Volume Ultrasound, rendering modes and clinical application
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GE Healthcare Volume Ultrasound, rendering modes and clinical application R. CHAOUI Center for Prenatal Diagnosis and Human Genetics, Berlin, Germany B. BENOIT Hospital Princesse Grace, Monaco, Monte Carlo
2 Introduction In recent years, three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound has become the most rapidly evolving technique in fetal imaging and meanwhile, it is currently used worldwide by more than half of all perinatologists. Some users are still using mainly 3D and 4D techniques to demonstrate the fetal face to the parents, which has made this new technique very popular as well. Volume ultrasound introduced into prenatal diagnosis a few years ago enabled a more comprehensive medical and clinical application of this new technique, opening new horizons for a future era of ultrasound. Numerous research papers were published describing the clinical potential of new techniques and rendering modes, but many colleagues may still be unfamiliar with all of these features, which are now well established in targeted prenatal diagnosis for ruling out or clearly demonstrating fetal malformations. The aim of this short review is to provide information on the potential of volume ultrasound and the application of some display modes in clinical work. Volume acquisition There are different ways to acquire a volume data set. The acquisition can be achieved either as a: static 3D Real-time 3D or 4D STIC for heart and vessels Static 3D (one volume data set): this is the 3D used in most fetal studies (face, hands etc.). The volume quality is defined by the choice of the acquisition time where max is the slowest acquisition with the highest numbers of images within a volume through high2 and high1 to min, which is then very rapid and of reduced quality. A later analysis of subtile structures from a volume data set using Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging (TUI) may necessitate a max acquisition whereas for the demonstration of large areas such as the 3D surface of the face or the body high1 or mid quality are sufficient. For the acquisition of a 3D heart volume, it is better to use the min to mid quality to avoid artifacts from wall movements. This static 3D can also be combined with Color Doppler, Power Doppler, High Definition (HD)-flow, and B-Flow depending on the question of interest. Real-time 3D or 4D-Ultrasound (many volume data set): Today this is achieved by a mechanical 3D transducer with a rapid acquisition from 1.5 to 40 volumes/sec. The advantage of a 4D examination is its easy use. The direct result on the screen enables online manipulation to acquire the best image by changing the gain and the contrast depending on the mode used. Furthermore, it allows the transducer to be moved depending on the insonation angle and it allows users to fully exploit the image. The technique is ideal for studying fetal movements and behavior throughout pregnancy, but also for use in Volume contrast Imaging (VCI) enabling online reconstruction of a volume slice of the C- or A-plane. It can be used for fetal echocardiography as well but requires a great deal of experience. STIC (one cardiac cycle including a data set up to 40 volumes): In this condition the volume of interest is not scanned in an instant. The slow acquisition of image slices (duration 7.5 to 15 sec) allows the acquisition of numerous planes including additional information from an entire cardiac cycle. The Spatial and Temporal Image Correlation (STIC) calculates the mean heart rate acquired and the images in the volume are re-arranged according to their temporal event within the heart cycle. The displayed volume then includes a single hypothetical heart cycle, which is reconstructed from single selected images of the A-Plane in the different phases of the heart cycle, whereas the B- and C-Planes are reconstructed digitally. STIC can be used with grayscale fetal echocardiography but can be also combined with color Doppler, power Doppler, High Definition (HD)-flow, B-Flow, etc. With B-flow, it can also be applied for peripheral vessels without a true calculation of the heart rate (e.g. demonstration of the umbilical cord). Once the acquisition of a volume is achieved, the information can be visualized either as single or as multiple 2D images regenerated from the volume and selected by the examiner or as a volume spatial information called 3D rendering allowing the application of different modes. Some of the actual display modes will be emphasized and illustrated in this article.
3 VOLUME DATA DISPLAY One plane of choice, multiplanar orthogonal planes or multiple tomographic parallel slices A volume data set consists of digital information on numerous images and thus allows the demonstration of infinite planes of choice as a so-called anyplane. From a 3D/4D data set the cross-sectional views can be obtained at any desired orientation, direction and depth. It must be borne in mind that the acquisition (A-) plane provides the best information, whereas the reconstructed planes B-, C- or others are of less quality. This should be considered during the volume acquisition. The 2D image analysis from a volume can be achieved from a 3D, 4D or STIC data set. The display format is either a single-plane view or a multiplanar view showing three planes which are perpendicular to each other. In the lateral view the intersection of the three planes is a dot and by moving the position of this dot, the examiner can navigate through the volume. The recent introduction of the multislice analysis known as Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging (TUI) is similar to the tomographic assessment known from CT and MR workstations. The examiner can define the slice thickness and the numbers of planes demonstrated. The multiplanar mode can be used to acquire a plane not directly seen on cross section 2D during live examination, mainly in cases with non-optimal fetal position, so as to demonstrate the corpus callosum, a fetal profile, a limb or the aortic arch. It can used to visualize exact midline planes after making adjustments in the two other orthogonal planes (for nasal bone assessment). One of the major advantages of a three dimensional data set is the possibility to achieve the examination off-line on few volumes at a remote station. One of the future potential uses of this mode could be the transfer of data via Internet to a remote site to get a second opinion or a complete offline evaluation without examining the patient. Multiplanar mode with the three orthogonal planes. The dot is the intersection of all 3 planes and can be used to get the best position for assessing the profile. In the C- plane (lower panel) the dot is on the nasal bone Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging TUI: with a volume of the fetal thorax and abdomen. All structures can be seen with one view Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging TUI of the brain demonstrating all important brain structures as the lateral ventricles, the cerebellum, the cavum septum pellucidum, insula and others However, since the quality of reconstructed images depends mainly on the original acquisition, the examiner should consider this aspect when acquiring volumes for future studies. We found that the four-chamber view or some intracranial structures as the lateral ventricles or cortex are best acquired in a transverse view, but the aortic arch, the spine or the nuchal translucency and midline brain structures are best viewed from a sagittal view. Organs with few details such as the stomach, urinary bladder, liver or kidneys can be acquired from any insonation angle. In a STIC volume the reconstructed cardiac volume can be displayed in the multiplanar or tomographic modes, and played in slow motion or stopped at any time for detailed analysis of specific phases of the cardiac cycle. When combined with color Doppler, events within the cardiac cycle during systole and diastole can be very well demonstrated. Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging TUI of the same volume with the demonstration of the corpus callosum Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging TUI can be used for the heart combined with STIC. Within one image mainly moving structures can be seen
4 Surface mode rendering The image rendering of the fetal surface is the most known and commonly used display modality in 3D and 4D. From the volume acquired, the skin is primarily demonstrated (surface) and not the organs inside the body. It is used to visualize a surface of a structure which is best achieved in the interlay between fluid and surface, as the face of a fetus in amniotic fluid, the valves within the heart or even the liver or abdominal organs, for example in ascites. After placing the volume box over the region of interest, the rendering should be chosen either as surface, surface smooth or gradient light or a combination of two of these options. The examiner should adjust the 2D image prior to volume acquisition to get a black amniotic fluid and a contrasty surface of the region of interest. The main advantage of the technique is its easy use and its impact on patients and doctors due to the lifelike image, or the comparison with postnatal appearance. Clinical applications are the demonstration of the whole fetus in the first trimester until 12 weeks gestation, then the demonstration of the face, limbs, etc. in order to rule out or confirm anomalies involving the skin as well as facial anomalies, spina bifida, limb anomalies and others. It is best demonstrated using 3D as well as 4D, whereas the latter can be used to analyze behavior such as fetal movements, grimacing, yawning or eye opening. Surface rendering can be applied to the fetal heart by using the interface