Full file at
|
|
|
- Tabitha Hodges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hands-on Networking Fundamentals Chapter 2 Solutions Answers to the Chapter 2 Review Questions 1. Your network computer can transmit faster than an older network printer can receive. What capability of the OSI model helps to manage transmissions so that the printer is not overrun by communications from your computer? a. flow control 2. When was the OSI model developed? c. 1970s 3. An advantage of token ring over Ethernet is that. a. broadcast storms are unlikely in token ring 4. Your network is beaconing. In which of the following networks would this occur? b. in token ring when no broadcasts are detected from the active monitor 5. Which of the following is an IEEE standard for Ethernet? (Choose all that apply.) c You have an Ethernet network on which the AppleTalk protocol is used with other protocols. Which of the following enables AppleTalk to work on your network? (Choose all that apply.) b. Ethernet SNAP 7. When your computer communicates with a server through the Physical layer (Physical layer to Physical layer) it uses. a. peer protocols 8. A router is able to route packets along the shortest path thanks to the routing capabilities provided by which OSI layer? d. Network 9. When you use My Network Neighborhood in Windows XP to view computers on your network, this is possible through which of the following? (Choose all that apply.) b. Microsoft Windows redirector and c. Capabilities specified in the OSI Application layer 10. Assume that your RBOC is Qwest and your long distance carrier is AT&T. What type of lines are used to connect Qwest to AT&T? a. interexchange carrier lines 11. When you monitor computers on a network using the physical address that is coded into their network interface cards, you are taking advantage of the sublayer in the Data Link layer. b. media access control (MAC) 12. What types of devices would you expect to see in a headend? (Choose all that apply.) a. cable connections, b. satellite dishes, c. antennas, and d. trunk lines 13. Statistical multiple access is more efficient than. (Choose all that apply.) a. Frequency Division Multiple Access and b. Time Division Multiple Access 1
2 14. In Ethernet a is measured by signal strength. c. collision 15. You are working on an older token ring network with an assistant, when your assistant asks the name of the device that connects the links of the network. You answer that the device is a(n). d. multistation access unit 16. You work in a community college system that consists of 15 community colleges throughout the state and a central administration center at one of the colleges. The central administration center processes the payroll and student information and needs to have communications of over 40 Mbps between it and the colleges. Which of the following would best provide this type of communications? c. T-3 or T-3C communications 17. Your network is currently busy and your monitoring shows that it has discovered frames with errors and there are retransmissions to correct the errors. The layer of the OSI model that is handling the error checking is the which is using information. b. Data Link layer, CRC 18. Which fields are in a token on a token ring network? (Choose all that apply.) a. start delimiter, c. end delimiter, and d. access control 19. You have received an from your sister who is on the same enterprise network and notice in the message header that the has traveled through four different points before reaching you. This is an example of. b. message switching 20. When a station on an Ethernet network is sending a packet, the other stations on that network are said to be. a. in defer mode Hands-On Projects Tips and Solutions for Chapter 2 Activity 2-1 In Step 6, the general reasons for standardization as provided by the ISO include: To ensure products are of good quality So that products fit their purpose To reduce incompatibilities So that products are not unreliable or dangerous Because standards have important economic and social repercussions Because standards are useful to industrial and business organizations of all types, to governments and other regulatory bodies, to trade officials, to conformity assessment professionals, to suppliers and customers of products and services in both public and private sectors, and, ultimately to people in general in their roles as consumers and end users. Because standards are good for: trade, product development, safety, environmental concerns, and the transfer of technology Activity 2-2 An optimal design for this project is a network that does not contain a network hub or switch and that is a legacy bus network consisting of coaxial cable connecting two or more workstations and servers. Another viable option is a network that uses unshielded twisted-pair cable and a hub or switch. 2
3 Yet another option is to use a wireless network and employ one or more wireless devices that you have already determined can cause interference, such as a specific cordless telephone or camera or a transmitter that you have obtained for this lab (talk to your school s amateur radio club for help). One method for displaying EMI/RFI problems is to first download a file of moderate size before applying EMI/RFI to the cable (or wireless) segment and observing the time it takes to download the file. Then place the EMI/RFI source as close as possible to the cable segment (or wireless card) and observe and compare the time again. Emphasize to the students that proper installation and placement of network media is vital to reliable and optimal network performance. Coaxial cable is more susceptible to EMI/RFI interference because of the cable design and individual interface design of the hardware logic contained in the network device. Unshielded twisted-pair cabling and the individual interface design of the associated hardware logic contained in the network device takes into account EMI/RFI or noise present on the cabling and can tolerate higher noise ratios by employing media filters and isolation transformers on each twisted-pair interface that acts as a filter to minimize EMI/RFI. If your test network has an intelligent hub or switch that interconnects the workstations and servers, the easiest method for detecting problems is to look for high error counts on the interface nearest the EMI/RFI source. You can observe these error counts on the hub or switch with the management software provided by the vendor or by utilizing the console port on the hub or switch. This project also demonstrates that a network having two or more workstations or servers should be interconnected via a hub or switch, and if possible, an intelligent hub or switch, to allow for better troubleshooting tools and for easier resolution of problems. Activity 2-3 This project illustrates valuable tools for your students to use in identifying address information for a NIC in the Microsoft Windows, Fedora, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux operating systems. If you have other devices running other operating systems on your network, you might have students use similar tools to provide this information (for example, you can use GUI tools or use ifconfig in a terminal window in Mac OS X). This is an example of why it is imperative that you have detailed documentation about your network. When problems arise, the device or devices that are causing the problems can be quickly located and repaired using the documentation. You might also emphasize that it is important to keep this information up to date as the network grows. Most intelligent network devices, such as hubs, switches, and routers provide network management applications either locally or remotely. These applications allow you to view Layer 2 MAC addresses associated with individual interfaces to quickly locate devices connected to them. This proves very useful in locating faulty devices on your network. Such management applications also provide you with a tool for troubleshooting problems when you first connect a device to a hub or switch by ensuring the hub or switch verifies the address associated with the device connected to the interface. Activity 2-4. This project enables students to view the SSL settings in Internet Explorer for Windows XP and Windows Server Consider using this project to initiate a discussion about the value of network security and encryption. You might also add a project in which students view how to set up encryption for a VPN or Web server and discuss the different types of encryption. In Step 5 of the first set of steps and in Step 3 of the second set of steps, note that the SSL options are: Use SSL 2.0 Use SSL 3.0 3
