3 October, 2013 MVA ENS Cachan. Lecture 2: Logistic regression & intro to MIL Iasonas Kokkinos
|
|
|
- Tiffany Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 3 October, 2013 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 2: Logistic regression & intro to MIL Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Department of Applied Mathematics Ecole Centrale Paris Galen Group INRIA-Saclay
2 Administrative details 2 Make sure you have all received my from last week
3 Lecture outline 3 Recap & problems of linear regression Logistic Regression Introduction to Multiple Instance Learning
4 4 Learning problem Recover input-output mapping Output: y Input: x Method: f Parameters: w Aspects of the learning problem Identify methods that fit the problem setting Determine parameters that properly classify the training set Measure and control the complexity of these functions
5 Linear Classifiers Find linear expression (hyperplane) to separate positive and negative examples 5 Feature coordinate j x x i i positive : negative : x x i i w + b w + b 0 < 0 Each data point has a class label: +1 ( ) y t = -1 ( ) Feature coordinate i
6 Learning problem formulation 6 Given: Training set of feature-label pairs Wanted: simple that works well for simple: penalizing function complexity, to guarantee generalization works well: quantified by loss criterion
7 Linear regression 7 Linear Loss function: quantify appropriateness of for Introduce vector notation
8 Inappropriateness of quadratic loss We chose the quadratic cost function for convenience Single, global minimum & closed form expression 8 But does it indicate classification performance? Computed Decision Boundary Linear Fit Desired decision boundary
9 Inappropriateness of quadratic loss Consider transformation: 9 Quadratic loss is not robust to outliers and penalizes outputs that are `too good
10 Lecture outline 10 Recap & problems of linear regression Logistic Regression Training criterion formulation Optimization Interpretation Application to boundary detection Introduction to Multiple Instance Learning
11 Probabilistic interpretation of least squares 11 Outputs: continuous random variables linear function of inputs + zero mean Gaussian r.v. Optimal w: maximizes likelihood of observed outputs But the labels are discrete!
12 A probabilistic criterion for training a classifier 12 Training set: y: discrete observations: model as samples from Bernoulli distribution Find w that maximizes the likelihood of labels in the training set
13 Sigmoidal function & logistic regression 13 sigmoidal Training criterion from previous slide: How do we optimize it with respect to w? What does it mean?
14 Lecture outline 14 Recap & problems of linear regression Logistic Regression Training criterion formulation Optimization Interpretation Application to boundary detection Introduction to Multiple Instance Learning
15 Maximization by gradient ascent 15 Gradient ascent:
16 Maximization with Newton-Raphson 16 Newton method for finding roots of 1D function : Newton method for finding maxima of 1D function : condition Newton-Raphson method for finding maxima of N-D function :
17 Newton-Raphson for Logistic Regression 17 Jacobian: Hessian: In statistics: Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares (IRLS)
18 Lecture outline 18 Recap & problems of linear regression Logistic Regression Training criterion formulation Optimization Interpretation Application to boundary detection Introduction to Support Vector Machines
19 A compact expression for the loss 19 Using, :
20 Log loss: 20
21 Log loss vs. quadratic loss 21
22 Logistic vs Linear Regression 22 Logistic regression is more robust Linear Regression Logistic Regression
23 Lecture outline 23 Recap & problems of linear regression Logistic Regression Training criterion formulation Optimization Interpretation Application to boundary detection Introduction to Multiple Instance Learning
24 Boundary detection problem Object/Surface Boundaries 24
25 25 Signal-level challenges Poor contrast Shadows Texture
26 Machine Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 2 Fundamental challenges: can humans do it? 26
27 Learning-based approaches 27 Boundary or non-boundary? Use human-annotated segmentations Use any visual cue as input to the decision function. Use decision trees/logisitic regression/boosting/ and learn to combine the individual inputs. S. Konishi, A.Yuille, J. Coughlan, S.C. Zhu, Statistical Edge Detection: Learning and Evaluating Edge Cues, IEEE PAMI, 2003 D. Martin, C. Fowlkes, J. Malik. "Learning to Detect Natural Image Boundaries Using Local Brightness, Color and Texture Cues", IEEE PAMI, 2004
28 Evaluation protocol 28 Threshold detector s output at certain level Match outputs to human ground-truth Count true/false positives (t/f)positives, misses (m) From precision, p and recall, r Quantify performance in terms of F-measure
29 29 Contours can be defined by any of a number of cues (P. Cavanagh) Slide credit: J. Malik, M. Maire
30 Cue-localization Gray level photographs 30 Objects from motion Objects from luminance Objects from disparity Line drawings Objects from texture Slide credit: J. Malik, M. Maire Grill-Spector et al., Neuron 1998
31 31 Local boundary cues Separate features per candidate orientation In specific: r (x,y) θ 1976 CIE L*a*b* colorspace Brightness Gradient BG(x,y,r,θ) Difference of L* distributions Color Gradient CG(x,y,r,θ) Difference of a*b* distributions Texture Gradient TG(x,y,r,θ) Difference of distributions of V1-like filter responses Slide credit: J. Malik, M. Maire
32 Boundary cues (horizontal) 32 Brightness Color (a, b channels) Texture
33 Boundary π/4 33 Brightness Color (a, b channels) Texture
34 Brightness π/2 34 Brightness Color (a, b channels) Texture
35 Brightness 3π/4 35 Brightness Color (a, b channels) Texture
36 Cue combinations with logistic regression 36 Slide credit: J. Malik, M. Maire
37 Exploiting global constraints: image Segmentation as Graph Partitioning Build a weighted graph G=(V,E) from image V: image pixels 37 E: connections between pairs of nearby pixels Partition graph so that similarity within group is large and similarity between groups is small -- Normalized Cuts [Shi & Malik 97] Slide credit: J. Malik, M. Maire
