Chapter 8 I/O. Computing Layers. I/O: Connecting to Outside World. I/O: Connecting to the Outside World
|
|
|
- Clifford Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computing Layers Problems Chapter 8 I/O Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Algorithms Language Instruction Set Architecture Microarchitecture Circuits Devices I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory But where does data in memory come from? And how does data get out of the system so that humans can use it? I/O: Connecting to the Outside World Types of I/O devices characterized by: behavior: input, output, storage input: keyboard, motion detector, network interface output: monitor, printer, network interface storage: disk, CD-ROM data rate: how fast can data be transferred? keyboard: < 100 bytes/sec disk: 30 MB/s network: 1 Mb/s - 1 Gb/s 1
2 I/O Controller Control/Status Registers CPU tells device what to do -- write to control register CPU checks if task is done -- read status register Data Registers CPU transfers data to/from device CPU Control/Status Graphics Controller Output Data Electronics display Device electronics performs actual operation pixels to screen, bits to disk, chars from keyboard Programming Interface How are device registers identified? Memory-mapped vs. special instructions How is timing of transfer managed? Asynchronous vs. synchronous Who controls transfer? CPU (polling) vs. device (interrupts) Memory-Mapped vs. I/O Instructions Transfer Timing Instructions designate opcode(s) for I/O register and operation encoded in instruction Memory-mapped assign a memory address to each device register use data movement instructions (load/store) for control and data transfer I/O events generally happen much slower than CPU cycles. Synchronous data supplied at a fixed, predictable rate CPU reads/writes every X cycles Asynchronous data rate less predictable CPU must synchronize with device, so that it doesn t miss data or write too quickly 2
3 Transfer Control Who determines when the next data transfer occurs? Polling CPU keeps checking status register until new data arrives OR device ready for next data Are we there yet? Are we there yet? Are we Interrupts Device sends a special signal to CPU when new data arrives OR device ready for next data CPU can be performing other tasks instead of polling device. Wake me when we get there. LC-3 Memory-mapped I/O (Table A.3) Location I/O Register Function xfe00 xfe02 xfe04 xfe06 Keyboard Status (KBSR) Keyboard Data (KBDR) Display Status (DSR) Display Data (DDR) Asynchronous devices synchronized through status registers Polling and Interrupts Interrupt details will be discussed in Chapter 10 Bit [15] is one when keyboard has received a new character. Bits [7:0] contain the last character typed on keyboard. Bit [15] is one when device ready to display char on screen. Character written to bits [7:0] will be displayed on screen. Input from Keyboard Basic Input Routine When a character is typed: its ASCII code is placed in bits [7:0] of KBDR (bits [15:8] are always zero) the ready bit (KBSR[15]) is set to one keyboard is disabled -- any typed characters will be ignored keyboard KBDR data ready bit When KBDR is read: KBSR[15] is set to zero keyboard is enabled KBSR Polling NO new char? YES read character POLL LDI R0, KBSRPtr BRzp POLL LDI R0, KBDRPtr... KBSRPtr.FILL xfe00 KBDRPtr.FILL xfe02 3
4 Simple Implementation: Memory- Mapped Input Address Control Logic determines whether MDR is loaded from Memory or from KBSR/KBDR. Output to Monitor When Monitor is ready to display another character: the ready bit (DSR[15]) is set to one output data ready bit When data is written to Display Data Register: DSR[15] is set to zero character in DDR[7:0] is displayed any other character data written to DDR is ignored DDR DSR Basic Output Routine Simple Implementation: Memory- Mapped Output Polling NO screen ready? YES write character POLL LDI R1, DSRPtr BRzp POLL STI R0, DDRPtr... DSRPtr.FILL xfe04 DDRPtr.FILL xfe06 Sets LD.DDR or selects DSR as input. 4
5 Keyboard Echo Routine Usually, input character is also printed to screen. User gets feedback on character typed and knows its ok to type the next character. POLL1 POLL2 LDI R0, KBSRPtr BRzp POLL1 LDI R0, KBDRPtr LDI R1, DSRPtr BRzp POLL2 STI R0, DDRPtr... KBSRPtr.FILL xfe00 KBDRPtr.FILL xfe02 DSRPtr.FILL xfe04 DDRPtr.FILL xfe06 NO NO new char? YES read character screen ready? YES write character External device can: Interrupt-Driven I/O (1)Force currently executing program to stop. (2)Have the processor satisfy the device needs. (3)Resume the program as if nothing happened. Why? Polling consumes a lot of cycles, especially for rare events these cycles can be used for more computation. I/O device is faster than the CPU. Example: Process previous input while collecting current input. (See Example 8.1 in text.) Interrupt-Driven I/O To implement an interrupt mechanism, we need: A way for the I/O device to signal the CPU that an interesting event has occurred. A way for the CPU to test if the interrupt signal is set and if its priority is higher than current program. Generating Signal Software sets "interrupt enable" bit in device register. When ready and IE bits are set, interrupt is signaled. interrupt enable bit ready bit KBSR interrupt signal to processor Priority Every instruction executes at a stated level of urgency. LC-3: 8 priority levels (PL0-PL7) Example: Payroll program runs at PL0. Nuclear power correction program runs at PL6. It s OK for PL6 device to interrupt PL0 program, but not the other way around. Priority encoder selects highest-priority device, compares to current processor priority level, and generates interrupt signal if appropriate. 5
6 Testing for Interrupt Signal CPU looks at signal between STORE and FETCH phases. If not set, continues with next instruction. If set, transfers control to interrupt service NO routine. Transfer to ISR YES interrupt signal? F D EA OP Full Implementation of LC-3 Memory- Mapped I/O More details in Chapter 10. EX S Because of interrupt enable bits, status registers (KBSR/DSR) must be written, as well as read. Review Questions Review Questions What is the danger of not testing the DSR before writing data to the screen? What is the danger of not testing the KBSR before reading data from the keyboard? What if the Monitor were a synchronous device, e.g., we know that it will be ready 1 microsecond after character is written. Can we avoid polling? How? What are advantages and disadvantages? Do you think polling is a good approach for other devices, such as a disk or a network interface? What is the advantage of using LDI/STI for accessing device registers? 6
