Illumination Under Trees. Nelson Max University of Tokyo, and University of California, Davis
|
|
|
- Scarlett Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Illumination Under Trees Nelson Max University of Tokyo, and University of California, Davis
2 Topics Hierarchical image based rendering for trees Atmospheric illumination and shadows Shadow penumbras with fast Fourier transforms Penumbras using image based rendering Plane parallel radiance transport in forests
3 Image Based Rendering (IBR) Pre-compute multilayer (A-buffer) RGBZ images from a number of viewpoints. Reconstruct an image for a new viewpoint by using the pixel locations and the Z values to get 3D colored points to project to the new view. Relight using a similar N x N y N z Z A-buffer. Re-project to light source view for z-buffer shadow algorithm.
4
5
6 Hierarchical IBR Build a hierarchy of tree part objects, defined in terms of subobjects. Struct object { bounding_sphere; list of polygons; list of subobjects with positioning matrices; }
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 decide (object K, matrix Q) { if (K.bounding_sphere intersects view volume) if (projected size of closest pixel < threshold) reproject(k, Q); else { for all polygons P in K render P using matrix Q; for all subobjects S in K decide (S, Q*S.matrix); } }
15
16
17
18 Hierarchical IBR in Hardware Alpha test for IBR reprojection (Schauffler) Store single layer RGBZ image as an RGBA texture, with Z in Alpha channel. Draw several textured polygons perpendicular to the original viewing direction, using the alpha test to select the appropriate parts of the texture.
19 Color matrix for shading (Westermann and Ertl) Use the color matrix to rotate N x N y N x texture by the current viewing matrix time the inverse of the viewing matrix of the original image. Adjust the color matrix to put the dot product of the normal with the light source in all three RGB components. Reproject N x N y N x Z images with this matrix. Multiply resulting B&W shading image by unshaded color image, using glblendfunc.
20 Minimizing texture switching Reorganize decide (K, Q) code to save a list of matrices Q for each object K, but not reproject. In the unshaded color pass for each object K load RGBZ textures for object K for all matrices Q in list for K reproject (k, Q); In the shading pass, do the same for the N x N y N x Ztextures.
21
22 Atmospheric illumination The shadow polygon algorithm of Frank Crow can compute the regions of light and shade along a viewing ray, but the shadow polygons for all the edges of all the leaves will cross scan lines in the lower part of the image. Therefore, use scan planes that pass though the viewpoint and the sun. The needed shadow polygons are only those generated by polygon edges intersecting that scan plane.
23
24
25
26
27 Process viewing rays from the sun direction outwards, so that all polygons that cast shadows on a viewing ray have been seen first.
28 These slanted scan plane intersect the view plane in slanted scan lines which must be resampled onto a standard raster.
29
30 Penumbras and Sky Illumination Assume the shadows are cast by a tree canopy mask, lying on a plane parallel to the ground. Assume the sky illumination is an image on an infinitely high plane, so that the color depends only on the viewing direction, and not the viewpoint position. Then the image of the visible part of the sky is the result of translating the tree canopy mask image across the sky illumination image.
31
32
33 Irradiance Computation Pre-multiply sky image by cos 4 θ, to account for solid angle per pixel and Lambert s Law. Assume the sky, mask, and ground images have resolution n by n. For each ground pixel, translate the mask image, multiply by the sky image, and sum. Cost: O(n 2 ) per ground pixel. Total cost for all ground pixels: O(n 4 ).
34 Fast Fourier Transform Method The ground image is a correlation of the sky and mask images, or a convolution of the sky image and the ground image rotated by 2π. Compute the Fourier transforms of the sky and rotated mask images, in time O(n 2 log n). Multiply these Fourier transforms in time O(n 2 ). Take inverse Fourier transform in time O(n 2 log n). Total cost is O(n 2 log n) instead of O(n 4 ).
35
36
37
38
39
40 Penumbras by image based rendering (by Brett Keating) Store object in an A buffer, with multiple depths at each pixel. Trace shadow rays through A buffer. Round depths both up and down to 32 discrete levels to reduce storage, speed up ray tracing, and reduce light leaks. Uses 32 bit logical operations for ray tracing.
41
42 Deterministic Random
43
44
45 Plane Parallel Radiance Transport Represent leaves and branches by tiny oriented semi-transparent surface flakes, whose density depends only on the height z above the ground and the surface normal of the flake. Solve transport differential equations for red, green, and blue direction-dependent radiance. Subtract attenuated direct sunlight from solution. Add back direct sunlight with z-buffer shadow algorithm. Use radiance solution for shading.
46 Equation of radiance transport di( X, ω) = κ ( X, ω) I( X, ω) + κ( X, ω) a r( X, ω, ω) I( X, ω ) dω' ds X is 3D position ω and ω are ray directions on the unit sphere I(X,ω) is radiance at X flowing in direction ω s is length along the ray in direction ω κ(x,ω) is the extinction coefficient, and depends on ω r(x,ω,ω) is the scattering phase function from ω to ω a, the albedo, is the scattered fraction of the extinction 4π
47 Simplifying assumptions Orientation isotropy: the distribution d(θ N,z) of surface normals depends only on z and θ N, not on φ N. Compute it from area of clipped polygons. BRDF and BRTF isotropy: invariant under rotation of the surface about the surface normal. Volume isotropy: r(x, ω, ω) depends only on z, θ, θ, and φ φ, not on φ and φ separately. Plane parallel: I(X, ω) depends on ω and z, but not on x and y.
