Using Integral Surfaces to Visualize CFD Data
|
|
|
- Nathan Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using Integral Surfaces to Visualize CFD Data Tony Mcloughlin, Matthew Edmunds,, Mark W. Jones, Guoning Chen, Eugene Zhang 1 1
2 Overview Flow Visualization with Integral Surfaces: Introduction to flow visualization Stream, path, and streaklines Integral surface-based flow visualization Advantages of surfaces over curves Stream and path surfaces Stream and path surface demo Streak surface demo Conclusions and Acknowledgments 2 2
3 Flow Visualization: Background direct: overview of vector field, minimal computation, e.g. glyphs, color mapping 3. geometric: a discrete object(s) whose geometry reflects flow characteristics, e.g. streamlines 4. feature-based: both automatic and interactive feature-based techniques, e.g. flow topology texture-based: covers domain with a convolved texture, e.g., Spot Noise, LIC, ISA, IBFV(S) 3 3
4 Stream, Path, and Streaklines Terminology: Streamline: a curve that is everywhere tangent to the flow (release 1 massless particle) Pathline: a curve that is everywhere tangent to an unsteady flow field (release 1 massless particle) Streakline: a curve traced by the continues release of particles in unsteady flow from the same position in space (release infinitely many massless particles) Each is equivalent in steady-state flow 4 4
5 Characteristics of Integral Lines Advantages: Implementation: various easy-toimplement streamline tracing algorithms (integration) Intuitive: interpretation is not difficult Applicability: generally applicable to all vector fields, also in three-dimensions Disadvantages: Perception: too many lines can lead to clutter and visual complexity Perception: depth is difficult to perceive, no well-defined normal vector Seeding: optimal placement is very challenging (unsolved problem) 5 5
6 Stream Surfaces Terminology: Stream surface: a surface that is everywhere tangent to flow Stream surface: the union of stream lines seeded at all points of a curve (the seed curve) Next higher dimensional equivalent to a streamline Unsteady flow can be visualized with a path surface or streak surface 6 6
7 Stream Surfaces: Advantages Motivation: Separates (steady) flow: flow cannot cross surface (stream surfaces only) Perception: Less visual clutter and complexity than many lines/curves Perception: well-defined normal vectors make shading easy, improving depth perception Rendering: surfaces provide more rendering options than lines: e.g., shading and texturemapping etc. Disadvantages: Construction/Implementation: more complicated algorithms are required to construct integral surfaces Occlusion: multiple surfaces hide one another Placement: placement of surfaces is still and unsolved problem 7 7
8 Easy Integral Surfaces Relies on use of quad primitives Use of local operations (per quad). Simple data structure Implicit parameterization Formulated as a reconstructive sampling of the vector field d_sample d_advance d_sep 8 8
9 Algorithm Overview Seed; While(not terminated) Advance front; Update Sampling Rate; End While Render; 9 9 9
10 Seeding and Advancement Interactive seeding curve: Position and orientation Length Prongs/number of seeds Integral surface front advance distance guided by Nyquist rate 0.5 d_sample
11 Stream and Path Surface Results: Video(s) 11 11
12 Constructing Streak Surfaces in 3D Unsteady Vector Fields Tony McLoughlin, and Eugene Zhang 12 12
13 3D, Unsteady Flow Discrete locations in 3D space 4-tuple (4D vector) for each sample x-, y-, z-, t- components Direction Magnitude Velocity field when describing the motion of a fluid Obtained from CFD simulations or constructed from empirical data Unsteady vector fields vary over time 13 13
14 Streak Surface: Terminology Terminology Streaklines: curved formed by joining all particles passing through same point in space (at different times) Strong relation to smoke/dye injection from experimental flow visualization. Streak surfaces are an extension of streak lines (next higher dimension) 14 14
15 Streak Surface Construction Challenges Challenges: Computational cost: surface advection is very expensive Mesh quality and maintaining an adequate sampling of the field. Divergence Convergence Shear Objects in domain and critical points Large size of time-dependent (unsteady) vector field data, out-of-core techniques Surface completely dynamic: entire surface (all vertices) advect at each time-step 15 15
16 Streaksurface Properties Properties: Surface constructed using quad primitives (as opposed to triangles) Local operations for surface refinement performed on a quad-by-quad basis No global optimization required Allows the construction of large surfaces CPU-based for easier implementation Fills the gap between methods of Burger et al. [2009] and Krishnan et al. [2009] Not as fast as GPU but interactive Fewer constraints than GPU implementation does not need to fit into GPU memory 16 16
17 Streak Surface Algorithm Do: Position seed with interactive rake Iteratively construct surface: Advect surface Refine Surface Test for boundary conditions Update Test for termination criteria Final rendering 17 17
18 Streak Surface Results: Video 18 18