7 Interrupt-Driven I/O (Part 2) See Chapter 10.2 Exception: Internal Interrupt When something unexpected happens inside the processor, it may cause an exception. Examples: Privileged operation (e.g., RTI in user mode) Executing an illegal opcode Divide by zero Accessing an illegal address (e.g., protected system memory) Handled just like an interrupt Vector is determined internally by type of exception Priority is the same as running program CS270 - Fall Semester Interrupt-Driven I/O (Part 2) Interrupts were introduced in Chapter External device signals need to be serviced. 2. Processor saves state and starts service routine. 3. When finished, processor restores state and resumes program. Interrupt is an unscripted subroutine call, triggered by an external event. Chapter 8 didn t explain how (2) and (3) occur, because it involves a stack. Now, we re ready Processor State What state is needed to completely capture the state of a running process? Processor Status Register Privilege [15], Priority Level [10:8], Condition Codes [2:0] Program Counter Pointer to next instruction to be executed. Registers Temporary process state that s not stored in memory
8 Where to Save Processor State? Can t use registers. Programmer doesn t know when interrupt might occur, so she can t prepare by saving critical registers. When resuming, need to restore state exactly as it was. Memory allocated by service routine? Must save state before invoking routine, so we wouldn t know where. Also, interrupts may be nested that is, an interrupt service routine might also get interrupted! Use a stack! Location of stack hard-wired. Push state to save, pop to restore. 29 Supervisor Stack A special region of memory used as the stack for interrupt service routines. Initial Supervisor Stack Pointer (SSP) stored in Saved.SSP. Another register for storing User Stack Pointer (USP): Saved.USP. Want to use R6 as stack pointer. So that our PUSH/POP routines still work. When switching from User mode to Supervisor mode (as result of interrupt), save R6 to Saved.USP. 30 Invoking the Service Routine (Details) 1. If Priv = 1 (user), Saved.USP = R6, then R6 = Saved.SSP. 2. Push PSR and to Supervisor Stack. 3. Set PSR[15] = 0 (supervisor mode). 4. Set PSR[10:8] = priority of interrupt being serviced. 5. Set PSR[2:0] = Set MAR = x01vv, where vv = 8-bit interrupt vector provided by interrupting device (e.g., keyboard = x80). 7. Load memory location (M[x01vv]) into MDR. 8. Set = MDR; now first instruction of ISR will be fetched. Note: This all happens between the STORE RESULT of the last user instruction and the FETCH of the first ISR instruction. 31 Returning from Interrupt Special instruction RTI that restores state. 1. Pop from supervisor stack: ( = M[R6]; R6 = R6 + 1) 2. Pop PSR from supervisor stack: (PSR = M[R6]; R6 = R6 + 1) 3. If going back to user mode, need to restore User Stack Pointer: (if PSR[15] = 1, R6 = Saved.USP) RTI is a privileged instruction. Can only be executed in Supervisor Mode. If executed in User Mode, causes an exception. (More about that later.) 32 8
9 Example (1) Example (2) Saved.SSP Device B R6 PSR for A x6210 RTI x3006 Executing ADD at location x3006 when Device B interrupts. Saved.USP = R6. R6 = Saved.SSP. Push PSR and onto stack, then transfer to Device B service routine (at ) Example (3) Example (4) R6 PSR for A Device B x6202 AND x6210 RTI R6 x6203 PSR for B PSR for A Device B x6202 AND x6210 RTI x6300 Device C x6203 x6300 x6315 RTI Executing AND at x6202 when Device C interrupts. Push PSR and onto stack, then transfer to Device C service routine (at x6300)
10 Example (5) Example (6) R6 x6203 PSR for B PSR for A Device B x6202 AND x6210 RTI x6300 Device C Saved.SSP x6203 PSR for B PSR for A Device B x6202 AND x6210 RTI x6300 Device C x6203 x6315 RTI x6315 RTI Execute RTI at x6315; pop and PSR from stack. Execute RTI at x6210; pop PSR and from stack. Restore R6. Continue as if nothing happened
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Computing Layers
 Chapter 8 I/O Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language Instruction
Chapter 8 I/O Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language Instruction
I/O. University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell
 I/O University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory
I/O University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory
LC-3 Input and Output
 LC-3 Input and Output I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory use the TRAP
LC-3 Input and Output I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory use the TRAP
LC-3 Input and Output
 LC-3 Input and Output I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory use the TRAP
LC-3 Input and Output I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory use the TRAP
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 8 & 9.1 I/O and Traps I/O: Connecting to Outside World So
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 8 & 9.1 I/O and Traps I/O: Connecting to Outside World So
Input & Output. Lecture 16. James Goodman (revised by Robert Sheehan) Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 Lecture Notes
 Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 Lecture Notes Lecture 16 Input & Output James Goodman (revised by Robert Sheehan) Credits: Slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University
Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 Lecture Notes Lecture 16 Input & Output James Goodman (revised by Robert Sheehan) Credits: Slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 8 & 9.1 I/O and Traps Aside Off-Topic: Memory Hierarchy 8-3
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 8 & 9.1 I/O and Traps Aside Off-Topic: Memory Hierarchy 8-3
Chapter 8 I/O. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. But where does data in memory come from?