between the cavities and the cardiac walls. It can be used in the brain to demonstrate the cavities such as the lateral ventricles, especially in the presence of brain anomalies. Surface mode rendering in early pregnancy Surface mode rendering of the face in later gestational age Surface mode rendering: can be used at the level of the heart to see the spatial appearance of the heart cavities rendering The maximum rendering mode highlights the maximal echo information of a volume data set and is an ideal tool for the 3D reconstruction of bony structures. In general, cranial bones, the ribs and other curvilinear bones can not be properly seen in a single 2D plane and are therefore better assessed in a maximum mode projection. This technique was applied in the demonstration of spine and limb abnormalities but was recently used in the assessment of the nasal bones, the cranial bones and corresponding sutures. This technique delivers a picture similar to an X-ray of the bony skeleton in the fetus. Prior to volume acquisition, the examiner should reduce the gain of the 2D image so that mainly the bones are highlighted but not the fetal skin. For 3D rendering, the examiner should then choose a narrow volume box to primarily include the region of interest, with only very little information from the neighboring tissue or skin. rendering: is used to visualize the fetal skeleton, here the bony face. On the left a normal fetus with a nasal bone and on the right a fetus with absent nasal bone rendering: demonstrating a normal hand (left) and radius aplasia (middle) and cleft hand (right)
5 The rendering mode chosen is then maximum mode. In some circumstances, it could be combined with surface mode. However, the threshold should be increased. Maximum mode can be used with 3D static, live 4D and elegantly with the Volume Contrast Imaging VCI-C, which is a modified live 4D in which only a defined slice of 1-20mm of a reconstructed C-plane is displayed. This technique is used to rapidly demonstrate the spine and ribs or the bony structures of the face or the skull bones. rendering: demonstrating here the skull from the side with the skull sutures rendering combined with Volume contrast imaging (VCI-C) rendering combined with Volume contrast imaging (VCI-C) Minimum mode rendering Another rendering mode is the minimum mode where the hypoechoic structures are emphasized. When this mode is selected, mainly structures with highest transparency (anechoic) can be demonstrated as a 3D projection of vessels, cysts, bladders, etc. that appear black against a surrounding of more echogenic tissue. It is preferable to choose the rendering box narrow in order to focus on including the region of interest. Within the box, the presence of amniotic fluid should be avoided as it casts a large black shadow. Images produced with this technique are similar to x-ray projection. Regions of interest are mainly the stomach, the bladder, the brain ventricles and the heart with the corresponding vessels. Minimum mode rendering demonstrating the abdomen with Bladder (BL), Gallbladder (GB), the umbilical vein (UV), the stomach (ST) the Vena Cava inferior (VCI) and aorta (AO) Minimum mode rendering used to demonstrate the aortic arch and a frontal view of the heart
6 Inversion mode rendering This recently introduced display mode starts from the minimum mode rendering and inverts merely the color of the information (similar to negative/positive film), thus presenting the hypoechoic structures as echogenic solids. It blackens most of the surrounding tissue information. By changing certain presets, such as increasing the threshold and decreasing the transparency, the image can be improved. We chose either the gradient light or the light rendering to get the most from the image. This technique was also called negative surface display and it was discovered that the images produced were similar to postmortem casting. Artifacts may result from rib shadowing or from amniotic fluid etc., but can be eliminated using the electronic scalpel Magicut. Recent reports analyzed the role of this technique in visualizing cardiac and extracardiac fluid filled structures in the fetus. Application fields are not only the heart and vessels, but also kidneys in hydronephrosis, brain ventricles and other hypoechoic cystic structures. Regions of interest in the fetus could be the fluid filled structures as the stomach, the urinary or gallbladder. The shape of the stomach and duodenum during the presence of a double bubble in duodenal atresia could be a clinical important application. The gallbladder and urinary bladder are other abdominal structures easily visualized by the inversion mode technique. The kidneys can mainly be demonstrated in anterior-posterior longitudinal projection and clinical benefit can be found in multicystic kidneys and hydronephrosis. Intracranial brain structures, especially the lateral ventricles in early pregnancy can be clearly demonstrated and malformations with disturbed anatomy of the lateral ventricles can be of clinical use with inversion mode. One of the further major fields of interest with inversion mode is the cardiovascular system. The examiner can visualize the heart and the vessels in a manner similar to 3D-Power Doppler Ultrasound at a better resolution and a more rapid acquisition rate. Particularly easily demonstrated is the crossing of the vessels of the heart or the relationship of the ventricles and their size. The main advantage of this technique is that the image is similar to the one acquired by power Doppler but without the difficulties encountered in adjusting the image. The volume can be acquired in grayscale as 3D static or as a STIC, at a high frame rate and resolution, whereas volumes with power Doppler information are at low frame rates and subject to movement artifacts. Thus, the image quality with inversion mode is superior to the quality obtained by power Doppler; however, it lacks the information of neighboring tissue demonstrated in the glass body mode. Since inversion mode can also be used for volume calculation as well, it could be easier used to calculate volumes of structures with irregular shape than with the VOCAL- Technique. The stomach demonstrated in 2D, minimum mode, inversion mode and for comparison a stomach as double bubble sign in a fetus with duodenal atresia Inversion mode in a fetus with vesico-ureteral reflux showing the dilated ureters Inversion mode of an abnormal bladder with subvesical obstruction Inversion mode to demonstrate the shape of the dilated ventricles in this fetus with spina bifida Inversion mode used to demonstrate the heart and the crossing of the great vessels
7 Glass-Body mode rendering If the volume data is not acquired from a simple gray scale image but combined with color Doppler, power Doppler or High- Definition (HD-) flow, the 3D volume includes the Doppler information as well. The acquisition can either be achieved as static 3D or as a STIC. Volume data can be displayed in 3 ways: either the color information alone or the gray scale information alone or a combination of both as a so called glass body mode. A prerequisite for a good volume is the optimal presetting of the color during 2D scan before acquiring a volume. Once the presetting of the 2D-power Doppler image is optimized, the acquisition can ideally be used to demonstrate the spatial relationship or size differences of the great vessels, connecting VSD, or even coarctation of the aorta or aberrant aortic arch vessels. One of the main application fields of this mode is the demonstration of the great vessels crossing or their parallel course in transposition of the great arteries. The clinical use of such new techniques, however, has yet to be evaluated. Peripheral vessels such as the umbilical cord, intraabdominal, thoracic and brain vessels can be well demonstrated. The use of Magicut permits selective removal of both grayscale and color information or one of the two, which allows for better highlighting of the region of interest. Glass body mode: on the left the color alone and on the right as glass body mode Glass body mode of the heart and abdominal vessels (left) and of the great vessels from a STIC volume (right) Glass body mode of a STIC volume combined with color demonstrating the crossing of the great vessels (left). On the right fetal heart and vessels seen with high-definition flow where gray scale information was partly removed by Magicut Volume calculation Biometry is an integral part of the antenatal ultrasound examination and has been achieved for years by measuring distances, circumferences and areas. The acquisition of a 3D volume data set allows easy reconstruction of a selected 2D plane to perform well known measurements such as nuchal translucency, biparietal diameter or femur length and others, but also offers the potential to accurately calculate the volume of a selected region of interest. Volume measurements can be achieved either using the multiplanar mode or by using the VOCAL software (VOLume CALculation). Recently, another possibility was developed for liquid-filled structures involving the threshold principle in combination with the inversion mode. Volume measurements are still time-consuming and thus limited to research purposes. Glass body mode combined with High- Definition (HD) Flow showing here the pericallosal artery (left) and the cord insertion on the placental site (right) Volume measurements and charts were reported for the placenta, the amniotic cavity, the first trimester fetus, the fetal brain, liver, and arm, but there was a special interest in measuring fetal lung volume. Fields of interest in these measurements focused chiefly on the detection of difference in volume in pregnancies complicated by chromosomal anomalies, diabetes, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital diaphragmatic hernia...