4 Activity 2-5 In this project, students view the SSL options in Mozilla. In Step 5, the SSL versions include: SSL version 2 SSL version 3 Activity 2-6 Students view the Microsoft redirector at work in this project. As a supplement to the project, you might have students monitor the activities of the redirector in Windows Server 2003 through the System Monitor. They can do this by selecting to view the Redirector object and one or more of its counters. To access the System Monitor, click Start, point to All Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and click Performance. Next, click the plus sign in the System Monitor, select Redirector as the performance object, and select to view one or more counters. For example, you might have students monitor Bytes Total/sec, so that students can view the total amount of activity handled by the redirector. Activity 2-7 In this project, students use the ping utility in UNIX/Linux to explore the Application layer via their loopback connection. In Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the loopback connection is typically configured automatically as localhost when the operating system is installed or students can use the loopback address Activity 2-8 One of the first things that the student will notice when viewing one or more RFC documents is that there is a standard format for an RFC. This is important because it defines the way in which the document is created and submitted for universal understanding. The standard format and design of the document also presents a good example of why standards are important from the initial creation of an idea, to its development, and finally to its implementation. Standards are very important for all aspects of computing, especially networks, because of the need for standard protocols or communications between networks. Many RFCs relate either directly or indirectly to networks, and the importance of these RFCs is that they define a standard structure for making network proposals, as well as for environments in which networks operate. In Step 5, Steve Crocker wrote the RFC, which is called Host Software, and it was submitted on April 7, Activity 2-9 For this project, students examine an Ethernet or token ring LAN. They should observe the types of network interface cards used and the cable in use. They also should examine how the cable is distributed and the network device(s) used to connect the cable. After determining the topology and the key network elements, students should be able to deduce whether the network is Ethernet or token ring. Activity 2-10 This project enables students to find out more about cable modems. One Web site that has received attention from the Wall Street Journal and other news media is Note that at this 4
5 writing changes are occurring in the industry caused by the bankruptcy and various mergers of cable TV companies. Cable TV does provide a means for WAN access in many areas and one that is relatively easy to install and maintain. Most providers install and configure the equipment necessary to make this connection possible. The providers also supply support and instructions for problem or service change resolution. This access method is now widely available in most areas that have one or more cable TV providers. Solutions to the Case Project Assignments In the following assignments, you consult for the newsroom of the Franklin Daily Herald, a newspaper in a midwestern city. All 17 of the news reporters have computers, and now their management has funded a project to network their computers and provide Internet access to the network. Having a network will enable the reporters to more easily collaborate on stories and exchange information. And it will save time for the news editor who checks all news articles before they are printed. The newsroom network will also connect to an existing network in the pressroom. Case Project 2-1: Implementing a Network Transport Method One member of the newspaper s management wants to implement token ring for this network. What is your recommendation and how would you explain it to the management? Students might recommend Ethernet or token ring and should defend their answers. However, in this context, Ethernet makes good sense for the following reasons: Ethernet enables the use of very fast transmission options, such as 100 Mbps for this network. There are many connection options for Ethernet to use high-speed networking and to quickly upgrade a network. There are many network testing and management tools available for Ethernet Most vendors support Ethernet. New standards are constantly evolving to broaden the capabilities of Ethernet. Case Project 2-2: Creating a Network that Can Communicate with Other Networks The management wants to know if there are any guarantees that the network you are proposing will communicate with other networks. What is your response? The existence of standards and standards organizations help ensure that one network can communicate with another. Both Ethernet and token ring are network standards. Ethernet is the IEEE standard and token ring is the IEEE standard. The IEEE is one of the major standards organizations. The IEEE is a professional society with scientific, technical, and educational members active in over 150 countries. The 802 standards committee and Project 802 have developed the 802 networking standards in use today. Both Ethernet and token ring are part of the 802 standards. Ethernet is a particularly good choice for a network because there are many standards pertaining to Ethernet communications and many vendors who follow those standards throughout the world. Case Project 2-3: Questions about the OSI Model 5
6 Brett Mason, a new colleague with whom you are working at Network Design Consultants, is unsure about some aspects of the OSI model. He has a list of questions for you and asks that you develop a table that he can use as a reference for the answers. Create a table containing two columns and seven rows. Label the left column Network Function, and label the right column OSI Layer. Enter each of the following functions in its own row under the left column and then specify the OSI layer that performs that function under the right column. Brett s questions about functions are as follows: Which layer resizes frames to match the receiving network? Which layer performs data compression? Which layer ensures data is received in the order it was sent? Which layer handles the data-carrying signal? Which layer provides file transfer services? Which layer enables routing? Which layer enables the receiving node to send an acknowledgment? Brett should thoroughly understand the technology and how it relates to the successful completion of the project. The creation and presentation of the table showing the relationship of the OSI model and the layer functionality s will be important for Brett in designing present and future projects. Directing Brett to other sources of information such as the regulatory organization s Web sites or documentation will also help Brett understand. Brett can visit the IEEE, IETF, and other networkrelated regulatory Web sites for further information. There are also many different trade periodicals that Brett can consult along with numerous training courses from several different training groups. FUNCTION Resizes frames to match the receiving network Performs data compression Ensures that data is received in the order it was sent Handles the data-carrying signal Provides file transfer services Enables routing Enables the receiving node to send acknowledgement OSI LAYER Transport Presentation Transport Physical Application Network LLC at the Data Link layer for connection-oriented service and the Transport layer Case Project 2-4: More Questions About the OSI Reference Model Brett likes your table and has another question. He would like you to explain MAC addressing.. Brett s MAC addressing question can be explained by the organizationally unique address assignment by the IEEE for each vendor company. Each network interface or NIC on a network device has a unique address that enables a frame to reach its destination. In this address, called the device or physical address, the first series of bytes identify the NIC vendor and are a valuable tool for 6
