High-Precision Positioning Unit 2.2 Student Exercise: Calculating Topographic Change
|
|
|
- Hilary Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 High-Precision Positioning Unit 2.2 Student Exercise: Calculating Topographic Change Ian Lauer and Ben Crosby (Idaho State University) Change is an inevitable part of our natural world and varies as a function of space and time. Geomorphic change is a diverse process manifesting as both diffuse and concentrated actions varying from channel migration to incision or hillslope creep to mass movement. Additionally, we can quantify many other objects including boulder or log migration down hillslopes or riverbeds. To assess and make informed decisions about the impact and variation of change within our environment, we must develop skills to categorize and quantify these processes. GPS/GNSS surveys that have the advantage of temporal and spatial data distribution allow us to quantify these changes with relative ease. Continuous monitoring or reoccupation of a site over time series allows us to analyze changes in position, which indicate direction and speed of landscape elements. Introduction In this unit, you will apply knowledge learned from working with GNSS surveys and point data to analyze and quantify changes in point data. Additionally, you will be challenged to think about how GNSS errors arise and how they might propagate through change detection equations. Change detection is the act of identifying and quantifying how an object has moved from one location to another. GNSS systems are excellent tools for detecting change due to their ability to produce time series data of an object s motion and to compare them in a georeferenced coordinate system. Quantifying Change: GNSS data describes the three-dimensional positioning of an object to some reference frame. Cartesian coordinate systems (X,Y,Z) and geographic coordinate systems (Latitude, Longitude, and Height) are two contrasting ways to approach establishing a reference frame and displaying data. The system that is used as a reference can have a great impact on the way data is visualized. However, both systems can be georeferenced for precision positioning, and they can be projected back and forth with relative ease. Cartesian GPS/GNSS point data is three-dimensional and can be described simply in a Cartesian system of X,Y,Z measurement. These measures are referenced around some origin, which can either be local or georeferenced. Local origins are arbitrary starting points that describe movements relative to each other and the origin with arbitrarily selected orientations for X,Y,Z. Usually Z is vertical distance, with X and Y describing perpendicular directions on a horizontal plane, often with one oriented north south and the other east west. Georeferenced origins are often geocentric, with the fixed origin of the X,Y,Z system at the approximated center of the Earth. However, geocentric coordinates and Cartesian systems can complicate the interpretation of positions, because the axis orientation is not relative to the ground s surface. By using a Cartesian system with a local origin, one that can arbitrarily be assigned, we can quickly compute the difference between any two points without need for complicated geometries Questions or comments please contact education_at_unavco.org, Version January 19, 2018 Page 1
2 such as ellipsoidal transformations in a geographic system. The distance between any two points on one axis of a three-dimensional position can be expressed as the difference between its initial and final position, example dx. dx = Xfinal Xinitial Any two dimensions in a Cartesian system can be differenced using Pythagoreans theorem. dxy = dx 2 + dy 2 Similarly, we can calculate a three-dimensional displacement in X,Y,Z. This is sometimes called slope distance, ds, and is the total distance from point A to B, where A and B describe the initial and final position of some object. ds = dx 2 + dy 2 + dz 2 Figure 1: An illustration of the geometry of three-dimensional distances between two points. In change detection, A and B would represent the same object with its locations taken at two different times, i.e. Time A and Time B. dx, dy, and dz represent the change in distance for a single axis. The slope distance, ds, is the total distance, or change in position, between A and B. A Cartesian coordinate plane has a local origin of (0,0,0). An object has moved from its original position at the origin, A (1,1,0) to a new position, B (2,4,3). 1. Calculate the total distance, ds, the object has moved. 2. How would the way location or orientation of the origin (0,0,0) affect the way you interpret results. (ie., as negative numbers). Which way is up? 3. What is the advantage of setting a local reference point e.g. a base station set to (0,0,0)? Geographic Geographic reference frames describe positions relative to the earth s surface often in latitude, longitude, and height. Latitude and longitude measure degrees of offset along the earth s surface Questions or comments please contact education_at_unavco.org, Version January 19, 2018 Page 2
3 oriented based on cardinal directions, north, south, east, and west. Because the Earth is neither perfectly circular nor elliptical, a significant amount of work is dedicated to producing the best fit model of the Earth s shape. The fundamentals of geodesy, which allow for these models and transformation between Cartesian and geographic systems, are beyond the scope of this assignment. In general these transformations can be done quickly in software such as ArcMap. Look at Figure 2, then discuss as a small group and individually answer the following: 4. How does projecting a planar measurement (e.g. line) onto a curved surface affect its distance? 5. How does height or elevation change with the reference point you choose? Figure 2: An angular slice of the globe, illustrating the measurement of various geodetic distances using grid, normal, and slope lengths. Note how the length of these lines would change with varying topography and with differences in how mapping planes are selected. Slope distance is measured from the topographic surface. Grid distance is measured along the flat mapping plane or projection. Normal Distance is measured along the Ellipsoid. The three distances shown all have the same angular separation. Surface Change and Visualization A common way to analyze geomorphic change is through differencing data sets, employing similar equations as described previously. Often GNSS data is used to create or reference digital elevation map (DEM) data derived from other sources as is described in Unit 2.1 Measuring Topography. Digital elevation maps contain data about surface elevations, which are interpolated from multiple point measurements such as GNSS or LiDAR. A DEM only describes a surface at a singular time. Landscape evolution often occurs at a rapid pace, and it is possible to record changes through time with multiple GNSS surveys. By differencing the time series from each other, you can extract the distance and direction of change over time. One way of visualizing GNSS and DEM changes is in map view through vectors and color gradients. GNSS velocities from a survey are shown as arrow vectors, with the length of the arrow symbolizing the magnitude of the velocity and the direction indicating the net direction of motion. The DEM underneath shows only movement in the Z-axis, changes in elevation. Changes in elevation on the DEM are shown using a bicolor color ramp. Questions or comments please contact education_at_unavco.org, Version January 19, 2018 Page 3
