surface Image reconstruction: 2D Fourier Transform
|
|
|
- Doris Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2/1/217 Chapter 2-3 K-space Intro to k-space sampling (chap 3) Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling (chap 2) Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling principles (chap 3) Basic Contrast mechanism (chap 4) K-space Intro to k-space sampling Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling Pulse Sequence Basic Contrast mechanisms Description of the reconstruction problem k-space k t k G( ) d k k z Need to fill k-space with data points which uniquel describe the imaged object. Think of phase- and frequenc encoding gradients as means of moving (adding new datapoints) in k-space. Limiting discussion to a slice (2D plane), magnetization distribution is given b the 2-dimensional Fourier transform of the spin distribution across the slice M T (t) (r) ep jk rdr slice (r) is obtained from the inverse Fourier transform of M T (t) under the influence of a known gradient configuration (,) 1 2 k M T (,k )ep j k d dk k-space = visualization of the distribution of spatial frequencies in the image. k-space = Fourier transform of the MR image 4 The phase angle of a spin in a slice at a t is given b: t,, tdt Gnt Gt Definition of k: t k i G i tdt Gradient on (in the i) surface The total transverse magnetisation is a function of, k and the position in the slice: M T (, k ) Image reconstruction: (,) 1 2 k 2D Fourier Transform pulsed field gradient along M T (,k )ep j k d dk 5 t K-space Intro to k-space sampling Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling Pulse Sequence Basic Contrast mechanisms 6 1
2 2/1/217 Frequenc and Phase encoding acquisition of a profile Phase encoding: needs multiple echo acquisitions Pulse sequence introduction Field gradients Spatial coding frequenc encoding (gradient on during signal acquisition) Phase encoding (gradient on before signal acquisition, repeated at different amplitudes) 7 FYS-KJM Spatiall encoded Echoes Spin-Echo: SE Use of gradient in a spin-echo eperiment to induce spatiall dependent dephasing and rephasing Gradient Echo: GRE Gradient induced echo Spin Echo: freq. encoding (frequenc encoding) t= t=/2 t= 9 18 dephasing echo FYS-KJM sampling of the signal which contains frequenc information (-ais) 1 Gradient Echo 9 Gradient Echo M T 2 * relaation (FID) t M z z z echo z z T G 2 _ rew dt T T read / 2 T _ rew dt G T _ rewt G read _ r
3 t=/2 2/1/217 Travelling in k-space Gradient Echo 9 k 1 sample k RF G FYS-KJM Gradient Echo 9 k Gradient Echo 9 k repeated N s t s Gradient Echo Spin-Echo k-space travelling 9 k t= t=/2 t= slice selection 9 18 echo 18º rf pulse k read-out phase encode Acquisition of a profile t=
4 2/1/217 acquisition of a profile acquisition of a profile (frequenc encoding) (frequenc encoding) Spatial information in G Spatial information in G 19 2 acquisition of a profile acquisition of a profile (frequenc encoding) (frequenc encoding) Spatial information in G Spatial information in G acquisition of a profile Acquisition of profile (frequenc encoding) (frequenc encoding) Spatial information in G Spatial information in G
5 2/1/217 acquisition of all profiles Repeated acquisition of profiles profiles (frequenc encoding) the field of view: FOV k Spatial information in G FOV depends on the - gradient strengths - sampling of a profile phase phase K K frequenc -127 frequenc Image generation k Signal intensit distribution in the selected slice IMAGE m, 1 2 frequenc encoding k M T 2D FT,k ep i k d dk frequenc frequenc
6 2/1/217 Digital signal sampling Discrete sampling K-space Intro to k-space sampling Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling Pulse Sequence Basic Contrast mechanisms FYS-KJM Discrete sampling PSF() T read / 2 T read / 2 A.e (i..t ) dt T read MR-signal (M T ) U(t) Sampling interval: U(t) = 1 if t [-T read /2, T read /2] and elsewhere Signal sampling is modulated b a Block Function U(t) T read = N.t s In frequenc domain, this translates to: PSF() FFTU(t) U(t)e (i..t ) dt PSF() A i e(i..t ) T read / 2 Tread / 2 PSF() A sin(..t read / 2) sin T read 2 PSF() T read T read 2 periodic function (See eq. 2-24) 33 FYS-KJM PSF() Field of View (FOV) P (,) 1 2 k M T (,k )ep j k d dk (,) 1 2 M T( )ep j d function (point object) image representation of the point object We can calculate the Full Width at Half Height (FWHH) T read, ma T read / 2 T read = N.t s ma 2, min 2 t s FOV 2 2 f s FOV t s FOV (smallest wavelength) wavelength is automaticall calculated b the scanner FOV is entered b the user (see Eq. 2-28) 2 / FYS-KJM FYS-KJM
7 2/1/217 FOV K-space properties Same definition can be done for the FOV 2 2 k, min G, n G, n1 T phase difference at the edge of the FOV Consider a square matri: N 2 = N.N Resolution (): 2 G N t Field of view ():,ma,min s 2 2 FoV k G t s Maimum frequenc in read-out () FoV / 2 ma Min sampling rate (): 1 s / t G FoV / 2 G,n G,n 1 G N G, ma (See Eq. 2-33) T FOV We need to have G N 2 G, ma Field of view ():,ma N FoV G T _ ma Sampling rate (): N G _ ma T FoV FYS-KJM K-space vs image space Back-folding / S(r) F(k) k k Increase 1/t s, N. ρ(,) FT FoV {FT} -1 Object FoV N k t s _ma FoV - ma = -FoV /2 ma = FoV /2 1 (, ) 2 k k M ( k, k ) ep T jk k dk dk N k t k G( ) d k k z 39 Image FoV discarded discarded 4 Back-folding / FFT 1D: Truncation Artefact Object FoV Image FoV Fold-Over artefact
8 2/1/217 FFT 2D: Truncation artefact Truncation artifact Ringing- (or truncation) artifacts in regions with high spatial frequencies (edges) in a phantom. The artifacts are more evident in the right image due to a lower matri (N=112, vs N=256 in the left image) Fold-Over artefact K-space Intro to k-space sampling Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling Pulse Sequence Basic Contrast mechanisms and TR Basic Contrast 1 9 o Longitudinal and Transverse Relaation: TR
