This tutorial will take you all the steps required to set up and run a basic simulation using ABAQUS/CAE and visualize the results;
|
|
|
- Muriel Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENGN 1750: Advanced Mechanics of Solids ABAQUS TUTORIAL School of Engineering Brown University This tutorial will take you all the steps required to set up and run a basic simulation using ABAQUS/CAE and visualize the results; Background 1. The figure shows an FEA simulation of a rigid sphere rebounding of a soft rubber thin film. The sphere is idealized as a near-incompressible neo-hookean hyperelastic material (we will discuss what this means later in the class for now, all you need to know is that this material model is often used to model elastomers). The solid has shear modulus µ, bulk modulus K and mass density ρ. We will focus on the limit where K >> µ. The sphere has radius R, mass m, and is launched with initial velocity V0 towards the rigid surface. In this tutorial you will run a finite element simulation of this problem. 1. Open ABAQUS/CAE (you will find a link on the Start menu). From the Start session menu select Create Model Database with Standard/Explicit Model 2. To set up and run a simulation in CAE, you can either work through the various Modules in the dropdown menu at the top of the screen, or you can click on the menus in the workflow tree on the left hand side of the screen. We will do the former in this tutorial.
2 3. The Part module is used to define the geometry of the various interacting solids in the simulation. Here, we will create the elastomeric film and the rigid cylinder as two separate parts. Start by creating the sphere: a. Select Part>Create from the top menu bar, then use the menu that comes up to name the part Sphere; select Axisymmetric and Discrete Rigid for the Modeling Space and Type, and enter an Approximate Size of (you can try Analytical Rigid as well if you like, but ABAQUS will sometimes throw an error when you try to make a semicircle with this option) b. Use the sketch tools from the left to draw a semicircle, centered at (0,0.05), with a radius of 0.05 c. To exit the sketch menu, click the circle sketch tool to unselect it (or you can click the sketch window with both mouse buttons and select cancel procedure ), then select Done from the menu below. Rigid surfaces need a reference point that can be used to define the motion of the part, or forces acting on the part. To add a reference point to the cylinder Select Tools>Reference Point in the Part module, and select the point at the center of the sphere. Next, create the film: a. Select Part>Create; name the part Film, and select Axisymmetric and Deformable; b. Draw a rectangle the exact dimensions are not important, but place the top left corner of the rectangle at the origin. Exit the sketch menu. If you need to make any changes to the parts, you can do so using the Model Database tree on the left- you can expand the various options and edit them as needed. 4. Next, we will define material properties, and assign them to the parts. a. Switch the Module to Property b. To create a hyperelastic material, select Material>Create c. Change the name of the material to Hyperelastic. To define properties, Select General on the popup window, and enter a density value of 1. d. Next select the Mechanical>Elastic>Hyperelastic. In the menu that comes up select Neo Hooke for the strain energy potential, click the Coefficients radio button, and enter a value of 1.0 for C10. Leave the D field blank if you do this, ABAQUS will assign an internal value that makes the material approximately incompressible. e. Next, you have to create a section. This makes more sense for parts like beams or truss elements, where you need to define the geometry of the cross section, but you have to do it even for a 3D part. Select Section> Create, then select Homogeneous Solid section from the menu, set the options in the Edit Section menu as shown, then check that press OK from the menu shown f. Switch the Part to Film, then select Assign>Section. Click on the rectangular film to select it (it should turn pink), then select Done from the bottom of the window. This has now assigned the hyperelastic material model to the part representing the film. If you want to make a part heterogeneous, you can partition it, and assign different properties to the different partition. g. Next, create the inertial properties of the rigid sphere. Switch the Part to Sphere, then select Special> Inertial Properties.