8 Conclusion Three-dimensional ultrasound has moved from a simple advertising gimmick directed at parents to a powerful tool in prenatal diagnosis. The different display modes available can be used for the demonstration of the spatial appearance of surface structures as well as the projection of bony structures for a better understanding of skeletal findings and others. The multiplanar mode and tomographic imaging allows the reconstruction of planes not directly seen on the screen and offers new insight into fetal anatomy similar to images made known by MRI as demonstrated for brain structures. Some of the other rendering displays present on the machine were not emphasized in this article. The numerous enthusiastic articles on 3D written in recent years confirm that we are rapidly moving today from the era of sonography in 2D planes to volume ultrasound. With this article, we aimed to stimulate the reader s curiosity with regard to this revolutionary technology and we hope to encourage the examiner to use volume ultrasound more often and to clinically apply the different rendering modes. GE Medical Systems Ultrasound United Kingdom Fax: (+44) , Tel: (+44) GE Medical Systems America: Milwaukee, WI, USA - Fax: (+1) GE Medical Systems Asia: Tokyo, Japan Fax: (+81) Shanghai, China Fax:(+86) Visit us online at: General Electric Company All rights reserved. GE Healthcare, a division of General Electric Company. General Electric Company reserves the right to make changes in specifications and features shown herein, or discontinue the product described at any time without notice or obligation. Contact your GE representative for the most current information. General Electric Company, doing business as GE Healthcare. GE, GE Monogram, Voluson and CrossXBeam CRI are trademarks of General Electric Company. Healthcare Re-imagined GE is dedicated to helping you transform healthcare delivery by driving critical breakthroughs in biology and technology. Our expertise in medical imaging and information technologies, medical diagnostics, patient monitoring systems, drug discovery, and biopharmaceutical manufacturing technologies is enabling healthcare professionals around the world discover new ways to predict, diagnose and treat disease earlier. We call this model of care "Early Health." The goal: to help clinicians detect disease earlier, access more information and intervene earlier with more targeted treatments, so they can help their patients live their lives to the fullest. Re-think, Re-discover, Re-invent, Re-imagine. GE Ultraschall Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG Beethovenstr. 239, D Solingen Fax: (+49) Tel: (+49) GE imagination at work Printed in Austria U022E
GE Healthcare. Vivid 7 Dimension 08 Cardiovascular ultrasound system
 GE Healthcare Vivid 7 Dimension 08 Cardiovascular ultrasound system ltra Definition. Technology. Performance. Start with a system that s proven its worth in LV quantification and 4D imaging. Then add even
GE Healthcare Vivid 7 Dimension 08 Cardiovascular ultrasound system ltra Definition. Technology. Performance. Start with a system that s proven its worth in LV quantification and 4D imaging. Then add even
The Supreme 3D/4D Ultrasound. The Supreme 3D/4D Ultrasound. CT-V20-ICM
 The Supreme 3D/4D Ultrasound The Supreme 3D/4D Ultrasound www.medison.com info@medison.com CT-V20-ICM-06.20.2008 The Supreme 3D/4D Ultrasound Since launching the first commercially available 3D ultrasound
The Supreme 3D/4D Ultrasound The Supreme 3D/4D Ultrasound www.medison.com info@medison.com CT-V20-ICM-06.20.2008 The Supreme 3D/4D Ultrasound Since launching the first commercially available 3D ultrasound
3D XI. Multi-Slice View. Oblique View. Demo és second hand ultrahang-diagnosztikai berendezések a honlapon!
 SONARMED Kereskedelmi és Egészségügyi Szolgáltató Kft. Tel.: +36 1 203 75 81 1119 Budapest, Nándorfejérvári út 31. fsz. 6-7. +36 20 982 63 11 / 12 info@sonarmed.hu Fax: +36 1 205 39 59 3D XI 3D extended
SONARMED Kereskedelmi és Egészségügyi Szolgáltató Kft. Tel.: +36 1 203 75 81 1119 Budapest, Nándorfejérvári út 31. fsz. 6-7. +36 20 982 63 11 / 12 info@sonarmed.hu Fax: +36 1 205 39 59 3D XI 3D extended
Chapter 32 3-D and 4-D imaging in Obstetrics and Gynecology
 Objectives Define common terms related to 3D/4D ultrasound Chapter 32 3-D and 4-D imaging in Obstetrics and Gynecology Bridgette Lunsford Describe how 3D and 4D imaging differs from 2D ultrasound Identify
Objectives Define common terms related to 3D/4D ultrasound Chapter 32 3-D and 4-D imaging in Obstetrics and Gynecology Bridgette Lunsford Describe how 3D and 4D imaging differs from 2D ultrasound Identify
LOGIQ. V2 Ultrasound. Part of LOGIQ Vision Series. Imagination at work LOGIQ is a trademark of General Electric Company.
 TM LOGIQ V2 Ultrasound Part of LOGIQ Vision Series Imagination at work The brilliance of color. The simplicity of GE. Now you can add the advanced capabilities of color Doppler to patient care with the
TM LOGIQ V2 Ultrasound Part of LOGIQ Vision Series Imagination at work The brilliance of color. The simplicity of GE. Now you can add the advanced capabilities of color Doppler to patient care with the
Focus on your needs. Ultrasound system HS60 SAMSUNG MEDISON CO., LTD. CT-HS60 V1.0-OB-FT EN
 Samsung Medison, an affiliate of Samsung Electronics, is a global medical company founded in 1985. With a mission to bring health and well-being to people's lives, the company manufactures diagnostic ultrasound
Samsung Medison, an affiliate of Samsung Electronics, is a global medical company founded in 1985. With a mission to bring health and well-being to people's lives, the company manufactures diagnostic ultrasound
US 1.
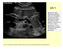 US 1 Sample image: Normal pancreas seen on sonogram. Looking up from abdomen toward the head of the patient. The liver is in front of the pancreas. A vein draining the spleen is behind the pancreas http://www.radiologyinfo.org/photocat/photos.cfm?image=abdo-us-pancr.jpg&&subcategory=abdomen&&stop=9
US 1 Sample image: Normal pancreas seen on sonogram. Looking up from abdomen toward the head of the patient. The liver is in front of the pancreas. A vein draining the spleen is behind the pancreas http://www.radiologyinfo.org/photocat/photos.cfm?image=abdo-us-pancr.jpg&&subcategory=abdomen&&stop=9
Leading the New Standards
 Samsung Medison is a global leading medical devices company. Founded in 1985, the company now sells cutting-edge medical devices including diagnostic ultrasound, digital X-ray and blood analyzer, in 110
Samsung Medison is a global leading medical devices company. Founded in 1985, the company now sells cutting-edge medical devices including diagnostic ultrasound, digital X-ray and blood analyzer, in 110
GE Healthcare CLINICAL GALLERY. Discovery * MR750w 3.0T. This brochure is intended for European healthcare professionals.
 GE Healthcare CLINICAL GALLERY Discovery * MR750w 3.0T This brochure is intended for European healthcare professionals. NEURO PROPELLER delivers high resolution, motion insensitive imaging in all planes.
GE Healthcare CLINICAL GALLERY Discovery * MR750w 3.0T This brochure is intended for European healthcare professionals. NEURO PROPELLER delivers high resolution, motion insensitive imaging in all planes.