19 Summary and Conclusions We claim surfaces offer advantages over traditional curves when visualizing 3D and 4D flow We present interactive algorithms for construction of stream, path and streak surfaces Algorithms are based on local operations performed on quads for mesh refinement Technique handles divergence, convergence and shear flow Splitting of surface to adapt to flow around object boundaries Demonstrated on a variety of data sets 19 19
20 Acknowledgements Thank you for your attention! Any questions? We thank the following for material used here: Tony McLoughlin This work was partially funded by EPSRC Grant EP/F002335/
Flow Visualization with Integral Surfaces
 Flow Visualization with Integral Surfaces Visual and Interactive Computing Group Department of Computer Science Swansea University R.S.Laramee@swansea.ac.uk 1 1 Overview Flow Visualization with Integral
Flow Visualization with Integral Surfaces Visual and Interactive Computing Group Department of Computer Science Swansea University R.S.Laramee@swansea.ac.uk 1 1 Overview Flow Visualization with Integral
Over Two Decades of IntegrationBased, Geometric Vector Field. Visualization
 Over Two Decades of IntegrationBased, Geometric Vector Field Visualization Tony McLoughlin1, 1, Ronald Peikert2, Frits H. Post3, and Min Chen1 1 The Visual and Interactive Computing Group Computer Science
Over Two Decades of IntegrationBased, Geometric Vector Field Visualization Tony McLoughlin1, 1, Ronald Peikert2, Frits H. Post3, and Min Chen1 1 The Visual and Interactive Computing Group Computer Science
Vector Field Visualisation
 Vector Field Visualisation Computer Animation and Visualization Lecture 14 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Visualising Vectors Examples of vector data: meteorological
Vector Field Visualisation Computer Animation and Visualization Lecture 14 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Visualising Vectors Examples of vector data: meteorological
Flow Visualization: The State-of-the-Art
 Flow Visualization: The State-of-the-Art The Visual and Interactive Computing Group Computer Science Department Swansea University Swansea, Wales, UK 1 Overview Introduction to Flow Visualization (FlowViz)
Flow Visualization: The State-of-the-Art The Visual and Interactive Computing Group Computer Science Department Swansea University Swansea, Wales, UK 1 Overview Introduction to Flow Visualization (FlowViz)
Vector Visualisation 1. global view
 Vector Field Visualisation : global view Visualisation Lecture 12 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Vector Visualisation 1 Vector Field Visualisation : local & global Vector
Vector Field Visualisation : global view Visualisation Lecture 12 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Vector Visualisation 1 Vector Field Visualisation : local & global Vector
Flow Visualisation 1
 Flow Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 13 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Flow Visualisation 1 Flow Visualisation... so far Vector Field Visualisation vector fields
Flow Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 13 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Flow Visualisation 1 Flow Visualisation... so far Vector Field Visualisation vector fields
Texture Advection. Ronald Peikert SciVis Texture Advection 6-1
 Texture Advection Ronald Peikert SciVis 2007 - Texture Advection 6-1 Texture advection Motivation: dense visualization of vector fields, no seed points needed. Methods for static fields: LIC - Line integral
Texture Advection Ronald Peikert SciVis 2007 - Texture Advection 6-1 Texture advection Motivation: dense visualization of vector fields, no seed points needed. Methods for static fields: LIC - Line integral
Vector Field Visualization: Introduction
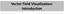 Vector Field Visualization: Introduction What is a Vector Field? A simple 2D steady vector field A vector valued function that assigns a vector (with direction and magnitude) to any given point. It typically
Vector Field Visualization: Introduction What is a Vector Field? A simple 2D steady vector field A vector valued function that assigns a vector (with direction and magnitude) to any given point. It typically
Data Visualization. Fall 2017
 Data Visualization Fall 2017 Vector Fields Vector field v: D R n D is typically 2D planar surface or 2D surface embedded in 3D n = 2 fields tangent to 2D surface n = 3 volumetric fields When visualizing
Data Visualization Fall 2017 Vector Fields Vector field v: D R n D is typically 2D planar surface or 2D surface embedded in 3D n = 2 fields tangent to 2D surface n = 3 volumetric fields When visualizing
Vector Field Visualization: Introduction
 Vector Field Visualization: Introduction What is a Vector Field? Why It is Important? Vector Fields in Engineering and Science Automotive design [Chen et al. TVCG07,TVCG08] Weather study [Bhatia and Chen
Vector Field Visualization: Introduction What is a Vector Field? Why It is Important? Vector Fields in Engineering and Science Automotive design [Chen et al. TVCG07,TVCG08] Weather study [Bhatia and Chen
Vector Visualization. CSC 7443: Scientific Information Visualization
 Vector Visualization Vector data A vector is an object with direction and length v = (v x,v y,v z ) A vector field is a field which associates a vector with each point in space The vector data is 3D representation
