administrivia talking about caches today including another in class worksheet
|
|
|
- Elizabeth Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 administrivia talking about caches today including another in class worksheet 1
2 memory hierarchy working on memory hierarchy now ranges from small and fast (registers) through big and almost fast (RAM) down to enormous and slow (disks) 2
3 Caches Cache goes between CPU and main memory 0.33ns CPU 70 ns RAM 3
4 Caches Cache goes between CPU and main memory 0.33ns CPU 70 ns RAM 3
5 Caches Cache goes between CPU and main memory 0.33ns CPU 5 ns cache 70 ns RAM 3
6 Caches data is held in main memory some data is more frequently used RAM A B C D E F G H I J K 4
7 Caches data is held in main memory some data is more frequently used Cache holds copy of some data from DRAM Cache A C D H J RAM A B C D E F G H I J K 4
8 Cache Hit If data looked for is in cache, called cache hit Cache A C D H J RAM A B C D E F G H I J K 5
9 Cache Miss If data looked for is not in cache, called cache miss Cache A C D H J RAM A B C D E F G H I J K 6
10 Cache line Cache is arranged as rows, each with address of first byte data starting with first byte data is called cache line ranges in size from 16 bytes to 256 bytes address always multiple of cache line size for 16 byte size, see 0, 16, 32, 48, 64,... address usually given in hex (0,10,20,30,40,...) 7
11 Cache example ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 8
12 finding data to read data from cache: 1) find cache line in cache (if its there) 2) find byte(s) in cache line 3) return bytes 9
13 finding ) find cache line in cache ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 10
14 finding ) find cache line in cache ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 10
15 finding data ) find byte(s) in cache line ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 11
16 finding data ) find byte(s) in cache line ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 11
17 Cache Miss If data is not in cache (cache miss) 1) choose line to replace 2) read in line from RAM (or lower cache) replacing chosen line 3) read data as before 12
18 Cache Miss 2000 line is not in cache ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 13
19 Cache Miss ) choose line to replace ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 14
20 Cache Miss ) read in line from RAM (or lower cache) ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 15
21 Cache Miss ) read in line from RAM (or lower cache) ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 15
22 Cache Miss ) read bytes from line as before A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 16
23 Fully Associative some caches allow any line to be anywhere must check all to find it can choose any line to replace called fully associative cache or set associative cache usually choose oldest line to replace longest since accessed least recently accessed 17
24 Direct Cache Direct cache only allows one place for any line usually driven off of address For address 21B4 assuming 16 byte cache line and 16 total lines in the cache 18
25 Direct Cache Direct cache only allows one place for any line usually driven off of address For address 21B4 4 is the byte within the cache line last digit gives 16 choices (0-F) for 16 bytes 19
26 Direct Cache Direct cache only allows one place for any line usually driven off of address For address 21B4 B (11) is which cache line gives 16 possible lines 2 digits would support 256 lines (1B in this case) 20
27 Direct Cache Direct cache only allows one place for any line usually driven off of address For address 21B4 21 become the tag (all the remaining parts) only data actually needed in address column my examples will use full address not tag 21
28 Direct Cache Example 3544 can only be one place ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 22
29 Direct Cache Example 3544 can only be one place ABCDEF FEDCBA A AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB ABABABAB FFFFFFFF AABB CCDDEEFF 22
30 An example Lets try to work an example in groups 23
31 Cache hit rate Hit rate is % of mem accesses found in cache need good hit rate for computer to run well Improved by bigger cache smaller cache line fully associative 24
32 cache line size big cache line easier to find (fewer to look through) slower to read in from memory often brings in memory unwanted hurts cache hit rate small cache line harder to find (more to look through) faster to read in from memory bring in just what s needed improves cache hit rate 25
ECE Lab 8. Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache. To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache.
 ECE 201 - Lab 8 Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache PURPOSE To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache. EQUIPMENT Simulation Software REQUIREMENTS Electronic copy of your
ECE 201 - Lab 8 Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache PURPOSE To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache. EQUIPMENT Simulation Software REQUIREMENTS Electronic copy of your
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
Memory Hierarchy. Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity. (Study Chapter 5)
 Memory Hierarchy Why are you dressed like that? Halloween was weeks ago! It makes me look faster, don t you think? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study
Memory Hierarchy Why are you dressed like that? Halloween was weeks ago! It makes me look faster, don t you think? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study
And in Review! ! Locality of reference is a Big Idea! 3. Load Word from 0x !