48 Computation of phase function Divide sphere into a number of direction bins. Separately for specular reflection, diffuse reflection and diffuse transmission, precompute square bin-to-bin scattering matrices for each θ N, by integrating analytically over φ N, and sampling in the direction bins. For each z, find r ij (z) = κ(x,ω) a r(x, ω, ω) by summing over θ N the bin to bin scattering matrix elements multiplied by d(θ N,z) and the reflection and transmission coefficients for each color.
49 Matrix version of transport equations Represent I(X,ω) by I i (z), for direction bins i. Replace ds by dz/µ i, where µ i = cos θ i. Subtract the extinction term κ(x,ω i ) from r ij (z). Then the integral-differential transport equation becomes the system of differential equations ' d X I X r a X X I X ds X di ω ω ω ω ω κ ω ω κ ω π ), ( ),, ( ), ( ), ( ), ( ), ( 4 + = ) ( ) ( ) ( z r z I dz z di ij j j i i = µ
50 Two point boundary conditions Split the vector I(z) into upward flowing I u (z) and downward flowing I d (z). I d (h) is known when z = h at the top of the trees. I u (0) = F(0) I d (0), where F(0) is the BRDF matrix for the ground at z = 0. Let F(z) be the BRDF of the ground and the vegetation up to height z, so I u (z) = F(z) I d (z). Write and solve a differential equation for F(z).
51 The volume isotropy assumption causes the differential equation for F(z) to split up into a collection of smaller systems. Shading is pre-integrated as a function of normal. For details see Plane Parallel Radiance Transport for Global Illumination in Vegetation, Nelson Max, Curtis Mobley, Brett Keating, and En-Hua Wu, EGWR 1997, (published by Springer as Rendering 97 ) pp , preprint version at
52
53
54
55
x ~ Hemispheric Lighting
 Irradiance and Incoming Radiance Imagine a sensor which is a small, flat plane centered at a point ~ x in space and oriented so that its normal points in the direction n. This sensor can compute the total
Irradiance and Incoming Radiance Imagine a sensor which is a small, flat plane centered at a point ~ x in space and oriented so that its normal points in the direction n. This sensor can compute the total
CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics. Ray Tracing: Shading
 CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Ray Tracing: Shading Last Week Until now we learned: How to create the primary rays from the given camera and image plane parameters How to intersect these rays
CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Ray Tracing: Shading Last Week Until now we learned: How to create the primary rays from the given camera and image plane parameters How to intersect these rays
Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination. Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker
 Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker Today Real-time indirect illumination Ray tracing vs. Rasterization Screen space techniques Visibility & shadows Instant
Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker Today Real-time indirect illumination Ray tracing vs. Rasterization Screen space techniques Visibility & shadows Instant
MIT Monte-Carlo Ray Tracing. MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1
 MIT 6.837 Monte-Carlo Ray Tracing MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1 Schedule Review Session: Tuesday November 18 th, 7:30 pm bring lots of questions! Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (one weeks
MIT 6.837 Monte-Carlo Ray Tracing MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1 Schedule Review Session: Tuesday November 18 th, 7:30 pm bring lots of questions! Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (one weeks
Hierarchical Image-Based Rendering Using Texture Mapping Hardware
 UCRL-JC-132830 PREPRINT Hierarchical Image-Based Rendering Using Texture Mapping Hardware Nelson Max This paper was prepared for submittal to the 10th Eurographics Workshop on Rendering Granada, Spain
UCRL-JC-132830 PREPRINT Hierarchical Image-Based Rendering Using Texture Mapping Hardware Nelson Max This paper was prepared for submittal to the 10th Eurographics Workshop on Rendering Granada, Spain
Global Illumination. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18. BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] 1 Global Illumination
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] 1 Global Illumination
Global Illumination. Global Illumination. Direct Illumination vs. Global Illumination. Indirect Illumination. Soft Shadows.