3 h. On the popup window rename the property to Sphere-Inertia, then select Point mass/inertia, then press Continue i. Select the reference point in the sketch window. j. On the menu that comes up, enter a mass of 0.2 units. The inertia can be left blank, since the axisymmetric boundary condition does not allow the sphere to rotate. 5. Now we create an assembly of the parts. a. Switch the Module to Assembly b. Select Instance>Create c. On the menu select the Sphere; check the Independent radio button, make sure the auto offset is unchecked, then press OK d. Repeat b-c to create an instance of the film. You should end up with the window shown below. 6. Save the model database to a file named Sphere-Film-Impact.cae 7. Next, we define the Step, which specifies the time interval of the simulation, as well as various options defining the finite element algorithms. The Step module is also used to define variables that will be saved to the output database during analysis. a. Select the Step module b. From the top menu select Step>Create c. In the menu that appears select Dynamic, Explicit, and make sure the Procedure type is General d. On the next menu name the step Impact, make sure the NLGEOM box is checked (this will ensure ABAQUS runs as finite strain computation) and enter a time period of 2.0 on the Basic tab. You can leave the other options at their default values, but take a look at the tabs to see what the Step menu allows you to control. e. The Step module also allows you to select variables to write to the database. In this example, we will set up ABAQUS to save the vertical displacement and velocity of the center of the sphere so it can be plotted later. We first need to define a node set that will contain the reference point at the sphere center: Tools>Set>Create; then in the Create Set menu name the set
4 Sphere-Ref-Point; select Geometry, and press Continue. Then, select the reference point on the sphere, and press Done. f. To create the output request use Output>History Output Requests> Create. Name the history output Sphere Motion and press continue. g. Then, in the Edit History Output Request menu, for the Domain select Set; and select Sphere-Ref-Point for the set. For Frequency, select Every n time increments and enter 1 for n. Check the Displacement/Velocity/Acceleration box, and then edit the menu to show U2,V2,A2 (the vertical displacement, velocity and acceleration). Finally, press OK. 8. Next, we set up the properties of the contact between the sphere and the film. Select the Interaction module to start a. First, define the properties of the contact. Select Interaction>Property>Create b. Name the property Hard-frictionless and select the Contact option, then press continue c. Select the Mechanical > Normal Behavior option and accept the defaults; d. Select the Mechanical > Tangential Behavior; check that the friction formulation says Frictionless, then press OK e. Next, specify the two surfaces that will contact: select Interaction>Create f. Name the interaction Sphere-Film-Interaction and apply it to the Impact step g. Select the Surface-to-surface contact option; press Continue h. Click the outline of the sphere in the window to select it, press Done, then select color of the arrow pointing towards the outer surface of the sphere (ABAQUS needs to know whether the contact will occur from inside the sphere or the outside) i. For the second surface, select the Surface option, then click the surface of the film, then press Done j. In the Edit Interaction menu, check that Finite Sliding is selected, the interaction property should be Hard-Frictionless. You can accept defaults for the other options. Press OK. You should see the interacting surfaces marked with small rectangles in the window Now that the interaction has been created, we can configure CAE to save results associated with the contact to the output database. To do this, return to the step module (i.e. part 7 above), then k. select Output>History Output Requests>Create l. Name the history request Contact-Force, and apply it to the Impact step m. Select Interaction for the domain dropdown menu; select Every n time increments and set n=5 for the Frequency, and then activate the total forces due to contact pressure and the total contact area (see the figure)
5 9. Next, we specify boundary conditions and initial conditions for the analysis. Switch to the Load module. a. To enforce the axial symmetry boundary condition for the film, select BC>Create; then in the Create Boundary Condition menu, name the boundary condition Film-Axial-Sym; select the initial step; the Mechanical category, and the Symmetry/Antisymmetry/Encastre type; then press Continue. b. Select the leftmost side of the rectangular film c. Select the XSYMM option, and press OK (note that the UR2 and UR3 degrees of freedom are not active for the film, even though they show up in the menu) d. To constrain the vertical velocity of the base of the film, select BC>Create; in the Create Boundary Condition menu name the boundary condition Film-Base; select the Initial step; select Displacement/Rotation, and press Continue e. Select the base of the film and press Done f. In the Edit Boundary Condition menu select U2 and press OK g. To enforce the axial symmetry boundary condition for the sphere, select BC>Create h. Name the boundary condition Sphere-Axial_Sym; select the Initial step, the Mechanical category and Symmetry/Antisymmetry/Encastre and press Continue i. Select the reference point (RP) on the sphere and press Done j. Select XSYMM on the Edit Boundary Condition menu and press OK k. To specify the initial downward velocity of the sphere, Predefined Field>Create l. Name the field Initial-Vel-Sphere; select the Initial step, the Mechanical category and the Velocity type. Press Continue m. Select the reference point (RP) on the sphere n. Enter in the V2 box on the Edit Boundary Condition menu, and leave the V1 box blank. Press OK.