38 38 Wij small when intervening contour strong, strong when weak.. Slide credit: J. Malik, M. Maire
39 Normalized Cuts as a Spring-Mass system 39 Each pixel is a point mass; each connection is a spring: ( D W ) y = λdy Fundamental modes are generalized eigenvectors of (D - W) x = λdx Slide credit: J. Malik, M. Maire
40 Contour information from eigenvectors 40 Slide credit: J. Malik, M. Maire
41 Classifier 41 Logistic regression
42 Progress during the last 40 years 42 Humans Berkeley gpb, 08 Berkeley PB, 04 Canny+ Hysteresis ( 85) Prewitt, good feature= 5 years of work
43 Lecture outline 43 Recap & problems of linear regression Logistic Regression Training criterion formulation Optimization Interpretation Application to boundary detection Introduction to Multiple Instance Learning
44 Machine Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 2 Learning symmetry detection S. Tsogkas & I.K., Learning-based symmetry detection in natural images, ECCV
45 Multi-scale and multi-orientation features 45 S. Tsogkas & I.K., Learning-based symmetry detection in natural images, ECCV 2012
46 Learning boundary detection 46 Problem I: inconsistent orientation information Problem II: inconsistent location information
47 Sneaking into the fun room 47 mom s keychain grandma s keychain dad s keychain We know that dad cannot enter the fun room, either Which key should we try? Slide Credit: B. Babenko/T. Dietterich
48 Multiple Instance Learning 48 Typical Learning Multiple Instance Learning Positive bag: at least one instance should be positive Negative bag: no instance should be positive Slide Credit: K. Grauman
49 Noisy-or classifier combination N classifier responses, {p 1,...,p N } p i : probability of positive label (classifier i) 1 p i : probability of negative (classifier i) Negative bag: all instance classifiers are negative NY (1 p i ) p =1 i=1 Probability of bag being positive: NY (1 p i ) i=1 49
50 Algorithm pipeline 50 Input image P(x,y) Features Brightness Texture Color Spectra l P(x,y) Training Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) non-maximum suppression softmax θ,s (P(x,y,θ,s)) 14x1 weight vector S. Tsogkas & I.K., Learning-based symmetry detection in natural images, ECCV 2012
51 51 Feature extraction Color: CIE Lab color space. Texture: texton map. Hard binning (32 bins for 3 color channels, 64 textons). Rectangle filters extract features at multiple scales and orientations. Differences of histograms ( gradients ) of color and texture content à symmetry indication. χ 2 distance à dissimilarity of feature content between adjacent rectangles. Integral images for fast extraction. S. Tsogkas & I.K., Learning-based symmetry detection in natural images, ECCV 2012
52 MIL Training 52 Input image θ = 22.5 θ = 45 Varying angle θ = 90 θ = 135 Varying scale θ = MIL training s = 4 s = 8 w w w = w s = 12 s = 24 s = 16 Probability map S. Tsogkas & I.K., Learning-based symmetry detection in natural images, ECCV 2012
53 53 Machine Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 2 Results Lindeberg Levinshtein This work State-of-the-art performance Large boost from color, texture and spectral cues. Long contours (region proposals) S. Tsogkas & I.K., Learning-based symmetry detection in natural images, ECCV 2012 Ground-truth
54 54 Machine Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 2 Some more results Lindeberg Levinshtein This work Ground-truth
55 Lecture recap 55 Logistic Regression Training criterion Optimization Application to boundary detection Introduction to MIL
56 Logistic regression training cost 56 Log loss Quadratic loss
57 Lecture recap 57 Logistic Regression Training criterion Optimization Application to boundary detection Introduction to MIL
58 Maximization with Newton-Raphson 58 Newton-Raphson method for finding maxima of N-D function: Condition for maximum: Jacobian: Hessian:
59 Lecture recap 59 Logistic Regression Training criterion Optimization Application to boundary detection Introduction to MIL
60 Progress during the last 40 years 60 Humans Berkeley gpb, 08 Berkeley PB, 04 Canny+ Hysteresis ( 85) Prewitt, good feature= 5 years of work
61 Lecture outline 61 Recap & problems of linear regression Logistic Regression Training criterion formulation Optimization Interpretation Application to boundary detection Introduction to Multiple Instance Learning
62 Appendix 62 Newton Raphson = Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares Masking problem in multi-class linear regression & softmax
63 Newton Raphson = Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares 63 Newton Raphson: Hessian: Rewrite Update: Transform: Weighted Least Squares Fit:
64 Multiple classes & linear regression 64 K classes: one-of-k coding 4 classes, i-th sample is in 3 rd class: Matrix notation: Loss function: Least squares fit:
65 Multiple classes & linear regression 65 One linear discriminant per class: Problem: ambiguous regions Solution: assign to discriminant with largest score
66 Masking Problem in linear regression Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 66 Nothing ever gets assigned to class 2! 2D version:
67 Multiple classes & logistic regression 67 Soft maximum of competing classes: Discriminants (inputs) Softmax (outputs) Label probability: Similar steps for parameter estimation (Bishop s book)
68 Logistic vs Linear Regression, n>2 classes 68 Linear regression Logistic regression Logistic regression does not exhibit the masking problem
Part III: Affinity Functions for Image Segmentation
 Part III: Affinity Functions for Image Segmentation Charless Fowlkes joint work with David Martin and Jitendra Malik at University of California at Berkeley 1 Q: What measurements should we use for constructing
Part III: Affinity Functions for Image Segmentation Charless Fowlkes joint work with David Martin and Jitendra Malik at University of California at Berkeley 1 Q: What measurements should we use for constructing