9 2/1/217 1 Longitudinal and Transverse Relaation: at the same moment 9 o magnetisation 1 short T1 9 o 9 o signal 49 5 short T1 long T1 1 9 o 9 o short T2 1 9 o 9 o long T1 repetition 9 o 9 o 9 o TR 9 o 1 long T
10 2/1/217 echo 9 o 9 o o 9 o Short Longer 2 different tissues with different T1/T2 1 9 o 9 o 1 9 o 9 o T1 contrast brain eample T1 contrast 1 9 o White matter 1 9 o 9 o WM Gre matter GM
11 2/1/217 T1 contrast T1 contrast 1 9 o 9 o WM 1 9 o 9 o WM GM GM T1 contrast T1-weighted images TR 4 ms 1 9 o 9 o WM GM 1 ms 3 ms 4 ms Fat bone marrow bright i.v.contrast T1 weighted images: white matter TR short (SE) < 6 ms (can be as low as 1.5ms) gre matter muscle bod fluids gre short < 25 ms bone air black TR < 6 ms < 25 ms
12 2/1/217 T1-w knee PD (*, proton densit) & T2 contrast 1 9 o 9 o * Denoted rho contrast in the compendium PD & T2 contrast PD & T2 contrast 9 o 9 o 9 o 9 o PD contrast long TR, short T2 contrast: increases 1 9 o 1 9 o
13 2/1/217 T2 contrast, long TR, long PD & T2 weighted images TR 25 ms 1 9 o 2 ms 6 ms 1 ms 14 ms Spine / summar T2 weighted images: TR long long > 18 ms > 8 ms T1 weighted T2 weighted Table of relaation s From: Greg J. Stanisz, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 54: (25) FYS-KJM
MRI Imaging Options. Frank R. Korosec, Ph.D. Departments of Radiology and Medical Physics University of Wisconsin Madison
 MRI Imaging Options Frank R. Korosec, Ph.D. Departments of Radiolog and Medical Phsics Universit of Wisconsin Madison f.korosec@hosp.wisc.edu As MR imaging becomes more developed, more imaging options
MRI Imaging Options Frank R. Korosec, Ph.D. Departments of Radiolog and Medical Phsics Universit of Wisconsin Madison f.korosec@hosp.wisc.edu As MR imaging becomes more developed, more imaging options
MRI image formation 8/3/2016. Disclosure. Outlines. Chen Lin, PhD DABR 3. Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health
 MRI image formation Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health Disclosure No conflict of interest for this presentation 2 Outlines Data acquisition Spatial (Slice/Slab) selection
MRI image formation Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health Disclosure No conflict of interest for this presentation 2 Outlines Data acquisition Spatial (Slice/Slab) selection
Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images
 16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
A Virtual MR Scanner for Education
 A Virtual MR Scanner for Education Hackländer T, Schalla C, Trümper A, Mertens H, Hiltner J, Cramer BM Hospitals of the University Witten/Herdecke, Department of Radiology Wuppertal, Germany Purpose A
A Virtual MR Scanner for Education Hackländer T, Schalla C, Trümper A, Mertens H, Hiltner J, Cramer BM Hospitals of the University Witten/Herdecke, Department of Radiology Wuppertal, Germany Purpose A
Improved Spatial Localization in 3D MRSI with a Sequence Combining PSF-Choice, EPSI and a Resolution Enhancement Algorithm
 Improved Spatial Localization in 3D MRSI with a Sequence Combining PSF-Choice, EPSI and a Resolution Enhancement Algorithm L.P. Panych 1,3, B. Madore 1,3, W.S. Hoge 1,3, R.V. Mulkern 2,3 1 Brigham and
Improved Spatial Localization in 3D MRSI with a Sequence Combining PSF-Choice, EPSI and a Resolution Enhancement Algorithm L.P. Panych 1,3, B. Madore 1,3, W.S. Hoge 1,3, R.V. Mulkern 2,3 1 Brigham and
MRI. When to use What sequences. Outline 2012/09/19. Sequence: Definition. Basic Principles: Step 2. Basic Principles: Step 1. Govind Chavhan, MD
 MRI When to use What sequences Govind Chavhan, MD Assistant Professor and Staff Radiologist The Hospital For Sick Children, Toronto Planning Acquisition Post processing Interpretation Patient history and
MRI When to use What sequences Govind Chavhan, MD Assistant Professor and Staff Radiologist The Hospital For Sick Children, Toronto Planning Acquisition Post processing Interpretation Patient history and
Module 4. K-Space Symmetry. Review. K-Space Review. K-Space Symmetry. Partial or Fractional Echo. Half or Partial Fourier HASTE
 MRES 7005 - Fast Imaging Techniques Module 4 K-Space Symmetry Review K-Space Review K-Space Symmetry Partial or Fractional Echo Half or Partial Fourier HASTE Conditions for successful reconstruction Interpolation
MRES 7005 - Fast Imaging Techniques Module 4 K-Space Symmetry Review K-Space Review K-Space Symmetry Partial or Fractional Echo Half or Partial Fourier HASTE Conditions for successful reconstruction Interpolation
(a Scrhon5 R2iwd b. P)jc%z 5. ivcr3. 1. I. ZOms Xn,s. 1E IDrAS boms. EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI. Assignment 8 Solutions
 EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 8 Solutions 1. Nishimura 7.1 P)jc%z 5 ivcr3. 1. I Due Wednesday April 10th, 2013 (a Scrhon5 R2iwd b 0 ZOms Xn,s r cx > qs 4-4 8ni6 4
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 8 Solutions 1. Nishimura 7.1 P)jc%z 5 ivcr3. 1. I Due Wednesday April 10th, 2013 (a Scrhon5 R2iwd b 0 ZOms Xn,s r cx > qs 4-4 8ni6 4
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis
 Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 2: Image Acquisition Systems Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 2: Image Acquisition Systems Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky
Imaging Notes, Part IV
 BME 483 MRI Notes 34 page 1 Imaging Notes, Part IV Slice Selective Excitation The most common approach for dealing with the 3 rd (z) dimension is to use slice selective excitation. This is done by applying
BME 483 MRI Notes 34 page 1 Imaging Notes, Part IV Slice Selective Excitation The most common approach for dealing with the 3 rd (z) dimension is to use slice selective excitation. This is done by applying
Slide 1. Technical Aspects of Quality Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Slide 2. Annual Compliance Testing. of MRI Systems.