7 network administration. The student might recommend that Brett visit the IEEE Web site at and follow the standards links to the organizational unique identifiers for a downloadable document with each vendor s address. Case Project 2-5: Implementing T-carrier Communications The newspaper is being purchased by a newspaper chain and the coordinators of the purchase transition want to have T-carrier communications with the newsroom network. The Franklin Daily Herald management would like you to give them an executive overview explaining T-carrier communications and the possible options. As discussed in the text, a T-carrier line is a dedicated telephone line that can be used for data communications to connect two different locations for continuous point-to-point communications. For example, it is useful for joining business branches in different locations or business subsidiaries. T-carrier lines offer dependable service over very long distances. They are generally offered by telecommunications companies, such as RBOCs. The available T-carrier speeds are outlined in Table 2-4 in the text, as replicated here: T-Carrier Data Transmission Rate T-1 Switched Channels Data Signal Level Fractional T1 64 Kbps 1 of 24 T-1 subchannels DS-0 T Mbps 1 DS-1 T-1C Mbps 2 DS-1C T Mbps 4 DS-2 T Mbps 28 DS-3 T-3C Mbps 56 DS-3C T Mbps 168 DS-4 T Mbps 336 DS-5 7
Full file at
 Hands-On Networking Fundamentals, Second Edition Chapter 2 Solutions Answers to the Chapter 2 Review Questions 1. You run a machine shop that houses many electrical machines, fans, and an air conditioning
Hands-On Networking Fundamentals, Second Edition Chapter 2 Solutions Answers to the Chapter 2 Review Questions 1. You run a machine shop that houses many electrical machines, fans, and an air conditioning
Chapter 2: LAN/WAN Interconnectivity
 Solutions Manual for A Guide to Designing and Implementing Local And Wide Area Networks 2nd Edition by Michael Palmer, Bruce Sinclair Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/a-guide-todesigning-and-implementing-local-and-wide-area-networks-2ndedition-by-palmer-and-sinclair-solutions/
Solutions Manual for A Guide to Designing and Implementing Local And Wide Area Networks 2nd Edition by Michael Palmer, Bruce Sinclair Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/a-guide-todesigning-and-implementing-local-and-wide-area-networks-2ndedition-by-palmer-and-sinclair-solutions/
Test Bank for A Guide to Designing and Implementing Local And Wide Area Networks 2nd Edition by Palmer and Sinclair
 Test Bank for A Guide to Designing and Implementing Local And Wide Area Networks 2nd Edition by Palmer and Sinclair Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-aguide-to-designing-and-implementing-local-and-wide-area-networks-2ndedition-by-palmer-and-sinclair/
Test Bank for A Guide to Designing and Implementing Local And Wide Area Networks 2nd Edition by Palmer and Sinclair Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-aguide-to-designing-and-implementing-local-and-wide-area-networks-2ndedition-by-palmer-and-sinclair/
Lesson 1: Network Communications
 Lesson 1: Network Communications This lesson introduces the basic building blocks of network communications and some of the structures used to construct data networks. There are many different kinds of
Lesson 1: Network Communications This lesson introduces the basic building blocks of network communications and some of the structures used to construct data networks. There are many different kinds of
What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources.
 NETWORKS What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources. Network Benefits Remote access Sharing files & resources Communication Cost Maintenance Communication
NETWORKS What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources. Network Benefits Remote access Sharing files & resources Communication Cost Maintenance Communication
Data Communication and Network. Introducing Networks
 Data Communication and Network Introducing Networks Introduction to Networking Computer network, or simply network Refers to the connection of two or more computers by some type of medium You can connect
Data Communication and Network Introducing Networks Introduction to Networking Computer network, or simply network Refers to the connection of two or more computers by some type of medium You can connect
ITEC 3800 Data Communication and Network. Introducing Networks
 ITEC 3800 Data Communication and Network Introducing Networks Introduction to Networking Computer network, or simply network Refers to the connection of two or more computers by some type of medium You
ITEC 3800 Data Communication and Network Introducing Networks Introduction to Networking Computer network, or simply network Refers to the connection of two or more computers by some type of medium You
Chapter 4: Network Access
 4.0.1.1 Chapter 4: Network Access To support our communication, the OSI model divides the functions of a data network into layers. Each layer works with the layers above and below to transmit data. 4.0.1.2
4.0.1.1 Chapter 4: Network Access To support our communication, the OSI model divides the functions of a data network into layers. Each layer works with the layers above and below to transmit data. 4.0.1.2
Chapter Seven. Local Area Networks: Part 1. Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User s Approach Seventh Edition
 Chapter Seven Local Area Networks: Part 1 Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User s Approach Seventh Edition After reading this chapter, you should be able to: State the definition of
Chapter Seven Local Area Networks: Part 1 Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User s Approach Seventh Edition After reading this chapter, you should be able to: State the definition of
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer
 CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition. Chapter 6: Network Reference Models and Standards
 Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition Chapter 6: Network Reference Models and Standards Objectives Explain the OSI reference model layers and their relationship to hardware and software Explain
Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition Chapter 6: Network Reference Models and Standards Objectives Explain the OSI reference model layers and their relationship to hardware and software Explain
IT 4504 Section 4.0. Network Architectures. 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1
 IT 4504 Section 4.0 Network Architectures 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1 Section 4.1 Introduction to Computer Networks 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 2 Introduction
IT 4504 Section 4.0 Network Architectures 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1 Section 4.1 Introduction to Computer Networks 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 2 Introduction
Objectives. Learn how computers are connected. Become familiar with different types of transmission media
 Objectives Learn how computers are connected Become familiar with different types of transmission media Learn the differences between guided and unguided media Learn how protocols enable networking 2 Objectives
Objectives Learn how computers are connected Become familiar with different types of transmission media Learn the differences between guided and unguided media Learn how protocols enable networking 2 Objectives
ก ก Information Technology II
 ก ก 202103 Information Technology II ก ก ก ก ก (LAN), ก LAN, ก ก (LAN) ก ก ก LAN ก LAN ก LAN Topology Bus LAN Star LAN Ring LAN Wireless LAN Wireless LAN Wireless ก (LAN) ก ก ก LAN ก LAN WAN ก Random Access
ก ก 202103 Information Technology II ก ก ก ก ก (LAN), ก LAN, ก ก (LAN) ก ก ก LAN ก LAN ก LAN Topology Bus LAN Star LAN Ring LAN Wireless LAN Wireless LAN Wireless ก (LAN) ก ก ก LAN ก LAN WAN ก Random Access