 CS61C L23 Caches II (1)! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 23 Caches II 2010-07-29!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! TOOLS THAT AUTOMATICALLY FIND SOFTWARE BUGS! Black Hat (a security
CS61C L23 Caches II (1)! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 23 Caches II 2010-07-29!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! TOOLS THAT AUTOMATICALLY FIND SOFTWARE BUGS! Black Hat (a security
Chapter 5. Memory Technology
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Memory Hierarchies. Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev. Fall Lecture 10, October 8, CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology
 Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Lecture 12: Memory hierarchy & caches
 Lecture 12: Memory hierarchy & caches A modern memory subsystem combines fast small memory, slower larger memories This lecture looks at why and how Focus today mostly on electronic memories. Next lecture
Lecture 12: Memory hierarchy & caches A modern memory subsystem combines fast small memory, slower larger memories This lecture looks at why and how Focus today mostly on electronic memories. Next lecture
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Fall 2017
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. Memory Hierarchy
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Hierarchy ECE468 memory.1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath Output Today s Topic:
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Hierarchy ECE468 memory.1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath Output Today s Topic:
COMP 3221: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems
 COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory
 Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures. Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI. Recall
 CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Memory Hierarchy (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Recall What is memory hierarchy? Where each level is located? Each level s speed,
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Memory Hierarchy (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Recall What is memory hierarchy? Where each level is located? Each level s speed,
Memory Hierarchy. Mehran Rezaei
 Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
UCB CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Asst. Proflecturer SOE Miki Garcia WHEN FIBER OPTICS IS TOO SLOW 07/16/2014: Wall Street Buys NATO Microwave Towers in
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Asst. Proflecturer SOE Miki Garcia WHEN FIBER OPTICS IS TOO SLOW 07/16/2014: Wall Street Buys NATO Microwave Towers in
and data combined) is equal to 7% of the number of instructions. Miss Rate with Second- Level Cache, Direct- Mapped Speed
 5.3 By convention, a cache is named according to the amount of data it contains (i.e., a 4 KiB cache can hold 4 KiB of data); however, caches also require SRAM to store metadata such as tags and valid
5.3 By convention, a cache is named according to the amount of data it contains (i.e., a 4 KiB cache can hold 4 KiB of data); however, caches also require SRAM to store metadata such as tags and valid
Chapter 5A. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
CS 3510 Comp&Net Arch
 CS 3510 Comp&Net Arch Cache P1 Dr. Ken Hoganson 2010 Von Neuman Architecture Instructions and Data Op Sys CPU Main Mem Secondary Store Disk I/O Dev Bus The Need for Cache Memory performance has not kept
CS 3510 Comp&Net Arch Cache P1 Dr. Ken Hoganson 2010 Von Neuman Architecture Instructions and Data Op Sys CPU Main Mem Secondary Store Disk I/O Dev Bus The Need for Cache Memory performance has not kept
Memory hierarchy and cache
 Memory hierarchy and cache QUIZ EASY 1). What is used to design Cache? a). SRAM b). DRAM c). Blend of both d). None. 2). What is the Hierarchy of memory? a). Processor, Registers, Cache, Tape, Main memory,
Memory hierarchy and cache QUIZ EASY 1). What is used to design Cache? a). SRAM b). DRAM c). Blend of both d). None. 2). What is the Hierarchy of memory? a). Processor, Registers, Cache, Tape, Main memory,
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2014 Lecture notes Get caching information form other lecture http://hssl.cs.jhu.edu/~randal/419/lectures/l8.5.caching.pdf
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2014 Lecture notes Get caching information form other lecture http://hssl.cs.jhu.edu/~randal/419/lectures/l8.5.caching.pdf
Administrivia. Expect new HW out today (functions in assembly!)