 Slide 1 Technical Aspects of Quality Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Slide 2 Compliance Testing of MRI Systems, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI Slide 3 Compliance Testing
Slide 1 Technical Aspects of Quality Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Slide 2 Compliance Testing of MRI Systems, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI Slide 3 Compliance Testing
MRI Physics II: Gradients, Imaging
 MRI Physics II: Gradients, Imaging Douglas C., Ph.D. Dept. of Biomedical Engineering University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Magnetic Fields in MRI B 0 The main magnetic field. Always on (0.5-7 T) Magnetizes
MRI Physics II: Gradients, Imaging Douglas C., Ph.D. Dept. of Biomedical Engineering University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Magnetic Fields in MRI B 0 The main magnetic field. Always on (0.5-7 T) Magnetizes
CHAPTER 9: Magnetic Susceptibility Effects in High Field MRI
 Figure 1. In the brain, the gray matter has substantially more blood vessels and capillaries than white matter. The magnified image on the right displays the rich vasculature in gray matter forming porous,
Figure 1. In the brain, the gray matter has substantially more blood vessels and capillaries than white matter. The magnified image on the right displays the rich vasculature in gray matter forming porous,
Exam 8N080 - Introduction MRI
 Exam 8N080 - Introduction MRI Friday January 23 rd 2015, 13.30-16.30h For this exam you may use an ordinary calculator (not a graphical one). In total there are 6 assignments and a total of 65 points can
Exam 8N080 - Introduction MRI Friday January 23 rd 2015, 13.30-16.30h For this exam you may use an ordinary calculator (not a graphical one). In total there are 6 assignments and a total of 65 points can
Diffusion MRI Acquisition. Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford
 Diffusion MRI Acquisition Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford karla@fmrib.ox.ac.uk Diffusion Imaging How is diffusion weighting achieved? How is the image acquired? What are the limitations,
Diffusion MRI Acquisition Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford karla@fmrib.ox.ac.uk Diffusion Imaging How is diffusion weighting achieved? How is the image acquired? What are the limitations,
Midterm Review
 Midterm Review - 2017 EE369B Concepts Noise Simulations with Bloch Matrices, EPG Gradient Echo Imaging 1 About the Midterm Monday Oct 30, 2017. CCSR 4107 Up to end of C2 1. Write your name legibly on this
Midterm Review - 2017 EE369B Concepts Noise Simulations with Bloch Matrices, EPG Gradient Echo Imaging 1 About the Midterm Monday Oct 30, 2017. CCSR 4107 Up to end of C2 1. Write your name legibly on this
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Fast Imaging Trajectories: Non-Cartesian Sampling (1)
 Fast Imaging Trajectories: Non-Cartesian Sampling (1) M229 Advanced Topics in MRI Holden H. Wu, Ph.D. 2018.05.03 Department of Radiological Sciences David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Class Business
Fast Imaging Trajectories: Non-Cartesian Sampling (1) M229 Advanced Topics in MRI Holden H. Wu, Ph.D. 2018.05.03 Department of Radiological Sciences David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Class Business
Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving
 Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving Sampling patterns and PSFs View ordering Modulation due to transients Temporal modulations Slice interleaving Sequential, Odd/even, bit-reversed Arbitrary Other considerations:
Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving Sampling patterns and PSFs View ordering Modulation due to transients Temporal modulations Slice interleaving Sequential, Odd/even, bit-reversed Arbitrary Other considerations:
Supplementary methods
 Supplementary methods This section provides additional technical details on the sample, the applied imaging and analysis steps and methods. Structural imaging Trained radiographers placed all participants
Supplementary methods This section provides additional technical details on the sample, the applied imaging and analysis steps and methods. Structural imaging Trained radiographers placed all participants
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class III
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class III 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class III 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Steen Moeller Center for Magnetic Resonance research University of Minnesota
 Steen Moeller Center for Magnetic Resonance research University of Minnesota moeller@cmrr.umn.edu Lot of material is from a talk by Douglas C. Noll Department of Biomedical Engineering Functional MRI Laboratory
Steen Moeller Center for Magnetic Resonance research University of Minnesota moeller@cmrr.umn.edu Lot of material is from a talk by Douglas C. Noll Department of Biomedical Engineering Functional MRI Laboratory
The SIMRI project A versatile and interactive MRI simulator *
 COST B21 Meeting, Lodz, 6-9 Oct. 2005 The SIMRI project A versatile and interactive MRI simulator * H. Benoit-Cattin 1, G. Collewet 2, B. Belaroussi 1, H. Saint-Jalmes 3, C. Odet 1 1 CREATIS, UMR CNRS
COST B21 Meeting, Lodz, 6-9 Oct. 2005 The SIMRI project A versatile and interactive MRI simulator * H. Benoit-Cattin 1, G. Collewet 2, B. Belaroussi 1, H. Saint-Jalmes 3, C. Odet 1 1 CREATIS, UMR CNRS
Institutionen för medicin och hälsa
 Institutionen för medicin och hälsa Department of Medical and Health Sciences Master Thesis Synthetic MRI for visualization of quantitative MRI Examensarbete utfört i medicinsk teknik vid Tekniska högskolan
Institutionen för medicin och hälsa Department of Medical and Health Sciences Master Thesis Synthetic MRI for visualization of quantitative MRI Examensarbete utfört i medicinsk teknik vid Tekniska högskolan
Lab Location: MRI, B2, Cardinal Carter Wing, St. Michael s Hospital, 30 Bond Street
 Lab Location: MRI, B2, Cardinal Carter Wing, St. Michael s Hospital, 30 Bond Street MRI is located in the sub basement of CC wing. From Queen or Victoria, follow the baby blue arrows and ride the CC south
Lab Location: MRI, B2, Cardinal Carter Wing, St. Michael s Hospital, 30 Bond Street MRI is located in the sub basement of CC wing. From Queen or Victoria, follow the baby blue arrows and ride the CC south