6 10. The analysis will need a finite element mesh (the film must be meshed; and if the sphere is a Discrete Rigid surface, it must also be meshed. It is not necessary to mesh an Analytical Rigid Surface). Select the Mesh module a. Start by meshing the film. To specify the element type that will be used in the analysis, select Mesh > Element Type; then click on the film, and select Done. b. In the Element Type menu, select the Explicit element library, and select the default settings c. To specify the mesh generation algorithm that will be used, select Mesh > Controls; then click on the film, and select Done. d. In the Mesh Controls option select Quad for the element shape, and the Medial Axis algorithm, and press OK. You may need to press Done in the assembly window again to exit the mesh controls menu e. To specify the element size to be used, select Seed>Instance, then select the film, and press Done. f. In the Global Seeds menu enter for the mesh size, and press OK. Press Done in the assembly window to exit the Seed definition. g. Finally, to mesh the film, select Mesh>Instance, select the film, and enter Done h. If the sphere is a Discrete Rigid part, it will also need to be meshed. To specify the mesh size, select Seed>Instance, then select the sphere. i. In the Global Seeds menu enter for the mesh size, and press OK. Press Done in the assembly window. j. To mesh the sphere, select Mesh>Instance, then select the sphere; press Done to exit. 11. Finally, you will need to set up and submit an analysis. Select the Job module to do this a. Select Job>Create b. Name the job Impact-Simulation. You can accept the defaults for all other options, and press OK c. To run the analysis, select Job>Submit. If ABAQUS detects any problems in defining the analysis, it will throw errors and warnings. d. You can view the progress of the analysis, along with warning messages, by selecting Job>Monitor. You will see one warning, which is harmless. As the analysis runs, information about each step will be displayed in the Impact Simulation Monitor window
7 12. ABAQUS also creates a large number of files during an analysis. You can find them in the ABAQUS working directory. The following files can be viewed using a text editor and may contain useful information (eg error messages if an analysis fails). It s worth checking each to see what they contain: a. Impact-Simulation.inp is an ASCII file that defines the finite element simulation. This is how ABAQUS/CAE (which is just a GUI) communicates with the ABAQUS finite element platform. We often edit this file and run ABAQUS with it directly when we use ABAQUS with userelement or user-material subroutines. See the last section of this tutorial for more details. b. Impact-Simulation.log summarizes the outcome of each phase of the analysis c. Impact-simulation.sta is updated during analysis to show its progress d. Impact-simulation.msg contains error messages e. Impact-simulation.dat contains both error messages and the output of an analysis. It is sometimes the only way to easily view results of an analysis that has user elements. 13. Once the job was completed, you can view the results. To do so, start by selecting the Visualization module. a. You will need to load the output database by using File>Open then navigate to the ABAQUS working directory (if needed), and open the file called Impact-Simulation.odb b. You can now explore the results of the simulation. For example, to plot von Mises stress contours on the deformed mesh, select c. You can now use the buttons to scroll through the history of the simulation. d. You can view an animation of the impact by selecting Animate > Time History. You can change the behavior of the animation by selecting the Options > Animation menu. e. If you would like to plot contours of variables other than the Von Mises stress, go to Result>Field Output. The Field Output menu will allow you to select different variables. If you don t see the variable you want to plot that usually means ABAQUS did not save it to the odb. To get it, you will need to go back to the Step menu, and use the Output> menu to add the variable you are interested in. The analysis will need to be re-run. f. You can change the way the contour plots look by using the Options>Common menu, or Options>Contour. g. Some additional features of the viewport can be controlled using the Viewport>Viewport Annotation Options. h. You often want to change the background of the viewport to save plots for reports you can do this using the View>Graphics Options menu i. ABAQUS can also plot graphs showing spatial or temporal variation of quantities of interest. For example, to plot the contact force acting between the sphere and the film as a function of time, you can use Result>History Output and then select Total force due to contact pressure: CFN2 ASSEMBLY_M_SURF-1/ASSEMBLY_S_SURF-1 (you can select either of the CFN2 variables one is the force on the sphere; the other is the force on the film. j. ABAQUS/CAE also allows you to post-process data. For example, you can save the contact force history to a dataset using Tools>XY Data>Create; then select Odb history from the XY Data menu. To change the data, you can use Tools>XY Data> Create, then select Operate on XY data. The menu that opens allows you to enter formulas that create new XY datasets by modifying existing ones. In practice it s usually easier to post-process odb data by writing a python script that will read and modify data extracted from an odb, however. k. Similarly, you can plot the velocity or displacement of the center of the sphere, by using Result>History Output, and then select Spatial velocity: V2 Pl: SPHERE-1 Node nn in NSET SPHERE-REF-POINT ; then press plot l. The visualization module has many other features; if you have time, the best way to learn them is just to explore all the various options and see what happens.
Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016)
 Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016) Problem Description A round bar with tapered diameter has a total load of 1000 N applied to its top face. The bottom of the bar is completely fixed. Determine
Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016) Problem Description A round bar with tapered diameter has a total load of 1000 N applied to its top face. The bottom of the bar is completely fixed. Determine
Workshop 15. Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate
 Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem
 ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem Problem Description In this problem, a segment of an electrical contact switch (steel) is modeled by displacing the upper
ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem Problem Description In this problem, a segment of an electrical contact switch (steel) is modeled by displacing the upper
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
This tutorial will take you all the steps required to import files into ABAQUS from SolidWorks
 ENGN 1750: Advanced Mechanics of Solids ABAQUS CAD INTERFACE TUTORIAL School of Engineering Brown University This tutorial will take you all the steps required to import files into ABAQUS from SolidWorks
ENGN 1750: Advanced Mechanics of Solids ABAQUS CAD INTERFACE TUTORIAL School of Engineering Brown University This tutorial will take you all the steps required to import files into ABAQUS from SolidWorks
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Fully-Coupled Thermo-Mechanical Analysis
 Fully-Coupled Thermo-Mechanical Analysis Type of solver: ABAQUS CAE/Standard Adapted from: ABAQUS Example Problems Manual Extrusion of a Cylindrical Aluminium Bar with Frictional Heat Generation Problem
Fully-Coupled Thermo-Mechanical Analysis Type of solver: ABAQUS CAE/Standard Adapted from: ABAQUS Example Problems Manual Extrusion of a Cylindrical Aluminium Bar with Frictional Heat Generation Problem
Analysis Steps 1. Start Abaqus and choose to create a new model database
 Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
ME Optimization of a Frame
 ME 475 - Optimization of a Frame Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus. 4 7 7 5,000 N 5,000 N 0,000 N 6 6 4 3 5 5 4 4 3 3 Figure. Full frame geometry and loading
ME 475 - Optimization of a Frame Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus. 4 7 7 5,000 N 5,000 N 0,000 N 6 6 4 3 5 5 4 4 3 3 Figure. Full frame geometry and loading
Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss
 ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss Lab TA: Xiaotong Huo EN 3029B xh0381@mun.ca Download link for Abaqus student edition: http://academy.3ds.com/software/simulia/abaqus-student-edition/
ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss Lab TA: Xiaotong Huo EN 3029B xh0381@mun.ca Download link for Abaqus student edition: http://academy.3ds.com/software/simulia/abaqus-student-edition/
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
ABAQUS/CAE Workshops
 ABAQUS/CAE Workshops University of Birmingham ABAQUS Training 27 th / 28 th October 2009 Workshop 1a: Create 3D Part Type: abaqus cae at the command prompt or select abaqus V6.9-1 from the start menu.
ABAQUS/CAE Workshops University of Birmingham ABAQUS Training 27 th / 28 th October 2009 Workshop 1a: Create 3D Part Type: abaqus cae at the command prompt or select abaqus V6.9-1 from the start menu.
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.11) Nonlinear Buckling Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.11) Nonlinear Buckling Tutorial Problem Description This is the NAFEMS 1 proposed benchmark (Lee s frame buckling) problem. The applied load is based on the normalized (EI/L 2 ) value
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.11) Nonlinear Buckling Tutorial Problem Description This is the NAFEMS 1 proposed benchmark (Lee s frame buckling) problem. The applied load is based on the normalized (EI/L 2 ) value
Installation Guide. Beginners guide to structural analysis
 Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007
 CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.9) Vibrations Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.9) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.9) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
ME Optimization of a Truss
 ME 475 - Optimization of a Truss Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus and optimized using HEEDS. 4 5 8 2 11 3 10 6 9 1 7 12 6 m 300 kn 300 kn 22 m 35 m Figure
ME 475 - Optimization of a Truss Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus and optimized using HEEDS. 4 5 8 2 11 3 10 6 9 1 7 12 6 m 300 kn 300 kn 22 m 35 m Figure
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Manual for Abaqus CAE Topology Optimization
 Abaqus CAE access: Manual for Abaqus CAE Topology Optimization 1. Open Exceed ondemand Client -> login and pass 2FA 2. Select Desktop_Mode_Full_Screen (or other user preferred resolution) for XConfig and
Abaqus CAE access: Manual for Abaqus CAE Topology Optimization 1. Open Exceed ondemand Client -> login and pass 2FA 2. Select Desktop_Mode_Full_Screen (or other user preferred resolution) for XConfig and
Abaqus/CAE Heat Transfer Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE Heat Transfer Tutorial Problem Description The thin L shaped steel part shown above (lengths in meters) is exposed to a temperature of 20 o C on the two surfaces of the inner corner, and 120
Abaqus/CAE Heat Transfer Tutorial Problem Description The thin L shaped steel part shown above (lengths in meters) is exposed to a temperature of 20 o C on the two surfaces of the inner corner, and 120
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial Problem Description A table made of steel tubing with a solid steel top and shelf is loaded with an oblique impulse load. Determine the transient response of the
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial Problem Description A table made of steel tubing with a solid steel top and shelf is loaded with an oblique impulse load. Determine the transient response of the
Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran
 Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Sliding Split Tube Telescope
 LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
EN1740 Computer Aided Visualization and Design Spring /26/2012 Brian C. P. Burke
 EN1740 Computer Aided Visualization and Design Spring 2012 4/26/2012 Brian C. P. Burke Last time: More motion analysis with Pro/E Tonight: Introduction to external analysis products ABAQUS External Analysis