 Caching 1/25/19 Administrivia Expect new HW out today (functions in assembly!) Memory so far Big array indexed by the memory address accessed by load and store of various types Implicitly assumed: One
Caching 1/25/19 Administrivia Expect new HW out today (functions in assembly!) Memory so far Big array indexed by the memory address accessed by load and store of various types Implicitly assumed: One
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Review : Pipelining. Memory Hierarchy
 CS61C L11 Caches (1) CS61CL : Machine Structures Review : Pipelining The Big Picture Lecture #11 Caches 2009-07-29 Jeremy Huddleston!! Pipeline challenge is hazards "! Forwarding helps w/many data hazards
CS61C L11 Caches (1) CS61CL : Machine Structures Review : Pipelining The Big Picture Lecture #11 Caches 2009-07-29 Jeremy Huddleston!! Pipeline challenge is hazards "! Forwarding helps w/many data hazards
www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/
 CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 34 - Caches II 11/16/2007 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 1 What to do on a write hit? Two Options: Write-through update
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 34 - Caches II 11/16/2007 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 1 What to do on a write hit? Two Options: Write-through update
Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring
 Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK The Ideal World Instruction Supply Pipeline (Instruction execution) Data Supply - Zero-cycle latency - Infinite capacity - Zero cost - Perfect
Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK The Ideal World Instruction Supply Pipeline (Instruction execution) Data Supply - Zero-cycle latency - Infinite capacity - Zero cost - Perfect
UCB CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Google Glass may be one vision of the future of post-pc interfaces augmented reality with video
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Google Glass may be one vision of the future of post-pc interfaces augmented reality with video
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #24 Cache II 27-8-6 Scott Beamer, Instructor New Flow Based Routers CS61C L24 Cache II (1) www.anagran.com Caching Terminology When we try
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #24 Cache II 27-8-6 Scott Beamer, Instructor New Flow Based Routers CS61C L24 Cache II (1) www.anagran.com Caching Terminology When we try
Overview IN this chapter we will study. William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6th Edition
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6th Edition Chapter 4 Cache Memory Overview IN this chapter we will study 4.1 COMPUTER MEMORY SYSTEM OVERVIEW 4.2 CACHE MEMORY PRINCIPLES 4.3 ELEMENTS
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6th Edition Chapter 4 Cache Memory Overview IN this chapter we will study 4.1 COMPUTER MEMORY SYSTEM OVERVIEW 4.2 CACHE MEMORY PRINCIPLES 4.3 ELEMENTS
Memory Hierarchy. Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity. (Study Chapter 5)
 Memory Hierarchy It makes me look faster, don t you think? Are you dressed like the Easter Bunny? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study Chapter 5)
Memory Hierarchy It makes me look faster, don t you think? Are you dressed like the Easter Bunny? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study Chapter 5)
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design
 CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Virtual Memory 11282011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Review Cache Virtual Memory Projects 3 Memory
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Virtual Memory 11282011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Review Cache Virtual Memory Projects 3 Memory
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Direct Mapped Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
1" 0" d" c" b" a" ...! ! Benefits of Larger Block Size. " Very applicable with Stored-Program Concept " Works well for sequential array accesses
 Asst. Proflecturer SOE Miki Garcia inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III WHEN FIBER OPTICS IS TOO SLOW 07/16/2014: Wall Street Buys NATO Microwave Towers in
Asst. Proflecturer SOE Miki Garcia inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III WHEN FIBER OPTICS IS TOO SLOW 07/16/2014: Wall Street Buys NATO Microwave Towers in
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17: Cache System
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Caches
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 218 More Caches 1 Announcements Prelim 2 stats High: 79.5 (out of 8), Mean: 65.9, Median: 68 Prelab 5(C) deadline extended to Saturday 3pm No further
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 218 More Caches 1 Announcements Prelim 2 stats High: 79.5 (out of 8), Mean: 65.9, Median: 68 Prelab 5(C) deadline extended to Saturday 3pm No further
Memory memories memory
 Memory Organization Memory Hierarchy Memory is used for storing programs and data that are required to perform a specific task. For CPU to operate at its maximum speed, it required an uninterrupted and
Memory Organization Memory Hierarchy Memory is used for storing programs and data that are required to perform a specific task. For CPU to operate at its maximum speed, it required an uninterrupted and
Spring 2016 :: CSE 502 Computer Architecture. Caches. Nima Honarmand
 Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Improving System. Performance: Caches
 Improving System Performance: Caches December 04 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 A Motivating Example Application: making a (mechanical) clock dozens of tools and pages of instructions, hundreds of parts