Gradient-Echo. Spin-Echo. Echo planar. Assessment of Regional Function Assessment of Global. Parallel Imaging. Function. Steady State Imaging
 Gradient-Echo Spin-Echo James W. Goldfarb Ph.D. Department of Research and Education St. Francis Hospital Program in Biomedical Engineering SUNY Stony Brook Echo planar Assessment of Regional Function
Gradient-Echo Spin-Echo James W. Goldfarb Ph.D. Department of Research and Education St. Francis Hospital Program in Biomedical Engineering SUNY Stony Brook Echo planar Assessment of Regional Function
White Pixel Artifact. Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space <--> sinusoid in image space
 White Pixel Artifact Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space sinusoid in image space Susceptibility Artifacts Off-resonance artifacts caused by adjacent regions with different
White Pixel Artifact Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space sinusoid in image space Susceptibility Artifacts Off-resonance artifacts caused by adjacent regions with different
Compressed Sensing And Joint Acquisition Techniques In Mri
 Wayne State University Wayne State University Theses 1-1-2013 Compressed Sensing And Joint Acquisition Techniques In Mri Rouhollah Hamtaei Wayne State University, Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/oa_theses
Wayne State University Wayne State University Theses 1-1-2013 Compressed Sensing And Joint Acquisition Techniques In Mri Rouhollah Hamtaei Wayne State University, Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/oa_theses
PHASE-ENCODED, RAPID, MULTIPLE-ECHO (PERME) NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
 PHASE-ENCODED, RAPID, MULTIPLE-ECHO (PERME) NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING Mark Steven Lawton Master of Engineering Thesis Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory University of California Berkeley, California
PHASE-ENCODED, RAPID, MULTIPLE-ECHO (PERME) NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING Mark Steven Lawton Master of Engineering Thesis Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory University of California Berkeley, California
Constrained Reconstruction of Sparse Cardiac MR DTI Data
 Constrained Reconstruction of Sparse Cardiac MR DTI Data Ganesh Adluru 1,3, Edward Hsu, and Edward V.R. DiBella,3 1 Electrical and Computer Engineering department, 50 S. Central Campus Dr., MEB, University
Constrained Reconstruction of Sparse Cardiac MR DTI Data Ganesh Adluru 1,3, Edward Hsu, and Edward V.R. DiBella,3 1 Electrical and Computer Engineering department, 50 S. Central Campus Dr., MEB, University
SIMULATED MRI-SCANNING
 SAHLGRENSKA ACADEMY SIMULATED MRI-SCANNING Visualising signal sampling and image reconstruction of a human brain M.Sc. Thesis Jens Johansson Essay/Thesis: Program and/or course: Level: Semester/year: Supervisor:
SAHLGRENSKA ACADEMY SIMULATED MRI-SCANNING Visualising signal sampling and image reconstruction of a human brain M.Sc. Thesis Jens Johansson Essay/Thesis: Program and/or course: Level: Semester/year: Supervisor:
T 1 MAPPING FOR DCE-MRI
 T 1 MAPPING FOR DCE-MRI A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Medical Physics By NURUN NAJWA BINTI
T 1 MAPPING FOR DCE-MRI A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Medical Physics By NURUN NAJWA BINTI
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Compressed Sensing for Rapid MR Imaging
 Compressed Sensing for Rapid Imaging Michael Lustig1, Juan Santos1, David Donoho2 and John Pauly1 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University 2 Statistics Department, Stanford University rapid
Compressed Sensing for Rapid Imaging Michael Lustig1, Juan Santos1, David Donoho2 and John Pauly1 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University 2 Statistics Department, Stanford University rapid
XI Signal-to-Noise (SNR)
 XI Signal-to-Noise (SNR) Lecture notes by Assaf Tal n(t) t. Noise. Characterizing Noise Noise is a random signal that gets added to all of our measurements. In D it looks like this: while in D
XI Signal-to-Noise (SNR) Lecture notes by Assaf Tal n(t) t. Noise. Characterizing Noise Noise is a random signal that gets added to all of our measurements. In D it looks like this: while in D
Intensity Transformations. Digital Image Processing. What Is Image Enhancement? Contents. Image Enhancement Examples. Intensity Transformations
 Digital Image Processing 2 Intensity Transformations Intensity Transformations (Point Processing) Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr It makes all the difference whether one sees darkness through the
Digital Image Processing 2 Intensity Transformations Intensity Transformations (Point Processing) Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr It makes all the difference whether one sees darkness through the
Applications Guide for Interleaved
 Applications Guide for Interleaved rephase/dephase MRAV Authors: Yongquan Ye, Ph.D. Dongmei Wu, MS. Tested MAGNETOM Systems : 7TZ, TRIO a Tim System, Verio MR B15A (N4_VB15A_LATEST_20070519) MR B17A (N4_VB17A_LATEST_20090307_P8)
Applications Guide for Interleaved rephase/dephase MRAV Authors: Yongquan Ye, Ph.D. Dongmei Wu, MS. Tested MAGNETOM Systems : 7TZ, TRIO a Tim System, Verio MR B15A (N4_VB15A_LATEST_20070519) MR B17A (N4_VB17A_LATEST_20090307_P8)
Histograms. h(r k ) = n k. p(r k )= n k /NM. Histogram: number of times intensity level rk appears in the image
 Histograms h(r k ) = n k Histogram: number of times intensity level rk appears in the image p(r k )= n k /NM normalized histogram also a probability of occurence 1 Histogram of Image Intensities Create
Histograms h(r k ) = n k Histogram: number of times intensity level rk appears in the image p(r k )= n k /NM normalized histogram also a probability of occurence 1 Histogram of Image Intensities Create
BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging
 1 Lucas Parra, CCNY BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture 4 Computed Tomography Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu some slides inspired by lecture notes of Andreas H. Hilscher at Columbia University.
1 Lucas Parra, CCNY BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture 4 Computed Tomography Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu some slides inspired by lecture notes of Andreas H. Hilscher at Columbia University.