 Chapter 8 I/O I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory But where does data
Chapter 8 I/O I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory But where does data
Chapter 8 Input/Output
 Lecture on Introduction to Computing Systems Chapter 8 Input/Output An Hong han@ustc.edu.cn 0 Fall School of Computer Science and Technology 0/11/3 1 Review So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values
Lecture on Introduction to Computing Systems Chapter 8 Input/Output An Hong han@ustc.edu.cn 0 Fall School of Computer Science and Technology 0/11/3 1 Review So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values
Midterm 2 Review Chapters 4-16 LC-3
 Midterm 2 Review Chapters 4-16 LC-3 ISA You will be allowed to use the one page summary. 8-2 LC-3 Overview: Instruction Set Opcodes 15 opcodes Operate instructions: ADD, AND, NOT Data movement instructions:
Midterm 2 Review Chapters 4-16 LC-3 ISA You will be allowed to use the one page summary. 8-2 LC-3 Overview: Instruction Set Opcodes 15 opcodes Operate instructions: ADD, AND, NOT Data movement instructions:
Subroutines & Traps. Announcements. New due date for assignment 2 5pm Wednesday, 5May
 Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 2010 Semester 1 Lecture Notes Lecture 19, 26Apr10: Subroutines & Traps James Goodman! Announcements New due date for assignment 2 5pm Wednesday, 5May Test is
Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 2010 Semester 1 Lecture Notes Lecture 19, 26Apr10: Subroutines & Traps James Goodman! Announcements New due date for assignment 2 5pm Wednesday, 5May Test is
Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University
 Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 2 Stack: An Abstract Data Type An important abstraction that
Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 2 Stack: An Abstract Data Type An important abstraction that
Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack
 Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack Memory Usage Instructions are stored in code segment Global data is stored in data segment Local variables, including arryas, uses stack Dynamically allocated memory
Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack Memory Usage Instructions are stored in code segment Global data is stored in data segment Local variables, including arryas, uses stack Dynamically allocated memory
Input/Output Interfaces: Ch
 Input/Output Interfaces: Ch 8.1-8.3 hardware software H/w s/w interface Problems Algorithms Prog. Lang & Interfaces Instruction Set Architecture Microarchitecture (Organization) Circuits Devices (Transistors)
Input/Output Interfaces: Ch 8.1-8.3 hardware software H/w s/w interface Problems Algorithms Prog. Lang & Interfaces Instruction Set Architecture Microarchitecture (Organization) Circuits Devices (Transistors)
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Computing Layers
 Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye, Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye, Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms
appendix a The LC-3 ISA A.1 Overview
 A.1 Overview The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of the LC-3 is defined as follows: Memory address space 16 bits, corresponding to 2 16 locations, each containing one word (16 bits). Addresses are numbered
A.1 Overview The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of the LC-3 is defined as follows: Memory address space 16 bits, corresponding to 2 16 locations, each containing one word (16 bits). Addresses are numbered
COSC121: Computer Systems. Exceptions and Interrupts
 COSC121: Computer Systems. Exceptions and Interrupts Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and
COSC121: Computer Systems. Exceptions and Interrupts Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and
Trap Vector Table. Interrupt Vector Table. Operating System and Supervisor Stack. Available for User Programs. Device Register Addresses
 Chapter 1 The LC-3b ISA 1.1 Overview The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of the LC-3b is defined as follows: Memory address space 16 bits, corresponding to 2 16 locations, each containing one byte (8
Chapter 1 The LC-3b ISA 1.1 Overview The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of the LC-3b is defined as follows: Memory address space 16 bits, corresponding to 2 16 locations, each containing one byte (8
Implement useq's FSM's --- Next-state function --- Output function. We know: Any function can be implemented in AND-OR
 Implement useq's FSM's --- Next-state function --- Output function We know: Any function can be implemented in AND-OR i --- # bits input to FSM (IR, PSR,...) j --- # bits of current state k = i + j ---
Implement useq's FSM's --- Next-state function --- Output function We know: Any function can be implemented in AND-OR i --- # bits input to FSM (IR, PSR,...) j --- # bits of current state k = i + j ---
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model
 Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program --
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program --
LC-3 Architecture. (Ch4 ish material)
 LC-3 Architecture (Ch4 ish material) 1 CISC vs. RISC CISC : Complex Instruction Set Computer Lots of instructions of variable size, very memory optimal, typically less registers. RISC : Reduced Instruction
LC-3 Architecture (Ch4 ish material) 1 CISC vs. RISC CISC : Complex Instruction Set Computer Lots of instructions of variable size, very memory optimal, typically less registers. RISC : Reduced Instruction
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model
 Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program --
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program --
8.1 I/O Basics Device Registers. chapter
 chapter 8 Up to now, we have paid little attention to input/output (I/O). We did note (in Chapter 4) that input/output is an important component of the von Neumann model. There must be a way to get information
chapter 8 Up to now, we have paid little attention to input/output (I/O). We did note (in Chapter 4) that input/output is an important component of the von Neumann model. There must be a way to get information