Improving System Performance: Caches December 04 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 A Motivating Example Application: making a (mechanical) clock dozens of tools and pages of instructions, hundreds of parts
Cache Memory Mapping Techniques. Continue to read pp
 Cache Memory Mapping Techniques Continue to read pp. 289-305 Cache Memory Mapping Again cache memory is a small and fast memory between CPU and main memory A block of words have to be brought in and out
Cache Memory Mapping Techniques Continue to read pp. 289-305 Cache Memory Mapping Again cache memory is a small and fast memory between CPU and main memory A block of words have to be brought in and out
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 2007-04-11 Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks says they may exclusively release movies in this format. It s based
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 2007-04-11 Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks says they may exclusively release movies in this format. It s based
Binghamton University. CS-220 Spring Cached Memory. Computer Systems Chapter
 Cached Memory Computer Systems Chapter 6.2-6.5 Cost Speed The Memory Hierarchy Capacity The Cache Concept CPU Registers Addresses Data Memory ALU Instructions The Cache Concept Memory CPU Registers Addresses
Cached Memory Computer Systems Chapter 6.2-6.5 Cost Speed The Memory Hierarchy Capacity The Cache Concept CPU Registers Addresses Data Memory ALU Instructions The Cache Concept Memory CPU Registers Addresses
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Lecture 33 Caches III What to do on a write hit? Block Size Tradeoff (1/3) Benefits of Larger Block Size
 CS61C L33 Caches III (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 27-4-11 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks
CS61C L33 Caches III (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 27-4-11 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-12a Caches-1 The basics of caches Shakil M. Khan Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-12a Caches-1 The basics of caches Shakil M. Khan Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB
Caches. Hiding Memory Access Times
 Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures CS61C L22 Caches II (1) CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 2005-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE,
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures CS61C L22 Caches II (1) CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 2005-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
Review: Performance Latency vs. Throughput. Time (seconds/program) is performance measure Instructions Clock cycles Seconds.
 Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Memory Hierarchy and Cache Ch 4-5
 Memory Hierarchy and Cache Ch 4-5 Memory Hierarchy Main Memory Cache Implementation 1 Teemu s Cheesecake hand table Register, on-chip cache, memory, disk, and tape speeds relative to times locating cheese
Memory Hierarchy and Cache Ch 4-5 Memory Hierarchy Main Memory Cache Implementation 1 Teemu s Cheesecake hand table Register, on-chip cache, memory, disk, and tape speeds relative to times locating cheese
Homework 6. BTW, This is your last homework. Assigned today, Tuesday, April 10 Due time: 11:59PM on Monday, April 23. CSCI 402: Computer Architectures
 Homework 6 BTW, This is your last homework 5.1.1-5.1.3 5.2.1-5.2.2 5.3.1-5.3.5 5.4.1-5.4.2 5.6.1-5.6.5 5.12.1 Assigned today, Tuesday, April 10 Due time: 11:59PM on Monday, April 23 1 CSCI 402: Computer
Homework 6 BTW, This is your last homework 5.1.1-5.1.3 5.2.1-5.2.2 5.3.1-5.3.5 5.4.1-5.4.2 5.6.1-5.6.5 5.12.1 Assigned today, Tuesday, April 10 Due time: 11:59PM on Monday, April 23 1 CSCI 402: Computer
CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches. Marco Paolieri Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook
 CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches Marco Paolieri (paolieri@usc.edu) Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook The Memory Hierarchy So far... We modeled the memory system as an abstract array
CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches Marco Paolieri (paolieri@usc.edu) Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook The Memory Hierarchy So far... We modeled the memory system as an abstract array
ELE 758 * DIGITAL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING * MIDTERM TEST * Circle the memory type based on electrically re-chargeable elements
 ELE 758 * DIGITAL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING * MIDTERM TEST * Student name: Date: Example 1 Section: Memory hierarchy (SRAM, DRAM) Question # 1.1 Circle the memory type based on electrically re-chargeable elements
ELE 758 * DIGITAL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING * MIDTERM TEST * Student name: Date: Example 1 Section: Memory hierarchy (SRAM, DRAM) Question # 1.1 Circle the memory type based on electrically re-chargeable elements
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-12 Caches-1 The basics of caches Shakil M. Khan Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-12 Caches-1 The basics of caches Shakil M. Khan Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB
UCB CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 32 Caches III 2008-04-16 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Hi to Chin Han from U Penn! Prem Kumar of Northwestern has created a quantum inverter
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 32 Caches III 2008-04-16 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Hi to Chin Han from U Penn! Prem Kumar of Northwestern has created a quantum inverter
Chapter 6 Objectives
 Chapter 6 Memory Chapter 6 Objectives Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured.