Hands-on Networking Fundamentals. Chapter 12 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Network
 Hands-on Networking Fundamentals Chapter 12 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Network Objectives Use hardware and software methods to monitor a network Perform backups over a network Solve a broad range
Hands-on Networking Fundamentals Chapter 12 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Network Objectives Use hardware and software methods to monitor a network Perform backups over a network Solve a broad range
M242 COMPUTER NETWORS AND SECURITY
 M242 COMPUTER NETWORS AND SECURITY 2.1. Network Models: UNIT - II OSI MODEL AND LAN PROTOCOLS 1. Explain Network model A network is a combination of hardware and software that sends data from one location
M242 COMPUTER NETWORS AND SECURITY 2.1. Network Models: UNIT - II OSI MODEL AND LAN PROTOCOLS 1. Explain Network model A network is a combination of hardware and software that sends data from one location
Introduction to LAN Protocols
 CHAPTER 2 Introduction to LAN Protocols This chapter introduces the various media-access methods, transmission methods, topologies, and devices used in a local area network (LAN). Topics addressed focus
CHAPTER 2 Introduction to LAN Protocols This chapter introduces the various media-access methods, transmission methods, topologies, and devices used in a local area network (LAN). Topics addressed focus
Introduction to LAN Protocols
 CHAPTER 2 Chapter Goals Learn about different LAN protocols. Understand the different methods used to deal with media contention. Learn about different LAN topologies. This chapter introduces the various
CHAPTER 2 Chapter Goals Learn about different LAN protocols. Understand the different methods used to deal with media contention. Learn about different LAN topologies. This chapter introduces the various
Computer Networks Question Bank
 Computer Networks Question Bank 1. Describe in detail OSI Model ANS: OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) is reference model for how applications can communicate over a network. A reference model is a conceptual
Computer Networks Question Bank 1. Describe in detail OSI Model ANS: OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) is reference model for how applications can communicate over a network. A reference model is a conceptual
SYLLABUS. Departmental Syllabus
 SYLLABUS DATE OF LAST REVIEW: 02/2013 CIP CODE: 11.0801 SEMESTER: COURSE TITLE: Networking I COURSE NUMBER: CIST- 0117 CREDIT HOURS: 3 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE LOCATION: OFFICE HOURS: TELEPHONE: EMAIL: PREREQUISITE(S):
SYLLABUS DATE OF LAST REVIEW: 02/2013 CIP CODE: 11.0801 SEMESTER: COURSE TITLE: Networking I COURSE NUMBER: CIST- 0117 CREDIT HOURS: 3 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE LOCATION: OFFICE HOURS: TELEPHONE: EMAIL: PREREQUISITE(S):
Computer Networking Fundamentals
 Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Computer Networking Fundamentals Test Code: 4414 / Version: 01 Measuring What Matters Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: PC Principles Identify physical
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Computer Networking Fundamentals Test Code: 4414 / Version: 01 Measuring What Matters Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: PC Principles Identify physical
INTRODUCTION TO ICT.
 INTRODUCTION TO ICT. (Introducing Basic Network Concepts) Lecture # 24-25 By: M.Nadeem Akhtar. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1 INTRODUCTION TO
INTRODUCTION TO ICT. (Introducing Basic Network Concepts) Lecture # 24-25 By: M.Nadeem Akhtar. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1 INTRODUCTION TO
A LAN is a high-speed data network that covers a relatively small geographic area. It typically connects workstations, personal computers, printers,
 CBCN4103 A LAN is a high-speed data network that covers a relatively small geographic area. It typically connects workstations, personal computers, printers, servers, and other devices. LANs offer computer
CBCN4103 A LAN is a high-speed data network that covers a relatively small geographic area. It typically connects workstations, personal computers, printers, servers, and other devices. LANs offer computer
Computer Networks and Internet
 Computer Networks and Internet Objectives Computer Networks Internet 2 Computer Networks Introducing Computer Networks A computer network consists of two or more computers linked together to exchange data
Computer Networks and Internet Objectives Computer Networks Internet 2 Computer Networks Introducing Computer Networks A computer network consists of two or more computers linked together to exchange data
KIBABII UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DEPARTMENT COMPUTER SCIENCE & IT ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A AND ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B
 KIBABII UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DEPARTMENT COMPUTER SCIENCE & IT TITLE: DATACOMMUNICATION COURSE CODE: 223 SECTION A: 30 Marks ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A AND ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B TIME ALLOWED:
KIBABII UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DEPARTMENT COMPUTER SCIENCE & IT TITLE: DATACOMMUNICATION COURSE CODE: 223 SECTION A: 30 Marks ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A AND ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B TIME ALLOWED:
Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Rabie Sayed
 1 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Rabie Sayed 2 A network is a group of two or more computer systems linked together to exchange data and share resources, including expensive peripherals. 3 A local area network (LAN)
1 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Rabie Sayed 2 A network is a group of two or more computer systems linked together to exchange data and share resources, including expensive peripherals. 3 A local area network (LAN)
Data Communications. Course Design Data Communications. Pre/Post Test (80 Questions/80 Points) Upon Request None No No No
 Data Communications Course Design 2005-2006 Course Information Organization Division EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Business Course Number CMP 205 Title Credits 3 Developed by Lecture/Lab Ratio Transfer Status
Data Communications Course Design 2005-2006 Course Information Organization Division EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Business Course Number CMP 205 Title Credits 3 Developed by Lecture/Lab Ratio Transfer Status
Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology_TCET3142/TC570 NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK
 NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT: COURSE CODE: COURSE TITLE: Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology TCET 3142/TC570 Computer Systems and
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT: COURSE CODE: COURSE TITLE: Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology TCET 3142/TC570 Computer Systems and
Data Communication. Introduction of Communication. Data Communication. Elements of Data Communication (Communication Model)
 Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Internetworking is connecting two or more computer networks with some sort of routing device to exchange traffic back and forth, and guide traffic on
 CBCN4103 Internetworking is connecting two or more computer networks with some sort of routing device to exchange traffic back and forth, and guide traffic on the correct path across the complete network
CBCN4103 Internetworking is connecting two or more computer networks with some sort of routing device to exchange traffic back and forth, and guide traffic on the correct path across the complete network
Fundamentals of Networking Introduction to Networking Devices
 Fundamentals of Networking Introduction to Networking Devices Kuldeep Sonar 1 NIC (Network Interface Card) A network interface provides connectivity from an end-user PC or laptop to the public network.
Fundamentals of Networking Introduction to Networking Devices Kuldeep Sonar 1 NIC (Network Interface Card) A network interface provides connectivity from an end-user PC or laptop to the public network.