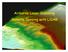
4 Precision of Movements and Error As discussed in Unit 1, GNSS positioning is the result of trilateration of the antenna by 3 or more satellites. The most favorable configuration is a wide spread of satellites across the available sky. This creates the greatest difference between individual signals and refines precision. However, even the greatest distribution of satellites across the horizon produces twice as much error in the vertical direction than the horizontal. This is because, unlike horizontal distances, vertical distances are poorly constrained due to geometry. You can think of it as physical lines connected to an object. If three people held cords attached to an object and they spread themselves evenly around said object, they could very well constrain its ability to move side to side. Figure 3: An elevation change map from the Salmon Falls landslide. The map was produced using two DEM maps derived from terrestrial LiDAR surveys. Additionally, GNSS surveys of 5 landmarks established on various features of the slide give a sense of velocity and direction for slide. Elevation change detected from the DEM is symbolized using a bicolor color ramp with red showing subsidence and blue uplift in cm. Notice the potential coregistration issue along the canyon rim. The canyon rim should be stationary, but seems to show uniform uplift along the whole rim. This is potentially a misalignment of images, a problem that can be corrected with proper GNSS survey of ground control points on the canyon rim. See Figure 3.1 A cross-section illustration of the landslide slump. Figure 3.1: A cartoon transect of an earth movement indicating surface color as they would be visualized on a DEM map. Red indicates the removal of the upper slump block resulting in decreased elevation. Blue indicates areas where the slump deposited and therefore surface elevation increased. Questions or comments please contact education_at_unavco.org, Version January 19, 2018 Page 4
5 Many sources of error contribute to the final position. However, the object would still be able to bounce up and down with significant freedom. Likewise, the vertical position of a GPS signal can only be constrained from above and not below, which significantly reduces its precision. Many sources of error contribute to the accuracy of the final position including clock timing, satellite position (ephemeris), multi-pathing, and atmospheric attenuation. These errors are summed in the product of dilution of precision (PDOP) and precision estimates provided by the receiver for any single data point. However, with change detection you are differencing two data points from each other and must therefore consider the error that is contributed by both. If the difference between two points is greater than the sum of their errors (1), then we can consider the change to be detectable. In the other case, if the total error is greater than the difference between the two points (2), then change is not detectable. Note that in (2) the error bars for A and B overlap, indicating their error is too great to detect change. Figure 4: Examples of detectable and no detectable change. Figure 5: A cartoon representation of satellite network geometry, Cartesian coordinates, GNSS positioning, and error. Clock, atmospheric, and multi-path error is significantly reduced by processing baseline between two stations. This is resolved by processing a base station through OPUS or another online solution and then correcting baselines with the rover or second station such as in the Kinematic GPS/GNSS Survey Methods manual, Section 5.3. Questions or comments please contact education_at_unavco.org, Version January 19, 2018 Page 5
6 Questions Think back to the Accuracy and Precision assignment and the Introductory lectures, and answer the following questions about how accuracy and precision relate to making measurements for change detection. 6. How does accuracy and precision relate to error? 7. How does accuracy and precision relate to our ability to measure change? Error? 8. How could you design a research problem so that the measurements you take are sufficient for the change you are trying to detect? 9. Think of one research problem that could be solved for a kinematic GNSS survey. Justify why the kinematic survey is the right technique for the given application and explicitly state the estimated amount of change you want to detect, the accuracy you need in order to detect this change, and the potential error that you can accommodate in your survey and still be able to detect change. Questions or comments please contact education_at_unavco.org, Version January 19, 2018 Page 6
7 Rubric Component Exemplary Basic Nonperformance General Considerations Part 1: Questions 1 8 Question 9: Exemplary work will not just answer all components of the given question but also answer correctly, completely, and thoughtfully. Attention to detail, as well as answers that are logical and make sense, is an important piece of this points: Answered all questions correctly. Students should illustrate: They know how local vs fixed-reference frames affect how you interpret positional measurement Depending on reference frames, distances measured can be significantly different on large scales (over 10+ km) Accuracy, Precision, and Error must all be accounted for in measurements. Errors from multiple sources add up and must be accounted for, along with estimated accuracy of the tools used. Error must be less than the amount of change detected in order for change to be considered significant. 5 points: Student provides the amount of change they need to detect and makes a reasonable estimate of the accuracy and error measurement. The accuracy doesn t exceed the capability of RTK, which is 2 3cm. Basic work may answer all components of the given question, but some answers are incorrect, illconsidered, or difficult to interpret given the context of the question. Basic work may also be missing components of a given question. 5 8 points: Answered all the questions, missing 1 2 critical points 3 4 point: Student demonstrates they understand the system and comes up with a survey that could be accomplished with GPS, but may make some unreasonable assumption in accuracy or error. Nonperformance occurs when students are missing large portions of the assignment, or when the answers simply do not make sense and are incorrect. 0 4 points: Missed more than 2 of the questions or did not complete them. 1 2 points: The student makes unreasonable assumptions on the accuracy of equipment or completely fails to justify how an RTK survey could solve the problem. Questions or comments please contact education_at_unavco.org, Version January 19, 2018 Page 7
8 Questions or comments please contact education_at_unavco.org, Version January 19, 2018 Page 8