Boundaries and Sketches
 Boundaries and Sketches Szeliski 4.2 Computer Vision James Hays Many slides from Michael Maire, Jitendra Malek Today s lecture Segmentation vs Boundary Detection Why boundaries / Grouping? Recap: Canny
Boundaries and Sketches Szeliski 4.2 Computer Vision James Hays Many slides from Michael Maire, Jitendra Malek Today s lecture Segmentation vs Boundary Detection Why boundaries / Grouping? Recap: Canny
Global Probability of Boundary
 Global Probability of Boundary Learning to Detect Natural Image Boundaries Using Local Brightness, Color, and Texture Cues Martin, Fowlkes, Malik Using Contours to Detect and Localize Junctions in Natural
Global Probability of Boundary Learning to Detect Natural Image Boundaries Using Local Brightness, Color, and Texture Cues Martin, Fowlkes, Malik Using Contours to Detect and Localize Junctions in Natural
22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan. Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos
 Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
CS 2770: Computer Vision. Edges and Segments. Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017
 CS 2770: Computer Vision Edges and Segments Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017 Edges vs Segments Figure adapted from J. Hays Edges vs Segments Edges More low-level Don t
CS 2770: Computer Vision Edges and Segments Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017 Edges vs Segments Figure adapted from J. Hays Edges vs Segments Edges More low-level Don t
Learning the Ecological Statistics of Perceptual Organization
 Learning the Ecological Statistics of Perceptual Organization Charless Fowlkes work with David Martin, Xiaofeng Ren and Jitendra Malik at University of California at Berkeley 1 How do ideas from perceptual
Learning the Ecological Statistics of Perceptual Organization Charless Fowlkes work with David Martin, Xiaofeng Ren and Jitendra Malik at University of California at Berkeley 1 How do ideas from perceptual
Segmentation. Bottom Up Segmentation
 Segmentation Bottom up Segmentation Semantic Segmentation Bottom Up Segmentation 1 Segmentation as clustering Depending on what we choose as the feature space, we can group pixels in different ways. Grouping
Segmentation Bottom up Segmentation Semantic Segmentation Bottom Up Segmentation 1 Segmentation as clustering Depending on what we choose as the feature space, we can group pixels in different ways. Grouping
Segmentation Computer Vision Spring 2018, Lecture 27
 Segmentation http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 218, Lecture 27 Course announcements Homework 7 is due on Sunday 6 th. - Any questions about homework 7? - How many of you have
Segmentation http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/ 16-385 Computer Vision Spring 218, Lecture 27 Course announcements Homework 7 is due on Sunday 6 th. - Any questions about homework 7? - How many of you have
Edge and Texture. CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University
 Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
Contour Detection and Hierarchical Image Segmentation Some Experiments
 Contour Detection and Hierarchical Image Segmentation Some Experiments CS395T Visual Recognition Presented by Elad Liebman Overview Understanding the method better: The importance of thresholding the ouput
Contour Detection and Hierarchical Image Segmentation Some Experiments CS395T Visual Recognition Presented by Elad Liebman Overview Understanding the method better: The importance of thresholding the ouput
The goals of segmentation
 Image segmentation The goals of segmentation Group together similar-looking pixels for efficiency of further processing Bottom-up process Unsupervised superpixels X. Ren and J. Malik. Learning a classification
Image segmentation The goals of segmentation Group together similar-looking pixels for efficiency of further processing Bottom-up process Unsupervised superpixels X. Ren and J. Malik. Learning a classification
Edges and Binary Images
 CS 699: Intro to Computer Vision Edges and Binary Images Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 5, 205 Plan for today Edge detection Binary image analysis Homework Due on 9/22, :59pm
CS 699: Intro to Computer Vision Edges and Binary Images Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 5, 205 Plan for today Edge detection Binary image analysis Homework Due on 9/22, :59pm
Outline. Segmentation & Grouping. Examples of grouping in vision. Grouping in vision. Grouping in vision 2/9/2011. CS 376 Lecture 7 Segmentation 1
 Outline What are grouping problems in vision? Segmentation & Grouping Wed, Feb 9 Prof. UT-Austin Inspiration from human perception Gestalt properties Bottom-up segmentation via clustering Algorithms: Mode
Outline What are grouping problems in vision? Segmentation & Grouping Wed, Feb 9 Prof. UT-Austin Inspiration from human perception Gestalt properties Bottom-up segmentation via clustering Algorithms: Mode
Lecture 7: Segmentation. Thursday, Sept 20
 Lecture 7: Segmentation Thursday, Sept 20 Outline Why segmentation? Gestalt properties, fun illusions and/or revealing examples Clustering Hierarchical K-means Mean Shift Graph-theoretic Normalized cuts
Lecture 7: Segmentation Thursday, Sept 20 Outline Why segmentation? Gestalt properties, fun illusions and/or revealing examples Clustering Hierarchical K-means Mean Shift Graph-theoretic Normalized cuts
Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods. Some slides: courtesy of O. Capms, Penn State, J.Ponce and D. Fortsyth, Computer Vision Book
 Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods Some slides: courtesy of O. Capms, Penn State, J.Ponce and D. Fortsyth, Computer Vision Book Previously Binary segmentation Segmentation by thresholding
Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods Some slides: courtesy of O. Capms, Penn State, J.Ponce and D. Fortsyth, Computer Vision Book Previously Binary segmentation Segmentation by thresholding
Segmentation and Grouping April 19 th, 2018