A powerful, software-based beamformer image reconstruction platform
 csound A powerful, software-based beamformer image reconstruction platform Figure 1: Vivid S70 and E90/95; first GE systems built upon the csound platform Background GE s cardiovascular ultrasound imaging
csound A powerful, software-based beamformer image reconstruction platform Figure 1: Vivid S70 and E90/95; first GE systems built upon the csound platform Background GE s cardiovascular ultrasound imaging
GE Healthcare. Vivid E9 XDclear. with. healthymagination. GE imagination at work
 GE Healthcare with Vivid E9 XDclear healthymagination GE imagination at work Extraordinary capabilities Whether in TTE or TEE, capture the entire heart in a single beat. Image a valve, or the entire ventricle
GE Healthcare with Vivid E9 XDclear healthymagination GE imagination at work Extraordinary capabilities Whether in TTE or TEE, capture the entire heart in a single beat. Image a valve, or the entire ventricle
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks
 Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
Tomographic Reconstruction
 Tomographic Reconstruction 3D Image Processing Torsten Möller Reading Gonzales + Woods, Chapter 5.11 2 Overview Physics History Reconstruction basic idea Radon transform Fourier-Slice theorem (Parallel-beam)
Tomographic Reconstruction 3D Image Processing Torsten Möller Reading Gonzales + Woods, Chapter 5.11 2 Overview Physics History Reconstruction basic idea Radon transform Fourier-Slice theorem (Parallel-beam)
Ultrasound To Go. MySono U5
 Ultrasound To Go MySono U5 Ultrasound To Go With the introduction of the MySono U5, Samsung Medison brings you a fully featured ultrasound imaging system to go. Delivering exceptional image quality and
Ultrasound To Go MySono U5 Ultrasound To Go With the introduction of the MySono U5, Samsung Medison brings you a fully featured ultrasound imaging system to go. Delivering exceptional image quality and
4D Auto MVQ (Mitral Valve Quantification)
 4D Auto MVQ (Mitral Valve Quantification) Federico Veronesi, Glenn Reidar Lie, Stein Inge Rabben GE Healthcare Introduction As the number of mitral valve repairs is on the rise, so is the need for mitral
4D Auto MVQ (Mitral Valve Quantification) Federico Veronesi, Glenn Reidar Lie, Stein Inge Rabben GE Healthcare Introduction As the number of mitral valve repairs is on the rise, so is the need for mitral
USER MANUAL VP PLANNING
 USER MANUAL VP PLANNING 1.0 Mobile application ios Visible Patient SAS RCS Strasbourg TI 794 458 125 1 place de l'ho pital 67000 Strasbourg, FRANCE Share capital: 58330 Tel.: 33 (0)3 88 11 90 00 Fax: 33
USER MANUAL VP PLANNING 1.0 Mobile application ios Visible Patient SAS RCS Strasbourg TI 794 458 125 1 place de l'ho pital 67000 Strasbourg, FRANCE Share capital: 58330 Tel.: 33 (0)3 88 11 90 00 Fax: 33
Ultrasound. Q-Station software. Streamlined workflow solutions. Philips Q-Station ultrasound workspace software
 Ultrasound Q-Station software Streamlined workflow solutions Philips Q-Station ultrasound workspace software Managing your off-cart workf low Everyone is being asked to do more with fewer resources it
Ultrasound Q-Station software Streamlined workflow solutions Philips Q-Station ultrasound workspace software Managing your off-cart workf low Everyone is being asked to do more with fewer resources it
USER MANUAL VP PLANNING
 USER MANUAL VP PLANNING 1.0 Mobile application Android Visible Patient SAS RCS Strasbourg TI 794 458 125 1 place de l'ho pital 67000 Strasbourg, FRANCE Share capital: 58330 Tel.: 33 (0)3 88 11 90 00 Fax:
USER MANUAL VP PLANNING 1.0 Mobile application Android Visible Patient SAS RCS Strasbourg TI 794 458 125 1 place de l'ho pital 67000 Strasbourg, FRANCE Share capital: 58330 Tel.: 33 (0)3 88 11 90 00 Fax:
GE Healthcare. Vivid E9 XDclear. with
 GE Healthcare Vivid E9 XDclear with capabilities for every day Whether in TTE or TEE, capture the entire heart in a single beat. Image a valve, or the entire ventricle with excellent image quality. And
GE Healthcare Vivid E9 XDclear with capabilities for every day Whether in TTE or TEE, capture the entire heart in a single beat. Image a valve, or the entire ventricle with excellent image quality. And
Anatomy 1 st Paper. Past Papers
 Anatomy 1 st Paper Past Papers September 2010 April 2010 September 2009 April 2009 September 2008 April 2008 September 2007 April 2007 September 2006 May 2006 September 2005 April 2005 September 2004 April
Anatomy 1 st Paper Past Papers September 2010 April 2010 September 2009 April 2009 September 2008 April 2008 September 2007 April 2007 September 2006 May 2006 September 2005 April 2005 September 2004 April
3D Echocardiography Development Timeline
 3D Acquisition Strategies and Display Lissa Sugeng, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Director of the Yale Echo Lab and Echo Core Lab (YCRG) And Peter Flueckiger, MD Advanced Imaging Cardiology Fellow
3D Acquisition Strategies and Display Lissa Sugeng, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Director of the Yale Echo Lab and Echo Core Lab (YCRG) And Peter Flueckiger, MD Advanced Imaging Cardiology Fellow
GE Healthcare. Vscan Extend Data Sheet
 GE Healthcare Vscan Extend Data Sheet Vscan Extend Vscan Extend is a general purpose diagnostic ultrasound imaging system that can enable qualified and trained healthcare professionals to visualize and
GE Healthcare Vscan Extend Data Sheet Vscan Extend Vscan Extend is a general purpose diagnostic ultrasound imaging system that can enable qualified and trained healthcare professionals to visualize and
Imaging Guide Pancreatic Imaging
 Imaging Guide Guide to Small Animal Pancreatic Imaging using the Vevo 2100 Imaging System Ver 1.0 Guide to Small Animal Pancreatic Imaging using the Vevo 2100 Imaging System Course Objectives: This guide
Imaging Guide Guide to Small Animal Pancreatic Imaging using the Vevo 2100 Imaging System Ver 1.0 Guide to Small Animal Pancreatic Imaging using the Vevo 2100 Imaging System Course Objectives: This guide
Medical Image Segmentation
 Medical Image Segmentation Xin Yang, HUST *Collaborated with UCLA Medical School and UCSB Segmentation to Contouring ROI Aorta & Kidney 3D Brain MR Image 3D Abdominal CT Image Liver & Spleen Caudate Nucleus
Medical Image Segmentation Xin Yang, HUST *Collaborated with UCLA Medical School and UCSB Segmentation to Contouring ROI Aorta & Kidney 3D Brain MR Image 3D Abdominal CT Image Liver & Spleen Caudate Nucleus
Clinical Importance. Aortic Stenosis. Aortic Regurgitation. Ultrasound vs. MRI. Carotid Artery Stenosis
 Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
3D Human Internal Organs Representation Model (Updates)
 3D Human Internal Organs Representation Model (Updates) ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 24/WG 9 & Web3D Meetings January 21-24, 2019 Myeong Won Lee (The University of Suwon) Requirements (1) 3D printing and scanning
3D Human Internal Organs Representation Model (Updates) ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 24/WG 9 & Web3D Meetings January 21-24, 2019 Myeong Won Lee (The University of Suwon) Requirements (1) 3D printing and scanning
Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans
 Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans Wits University Dec 05, 2012 Roadmap Introduction to the problem Motivation Related Work Our approach Expected Results Introduction Nowadays, imaging devices like
Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans Wits University Dec 05, 2012 Roadmap Introduction to the problem Motivation Related Work Our approach Expected Results Introduction Nowadays, imaging devices like
UGEO G60 Performance in style
 CT-UGEO-G60-CWW-MCI-0731-EN Performance in style 2012 Samsung Electronics All Rights Reserved. Samsung Electronics Reserves The Right To Modify The Design, Packaging, Specifications And Features Shown
CT-UGEO-G60-CWW-MCI-0731-EN Performance in style 2012 Samsung Electronics All Rights Reserved. Samsung Electronics Reserves The Right To Modify The Design, Packaging, Specifications And Features Shown
Mohammad Baharvandy & Sina Fazelpour
 Mohammad Baharvandy & Sina Fazelpour Ultrasound Basics Data acquisition in 3D Reconstruction of 2D images 3D Ultrasound Modeling Medical applications 4D Ultrasound 2 Ultrasound consist of sound waves of
Mohammad Baharvandy & Sina Fazelpour Ultrasound Basics Data acquisition in 3D Reconstruction of 2D images 3D Ultrasound Modeling Medical applications 4D Ultrasound 2 Ultrasound consist of sound waves of
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization
 Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Medical Images Analysis and Processing