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION. Lecture 6
 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION Lecture 6 SGU 1053 SURVEY COMPUTATION 1 Introduction Geomatic professional are mostly confronted in their work with transformations from one two/three-dimensional coordinate system
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION Lecture 6 SGU 1053 SURVEY COMPUTATION 1 Introduction Geomatic professional are mostly confronted in their work with transformations from one two/three-dimensional coordinate system
Surveying. Session GPS Surveying 1. GPS Surveying. Carrier-Phase (RTK) Pseudo-Range (DGPS) Slide 1
 GPS Surveying Slide 1 GPS Surveying Surveying Mapping Standalone Relative Relative Standalone Post-Processed Real-Time Static / Fast Static Kinematic Stop & Go Rapid-Static Carrier-Phase (RTK) Pseudo-Range
GPS Surveying Slide 1 GPS Surveying Surveying Mapping Standalone Relative Relative Standalone Post-Processed Real-Time Static / Fast Static Kinematic Stop & Go Rapid-Static Carrier-Phase (RTK) Pseudo-Range
Updating Autonomous Start to an RTK Field Survey (Part II)
 Updating Autonomous Start to an RTK Field Survey (Part II) Oscar R. Cantu Topcon University FTP Site For access to previously offered webinars and supporting documentation, please go to: ftp://tulive+topconuniversity.com:tulive@ftp.topconuniversity.com
Updating Autonomous Start to an RTK Field Survey (Part II) Oscar R. Cantu Topcon University FTP Site For access to previously offered webinars and supporting documentation, please go to: ftp://tulive+topconuniversity.com:tulive@ftp.topconuniversity.com
Unit 3.5: Geodetic Data for Hillslope Diffusion in MATLAB Student Exercise
 Unit 3.5: Geodetic Data for Hillslope Diffusion in MATLAB Student Exercise Assignment design by Ramon Arrowsmith (Arizona State University) Modified by Katherine Shervais (UNAVCO), Nathan Niemi (University
Unit 3.5: Geodetic Data for Hillslope Diffusion in MATLAB Student Exercise Assignment design by Ramon Arrowsmith (Arizona State University) Modified by Katherine Shervais (UNAVCO), Nathan Niemi (University
Navigation coordinate systems
 Lecture 3 Navigation coordinate systems Topic items: 1. Basic Coordinate Systems. 2. Plane Cartesian Coordinate Systems. 3. Polar Coordinate Systems. 4. Earth-Based Locational Reference Systems. 5. Reference
Lecture 3 Navigation coordinate systems Topic items: 1. Basic Coordinate Systems. 2. Plane Cartesian Coordinate Systems. 3. Polar Coordinate Systems. 4. Earth-Based Locational Reference Systems. 5. Reference
Central Coast LIDAR Project, 2011 Delivery 1 QC Analysis LIDAR QC Report February 17 th, 2012
 O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S OLC Central Coast Delivery 1 Acceptance Report. Department of Geology & Mineral Industries 800 NE Oregon St, Suite
O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S OLC Central Coast Delivery 1 Acceptance Report. Department of Geology & Mineral Industries 800 NE Oregon St, Suite
LOCAL GEODETIC HORIZON COORDINATES
 LOCAL GEODETIC HOIZON COODINATES In many surveying applications it is necessary to convert geocentric Cartesian coordinates X,,Z to local geodetic horizon Cartesian coordinates E,N,U (East,North,Up). Figure
LOCAL GEODETIC HOIZON COODINATES In many surveying applications it is necessary to convert geocentric Cartesian coordinates X,,Z to local geodetic horizon Cartesian coordinates E,N,U (East,North,Up). Figure
TOPOGRAPHY - a LIDAR Simulation
 Title TOPOGRAPHY - a LIDAR Simulation Grade Level(s): 9-12 Estimated Time: 1.5 hours Discussion of Technology: Appendix A Construction Details: Appendix B MSDE Indicator(s) Goal 1: Skills and Processes
Title TOPOGRAPHY - a LIDAR Simulation Grade Level(s): 9-12 Estimated Time: 1.5 hours Discussion of Technology: Appendix A Construction Details: Appendix B MSDE Indicator(s) Goal 1: Skills and Processes
Horizontal Positional Accuracy (HPA) How is it calculated? Gord Gamble and Peter Goodier, Practice Advisory Department
 Horizontal Positional Accuracy (HPA) How is it calculated? Gord Gamble and Peter Goodier, Practice Advisory Department In the December 2014 issue of The Link, the Practice Advisory Department published
Horizontal Positional Accuracy (HPA) How is it calculated? Gord Gamble and Peter Goodier, Practice Advisory Department In the December 2014 issue of The Link, the Practice Advisory Department published
Preview. Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1 Preview Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1 Preview Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods
 TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, October 20 th, 2017 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, October 20 th, 2017 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges
 Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges Objectives In this lab, you will analyze the relief structure of the San Gabriel Mountains in southern California and how it relates to
Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges Objectives In this lab, you will analyze the relief structure of the San Gabriel Mountains in southern California and how it relates to
Sandy River, OR Bathymetric Lidar Project, 2012 Delivery QC Analysis Lidar QC Report March 26 th, 2013
 O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S OLC Sandy River, OR Bathymetric Lidar Project Delivery Acceptance Report. Department of Geology & Mineral Industries
O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S OLC Sandy River, OR Bathymetric Lidar Project Delivery Acceptance Report. Department of Geology & Mineral Industries
Fundamentals of Surveying MSS 220 Prof. Gamal El-Fiky
 Fundamentals of Surveying MSS 220 Prof. Gamal l-fiky Maritime Studies Department, Faculty of Marine Science King Abdulaziz University gamal_elfiky@yahoo.com Room 221 What is Surveying? Surveying is defined
Fundamentals of Surveying MSS 220 Prof. Gamal l-fiky Maritime Studies Department, Faculty of Marine Science King Abdulaziz University gamal_elfiky@yahoo.com Room 221 What is Surveying? Surveying is defined
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods
 TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO June 20 th, 2014 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point clouds.
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO June 20 th, 2014 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point clouds.
Geometry of Aerial photogrammetry. Panu Srestasathiern, PhD. Researcher Geo-Informatics and Space Technology Development Agency (Public Organization)
 Geometry of Aerial photogrammetry Panu Srestasathiern, PhD. Researcher Geo-Informatics and Space Technology Development Agency (Public Organization) Image formation - Recap The geometry of imaging system
Geometry of Aerial photogrammetry Panu Srestasathiern, PhD. Researcher Geo-Informatics and Space Technology Development Agency (Public Organization) Image formation - Recap The geometry of imaging system
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P DIGITAL TOPOGRAPHIC DATABASES FOR PROPAGATION STUDIES. (Question ITU-R 202/3)
 Rec. ITU-R P.1058-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.1058-1 DIGITAL TOPOGRAPHIC DATABASES FOR PROPAGATION STUDIES (Question ITU-R 202/3) Rec. ITU-R P.1058-1 (1994-1997) The ITU Radiocommunication Assembly, considering