 Segmentation and Grouping April 19 th, 2018 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Features and filters Transforming and describing images; textures, edges 2 Grouping and fitting [fig from Shi et al] Clustering, segmentation,
Segmentation and Grouping April 19 th, 2018 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Features and filters Transforming and describing images; textures, edges 2 Grouping and fitting [fig from Shi et al] Clustering, segmentation,
Ulrik Söderström 16 Feb Image Processing. Segmentation
 Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
Patterns and Computer Vision
 Patterns and Computer Vision Michael Anderson, Bryan Catanzaro, Jike Chong, Katya Gonina, Kurt Keutzer, Tim Mattson, Mark Murphy, David Sheffield, Bor-Yiing Su, Narayanan Sundaram and the rest of the PALLAS
Patterns and Computer Vision Michael Anderson, Bryan Catanzaro, Jike Chong, Katya Gonina, Kurt Keutzer, Tim Mattson, Mark Murphy, David Sheffield, Bor-Yiing Su, Narayanan Sundaram and the rest of the PALLAS
6.801/866. Segmentation and Line Fitting. T. Darrell
 6.801/866 Segmentation and Line Fitting T. Darrell Segmentation and Line Fitting Gestalt grouping Background subtraction K-Means Graph cuts Hough transform Iterative fitting (Next time: Probabilistic segmentation)
6.801/866 Segmentation and Line Fitting T. Darrell Segmentation and Line Fitting Gestalt grouping Background subtraction K-Means Graph cuts Hough transform Iterative fitting (Next time: Probabilistic segmentation)
Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 12 th, 2018
 4/2/208 Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 2 th, 208 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Previously Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
4/2/208 Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 2 th, 208 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Previously Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
Previously. Edge detection. Today. Thresholding. Gradients -> edges 2/1/2011. Edges and Binary Image Analysis
 2//20 Previously Edges and Binary Image Analysis Mon, Jan 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
2//20 Previously Edges and Binary Image Analysis Mon, Jan 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
Edge Detection. Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City
 Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping
 CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation - 1 Outlines Mid-level vision What is segmentation Perceptual Grouping Segmentation
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation - 1 Outlines Mid-level vision What is segmentation Perceptual Grouping Segmentation
18 October, 2013 MVA ENS Cachan. Lecture 6: Introduction to graphical models Iasonas Kokkinos
 Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 18 October, 2013 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 6: Introduction to graphical models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 18 October, 2013 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 6: Introduction to graphical models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
Segmentation and Grouping
 Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Normalized cuts and image segmentation
 Normalized cuts and image segmentation Department of EE University of Washington Yeping Su Xiaodan Song Normalized Cuts and Image Segmentation, IEEE Trans. PAMI, August 2000 5/20/2003 1 Outline 1. Image
Normalized cuts and image segmentation Department of EE University of Washington Yeping Su Xiaodan Song Normalized Cuts and Image Segmentation, IEEE Trans. PAMI, August 2000 5/20/2003 1 Outline 1. Image
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
 The image part with relationship ID rid2 was not found in the file. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture 6 Wavelets (cont), Lines and edges Tammy Riklin Raviv Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion
The image part with relationship ID rid2 was not found in the file. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture 6 Wavelets (cont), Lines and edges Tammy Riklin Raviv Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion
Learning-Based Symmetry Detection in Natural Images
 Learning-Based Symmetry Detection in Natural Images Stavros Tsogkas, Iasonas Kokkinos To cite this version: Stavros Tsogkas, Iasonas Kokkinos. Learning-Based Symmetry Detection in Natural Images. ECCV
Learning-Based Symmetry Detection in Natural Images Stavros Tsogkas, Iasonas Kokkinos To cite this version: Stavros Tsogkas, Iasonas Kokkinos. Learning-Based Symmetry Detection in Natural Images. ECCV
Image gradients and edges
 Image gradients and edges Thurs Sept 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Last time Various models for image noise Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, remov ing noise Box filter Gaussian
Image gradients and edges Thurs Sept 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Last time Various models for image noise Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, remov ing noise Box filter Gaussian
Edge detection. Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek
 Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image
Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image
ShadowDraw Real-Time User Guidance for Freehand Drawing. Harshal Priyadarshi
 ShadowDraw Real-Time User Guidance for Freehand Drawing Harshal Priyadarshi Demo Components of Shadow-Draw Inverted File Structure for indexing Database of images Corresponding Edge maps Query method Dynamically
ShadowDraw Real-Time User Guidance for Freehand Drawing Harshal Priyadarshi Demo Components of Shadow-Draw Inverted File Structure for indexing Database of images Corresponding Edge maps Query method Dynamically
Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods
 Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods Previously Images as graphs Fully-connected graph node (vertex) for every pixel link between every pair of pixels, p,q affinity weight w pq for each link