 Medical Images Analysis and Processing - 25642 Emad Course Introduction Course Information: Type: Graduated Credits: 3 Prerequisites: Digital Image Processing Course Introduction Reference(s): Insight
Medical Images Analysis and Processing - 25642 Emad Course Introduction Course Information: Type: Graduated Credits: 3 Prerequisites: Digital Image Processing Course Introduction Reference(s): Insight
Tissue Doppler gated (TDOG) dynamic three-dimensional ultrasound imaging of the fetal heart
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 192 198 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1094 Tissue Doppler gated (TDOG) dynamic three-dimensional ultrasound imaging
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 192 198 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1094 Tissue Doppler gated (TDOG) dynamic three-dimensional ultrasound imaging
FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA
 FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA by: John A. Rumberger, PhD, MD, FACC Your patient has chest pain. The Cardiac CT Angiography shows plaque in the LAD. You adjust the viewing window trying to evaluate the stenosis
FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA by: John A. Rumberger, PhD, MD, FACC Your patient has chest pain. The Cardiac CT Angiography shows plaque in the LAD. You adjust the viewing window trying to evaluate the stenosis
IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation
 Getting started guide IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation This guide outlines the basic steps to perform and manipulate a 3D reconstruction of volumetric image data using IMPAX Volume
Getting started guide IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation This guide outlines the basic steps to perform and manipulate a 3D reconstruction of volumetric image data using IMPAX Volume
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis. A. Criminisi
 Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Beyond Performance and Value
 Putting the back in ultrasound Beyond Performance and Value Esaote s new ultra-performance MyLab 9 exp ultrasound system is designed to support a full range of shared service diagnostic imaging environments.
Putting the back in ultrasound Beyond Performance and Value Esaote s new ultra-performance MyLab 9 exp ultrasound system is designed to support a full range of shared service diagnostic imaging environments.
Mindray. Hand-carried Diagnostic Ultrasound System. Expanding the Envelope of Performance and Flexibility
 M7 Mindray M7 Hand-carried Diagnostic Ultrasound System Expanding the Envelope of Performance and Flexibility M7 Diagnostic Ultrasound System Equipped for Quality Radiology Cardiology Outpatient Emergency
M7 Mindray M7 Hand-carried Diagnostic Ultrasound System Expanding the Envelope of Performance and Flexibility M7 Diagnostic Ultrasound System Equipped for Quality Radiology Cardiology Outpatient Emergency
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing SPECIAL TOPICS CT IMAGES Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 What is an image? 2 Are images only about visual concepts? We ve already seen that there are other kinds of image. In this lecture
Digital Image Processing SPECIAL TOPICS CT IMAGES Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 What is an image? 2 Are images only about visual concepts? We ve already seen that there are other kinds of image. In this lecture
VEVO 1100 Sole Source Specifications
 VEVO 1100 Sole Source Specifications Table of Contents 1.SYSTEM... 2 1-1 Licensing for the User... 2 1-2 Safety... 2 1-3 Portability... 2 2.TRANSDUCERS... 2 2-1 MicroScan transducers... 2 3. IMAGING STATION...
VEVO 1100 Sole Source Specifications Table of Contents 1.SYSTEM... 2 1-1 Licensing for the User... 2 1-2 Safety... 2 1-3 Portability... 2 2.TRANSDUCERS... 2 2-1 MicroScan transducers... 2 3. IMAGING STATION...
Comprehensive treatment planning for brachytherapy. Advanced planning made easy
 Comprehensive treatment planning for brachytherapy Advanced planning made easy Oncentra Brachy offers a variety of smart tools that facilitate many of the repetitive tasks for you. In contemporary brachytherapy,
Comprehensive treatment planning for brachytherapy Advanced planning made easy Oncentra Brachy offers a variety of smart tools that facilitate many of the repetitive tasks for you. In contemporary brachytherapy,
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Physics Tutorial Physics Tutorial Purpose: Training: Assessments: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Physics Tutorial Physics Tutorial Purpose: Training: Assessments: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for
Ultrasound To Go. The MySono U5 -
 Ultrasound To Go The MySono U5 - Ultrasound To Go With the introduction of the MySono U5, MEDISON brings you a fully featured ultrasound imaging system to go. Delivering exceptional image quality and featuring
Ultrasound To Go The MySono U5 - Ultrasound To Go With the introduction of the MySono U5, MEDISON brings you a fully featured ultrasound imaging system to go. Delivering exceptional image quality and featuring
Medical Image Registration
 Medical Image Registration Submitted by NAREN BALRAJ SINGH SB ID# 105299299 Introduction Medical images are increasingly being used within healthcare for diagnosis, planning treatment, guiding treatment
Medical Image Registration Submitted by NAREN BALRAJ SINGH SB ID# 105299299 Introduction Medical images are increasingly being used within healthcare for diagnosis, planning treatment, guiding treatment
Beginner s Guide to Vevo 2100
 PN 12090 Beginner s Guide to Vevo 2100 December 2008 This Beginner s Guide to Vevo 2100 provides a quick overview of the Vevo 2100 imaging modes and provides key tips to allow users to start a study, acquire
PN 12090 Beginner s Guide to Vevo 2100 December 2008 This Beginner s Guide to Vevo 2100 provides a quick overview of the Vevo 2100 imaging modes and provides key tips to allow users to start a study, acquire
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) of Liver Disease
 Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) of Liver Disease Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics Inc. jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com 1-585-249-6231 1. Overview of MRE Imaging MRE is a magnetic
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) of Liver Disease Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics Inc. jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com 1-585-249-6231 1. Overview of MRE Imaging MRE is a magnetic
Data Fusion Virtual Surgery Medical Virtual Reality Team. Endo-Robot. Database Functional. Database
 2017 29 6 16 GITI 3D From 3D to 4D imaging Data Fusion Virtual Surgery Medical Virtual Reality Team Morphological Database Functional Database Endo-Robot High Dimensional Database Team Tele-surgery Robotic
2017 29 6 16 GITI 3D From 3D to 4D imaging Data Fusion Virtual Surgery Medical Virtual Reality Team Morphological Database Functional Database Endo-Robot High Dimensional Database Team Tele-surgery Robotic
ULTRASOUND is the most common imaging modality in
 1054 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 33, NO. 5, MAY 2014 Automatic Detection and Measurement of Structures in Fetal Head Ultrasound Volumes Using Sequential Estimation and Integrated Detection
1054 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 33, NO. 5, MAY 2014 Automatic Detection and Measurement of Structures in Fetal Head Ultrasound Volumes Using Sequential Estimation and Integrated Detection
rscriptor Tutorial 1 Introduction Table of Contents
 rscriptor Tutorial sales@scriptorsoftware.com www.scriptorsoftware.com 1-844-230-0455 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Tutorial #1 rscriptor header... 2 3 Tutorial #2 Narrative Reporting... 3 4
rscriptor Tutorial sales@scriptorsoftware.com www.scriptorsoftware.com 1-844-230-0455 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Tutorial #1 rscriptor header... 2 3 Tutorial #2 Narrative Reporting... 3 4
How to Adjust the 16-Bit CLUT (Color Look Up Table) Editor in OsiriX
 How to Adjust the 16-Bit CLUT (Color Look Up Table) Editor in OsiriX 1. Import the series you are interested in into the 2D/3D Viewer. I m using the OBELIX data set, slices 1-395, available for download
How to Adjust the 16-Bit CLUT (Color Look Up Table) Editor in OsiriX 1. Import the series you are interested in into the 2D/3D Viewer. I m using the OBELIX data set, slices 1-395, available for download
Beyond Performance and Value
 Putting the back in ultrasound Beyond Performance and Value Esaote s new ultra-performance MyLab 9 exp ultrasound system is designed to support a full range of shared service diagnostic imaging environments.