Lec-memMapIOtrapJSR SYS_BUS
 Lec-memMapIOtrapJSR Memory Mapped I/O: I/O Devices have read/write access via device registers. To send a word of data to a device, write to its memory-mapped address: ST R1, To receive a word
Lec-memMapIOtrapJSR Memory Mapped I/O: I/O Devices have read/write access via device registers. To send a word of data to a device, write to its memory-mapped address: ST R1, To receive a word
Computing Layers. Chapter 5 The LC-3
 Computing Layers Problems Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Algorithms Language Instruction
Computing Layers Problems Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Algorithms Language Instruction
COSC121: Computer Systems: Review
 COSC121: Computer Systems: Review Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and Hennessy Computer
COSC121: Computer Systems: Review Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and Hennessy Computer
20/08/14. Computer Systems 1. Instruction Processing: FETCH. Instruction Processing: DECODE
 Computer Science 210 Computer Systems 1 Lecture 11 The Instruction Cycle Ch. 5: The LC-3 ISA Credits: McGraw-Hill slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University Instruction Processing:
Computer Science 210 Computer Systems 1 Lecture 11 The Instruction Cycle Ch. 5: The LC-3 ISA Credits: McGraw-Hill slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University Instruction Processing:
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252 Prof. Mark D. Hill Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252 Prof. Mark D. Hill Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252 Prof. Mark D. Hill Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper
System Calls. Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines
 System Calls Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Certain operations require
System Calls Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Certain operations require
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model
 Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atananasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atananasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program
CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 09, SPRING 2013
 CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 09, SPRING 2013 TOPICS TODAY I/O Architectures Interrupts Exceptions FETCH EXECUTE CYCLE 1.7 The von Neumann Model This is a general
CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 09, SPRING 2013 TOPICS TODAY I/O Architectures Interrupts Exceptions FETCH EXECUTE CYCLE 1.7 The von Neumann Model This is a general
C Functions and Pointers. C Pointers. CS270 - Fall Colorado State University. CS270 - Fall Colorado State University
 1 C Pointers C unctions and Pointers 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 our-bit Adder Logical Completeness (Example)! Can implement ANY truth table with combo of AN, OR, NOT gates. Implementing a inite tate Machine (equential
1 C Pointers C unctions and Pointers 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 our-bit Adder Logical Completeness (Example)! Can implement ANY truth table with combo of AN, OR, NOT gates. Implementing a inite tate Machine (equential
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Computing Layers
 Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language
Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language
Ch. 5: The LC-3. PC-Relative Addressing Mode. Data Movement Instructions. James Goodman!
 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ADD + 0001 1 0 00 2 Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 2012 Semester 1 Lecture Notes ADD + AND + AND + BR JMP 0001 1 1 imm5 0101 1 0 00 2 0101 1 1 imm5 0000
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ADD + 0001 1 0 00 2 Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 2012 Semester 1 Lecture Notes ADD + AND + AND + BR JMP 0001 1 1 imm5 0101 1 0 00 2 0101 1 1 imm5 0000
Register Files. Single Bus Architecture. Register Files. Single Bus Processor. Term Project: using VHDL. Accumulator based architecture
 Register Files DR 3 SelS Design and simulate the LC-3 processor using VHDL Term Project: Single Processor Decoder... R R3 R6...... mux mux S S SelDR 3 DRin Clock 3 SelS LC-3 Architecture 3 Register File
Register Files DR 3 SelS Design and simulate the LC-3 processor using VHDL Term Project: Single Processor Decoder... R R3 R6...... mux mux S S SelDR 3 DRin Clock 3 SelS LC-3 Architecture 3 Register File
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION
 INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications. Lecture 7. Part 1. Interrupt. Dr. Tao Li 1
 EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 Part 1 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 M&M: Chapter 8 Or Reading Assignment Software and Hardware Engineering (new version): Chapter 12 Dr. Tao Li 2 Interrupt An
EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 Part 1 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 M&M: Chapter 8 Or Reading Assignment Software and Hardware Engineering (new version): Chapter 12 Dr. Tao Li 2 Interrupt An
Reading Assignment. Interrupt. Interrupt. Interrupt. EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications. Lecture 7. Part 1
 Reading Assignment EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 M&M: Chapter 8 Or Software and Hardware Engineering (new version): Chapter 12 Part 1 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 Dr. Tao Li 2 Interrupt An
Reading Assignment EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 M&M: Chapter 8 Or Software and Hardware Engineering (new version): Chapter 12 Part 1 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 Dr. Tao Li 2 Interrupt An
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Review Topics. parameter passing, memory model)
 Final Exam Review Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Review Topics! Number Representation & Arithmetic!
Final Exam Review Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Review Topics! Number Representation & Arithmetic!