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] March 28, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] March 28, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California
Ray tracing. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1
 Ray tracing Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1 From last time Hidden surface removal Painter s algorithm Clipping algorithms Area subdivision BSP trees Z-Buffer
Ray tracing Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1 From last time Hidden surface removal Painter s algorithm Clipping algorithms Area subdivision BSP trees Z-Buffer
Spherical Harmonic Lighting: The Gritty Details Robin Green
 Spherical Harmonic Lighting: The Gritty Details Robin Green R&D Programmer Sony Computer Entertainment America What This Talk Is About Advanced Lecture Explicit equations will be shown This talk is one
Spherical Harmonic Lighting: The Gritty Details Robin Green R&D Programmer Sony Computer Entertainment America What This Talk Is About Advanced Lecture Explicit equations will be shown This talk is one
Photorealism: Ray Tracing
 Photorealism: Ray Tracing Reading Assignment: Chapter 13 Local vs. Global Illumination Local Illumination depends on local object and light sources only Global Illumination at a point can depend on any
Photorealism: Ray Tracing Reading Assignment: Chapter 13 Local vs. Global Illumination Local Illumination depends on local object and light sources only Global Illumination at a point can depend on any
6. Illumination, Lighting
 Jorg s Graphics Lecture Notes 6. Illumination, Lighting 1 6. Illumination, Lighting No ray tracing in OpenGL! ray tracing: direct paths COP interreflection: soft shadows, color bleeding. umbra, penumbra,
Jorg s Graphics Lecture Notes 6. Illumination, Lighting 1 6. Illumination, Lighting No ray tracing in OpenGL! ray tracing: direct paths COP interreflection: soft shadows, color bleeding. umbra, penumbra,
CS 130 Final. Fall 2015
 CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
Global Illumination. CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 Global Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Reading Foley, van Dam (better): Chapter 16.7-13 Angel: Chapter 5.11, 11.1-11.5 2 Limitation of local illumination A concrete
Global Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Reading Foley, van Dam (better): Chapter 16.7-13 Angel: Chapter 5.11, 11.1-11.5 2 Limitation of local illumination A concrete
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods. Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
Lecture 7 - Path Tracing
 INFOMAGR Advanced Graphics Jacco Bikker - November 2016 - February 2017 Lecture 7 - I x, x = g(x, x ) ε x, x + S ρ x, x, x I x, x dx Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Advanced Graphics 3 Introduction
INFOMAGR Advanced Graphics Jacco Bikker - November 2016 - February 2017 Lecture 7 - I x, x = g(x, x ) ε x, x + S ρ x, x, x I x, x dx Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Advanced Graphics 3 Introduction
Schedule. MIT Monte-Carlo Ray Tracing. Radiosity. Review of last week? Limitations of radiosity. Radiosity
 Schedule Review Session: Tuesday November 18 th, 7:30 pm, Room 2-136 bring lots of questions! MIT 6.837 Monte-Carlo Ray Tracing Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (one weeks from today) MIT EECS
Schedule Review Session: Tuesday November 18 th, 7:30 pm, Room 2-136 bring lots of questions! MIT 6.837 Monte-Carlo Ray Tracing Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (one weeks from today) MIT EECS
CS 428: Fall Introduction to. Raytracing. Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, /18/2009 1
 CS 428: Fall 2009 Introduction to Computer Graphics Raytracing 11/18/2009 1 Forward ray tracing From the light sources Simulate light transport one ray at a time Rays start from lights + bounce around
CS 428: Fall 2009 Introduction to Computer Graphics Raytracing 11/18/2009 1 Forward ray tracing From the light sources Simulate light transport one ray at a time Rays start from lights + bounce around
Other Rendering Techniques CSE 872 Fall Intro You have seen Scanline converter (+z-buffer) Painter s algorithm Radiosity CSE 872 Fall
 Other Rendering Techniques 1 Intro You have seen Scanline converter (+z-buffer) Painter s algorithm Radiosity 2 Intro Some more Raytracing Light maps Photon-map Reyes Shadow maps Sahdow volumes PRT BSSRF
Other Rendering Techniques 1 Intro You have seen Scanline converter (+z-buffer) Painter s algorithm Radiosity 2 Intro Some more Raytracing Light maps Photon-map Reyes Shadow maps Sahdow volumes PRT BSSRF
Computer Graphics. Lecture 13. Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity. Taku Komura
 Computer Graphics Lecture 13 Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity Taku Komura 1 Rendering techniques Can be classified as Local Illumination techniques Global Illumination techniques Local
Computer Graphics Lecture 13 Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity Taku Komura 1 Rendering techniques Can be classified as Local Illumination techniques Global Illumination techniques Local
Other approaches to obtaining 3D structure
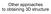 Other approaches to obtaining 3D structure Active stereo with structured light Project structured light patterns onto the object simplifies the correspondence problem Allows us to use only one camera camera
Other approaches to obtaining 3D structure Active stereo with structured light Project structured light patterns onto the object simplifies the correspondence problem Allows us to use only one camera camera
Global Illumination. Global Illumination. Direct Illumination vs. Global Illumination. Indirect Illumination. Soft Shadows.
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Angel Ch. 11] 1 Global Illumination
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Angel Ch. 11] 1 Global Illumination
A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere
 Spring Conference on Computer Graphics 00 A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere Jaroslav Sloup Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague
Spring Conference on Computer Graphics 00 A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere Jaroslav Sloup Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague
Computer Graphics. Lecture 10. Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity. Taku Komura 12/03/15
 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity Taku Komura 1 Rendering techniques Can be classified as Local Illumination techniques Global Illumination techniques Local
Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity Taku Komura 1 Rendering techniques Can be classified as Local Illumination techniques Global Illumination techniques Local
Radiance. Radiance properties. Radiance properties. Computer Graphics (Fall 2008)
 Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 19: Illumination and Shading 2 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 Radiance Power per unit projected area perpendicular to the ray per unit solid angle in
Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 19: Illumination and Shading 2 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 Radiance Power per unit projected area perpendicular to the ray per unit solid angle in
Lighting and Shading Computer Graphics I Lecture 7. Light Sources Phong Illumination Model Normal Vectors [Angel, Ch
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 7 Lighting and Shading February 12, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/ Light Sources Phong Illumination Model
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 7 Lighting and Shading February 12, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/ Light Sources Phong Illumination Model
INFOGR Computer Graphics. J. Bikker - April-July Lecture 10: Shading Models. Welcome!
 INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2016 - Lecture 10: Shading Models Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Light Transport Materials Sensors Shading INFOGR Lecture 10 Shading Models 3 Introduction
INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2016 - Lecture 10: Shading Models Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Light Transport Materials Sensors Shading INFOGR Lecture 10 Shading Models 3 Introduction
Spring 2012 Final. CS184 - Foundations of Computer Graphics. University of California at Berkeley
 Spring 2012 Final CS184 - Foundations of Computer Graphics University of California at Berkeley Write your name HERE: Write your login HERE: Closed book. You may not use any notes or printed/electronic
Spring 2012 Final CS184 - Foundations of Computer Graphics University of California at Berkeley Write your name HERE: Write your login HERE: Closed book. You may not use any notes or printed/electronic
Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization
 Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization GPU Volume Raycasting Christof Rezk-Salama University of Siegen, Germany Volume Rendering in a Nutshell Image Plane Eye Data Set Back-to-front iteration
Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization GPU Volume Raycasting Christof Rezk-Salama University of Siegen, Germany Volume Rendering in a Nutshell Image Plane Eye Data Set Back-to-front iteration
Topic 12: Texture Mapping. Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping
 Topic 12: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Topic 12: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Volume Illumination. Visualisation Lecture 11. Taku Komura. Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics
 Volume Illumination Visualisation Lecture 11 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Volume Illumination & Vector Vis. 1 Previously : Volume Rendering
Volume Illumination Visualisation Lecture 11 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Volume Illumination & Vector Vis. 1 Previously : Volume Rendering
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing. Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19
 Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
The Rendering Equation and Path Tracing
 The Rendering Equation and Path Tracing Louis Feng April 22, 2004 April 21, 2004 Realistic Image Synthesis (Spring 2004) 1 Topics The rendering equation Original form Meaning of the terms Integration Path
The Rendering Equation and Path Tracing Louis Feng April 22, 2004 April 21, 2004 Realistic Image Synthesis (Spring 2004) 1 Topics The rendering equation Original form Meaning of the terms Integration Path
Recall: Basic Ray Tracer
 1 Recall: Ray Tracing Generate an image by backwards tracing the path of light through pixels on an image plane Simulate the interaction of light with objects Recall: Basic Ray Tracer Trace a primary ray
1 Recall: Ray Tracing Generate an image by backwards tracing the path of light through pixels on an image plane Simulate the interaction of light with objects Recall: Basic Ray Tracer Trace a primary ray
Computer Graphics and GPGPU Programming
 Computer Graphics and GPGPU Programming Donato D Ambrosio Department of Mathematics and Computer Science and Center of Excellence for High Performace Computing Cubo 22B, University of Calabria, Rende 87036,
Computer Graphics and GPGPU Programming Donato D Ambrosio Department of Mathematics and Computer Science and Center of Excellence for High Performace Computing Cubo 22B, University of Calabria, Rende 87036,
Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics DH2320, Fall 2015 Prof. Dr. Tino Weinkauf Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics Visibility Shading 3D Rendering Geometric Model Color Perspective
Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics DH2320, Fall 2015 Prof. Dr. Tino Weinkauf Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics Visibility Shading 3D Rendering Geometric Model Color Perspective
Illumination. Courtesy of Adam Finkelstein, Princeton University
 llumination Courtesy of Adam Finkelstein, Princeton University Ray Casting mage RayCast(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int height) { mage image = new mage(width, height); for (int i = 0; i < width;
llumination Courtesy of Adam Finkelstein, Princeton University Ray Casting mage RayCast(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int height) { mage image = new mage(width, height); for (int i = 0; i < width;
Topic 11: Texture Mapping 11/13/2017. Texture sources: Solid textures. Texture sources: Synthesized
 Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Computer Vision Systems. Viewing Systems Projections Illuminations Rendering Culling and Clipping Implementations
 Computer Vision Systems Viewing Systems Projections Illuminations Rendering Culling and Clipping Implementations Viewing Systems Viewing Transformation Projective Transformation 2D Computer Graphics Devices
Computer Vision Systems Viewing Systems Projections Illuminations Rendering Culling and Clipping Implementations Viewing Systems Viewing Transformation Projective Transformation 2D Computer Graphics Devices
Raytracing CS148 AS3. Due :59pm PDT
 Raytracing CS148 AS3 Due 2010-07-25 11:59pm PDT We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description of scene into an image. We will do this by building
Raytracing CS148 AS3 Due 2010-07-25 11:59pm PDT We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description of scene into an image. We will do this by building
- Volume Rendering -
 Computer Graphics - Volume Rendering - Pascal Grittmann, Jaroslav Křivánek Using pictures from: Monte Carlo Methods for Physically Based Volume Rendering; SIGGRAPH 2018 Course; Jan Novák, Iliyan Georgiev,
Computer Graphics - Volume Rendering - Pascal Grittmann, Jaroslav Křivánek Using pictures from: Monte Carlo Methods for Physically Based Volume Rendering; SIGGRAPH 2018 Course; Jan Novák, Iliyan Georgiev,
Soft shadows. Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February
 Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Lighting and Shading
 Lighting and Shading Today: Local Illumination Solving the rendering equation is too expensive First do local illumination Then hack in reflections and shadows Local Shading: Notation light intensity in,
Lighting and Shading Today: Local Illumination Solving the rendering equation is too expensive First do local illumination Then hack in reflections and shadows Local Shading: Notation light intensity in,
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
CS-184: Computer Graphics. Today. Lecture 22: Radiometry! James O Brien University of California, Berkeley! V2014-S
 CS-184: Computer Graphics Lecture 22: Radiometry James O Brien University of California, Berkeley V2014-S-15-1.0 Today Radiometry: measuring light Local Illumination and Raytracing were discussed in an
CS-184: Computer Graphics Lecture 22: Radiometry James O Brien University of California, Berkeley V2014-S-15-1.0 Today Radiometry: measuring light Local Illumination and Raytracing were discussed in an
Topic 11: Texture Mapping 10/21/2015. Photographs. Solid textures. Procedural
 Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Topic 11: Photographs Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates
Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Topic 11: Photographs Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates
INFOGR Computer Graphics. J. Bikker - April-July Lecture 10: Ground Truth. Welcome!
 INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2015 - Lecture 10: Ground Truth Welcome! Today s Agenda: Limitations of Whitted-style Ray Tracing Monte Carlo Path Tracing INFOGR Lecture 10 Ground Truth
INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2015 - Lecture 10: Ground Truth Welcome! Today s Agenda: Limitations of Whitted-style Ray Tracing Monte Carlo Path Tracing INFOGR Lecture 10 Ground Truth
Today s class. Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL. Informationsteknologi. Wednesday, November 21, 2007 Computer Graphics - Class 10 1
 Today s class Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL Wednesday, November 21, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 1 1 Simple shadows Simple shadows can be gotten by using projection matrices Consider a light
Today s class Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL Wednesday, November 21, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 1 1 Simple shadows Simple shadows can be gotten by using projection matrices Consider a light
RASTERISED RENDERING
 DH2323 DGI16 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND INTERACTION RASTERISED RENDERING Christopher Peters HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se http://kth.academia.edu/christopheredwardpeters
DH2323 DGI16 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND INTERACTION RASTERISED RENDERING Christopher Peters HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se http://kth.academia.edu/christopheredwardpeters
Overview. Radiometry and Photometry. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lecture 21: Radiometry http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Overview Lighting and shading key in computer graphics HW 2 etc. ad-hoc shading models,
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lecture 21: Radiometry http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Overview Lighting and shading key in computer graphics HW 2 etc. ad-hoc shading models,
Announcements. Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) Computer Graphics
 Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Reflection and Shading
 Reflection and Shading R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 10/19/2015 Light Sources Realistic rendering requires that we model the interaction between light
Reflection and Shading R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 10/19/2015 Light Sources Realistic rendering requires that we model the interaction between light
BRDF Computer Graphics (Spring 2008)
 BRDF Computer Graphics (Spring 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 20: Illumination and Shading 2 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 Reflected Radiance proportional to Irradiance Constant proportionality: BRDF [CW
BRDF Computer Graphics (Spring 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 20: Illumination and Shading 2 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 Reflected Radiance proportional to Irradiance Constant proportionality: BRDF [CW
The Traditional Graphics Pipeline
 Last Time? The Traditional Graphics Pipeline Participating Media Measuring BRDFs 3D Digitizing & Scattering BSSRDFs Monte Carlo Simulation Dipole Approximation Today Ray Casting / Tracing Advantages? Ray
Last Time? The Traditional Graphics Pipeline Participating Media Measuring BRDFs 3D Digitizing & Scattering BSSRDFs Monte Carlo Simulation Dipole Approximation Today Ray Casting / Tracing Advantages? Ray
CS 488. More Shading and Illumination. Luc RENAMBOT
 CS 488 More Shading and Illumination Luc RENAMBOT 1 Illumination No Lighting Ambient model Light sources Diffuse reflection Specular reflection Model: ambient + specular + diffuse Shading: flat, gouraud,
CS 488 More Shading and Illumination Luc RENAMBOT 1 Illumination No Lighting Ambient model Light sources Diffuse reflection Specular reflection Model: ambient + specular + diffuse Shading: flat, gouraud,
Lighting and Reflectance COS 426
 ighting and Reflectance COS 426 Ray Casting R2mage *RayCast(R3Scene *scene, int width, int height) { R2mage *image = new R2mage(width, height); for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < height;
ighting and Reflectance COS 426 Ray Casting R2mage *RayCast(R3Scene *scene, int width, int height) { R2mage *image = new R2mage(width, height); for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < height;
Capturing light. Source: A. Efros
 Capturing light Source: A. Efros Review Pinhole projection models What are vanishing points and vanishing lines? What is orthographic projection? How can we approximate orthographic projection? Lenses
Capturing light Source: A. Efros Review Pinhole projection models What are vanishing points and vanishing lines? What is orthographic projection? How can we approximate orthographic projection? Lenses
Today. Participating media. Participating media. Rendering Algorithms: Participating Media and. Subsurface scattering
 Today Rendering Algorithms: Participating Media and Subsurface Scattering Introduction Rendering participating media Rendering subsurface scattering Spring 2009 Matthias Zwicker Participating media Participating
Today Rendering Algorithms: Participating Media and Subsurface Scattering Introduction Rendering participating media Rendering subsurface scattering Spring 2009 Matthias Zwicker Participating media Participating
lecture 19 Shadows - ray tracing - shadow mapping - ambient occlusion Interreflections