Rec. ITU-R P.1058-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.1058-1 DIGITAL TOPOGRAPHIC DATABASES FOR PROPAGATION STUDIES (Question ITU-R 202/3) Rec. ITU-R P.1058-1 (1994-1997) The ITU Radiocommunication Assembly, considering
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods
 Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods
 TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, September 23 rd, 2016 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, September 23 rd, 2016 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
BLM Fire Project, 2013 QC Analysis Lidar and Orthophoto QC Report November 25th, 2013
 O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y 1937 A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S Department of Geology & Mineral Industries 800 NE Oregon St, Suite 965 Portland, OR 97232 BLM Fire Project,
O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y 1937 A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S Department of Geology & Mineral Industries 800 NE Oregon St, Suite 965 Portland, OR 97232 BLM Fire Project,
Rogue River LIDAR Project, 2012 Delivery 1 QC Analysis LIDAR QC Report September 6 th, 2012
 O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S OLC Rogue River Delivery 1 Acceptance Report. Department of Geology & Mineral Industries 800 NE Oregon St, Suite
O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S OLC Rogue River Delivery 1 Acceptance Report. Department of Geology & Mineral Industries 800 NE Oregon St, Suite
Burns, OR LIDAR Project, 2011 Delivery QC Analysis LIDAR QC Report February 13th, 2012
 O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S OLC Burns, OR Delivery Acceptance Report. Department of Geology & Mineral Industries 800 NE Oregon St, Suite 965
O R E G O N D E P A R T M E N T O F G E O L O G Y A N D M I N E R A L I N D U S T R I E S OLC Burns, OR Delivery Acceptance Report. Department of Geology & Mineral Industries 800 NE Oregon St, Suite 965
Chapter 5. Transforming Shapes
 Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
Terrain correction. Backward geocoding. Terrain correction and ortho-rectification. Why geometric terrain correction? Rüdiger Gens
 Terrain correction and ortho-rectification Terrain correction Rüdiger Gens Why geometric terrain correction? Backward geocoding remove effects of side looking geometry of SAR images necessary step to allow
Terrain correction and ortho-rectification Terrain correction Rüdiger Gens Why geometric terrain correction? Backward geocoding remove effects of side looking geometry of SAR images necessary step to allow
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
GPS/GIS Activities Summary
 GPS/GIS Activities Summary Group activities Outdoor activities Use of GPS receivers Use of computers Calculations Relevant to robotics Relevant to agriculture 1. Information technologies in agriculture
GPS/GIS Activities Summary Group activities Outdoor activities Use of GPS receivers Use of computers Calculations Relevant to robotics Relevant to agriculture 1. Information technologies in agriculture
Geocoding and Georeferencing. Scott Bell GIS Institute
 Geocoding and Georeferencing Scott Bell GIS Institute Learning Outcomes Define coordinate system and map projection Relate coordinate systems and map projections Distinguish between defining and changing
Geocoding and Georeferencing Scott Bell GIS Institute Learning Outcomes Define coordinate system and map projection Relate coordinate systems and map projections Distinguish between defining and changing
Kinematics Review. Physics 2012
 Kinematics Review Physics 2012 Question 1 Mom and Junior are driving north in a car. They pass Spike who is standing on the side of the road. Which of these statements are correct? 1. Spike sees mom and
Kinematics Review Physics 2012 Question 1 Mom and Junior are driving north in a car. They pass Spike who is standing on the side of the road. Which of these statements are correct? 1. Spike sees mom and
Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( ) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent
 Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
THE FUTURE OF STATE PLANE COORDINATES AT ODOT
 THE FUTURE OF STATE PLANE COORDINATES AT ODOT BY: RAY FOOS P.S. AND BRIAN MEADE P.S. THE OHIO DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION WORKING WITH STATE PLANE COORDINATES OR HOW TO MAKE THE EARTH FLAT SURVEYORS AND
THE FUTURE OF STATE PLANE COORDINATES AT ODOT BY: RAY FOOS P.S. AND BRIAN MEADE P.S. THE OHIO DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION WORKING WITH STATE PLANE COORDINATES OR HOW TO MAKE THE EARTH FLAT SURVEYORS AND
The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), Goals. Warm-up: Differentiability. Notes. Notes.
 The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), 14.5 10 March 2014 Goals. We will: Define the differential df and use it to approximate changes in a function s value.
The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), 14.5 10 March 2014 Goals. We will: Define the differential df and use it to approximate changes in a function s value.
UNIVERSITY CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE AERIAL TARGET GROUND CONTROL SURVEY REPORT JOB # DATE: MARCH 2011
 UNIVERSITY CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE AERIAL TARGET GROUND CONTROL SURVEY REPORT JOB # 2011018 DATE: MARCH 2011 UNIVERSITY CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE AERIAL TARGET GROUND CONTROL SURVEY REPORT I. INTRODUCTION II.
UNIVERSITY CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE AERIAL TARGET GROUND CONTROL SURVEY REPORT JOB # 2011018 DATE: MARCH 2011 UNIVERSITY CALIFORNIA, RIVERSIDE AERIAL TARGET GROUND CONTROL SURVEY REPORT I. INTRODUCTION II.
Third Rock from the Sun
 Geodesy 101 AHD LiDAR Best Practice The Mystery of LiDAR Best Practice Glenn Jones SSSi GIS in the Coastal Environment Batemans Bay November 9, 2010 Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) Basic principles
Geodesy 101 AHD LiDAR Best Practice The Mystery of LiDAR Best Practice Glenn Jones SSSi GIS in the Coastal Environment Batemans Bay November 9, 2010 Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) Basic principles
Use of n-vector for Radar Applications
 Use of n-vector for Radar Applications Nina Ødegaard, Kenneth Gade Norwegian Defence Research Establishment Kjeller, NORWAY email: Nina.Odegaard@ffi.no Kenneth.Gade@ffi.no Abstract: This paper aims to
Use of n-vector for Radar Applications Nina Ødegaard, Kenneth Gade Norwegian Defence Research Establishment Kjeller, NORWAY email: Nina.Odegaard@ffi.no Kenneth.Gade@ffi.no Abstract: This paper aims to
1. Introduction Surveying Method chosen depends on:
 1. Introduction Surveying Method chosen depends on: by the purpose of the survey e.g. map making, location of specific points, definition of land ownership etc., by the nature of the survey itself e.g.
1. Introduction Surveying Method chosen depends on: by the purpose of the survey e.g. map making, location of specific points, definition of land ownership etc., by the nature of the survey itself e.g.