Image Segmentation continued Graph Based Methods Previously Images as graphs Fully-connected graph node (vertex) for every pixel link between every pair of pixels, p,q affinity weight w pq for each link
Recap from Monday. Visualizing Networks Caffe overview Slides are now online
 Recap from Monday Visualizing Networks Caffe overview Slides are now online Today Edges and Regions, GPB Fast Edge Detection Using Structured Forests Zhihao Li Holistically-Nested Edge Detection Yuxin
Recap from Monday Visualizing Networks Caffe overview Slides are now online Today Edges and Regions, GPB Fast Edge Detection Using Structured Forests Zhihao Li Holistically-Nested Edge Detection Yuxin
Deformable Part Models
 CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Deformable Part Models Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 9, 2016 Today: Object category detection Window-based approaches: Last time: Viola-Jones
CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Deformable Part Models Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 9, 2016 Today: Object category detection Window-based approaches: Last time: Viola-Jones
Segmentation & Grouping Kristen Grauman UT Austin. Announcements
 Segmentation & Grouping Kristen Grauman UT Austin Tues Feb 7 A0 on Canvas Announcements No office hours today TA office hours this week as usual Guest lecture Thursday by Suyog Jain Interactive segmentation
Segmentation & Grouping Kristen Grauman UT Austin Tues Feb 7 A0 on Canvas Announcements No office hours today TA office hours this week as usual Guest lecture Thursday by Suyog Jain Interactive segmentation
Segmentation and Grouping April 21 st, 2015
 Segmentation and Grouping April 21 st, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS0 grades are up on SmartSite Please put name on answer sheet 2 Features and filters Transforming and describing images;
Segmentation and Grouping April 21 st, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS0 grades are up on SmartSite Please put name on answer sheet 2 Features and filters Transforming and describing images;
Edge Detection CSC 767
 Edge Detection CSC 767 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels
Edge Detection CSC 767 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels
Computer Vision I. Announcement. Corners. Edges. Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 11
 Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment. Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018
 CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018 Lecture Overview Dense Feature Correspondences Bundle Adjustment in Structure-from-Motion Image Matching Algorithm
CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018 Lecture Overview Dense Feature Correspondences Bundle Adjustment in Structure-from-Motion Image Matching Algorithm
Machine Learning. Topic 5: Linear Discriminants. Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013
 Machine Learning Topic 5: Linear Discriminants Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013 Thanks to Mark Cartwright for his extensive contributions to these slides Thanks to Alpaydin, Bishop, and Duda/Hart/Stork
Machine Learning Topic 5: Linear Discriminants Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013 Thanks to Mark Cartwright for his extensive contributions to these slides Thanks to Alpaydin, Bishop, and Duda/Hart/Stork
Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift. CAP 5415 Fall 2007
 Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift CAP 5415 Fall 2007 Review on Segmentation by Clustering Each Pixel Data Vector Example (From Comanciu and Meer) Review of k-means Let's find three clusters in this data These
Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift CAP 5415 Fall 2007 Review on Segmentation by Clustering Each Pixel Data Vector Example (From Comanciu and Meer) Review of k-means Let's find three clusters in this data These
What is an edge? Paint. Depth discontinuity. Material change. Texture boundary
 EDGES AND TEXTURES The slides are from several sources through James Hays (Brown); Srinivasa Narasimhan (CMU); Silvio Savarese (U. of Michigan); Bill Freeman and Antonio Torralba (MIT), including their
EDGES AND TEXTURES The slides are from several sources through James Hays (Brown); Srinivasa Narasimhan (CMU); Silvio Savarese (U. of Michigan); Bill Freeman and Antonio Torralba (MIT), including their
Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors
 #1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
#1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
Grouping and Segmentation
 Grouping and Segmentation CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University (Source:Kristen Grauman ) Goals: Grouping in vision Gather features that belong together Obtain an intermediate representation
Grouping and Segmentation CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University (Source:Kristen Grauman ) Goals: Grouping in vision Gather features that belong together Obtain an intermediate representation
Discriminative classifiers for image recognition
 Discriminative classifiers for image recognition May 26 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Outline Last time: window-based generic object detection basic pipeline face detection with boosting as case study
Discriminative classifiers for image recognition May 26 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Outline Last time: window-based generic object detection basic pipeline face detection with boosting as case study
Review of Filtering. Filtering in frequency domain
 Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
CMPSCI 670: Computer Vision! Grouping
 CMPSCI 670: Computer Vision! Grouping University of Massachusetts, Amherst October 14, 2014 Instructor: Subhransu Maji Slides credit: Kristen Grauman and others Final project guidelines posted Milestones
CMPSCI 670: Computer Vision! Grouping University of Massachusetts, Amherst October 14, 2014 Instructor: Subhransu Maji Slides credit: Kristen Grauman and others Final project guidelines posted Milestones
Segmentation and low-level grouping.