 lecture 19 Shadows - ray tracing - shadow mapping - ambient occlusion Interreflections In cinema and photography, shadows are important for setting mood and directing attention. Shadows indicate spatial
lecture 19 Shadows - ray tracing - shadow mapping - ambient occlusion Interreflections In cinema and photography, shadows are important for setting mood and directing attention. Shadows indicate spatial
CPSC GLOBAL ILLUMINATION
 CPSC 314 21 GLOBAL ILLUMINATION Textbook: 20 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Mikhail Bessmeltsev ILLUMINATION MODELS/ALGORITHMS Local illumination - Fast Ignore real physics, approximate the look Interaction of
CPSC 314 21 GLOBAL ILLUMINATION Textbook: 20 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Mikhail Bessmeltsev ILLUMINATION MODELS/ALGORITHMS Local illumination - Fast Ignore real physics, approximate the look Interaction of
Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018
 Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Theoretical foundations Ray Tracing from the Ground Up Chapters 13-15 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF
Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Theoretical foundations Ray Tracing from the Ground Up Chapters 13-15 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF
Global Illumination and the Rendering Equation
 CS294-13: Special Topics Lecture #3 Advanced Computer Graphics University of California, Berkeley Handout Date??? Global Illumination and the Rendering Equation Lecture #3: Wednesday, 9 September 2009
CS294-13: Special Topics Lecture #3 Advanced Computer Graphics University of California, Berkeley Handout Date??? Global Illumination and the Rendering Equation Lecture #3: Wednesday, 9 September 2009
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting)! Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness! The illumination can be computed either at vertices or
Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting)! Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness! The illumination can be computed either at vertices or
Movie: For The Birds. Announcements. Ray Tracing 1. Programming 2 Recap. Programming 3 Info Test data for part 1 (Lines) is available
 Now Playing: Movie: For The Birds Pixar, 2000 Liar Built To Spill from You In Reverse Released April 11, 2006 Ray Tracing 1 Rick Skarbez, Instructor COMP 575 November 1, 2007 Announcements Programming
Now Playing: Movie: For The Birds Pixar, 2000 Liar Built To Spill from You In Reverse Released April 11, 2006 Ray Tracing 1 Rick Skarbez, Instructor COMP 575 November 1, 2007 Announcements Programming
RASTERIZING POLYGONS IN IMAGE SPACE
 On-Line Computer Graphics Notes RASTERIZING POLYGONS IN IMAGE SPACE Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis A fundamental
On-Line Computer Graphics Notes RASTERIZING POLYGONS IN IMAGE SPACE Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis A fundamental
Precomputed Radiance Transfer: Theory and Practice
 1 Precomputed Radiance Transfer: Peter-Pike Sloan Microsoft Jaakko Lehtinen Helsinki Univ. of Techn. & Remedy Entertainment Jan Kautz MIT 2 Introduction Jan Kautz MIT 3 Introduction We see here an example
1 Precomputed Radiance Transfer: Peter-Pike Sloan Microsoft Jaakko Lehtinen Helsinki Univ. of Techn. & Remedy Entertainment Jan Kautz MIT 2 Introduction Jan Kautz MIT 3 Introduction We see here an example
The Light Field. Last lecture: Radiometry and photometry
 The Light Field Last lecture: Radiometry and photometry This lecture: Light field = radiance function on rays Conservation of radiance Measurement equation Throughput and counting rays Irradiance calculations
The Light Field Last lecture: Radiometry and photometry This lecture: Light field = radiance function on rays Conservation of radiance Measurement equation Throughput and counting rays Irradiance calculations
Ambien Occlusion. Lighting: Ambient Light Sources. Lighting: Ambient Light Sources. Summary
 Summary Ambien Occlusion Kadi Bouatouch IRISA Email: kadi@irisa.fr 1. Lighting 2. Definition 3. Computing the ambient occlusion 4. Ambient occlusion fields 5. Dynamic ambient occlusion 1 2 Lighting: Ambient
Summary Ambien Occlusion Kadi Bouatouch IRISA Email: kadi@irisa.fr 1. Lighting 2. Definition 3. Computing the ambient occlusion 4. Ambient occlusion fields 5. Dynamic ambient occlusion 1 2 Lighting: Ambient
- Volume Rendering -
 Computer Graphics - Volume Rendering - Pascal Grittmann Using pictures from: Monte Carlo Methods for Physically Based Volume Rendering; SIGGRAPH 2018 Course; Jan Novák, Iliyan Georgiev, Johannes Hanika,
Computer Graphics - Volume Rendering - Pascal Grittmann Using pictures from: Monte Carlo Methods for Physically Based Volume Rendering; SIGGRAPH 2018 Course; Jan Novák, Iliyan Georgiev, Johannes Hanika,
Photorealism vs. Non-Photorealism in Computer Graphics
 The Art and Science of Depiction Photorealism vs. Non-Photorealism in Computer Graphics Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Global illumination How to take into account all light inter-reflections
The Art and Science of Depiction Photorealism vs. Non-Photorealism in Computer Graphics Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Global illumination How to take into account all light inter-reflections
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting & shading? Sphere
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting & shading? Sphere
Graphics for VEs. Ruth Aylett