2.1 Signal Production. RF_Coil. Scanner. Phantom. Image. Image Production
 An Extensible MRI Simulator for Post-Processing Evaluation Remi K.-S. Kwan?, Alan C. Evans, and G. Bruce Pike McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, Montreal,
An Extensible MRI Simulator for Post-Processing Evaluation Remi K.-S. Kwan?, Alan C. Evans, and G. Bruce Pike McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, Montreal,
G Practical Magnetic Resonance Imaging II Sackler Institute of Biomedical Sciences New York University School of Medicine. Compressed Sensing
 G16.4428 Practical Magnetic Resonance Imaging II Sackler Institute of Biomedical Sciences New York University School of Medicine Compressed Sensing Ricardo Otazo, PhD ricardo.otazo@nyumc.org Compressed
G16.4428 Practical Magnetic Resonance Imaging II Sackler Institute of Biomedical Sciences New York University School of Medicine Compressed Sensing Ricardo Otazo, PhD ricardo.otazo@nyumc.org Compressed
SIEMENS MAGNETOM Verio syngo MR B17
 \\USER\Dr. Behrmann\routine\Ilan\ep2d_bold_PMU_resting TA: 8:06 PAT: Voxel size: 3.03.03.0 mm Rel. SNR: 1.00 USER: ep2d_bold_pmu Properties Special sat. Prio Recon System Before measurement Body After
\\USER\Dr. Behrmann\routine\Ilan\ep2d_bold_PMU_resting TA: 8:06 PAT: Voxel size: 3.03.03.0 mm Rel. SNR: 1.00 USER: ep2d_bold_pmu Properties Special sat. Prio Recon System Before measurement Body After
Orthopedic MRI Protocols. Philips Panorama HFO
 Orthopedic MRI Protocols Philips Panorama HFO 1 2 Prepared in collaboration with Dr. John F. Feller, Medical Director of Desert Medical Imaging, Palm Springs, CA. Desert Medical Imaging will provide the
Orthopedic MRI Protocols Philips Panorama HFO 1 2 Prepared in collaboration with Dr. John F. Feller, Medical Director of Desert Medical Imaging, Palm Springs, CA. Desert Medical Imaging will provide the
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) of Liver Disease
 Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) of Liver Disease Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics Inc. jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com 1-585-249-6231 1. Overview of MRE Imaging MRE is a magnetic
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) of Liver Disease Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics Inc. jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com 1-585-249-6231 1. Overview of MRE Imaging MRE is a magnetic
Clinical Importance. Aortic Stenosis. Aortic Regurgitation. Ultrasound vs. MRI. Carotid Artery Stenosis
 Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
Spatially selective RF excitation using k-space analysis
 Spatially selective RF excitation using k-space analysis Dimitrios Pantazis a, a Signal and Image Processing Institute, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089-2564 Abstract This project
Spatially selective RF excitation using k-space analysis Dimitrios Pantazis a, a Signal and Image Processing Institute, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089-2564 Abstract This project
SIEMENS MAGNETOM Verio syngo MR B15V
 \\USER\ZAHID_RESEARCH\MS\No Name\3D SWI TA: 6:39 PAT: 2 Voxel size: 1.0 0.5 2.0 mm Rel. SNR: 1.00 SIEMENS: gre Properties Prio Recon Before measurement After measurement Load to viewer Inline movie Auto
\\USER\ZAHID_RESEARCH\MS\No Name\3D SWI TA: 6:39 PAT: 2 Voxel size: 1.0 0.5 2.0 mm Rel. SNR: 1.00 SIEMENS: gre Properties Prio Recon Before measurement After measurement Load to viewer Inline movie Auto
COBRE Scan Information
 COBRE Scan Information Below is more information on the directory structure for the COBRE imaging data. Also below are the imaging parameters for each series. Directory structure: var/www/html/dropbox/1139_anonymized/human:
COBRE Scan Information Below is more information on the directory structure for the COBRE imaging data. Also below are the imaging parameters for each series. Directory structure: var/www/html/dropbox/1139_anonymized/human:
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography Course: Advance MRI (BIOE 594) Instructors: Dr Xiaohong Joe Zhou Dr. Shadi Othman By, Nayan Pasad Phase Contrast Angiography By Moran 1982, Bryan et. Al. 1984 and Moran et.
Magnetic Resonance Angiography Course: Advance MRI (BIOE 594) Instructors: Dr Xiaohong Joe Zhou Dr. Shadi Othman By, Nayan Pasad Phase Contrast Angiography By Moran 1982, Bryan et. Al. 1984 and Moran et.
Module 5: Dynamic Imaging and Phase Sharing. (true-fisp, TRICKS, CAPR, DISTAL, DISCO, HYPR) Review. Improving Temporal Resolution.
 MRES 7005 - Fast Imaging Techniques Module 5: Dynamic Imaging and Phase Sharing (true-fisp, TRICKS, CAPR, DISTAL, DISCO, HYPR) Review Improving Temporal Resolution True-FISP (I) True-FISP (II) Keyhole
MRES 7005 - Fast Imaging Techniques Module 5: Dynamic Imaging and Phase Sharing (true-fisp, TRICKS, CAPR, DISTAL, DISCO, HYPR) Review Improving Temporal Resolution True-FISP (I) True-FISP (II) Keyhole
A Novel Iterative Thresholding Algorithm for Compressed Sensing Reconstruction of Quantitative MRI Parameters from Insufficient Data
 A Novel Iterative Thresholding Algorithm for Compressed Sensing Reconstruction of Quantitative MRI Parameters from Insufficient Data Alexey Samsonov, Julia Velikina Departments of Radiology and Medical
A Novel Iterative Thresholding Algorithm for Compressed Sensing Reconstruction of Quantitative MRI Parameters from Insufficient Data Alexey Samsonov, Julia Velikina Departments of Radiology and Medical
Role of Parallel Imaging in High Field Functional MRI
 Role of Parallel Imaging in High Field Functional MRI Douglas C. Noll & Bradley P. Sutton Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan Supported by NIH Grant DA15410 & The Whitaker Foundation
Role of Parallel Imaging in High Field Functional MRI Douglas C. Noll & Bradley P. Sutton Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan Supported by NIH Grant DA15410 & The Whitaker Foundation
New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan
 These images were acquired with an investigational device. PD T2 T2 FLAIR T1 MAP T1 FLAIR PSIR T1 New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan MR exams can be time consuming. A typical
These images were acquired with an investigational device. PD T2 T2 FLAIR T1 MAP T1 FLAIR PSIR T1 New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan MR exams can be time consuming. A typical
Field Maps. 1 Field Map Acquisition. John Pauly. October 5, 2005
 Field Maps John Pauly October 5, 25 The acquisition and reconstruction of frequency, or field, maps is important for both the acquisition of MRI data, and for its reconstruction. Many of the imaging methods
Field Maps John Pauly October 5, 25 The acquisition and reconstruction of frequency, or field, maps is important for both the acquisition of MRI data, and for its reconstruction. Many of the imaging methods
Lucy Phantom MR Grid Evaluation
 Lucy Phantom MR Grid Evaluation Anil Sethi, PhD Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, IL 60153 November 2015 I. Introduction: The MR distortion grid, used as an insert with Lucy 3D QA phantom, is
Lucy Phantom MR Grid Evaluation Anil Sethi, PhD Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, IL 60153 November 2015 I. Introduction: The MR distortion grid, used as an insert with Lucy 3D QA phantom, is
IMAGING. Images are stored by capturing the binary data using some electronic devices (SENSORS)
 IMAGING Film photography Digital photography Images are stored by capturing the binary data using some electronic devices (SENSORS) Sensors: Charge Coupled Device (CCD) Photo multiplier tube (PMT) The
IMAGING Film photography Digital photography Images are stored by capturing the binary data using some electronic devices (SENSORS) Sensors: Charge Coupled Device (CCD) Photo multiplier tube (PMT) The
Following on from the previous chapter, which considered the model of the simulation
 Chapter 4 Simulator implementation Following on from the previous chapter, which considered the model of the simulation process, this chapter is concerned with how simulations are implemented in software.