EN1740 Computer Aided Visualization and Design Spring 2012 4/26/2012 Brian C. P. Burke Last time: More motion analysis with Pro/E Tonight: Introduction to external analysis products ABAQUS External Analysis
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ME Week 12 Piston Mechanical Event Simulation
 Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
ME 475 FEA of a Composite Panel
 ME 475 FEA of a Composite Panel Objectives: To determine the deflection and stress state of a composite panel subjected to asymmetric loading. Introduction: Composite laminates are composed of thin layers
ME 475 FEA of a Composite Panel Objectives: To determine the deflection and stress state of a composite panel subjected to asymmetric loading. Introduction: Composite laminates are composed of thin layers
ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis
 R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization
 Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner with
Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner with
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Large Deformation Analysis of Beam-Plate in Bending
 H. Kim 2004 1 ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Large Deformation Analysis of Beam-Plate in Bending Hyonny Kim September 28, 2004 In this tutorial, you ll learn how to: Create a 3D model using shell elements. Conduct
H. Kim 2004 1 ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Large Deformation Analysis of Beam-Plate in Bending Hyonny Kim September 28, 2004 In this tutorial, you ll learn how to: Create a 3D model using shell elements. Conduct
Tutorial. How to use the Visualization module
 Page i Preface The purpose of this tutorial aims to describe certain visualization techniques in BRIGADE/Plus to facilitate and improve the users post-processing procedure. Page ii Contents 1. OVERVIEW...
Page i Preface The purpose of this tutorial aims to describe certain visualization techniques in BRIGADE/Plus to facilitate and improve the users post-processing procedure. Page ii Contents 1. OVERVIEW...
Manual for Computational Exercises
 Manual for the computational exercise in TMM4160 Fracture Mechanics Page 1 of 32 TMM4160 Fracture Mechanics Manual for Computational Exercises Version 3.0 Zhiliang Zhang Dept. of Structural Engineering
Manual for the computational exercise in TMM4160 Fracture Mechanics Page 1 of 32 TMM4160 Fracture Mechanics Manual for Computational Exercises Version 3.0 Zhiliang Zhang Dept. of Structural Engineering
Abaqus 6.9SE Handout
 MANE 4240/ CIVL 4240: Introduction to Finite Elements Abaqus 6.9SE Handout Professor Suvranu De Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Table of Contents
MANE 4240/ CIVL 4240: Introduction to Finite Elements Abaqus 6.9SE Handout Professor Suvranu De Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Table of Contents
ES 128: Computer Assignment #4. Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010
 ES 128: Computer Assignment #4 Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010 Task 1. Study an elastic-plastic indentation problem. This problem combines plasticity with contact mechanics and has many rich aspects.
ES 128: Computer Assignment #4 Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010 Task 1. Study an elastic-plastic indentation problem. This problem combines plasticity with contact mechanics and has many rich aspects.
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v12.0, OptiStruct, HyperView This tutorial
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v12.0, OptiStruct, HyperView This tutorial
Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 LESSON 4 Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam LEGEND 75000. 50000. 25000. 0. -25000. -50000. -75000. 0. 3.50 7.00 10.5 14.0 17.5 21.0 Objectives: Demonstrate multi-step analysis set up in MSC/Advanced_FEA.
LESSON 4 Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam LEGEND 75000. 50000. 25000. 0. -25000. -50000. -75000. 0. 3.50 7.00 10.5 14.0 17.5 21.0 Objectives: Demonstrate multi-step analysis set up in MSC/Advanced_FEA.
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v2017.2, OptiStruct,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v2017.2, OptiStruct,
Introduction to MSC.Patran
 Exercise 1 Introduction to MSC.Patran Objectives: Create geometry for a Beam. Add Loads and Boundary Conditions. Review analysis results. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook - Release 9.0 1-1 1-2 MSC.Patran
Exercise 1 Introduction to MSC.Patran Objectives: Create geometry for a Beam. Add Loads and Boundary Conditions. Review analysis results. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook - Release 9.0 1-1 1-2 MSC.Patran
Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models
 Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
Appendix: To be performed during the lab session
 Appendix: To be performed during the lab session Flow over a Cylinder Two Dimensional Case Using ANSYS Workbench Simple Mesh Latest revision: September 18, 2014 The primary objective of this Tutorial is
Appendix: To be performed during the lab session Flow over a Cylinder Two Dimensional Case Using ANSYS Workbench Simple Mesh Latest revision: September 18, 2014 The primary objective of this Tutorial is
2: Static analysis of a plate
 2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
SIMCENTER 12 ACOUSTICS Beta
 SIMCENTER 12 ACOUSTICS Beta 1/80 Contents FEM Fluid Tutorial Compressor Sound Radiation... 4 1. Import Structural Mesh... 5 2. Create an Acoustic Mesh... 7 3. Load Recipe... 20 4. Vibro-Acoustic Response
SIMCENTER 12 ACOUSTICS Beta 1/80 Contents FEM Fluid Tutorial Compressor Sound Radiation... 4 1. Import Structural Mesh... 5 2. Create an Acoustic Mesh... 7 3. Load Recipe... 20 4. Vibro-Acoustic Response
New Capabilities in Project Hydra for Autodesk Simulation Mechanical
 New Capabilities in Project Hydra for Autodesk Simulation Mechanical Sualp Ozel, PE. Autodesk SM2447-L In this hands-on lab, we will go through several exercises and cover several new capabilities included
New Capabilities in Project Hydra for Autodesk Simulation Mechanical Sualp Ozel, PE. Autodesk SM2447-L In this hands-on lab, we will go through several exercises and cover several new capabilities included
Introduction to CFX. Workshop 2. Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. WS2-1. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Workshop 2 Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. Introduction to CFX WS2-1 Goals The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the user to modelling flow in high speed external aerodynamic applications.