Chapter 6 Memory Chapter 6 Objectives Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured.
Caches. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Caches Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns
Caches Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ 10/18/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ 10/18/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
Registers. Instruction Memory A L U. Data Memory C O N T R O L M U X A D D A D D. Sh L 2 M U X. Sign Ext M U X ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH
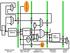 PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
Lecture 8: Virtual Memory. Today: DRAM innovations, virtual memory (Sections )
 Lecture 8: Virtual Memory Today: DRAM innovations, virtual memory (Sections 5.3-5.4) 1 DRAM Technology Trends Improvements in technology (smaller devices) DRAM capacities double every two years, but latency
Lecture 8: Virtual Memory Today: DRAM innovations, virtual memory (Sections 5.3-5.4) 1 DRAM Technology Trends Improvements in technology (smaller devices) DRAM capacities double every two years, but latency
MIPS) ( MUX
 Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
Chapter 7: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 7: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Basic Memory Requirements Users/Programmers Demand: Large computer memory ery Fast access memory Technology Limitations Large Computer memory relatively
Chapter 7: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Basic Memory Requirements Users/Programmers Demand: Large computer memory ery Fast access memory Technology Limitations Large Computer memory relatively
Internal Memory Cache Stallings: Ch 4, Ch 5 Key Characteristics Locality Cache Main Memory
 Lecture 3 Internal Memory Cache Stallings: Ch 4, Ch 5 Key Characteristics Locality Cache Main Memory Key Characterics of Memories / Storage (Sta06 Table 4.1) 26.1.2010 2 Goals I want my memory lightning
Lecture 3 Internal Memory Cache Stallings: Ch 4, Ch 5 Key Characteristics Locality Cache Main Memory Key Characterics of Memories / Storage (Sta06 Table 4.1) 26.1.2010 2 Goals I want my memory lightning
Memory Hierarchy and Cache Ch 4-5. Memory Hierarchy Main Memory Cache Implementation
 Memory Hierarchy and Cache Ch 4-5 Memory Hierarchy Main Memory Cache Implementation 1 Teemu s Cheesecake hand table Register, on-chip cache, memory, disk, and tape speeds relative to times locating cheese
Memory Hierarchy and Cache Ch 4-5 Memory Hierarchy Main Memory Cache Implementation 1 Teemu s Cheesecake hand table Register, on-chip cache, memory, disk, and tape speeds relative to times locating cheese
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Locality. Cache. Direct Mapped Cache. Direct Mapped Cache
 Locality A principle that makes having a memory hierarchy a good idea If an item is referenced, temporal locality: it will tend to be referenced again soon spatial locality: nearby items will tend to be
Locality A principle that makes having a memory hierarchy a good idea If an item is referenced, temporal locality: it will tend to be referenced again soon spatial locality: nearby items will tend to be
Main Memory Supporting Caches
 Main Memory Supporting Caches Use DRAMs for main memory Fixed width (e.g., 1 word) Connected by fixed-width clocked bus Bus clock is typically slower than CPU clock Cache Issues 1 Example cache block read
Main Memory Supporting Caches Use DRAMs for main memory Fixed width (e.g., 1 word) Connected by fixed-width clocked bus Bus clock is typically slower than CPU clock Cache Issues 1 Example cache block read
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology CACHE MEMORY. Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy.
 Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture CACHE MEMORY Introduction Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy. At the highest
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture CACHE MEMORY Introduction Computer memory is organized into a hierarchy. At the highest
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS. Spring 2014 Lecture 14
 CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2014 Lecture 14 LAST TIME! Examined several memory technologies: SRAM volatile memory cells built from transistors! Fast to use, larger memory cells (6+ transistors
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2014 Lecture 14 LAST TIME! Examined several memory technologies: SRAM volatile memory cells built from transistors! Fast to use, larger memory cells (6+ transistors
Memory. Lecture 22 CS301
 Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Cache Memory - II. Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB)
 Cache Memory - II Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB) Outline Direct-Mapped Cache Types of Cache Misses A (long) detailed example Peer - to - peer education example Block Size Tradeoff
Cache Memory - II Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB) Outline Direct-Mapped Cache Types of Cache Misses A (long) detailed example Peer - to - peer education example Block Size Tradeoff
! CS61C : Machine Structures. Lecture 22 Caches I. !!Instructor Paul Pearce! ITʼS NOW LEGAL TO JAILBREAK YOUR PHONE!
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 22 Caches I 2010-07-28!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! ITʼS NOW LEGAL TO JAILBREAK YOUR PHONE! On Monday the Library of Congress added 5 exceptions
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 22 Caches I 2010-07-28!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! ITʼS NOW LEGAL TO JAILBREAK YOUR PHONE! On Monday the Library of Congress added 5 exceptions
Key Point. What are Cache lines
 Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Cache memory. Lecture 4. Principles, structure, mapping
 Cache memory Lecture 4 Principles, structure, mapping Computer memory overview Computer memory overview By analyzing memory hierarchy from top to bottom, the following conclusions can be done: a. Cost
Cache memory Lecture 4 Principles, structure, mapping Computer memory overview Computer memory overview By analyzing memory hierarchy from top to bottom, the following conclusions can be done: a. Cost
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1)
 Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
LECTURE 11. Memory Hierarchy
 LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
WEEK 7. Chapter 4. Cache Memory Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved.
 WEEK 7 + Chapter 4 Cache Memory Location Internal (e.g. processor registers, cache, main memory) External (e.g. optical disks, magnetic disks, tapes) Capacity Number of words Number of bytes Unit of Transfer
WEEK 7 + Chapter 4 Cache Memory Location Internal (e.g. processor registers, cache, main memory) External (e.g. optical disks, magnetic disks, tapes) Capacity Number of words Number of bytes Unit of Transfer
Memory Hierarchy. Goal: Fast, unlimited storage at a reasonable cost per bit.
 Memory Hierarchy Goal: Fast, unlimited storage at a reasonable cost per bit. Recall the von Neumann bottleneck - single, relatively slow path between the CPU and main memory. Fast: When you need something
Memory Hierarchy Goal: Fast, unlimited storage at a reasonable cost per bit. Recall the von Neumann bottleneck - single, relatively slow path between the CPU and main memory. Fast: When you need something
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
Lctures 33: Cache Memory - I. Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB)
 Lctures 33: Cache Memory - I Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB) Outline Memory Hierarchy On-Chip SRAM Direct-Mapped Cache Review: ARM System Architecture Fast on-chip RAM External
Lctures 33: Cache Memory - I Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB) Outline Memory Hierarchy On-Chip SRAM Direct-Mapped Cache Review: ARM System Architecture Fast on-chip RAM External
MEMORY. Objectives. L10 Memory
 MEMORY Reading: Chapter 6, except cache implementation details (6.4.1-6.4.6) and segmentation (6.5.5) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/probability 2 Objectives Understand the concepts and terminology of hierarchical
MEMORY Reading: Chapter 6, except cache implementation details (6.4.1-6.4.6) and segmentation (6.5.5) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/probability 2 Objectives Understand the concepts and terminology of hierarchical
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University The Simple View of Memory The simplest view
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University The Simple View of Memory The simplest view
Block Size Tradeoff (1/3) Benefits of Larger Block Size. Lecture #22 Caches II Block Size Tradeoff (3/3) Block Size Tradeoff (2/3)
 CS61C L22 Caches II (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 25-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE, new
CS61C L22 Caches II (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 25-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE, new
Let!s go back to a course goal... Let!s go back to a course goal... Question? Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies
 1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of
1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of
Physical characteristics (such as packaging, volatility, and erasability Organization.