Putting the back in ultrasound Beyond Performance and Value Esaote s new ultra-performance MyLab 9 exp ultrasound system is designed to support a full range of shared service diagnostic imaging environments.
Simpler on the outside. Smarter on the inside.
 GE Healthcare Simpler on the outside. Smarter on the inside. The MAC 1600 electrocardiograph Imagine a scalable ECG device that evolves with the demanding needs of your practice; one that is simple to
GE Healthcare Simpler on the outside. Smarter on the inside. The MAC 1600 electrocardiograph Imagine a scalable ECG device that evolves with the demanding needs of your practice; one that is simple to
Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation
 Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation Qian Huang Wright State University, Computer Science Department Abstract The volume information extracted from computed tomography angiogram (CTA) datasets makes
Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation Qian Huang Wright State University, Computer Science Department Abstract The volume information extracted from computed tomography angiogram (CTA) datasets makes
Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
Your versatile performer to depend on. Ultrasound. Philips ClearVue ultrasound family
 Ultrasound ClearVue Your versatile performer to depend on Philips ClearVue ultrasound family Over 70 countries More than 5,000 systems Touching 25 million lives every year For one versatile family Dependability
Ultrasound ClearVue Your versatile performer to depend on Philips ClearVue ultrasound family Over 70 countries More than 5,000 systems Touching 25 million lives every year For one versatile family Dependability
GE Healthcare. AppsLinq* remote courses catalogue
 GE Healthcare AppsLinq* remote courses catalogue AppsLinq * remote training for MR Magnetic Resonance AppsLinq* a GE Training in Partnership (TiP) program, revolutionizes applications training with live,
GE Healthcare AppsLinq* remote courses catalogue AppsLinq * remote training for MR Magnetic Resonance AppsLinq* a GE Training in Partnership (TiP) program, revolutionizes applications training with live,
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class III
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class III 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class III 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
CT Basics Principles of Spiral CT Dose. Always Thinking Ahead.
 1 CT Basics Principles of Spiral CT Dose 2 Who invented CT? 1963 - Alan Cormack developed a mathematical method of reconstructing images from x-ray projections Sir Godfrey Hounsfield worked for the Central
1 CT Basics Principles of Spiral CT Dose 2 Who invented CT? 1963 - Alan Cormack developed a mathematical method of reconstructing images from x-ray projections Sir Godfrey Hounsfield worked for the Central
Shadow casting. What is the problem? Cone Beam Computed Tomography THE OBJECTIVES OF DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING IDEAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING STUDY LIMITATIONS
 Cone Beam Computed Tomography THE OBJECTIVES OF DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Reveal pathology Reveal the anatomic truth Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu IDEAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING STUDY Provides desired diagnostic
Cone Beam Computed Tomography THE OBJECTIVES OF DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Reveal pathology Reveal the anatomic truth Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu IDEAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING STUDY Provides desired diagnostic
Prostate Detection Using Principal Component Analysis
 Prostate Detection Using Principal Component Analysis Aamir Virani (avirani@stanford.edu) CS 229 Machine Learning Stanford University 16 December 2005 Introduction During the past two decades, computed
Prostate Detection Using Principal Component Analysis Aamir Virani (avirani@stanford.edu) CS 229 Machine Learning Stanford University 16 December 2005 Introduction During the past two decades, computed
Volumetric Analysis of the Heart from Tagged-MRI. Introduction & Background
 Volumetric Analysis of the Heart from Tagged-MRI Dimitris Metaxas Center for Computational Biomedicine, Imaging and Modeling (CBIM) Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ Collaboration with Dr. Leon Axel,
Volumetric Analysis of the Heart from Tagged-MRI Dimitris Metaxas Center for Computational Biomedicine, Imaging and Modeling (CBIM) Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ Collaboration with Dr. Leon Axel,
Whole Body Submillimeter Scan
 128 Whole Body Submillimeter Scan The real value of 64ch/128slice CT systems does not come from the ability to perfom cardiac scans but the capability to scan all parts of the body in high definition submillimeter
128 Whole Body Submillimeter Scan The real value of 64ch/128slice CT systems does not come from the ability to perfom cardiac scans but the capability to scan all parts of the body in high definition submillimeter
Katja the 24 th week of virtual pregnancy for dosimetric calculations
 Pol J Med Phys Eng. 2008;14(1):13-19. PL ISSN 1425-4689 doi: 10.2478/v10013-008-0002-4 website: http://www.pjmpe.waw.pl Janine Becker, Maria Zankl, Ute Fill, Christoph Hoeschen Katja the 24 th week of
Pol J Med Phys Eng. 2008;14(1):13-19. PL ISSN 1425-4689 doi: 10.2478/v10013-008-0002-4 website: http://www.pjmpe.waw.pl Janine Becker, Maria Zankl, Ute Fill, Christoph Hoeschen Katja the 24 th week of
Fundamentals of CT imaging
 SECTION 1 Fundamentals of CT imaging I History In the early 1970s Sir Godfrey Hounsfield s research produced the first clinically useful CT scans. Original scanners took approximately 6 minutes to perform
SECTION 1 Fundamentals of CT imaging I History In the early 1970s Sir Godfrey Hounsfield s research produced the first clinically useful CT scans. Original scanners took approximately 6 minutes to perform
Process to Convert DICOM Data to 3D Printable STL Files
 HOW-TO GUIDE Process to Convert DICOM Data to 3D Printable STL Files Mac Cameron, Application Engineer Anatomical models have several applications in the medical space from patient-specific models used
HOW-TO GUIDE Process to Convert DICOM Data to 3D Printable STL Files Mac Cameron, Application Engineer Anatomical models have several applications in the medical space from patient-specific models used
Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings
 Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings 김보형 서울대학교컴퓨터공학부 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Lab. 2011. 3. 23 1 Computer Graphics & Image Processing Computer Graphics : Create,
Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings 김보형 서울대학교컴퓨터공학부 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Lab. 2011. 3. 23 1 Computer Graphics & Image Processing Computer Graphics : Create,
icatvision Quick Reference
 icatvision Quick Reference Navigating the i-cat Interface This guide shows how to: View reconstructed images Use main features and tools to optimize an image. REMINDER Images are displayed as if you are
icatvision Quick Reference Navigating the i-cat Interface This guide shows how to: View reconstructed images Use main features and tools to optimize an image. REMINDER Images are displayed as if you are
VieW 3D. 3D Post-Processing WorKstation THE THIRD DIMENSION. Version 3.1
 VieW 3D 3D Post-Processing WorKstation THE THIRD DIMENSION Version 3.1 iq-view 3D THE FULLY-FEATURED 3D MEDICAL IMAGING SOLUTION FOR RADIOLOGISTS iq-view 3D contains all components of iq-view with the