Technology in Action. Chapter Topics. Participation Question. Participation Question 8/17/11. Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices
 Technology in Action Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices 1 2 Chapter Topics Networking fundamentals Network architecture Network components Peer-to-peer networks Ethernet networks Power-line
Technology in Action Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices 1 2 Chapter Topics Networking fundamentals Network architecture Network components Peer-to-peer networks Ethernet networks Power-line
(Network Programming) Basic Networking Hardware
 EEE 448 Computer Networks with (Network Programming) Basic Networking Hardware Lecture #2 Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Çukurova University Agenda What is a network device? Network Media
EEE 448 Computer Networks with (Network Programming) Basic Networking Hardware Lecture #2 Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Çukurova University Agenda What is a network device? Network Media
Netwoking Essentials
 Mark Sportack Walter J. Glenn Sams' Teach Yourself MCSE Netwoking Essentials SAMS PUBLISHING IN 14 DAYS Sams Publishing is an independant entity from Microsoft Corporation, and not affiliated with Microsoft
Mark Sportack Walter J. Glenn Sams' Teach Yourself MCSE Netwoking Essentials SAMS PUBLISHING IN 14 DAYS Sams Publishing is an independant entity from Microsoft Corporation, and not affiliated with Microsoft
2. LAN Topologies Gilbert Ndjatou Page 1
 2. LAN Topologies Two basic categories of network topologies exist, physical topologies and logical topologies. The physical topology of a network is the cabling layout used to link devices. This refers
2. LAN Topologies Two basic categories of network topologies exist, physical topologies and logical topologies. The physical topology of a network is the cabling layout used to link devices. This refers
CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW
 CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW P. 447 LAN (Local Area Network) A LAN consists of a shared transmission medium and a set of hardware and software for interfacing devices to the medium and regulating
CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW P. 447 LAN (Local Area Network) A LAN consists of a shared transmission medium and a set of hardware and software for interfacing devices to the medium and regulating
Module 11. OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards
 Module 11 OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards Objectives 1. Networking A.Differentiate between layers of the OSI model B.2.9 Compare network devices C.Compare network standards D.2.7 Compare
Module 11 OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards Objectives 1. Networking A.Differentiate between layers of the OSI model B.2.9 Compare network devices C.Compare network standards D.2.7 Compare
Typical Network Uses
 Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Data Communication. Chapter # 1: Introduction. By: William Stalling
 Data Communication Chapter # 1: By: Introduction William Stalling Data Communication The exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as cable wire. For data communications
Data Communication Chapter # 1: By: Introduction William Stalling Data Communication The exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as cable wire. For data communications
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals. Chapter 10 Planning and Cabling Networks
 CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 10 Planning and Cabling Networks Updated: 15/07/2008 1 10.0.1 Introduction 2 10.0.1 Introduction The following have been covered in previous chapters: considered
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 10 Planning and Cabling Networks Updated: 15/07/2008 1 10.0.1 Introduction 2 10.0.1 Introduction The following have been covered in previous chapters: considered
1: Review Of Semester Provide an overview of encapsulation.
 1: Review Of Semester 1 1.1.1.1. Provide an overview of encapsulation. Networking evolves to support current and future applications. By dividing and organizing the networking tasks into separate layers/functions,
1: Review Of Semester 1 1.1.1.1. Provide an overview of encapsulation. Networking evolves to support current and future applications. By dividing and organizing the networking tasks into separate layers/functions,
Introductions. Computer Networking Lecture 01. January 16, HKU SPACE Community College. HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 01 1/36
 Introductions Computer Networking Lecture 01 HKU SPACE Community College January 16, 2012 HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 01 1/36 Outline What is a Computer Network? Basic Requirements of Building a Computer Network
Introductions Computer Networking Lecture 01 HKU SPACE Community College January 16, 2012 HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 01 1/36 Outline What is a Computer Network? Basic Requirements of Building a Computer Network
CARRIER SENSE MULTIPLE ACCESS (CSMA):
 Lecture Handout Computer Networks Lecture No. 8 CARRIER SENSE MULTIPLE ACCESS (CSMA): There is no central control management when computers transmit on Ethernet. For this purpose the Ethernet employs CSMA
Lecture Handout Computer Networks Lecture No. 8 CARRIER SENSE MULTIPLE ACCESS (CSMA): There is no central control management when computers transmit on Ethernet. For this purpose the Ethernet employs CSMA
Chapter 7. OSI Data Link Layer. CCNA1-1 Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Layer CCNA1-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go
Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Layer CCNA1-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go
Chapter 7. OSI Data Link Layer
 Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Layer CCNA1-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go
Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Layer CCNA1-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go
Computers Are Your Future
 Computers Are Your Future Networks: Communicating and Sharing Resources. Network Fundamentals What You Will Learn About Basic networking concepts Advantages and disadvantages of networks Peer-to-peer and
Computers Are Your Future Networks: Communicating and Sharing Resources. Network Fundamentals What You Will Learn About Basic networking concepts Advantages and disadvantages of networks Peer-to-peer and
Chapter 16 Networking
 Chapter 16 Networking Outline 16.1 Introduction 16.2 Network Topology 16.3 Network Types 16.4 TCP/IP Protocol Stack 16.5 Application Layer 16.5.1 Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 16.5.2 File Transfer
Chapter 16 Networking Outline 16.1 Introduction 16.2 Network Topology 16.3 Network Types 16.4 TCP/IP Protocol Stack 16.5 Application Layer 16.5.1 Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 16.5.2 File Transfer
Local Area Network(LAN)
 Local Area Network(LAN) A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area. Example: a residence, school, laboratory, university campus,office building
Local Area Network(LAN) A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area. Example: a residence, school, laboratory, university campus,office building
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK
 1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer
 Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer Q1 What is a computer network? A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware
Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer Q1 What is a computer network? A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware
Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT
 Network Basics Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT E-mail :Agha.m@mcit.gov.af Cell:0700148122 After this lesson,you will be able to : Define
Network Basics Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT E-mail :Agha.m@mcit.gov.af Cell:0700148122 After this lesson,you will be able to : Define
Identify the features of network and client operating systems (Windows, NetWare, Linux, Mac OS)
 Course Outline Network+ Duration: 5 days (30 hours) Learning Objectives: Install and configure a network card Define the concepts of network layers Understand and implement the TCP/IP protocol Install
Course Outline Network+ Duration: 5 days (30 hours) Learning Objectives: Install and configure a network card Define the concepts of network layers Understand and implement the TCP/IP protocol Install
Entry Level Assessment Blueprint Computer Networking Fundamentals
 Blueprint Computer Networking Fundamentals Test Code: 4514 / Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: PC Principles Identify physical and equipment safety and maintenance
Blueprint Computer Networking Fundamentals Test Code: 4514 / Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: PC Principles Identify physical and equipment safety and maintenance
Computer Networking Fundamentals
 Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Computer Networking Fundamentals Test Code: 4514 / Version: 01 Copyright 2016. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Computer Networking Fundamentals Blueprint
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Computer Networking Fundamentals Test Code: 4514 / Version: 01 Copyright 2016. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Computer Networking Fundamentals Blueprint
Local Area Network Overview
 Local Area Network Overview Chapter 15 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 LAN Applications (1) Personal computer LANs Low cost Limited data rate Back end networks Interconnecting large systems (mainframes and
Local Area Network Overview Chapter 15 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 LAN Applications (1) Personal computer LANs Low cost Limited data rate Back end networks Interconnecting large systems (mainframes and
Chapter 12. Network Organization and Architecture
 Chapter 12 Network Organization and Architecture Chapter 12 Objectives Learn the basic physical components of networks. Become familiar with routing protocols. 2 Computer networks are often classified
Chapter 12 Network Organization and Architecture Chapter 12 Objectives Learn the basic physical components of networks. Become familiar with routing protocols. 2 Computer networks are often classified
CHAPTER -1. Introduction to Computer Networks
 CHAPTER -1 Introduction to Computer Networks PRELIMINARY DEFINITIONS computer network :: [Tanenbaum] a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. communications network ::a
CHAPTER -1 Introduction to Computer Networks PRELIMINARY DEFINITIONS computer network :: [Tanenbaum] a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. communications network ::a
Computer Communications and Network Basics p. 1 Overview of Computer Communications and Networking p. 2 What Does Computer Communications and
 Computer Communications and Network Basics p. 1 Overview of Computer Communications and Networking p. 2 What Does Computer Communications and Networking Technologies Mean? p. 3 What Is a Computer Network?
Computer Communications and Network Basics p. 1 Overview of Computer Communications and Networking p. 2 What Does Computer Communications and Networking Technologies Mean? p. 3 What Is a Computer Network?
Introduction to Networking
 Networking BASICS Introduction to Networking... 2 Network Media... 4 Network Design... 5 Network Architectures... 7 Protocols and Network Software... 9 1 Introduction to Networking A computer network is
Networking BASICS Introduction to Networking... 2 Network Media... 4 Network Design... 5 Network Architectures... 7 Protocols and Network Software... 9 1 Introduction to Networking A computer network is
Networks. Computer Technology
 Networks Computer Technology Network Two or more computers and other devices (printers or scanners) that are connected, for the purpose of sharing data and programs Advantages of Networks Communication
Networks Computer Technology Network Two or more computers and other devices (printers or scanners) that are connected, for the purpose of sharing data and programs Advantages of Networks Communication
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
LAN Protocols. Required reading: Forouzan 13.1 to 13.5 Garcia 6.7, 6.8. CSE 3213, Fall 2015 Instructor: N. Vlajic
 1 LAN Protocols Required reading: Forouzan 13.1 to 13.5 Garcia 6.7, 6.8 CSE 3213, Fall 2015 Instructor: N. Vlajic What is LAN? 2 Local Area Network (LAN) properties private ownership freedom to choose/change/upgrade
1 LAN Protocols Required reading: Forouzan 13.1 to 13.5 Garcia 6.7, 6.8 CSE 3213, Fall 2015 Instructor: N. Vlajic What is LAN? 2 Local Area Network (LAN) properties private ownership freedom to choose/change/upgrade
OSI Model. Teran Subasinghe MBCS, Bsc.(Hons) in Computer Science - University of Greenwich, UK
 OSI Model Teran Subasinghe MBCS, Bsc.(Hons) in Computer Science - University of Greenwich, UK What is OSI Model? Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model Developed in 1984 by the International Standards
OSI Model Teran Subasinghe MBCS, Bsc.(Hons) in Computer Science - University of Greenwich, UK What is OSI Model? Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model Developed in 1984 by the International Standards
Applied Information and Communication Technology Assessment Unit A2 13
 71 Centre Number Candidate Number ADVANCED General Certificate of Education January 2012 Applied Information and Communication Technology Assessment Unit A2 13 assessing Unit 13 : Networking and Communications
71 Centre Number Candidate Number ADVANCED General Certificate of Education January 2012 Applied Information and Communication Technology Assessment Unit A2 13 assessing Unit 13 : Networking and Communications
Objectives. Network Structure. Network Structure
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Communicating over the Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Chapter 1 1 Describe the structure of a network, including the devices
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Communicating over the Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Chapter 1 1 Describe the structure of a network, including the devices
Chapter Topics Part 1. Network Definitions. Behind the Scenes: Networking and Security
 Chapter Topics Part 1 Behind the Scenes: Networking and Security CS10001 Computer Literacy Business Networks Network Advantages Client/Server Networks Network Classifications Servers Toplogies Chapter
Chapter Topics Part 1 Behind the Scenes: Networking and Security CS10001 Computer Literacy Business Networks Network Advantages Client/Server Networks Network Classifications Servers Toplogies Chapter
Contents. Introduction to Networking. Preface...i. Introduction... xix