Chapter 5 The LC-3. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2
 Chapter 5 The LC-3 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the programmer-visible components
Chapter 5 The LC-3 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the programmer-visible components
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION
 INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof Mark D. Hill and Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Rebecca Lam, Mona Jalal, Preeti Agarwal, Pradip Vallathol Midterm Examination
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof Mark D. Hill and Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Rebecca Lam, Mona Jalal, Preeti Agarwal, Pradip Vallathol Midterm Examination
Our Simulation Equivalent: -- readmemb( "os.bin" ) -- PC <== x0200
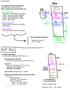 LC3 OS basics LC3 System Start-Up Assumptions We will write an OS for the LC3. What would a real LC3 do at start up? 1. BIOS execution --- PC points to BIOS (Basic IO System). --- POST: Test and initialize
LC3 OS basics LC3 System Start-Up Assumptions We will write an OS for the LC3. What would a real LC3 do at start up? 1. BIOS execution --- PC points to BIOS (Basic IO System). --- POST: Test and initialize
Introduction to Embedded Systems. Lab Logistics
 Introduction to Embedded Systems CS/ECE 6780/5780 Al Davis Today s topics: lab logistics interrupt synchronization reentrant code 1 CS 5780 Lab Logistics Lab2 Status Wed: 3/11 teams have completed their
Introduction to Embedded Systems CS/ECE 6780/5780 Al Davis Today s topics: lab logistics interrupt synchronization reentrant code 1 CS 5780 Lab Logistics Lab2 Status Wed: 3/11 teams have completed their
EE458 - Embedded Systems Exceptions and Interrupts
 EE458 - Embedded Systems Exceptions and Interrupts Outline Exceptions Interrupts References RTC: Chapters 10 CUG: Chapters 8, 21, 23 1 Introduction An exception is any event that disrupts the normal execution
EE458 - Embedded Systems Exceptions and Interrupts Outline Exceptions Interrupts References RTC: Chapters 10 CUG: Chapters 8, 21, 23 1 Introduction An exception is any event that disrupts the normal execution
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2016 Lecture 2 Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 2 System I/O System I/O (Chap 13) Central
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2016 Lecture 2 Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 2 System I/O System I/O (Chap 13) Central
hardware interrupts software interrupts
 CS 5212Operating Systems wk 4 Interrupts An interrupt is a signal received by the CPU that causes a temporary halt in the execution of a program while some other task is performed. Interrupts may be generated
CS 5212Operating Systems wk 4 Interrupts An interrupt is a signal received by the CPU that causes a temporary halt in the execution of a program while some other task is performed. Interrupts may be generated
I/O - input/output. system components: CPU, memory, and bus -- now add I/O controllers and peripheral devices. CPU Cache
 I/O - input/output system components: CPU, memory, and bus -- now add I/O controllers and peripheral devices CPU Cache CPU must perform all transfers to/from simple controller, e.g., CPU reads byte from
I/O - input/output system components: CPU, memory, and bus -- now add I/O controllers and peripheral devices CPU Cache CPU must perform all transfers to/from simple controller, e.g., CPU reads byte from
PC Interrupt Structure and 8259 DMA Controllers
 ELEC 379 : DESIGN OF DIGITAL AND MICROCOMPUTER SYSTEMS 1998/99 WINTER SESSION, TERM 2 PC Interrupt Structure and 8259 DMA Controllers This lecture covers the use of interrupts and the vectored interrupt
ELEC 379 : DESIGN OF DIGITAL AND MICROCOMPUTER SYSTEMS 1998/99 WINTER SESSION, TERM 2 PC Interrupt Structure and 8259 DMA Controllers This lecture covers the use of interrupts and the vectored interrupt
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Review Topics
 Second Midterm Review Slides Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Review Topics LC-3 Programming /Stack Execution
Second Midterm Review Slides Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Review Topics LC-3 Programming /Stack Execution
Digital System Design Using Verilog. - Processing Unit Design
 Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
HANDLING MULTIPLE DEVICES
 HANDLING MULTIPLE DEVICES Let us now consider the situation where a number of devices capable of initiating interrupts are connected to the processor. Because these devices are operationally independent,
HANDLING MULTIPLE DEVICES Let us now consider the situation where a number of devices capable of initiating interrupts are connected to the processor. Because these devices are operationally independent,
Hardware OS & OS- Application interface
 CS 4410 Operating Systems Hardware OS & OS- Application interface Summer 2013 Cornell University 1 Today How my device becomes useful for the user? HW-OS interface Device controller Device driver Interrupts
CS 4410 Operating Systems Hardware OS & OS- Application interface Summer 2013 Cornell University 1 Today How my device becomes useful for the user? HW-OS interface Device controller Device driver Interrupts
ECE 372 Microcontroller Design Parallel IO Ports - Interrupts. ECE 372 Microcontroller Design Parallel IO Ports - Interrupts
 Interrupts An interrupt can be compared with a phone call interrupting your task which you will resume when the call is finished You can mask an interrupt just as you can decide not to answer any phone
Interrupts An interrupt can be compared with a phone call interrupting your task which you will resume when the call is finished You can mask an interrupt just as you can decide not to answer any phone
by I.-C. Lin, Dept. CS, NCTU. Textbook: Operating System Concepts 8ed CHAPTER 13: I/O SYSTEMS
 by I.-C. Lin, Dept. CS, NCTU. Textbook: Operating System Concepts 8ed CHAPTER 13: I/O SYSTEMS Chapter 13: I/O Systems I/O Hardware Application I/O Interface Kernel I/O Subsystem Transforming I/O Requests
by I.-C. Lin, Dept. CS, NCTU. Textbook: Operating System Concepts 8ed CHAPTER 13: I/O SYSTEMS Chapter 13: I/O Systems I/O Hardware Application I/O Interface Kernel I/O Subsystem Transforming I/O Requests
Beyond One Core. Multi-Cores. Evolution in Frequency Has Stalled. Source: ISCA 2009 Keynote of Kathy Yelick
 Beyond One Multi-s Evolution in Frequency Has Stalled Source: ISCA 2009 Keynote of Kathy Yelick 1 Multi-s Network or Bus Memory Private and/or shared caches Bus Network (on chip = NoC) Example: ARM Cortex
Beyond One Multi-s Evolution in Frequency Has Stalled Source: ISCA 2009 Keynote of Kathy Yelick 1 Multi-s Network or Bus Memory Private and/or shared caches Bus Network (on chip = NoC) Example: ARM Cortex
CIT 593: Intro to Computer Systems Homework #4: Assembly Language Due October 18, 2012, 4:30pm. Name
 CIT 593: Intro to Computer Systems Homework #4: Assembly Language Due October 18, 2012, 4:30pm Instructions You may print this document and write your answers here, or submit solutions on a separate piece
CIT 593: Intro to Computer Systems Homework #4: Assembly Language Due October 18, 2012, 4:30pm Instructions You may print this document and write your answers here, or submit solutions on a separate piece
Computer System Overview OPERATING SYSTEM TOP-LEVEL COMPONENTS. Simplified view: Operating Systems. Slide 1. Slide /S2. Slide 2.
