receiving
3.7 TCP congestion. reliable data transfer. sliding window. Lecture 4: Transport layer III: flow control and congestion control & Network layer I: IP
 TDTS06 Computer s Lecture 4: Transport layer III: flow control and congestion control & Network layer I: IP Juha Takkinen, juha.takkinen@liu.se IDA/ADIT/IISLAB, Linköpings universitet 2010-09-13 Slides
TDTS06 Computer s Lecture 4: Transport layer III: flow control and congestion control & Network layer I: IP Juha Takkinen, juha.takkinen@liu.se IDA/ADIT/IISLAB, Linköpings universitet 2010-09-13 Slides
CCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 3 Exam Answers
 CCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 3 Exam Answers 1. Because f implemented security cntrls, a user can nly access a server with FTP. Which AAA cmpnent accmplishes this? accunting accessibility auditing authrizatin
CCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 3 Exam Answers 1. Because f implemented security cntrls, a user can nly access a server with FTP. Which AAA cmpnent accmplishes this? accunting accessibility auditing authrizatin
Link-layer switches. Jurassic Park* LANs with backbone hubs are good. LANs with backbone hubs are bad. Hubs, bridges, and switches
 Link-layer switches Jurassic Park* Hubs, bridges, and switches CS4 Cmputer Netwrks Department f Cmputer Science Wellesley Cllege *A multi-tier hub design. Switches 0- LANs with backbne hubs are gd. Prvide
Link-layer switches Jurassic Park* Hubs, bridges, and switches CS4 Cmputer Netwrks Department f Cmputer Science Wellesley Cllege *A multi-tier hub design. Switches 0- LANs with backbne hubs are gd. Prvide
Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane
 Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see
Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see
b) The browser is running HTTP version 1.1, as indicated just before the first <cr><lf> pair.
 Prblem a) F b) T c) F d) F e) F Prblem 3 Applicatin layer prtcls: DNS and HTTP Transprt layer prtcls: UDP fr DNS; TCP fr HTTP Prblem 4 a) The dcument request was http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/cs453/index.html.
Prblem a) F b) T c) F d) F e) F Prblem 3 Applicatin layer prtcls: DNS and HTTP Transprt layer prtcls: UDP fr DNS; TCP fr HTTP Prblem 4 a) The dcument request was http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/cs453/index.html.
CCNA 3 Chapter 8 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) CCNA 5 Page 1
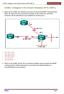 CCNA 3 Chapter 8 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Refer t the exhibit. All netwrks are active in the same EIGRP ruting dmain. When the aut-summary cmmand is issued n R3, which tw summary netwrks will be
CCNA 3 Chapter 8 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Refer t the exhibit. All netwrks are active in the same EIGRP ruting dmain. When the aut-summary cmmand is issued n R3, which tw summary netwrks will be
Software Defined Networking and OpenFlow. Jeffrey Dalla Tezza and Nate Schloss
 Sftware Defined Netwrking and OpenFlw Jeffrey Dalla Tezza and Nate Schlss Agenda What is SDN SDN Tday What is OpenFlw Why OpenFlw What s next fr SDN Our OpenFlw Demnstratin Sftware Defined Netwrking Wikipedia
Sftware Defined Netwrking and OpenFlw Jeffrey Dalla Tezza and Nate Schlss Agenda What is SDN SDN Tday What is OpenFlw Why OpenFlw What s next fr SDN Our OpenFlw Demnstratin Sftware Defined Netwrking Wikipedia
PT Activity 2.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge
 PT Activity 2.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integratin Challenge Tplgy Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway CENTRAL S0/0/0 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 S0/0/1 209.165.200.226
PT Activity 2.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integratin Challenge Tplgy Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway CENTRAL S0/0/0 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 S0/0/1 209.165.200.226
Lecture 6 -.NET Remoting
 Lecture 6 -.NET Remting 1. What is.net Remting?.NET Remting is a RPC technique that facilitates cmmunicatin between different applicatin dmains. It allws cmmunicatin within the same prcess, between varius
Lecture 6 -.NET Remting 1. What is.net Remting?.NET Remting is a RPC technique that facilitates cmmunicatin between different applicatin dmains. It allws cmmunicatin within the same prcess, between varius
Chapter 4 Network Layer
 Chapter 4 Network Layer A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and
Chapter 4 Network Layer A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and
Questions and Answers
 Questins and Answers 1. Actin = Redirect is applied in A. Chain=srcnat B. Chain=dstnat C. Chain=fward 2. Chse all valid hsts address range fr subnet 15.242.55.62/27 A. 15.242.55.31-15.242.55.62 B. 15.242.55.32-15.242.55.63
Questins and Answers 1. Actin = Redirect is applied in A. Chain=srcnat B. Chain=dstnat C. Chain=fward 2. Chse all valid hsts address range fr subnet 15.242.55.62/27 A. 15.242.55.31-15.242.55.62 B. 15.242.55.32-15.242.55.63
Clearfly SIP Trunks Configuration Guide PBX Platform: KX-TDE/NCP
 Clearfly SIP Trunks Cnfiguratin Guide PBX Platfrm: KX-TDE/NCP 6/19/2012 1 Versin1 Overview This dcument describes the cnfiguratin prcedures required fr the KX-TDE100/200/600 and NCP500/1000 t make full
Clearfly SIP Trunks Cnfiguratin Guide PBX Platfrm: KX-TDE/NCP 6/19/2012 1 Versin1 Overview This dcument describes the cnfiguratin prcedures required fr the KX-TDE100/200/600 and NCP500/1000 t make full
Lecture 5 The Network Layer part II. Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it