Vector Visualization Vector data A vector is an object with direction and length v = (v x,v y,v z ) A vector field is a field which associates a vector with each point in space The vector data is 3D representation
Chapter 6 Visualization Techniques for Vector Fields
 Chapter 6 Visualization Techniques for Vector Fields 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Vector Glyphs 6.3 Particle Advection 6.4 Streamlines 6.5 Line Integral Convolution 6.6 Vector Topology 6.7 References 2006 Burkhard
Chapter 6 Visualization Techniques for Vector Fields 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Vector Glyphs 6.3 Particle Advection 6.4 Streamlines 6.5 Line Integral Convolution 6.6 Vector Topology 6.7 References 2006 Burkhard
Lecture overview. Visualisatie BMT. Vector algorithms. Vector algorithms. Time animation. Time animation
 Visualisatie BMT Lecture overview Vector algorithms Tensor algorithms Modeling algorithms Algorithms - 2 Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 2 Vector algorithms Vector 2 or 3 dimensional representation of direction
Visualisatie BMT Lecture overview Vector algorithms Tensor algorithms Modeling algorithms Algorithms - 2 Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 2 Vector algorithms Vector 2 or 3 dimensional representation of direction
Vector Visualization
 Vector Visualization Vector Visulization Divergence and Vorticity Vector Glyphs Vector Color Coding Displacement Plots Stream Objects Texture-Based Vector Visualization Simplified Representation of Vector
Vector Visualization Vector Visulization Divergence and Vorticity Vector Glyphs Vector Color Coding Displacement Plots Stream Objects Texture-Based Vector Visualization Simplified Representation of Vector
The State of the Art in Flow Visualization: Dense and Texture-Based Techniques
 Volume 22 (2003), Number 2, yet unknown pages The State of the Art in Flow Visualization: Dense and Texture-Based Techniques Robert S. Laramee, 1 Helwig Hauser, 1 Helmut Doleisch, 1 Benjamin Vrolijk, 2
Volume 22 (2003), Number 2, yet unknown pages The State of the Art in Flow Visualization: Dense and Texture-Based Techniques Robert S. Laramee, 1 Helwig Hauser, 1 Helmut Doleisch, 1 Benjamin Vrolijk, 2
Flow Visualisation - Background. CITS4241 Visualisation Lectures 20 and 21
 CITS4241 Visualisation Lectures 20 and 21 Flow Visualisation Flow visualisation is important in both science and engineering From a "theoretical" study of o turbulence or o a fusion reactor plasma, to
CITS4241 Visualisation Lectures 20 and 21 Flow Visualisation Flow visualisation is important in both science and engineering From a "theoretical" study of o turbulence or o a fusion reactor plasma, to
1. Interpreting the Results: Visualization 1
 1. Interpreting the Results: Visualization 1 visual/graphical/optical representation of large sets of data: data from experiments or measurements: satellite images, tomography in medicine, microsopy,...
1. Interpreting the Results: Visualization 1 visual/graphical/optical representation of large sets of data: data from experiments or measurements: satellite images, tomography in medicine, microsopy,...
The State of the Art in Flow Visualization: Dense and Texture-Based Techniques
 Volume 23 (2004), number 2 pp. 203 221 COMPUTER GRAPHICS forum The State of the Art in Flow Visualization: Dense and Texture-Based Techniques Robert S. Laramee, 1 Helwig Hauser, 1 Helmut Doleisch, 1 Benjamin
Volume 23 (2004), number 2 pp. 203 221 COMPUTER GRAPHICS forum The State of the Art in Flow Visualization: Dense and Texture-Based Techniques Robert S. Laramee, 1 Helwig Hauser, 1 Helmut Doleisch, 1 Benjamin
3D vector fields. Contents. Introduction 3D vector field topology Representation of particle lines. 3D LIC Combining different techniques
 3D vector fields Scientific Visualization (Part 9) PD Dr.-Ing. Peter Hastreiter Contents Introduction 3D vector field topology Representation of particle lines Path lines Ribbons Balls Tubes Stream tetrahedra
3D vector fields Scientific Visualization (Part 9) PD Dr.-Ing. Peter Hastreiter Contents Introduction 3D vector field topology Representation of particle lines Path lines Ribbons Balls Tubes Stream tetrahedra
A Broad Overview of Scientific Visualization with a Focus on Geophysical Turbulence Simulation Data (SciVis
 A Broad Overview of Scientific Visualization with a Focus on Geophysical Turbulence Simulation Data (SciVis 101 for Turbulence Researchers) John Clyne clyne@ucar.edu Examples: Medicine Examples: Biology
A Broad Overview of Scientific Visualization with a Focus on Geophysical Turbulence Simulation Data (SciVis 101 for Turbulence Researchers) John Clyne clyne@ucar.edu Examples: Medicine Examples: Biology
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich
 Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich 1 Computational Fluid dynamics Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the analysis of systems involving fluid flow, heat
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich 1 Computational Fluid dynamics Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the analysis of systems involving fluid flow, heat
Data Visualization (CIS/DSC 468)
 Data Visualization (CIS/DSC 468) Vector Visualization Dr. David Koop Visualizing Volume (3D) Data 2D visualization slice images (or multi-planar reformating MPR) Indirect 3D visualization isosurfaces (or