 Contents Introduction to Networking Introduction to Networking Preface...i Key Topics...i Course Objectives...ii Pedagogical Features...ii Learning Objectives, Unit Summaries, Discussion Questions, and
Contents Introduction to Networking Introduction to Networking Preface...i Key Topics...i Course Objectives...ii Pedagogical Features...ii Learning Objectives, Unit Summaries, Discussion Questions, and
Discovering Computers Chapter 9 Communications and Networks
 Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks Chapter 9 Objectives Discuss the components required for successful communications Identify various sending and receiving devices Describe
Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks Chapter 9 Objectives Discuss the components required for successful communications Identify various sending and receiving devices Describe
Department of Industrial Engineering. Sharif University of Technology. Contents: The role of managers in Information Technology (IT)
 Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology Session# 14 Contents: The role of managers in Information Technology (IT) Organizational Issues Information Technology Operational and
Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology Session# 14 Contents: The role of managers in Information Technology (IT) Organizational Issues Information Technology Operational and
Local Area Networks. Ethernet LAN
 Local Area Networks Ethernet 802.3 LAN -7-1 Local Area Networks (Lokale Netze) Wide Area Network LAN -7-2 Local Area Networks What is a LAN? Multiple systems attached to an often shared medium high total
Local Area Networks Ethernet 802.3 LAN -7-1 Local Area Networks (Lokale Netze) Wide Area Network LAN -7-2 Local Area Networks What is a LAN? Multiple systems attached to an often shared medium high total
Objectives. Hexadecimal Numbering and Addressing. Ethernet / IEEE LAN Technology. Ethernet
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Ethernet Network Fundamentals Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 1 Introduce Hexadecimal number system Describe the features of various
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Ethernet Network Fundamentals Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 1 Introduce Hexadecimal number system Describe the features of various
04/03/33. Dr.Gihan Naguib. Overview. Dr.Gihan Naguib Behrouz A. Forouzan Data communications and Networking
 PART I Overview of Data Communications and Networking Dr.Gihan Naguib Behrouz A. Forouzan Data communications and Networking 1 Overview 2 1 Chapters Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter 2 Network Models 3 Chapter
PART I Overview of Data Communications and Networking Dr.Gihan Naguib Behrouz A. Forouzan Data communications and Networking 1 Overview 2 1 Chapters Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter 2 Network Models 3 Chapter
INTRODUCTION. What You Need to Read. What this LANbook Covers
 Qwest DSLSM LANbook INTRODUCTION What You Need to Read If you are self-installing Qwest DSL on a local area network in your home or business, start with Chapter 1: Welcome to the Qwest DSL LANbook on page
Qwest DSLSM LANbook INTRODUCTION What You Need to Read If you are self-installing Qwest DSL on a local area network in your home or business, start with Chapter 1: Welcome to the Qwest DSL LANbook on page
Chapter 1. What is Data Communications 8/19/2010. The Data Communications Industry. Approach to Data Communications
 Chapter 1 The Data Communications Industry http://cis.msjc.edu Approach to Data Communications You will never know all there is to know about data communications. Be honest with yourself concerning what
Chapter 1 The Data Communications Industry http://cis.msjc.edu Approach to Data Communications You will never know all there is to know about data communications. Be honest with yourself concerning what
Introductory to Computer Networks Local Area Networks. Lecture 16 Fall Isfahan University of technology Dr.
 Introductory to Computer Networks Local Area Networks Lecture 16 Fall 2010 Isfahan University of technology Dr. Faramarz Hendessi What is a LAN? Local area means: Private ownership freedom from regulatory
Introductory to Computer Networks Local Area Networks Lecture 16 Fall 2010 Isfahan University of technology Dr. Faramarz Hendessi What is a LAN? Local area means: Private ownership freedom from regulatory
Computer Network : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan
 Computer Network : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapter3: OSI Reference Model: Network Software: Network
Computer Network : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapter3: OSI Reference Model: Network Software: Network
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 2
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 2 IP Addressing and Subnetting: Establishing Elementary Networks using Hubs, Switches and Routers. Objectives:
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 2 IP Addressing and Subnetting: Establishing Elementary Networks using Hubs, Switches and Routers. Objectives:
Chapter 3. Underlying Technology. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 3 Underlying Technology TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. OBJECTIVES: To briefly discuss the technology of dominant
Chapter 3 Underlying Technology TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. OBJECTIVES: To briefly discuss the technology of dominant
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005
 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 Network and Telecommunications Basics Chapter Outline The telecommunications system Network services
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 Network and Telecommunications Basics Chapter Outline The telecommunications system Network services
Integrating Information Systems: Technology, Strategy, and Organizational Factors
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SLOAN SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT 15.565 Integrating Information Systems: Technology, Strategy, and Organizational Factors 15.578 Global Information Systems: Communications
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SLOAN SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT 15.565 Integrating Information Systems: Technology, Strategy, and Organizational Factors 15.578 Global Information Systems: Communications
Computer Network Architecture
 Computer Network Architecture Lecture 2: Fundamental of Network Internet and Intranet Intranet: An intranet is a private network that is contained within an enterprise. It may consist of many interlinked
Computer Network Architecture Lecture 2: Fundamental of Network Internet and Intranet Intranet: An intranet is a private network that is contained within an enterprise. It may consist of many interlinked
1. Data Link Layer Protocols
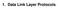 1. Data Link Layer Protocols Purpose of the Data Link Layer The Data Link Layer Purpose of the Data Link Layer Data Link Sublayers Network LLC Sublayer Data Link Physical MAC Sublayer 802.3 Ethernet 802.11
1. Data Link Layer Protocols Purpose of the Data Link Layer The Data Link Layer Purpose of the Data Link Layer Data Link Sublayers Network LLC Sublayer Data Link Physical MAC Sublayer 802.3 Ethernet 802.11
Networking 101. Introduction to Ethernet networking basics; Network types, components, configurations. Routers. Switches. Servers.