 Graphics for VEs Ruth Aylett Overview VE Software Graphics for VEs The graphics pipeline Projections Lighting Shading VR software Two main types of software used: off-line authoring or modelling packages
Graphics for VEs Ruth Aylett Overview VE Software Graphics for VEs The graphics pipeline Projections Lighting Shading VR software Two main types of software used: off-line authoring or modelling packages
Lighting. To do. Course Outline. This Lecture. Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project
 To do Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project Lighting Course Outline 3D Graphics Pipeline Modeling (Creating 3D Geometry) Mesh; modeling; sampling; Interaction
To do Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project Lighting Course Outline 3D Graphics Pipeline Modeling (Creating 3D Geometry) Mesh; modeling; sampling; Interaction
13 Distribution Ray Tracing
 13 In (hereafter abbreviated as DRT ), our goal is to render a scene as accurately as possible. Whereas Basic Ray Tracing computed a very crude approximation to radiance at a point, in DRT we will attempt
13 In (hereafter abbreviated as DRT ), our goal is to render a scene as accurately as possible. Whereas Basic Ray Tracing computed a very crude approximation to radiance at a point, in DRT we will attempt
Distributed Ray Tracing
 CT5510: Computer Graphics Distributed Ray Tracing BOCHANG MOON Distributed Ray Tracing Motivation The classical ray tracing produces very clean images (look fake) Perfect focus Perfect reflections Sharp
CT5510: Computer Graphics Distributed Ray Tracing BOCHANG MOON Distributed Ray Tracing Motivation The classical ray tracing produces very clean images (look fake) Perfect focus Perfect reflections Sharp
Supplement to Lecture 16
 Supplement to Lecture 16 Global Illumination: View Dependent CS 354 Computer Graphics http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~bajaj/ Notes and figures from Ed Angel: Interactive Computer Graphics, 6 th Ed., 2012 Addison
Supplement to Lecture 16 Global Illumination: View Dependent CS 354 Computer Graphics http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~bajaj/ Notes and figures from Ed Angel: Interactive Computer Graphics, 6 th Ed., 2012 Addison
Ray Tracing Part 1. CSC418/2504 Introduction to Computer Graphics. TA: Muhammed Anwar & Kevin Gibson
 Ray Tracing Part 1 CSC418/2504 Introduction to Computer Graphics TA: Muhammed Anwar & Kevin Gibson Email: manwar@cs.toronto.edu Overview Introduction / Motivation Rasterization vs Ray Tracing Basic Pseudocode
Ray Tracing Part 1 CSC418/2504 Introduction to Computer Graphics TA: Muhammed Anwar & Kevin Gibson Email: manwar@cs.toronto.edu Overview Introduction / Motivation Rasterization vs Ray Tracing Basic Pseudocode
CS 5625 Lec 2: Shading Models
 CS 5625 Lec 2: Shading Models Kavita Bala Spring 2013 Shading Models Chapter 7 Next few weeks Textures Graphics Pipeline Light Emission To compute images What are the light sources? Light Propagation Fog/Clear?
CS 5625 Lec 2: Shading Models Kavita Bala Spring 2013 Shading Models Chapter 7 Next few weeks Textures Graphics Pipeline Light Emission To compute images What are the light sources? Light Propagation Fog/Clear?
Introduction Rasterization Z-buffering Shading. Graphics 2012/2013, 4th quarter. Lecture 09: graphics pipeline (rasterization and shading)
 Lecture 9 Graphics pipeline (rasterization and shading) Graphics pipeline - part 1 (recap) Perspective projection by matrix multiplication: x pixel y pixel z canonical 1 x = M vpm per M cam y z 1 This
Lecture 9 Graphics pipeline (rasterization and shading) Graphics pipeline - part 1 (recap) Perspective projection by matrix multiplication: x pixel y pixel z canonical 1 x = M vpm per M cam y z 1 This
Lecture 10: Ray tracing
 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 10: Ray tracing Graphics Lecture 10: Slide 1 Some slides adopted from H. Pfister, Harvard Graphics Lecture 10: Slide 2 Direct and Global Illumination Direct illumination:
Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 10: Ray tracing Graphics Lecture 10: Slide 1 Some slides adopted from H. Pfister, Harvard Graphics Lecture 10: Slide 2 Direct and Global Illumination Direct illumination:
The Traditional Graphics Pipeline
 Final Projects Proposals due Thursday 4/8 Proposed project summary At least 3 related papers (read & summarized) Description of series of test cases Timeline & initial task assignment The Traditional Graphics
Final Projects Proposals due Thursday 4/8 Proposed project summary At least 3 related papers (read & summarized) Description of series of test cases Timeline & initial task assignment The Traditional Graphics
Consider a partially transparent object that is illuminated with two lights, one visible from each side of the object. Start with a ray from the eye
 Ray Tracing What was the rendering equation? Motivate & list the terms. Relate the rendering equation to forward ray tracing. Why is forward ray tracing not good for image formation? What is the difference
Ray Tracing What was the rendering equation? Motivate & list the terms. Relate the rendering equation to forward ray tracing. Why is forward ray tracing not good for image formation? What is the difference
CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3
 ?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 12 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 12 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting
Lecture 11: Ray tracing (cont.)