ENGI Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01
 ENGI 3425 2. Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01 2. Parametric and Polar Curves Contents: 2.1 Parametric Vector Functions 2.2 Parametric Curve Sketching 2.3 Polar Coordinates r f 2.4 Polar Curve Sketching
ENGI 3425 2. Parametric & Polar Curves Page 2-01 2. Parametric and Polar Curves Contents: 2.1 Parametric Vector Functions 2.2 Parametric Curve Sketching 2.3 Polar Coordinates r f 2.4 Polar Curve Sketching
Fall 2016 Semester METR 3113 Atmospheric Dynamics I: Introduction to Atmospheric Kinematics and Dynamics
 Fall 2016 Semester METR 3113 Atmospheric Dynamics I: Introduction to Atmospheric Kinematics and Dynamics Lecture 5 August 31 2016 Topics: Polar coordinate system Conversion of polar coordinates to 2-D
Fall 2016 Semester METR 3113 Atmospheric Dynamics I: Introduction to Atmospheric Kinematics and Dynamics Lecture 5 August 31 2016 Topics: Polar coordinate system Conversion of polar coordinates to 2-D
Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR
 Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR ALS / LIDAR OUTLINE Laser remote sensing background Basic components of an ALS/LIDAR system Two distinct families of ALS systems Waveform Discrete Return
Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR ALS / LIDAR OUTLINE Laser remote sensing background Basic components of an ALS/LIDAR system Two distinct families of ALS systems Waveform Discrete Return
L7 Raster Algorithms
 L7 Raster Algorithms NGEN6(TEK23) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems by: Abdulghani Hasan, updated Nov 216 by Per-Ola Olsson Background Store and analyze the geographic information: Raster
L7 Raster Algorithms NGEN6(TEK23) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems by: Abdulghani Hasan, updated Nov 216 by Per-Ola Olsson Background Store and analyze the geographic information: Raster
Novel Real-Time Coordinate Transformations based on N-Dimensional Geo-Registration Parameters' Matrices
 FIG Working Week 009, Eilat, Israel, -8 May 009 Novel Real-Time Coordinate Transformations based on N-Dimensional Geo-Registration Parameters' Matrices Sagi Dalyot, Ariel Gershkovich, Yerach Doythser Mapping
FIG Working Week 009, Eilat, Israel, -8 May 009 Novel Real-Time Coordinate Transformations based on N-Dimensional Geo-Registration Parameters' Matrices Sagi Dalyot, Ariel Gershkovich, Yerach Doythser Mapping
Base Configurations Carlson SurvCE
 There are six methods to set the stationary base position, organized into 2 categories: From New Position includes Read from GPS, Enter Lat/Long and Enter Grid System Coordinates. The From Known Position
There are six methods to set the stationary base position, organized into 2 categories: From New Position includes Read from GPS, Enter Lat/Long and Enter Grid System Coordinates. The From Known Position
5 Applications of Definite Integrals
 5 Applications of Definite Integrals The previous chapter introduced the concepts of a definite integral as an area and as a limit of Riemann sums, demonstrated some of the properties of integrals, introduced
5 Applications of Definite Integrals The previous chapter introduced the concepts of a definite integral as an area and as a limit of Riemann sums, demonstrated some of the properties of integrals, introduced
A SYSTEM OF COORDINATES FOR 3D
 CHAPTER 1: A SYSTEM OF COORDINATES FOR 3D 1.1 DEFINING AND USING COORDINATES DEFINING A SYSTEM OF COORDINATES IN 3-D If we are centered in San Juan, Puerto Rico, we can define a system of coordinates in
CHAPTER 1: A SYSTEM OF COORDINATES FOR 3D 1.1 DEFINING AND USING COORDINATES DEFINING A SYSTEM OF COORDINATES IN 3-D If we are centered in San Juan, Puerto Rico, we can define a system of coordinates in
ACTIVITY TWO CONSTANT VELOCITY IN TWO DIRECTIONS
 1 ACTIVITY TWO CONSTANT VELOCITY IN TWO DIRECTIONS Purpose The overall goal of this activity is for students to analyze the motion of an object moving with constant velocity along a diagonal line. In this
1 ACTIVITY TWO CONSTANT VELOCITY IN TWO DIRECTIONS Purpose The overall goal of this activity is for students to analyze the motion of an object moving with constant velocity along a diagonal line. In this
Chapters 1 9: Overview
 Chapters 1 9: Overview Chapter 1: Introduction Chapters 2 4: Data acquisition Chapters 5 9: Data manipulation Chapter 5: Vertical imagery Chapter 6: Image coordinate measurements and refinements Chapters
Chapters 1 9: Overview Chapter 1: Introduction Chapters 2 4: Data acquisition Chapters 5 9: Data manipulation Chapter 5: Vertical imagery Chapter 6: Image coordinate measurements and refinements Chapters
How to Use GOCE Level 2 Products
 How to Use GOCE Level 2 Products Thomas Gruber 1), Reiner Rummel 1), Radboud Koop 2) 1) Institute of Astronomical and Physical Geodesy, Technical University Munich 2) Netherlands Institute for Space Research
How to Use GOCE Level 2 Products Thomas Gruber 1), Reiner Rummel 1), Radboud Koop 2) 1) Institute of Astronomical and Physical Geodesy, Technical University Munich 2) Netherlands Institute for Space Research
Edge and local feature detection - 2. Importance of edge detection in computer vision
 Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Real Geodetic Map (Map without Projection) Abstract Keywords: 1. Introduction
 Real ( without Projection) Ahmad Shaker 1 Abdullah Saad 1 Abdurrahman Arafa 2* 1.Surveying Dep., Shoubra Faculty of Engineering, Benha University, Egypt 2.Manager of Surveying Dep. in Horse Company. Egypt
Real ( without Projection) Ahmad Shaker 1 Abdullah Saad 1 Abdurrahman Arafa 2* 1.Surveying Dep., Shoubra Faculty of Engineering, Benha University, Egypt 2.Manager of Surveying Dep. in Horse Company. Egypt
Ground Subsidence Monitored by L-band Satellite Radar. Interferometry
 Ground Subsidence Monitored by L-band Satellite Radar Interferometry Hsing-Chung Chang, Ming-han Chen, Lijiong Qin, Linlin Ge and Chris Rizos Satellite Navigation And Positioning Group School of Surveying
Ground Subsidence Monitored by L-band Satellite Radar Interferometry Hsing-Chung Chang, Ming-han Chen, Lijiong Qin, Linlin Ge and Chris Rizos Satellite Navigation And Positioning Group School of Surveying
Terrestrial GPS setup Fundamentals of Airborne LiDAR Systems, Collection and Calibration. JAMIE YOUNG Senior Manager LiDAR Solutions
 Terrestrial GPS setup Fundamentals of Airborne LiDAR Systems, Collection and Calibration JAMIE YOUNG Senior Manager LiDAR Solutions Topics Terrestrial GPS reference Planning and Collection Considerations
Terrestrial GPS setup Fundamentals of Airborne LiDAR Systems, Collection and Calibration JAMIE YOUNG Senior Manager LiDAR Solutions Topics Terrestrial GPS reference Planning and Collection Considerations
Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
Question: What are the origins of the forces of magnetism (how are they produced/ generated)?