Data Visualization (CIS/DSC 468) Vector Visualization Dr. David Koop Visualizing Volume (3D) Data 2D visualization slice images (or multi-planar reformating MPR) Indirect 3D visualization isosurfaces (or
1 Mathematical Concepts
 1 Mathematical Concepts Mathematics is the language of geophysical fluid dynamics. Thus, in order to interpret and communicate the motions of the atmosphere and oceans. While a thorough discussion of the
1 Mathematical Concepts Mathematics is the language of geophysical fluid dynamics. Thus, in order to interpret and communicate the motions of the atmosphere and oceans. While a thorough discussion of the
Volume Illumination & Vector Field Visualisation
 Volume Illumination & Vector Field Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 11 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Volume Illumination & Vector Vis. 1 Previously : Volume Rendering
Volume Illumination & Vector Field Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 11 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Volume Illumination & Vector Vis. 1 Previously : Volume Rendering
mjb March 9, 2015 Chuck Evans
 Vector Visualization What is a Vector Visualization Problem? A vector has direction and magnitude. Typically science and engineering problems that work this way are those involving fluid flow through a
Vector Visualization What is a Vector Visualization Problem? A vector has direction and magnitude. Typically science and engineering problems that work this way are those involving fluid flow through a
CFD Project Workflow Guide
 CFD Project Workflow Guide Contents Select a problem with known results for proof-of-concept testing... 1 Set up and run a coarse test case... 2 Select and calibrate numerical methods... 3 Minimize & quantify
CFD Project Workflow Guide Contents Select a problem with known results for proof-of-concept testing... 1 Set up and run a coarse test case... 2 Select and calibrate numerical methods... 3 Minimize & quantify
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 5: Fluid Kinematics Spring Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
 MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 5: Fluid Kinematics Spring 2003 Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Outline Introduction Velocity Field Acceleration Field Control Volume and System Representation
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 5: Fluid Kinematics Spring 2003 Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Outline Introduction Velocity Field Acceleration Field Control Volume and System Representation
Part I: Theoretical Background and Integration-Based Methods
 Large Vector Field Visualization: Theory and Practice Part I: Theoretical Background and Integration-Based Methods Christoph Garth Overview Foundations Time-Varying Vector Fields Numerical Integration
Large Vector Field Visualization: Theory and Practice Part I: Theoretical Background and Integration-Based Methods Christoph Garth Overview Foundations Time-Varying Vector Fields Numerical Integration
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics. D. Murrin
 Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
An Introduction to Flow Visualization (1) Christoph Garth
 An Introduction to Flow Visualization (1) Christoph Garth cgarth@ucdavis.edu Motivation What will I be talking about? Classical: Physical experiments to understand flow. 2 Motivation What will I be talking
An Introduction to Flow Visualization (1) Christoph Garth cgarth@ucdavis.edu Motivation What will I be talking about? Classical: Physical experiments to understand flow. 2 Motivation What will I be talking
Higher Dimensional Vector Field Visualization: A Survey
 EG UK Theory and Practice of Computer Graphics (2009) Wen Tang, John Collomosse (Editors) Higher Dimensional Vector Field Visualization: A Survey Zhenmin Peng and Robert S. Laramee Visual and Interactive
EG UK Theory and Practice of Computer Graphics (2009) Wen Tang, John Collomosse (Editors) Higher Dimensional Vector Field Visualization: A Survey Zhenmin Peng and Robert S. Laramee Visual and Interactive
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Computers & Graphics Manuscript Draft
 Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Computers & Graphics Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: CAG-D-12-00026R2 Title: Surface-Based Flow Visualization Article Type: Survey Paper Keywords: Survey; Flow Visualization;
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Computers & Graphics Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: CAG-D-12-00026R2 Title: Surface-Based Flow Visualization Article Type: Survey Paper Keywords: Survey; Flow Visualization;
Discrete representations of geometric objects: Features, data structures and adequacy for dynamic simulation. Part I : Solid geometry
 Discrete representations of geometric objects: Features, data structures and adequacy for dynamic simulation. Surfaces Part I : Solid geometry hachar Fleishman Tel Aviv University David Levin Claudio T.
Discrete representations of geometric objects: Features, data structures and adequacy for dynamic simulation. Surfaces Part I : Solid geometry hachar Fleishman Tel Aviv University David Levin Claudio T.