 Interactive Computer Graphics Ray tracing - Summary Lecture 11: Ray tracing (cont.) Graphics Lecture 10: Slide 1 Some slides adopted from H. Pfister, Harvard Graphics Lecture 10: Slide 2 Ray tracing -
Interactive Computer Graphics Ray tracing - Summary Lecture 11: Ray tracing (cont.) Graphics Lecture 10: Slide 1 Some slides adopted from H. Pfister, Harvard Graphics Lecture 10: Slide 2 Ray tracing -
Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011
 Computer graphics Assignment 4 1 Overview Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer, and a basic ray tracing algorithm.
Computer graphics Assignment 4 1 Overview Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer, and a basic ray tracing algorithm.
Local Illumination. CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 Local Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Graphics Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism
Local Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Graphics Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism
Introduction to Radiosity
 Introduction to Radiosity Produce photorealistic pictures using global illumination Mathematical basis from the theory of heat transfer Enables color bleeding Provides view independent representation Unfortunately,
Introduction to Radiosity Produce photorealistic pictures using global illumination Mathematical basis from the theory of heat transfer Enables color bleeding Provides view independent representation Unfortunately,
Computer Graphics. Ray Tracing. Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College
 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Ray Tracing Example Created by Anto Matkovic Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Most light rays do not reach
Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Ray Tracing Example Created by Anto Matkovic Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Most light rays do not reach
Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm
 CMSC 23700 Autumn 2017 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 November 2, 2017 Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm 1 Summary This assignment uses the same application architecture
CMSC 23700 Autumn 2017 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 November 2, 2017 Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm 1 Summary This assignment uses the same application architecture
The Rendering Equation & Monte Carlo Ray Tracing
 Last Time? Local Illumination & Monte Carlo Ray Tracing BRDF Ideal Diffuse Reflectance Ideal Specular Reflectance The Phong Model Radiosity Equation/Matrix Calculating the Form Factors Aj Ai Reading for
Last Time? Local Illumination & Monte Carlo Ray Tracing BRDF Ideal Diffuse Reflectance Ideal Specular Reflectance The Phong Model Radiosity Equation/Matrix Calculating the Form Factors Aj Ai Reading for
Photometric Stereo. Lighting and Photometric Stereo. Computer Vision I. Last lecture in a nutshell BRDF. CSE252A Lecture 7
 Lighting and Photometric Stereo Photometric Stereo HW will be on web later today CSE5A Lecture 7 Radiometry of thin lenses δa Last lecture in a nutshell δa δa'cosα δacos β δω = = ( z' / cosα ) ( z / cosα
Lighting and Photometric Stereo Photometric Stereo HW will be on web later today CSE5A Lecture 7 Radiometry of thin lenses δa Last lecture in a nutshell δa δa'cosα δacos β δω = = ( z' / cosα ) ( z / cosα
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
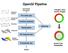 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
Assignment 3: Path tracing
 Assignment 3: Path tracing EDAN30 April 2, 2011 In this assignment you will be asked to extend your ray tracer to support path tracing. In order to pass the assignment you need to complete all tasks. Make
Assignment 3: Path tracing EDAN30 April 2, 2011 In this assignment you will be asked to extend your ray tracer to support path tracing. In order to pass the assignment you need to complete all tasks. Make
CMSC427 Shading Intro. Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
Global Illumination CS334. Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Global Illumination CS334 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Recall: Lighting and Shading Light sources Point light Models an omnidirectional light source (e.g., a bulb)
Global Illumination CS334 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Recall: Lighting and Shading Light sources Point light Models an omnidirectional light source (e.g., a bulb)
Rendering Smoke & Clouds
 Rendering Smoke & Clouds Game Design Seminar 2007 Jürgen Treml Talk Overview 1. Introduction to Clouds 2. Virtual Clouds based on physical Models 1. Generating Clouds 2. Rendering Clouds using Volume Rendering
Rendering Smoke & Clouds Game Design Seminar 2007 Jürgen Treml Talk Overview 1. Introduction to Clouds 2. Virtual Clouds based on physical Models 1. Generating Clouds 2. Rendering Clouds using Volume Rendering
Computer Graphics I Lecture 11
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 11 Midterm Review Assignment 3 Movie Midterm Review Midterm Preview February 26, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 11 Midterm Review Assignment 3 Movie Midterm Review Midterm Preview February 26, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/
Lecture 15: Shading-I. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