Chapter 4 Simulator implementation Following on from the previous chapter, which considered the model of the simulation process, this chapter is concerned with how simulations are implemented in software.
SIEMENS MAGNETOM Skyra syngo MR D13
 Page 1 of 8 SIEMENS MAGNETOM Skyra syngo MR D13 \\USER\CIND\StudyProtocols\PTSA\*dm_ep2d_mono70_b0_p2_iso2.0 TA:1:05 PAT:2 Voxel size:2.0 2.0 2.0 mm Rel. SNR:1.00 :epse Properties Routine Prio Recon Load
Page 1 of 8 SIEMENS MAGNETOM Skyra syngo MR D13 \\USER\CIND\StudyProtocols\PTSA\*dm_ep2d_mono70_b0_p2_iso2.0 TA:1:05 PAT:2 Voxel size:2.0 2.0 2.0 mm Rel. SNR:1.00 :epse Properties Routine Prio Recon Load
SIEMENS MAGNETOM Avanto syngo MR B15
 \\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Ravi\ADNI-phantom\QC Phantom-Localizer TA: 0:10 PAT: Voxel size: 1.9 1.5 8.0 mm Rel. SNR: 1.00 SIEMENS: gre Properties Prio Recon Before measurement After measurement Load to viewer
\\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Ravi\ADNI-phantom\QC Phantom-Localizer TA: 0:10 PAT: Voxel size: 1.9 1.5 8.0 mm Rel. SNR: 1.00 SIEMENS: gre Properties Prio Recon Before measurement After measurement Load to viewer
A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction
 Tina Memo No. 2007-003 Published in Proc. MIUA 2007 A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction P. A. Bromiley and N.A. Thacker Last updated 13 / 4 / 2007 Imaging Science and
Tina Memo No. 2007-003 Published in Proc. MIUA 2007 A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction P. A. Bromiley and N.A. Thacker Last updated 13 / 4 / 2007 Imaging Science and
Optimizing MR Scan Design for Parameter Estimation (with Application to T 1, T 2 Relaxometry)
 Optimizing MR Scan Design for Parameter Estimation (with Application to T 1, T 2 Relaxometry) Gopal Nataraj *, Jon-Fredrik Nielsen, and Jeffrey A. Fessler * Depts. of * EECS and Biomedical Engineering
Optimizing MR Scan Design for Parameter Estimation (with Application to T 1, T 2 Relaxometry) Gopal Nataraj *, Jon-Fredrik Nielsen, and Jeffrey A. Fessler * Depts. of * EECS and Biomedical Engineering
design as a constrained maximization problem. In principle, CODE seeks to maximize the b-value, defined as, where
 Optimal design of motion-compensated diffusion gradient waveforms Óscar Peña-Nogales 1, Rodrigo de Luis-Garcia 1, Santiago Aja-Fernández 1,Yuxin Zhang 2,3, James H. Holmes 2,Diego Hernando 2,3 1 Laboratorio
Optimal design of motion-compensated diffusion gradient waveforms Óscar Peña-Nogales 1, Rodrigo de Luis-Garcia 1, Santiago Aja-Fernández 1,Yuxin Zhang 2,3, James H. Holmes 2,Diego Hernando 2,3 1 Laboratorio
Learning a Spatiotemporal Dictionary for Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting with Compressed Sensing
 Learning a Spatiotemporal Dictionary for Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting with Compressed Sensing Pedro A Gómez 1,2,3, Cagdas Ulas 1, Jonathan I Sperl 3, Tim Sprenger 1,2,3, Miguel Molina-Romero 1,2,3,
Learning a Spatiotemporal Dictionary for Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting with Compressed Sensing Pedro A Gómez 1,2,3, Cagdas Ulas 1, Jonathan I Sperl 3, Tim Sprenger 1,2,3, Miguel Molina-Romero 1,2,3,
Partial k-space Reconstruction
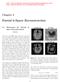 Chapter 2 Partial k-space Reconstruction 2.1 Motivation for Partial k- Space Reconstruction a) Magnitude b) Phase In theory, most MRI images depict the spin density as a function of position, and hence
Chapter 2 Partial k-space Reconstruction 2.1 Motivation for Partial k- Space Reconstruction a) Magnitude b) Phase In theory, most MRI images depict the spin density as a function of position, and hence
Non-Cartesian Parallel Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Non-Cartesian Parallel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Dissertation zur Erlangung des naturwissenschaftlichen Doktorgrades der Bayerischen Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg vorgelegt von Robin Heidemann
Non-Cartesian Parallel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Dissertation zur Erlangung des naturwissenschaftlichen Doktorgrades der Bayerischen Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg vorgelegt von Robin Heidemann
Partial k-space Recconstruction
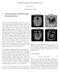 Partial k-space Recconstruction John Pauly September 29, 2005 1 Motivation for Partial k-space Reconstruction a) Magnitude b) Phase In theory, most MRI images depict the spin density as a function of position,
Partial k-space Recconstruction John Pauly September 29, 2005 1 Motivation for Partial k-space Reconstruction a) Magnitude b) Phase In theory, most MRI images depict the spin density as a function of position,
Dynamic Image and Fieldmap Joint Estimation Methods for MRI Using Single-Shot Trajectories
 Dynamic Image and Fieldmap Joint Estimation Methods for MRI Using Single-Shot Trajectories by Antonis Matakos A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Dynamic Image and Fieldmap Joint Estimation Methods for MRI Using Single-Shot Trajectories by Antonis Matakos A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Parallel Imaging. Marcin.
 Parallel Imaging Marcin m.jankiewicz@gmail.com Parallel Imaging initial thoughts Over the last 15 years, great progress in the development of pmri methods has taken place, thereby producing a multitude
Parallel Imaging Marcin m.jankiewicz@gmail.com Parallel Imaging initial thoughts Over the last 15 years, great progress in the development of pmri methods has taken place, thereby producing a multitude
Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving
 Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving Sampling patterns and PSFs View ordering Modulation due to transients Temporal modulations Timing: cine, gating, triggering Slice interleaving Sequential, Odd/even, bit-reversed
Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving Sampling patterns and PSFs View ordering Modulation due to transients Temporal modulations Timing: cine, gating, triggering Slice interleaving Sequential, Odd/even, bit-reversed
Breast MRI Accreditation Program Clinical Image Quality Guide
 Breast MRI Accreditation Program Clinical Image Quality Guide Introduction This document provides guidance on breast MRI clinical image quality and describes the criteria used by the ACR Breast MRI Accreditation
Breast MRI Accreditation Program Clinical Image Quality Guide Introduction This document provides guidance on breast MRI clinical image quality and describes the criteria used by the ACR Breast MRI Accreditation
Fast methods for magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
 Fast methods for magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) Bahareh Vafadar Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering A thesis presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy University of Canterbury,
Fast methods for magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) Bahareh Vafadar Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering A thesis presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy University of Canterbury,
Following on from the two previous chapters, which considered the model of the
 Chapter 5 Simulator validation Following on from the two previous chapters, which considered the model of the simulation process and how this model was implemented in software, this chapter is concerned
Chapter 5 Simulator validation Following on from the two previous chapters, which considered the model of the simulation process and how this model was implemented in software, this chapter is concerned