8. Tensor Field Visualization
 8. Tensor Field Visualization Tensor: extension of concept of scalar and vector Tensor data for a tensor of level k is given by t i1,i2,,ik (x 1,,x n ) Second-order tensor often represented by matrix Examples:
8. Tensor Field Visualization Tensor: extension of concept of scalar and vector Tensor data for a tensor of level k is given by t i1,i2,,ik (x 1,,x n ) Second-order tensor often represented by matrix Examples:
High-Order Numerical Algorithms for Steady and Unsteady Simulation of Viscous Compressible Flow with Shocks (Grant FA )
 High-Order Numerical Algorithms for Steady and Unsteady Simulation of Viscous Compressible Flow with Shocks (Grant FA9550-07-0195) Sachin Premasuthan, Kui Ou, Patrice Castonguay, Lala Li, Yves Allaneau,
High-Order Numerical Algorithms for Steady and Unsteady Simulation of Viscous Compressible Flow with Shocks (Grant FA9550-07-0195) Sachin Premasuthan, Kui Ou, Patrice Castonguay, Lala Li, Yves Allaneau,
Vector Visualization Chap. 6 March 7, 2013 March 26, Jie Zhang Copyright
 ector isualization Chap. 6 March 7, 2013 March 26, 2013 Jie Zhang Copyright CDS 301 Spring, 2013 Outline 6.1. Divergence and orticity 6.2. ector Glyphs 6.3. ector Color Coding 6.4. Displacement Plots (skip)
ector isualization Chap. 6 March 7, 2013 March 26, 2013 Jie Zhang Copyright CDS 301 Spring, 2013 Outline 6.1. Divergence and orticity 6.2. ector Glyphs 6.3. ector Color Coding 6.4. Displacement Plots (skip)
CIS 467/602-01: Data Visualization
 CIS 467/602-01: Data Visualization Vector Field Visualization Dr. David Koop Fields Tables Networks & Trees Fields Geometry Clusters, Sets, Lists Items Items (nodes) Grids Items Items Attributes Links
CIS 467/602-01: Data Visualization Vector Field Visualization Dr. David Koop Fields Tables Networks & Trees Fields Geometry Clusters, Sets, Lists Items Items (nodes) Grids Items Items Attributes Links
Cloth Simulation on the GPU. Cyril Zeller NVIDIA Corporation
 Cloth Simulation on the GPU Cyril Zeller NVIDIA Corporation Overview A method to simulate cloth on any GPU supporting Shader Model 3 (Quadro FX 4500, 4400, 3400, 1400, 540, GeForce 6 and above) Takes advantage
Cloth Simulation on the GPU Cyril Zeller NVIDIA Corporation Overview A method to simulate cloth on any GPU supporting Shader Model 3 (Quadro FX 4500, 4400, 3400, 1400, 540, GeForce 6 and above) Takes advantage
Interactive 3D Flow Visualization Based on Textures and Geometric Primitives
 Interactive 3D Flow Visualization Based on Textures and Geometric Primitives Robert S. Laramee and Helwig Hauser www.vrvis.at September 14, 2004 Abstract As the size of CFD simulation data sets expand,
Interactive 3D Flow Visualization Based on Textures and Geometric Primitives Robert S. Laramee and Helwig Hauser www.vrvis.at September 14, 2004 Abstract As the size of CFD simulation data sets expand,
Fundamental Algorithms
 Fundamental Algorithms Fundamental Algorithms 3-1 Overview This chapter introduces some basic techniques for visualizing different types of scientific data sets. We will categorize visualization methods
Fundamental Algorithms Fundamental Algorithms 3-1 Overview This chapter introduces some basic techniques for visualizing different types of scientific data sets. We will categorize visualization methods
CS GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 2: Introduction; GPU Architecture 1. Markus Hadwiger, KAUST
 CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 2: Introduction; GPU Architecture 1 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #2 (until Feb. 17) Read (required): GLSL book, chapter 4 (The OpenGL Programmable
CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 2: Introduction; GPU Architecture 1 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #2 (until Feb. 17) Read (required): GLSL book, chapter 4 (The OpenGL Programmable
Over Two Decades of Integration-Based, Geometric Flow Visualization
 Volume xx (200y), Number z, pp. 1 23 Over Two Decades of Integration-Based, Geometric Flow Visualization Tony McLoughlin 1, Robert S. Laramee 1, Ronald Peikert 2, Frits H. Post 3, and Min Chen 1 1 Visual
Volume xx (200y), Number z, pp. 1 23 Over Two Decades of Integration-Based, Geometric Flow Visualization Tony McLoughlin 1, Robert S. Laramee 1, Ronald Peikert 2, Frits H. Post 3, and Min Chen 1 1 Visual
Ray Casting of Trimmed NURBS Surfaces on the GPU
 Ray Casting of Trimmed NURBS Surfaces on the GPU Hans-Friedrich Pabst Jan P. Springer André Schollmeyer Robert Lenhardt Christian Lessig Bernd Fröhlich Bauhaus University Weimar Faculty of Media Virtual
Ray Casting of Trimmed NURBS Surfaces on the GPU Hans-Friedrich Pabst Jan P. Springer André Schollmeyer Robert Lenhardt Christian Lessig Bernd Fröhlich Bauhaus University Weimar Faculty of Media Virtual