 This is an additional material to the one in the internet and may help you to develop interest with the method. You should try to integrate some of the discussions here while you are trying to answer the
This is an additional material to the one in the internet and may help you to develop interest with the method. You should try to integrate some of the discussions here while you are trying to answer the
Objectives for Terrain Week
 The Terrain Correction Chuck Connor, Laura Connor Potential Fields Geophysics: Terrain Week for Terrain Week Learn about the terrain correction The inner terrain correction Learn about The outer terrain
The Terrain Correction Chuck Connor, Laura Connor Potential Fields Geophysics: Terrain Week for Terrain Week Learn about the terrain correction The inner terrain correction Learn about The outer terrain
Research in Computational Differential Geomet
 Research in Computational Differential Geometry November 5, 2014 Approximations Often we have a series of approximations which we think are getting close to looking like some shape. Approximations Often
Research in Computational Differential Geometry November 5, 2014 Approximations Often we have a series of approximations which we think are getting close to looking like some shape. Approximations Often
TxDOT Survey Manual. Manual Notice Archive. by Texas Department of Transportation (512) - all rights reserved
 TxDOT Survey Manual Manual Notice Archive by Texas Department of Transportation (512) - all rights reserved Manual Notice 2011-1 From: Manual: Judy Skeen, P. E., Director, Technology Services Division
TxDOT Survey Manual Manual Notice Archive by Texas Department of Transportation (512) - all rights reserved Manual Notice 2011-1 From: Manual: Judy Skeen, P. E., Director, Technology Services Division
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 1, January ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 1, January-2016 1657 Evaluation of GPS Data in Point Feature and 3D Building Modeling Prof. Dr. Essam M. Fawaz, Prof. Dr. Said
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 1, January-2016 1657 Evaluation of GPS Data in Point Feature and 3D Building Modeling Prof. Dr. Essam M. Fawaz, Prof. Dr. Said
Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3
 Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of more than two variables and their level surfaces.
Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of more than two variables and their level surfaces.
Finite Elements Method and its Space Application in the Study of Movements of GNSS BULiPOS Reference Stations in Bulgaria
 Kerana VASSILEVA 1, Georgi VALEV 2, 1 National Institute of Geophysics, Geodesy and Geography n Academy of Sciences 2 University of Architecture, Civil Engineering and Geodesy FIG Woring Wee 2015 1 INTRODUCTION
Kerana VASSILEVA 1, Georgi VALEV 2, 1 National Institute of Geophysics, Geodesy and Geography n Academy of Sciences 2 University of Architecture, Civil Engineering and Geodesy FIG Woring Wee 2015 1 INTRODUCTION
Purpose : Understanding Projections, 12D, and the System 1200.
 Purpose : Understanding Projections, 12D, and the System 1200. 1. For any Cad work created inside 12D, the distances entered are plane (Horizontal Chord) distances. 2. Setting a projection, or changing
Purpose : Understanding Projections, 12D, and the System 1200. 1. For any Cad work created inside 12D, the distances entered are plane (Horizontal Chord) distances. 2. Setting a projection, or changing
Patterning Math Lab 4a
 Patterning Math Lab 4a This lab is an exploration of transformations of functions, a topic covered in your Precalculus textbook in Section 1.5. As you do the exercises in this lab you will be closely reading
Patterning Math Lab 4a This lab is an exploration of transformations of functions, a topic covered in your Precalculus textbook in Section 1.5. As you do the exercises in this lab you will be closely reading
Computation of Slope
 Computation of Slope Prepared by David R. Maidment and David Tarboton GIS in Water Resources Class University of Texas at Austin September 2011, Revised December 2011 There are various ways in which slope
Computation of Slope Prepared by David R. Maidment and David Tarboton GIS in Water Resources Class University of Texas at Austin September 2011, Revised December 2011 There are various ways in which slope
Lateral Ground Movement Estimation from Space borne Radar by Differential Interferometry.
 Lateral Ground Movement Estimation from Space borne Radar by Differential Interferometry. Abstract S.Sircar 1, 2, C.Randell 1, D.Power 1, J.Youden 1, E.Gill 2 and P.Han 1 Remote Sensing Group C-CORE 1
Lateral Ground Movement Estimation from Space borne Radar by Differential Interferometry. Abstract S.Sircar 1, 2, C.Randell 1, D.Power 1, J.Youden 1, E.Gill 2 and P.Han 1 Remote Sensing Group C-CORE 1
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
SPH3U1 Lesson 09 Kinematics
 VECTORS IN TWO-DIMENSIONS LEARNING GOALS Students will Draw vector scale diagrams to visualize and analyze the nature of motion in a plane. Analyze motion by using scale diagrams to add vectors. Solve
VECTORS IN TWO-DIMENSIONS LEARNING GOALS Students will Draw vector scale diagrams to visualize and analyze the nature of motion in a plane. Analyze motion by using scale diagrams to add vectors. Solve
Free Fall. Objective. Materials. Part 1: Determining Gravitational Acceleration, g
 Free Fall Objective Students will work in groups to investigate free fall acceleration on the Earth. Students will measure the fundamental physical constant, g, and evaluate the dependence of free fall
Free Fall Objective Students will work in groups to investigate free fall acceleration on the Earth. Students will measure the fundamental physical constant, g, and evaluate the dependence of free fall
Local Linearity (Tangent Plane) Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3
 Local Linearity and the Tangent Plane - 1 Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of
Local Linearity and the Tangent Plane - 1 Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of
The Rectangular Coordinate System and Equations of Lines. College Algebra
 The Rectangular Coordinate System and Equations of Lines College Algebra Cartesian Coordinate System A grid system based on a two-dimensional plane with perpendicular axes: horizontal axis is the x-axis
The Rectangular Coordinate System and Equations of Lines College Algebra Cartesian Coordinate System A grid system based on a two-dimensional plane with perpendicular axes: horizontal axis is the x-axis
WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE
 world from others, leica geosystems WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE A NEW BULLETIN COLUMN BY CHARLES GHILANI ON PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF SURVEYING WITH A THEORETICAL SLANT february 2012 ² ACSM BULLETIN ² 27 USGS
world from others, leica geosystems WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE A NEW BULLETIN COLUMN BY CHARLES GHILANI ON PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF SURVEYING WITH A THEORETICAL SLANT february 2012 ² ACSM BULLETIN ² 27 USGS
Correcting INS Drift in Terrain Surface Measurements. Heather Chemistruck Ph.D. Student Mechanical Engineering Vehicle Terrain Performance Lab
 Correcting INS Drift in Terrain Surface Measurements Ph.D. Student Mechanical Engineering Vehicle Terrain Performance Lab October 25, 2010 Outline Laboratory Overview Vehicle Terrain Measurement System
Correcting INS Drift in Terrain Surface Measurements Ph.D. Student Mechanical Engineering Vehicle Terrain Performance Lab October 25, 2010 Outline Laboratory Overview Vehicle Terrain Measurement System
Navigational Aids 1 st Semester/2007/TF 7:30 PM -9:00 PM
 Glossary of Navigation Terms accelerometer. A device that senses inertial reaction to measure linear or angular acceleration. In its simplest form, it consists of a case-mounted spring and mass arrangement