VieW 3D 3D Post-Processing WorKstation THE THIRD DIMENSION Version 3.1 iq-view 3D THE FULLY-FEATURED 3D MEDICAL IMAGING SOLUTION FOR RADIOLOGISTS iq-view 3D contains all components of iq-view with the
7D Cardiac Flow MRI: Techniques & Automation of Reconstruction
 Cleveland State University EngagedScholarship@CSU ETD Archive 2012 7D Cardiac Flow MRI: Techniques & Automation of Reconstruction Michael G. Ambrosia Cleveland State University Follow this and additional
Cleveland State University EngagedScholarship@CSU ETD Archive 2012 7D Cardiac Flow MRI: Techniques & Automation of Reconstruction Michael G. Ambrosia Cleveland State University Follow this and additional
Chapter 9 Conclusions
 Chapter 9 Conclusions This dissertation has described a new method for using local medial properties of shape to identify and measure anatomical structures. A bottom up approach based on image properties
Chapter 9 Conclusions This dissertation has described a new method for using local medial properties of shape to identify and measure anatomical structures. A bottom up approach based on image properties
step into the future Ultrasound Diagnostic Imaging System
 step into the future Ultrasound Diagnostic Imaging System Moving into a new era for ultrasound diagnostics. With a proven track record in medical imaging, FUJIFILM has partnered with SonoSite, an innovator
step into the future Ultrasound Diagnostic Imaging System Moving into a new era for ultrasound diagnostics. With a proven track record in medical imaging, FUJIFILM has partnered with SonoSite, an innovator
This is your imaging dashboard. There is a bevy of valuable information to read from here. Let s break it up.
 The Volume Strikes Back Press the (4D) button. This is your imaging dashboard. There is a bevy of valuable information to read from here. Let s break it up. In the Left GUI (Graphic User Interface), you
The Volume Strikes Back Press the (4D) button. This is your imaging dashboard. There is a bevy of valuable information to read from here. Let s break it up. In the Left GUI (Graphic User Interface), you
Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets
 Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets Stefan C. Saur 1, Caroline Kühnel 2, Tobias Boskamp 2, Gábor Székely 1, Philippe Cattin 1,3 1 Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets Stefan C. Saur 1, Caroline Kühnel 2, Tobias Boskamp 2, Gábor Székely 1, Philippe Cattin 1,3 1 Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
A Study of Medical Image Analysis System
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
NON OB ULTRASOUND MORPHOMETRICS AS BIOMARKERS
 NON OB ULTRASOUND MORPHOMETRICS AS BIOMARKERS Brian S Garra Washington DC VA Medical Center and Division of Imaging & Applied Mathematics, OSEL, CDRH, FDA GOALS Review Major Types of Clinical Ultrasonic
NON OB ULTRASOUND MORPHOMETRICS AS BIOMARKERS Brian S Garra Washington DC VA Medical Center and Division of Imaging & Applied Mathematics, OSEL, CDRH, FDA GOALS Review Major Types of Clinical Ultrasonic
MRI. When to use What sequences. Outline 2012/09/19. Sequence: Definition. Basic Principles: Step 2. Basic Principles: Step 1. Govind Chavhan, MD
 MRI When to use What sequences Govind Chavhan, MD Assistant Professor and Staff Radiologist The Hospital For Sick Children, Toronto Planning Acquisition Post processing Interpretation Patient history and
MRI When to use What sequences Govind Chavhan, MD Assistant Professor and Staff Radiologist The Hospital For Sick Children, Toronto Planning Acquisition Post processing Interpretation Patient history and
Brilliance CT Big Bore.
 1 2 2 There are two methods of RCCT acquisition in widespread clinical use: cine axial and helical. In RCCT with cine axial acquisition, repeat CT images are taken each couch position while recording respiration.
1 2 2 There are two methods of RCCT acquisition in widespread clinical use: cine axial and helical. In RCCT with cine axial acquisition, repeat CT images are taken each couch position while recording respiration.
Image Acquisition Systems
 Image Acquisition Systems Goals and Terminology Conventional Radiography Axial Tomography Computer Axial Tomography (CAT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) PET, SPECT Ultrasound Microscopy Imaging ITCS
Image Acquisition Systems Goals and Terminology Conventional Radiography Axial Tomography Computer Axial Tomography (CAT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) PET, SPECT Ultrasound Microscopy Imaging ITCS
Copyright 2017 Medical IP - Tutorial Medip v /2018, Revision
 Copyright 2017 Medical IP - Tutorial Medip v.1.0.0.9 01/2018, Revision 1.0.0.2 List of Contents 1. Introduction......................................................... 2 2. Overview..............................................................
Copyright 2017 Medical IP - Tutorial Medip v.1.0.0.9 01/2018, Revision 1.0.0.2 List of Contents 1. Introduction......................................................... 2 2. Overview..............................................................
11/18/ CPT Preauthorization Groupings Effective January 1, Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6. CPT Description SEGR CT01
 Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Description SEGR 74150 74160
Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Description SEGR 74150 74160
Compact Delta II with
 W E R E A L L A B O U T P E O P L E. The Dornier Compact Delta II with Integrated Transportable Lithotripter The Dornier The Optimal Solution: The Dornier Compact Delta II Optimal Solution Compact DeltaII
W E R E A L L A B O U T P E O P L E. The Dornier Compact Delta II with Integrated Transportable Lithotripter The Dornier The Optimal Solution: The Dornier Compact Delta II Optimal Solution Compact DeltaII
Development and anatomical details of Japanese adult male/female voxel models
 Development and anatomical details of Japanese adult male/female voxel models Tomoaki Nagaoka, Soichi Watanabe, *Etsuo kunieda, **Masao Taki and Yukio Yamanaka National Institute of Information and Communications
Development and anatomical details of Japanese adult male/female voxel models Tomoaki Nagaoka, Soichi Watanabe, *Etsuo kunieda, **Masao Taki and Yukio Yamanaka National Institute of Information and Communications
Improve your image. ClearVue 550 ultrasound system. The print quality of this copy is not an accurate representation of the original.
 Improve your image ClearVue 550 ultrasound system Not yet available in the U.S. Smart and intuitive One look at the Philips ClearVue 550 ultrasound system and you ll see the smooth, graceful lines and
Improve your image ClearVue 550 ultrasound system Not yet available in the U.S. Smart and intuitive One look at the Philips ClearVue 550 ultrasound system and you ll see the smooth, graceful lines and
Lecture 6: Medical imaging and image-guided interventions
 ME 328: Medical Robotics Winter 2019 Lecture 6: Medical imaging and image-guided interventions Allison Okamura Stanford University Updates Assignment 3 Due this Thursday, Jan. 31 Note that this assignment
ME 328: Medical Robotics Winter 2019 Lecture 6: Medical imaging and image-guided interventions Allison Okamura Stanford University Updates Assignment 3 Due this Thursday, Jan. 31 Note that this assignment
Resona 7. New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation. Premium Ultrasound System
 Resona 7 Premium Ultrasound System New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation With over 20 years of experience, Mindray hosts a wide range of ultrasound imaging solutions including cart-based and portable systems.