Driven Cavity Example
 BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
Outline. Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete. Noise
 Fundamentals Data Outline Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete Noise 2 Data Data : Function dependent on one or more variables. Example Audio (1D) - depends
Fundamentals Data Outline Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete Noise 2 Data Data : Function dependent on one or more variables. Example Audio (1D) - depends
The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a
 The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a coordinate system and then the measuring of the point with
The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a coordinate system and then the measuring of the point with
Simulation in Computer Graphics. Deformable Objects. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Deformable Objects Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction forces performance collision handling visualization University
Simulation in Computer Graphics Deformable Objects Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction forces performance collision handling visualization University
2D vector fields 3. Contents. Line Integral Convolution (LIC) Image based flow visualization Vector field topology. Fast LIC Oriented LIC
 2D vector fields 3 Scientific Visualization (Part 8) PD Dr.-Ing. Peter Hastreiter Contents Line Integral Convolution (LIC) Fast LIC Oriented LIC Image based flow visualization Vector field topology 2 Applied
2D vector fields 3 Scientific Visualization (Part 8) PD Dr.-Ing. Peter Hastreiter Contents Line Integral Convolution (LIC) Fast LIC Oriented LIC Image based flow visualization Vector field topology 2 Applied
CFD Application in Offshore Structures Design at PETROBRAS
 CFD Application in Offshore Structures Design at PETROBRAS Marcus Reis ESSS CFD Director Mooring System Design of Floating Production Systems; Current and Wind Loads; Wave Induced Drag Coefficients. Case
CFD Application in Offshore Structures Design at PETROBRAS Marcus Reis ESSS CFD Director Mooring System Design of Floating Production Systems; Current and Wind Loads; Wave Induced Drag Coefficients. Case
ADVANCED FLOW VISUALIZATION
 ADVANCED FLOW VISUALIZATION DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of The Ohio State University By Liya Li, B.E., M.S.
ADVANCED FLOW VISUALIZATION DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of The Ohio State University By Liya Li, B.E., M.S.
WSCG 2010, Plzen, Czech Republic LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY
 Evolving Time Surfaces in a Virtual Stirred Tank Bidur Bohara, Farid Harhad, Werner Benger, Nathan Brener, S. Sitharama Iyengar, Bijaya B. Karki, Marcel Ritter, Kexi Liu, Brygg Ullmer, Nikhil Shetty, Vignesh
Evolving Time Surfaces in a Virtual Stirred Tank Bidur Bohara, Farid Harhad, Werner Benger, Nathan Brener, S. Sitharama Iyengar, Bijaya B. Karki, Marcel Ritter, Kexi Liu, Brygg Ullmer, Nikhil Shetty, Vignesh
Interactive 3D Flow Visualization Based on Textures and Geometric Primitives
 Interactive 3D Flow Visualization Based on Textures and Geometric Primitives Robert S. Laramee and Helwig Hauser www.vrvis.at 1 SUMMARY As the size of CFD simulation data sets expand, the job of the engineer
Interactive 3D Flow Visualization Based on Textures and Geometric Primitives Robert S. Laramee and Helwig Hauser www.vrvis.at 1 SUMMARY As the size of CFD simulation data sets expand, the job of the engineer
A Volume Rendering Framework for Visualizing 3D Flow Fields
 A Volume Rendering Framework for Visualizing 3D Flow Fields Hsien-Hsi HSIEH,, Liya LI, Han-Wei SHEN and Wen-Kai TAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering, The Ohio State University Columbus, OH
A Volume Rendering Framework for Visualizing 3D Flow Fields Hsien-Hsi HSIEH,, Liya LI, Han-Wei SHEN and Wen-Kai TAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering, The Ohio State University Columbus, OH
Mesh Processing Pipeline
 Mesh Smoothing 1 Mesh Processing Pipeline... Scan Reconstruct Clean Remesh 2 Mesh Quality Visual inspection of sensitive attributes Specular shading Flat Shading Gouraud Shading Phong Shading 3 Mesh Quality
Mesh Smoothing 1 Mesh Processing Pipeline... Scan Reconstruct Clean Remesh 2 Mesh Quality Visual inspection of sensitive attributes Specular shading Flat Shading Gouraud Shading Phong Shading 3 Mesh Quality
Polygonization of Implicit Surfaces
 Polygonization of Implicit Surfaces Hongxin Zhang and Jieqing Feng 2007-01-11 State Key Lab of CAD&CG Zhejiang University Contents Polygonization of Implicit Surfaces Other Methods for Displaying Implicit