Workshop 2 Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. Introduction to CFX WS2-1 Goals The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the user to modelling flow in high speed external aerodynamic applications.
RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS
 RADIOSS, MotionSolve, and OptiStruct RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS In this tutorial, you will learn the method of modeling an axi- symmetry problem in RADIOSS. The figure
RADIOSS, MotionSolve, and OptiStruct RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS In this tutorial, you will learn the method of modeling an axi- symmetry problem in RADIOSS. The figure
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description
 Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Creo Simulate 3.0 Tutorial
 Creo Simulate 3.0 Tutorial Structure and Thermal Roger Toogood, Ph.D., P. Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Creo Simulate 3.0 Tutorial Structure and Thermal Roger Toogood, Ph.D., P. Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
DMU Engineering Analysis Review
 Page 1 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Inserting a CATAnalysis Document Using DMU Space Analysis From CATAnalysis
Page 1 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Inserting a CATAnalysis Document Using DMU Space Analysis From CATAnalysis
Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model
 Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model 1 Introduction This tutorial is created to outline the steps required to compute radiated noise from a gearbox housing using Coustyx software. Detailed steps are given on
Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model 1 Introduction This tutorial is created to outline the steps required to compute radiated noise from a gearbox housing using Coustyx software. Detailed steps are given on
Development of a Durable Automotive Bushing with fe-safe/rubber
 Development of a Durable Automotive Bushing with fe-safe/rubber Jing Bi, Gergana Dimitrova, Sandy Eyl Dassault Systemes Simulia Corp 1301 Atwood Ave, Suite 101W, Johnston RI 02919 Abstract Fatigue life
Development of a Durable Automotive Bushing with fe-safe/rubber Jing Bi, Gergana Dimitrova, Sandy Eyl Dassault Systemes Simulia Corp 1301 Atwood Ave, Suite 101W, Johnston RI 02919 Abstract Fatigue life
Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus
 Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Transient Response of a Rocket
 Transient Response of a Rocket 100 Force 0 1.0 1.001 3.0 Time Objectives: Develope a finite element model that represents an axial force (thrust) applied to a rocket over time. Perform a linear transient
Transient Response of a Rocket 100 Force 0 1.0 1.001 3.0 Time Objectives: Develope a finite element model that represents an axial force (thrust) applied to a rocket over time. Perform a linear transient
FEA of Composites Classical Lamination Theory Example 1
 FEA of Composites Classical Lamination Theory Example 1 22.514 Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Author: Dimitri Soteropoulos Revised by Jacob Wardell Problem Description: A four layer [0/90] s graphite-epoxy
FEA of Composites Classical Lamination Theory Example 1 22.514 Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Author: Dimitri Soteropoulos Revised by Jacob Wardell Problem Description: A four layer [0/90] s graphite-epoxy
3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE
 3.1 Create new model database 3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE A finite element analysis in ABAQUS/CAE starts from create new model database in the toolbar. Then save it with a name user defined. To build
3.1 Create new model database 3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE A finite element analysis in ABAQUS/CAE starts from create new model database in the toolbar. Then save it with a name user defined. To build
Getting Started. These tasks should take about 20 minutes to complete. Getting Started
 Getting Started Getting Started This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through your first ELFINI and Generative Part Structural Analysis session, allowing you to get acquainted with the product. You
Getting Started Getting Started This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through your first ELFINI and Generative Part Structural Analysis session, allowing you to get acquainted with the product. You
Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
WORKSHOP 6.3 WELD FATIGUE USING NOMINAL STRESS METHOD. For ANSYS release 14
 WORKSHOP 6.3 WELD FATIGUE USING NOMINAL STRESS METHOD For ANSYS release 14 Objective: In this workshop, a weld fatigue analysis on a VKR-beam with a plate on top using the nominal stress method is demonstrated.