Glossary of Navigation Terms accelerometer. A device that senses inertial reaction to measure linear or angular acceleration. In its simplest form, it consists of a case-mounted spring and mass arrangement
Section 1.2: Points and Lines
 Section 1.2: Points and Lines Objective: Graph points and lines using x and y coordinates. Often, to get an idea of the behavior of an equation we will make a picture that represents the solutions to the
Section 1.2: Points and Lines Objective: Graph points and lines using x and y coordinates. Often, to get an idea of the behavior of an equation we will make a picture that represents the solutions to the
Where s the Boss? : Monte Carlo Localization for an Autonomous Ground Vehicle using an Aerial Lidar Map
 Where s the Boss? : Monte Carlo Localization for an Autonomous Ground Vehicle using an Aerial Lidar Map Sebastian Scherer, Young-Woo Seo, and Prasanna Velagapudi October 16, 2007 Robotics Institute Carnegie
Where s the Boss? : Monte Carlo Localization for an Autonomous Ground Vehicle using an Aerial Lidar Map Sebastian Scherer, Young-Woo Seo, and Prasanna Velagapudi October 16, 2007 Robotics Institute Carnegie
Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module - 2 Lecture - 1
 Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 2 Lecture - 1 The topic of today s lecture is mobility analysis. By mobility
Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 2 Lecture - 1 The topic of today s lecture is mobility analysis. By mobility
Exercise 4: Extracting Information from DEMs in ArcMap
 Exercise 4: Extracting Information from DEMs in ArcMap Introduction This exercise covers sample activities for extracting information from DEMs in ArcMap. Topics include point and profile queries and surface
Exercise 4: Extracting Information from DEMs in ArcMap Introduction This exercise covers sample activities for extracting information from DEMs in ArcMap. Topics include point and profile queries and surface
The 2017 InSAR package also provides support for the generation of interferograms for: PALSAR-2, TanDEM-X
 Technical Specifications InSAR The Interferometric SAR (InSAR) package can be used to generate topographic products to characterize digital surface models (DSMs) or deformation products which identify
Technical Specifications InSAR The Interferometric SAR (InSAR) package can be used to generate topographic products to characterize digital surface models (DSMs) or deformation products which identify
Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE SCOPE DEFINITIONS PROCEDURE... 5
 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 3 2 SCOPE... 3 3 DEFINITIONS... 4 4 PROCEDURE... 5 4.1 Overview - Performing a Site Calibration... 5 4.1.1 Upload Mine Grid Control... 6 4.1.2 Obtain SSM Data... 7 4.1.3
Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 3 2 SCOPE... 3 3 DEFINITIONS... 4 4 PROCEDURE... 5 4.1 Overview - Performing a Site Calibration... 5 4.1.1 Upload Mine Grid Control... 6 4.1.2 Obtain SSM Data... 7 4.1.3
LECTURE TWO Representations, Projections and Coordinates
 LECTURE TWO Representations, Projections and Coordinates GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS Why project? What is the difference between a Geographic and Projected coordinate system? PROJECTED COORDINATE SYSTEMS
LECTURE TWO Representations, Projections and Coordinates GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS Why project? What is the difference between a Geographic and Projected coordinate system? PROJECTED COORDINATE SYSTEMS
GPS SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects.
 GPS SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects. b. Compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. SCALARS AND VECTORS Scalars only have magnitude
GPS SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects. b. Compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. SCALARS AND VECTORS Scalars only have magnitude
Quantifying Three-Dimensional Deformations of Migrating Fibroblasts
 45 Chapter 4 Quantifying Three-Dimensional Deformations of Migrating Fibroblasts This chapter presents the full-field displacements and tractions of 3T3 fibroblast cells during migration on polyacrylamide
45 Chapter 4 Quantifying Three-Dimensional Deformations of Migrating Fibroblasts This chapter presents the full-field displacements and tractions of 3T3 fibroblast cells during migration on polyacrylamide
The Determination of Telescope and Antenna Invariant Point (IVP)
 The Determination of Telescope and Antenna Invariant Point (IVP) John Dawson, Gary Johnston, and Bob Twilley Minerals and Geohazards Division, Geoscience Australia, Cnr Jerrabomberra Ave and Hindmarsh
The Determination of Telescope and Antenna Invariant Point (IVP) John Dawson, Gary Johnston, and Bob Twilley Minerals and Geohazards Division, Geoscience Australia, Cnr Jerrabomberra Ave and Hindmarsh
State Plane Coordinates and Computations using them GISC Spring 2013
 State Plane Coordinates and Computations using them GISC-3325 - Spring 2013 Map Projections From UNAVCO site hosting.soonet.ca/eliris/gpsgis/lec2geodesy.html Taken from Ghilani, SPC State Plane Coordinate
State Plane Coordinates and Computations using them GISC-3325 - Spring 2013 Map Projections From UNAVCO site hosting.soonet.ca/eliris/gpsgis/lec2geodesy.html Taken from Ghilani, SPC State Plane Coordinate
Determination of Geoid and Transformation Parameters By Using GPS On The Region of Kadinhani in Konya
 INTRODUCTION Determination of Geoid and Transformation Parameters By Using GPS On The Region of Kadinhani in Konya Fuat BASÇIFTÇI, Hasan Ç AGLA, Turgut AYTEN, Sabahattin Akkus, Ismail SANLIOGLU and Beytullah
INTRODUCTION Determination of Geoid and Transformation Parameters By Using GPS On The Region of Kadinhani in Konya Fuat BASÇIFTÇI, Hasan Ç AGLA, Turgut AYTEN, Sabahattin Akkus, Ismail SANLIOGLU and Beytullah
APPLICATIONS FOR COORDINATED MOTION IN RADOME TESTING
 APPLICATIONS FOR COORDINATED MOTION IN RADOME TESTING Scott McBride Evan Langman Marion Baggett MI Technologies, LLC 4500 River Green Parkway, Suite 200 Duluth, GA 30096 ABSTRACT Traditional data collection
APPLICATIONS FOR COORDINATED MOTION IN RADOME TESTING Scott McBride Evan Langman Marion Baggett MI Technologies, LLC 4500 River Green Parkway, Suite 200 Duluth, GA 30096 ABSTRACT Traditional data collection
National GNSS/BDS CORS Services in China
 National GNSS/BDS CORS Services in China Prof. Yamin Dang Chinese Academy of Surveying & Mapping E-mail:dangym@casm.ac.cn Outline 1 2 3 Reference Frame in China: CGCS 2000 GNSS/BDS CORS Service System
National GNSS/BDS CORS Services in China Prof. Yamin Dang Chinese Academy of Surveying & Mapping E-mail:dangym@casm.ac.cn Outline 1 2 3 Reference Frame in China: CGCS 2000 GNSS/BDS CORS Service System
An Introduction to Lidar & Forestry May 2013
 An Introduction to Lidar & Forestry May 2013 Introduction to Lidar & Forestry Lidar technology Derivatives from point clouds Applied to forestry Publish & Share Futures Lidar Light Detection And Ranging
An Introduction to Lidar & Forestry May 2013 Introduction to Lidar & Forestry Lidar technology Derivatives from point clouds Applied to forestry Publish & Share Futures Lidar Light Detection And Ranging
2. POINT CLOUD DATA PROCESSING
 Point Cloud Generation from suas-mounted iphone Imagery: Performance Analysis A. D. Ladai, J. Miller Towill, Inc., 2300 Clayton Road, Suite 1200, Concord, CA 94520-2176, USA - (andras.ladai, jeffrey.miller)@towill.com
Point Cloud Generation from suas-mounted iphone Imagery: Performance Analysis A. D. Ladai, J. Miller Towill, Inc., 2300 Clayton Road, Suite 1200, Concord, CA 94520-2176, USA - (andras.ladai, jeffrey.miller)@towill.com
Big Mathematical Ideas and Understandings
 Big Mathematical Ideas and Understandings A Big Idea is a statement of an idea that is central to the learning of mathematics, one that links numerous mathematical understandings into a coherent whole.