 BASIC ELEMENTS Simplified view: Processor Slide 1 Computer System Overview Operating Systems Slide 3 Main Memory referred to as real memory or primary memory volatile modules 2004/S2 secondary memory devices
BASIC ELEMENTS Simplified view: Processor Slide 1 Computer System Overview Operating Systems Slide 3 Main Memory referred to as real memory or primary memory volatile modules 2004/S2 secondary memory devices
Computer Architecture 5.1. Computer Architecture. 5.2 Vector Address: Interrupt sources (IS) such as I/O, Timer 5.3. Computer Architecture
 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3./ Hardware interrupt: 5. If in an eternal device (for eample I/O interface) a predefined event occurs this device issues an interrupt request to
License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3./ Hardware interrupt: 5. If in an eternal device (for eample I/O interface) a predefined event occurs this device issues an interrupt request to
LC-3 Subroutines and Traps. (Textbook Chapter 9)"
 LC-3 Subroutines and Traps (Textbook Chapter 9)" Subroutines" Blocks can be encoded as subroutines" A subroutine is a program fragment that:" lives in user space" performs a well-defined task" is invoked
LC-3 Subroutines and Traps (Textbook Chapter 9)" Subroutines" Blocks can be encoded as subroutines" A subroutine is a program fragment that:" lives in user space" performs a well-defined task" is invoked
1/17/2018. Task: Print a Number in Binary. ECE 220: Computer Systems & Programming. First Step: Break the Task into a Sequence of Two
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 220: Computer Systems & Programming LC-3 I/O Usage Example Task: Print a Number in Binary Let s write some code
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 220: Computer Systems & Programming LC-3 I/O Usage Example Task: Print a Number in Binary Let s write some code
ECEN 449 Microprocessor System Design. Hardware-Software Communication. Texas A&M University
 ECEN 449 Microprocessor System Design Hardware-Software Communication 1 Objectives of this Lecture Unit Learn basics of Hardware-Software communication Memory Mapped I/O Polling/Interrupts 2 Motivation
ECEN 449 Microprocessor System Design Hardware-Software Communication 1 Objectives of this Lecture Unit Learn basics of Hardware-Software communication Memory Mapped I/O Polling/Interrupts 2 Motivation
Interrupt-Driven Input/Output
 Interrupt-Driven Input/Output Textbook: Chapter 11 (Interrupts) ARM Cortex-M4 User Guide (Interrupts, exceptions, NVIC) Sections 2.1.4, 2.3 Exceptions and interrupts Section 4.2 Nested Vectored Interrupt
Interrupt-Driven Input/Output Textbook: Chapter 11 (Interrupts) ARM Cortex-M4 User Guide (Interrupts, exceptions, NVIC) Sections 2.1.4, 2.3 Exceptions and interrupts Section 4.2 Nested Vectored Interrupt
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3. Annalisa Massini /2015
 Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
PESIT Bangalore South Campus
 INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST I Date: 30/08/2017 Max Marks: 40 Subject & Code: Computer Organization 15CS34 Semester: III (A & B) Name of the faculty: Mrs.Sharmila Banu.A Time: 8.30 am 10.00 am Answer any FIVE
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST I Date: 30/08/2017 Max Marks: 40 Subject & Code: Computer Organization 15CS34 Semester: III (A & B) Name of the faculty: Mrs.Sharmila Banu.A Time: 8.30 am 10.00 am Answer any FIVE
LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture. Textbook Chapter 5
 LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture Textbook Chapter 5 Instruction set architecture What is an instruction set architecture (ISA)? It is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer
LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture Textbook Chapter 5 Instruction set architecture What is an instruction set architecture (ISA)? It is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer
컴퓨터개념및실습. 기말고사 review
 컴퓨터개념및실습 기말고사 review Sorting results Sort Size Compare count Insert O(n 2 ) Select O(n 2 ) Bubble O(n 2 ) Merge O(n log n) Quick O(n log n) 5 4 (lucky data set) 9 24 5 10 9 36 5 15 9 40 14 39 15 45 (unlucky
컴퓨터개념및실습 기말고사 review Sorting results Sort Size Compare count Insert O(n 2 ) Select O(n 2 ) Bubble O(n 2 ) Merge O(n log n) Quick O(n log n) 5 4 (lucky data set) 9 24 5 10 9 36 5 15 9 40 14 39 15 45 (unlucky
Q.1 Explain Computer s Basic Elements
 Q.1 Explain Computer s Basic Elements Ans. At a top level, a computer consists of processor, memory, and I/O components, with one or more modules of each type. These components are interconnected in some
Q.1 Explain Computer s Basic Elements Ans. At a top level, a computer consists of processor, memory, and I/O components, with one or more modules of each type. These components are interconnected in some
8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses:
 UNIT-III PART -A INTERRUPTS AND PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS Contents at a glance: 8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses Introduction to DOS and BIOS interrupts 8259A Priority Interrupt Controller
UNIT-III PART -A INTERRUPTS AND PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS Contents at a glance: 8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses Introduction to DOS and BIOS interrupts 8259A Priority Interrupt Controller
Grundlagen Microcontroller Interrupts. Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss
 Grundlagen Microcontroller Interrupts Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Interrupts Lecture Overview Definition Sources ISR Priorities & Nesting 2 Definition Interrupt: reaction to (asynchronous) external
Grundlagen Microcontroller Interrupts Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Interrupts Lecture Overview Definition Sources ISR Priorities & Nesting 2 Definition Interrupt: reaction to (asynchronous) external
LC-3 TRAP Routines. Textbook Chapter 9
 LC-3 TRAP Routines Textbook Chapter 9 System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge of I/O device registers and the sequence of operations needed to use
LC-3 TRAP Routines Textbook Chapter 9 System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge of I/O device registers and the sequence of operations needed to use
Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines
 Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2 System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge
Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2 System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge
Last class: Today: Course administration OS definition, some history. Background on Computer Architecture
 1 Last class: Course administration OS definition, some history Today: Background on Computer Architecture 2 Canonical System Hardware CPU: Processor to perform computations Memory: Programs and data I/O
1 Last class: Course administration OS definition, some history Today: Background on Computer Architecture 2 Canonical System Hardware CPU: Processor to perform computations Memory: Programs and data I/O
The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture. ISA Overview Operate instructions Data Movement instructions Control Instructions LC-3 data path
 Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA Overview Operate instructions Data Movement instructions Control Instructions LC-3 data path A specific ISA: The LC-3 We have: Reviewed data encoding
Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA Overview Operate instructions Data Movement instructions Control Instructions LC-3 data path A specific ISA: The LC-3 We have: Reviewed data encoding
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Sujith Surendran, Lisa Ossian, Minsub Shin Midterm Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Sujith Surendran, Lisa Ossian, Minsub Shin Midterm Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday,
EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications. Lecture 7. Part 2. M68HC12 Interrupt. Dr. Tao Li 1
 EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 Part 2 M68HC12 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 Reading Assignment Software and Hardware Engineering (New version): Chapter 12 or SHE (old version) Chapter 8 And
EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 Part 2 M68HC12 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 Reading Assignment Software and Hardware Engineering (New version): Chapter 12 or SHE (old version) Chapter 8 And
The von Neuman architecture characteristics are: Data and Instruction in same memory, memory contents addressable by location, execution in sequence.
 CS 320 Ch. 3 The von Neuman architecture characteristics are: Data and Instruction in same memory, memory contents addressable by location, execution in sequence. The CPU consists of an instruction interpreter,
CS 320 Ch. 3 The von Neuman architecture characteristics are: Data and Instruction in same memory, memory contents addressable by location, execution in sequence. The CPU consists of an instruction interpreter,
Concurrent programming: Introduction I
 Computer Architecture course Real-Time Operating Systems Concurrent programming: Introduction I Anna Lina Ruscelli - Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Contact info Email a.ruscelli@sssup.it Computer Architecture
Computer Architecture course Real-Time Operating Systems Concurrent programming: Introduction I Anna Lina Ruscelli - Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Contact info Email a.ruscelli@sssup.it Computer Architecture
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON. Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Mohit Verma, Annie Lin
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Mohit Verma, Annie Lin Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, May 3rd, 2017 Weight:
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Mohit Verma, Annie Lin Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, May 3rd, 2017 Weight:
And. Fin a l l i... The Slack
 chapter 10 And. Fin a l l i... The Slack We have finished our treatment of the LC-3 ISA. Before moving up another level of abstraction in Chapter 11 to programming in C, there is a particularly important
chapter 10 And. Fin a l l i... The Slack We have finished our treatment of the LC-3 ISA. Before moving up another level of abstraction in Chapter 11 to programming in C, there is a particularly important
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 17: Interrupts and Exceptions. Interrupts Exceptions and Traps. Visualizing an Interrupt
 CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 17: Interrupts and Exceptions Robert Wagner cps 104 Int.1 RW Fall 2000 Interrupts Exceptions and Traps Interrupts, Exceptions and Traps are asynchronous
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 17: Interrupts and Exceptions Robert Wagner cps 104 Int.1 RW Fall 2000 Interrupts Exceptions and Traps Interrupts, Exceptions and Traps are asynchronous
CPSC 213. Introduction to Computer Systems. I/O Devices, Interrupts and DMA. Unit 2a Oct 27, 29, 31. Winter Session 2014, Term 1
 CPSC 213 Introduction to Computer Systems Winter Session 2014, Term 1 Unit 2a Oct 27, 29, 31 I/O Devices, Interrupts and DMA Overview Reading in Text 8.1, 8.2.1, 8.5.1-8.5.3 Learning Goals Explain what
CPSC 213 Introduction to Computer Systems Winter Session 2014, Term 1 Unit 2a Oct 27, 29, 31 I/O Devices, Interrupts and DMA Overview Reading in Text 8.1, 8.2.1, 8.5.1-8.5.3 Learning Goals Explain what
OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136
 OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136 Jialiang LU Jialiang.lu@sjtu.edu.cn Based on Lecture Notes of Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, 1 Chapter 5 INPUT/OUTPUT 2 Overview o OS controls I/O devices => o Issue commands,
OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136 Jialiang LU Jialiang.lu@sjtu.edu.cn Based on Lecture Notes of Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, 1 Chapter 5 INPUT/OUTPUT 2 Overview o OS controls I/O devices => o Issue commands,
ECE 485/585 Microprocessor System Design
 Microprocessor System Design Lecture 3: Polling and Interrupts Programmed I/O and DMA Interrupts Zeshan Chishti Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer Science
Microprocessor System Design Lecture 3: Polling and Interrupts Programmed I/O and DMA Interrupts Zeshan Chishti Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer Science