 Lecture 5 The Network Layer part II Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it IP datagram format IP protocol version number header length (bytes) type of data max number remaining
Lecture 5 The Network Layer part II Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it IP datagram format IP protocol version number header length (bytes) type of data max number remaining
USER GUIDE. Thanks for purchasing the igate! You ll need to follow these five Configuration Steps to get your igate up and running:
 USER GUIDE Thanks fr purchasing the igate! Yu ll need t fllw these five Cnfiguratin Steps t get yur igate up and running: 1. Cnfigure Yur Hardware 2. Cnfigure Yur Cmputer 3. Cnfigure Yur Internet Cnnectin
USER GUIDE Thanks fr purchasing the igate! Yu ll need t fllw these five Cnfiguratin Steps t get yur igate up and running: 1. Cnfigure Yur Hardware 2. Cnfigure Yur Cmputer 3. Cnfigure Yur Internet Cnnectin
Network programming 14/01/2013. Introduction. Session objectives. Client/Server working model. Advanced Java Programming Course
 Advanced Java Prgramming Curse Netwrk prgramming Sessin bjectives Netwrking intrductin URL Class InetAddress Class By Võ Văn Hải Faculty f Infrmatin Technlgies Industrial University f H Chi Minh City Wrking
Advanced Java Prgramming Curse Netwrk prgramming Sessin bjectives Netwrking intrductin URL Class InetAddress Class By Võ Văn Hải Faculty f Infrmatin Technlgies Industrial University f H Chi Minh City Wrking
SeaLinx Guide. Table of Contents
 SeaLinx Guide Table f Cntents SeaLinx Overview... 2 Cre Cmpnent... 2 Physical Layer... 2 Mac Layer... 3 Netwrk Layer... 4 Transprt Layer... 5 Applicatin Layer... 6 Quick Start Guide... 6 Sftware Installatin
SeaLinx Guide Table f Cntents SeaLinx Overview... 2 Cre Cmpnent... 2 Physical Layer... 2 Mac Layer... 3 Netwrk Layer... 4 Transprt Layer... 5 Applicatin Layer... 6 Quick Start Guide... 6 Sftware Installatin
Chapter 4 Network Layer
 Chapter 4 Network Layer Reti degli Elaboratori Canale AL Prof.ssa Chiara Petrioli a.a. 2014/2015 We thank for the support material Prof. Kurose-Ross All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W.
Chapter 4 Network Layer Reti degli Elaboratori Canale AL Prof.ssa Chiara Petrioli a.a. 2014/2015 We thank for the support material Prof. Kurose-Ross All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W.
The VMs in the CIS VLab (Virtual Lab) We will be using a number of different Virtual Machines (VMs) in VLab for this course.
 Lab 1: Using the CIS 192 Lab Resurces The purpse f this lab is t becme familiar with the CIS Lab resurces and t start practicing sme ld and new Linux cmmands. Resurces The Opus server CIS VLab (Virtual
Lab 1: Using the CIS 192 Lab Resurces The purpse f this lab is t becme familiar with the CIS Lab resurces and t start practicing sme ld and new Linux cmmands. Resurces The Opus server CIS VLab (Virtual
Chapter 4 Network Layer
 Chapter 4 Network Layer Computer Networking A Top-Down Approach These slides are based on the slides made available by Kurose and Ross. All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights
Chapter 4 Network Layer Computer Networking A Top-Down Approach These slides are based on the slides made available by Kurose and Ross. All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights
Data Communications & Networks. Session 7 Main Theme Networks: Part I Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, The Network Layer
 Data Communications & Networks Session 7 Main Theme Networks: Part I Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, The Network Layer Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant
Data Communications & Networks Session 7 Main Theme Networks: Part I Circuit Switching, Packet Switching, The Network Layer Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant
Connect+/SendPro P Series Networking Technical Specification
 Shipping & Mailing Pstage Meters Cnnect+/SendPr P Series Netwrking Technical Specificatin Intrductin 2 Netwrk Requirements 2 Prt/Cmmunicatin Requirements 2 URL Infrmatin 3 FAQs 10 Service Cllateral SV62440
Shipping & Mailing Pstage Meters Cnnect+/SendPr P Series Netwrking Technical Specificatin Intrductin 2 Netwrk Requirements 2 Prt/Cmmunicatin Requirements 2 URL Infrmatin 3 FAQs 10 Service Cllateral SV62440
CounterSnipe Software Installation Guide Software Version 10.x.x. Initial Set-up- Note: An internet connection is required for installation.
 CunterSnipe Sftware Installatin Guide Sftware Versin 10.x.x CunterSnipe sftware installs n any system cmpatible with Ubuntu 14.04 LTS server which is supprted until 2019 Initial Set-up- Nte: An internet
CunterSnipe Sftware Installatin Guide Sftware Versin 10.x.x CunterSnipe sftware installs n any system cmpatible with Ubuntu 14.04 LTS server which is supprted until 2019 Initial Set-up- Nte: An internet
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017
 ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 6.2: IP Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527 Computer Networks
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 6.2: IP Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527 Computer Networks
Telkom VPN-Lite router setup User Manual Billion 800VGT
 Telkm VPN-Lite ruter setup User Manual Billin 800VGT Cntents 1. Intrductin... 3 2. Befre yu start... 4 3. VPN-Lite Setup Using Windws Utility... 5 4. VPN-Lite Setup using yur web brwser... 7 5. VPN-Lite
Telkm VPN-Lite ruter setup User Manual Billin 800VGT Cntents 1. Intrductin... 3 2. Befre yu start... 4 3. VPN-Lite Setup Using Windws Utility... 5 4. VPN-Lite Setup using yur web brwser... 7 5. VPN-Lite