Polygonization of Implicit Surfaces Hongxin Zhang and Jieqing Feng 2007-01-11 State Key Lab of CAD&CG Zhejiang University Contents Polygonization of Implicit Surfaces Other Methods for Displaying Implicit
CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality
 CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality Judd Kaiser ANSYS Inc. judd.kaiser@ansys.com 2005 ANSYS, Inc. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Overview
CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality Judd Kaiser ANSYS Inc. judd.kaiser@ansys.com 2005 ANSYS, Inc. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Overview
FLOWING FLUIDS AND PRESSURE VARIATION
 Chapter 4 Pressure differences are (often) the forces that move fluids FLOWING FLUIDS AND PRESSURE VARIATION Fluid Mechanics, Spring Term 2011 e.g., pressure is low at the center of a hurricane. For your
Chapter 4 Pressure differences are (often) the forces that move fluids FLOWING FLUIDS AND PRESSURE VARIATION Fluid Mechanics, Spring Term 2011 e.g., pressure is low at the center of a hurricane. For your
Vector Visualization
 Vector Visualization 5-1 Vector Algorithms Vector data is a three-dimensional representation of direction and magnitude. Vector data often results from the study of fluid flow, or when examining derivatives,
Vector Visualization 5-1 Vector Algorithms Vector data is a three-dimensional representation of direction and magnitude. Vector data often results from the study of fluid flow, or when examining derivatives,
Geometric Modeling in Graphics
 Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Evenly Spaced Streamlines for Surfaces: An Image-Based Approach
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2009.01352.x COMPUTER GRAPHICS forum Volume 28 (2009), number 6 pp. 1618 1631 Evenly Spaced Streamlines for Surfaces: An Image-Based Approach Benjamin Spencer 1, Robert S. Laramee
DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2009.01352.x COMPUTER GRAPHICS forum Volume 28 (2009), number 6 pp. 1618 1631 Evenly Spaced Streamlines for Surfaces: An Image-Based Approach Benjamin Spencer 1, Robert S. Laramee
Mathematical Tools in Computer Graphics with C# Implementations Table of Contents
 Mathematical Tools in Computer Graphics with C# Implementations by Hardy Alexandre, Willi-Hans Steeb, World Scientific Publishing Company, Incorporated, 2008 Table of Contents List of Figures Notation
Mathematical Tools in Computer Graphics with C# Implementations by Hardy Alexandre, Willi-Hans Steeb, World Scientific Publishing Company, Incorporated, 2008 Table of Contents List of Figures Notation
Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods
 Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods I.Lyulina Scientific Computing Group May, 2002 Overview Existing Techniques for Tracking Interfaces Basic Ideas of Level Set Method and Fast Marching Method
Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods I.Lyulina Scientific Computing Group May, 2002 Overview Existing Techniques for Tracking Interfaces Basic Ideas of Level Set Method and Fast Marching Method
FLUID MECHANICS TESTS
 FLUID MECHANICS TESTS Attention: there might be more correct answers to the questions. Chapter 1: Kinematics and the continuity equation T.2.1.1A flow is steady if a, the velocity direction of a fluid
FLUID MECHANICS TESTS Attention: there might be more correct answers to the questions. Chapter 1: Kinematics and the continuity equation T.2.1.1A flow is steady if a, the velocity direction of a fluid
CFD Analysis of 2-D Unsteady Flow Past a Square Cylinder at an Angle of Incidence
 CFD Analysis of 2-D Unsteady Flow Past a Square Cylinder at an Angle of Incidence Kavya H.P, Banjara Kotresha 2, Kishan Naik 3 Dept. of Studies in Mechanical Engineering, University BDT College of Engineering,
CFD Analysis of 2-D Unsteady Flow Past a Square Cylinder at an Angle of Incidence Kavya H.P, Banjara Kotresha 2, Kishan Naik 3 Dept. of Studies in Mechanical Engineering, University BDT College of Engineering,
A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY. Sheng-Wen Wang
 Effectively Identifying and Segmenting Individual Vortices in 3D Turbulent Flow A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Sheng-Wen Wang IN PARTIAL
Effectively Identifying and Segmenting Individual Vortices in 3D Turbulent Flow A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Sheng-Wen Wang IN PARTIAL
ENERGY-224 Reservoir Simulation Project Report. Ala Alzayer
 ENERGY-224 Reservoir Simulation Project Report Ala Alzayer Autumn Quarter December 3, 2014 Contents 1 Objective 2 2 Governing Equations 2 3 Methodolgy 3 3.1 BlockMesh.........................................
ENERGY-224 Reservoir Simulation Project Report Ala Alzayer Autumn Quarter December 3, 2014 Contents 1 Objective 2 2 Governing Equations 2 3 Methodolgy 3 3.1 BlockMesh.........................................