Fill in your name, section, and username. DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
 NAME: SECTION: USENAME: CS 20 Exam 2 D-Term 2006 Question : (5) Question 2: (5) Question 3: (20) Question 4: (20) Question 5: (0) Question 6: (0) Question 7: (0) TOTAL: (00) Fill in your name, section,
NAME: SECTION: USENAME: CS 20 Exam 2 D-Term 2006 Question : (5) Question 2: (5) Question 3: (20) Question 4: (20) Question 5: (0) Question 6: (0) Question 7: (0) TOTAL: (00) Fill in your name, section,
Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer Function
 Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer Function Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 3 - Top Level View 1 / 127 Table of Contents I 1 Introduction 2 Computer Components
Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer Function Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 3 - Top Level View 1 / 127 Table of Contents I 1 Introduction 2 Computer Components
Computer System Overview
 Computer System Overview Operating Systems 2005/S2 1 What are the objectives of an Operating System? 2 What are the objectives of an Operating System? convenience & abstraction the OS should facilitate
Computer System Overview Operating Systems 2005/S2 1 What are the objectives of an Operating System? 2 What are the objectives of an Operating System? convenience & abstraction the OS should facilitate
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION
 INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY MASTER OF COMPUTER APPLICATION SEMESTER: III
 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY MASTER OF COMPUTER APPLICATION SEMESTER: III Subject Name: Operating System (OS) Subject Code: 630004 Unit-1: Computer System Overview, Operating System Overview, Processes
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY MASTER OF COMPUTER APPLICATION SEMESTER: III Subject Name: Operating System (OS) Subject Code: 630004 Unit-1: Computer System Overview, Operating System Overview, Processes
Computing Layers. Chapter 7 Assembly Language
 Computing Layers Problems Chapter 7 Assembly Language Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Algorithms Language Instruction
Computing Layers Problems Chapter 7 Assembly Language Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Algorithms Language Instruction
INTERRUPTS in microprocessor systems
 INTERRUPTS in microprocessor systems Microcontroller Power Supply clock fx (Central Proccesor Unit) CPU Reset Hardware Interrupts system IRQ Internal address bus Internal data bus Internal control bus
INTERRUPTS in microprocessor systems Microcontroller Power Supply clock fx (Central Proccesor Unit) CPU Reset Hardware Interrupts system IRQ Internal address bus Internal data bus Internal control bus
1 Execution of main program is suspended. 2 All registers are pushed onto the stack. 3 The ISR, or background thread, is executed.
 Introduction ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design Chris J. Myers Lecture 7: Interrupt Synchronization Interrupts provide guarantee on response time. Interrupts allow response to rare but important
Introduction ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design Chris J. Myers Lecture 7: Interrupt Synchronization Interrupts provide guarantee on response time. Interrupts allow response to rare but important
Chapter 5 - ISA. 1.The Von Neumann Model. The Stored Program Computer. Von Neumann Model. Memory
 Chapter 5 - ISA 1.The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program
Chapter 5 - ISA 1.The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program
I/O and Device Drivers
 I/O and Device Drivers Minsoo Ryu Real-Time Computing and Communications Lab. Hanyang University msryu@hanyang.ac.kr Topics Covered I/O Components I/O Interface I/O Operations Device Drivers 2 I/O Components
I/O and Device Drivers Minsoo Ryu Real-Time Computing and Communications Lab. Hanyang University msryu@hanyang.ac.kr Topics Covered I/O Components I/O Interface I/O Operations Device Drivers 2 I/O Components
ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design
 ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design Scott R. Little Lecture 8: Interrupt Synchronization Scott R. Little (Lecture 8: Interrupts) ECE/CS 5780/6780 1 / 22 Administrivia Midterm 1 will be on February
ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design Scott R. Little Lecture 8: Interrupt Synchronization Scott R. Little (Lecture 8: Interrupts) ECE/CS 5780/6780 1 / 22 Administrivia Midterm 1 will be on February
Architectural Support for Operating Systems
 Architectural Support for Operating Systems (Chapter 2) CS 4410 Operating Systems [R. Agarwal, L. Alvisi, A. Bracy, M. George, E. Sirer, R. Van Renesse] Let s start at the very beginning 2 A Short History
Architectural Support for Operating Systems (Chapter 2) CS 4410 Operating Systems [R. Agarwal, L. Alvisi, A. Bracy, M. George, E. Sirer, R. Van Renesse] Let s start at the very beginning 2 A Short History
CS 2461: Computer Architecture I
 Computer Architecture is... CS 2461: Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs2461/ Instruction Set Architecture Organization
Computer Architecture is... CS 2461: Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs2461/ Instruction Set Architecture Organization
Preemptive Scheduling
 Preemptive Scheduling Lecture 18 18-1 Big Picture Methods learned so far We ve been using a foreground/background system Interrupt service routines run in foreground Task code runs in background Limitations
Preemptive Scheduling Lecture 18 18-1 Big Picture Methods learned so far We ve been using a foreground/background system Interrupt service routines run in foreground Task code runs in background Limitations
CS 134. Operating Systems. April 8, 2013 Lecture 20. Input/Output. Instructor: Neil Rhodes. Monday, April 7, 14
 CS 134 Operating Systems April 8, 2013 Lecture 20 Input/Output Instructor: Neil Rhodes Hardware How hardware works Operating system layer What the kernel does API What the programmer does Overview 2 kinds
CS 134 Operating Systems April 8, 2013 Lecture 20 Input/Output Instructor: Neil Rhodes Hardware How hardware works Operating system layer What the kernel does API What the programmer does Overview 2 kinds
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the