WORKSHOP 6.3 WELD FATIGUE USING NOMINAL STRESS METHOD For ANSYS release 14 Objective: In this workshop, a weld fatigue analysis on a VKR-beam with a plate on top using the nominal stress method is demonstrated.
equivalent stress to the yield stess.
 Example 10.2-1 [Ansys Workbench/Thermal Stress and User Defined Result] A 50m long deck sitting on superstructures that sit on top of substructures is modeled by a box shape of size 20 x 5 x 50 m 3. It
Example 10.2-1 [Ansys Workbench/Thermal Stress and User Defined Result] A 50m long deck sitting on superstructures that sit on top of substructures is modeled by a box shape of size 20 x 5 x 50 m 3. It
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366
 FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366 Problem statement Consider a spherical particle of radius r s moving with constant velocity U in an infinitely long cylinder of radius R that contains a Newtonian fluid. Let
FEMLAB Exercise 1 for ChE366 Problem statement Consider a spherical particle of radius r s moving with constant velocity U in an infinitely long cylinder of radius R that contains a Newtonian fluid. Let
Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Oct. 10, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim,
Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Oct. 10, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim,
Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing
 Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to simulate a ball check valve with small displacement
Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to simulate a ball check valve with small displacement
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book:
 Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4. ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I. Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC
 Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
SDC. Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks. Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003
 Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
DMU Engineering Analysis Review
 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering DMU Engineering Analysis Review Workbench Generating an Image Visualizing Extrema Generating a Basic Analysis Report
DMU Engineering Analysis Review Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering DMU Engineering Analysis Review Workbench Generating an Image Visualizing Extrema Generating a Basic Analysis Report
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
MAE 323: Lab 7. Instructions. Pressure Vessel Alex Grishin MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1
 Instructions MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1 Problem Definition Determine how different element types perform for modeling a cylindrical pressure vessel over a wide range of r/t ratios, and how the hoop stress
Instructions MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1 Problem Definition Determine how different element types perform for modeling a cylindrical pressure vessel over a wide range of r/t ratios, and how the hoop stress
ME 475 Modal Analysis and Optimization of a Tapered Beam
 ME 475 Modal Analysis and Optimization of a Tapered Beam Objectives: To optimize the shape of a tapered beam to minimize the mass, while holding the first three natural frequencies above those of the baseline
ME 475 Modal Analysis and Optimization of a Tapered Beam Objectives: To optimize the shape of a tapered beam to minimize the mass, while holding the first three natural frequencies above those of the baseline
The viscous forces on the cylinder are proportional to the gradient of the velocity field at the
 Fluid Dynamics Models : Flow Past a Cylinder Flow Past a Cylinder Introduction The flow of fluid behind a blunt body such as an automobile is difficult to compute due to the unsteady flows. The wake behind
Fluid Dynamics Models : Flow Past a Cylinder Flow Past a Cylinder Introduction The flow of fluid behind a blunt body such as an automobile is difficult to compute due to the unsteady flows. The wake behind
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Tutorial 23: Sloshing in a tank modelled using SPH as an example
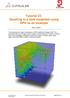 Tutorial 23: Sloshing in a tank modelled using SPH as an example This tutorial gives a basic introduction to SPH modelling in Abaqus CAE. The tutorial will take you through a basic model of g forces acting
Tutorial 23: Sloshing in a tank modelled using SPH as an example This tutorial gives a basic introduction to SPH modelling in Abaqus CAE. The tutorial will take you through a basic model of g forces acting
Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly
 Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000 pound tensile load acting on a connecting rod assembly (consisting of the rod and two pins).
Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000 pound tensile load acting on a connecting rod assembly (consisting of the rod and two pins).