 Segmentation and low-level grouping. Bill Freeman, MIT 6.869 April 14, 2005 Readings: Mean shift paper and background segmentation paper. Mean shift IEEE PAMI paper by Comanici and Meer, http://www.caip.rutgers.edu/~comanici/papers/msrobustapproach.pdf
Segmentation and low-level grouping. Bill Freeman, MIT 6.869 April 14, 2005 Readings: Mean shift paper and background segmentation paper. Mean shift IEEE PAMI paper by Comanici and Meer, http://www.caip.rutgers.edu/~comanici/papers/msrobustapproach.pdf
Lecture 6: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
#1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
Edge Detection. CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy. René Magritte, Decalcomania. Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins
 Edge Detection René Magritte, Decalcomania Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy Discontinuities in Intensity Source: Robert Collins Origin
Edge Detection René Magritte, Decalcomania Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy Discontinuities in Intensity Source: Robert Collins Origin
Edge Pixel Classification Using Automatic Programming
 Edge Pixel Classification Using Automatic Programming Kristin Larsen, Lars Vidar Magnusson and Roland Olsson Østfold University College Abstract We have considered edge detection as a classification problem,
Edge Pixel Classification Using Automatic Programming Kristin Larsen, Lars Vidar Magnusson and Roland Olsson Østfold University College Abstract We have considered edge detection as a classification problem,
IMAGE PROCESSING >FILTERS AND EDGE DETECTION FOR COLOR IMAGES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE
 IMAGE PROCESSING >FILTERS AND EDGE DETECTION FOR COLOR IMAGES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE OUTLINE Filters for color images Edge detection for color images Canny edge detection FILTERS FOR COLOR IMAGES
IMAGE PROCESSING >FILTERS AND EDGE DETECTION FOR COLOR IMAGES UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE OUTLINE Filters for color images Edge detection for color images Canny edge detection FILTERS FOR COLOR IMAGES
Segmentation and Grouping
 CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Segmentation and Grouping Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 24, 2015 Goals: Grouping in vision Gather features that belong together Obtain an intermediate
CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Segmentation and Grouping Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 24, 2015 Goals: Grouping in vision Gather features that belong together Obtain an intermediate
Segmentation (continued)
 Segmentation (continued) Lecture 05 Computer Vision Material Citations Dr George Stockman Professor Emeritus, Michigan State University Dr Mubarak Shah Professor, University of Central Florida The Robotics
Segmentation (continued) Lecture 05 Computer Vision Material Citations Dr George Stockman Professor Emeritus, Michigan State University Dr Mubarak Shah Professor, University of Central Florida The Robotics
 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/the_dress Recap: Viola-Jones sliding window detector Fast detection through two mechanisms Quickly eliminate unlikely windows Use features that are fast to compute Viola
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/the_dress Recap: Viola-Jones sliding window detector Fast detection through two mechanisms Quickly eliminate unlikely windows Use features that are fast to compute Viola
Classification. Vladimir Curic. Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University
 Classification Vladimir Curic Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline An overview on classification Basics of classification How to choose appropriate
Classification Vladimir Curic Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline An overview on classification Basics of classification How to choose appropriate
Edge and corner detection
 Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Modern Object Detection. Most slides from Ali Farhadi
 Modern Object Detection Most slides from Ali Farhadi Comparison of Classifiers assuming x in {0 1} Learning Objective Training Inference Naïve Bayes maximize j i logp + logp ( x y ; θ ) ( y ; θ ) i ij
Modern Object Detection Most slides from Ali Farhadi Comparison of Classifiers assuming x in {0 1} Learning Objective Training Inference Naïve Bayes maximize j i logp + logp ( x y ; θ ) ( y ; θ ) i ij
Generative and discriminative classification techniques
 Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 013-014 Jakob Verbeek, December 13+0, 013 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.13.14
Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 013-014 Jakob Verbeek, December 13+0, 013 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.13.14
Edges and Binary Image Analysis. Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin. Today. Edge detection and matching
 /25/207 Edges and Binary Image Analysis Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Today Edge detection and matching process the image gradient to find curves/contours comparing contours Binary image analysis
/25/207 Edges and Binary Image Analysis Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Today Edge detection and matching process the image gradient to find curves/contours comparing contours Binary image analysis
30 September 2013 MVA ENS Cachan
 Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 30 September 2013 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 1: Introduction to Classification Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Computational Vision / Galen Group
Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 30 September 2013 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 1: Introduction to Classification Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Computational Vision / Galen Group
Edge detection. Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek
 Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, edges carry most of the semantic and shape information
Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, edges carry most of the semantic and shape information
Image processing and features
 Image processing and features Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Thanks to Harald Wuest, Folker Wientapper and Marc Pollefeys Introduction Previous lectures: geometry Pose estimation Epipolar geometry
Image processing and features Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Thanks to Harald Wuest, Folker Wientapper and Marc Pollefeys Introduction Previous lectures: geometry Pose estimation Epipolar geometry
Robust Zero Watermarking for Still and Similar Images Using a Learning Based Contour Detection
 Robust Zero Watermarking for Still and Similar Images Using a Learning Based Contour Detection Shahryar Ehsaee and Mansour Jamzad (&) Department of Computer Engineering, Sharif University of Technology,
Robust Zero Watermarking for Still and Similar Images Using a Learning Based Contour Detection Shahryar Ehsaee and Mansour Jamzad (&) Department of Computer Engineering, Sharif University of Technology,
Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc.
 Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc. Edges vs. Corners Edges = maxima in intensity gradient Edges vs. Corners Corners = lots of variation in direction of gradient in a small neighborhood
Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc. Edges vs. Corners Edges = maxima in intensity gradient Edges vs. Corners Corners = lots of variation in direction of gradient in a small neighborhood
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images. Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009
 Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Multiple cosegmentation
 Armand Joulin, Francis Bach and Jean Ponce. INRIA -Ecole Normale Supérieure April 25, 2012 Segmentation Introduction Segmentation Supervised and weakly-supervised segmentation Cosegmentation Segmentation
Armand Joulin, Francis Bach and Jean Ponce. INRIA -Ecole Normale Supérieure April 25, 2012 Segmentation Introduction Segmentation Supervised and weakly-supervised segmentation Cosegmentation Segmentation
Estimating Human Pose in Images. Navraj Singh December 11, 2009
 Estimating Human Pose in Images Navraj Singh December 11, 2009 Introduction This project attempts to improve the performance of an existing method of estimating the pose of humans in still images. Tasks
Estimating Human Pose in Images Navraj Singh December 11, 2009 Introduction This project attempts to improve the performance of an existing method of estimating the pose of humans in still images. Tasks
Image Analysis. Edge Detection
 Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors
 AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors 1 Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors: Motivation 2 Step 1: Detect local features should be invariant to scale and rotation, or perspective
AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors 1 Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors: Motivation 2 Step 1: Detect local features should be invariant to scale and rotation, or perspective
CS 4495 Computer Vision. Segmentation. Aaron Bobick (slides by Tucker Hermans) School of Interactive Computing. Segmentation
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Aaron Bobick (slides by Tucker Hermans) School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS 4: Out but I was a bit late so due date pushed back to Oct 29. OpenCV now has real SIFT
CS 4495 Computer Vision Aaron Bobick (slides by Tucker Hermans) School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS 4: Out but I was a bit late so due date pushed back to Oct 29. OpenCV now has real SIFT
convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB
 Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Modern Medical Image Analysis 8DC00 Exam
 Parts of answers are inside square brackets [... ]. These parts are optional. Answers can be written in Dutch or in English, as you prefer. You can use drawings and diagrams to support your textual answers.
Parts of answers are inside square brackets [... ]. These parts are optional. Answers can be written in Dutch or in English, as you prefer. You can use drawings and diagrams to support your textual answers.
CS 4495 Computer Vision. Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges. Aaron Bobick. School of Interactive Computing. Templates/Edges
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
COSC160: Detection and Classification. Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor
 COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Object Detection Design challenges
 Object Detection Design challenges How to efficiently search for likely objects Even simple models require searching hundreds of thousands of positions and scales Feature design and scoring How should
Object Detection Design challenges How to efficiently search for likely objects Even simple models require searching hundreds of thousands of positions and scales Feature design and scoring How should
Applied Bayesian Nonparametrics 5. Spatial Models via Gaussian Processes, not MRFs Tutorial at CVPR 2012 Erik Sudderth Brown University
 Applied Bayesian Nonparametrics 5. Spatial Models via Gaussian Processes, not MRFs Tutorial at CVPR 2012 Erik Sudderth Brown University NIPS 2008: E. Sudderth & M. Jordan, Shared Segmentation of Natural
Applied Bayesian Nonparametrics 5. Spatial Models via Gaussian Processes, not MRFs Tutorial at CVPR 2012 Erik Sudderth Brown University NIPS 2008: E. Sudderth & M. Jordan, Shared Segmentation of Natural
Computer Vision I - Basics of Image Processing Part 2
 Computer Vision I - Basics of Image Processing Part 2 Carsten Rother 07/11/2014 Computer Vision I: Basics of Image Processing Roadmap: Basics of Digital Image Processing Computer Vision I: Basics of Image
Computer Vision I - Basics of Image Processing Part 2 Carsten Rother 07/11/2014 Computer Vision I: Basics of Image Processing Roadmap: Basics of Digital Image Processing Computer Vision I: Basics of Image
Line, edge, blob and corner detection
 Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Lecture 8: Fitting. Tuesday, Sept 25
 Lecture 8: Fitting Tuesday, Sept 25 Announcements, schedule Grad student extensions Due end of term Data sets, suggestions Reminder: Midterm Tuesday 10/9 Problem set 2 out Thursday, due 10/11 Outline Review
Lecture 8: Fitting Tuesday, Sept 25 Announcements, schedule Grad student extensions Due end of term Data sets, suggestions Reminder: Midterm Tuesday 10/9 Problem set 2 out Thursday, due 10/11 Outline Review
Classification and Detection in Images. D.A. Forsyth
 Classification and Detection in Images D.A. Forsyth Classifying Images Motivating problems detecting explicit images classifying materials classifying scenes Strategy build appropriate image features train
Classification and Detection in Images D.A. Forsyth Classifying Images Motivating problems detecting explicit images classifying materials classifying scenes Strategy build appropriate image features train
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests. Daniel Munoz Februrary 9, 2009
 Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests Daniel Munoz 16-721 Februrary 9, 2009 Papers [shotton-eccv-06] J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi, TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context
Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests Daniel Munoz 16-721 Februrary 9, 2009 Papers [shotton-eccv-06] J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi, TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context
CS395T paper review. Indoor Segmentation and Support Inference from RGBD Images. Chao Jia Sep
 CS395T paper review Indoor Segmentation and Support Inference from RGBD Images Chao Jia Sep 28 2012 Introduction What do we want -- Indoor scene parsing Segmentation and labeling Support relationships
CS395T paper review Indoor Segmentation and Support Inference from RGBD Images Chao Jia Sep 28 2012 Introduction What do we want -- Indoor scene parsing Segmentation and labeling Support relationships
Computer Vision for HCI. Topics of This Lecture
 Computer Vision for HCI Interest Points Topics of This Lecture Local Invariant Features Motivation Requirements, Invariances Keypoint Localization Features from Accelerated Segment Test (FAST) Harris Shi-Tomasi
Computer Vision for HCI Interest Points Topics of This Lecture Local Invariant Features Motivation Requirements, Invariances Keypoint Localization Features from Accelerated Segment Test (FAST) Harris Shi-Tomasi
Announcements. Image Segmentation. From images to objects. Extracting objects. Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class
 Image Segmentation Announcements Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class Project voting From Sandlot Science Today s Readings Forsyth & Ponce, Chapter 1 (plus lots of optional references
Image Segmentation Announcements Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class Project voting From Sandlot Science Today s Readings Forsyth & Ponce, Chapter 1 (plus lots of optional references
Content-based Image and Video Retrieval. Image Segmentation
 Content-based Image and Video Retrieval Vorlesung, SS 2011 Image Segmentation 2.5.2011 / 9.5.2011 Image Segmentation One of the key problem in computer vision Identification of homogenous region in the
Content-based Image and Video Retrieval Vorlesung, SS 2011 Image Segmentation 2.5.2011 / 9.5.2011 Image Segmentation One of the key problem in computer vision Identification of homogenous region in the
Outline
 Internship at the project team PULSAR A. Schnaars 1 1 University of Magdeburg Supervisor: Guillaume Charpiat PhD Pulsar - INRIA Sophia-Antipolis INRIA Sophia-Antipolis, 15th march 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4
Internship at the project team PULSAR A. Schnaars 1 1 University of Magdeburg Supervisor: Guillaume Charpiat PhD Pulsar - INRIA Sophia-Antipolis INRIA Sophia-Antipolis, 15th march 2010 Outline 1 2 3 4
Image Analysis. Edge Detection
 Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Targil 12 : Image Segmentation. Image segmentation. Why do we need it? Image segmentation
 Targil : Image Segmentation Image segmentation Many slides from Steve Seitz Segment region of the image which: elongs to a single object. Looks uniform (gray levels, color ) Have the same attributes (texture
Targil : Image Segmentation Image segmentation Many slides from Steve Seitz Segment region of the image which: elongs to a single object. Looks uniform (gray levels, color ) Have the same attributes (texture
[ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16
![[ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16 [ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16](/thumbs/89/98496315.jpg) Review Edges and Binary Images Tuesday, Sept 6 Thought question: how could we compute a temporal gradient from video data? What filter is likely to have produced this image output? original filtered output
Review Edges and Binary Images Tuesday, Sept 6 Thought question: how could we compute a temporal gradient from video data? What filter is likely to have produced this image output? original filtered output
Classification: Linear Discriminant Functions
 Classification: Linear Discriminant Functions CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Discriminant functions Linear Discriminant functions
Classification: Linear Discriminant Functions CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Discriminant functions Linear Discriminant functions
Large-Scale Lasso and Elastic-Net Regularized Generalized Linear Models
 Large-Scale Lasso and Elastic-Net Regularized Generalized Linear Models DB Tsai Steven Hillion Outline Introduction Linear / Nonlinear Classification Feature Engineering - Polynomial Expansion Big-data
Large-Scale Lasso and Elastic-Net Regularized Generalized Linear Models DB Tsai Steven Hillion Outline Introduction Linear / Nonlinear Classification Feature Engineering - Polynomial Expansion Big-data
OCCLUSION BOUNDARIES ESTIMATION FROM A HIGH-RESOLUTION SAR IMAGE
 OCCLUSION BOUNDARIES ESTIMATION FROM A HIGH-RESOLUTION SAR IMAGE Wenju He, Marc Jäger, and Olaf Hellwich Berlin University of Technology FR3-1, Franklinstr. 28, 10587 Berlin, Germany {wenjuhe, jaeger,
OCCLUSION BOUNDARIES ESTIMATION FROM A HIGH-RESOLUTION SAR IMAGE Wenju He, Marc Jäger, and Olaf Hellwich Berlin University of Technology FR3-1, Franklinstr. 28, 10587 Berlin, Germany {wenjuhe, jaeger,
Solution: filter the image, then subsample F 1 F 2. subsample blur subsample. blur
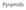 Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Applications. Foreground / background segmentation Finding skin-colored regions. Finding the moving objects. Intelligent scissors
 Segmentation I Goal Separate image into coherent regions Berkeley segmentation database: http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/research/projects/cs/vision/grouping/segbench/ Slide by L. Lazebnik Applications Intelligent
Segmentation I Goal Separate image into coherent regions Berkeley segmentation database: http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/research/projects/cs/vision/grouping/segbench/ Slide by L. Lazebnik Applications Intelligent
Segmentation & Clustering
 EECS 442 Computer vision Segmentation & Clustering Segmentation in human vision K-mean clustering Mean-shift Graph-cut Reading: Chapters 14 [FP] Some slides of this lectures are courtesy of prof F. Li,
EECS 442 Computer vision Segmentation & Clustering Segmentation in human vision K-mean clustering Mean-shift Graph-cut Reading: Chapters 14 [FP] Some slides of this lectures are courtesy of prof F. Li,