1 Introduction Goal of the study Study and thesis outline Background General MRI MRI Parameters...
 1 ABSTRACT Objectives: In current head and neck oncology practice, three-dimensional (3D) virtual planning of resection and reconstruction followed by guided surgery are standard of care. Multimodality
1 ABSTRACT Objectives: In current head and neck oncology practice, three-dimensional (3D) virtual planning of resection and reconstruction followed by guided surgery are standard of care. Multimodality
Acquisition Methods for fmri at 7 Tesla
 Acquisition Methods for fmri at 7 Tesla Peter J. Koopmans, Nuffield department for clinical neurosciences, University of Oxford, UK fmri at 7 Tesla is mostly used in the context of high spatial resolution
Acquisition Methods for fmri at 7 Tesla Peter J. Koopmans, Nuffield department for clinical neurosciences, University of Oxford, UK fmri at 7 Tesla is mostly used in the context of high spatial resolution
Philips MRI Protocol Dump Created on Comment Software Stream
 Page 1 of 5 Philips MRI Protocol Dump Created on 2/17/2011 4:11:01 PM Comment Created by ExamCard_to_XML with inputs: "J:\ADNI GO - ADNI 2 Phantom5.ExamCard" on system (BU SCHOOL OF MEDICINE :: 192.168.71.10)
Page 1 of 5 Philips MRI Protocol Dump Created on 2/17/2011 4:11:01 PM Comment Created by ExamCard_to_XML with inputs: "J:\ADNI GO - ADNI 2 Phantom5.ExamCard" on system (BU SCHOOL OF MEDICINE :: 192.168.71.10)
MB-EPI PCASL. Release Notes for Version February 2015
 MB-EPI PCASL Release Notes for Version 1.0 20 February 2015 1 Background High-resolution arterial spin labeling (ASL) imaging is highly desirable in both neuroscience research and clinical applications
MB-EPI PCASL Release Notes for Version 1.0 20 February 2015 1 Background High-resolution arterial spin labeling (ASL) imaging is highly desirable in both neuroscience research and clinical applications
University of Cape Town
 Development of a 3D radial MR Imaging sequence to be used for (self) navigation during the scanning of the fetal brain in utero by Leah Morgan Thesis presented for the degree of Master of Science June
Development of a 3D radial MR Imaging sequence to be used for (self) navigation during the scanning of the fetal brain in utero by Leah Morgan Thesis presented for the degree of Master of Science June
ADNI, ADNI_QH, SURVEY. Geometry. connection
 ADNI, ADNI_QH, SURVEY Geometry Coil selection = Head connection = d Multi coil Homogeneity correction ne FOV (mm) = 250.00 RFOV (%) = 100.00 Foldover suppression Matrix scan = 256 reconstruction = 256
ADNI, ADNI_QH, SURVEY Geometry Coil selection = Head connection = d Multi coil Homogeneity correction ne FOV (mm) = 250.00 RFOV (%) = 100.00 Foldover suppression Matrix scan = 256 reconstruction = 256
MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS
 SECOND EDITION MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS ATAM P. DHAWAN g, A B IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Sponsor IEEE Press Series in Biomedical Engineering Metin Akay, Series Editor +IEEE IEEE PRESS
SECOND EDITION MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS ATAM P. DHAWAN g, A B IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Sponsor IEEE Press Series in Biomedical Engineering Metin Akay, Series Editor +IEEE IEEE PRESS
2D spatially selective excitation pulse design and the artifact evaluation
 EE 591 Project 2D spatially selective excitation pulse design and the artifact evaluation 12/08/2004 Zungho Zun Two-dimensional spatially selective excitation is used to excite a volume such as pencil
EE 591 Project 2D spatially selective excitation pulse design and the artifact evaluation 12/08/2004 Zungho Zun Two-dimensional spatially selective excitation is used to excite a volume such as pencil
Fast Magnetic Resonance Imaging via Adaptive Broadband Encoding of the MR Signal Content
 1 Fast Magnetic Resonance Imaging via Adaptive Broadband Encoding of the MR Signal Content Dimitris Mitsouras, Frank J. Rybicki, Alan Edelman, Gary P. Zientara Abstract Our goal is to increase the time-efficiency
1 Fast Magnetic Resonance Imaging via Adaptive Broadband Encoding of the MR Signal Content Dimitris Mitsouras, Frank J. Rybicki, Alan Edelman, Gary P. Zientara Abstract Our goal is to increase the time-efficiency
Abbie M. Diak, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Dept. of Radiation Oncology
 Abbie M. Diak, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Dept. of Radiation Oncology Outline High Spectral and Spatial Resolution MR Imaging (HiSS) What it is How to do it Ways to use it HiSS for Radiation
Abbie M. Diak, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Dept. of Radiation Oncology Outline High Spectral and Spatial Resolution MR Imaging (HiSS) What it is How to do it Ways to use it HiSS for Radiation
Lecture 4. Digital Image Enhancement. 1. Principle of image enhancement 2. Spatial domain transformation. Histogram processing
 Lecture 4 Digital Image Enhancement 1. Principle of image enhancement 2. Spatial domain transformation Basic intensity it tranfomation ti Histogram processing Principle Objective of Enhancement Image enhancement
Lecture 4 Digital Image Enhancement 1. Principle of image enhancement 2. Spatial domain transformation Basic intensity it tranfomation ti Histogram processing Principle Objective of Enhancement Image enhancement
Functional MRI. Jerry Allison, Ph. D. Medical College of Georgia
 Functional MRI Jerry Allison, Ph. D. Medical College of Georgia BOLD Imaging Technique Blood Oxygen Level Dependent contrast can be used to map brain function Right Hand Motor Task Outline fmri BOLD Contrast
Functional MRI Jerry Allison, Ph. D. Medical College of Georgia BOLD Imaging Technique Blood Oxygen Level Dependent contrast can be used to map brain function Right Hand Motor Task Outline fmri BOLD Contrast
We have proposed a new method of image reconstruction in EIT (Electrical Impedance
 Impedance tomography using internal current density distribution measured by nuclear magnetic resonance Eung Je Woo, Soo Yeol Lee, Chi Woong Mun Kon Kuk University, Department of Biomedical Engineering
Impedance tomography using internal current density distribution measured by nuclear magnetic resonance Eung Je Woo, Soo Yeol Lee, Chi Woong Mun Kon Kuk University, Department of Biomedical Engineering
High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves
 Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 41:1199 1205 (1999) High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves Michael H. Buonocore* and David C. Zhu Ghost artifacts in echoplanar imaging (EPI) arise
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 41:1199 1205 (1999) High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves Michael H. Buonocore* and David C. Zhu Ghost artifacts in echoplanar imaging (EPI) arise
Siemens AG, Healthcare Sector. syngo MR D13 0. Supplement - Parameters and image text 0.