Static Stress Analysis
 Static Stress Analysis Determine stresses and displacements in a connecting rod assembly. Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000-pound
Static Stress Analysis Determine stresses and displacements in a connecting rod assembly. Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000-pound
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation
 ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation Lecture #8: Introduction to FEA & ANSYS Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. March 23 rd 2015 Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. 1 Outline Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Introduction
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016
 FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering. Introduction
 Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Abstract. Introduction:
 Abstract This project analyzed a lifecycle test fixture for stress under generic test loading. The maximum stress is expected to occur near the shrink fit pin on the lever arm. The model was constructed
Abstract This project analyzed a lifecycle test fixture for stress under generic test loading. The maximum stress is expected to occur near the shrink fit pin on the lever arm. The model was constructed
Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows
 Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD PRELAB 1 By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD PRELAB 1 By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
PTC Creo Simulate. Features and Specifications. Data Sheet
 PTC Creo Simulate PTC Creo Simulate gives designers and engineers the power to evaluate structural and thermal product performance on your digital model before resorting to costly, time-consuming physical
PTC Creo Simulate PTC Creo Simulate gives designers and engineers the power to evaluate structural and thermal product performance on your digital model before resorting to costly, time-consuming physical
Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism
 Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism In the present study, KED analysis of four bar planar mechanism using MATLAB program and ANSYS software has been carried out. The analysis has also been carried
Chapter 5 Modeling and Simulation of Mechanism In the present study, KED analysis of four bar planar mechanism using MATLAB program and ANSYS software has been carried out. The analysis has also been carried
Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition
 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition Objectives: Use MPCs to replicate a Solid with a Surface. Compare stress results of the Solid and Surface 9-1 9-2 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a
LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition Objectives: Use MPCs to replicate a Solid with a Surface. Compare stress results of the Solid and Surface 9-1 9-2 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
This tutorial illustrates how to set up and solve a problem involving solidification. This tutorial will demonstrate how to do the following:
 Tutorial 22. Modeling Solidification Introduction This tutorial illustrates how to set up and solve a problem involving solidification. This tutorial will demonstrate how to do the following: Define a
Tutorial 22. Modeling Solidification Introduction This tutorial illustrates how to set up and solve a problem involving solidification. This tutorial will demonstrate how to do the following: Define a
Post-Buckling Analysis of a Thin Plate
 LESSON 13b Post-Buckling Analysis of a Thin Plate Objectives: Construct a thin plate (with slight imperfection) Place an axial load on the plate. Run an Advanced FEA nonlinear static analysis in order
LESSON 13b Post-Buckling Analysis of a Thin Plate Objectives: Construct a thin plate (with slight imperfection) Place an axial load on the plate. Run an Advanced FEA nonlinear static analysis in order
Introduction to Abaqus. About this Course
 Introduction to Abaqus R 6.12 About this Course Course objectives Upon completion of this course you will be able to: Use Abaqus/CAE to create complete finite element models. Use Abaqus/CAE to submit and
Introduction to Abaqus R 6.12 About this Course Course objectives Upon completion of this course you will be able to: Use Abaqus/CAE to create complete finite element models. Use Abaqus/CAE to submit and
Example 24 Spring-back
 Example 24 Spring-back Summary The spring-back simulation of sheet metal bent into a hat-shape is studied. The problem is one of the famous tests from the Numisheet 93. As spring-back is generally a quasi-static
Example 24 Spring-back Summary The spring-back simulation of sheet metal bent into a hat-shape is studied. The problem is one of the famous tests from the Numisheet 93. As spring-back is generally a quasi-static
Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0
 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench
 Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench Contents Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 2 1. Starting Windows on the MAC... 2 2. Login into Windows... 2 3. Start ANSYS Workbench... 2 4. Configuring
Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench Contents Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 2 1. Starting Windows on the MAC... 2 2. Login into Windows... 2 3. Start ANSYS Workbench... 2 4. Configuring
Problem description. Initial velocity mm/sec. Beveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1. Tube cross-section.
 Problem 52: rushing of a crash tube Problem description onsider the crushing of a crash tube by a rigid weight: Initial velocity 12000 mm/sec eveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1
Problem 52: rushing of a crash tube Problem description onsider the crushing of a crash tube by a rigid weight: Initial velocity 12000 mm/sec eveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1
Problem description. The figure shows a disc braking system.
 Problem description Problem 34: Thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of a disc braking system The figure shows a disc braking system. Applied pressure Piston Brake pad Brake disc Fixed plate Initially,
Problem description Problem 34: Thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of a disc braking system The figure shows a disc braking system. Applied pressure Piston Brake pad Brake disc Fixed plate Initially,
TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS.
 Ex_1_2D Plate.doc 1 TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS. 1. INTRODUCTION Two-dimensional problem of the theory of elasticity is a particular
Ex_1_2D Plate.doc 1 TWO-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEM OF THE THEORY OF ELASTICITY. INVESTIGATION OF STRESS CONCENTRATION FACTORS. 1. INTRODUCTION Two-dimensional problem of the theory of elasticity is a particular
TRINITAS. a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis. Introductional Manual
 TRINITAS a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis Introductional Manual Bo Torstenfelt Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Starting the Program
TRINITAS a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis Introductional Manual Bo Torstenfelt Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Starting the Program
Femap Version
 Femap Version 11.3 Benefits Easier model viewing and handling Faster connection definition and setup Faster and easier mesh refinement process More accurate meshes with minimal triangle element creation
Femap Version 11.3 Benefits Easier model viewing and handling Faster connection definition and setup Faster and easier mesh refinement process More accurate meshes with minimal triangle element creation