 CS 320 Ch 4 Cache Memory 1. The author list 8 classifications for memory systems; Location Capacity Unit of transfer Access method (there are four:sequential, Direct, Random, and Associative) Performance
CS 320 Ch 4 Cache Memory 1. The author list 8 classifications for memory systems; Location Capacity Unit of transfer Access method (there are four:sequential, Direct, Random, and Associative) Performance
EE 457 Unit 7a. Cache and Memory Hierarchy
 EE 457 Unit 7a Cache and Memory Hierarchy 2 Memory Hierarchy & Caching Use several levels of faster and faster memory to hide delay of upper levels Registers Unit of Transfer:, Half, or Byte (LW, LH, LB
EE 457 Unit 7a Cache and Memory Hierarchy 2 Memory Hierarchy & Caching Use several levels of faster and faster memory to hide delay of upper levels Registers Unit of Transfer:, Half, or Byte (LW, LH, LB
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 35 Caches IV / VM I 2004-11-19 Andy Carle inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c-ta Google strikes back against recent encroachments into the Search
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 35 Caches IV / VM I 2004-11-19 Andy Carle inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c-ta Google strikes back against recent encroachments into the Search
Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches. Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky
 Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky Review Hazards reduce effectiveness of pipelining Cause stalls/bubbles Structural Hazards Conflict in use of datapath component Data
Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky Review Hazards reduce effectiveness of pipelining Cause stalls/bubbles Structural Hazards Conflict in use of datapath component Data
Advanced Memory Organizations
 CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
Cache Policies. Philipp Koehn. 6 April 2018
 Cache Policies Philipp Koehn 6 April 2018 Memory Tradeoff 1 Fastest memory is on same chip as CPU... but it is not very big (say, 32 KB in L1 cache) Slowest memory is DRAM on different chips... but can
Cache Policies Philipp Koehn 6 April 2018 Memory Tradeoff 1 Fastest memory is on same chip as CPU... but it is not very big (say, 32 KB in L1 cache) Slowest memory is DRAM on different chips... but can
Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" Why it s important " Fundamental lesson(s)" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter
 Processor components" Multicore processors and programming" Processor comparison" vs." Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" CSE 30321" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter 5.1-5.2)" Writing more "
Processor components" Multicore processors and programming" Processor comparison" vs." Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" CSE 30321" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter 5.1-5.2)" Writing more "
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Caches
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 More Caches 1 Prelim 2 stats High: 9 (out of 9) Mean: 7.2, Median: 73 Announcements Prelab 5(C) due tomorrow 2 Example: Direct Mapped (DM) Cache
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 More Caches 1 Prelim 2 stats High: 9 (out of 9) Mean: 7.2, Median: 73 Announcements Prelab 5(C) due tomorrow 2 Example: Direct Mapped (DM) Cache
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/16/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/16/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved.
 + William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved. 2 + Chapter 4 Cache Memory 3 Location Internal (e.g. processor registers,
+ William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved. 2 + Chapter 4 Cache Memory 3 Location Internal (e.g. processor registers,
Chapter Seven. Memories: Review. Exploiting Memory Hierarchy CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY
 Chapter Seven CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY 1 Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored
Chapter Seven CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY 1 Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
CPU Pipelining Issues
 CPU Pipelining Issues What have you been beating your head against? This pipe stuff makes my head hurt! L17 Pipeline Issues & Memory 1 Pipelining Improve performance by increasing instruction throughput
CPU Pipelining Issues What have you been beating your head against? This pipe stuff makes my head hurt! L17 Pipeline Issues & Memory 1 Pipelining Improve performance by increasing instruction throughput
10/16/17. Outline. Outline. Typical Memory Hierarchy. Adding Cache to Computer. Key Cache Concepts
 // CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ Organization and Principles Write Back vs Write Through
// CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ Organization and Principles Write Back vs Write Through