 Siemens AG, Healthcare Sector 0 0 n.a. English Cs2 syngo Neuro Operator MR-05014 630 05/2010 01 02 Informatik, Manual D11 Cape syngo MR D13 0.0 Supplement - Parameters and image text 0. syngo MR D13 0.
Siemens AG, Healthcare Sector 0 0 n.a. English Cs2 syngo Neuro Operator MR-05014 630 05/2010 01 02 Informatik, Manual D11 Cape syngo MR D13 0.0 Supplement - Parameters and image text 0. syngo MR D13 0.
Image Sampling and Quantisation
 Image Sampling and Quantisation Introduction to Signal and Image Processing Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel 1 of 46 22.02.2016 09:17 Contents Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction
Image Sampling and Quantisation Introduction to Signal and Image Processing Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel 1 of 46 22.02.2016 09:17 Contents Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction
Single-sided Magnet Diffusion Measurements
 Single-sided Magnet Diffusion Measurements Kuldeep S. Panesar April 2013 (kuldeep.panesar@gmail.com) Contents 1. Initial configuration... 2 2. Preparation for diffusion measurement... 5 3. Starting a diffusion
Single-sided Magnet Diffusion Measurements Kuldeep S. Panesar April 2013 (kuldeep.panesar@gmail.com) Contents 1. Initial configuration... 2 2. Preparation for diffusion measurement... 5 3. Starting a diffusion
X-ray tomography. X-ray tomography. Applications in Science. X-Rays. Notes. Notes. Notes. Notes
 X-ray tomography Important application of the Fast Fourier transform: X-ray tomography. Also referred to as CAT scan (Computerized Axial Tomography) X-ray tomography This has revolutionized medical diagnosis.
X-ray tomography Important application of the Fast Fourier transform: X-ray tomography. Also referred to as CAT scan (Computerized Axial Tomography) X-ray tomography This has revolutionized medical diagnosis.
Image Sampling & Quantisation
 Image Sampling & Quantisation Biomedical Image Analysis Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction and Motivation Sampling Example Quantisation Example
Image Sampling & Quantisation Biomedical Image Analysis Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction and Motivation Sampling Example Quantisation Example
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces 1/4
 Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Advanced Robotic - MAE 6D - Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - UCLA Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot is often used to manipulate
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Advanced Robotic - MAE 6D - Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - UCLA Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot is often used to manipulate
MRI Reconstruction using Real-Time Motion Tracking: A Simulation Study
 MRI Reconstruction using Real-Time Motion Tracking: A Simulation Study Jeff Orchard David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON Canada, N2L 3G1 e-mail: jorchard@uwaterloo.ca
MRI Reconstruction using Real-Time Motion Tracking: A Simulation Study Jeff Orchard David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON Canada, N2L 3G1 e-mail: jorchard@uwaterloo.ca
Introduction to Biomedical Imaging
 Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu X-ray Projection Imaging Computed Tomography Digital X-ray
Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu X-ray Projection Imaging Computed Tomography Digital X-ray
BOSTON UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING. Dissertation. Adaptive Non-Fourier Spatial Encoding For Dynamic MRI PAIRASH SAIVIROONPORN
 BOSTON UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Dissertation Adaptive Non-Fourier Spatial Encoding For Dynamic MRI by PAIRASH SAIVIROONPORN M.S., Boston University, 1992 B.S., KMITL, 1987 Submitted in partial
BOSTON UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Dissertation Adaptive Non-Fourier Spatial Encoding For Dynamic MRI by PAIRASH SAIVIROONPORN M.S., Boston University, 1992 B.S., KMITL, 1987 Submitted in partial
Red Orange the reflected ray. Yellow Green and the normal. Blue Indigo line. Colours of visible reflection
 distance the carrying the moves away from rest position Brightness Loudness The angle between the incident ray and the normal line Amplitude Amplitude of a light Amplitude of a sound incidence Angle between
distance the carrying the moves away from rest position Brightness Loudness The angle between the incident ray and the normal line Amplitude Amplitude of a light Amplitude of a sound incidence Angle between
SIEMENS MAGNETOM Avanto syngo MR B15
 \\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Ravi\ADNI-Subject\Localizer TA: 0:10 PAT: Voxel size: 1.9 1.5 8.0 mm Rel. SNR: 1.00 SIEMENS: gre Properties Prio Recon Before measurement After measurement Load to viewer Inline movie
\\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Ravi\ADNI-Subject\Localizer TA: 0:10 PAT: Voxel size: 1.9 1.5 8.0 mm Rel. SNR: 1.00 SIEMENS: gre Properties Prio Recon Before measurement After measurement Load to viewer Inline movie
A Transmission Line Matrix Model for Shielding Effects in Stents
 A Transmission Line Matrix Model for hielding Effects in tents Razvan Ciocan (1), Nathan Ida (2) (1) Clemson University Physics and Astronomy Department Clemson University, C 29634-0978 ciocan@clemon.edu
A Transmission Line Matrix Model for hielding Effects in tents Razvan Ciocan (1), Nathan Ida (2) (1) Clemson University Physics and Astronomy Department Clemson University, C 29634-0978 ciocan@clemon.edu
A more accurate account of the effect of k-space sampling and signal decay on the effective spatial resolution in functional MRI
 A more accurate account of the effect of k-space sampling and signal decay on the effective spatial resolution in functional MRI Denis Chaimow 1 and Amir Shmuel 1,2 1 Centre for Magnetic Resonance Research
A more accurate account of the effect of k-space sampling and signal decay on the effective spatial resolution in functional MRI Denis Chaimow 1 and Amir Shmuel 1,2 1 Centre for Magnetic Resonance Research