Resona 7 Premium Ultrasound System New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation With over 20 years of experience, Mindray hosts a wide range of ultrasound imaging solutions including cart-based and portable systems.
연구용유방초음파질관리 원광대학병원김혜원
 연구용유방초음파질관리 원광대학병원김혜원 Why US QC? Quality control (QC) testing of ultrasound scanners is important to verify the proper and consistent operation of these devices. main goal ; quality improvement Guidelines
연구용유방초음파질관리 원광대학병원김혜원 Why US QC? Quality control (QC) testing of ultrasound scanners is important to verify the proper and consistent operation of these devices. main goal ; quality improvement Guidelines
Joint CI-JAI advanced accelerator lecture series Imaging and detectors for medical physics Lecture 1: Medical imaging
 Joint CI-JAI advanced accelerator lecture series Imaging and detectors for medical physics Lecture 1: Medical imaging Dr Barbara Camanzi barbara.camanzi@stfc.ac.uk Course layout Day AM 09.30 11.00 PM 15.30
Joint CI-JAI advanced accelerator lecture series Imaging and detectors for medical physics Lecture 1: Medical imaging Dr Barbara Camanzi barbara.camanzi@stfc.ac.uk Course layout Day AM 09.30 11.00 PM 15.30
ANATOMIA Tutorial. Fig. 1 Obtaining CT scan data
 ANATOMIA Tutorial Step 1: Get CT scan data from Hospital Go to the hospital where you received CT scan, and request the CT scan data copied to CD-ROM media. CT scan data is personal information, and therefore,
ANATOMIA Tutorial Step 1: Get CT scan data from Hospital Go to the hospital where you received CT scan, and request the CT scan data copied to CD-ROM media. CT scan data is personal information, and therefore,
Simplicity, quality, and flexibility
 Ultrasound Lumify Simplicity, quality, and flexibility Philips Lumify ultrasound system specifications Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Applications 3 2 System overview 4 2.1 System architecture 4 2.2 Imaging
Ultrasound Lumify Simplicity, quality, and flexibility Philips Lumify ultrasound system specifications Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Applications 3 2 System overview 4 2.1 System architecture 4 2.2 Imaging
Extraction and recognition of the thoracic organs based on 3D CT images and its application
 1 Extraction and recognition of the thoracic organs based on 3D CT images and its application Xiangrong Zhou, PhD a, Takeshi Hara, PhD b, Hiroshi Fujita, PhD b, Yoshihiro Ida, RT c, Kazuhiro Katada, MD
1 Extraction and recognition of the thoracic organs based on 3D CT images and its application Xiangrong Zhou, PhD a, Takeshi Hara, PhD b, Hiroshi Fujita, PhD b, Yoshihiro Ida, RT c, Kazuhiro Katada, MD
Resona 7. Premium Ultrasound System. New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation
 Resona 7 Premium Ultrasound System New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation Since the company was founded, Mindray is continuously exploring new ways to improve diagnostic
Resona 7 Premium Ultrasound System New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation Since the company was founded, Mindray is continuously exploring new ways to improve diagnostic
Healthcare mobility: selecting the right device for better patient care
 Healthcare mobility: selecting the right device for better patient care How Fujitsu Mobile Solutions help accelerate digital transformation with human-centric innovation* Fujitsu Thought Leadership Report
Healthcare mobility: selecting the right device for better patient care How Fujitsu Mobile Solutions help accelerate digital transformation with human-centric innovation* Fujitsu Thought Leadership Report
Blood Particle Trajectories in Phase-Contrast-MRI as Minimal Paths Computed with Anisotropic Fast Marching
 Blood Particle Trajectories in Phase-Contrast-MRI as Minimal Paths Computed with Anisotropic Fast Marching Michael Schwenke 1, Anja Hennemuth 1, Bernd Fischer 2, Ola Friman 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute
Blood Particle Trajectories in Phase-Contrast-MRI as Minimal Paths Computed with Anisotropic Fast Marching Michael Schwenke 1, Anja Hennemuth 1, Bernd Fischer 2, Ola Friman 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute
Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography
 Clinical applications Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography J. Oliván Bescós J. Sonnemans R. Habets J. Peters H. van den Bosch T. Leiner Healthcare Informatics/Patient
Clinical applications Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography J. Oliván Bescós J. Sonnemans R. Habets J. Peters H. van den Bosch T. Leiner Healthcare Informatics/Patient
Overview. Digital X-ray imaging
 Overview Digital X-ray imaging OR Technology Headquarters The OR Technology competence group: Your competent partner for digital X-ray imaging Producing digital X-ray technology and developing image management
Overview Digital X-ray imaging OR Technology Headquarters The OR Technology competence group: Your competent partner for digital X-ray imaging Producing digital X-ray technology and developing image management
GE Healthcare. Agile Ultrasound. The Next Revolution in Ultrasound Imaging
 Agile Ultrasound The Next Revolution in Ultrasound Imaging Abstract Diagnostic use of ultrasound has greatly expanded over the past couple of decades because it offers many advantages as an imaging modality.
Agile Ultrasound The Next Revolution in Ultrasound Imaging Abstract Diagnostic use of ultrasound has greatly expanded over the past couple of decades because it offers many advantages as an imaging modality.
DICOM VIEWER. Version 3.2. Software User Guide Revision 1.1. Copyright 2017, Brainlab AG Germany. All rights reserved.
 DICOM VIEWER Version 3.2 Software User Guide Revision 1.1 Copyright 2017, Brainlab AG Germany. All rights reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 GENERAL INFORMATION...5 1.1 Contact Data...5 1.2
DICOM VIEWER Version 3.2 Software User Guide Revision 1.1 Copyright 2017, Brainlab AG Germany. All rights reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 GENERAL INFORMATION...5 1.1 Contact Data...5 1.2
The Dornier Compact Delta II. Integrated Transportable Lithotripter
 The Dornier Compact Delta II Integrated Transportable Lithotripter The Optimal Solution: The Dornier Compact Delta II 2 The compact and easily transportable Compact Delta II is effective and easy to use.
The Dornier Compact Delta II Integrated Transportable Lithotripter The Optimal Solution: The Dornier Compact Delta II 2 The compact and easily transportable Compact Delta II is effective and easy to use.
RSNA, /rg
 RSNA, 2015 10.1148/rg.2015140320 Appendix As noted in the main article, DICOM image files cannot be used directly for 3D printing; further steps are necessary to make them readable by 3D printers. The
RSNA, 2015 10.1148/rg.2015140320 Appendix As noted in the main article, DICOM image files cannot be used directly for 3D printing; further steps are necessary to make them readable by 3D printers. The
New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan
 These images were acquired with an investigational device. PD T2 T2 FLAIR T1 MAP T1 FLAIR PSIR T1 New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan MR exams can be time consuming. A typical
These images were acquired with an investigational device. PD T2 T2 FLAIR T1 MAP T1 FLAIR PSIR T1 New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan MR exams can be time consuming. A typical
Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications
 University of Szeged Department of Image Processing and Computer Graphics Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications Ph. D. Thesis László Ruskó Thesis Advisor Dr. Antal
University of Szeged Department of Image Processing and Computer Graphics Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications Ph. D. Thesis László Ruskó Thesis Advisor Dr. Antal