 Switches Routers PCs Networking 101 Introduction to Ethernet networking basics; Network types, components, configurations Servers Hubs Protocols Cat-5 UTP NICs Page 1 July 28, 2000 Network Types LAN Local
Switches Routers PCs Networking 101 Introduction to Ethernet networking basics; Network types, components, configurations Servers Hubs Protocols Cat-5 UTP NICs Page 1 July 28, 2000 Network Types LAN Local
Layering in Networked computing. OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer
 Layering in Networked computing OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer Learning outcomes Understand the need of layering in Networked computing Understand the OSI model and the tcp/ip model Understand
Layering in Networked computing OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer Learning outcomes Understand the need of layering in Networked computing Understand the OSI model and the tcp/ip model Understand
Networking Fundamentals
 Networking Fundamentals Cable types and connectors Fiber A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves. Fiber optics
Networking Fundamentals Cable types and connectors Fiber A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves. Fiber optics
Review For Exam 2. Internetworking. Summary Questions. School of Business Eastern Illinois University. School of Business Eastern Illinois University
 School of Business Review For Exam 2 Wednesday 10/6/2004) Abdou Illia, Fall 2004 School of Business Internetworking 3 1. Name the two most known Medium Access Control Protocols found in LANs. How they
School of Business Review For Exam 2 Wednesday 10/6/2004) Abdou Illia, Fall 2004 School of Business Internetworking 3 1. Name the two most known Medium Access Control Protocols found in LANs. How they
Chapter 10: Planning and Cabling Networks
 Chapter 10: Planning and Cabling Networks Before using an IP phone, accessing instant messaging, or conducting any number of other interactions over a data network, we must connect end devices and intermediary
Chapter 10: Planning and Cabling Networks Before using an IP phone, accessing instant messaging, or conducting any number of other interactions over a data network, we must connect end devices and intermediary
Home Networking. A home network generally conforms to one of the following configurations
 Home Networking A home network generally conforms to one of the following configurations A stand-alone computer connected to the Internet. A peer-to-peer network containing two or more computers with no
Home Networking A home network generally conforms to one of the following configurations A stand-alone computer connected to the Internet. A peer-to-peer network containing two or more computers with no
The Internet software layers
 1 2 The Internet software layers SMTP, Telnet, FTP, POP3, IMAP TCP, UDP IP: RIP, BGP, OSPF Ethernet, Wireless LAN, Token Ring Twisted pair, coaxial, microwave, optical fiber 3 4 Ethernet 1973 Xerox s researcher
1 2 The Internet software layers SMTP, Telnet, FTP, POP3, IMAP TCP, UDP IP: RIP, BGP, OSPF Ethernet, Wireless LAN, Token Ring Twisted pair, coaxial, microwave, optical fiber 3 4 Ethernet 1973 Xerox s researcher
COMPUTER AND DATA NETWORKS
 COMPUTER AND DATA NETWORKS (EE2.CDN, Spring 2003) Dr. Z. SUN University of Surrey Guildford Surrey GU2 5XH Tel: 01483 68 9493 Fax: 01483 68 6011 Email: Z.Sun@eim.surrey.ac.uk 1 Dr.Z.Sun SCHEDULE Week 1
COMPUTER AND DATA NETWORKS (EE2.CDN, Spring 2003) Dr. Z. SUN University of Surrey Guildford Surrey GU2 5XH Tel: 01483 68 9493 Fax: 01483 68 6011 Email: Z.Sun@eim.surrey.ac.uk 1 Dr.Z.Sun SCHEDULE Week 1
UNIT IV - COMPUTER NETWORK DEVICES AND OSI LAYERS
 UNIT IV - COMPUTER NETWORK DEVICES AND OSI LAYERS 4.1 Data Communication: Data communication is the exchange of data (in the form of 1s and 0s) between two devices via some form of transmission medium
UNIT IV - COMPUTER NETWORK DEVICES AND OSI LAYERS 4.1 Data Communication: Data communication is the exchange of data (in the form of 1s and 0s) between two devices via some form of transmission medium
Layer 2 functionality bridging and switching
 Layer 2 functionality bridging and switching BSAD 141 Dave Novak Sources: Network+ Guide to Networks, Dean 2013 Overview Layer 2 functionality Error detection Bridges Broadcast and collision domains How
Layer 2 functionality bridging and switching BSAD 141 Dave Novak Sources: Network+ Guide to Networks, Dean 2013 Overview Layer 2 functionality Error detection Bridges Broadcast and collision domains How
Types of Computer Networks. ICS 614: Computer Networks Concepts and Principles 11
 Types of Computer Networks ICS 614: Computer Networks Concepts and Principles 11 Types of networks Networks are categorized by distribution, size, and architecture. A network can be as simple as a single
Types of Computer Networks ICS 614: Computer Networks Concepts and Principles 11 Types of networks Networks are categorized by distribution, size, and architecture. A network can be as simple as a single
CS 3201 Computer Networks 2014/2015 Handout: Lab 3
 Lab Content: - Network Devices - Ethernet Network - MAC Address Network Devices: - Hubs, MAU s, and Repeaters Hubs Hubs are one of the most important components of a network because they act as a central
Lab Content: - Network Devices - Ethernet Network - MAC Address Network Devices: - Hubs, MAU s, and Repeaters Hubs Hubs are one of the most important components of a network because they act as a central
The OSI Model. Open Systems Interconnection (OSI). Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
 Network Models The OSI Model Open Systems Interconnection (OSI). Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Model for understanding and developing computer-to-computer communication
Network Models The OSI Model Open Systems Interconnection (OSI). Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Model for understanding and developing computer-to-computer communication
Defining Networks with the OSI Model. Module 2
 Defining Networks with the OSI Model Module 2 Objectives Skills Concepts Objective Domain Description Objective Domain Number Understanding OSI Basics Defining the Communications Subnetwork Defining the
Defining Networks with the OSI Model Module 2 Objectives Skills Concepts Objective Domain Description Objective Domain Number Understanding OSI Basics Defining the Communications Subnetwork Defining the
Networking Essentials
 Networking Essentials Mark A. Sportack / SÄNiS PUBLISHING 201 West 103rd Street Indianapolis, IN 46290 Introduction xxiii Part I Network Fundamentals 1 A Networking Primer 3 Evolution of Networks 4 Standards
Networking Essentials Mark A. Sportack / SÄNiS PUBLISHING 201 West 103rd Street Indianapolis, IN 46290 Introduction xxiii Part I Network Fundamentals 1 A Networking Primer 3 Evolution of Networks 4 Standards
TCP/IP and OSI Model Ethernet LAN Network Cables Network Devices Network Topologies Redundant Internet Connections VLANs Wireless LANs Upcoming
 2 TCP/IP and OSI Model Ethernet LAN Network Cables Network Devices Network Topologies Redundant Internet Connections VLANs Wireless LANs Upcoming Network Technologies 3 4 Elements of the Network Sender
2 TCP/IP and OSI Model Ethernet LAN Network Cables Network Devices Network Topologies Redundant Internet Connections VLANs Wireless LANs Upcoming Network Technologies 3 4 Elements of the Network Sender
Unit 10. Networks. Copyright 2005 Heathkit Company, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Unit 10 Networks Copyright 2005 Heathkit Company, Inc. All rights reserved. The basic components of a network: Connections (Physical Medium) Protocols (Common language) Services (Clients, Servers, and
Unit 10 Networks Copyright 2005 Heathkit Company, Inc. All rights reserved. The basic components of a network: Connections (Physical Medium) Protocols (Common language) Services (Clients, Servers, and
Network protocols and. network systems INTRODUCTION CHAPTER
 CHAPTER Network protocols and 2 network systems INTRODUCTION The technical area of telecommunications and networking is a mature area of engineering that has experienced significant contributions for more
CHAPTER Network protocols and 2 network systems INTRODUCTION The technical area of telecommunications and networking is a mature area of engineering that has experienced significant contributions for more