Big Mathematical Ideas and Understandings A Big Idea is a statement of an idea that is central to the learning of mathematics, one that links numerous mathematical understandings into a coherent whole.
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects. William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA
 Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
4.5 Conservative Forces
 4 CONSERVATION LAWS 4.5 Conservative Forces Name: 4.5 Conservative Forces In the last activity, you looked at the case of a block sliding down a curved plane, and determined the work done by gravity as
4 CONSERVATION LAWS 4.5 Conservative Forces Name: 4.5 Conservative Forces In the last activity, you looked at the case of a block sliding down a curved plane, and determined the work done by gravity as
RT-2 L1TE NovAtel s Single Frequency RTK Solution
 RT-2 L1TE NovAtel s Single Frequency RTK Solution Precise thinking 2009 NovAtel Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in Canada. D12699 www.novatel.com 1-800-NOVATEL (U.S. & Canada) or 403-295-4900 Europe
RT-2 L1TE NovAtel s Single Frequency RTK Solution Precise thinking 2009 NovAtel Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in Canada. D12699 www.novatel.com 1-800-NOVATEL (U.S. & Canada) or 403-295-4900 Europe
FAULT SLIP. GG303 Lab 13 11/29/16 1
 GG303 Lab 13 11/29/16 1 FAULT SLIP Lab 13 The purpose of this lab is to develop your ability to evaluate the slip along faults. The lab has three parts. The first requires you to evaluate the slip at a
GG303 Lab 13 11/29/16 1 FAULT SLIP Lab 13 The purpose of this lab is to develop your ability to evaluate the slip along faults. The lab has three parts. The first requires you to evaluate the slip at a
2.1 Motion in Two Dimensions A Scale Diagram Approach
 Figure The motion of these cyclists is two-dimensional in the plane of the road. carr LInK aval offi cers use gyroscopic compasses and satellite navigation to navigate Canada s naval fl eet. However, every
Figure The motion of these cyclists is two-dimensional in the plane of the road. carr LInK aval offi cers use gyroscopic compasses and satellite navigation to navigate Canada s naval fl eet. However, every
3GSM GmbH. Plüddemanngasse 77 A-8010 Graz, Austria Tel Fax:
 White Paper Graz, April 2014 3GSM GmbH Plüddemanngasse 77 A-8010 Graz, Austria Tel. +43-316-464744 Fax: +43-316-464744-11 office@3gsm.at www.3gsm.at Measurement and assessment of rock and terrain surfaces
White Paper Graz, April 2014 3GSM GmbH Plüddemanngasse 77 A-8010 Graz, Austria Tel. +43-316-464744 Fax: +43-316-464744-11 office@3gsm.at www.3gsm.at Measurement and assessment of rock and terrain surfaces
Data Representation in Visualisation
 Data Representation in Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 4 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Data Representation 1 Data Representation We have
Data Representation in Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 4 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Data Representation 1 Data Representation We have
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models
 Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Relating Local Vision Measurements to Global Navigation Satellite Systems Using Waypoint Based Maps
 Relating Local Vision Measurements to Global Navigation Satellite Systems Using Waypoint Based Maps John W. Allen Samuel Gin College of Engineering GPS and Vehicle Dynamics Lab Auburn University Auburn,
Relating Local Vision Measurements to Global Navigation Satellite Systems Using Waypoint Based Maps John W. Allen Samuel Gin College of Engineering GPS and Vehicle Dynamics Lab Auburn University Auburn,
EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015
 EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015 EMIGMA for Gravity EMIGMA for Gravity license is a comprehensive package that offers a wide array of processing, visualization and interpretation tools. The package
EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015 EMIGMA for Gravity EMIGMA for Gravity license is a comprehensive package that offers a wide array of processing, visualization and interpretation tools. The package
Projectile Motion SECTION 3. Two-Dimensional Motion. Objectives. Use of components avoids vector multiplication.
 Projectile Motion Key Term projectile motion Two-Dimensional Motion Previously, we showed how quantities such as displacement and velocity were vectors that could be resolved into components. In this section,
Projectile Motion Key Term projectile motion Two-Dimensional Motion Previously, we showed how quantities such as displacement and velocity were vectors that could be resolved into components. In this section,
Measurement of Direction: Bearing vs. Azimuth
 Week 5 Monday Measurement of Direction: Bearing vs. Azimuth Bearing Is an angle of 90 o or less Measured from either North or South in easterly & westerly directions. North 22 o West, South 89 o West,
Week 5 Monday Measurement of Direction: Bearing vs. Azimuth Bearing Is an angle of 90 o or less Measured from either North or South in easterly & westerly directions. North 22 o West, South 89 o West,
SurvNET Lesson One - Processing an Assumed Coordinate System 2D Total Station Network
 SurvNET Lesson One - Processing an Assumed Coordinate System 2D Total Station Network This tutorial is divided into two lessons covering the process of reducing and adjusting raw survey data into final
SurvNET Lesson One - Processing an Assumed Coordinate System 2D Total Station Network This tutorial is divided into two lessons covering the process of reducing and adjusting raw survey data into final