Single Scattering in Refractive Media with Triangle Mesh Boundaries
 Single Scattering in Refractive Media with Triangle Mesh Boundaries Bruce Walter Shuang Zhao Nicolas Holzschuch Kavita Bala Cornell Univ. Cornell Univ. Grenoble Univ. Cornell Univ. Presented at SIGGRAPH
Single Scattering in Refractive Media with Triangle Mesh Boundaries Bruce Walter Shuang Zhao Nicolas Holzschuch Kavita Bala Cornell Univ. Cornell Univ. Grenoble Univ. Cornell Univ. Presented at SIGGRAPH
The State of the Art in Flow Visualization, part 1: Direct, Texture-based, and Geometric Techniques
 Volume 22 (2003), Number 2, yet unknown pages The State of the Art in Flow Visualization, part 1: Direct, Texture-based, and Geometric Techniques Helwig Hauser, Robert S. Laramee, Helmut Doleisch, Frits
Volume 22 (2003), Number 2, yet unknown pages The State of the Art in Flow Visualization, part 1: Direct, Texture-based, and Geometric Techniques Helwig Hauser, Robert S. Laramee, Helmut Doleisch, Frits
Mathematical Surface Representations for Conceptual Design
 Mathematical Surface Representations for Conceptual Design Karan Singh University of Toronto Ravin Balakrishnan (U of T) Eugene Fiume (U of T) Pierre Poulin (U of Montreal) Michiel van de Panne (UBC) Richard
Mathematical Surface Representations for Conceptual Design Karan Singh University of Toronto Ravin Balakrishnan (U of T) Eugene Fiume (U of T) Pierre Poulin (U of Montreal) Michiel van de Panne (UBC) Richard
ACGV 2008, Lecture 1 Tuesday January 22, 2008
 Advanced Computer Graphics and Visualization Spring 2008 Ch 1: Introduction Ch 4: The Visualization Pipeline Ch 5: Basic Data Representation Organization, Spring 2008 Stefan Seipel Filip Malmberg Mats
Advanced Computer Graphics and Visualization Spring 2008 Ch 1: Introduction Ch 4: The Visualization Pipeline Ch 5: Basic Data Representation Organization, Spring 2008 Stefan Seipel Filip Malmberg Mats
Visualization, Lecture #2d. Part 3 (of 3)
 Visualization, Lecture #2d Flow visualization Flow visualization, Part 3 (of 3) Retrospect: Lecture #2c Flow Visualization, Part 2: FlowVis with arrows numerical integration Euler-integration Runge-Kutta-integration
Visualization, Lecture #2d Flow visualization Flow visualization, Part 3 (of 3) Retrospect: Lecture #2c Flow Visualization, Part 2: FlowVis with arrows numerical integration Euler-integration Runge-Kutta-integration
Mesh Morphing. Ligang Liu Graphics&Geometric Computing Lab USTC
 Mesh Morphing Ligang Liu Graphics&Geometric Computing Lab USTC http://staff.ustc.edu.cn/~lgliu Morphing Given two objects produce sequence of intermediate objects that gradually evolve from one object
Mesh Morphing Ligang Liu Graphics&Geometric Computing Lab USTC http://staff.ustc.edu.cn/~lgliu Morphing Given two objects produce sequence of intermediate objects that gradually evolve from one object
Introduction to Scientific Visualization
 Visualization Definition Introduction to Scientific Visualization Stefan Bruckner visualization: to form a mental vision, image, or picture of (something not visible or present to the sight, or of an abstraction);
Visualization Definition Introduction to Scientific Visualization Stefan Bruckner visualization: to form a mental vision, image, or picture of (something not visible or present to the sight, or of an abstraction);
Parallel Computation of Spherical Parameterizations for Mesh Analysis. Th. Athanasiadis and I. Fudos University of Ioannina, Greece
 Parallel Computation of Spherical Parameterizations for Mesh Analysis Th. Athanasiadis and I. Fudos, Greece Introduction Mesh parameterization is a powerful geometry processing tool Applications Remeshing
Parallel Computation of Spherical Parameterizations for Mesh Analysis Th. Athanasiadis and I. Fudos, Greece Introduction Mesh parameterization is a powerful geometry processing tool Applications Remeshing
Lecture notes: Object modeling
 Lecture notes: Object modeling One of the classic problems in computer vision is to construct a model of an object from an image of the object. An object model has the following general principles: Compact
Lecture notes: Object modeling One of the classic problems in computer vision is to construct a model of an object from an image of the object. An object model has the following general principles: Compact
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Hierarchical Streamarrows for the Visualization of Dynamical Systems
 Hierarchical Streamarrows for the Visualization of Dynamical Systems Helwig Löffelmann Lukas Mroz Eduard Gröller Institute of Computer Graphics, Vienna University of Technology Abstract. Streamarrows are
Hierarchical Streamarrows for the Visualization of Dynamical Systems Helwig Löffelmann Lukas Mroz Eduard Gröller Institute of Computer Graphics, Vienna University of Technology Abstract. Streamarrows are
Level of Details in Computer Rendering
 Level of Details in Computer Rendering Ariel Shamir Overview 1. Photo realism vs. Non photo realism (NPR) 2. Objects representations 3. Level of details Photo Realism Vs. Non Pixar Demonstrations Sketching,
Level of Details in Computer Rendering Ariel Shamir Overview 1. Photo realism vs. Non photo realism (NPR) 2. Objects representations 3. Level of details Photo Realism Vs. Non Pixar Demonstrations Sketching,
EFFECTIVE VISUALIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER
 12TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON FLOW VISUALIZATION September 10-14, 2006, German Aerospace Center (DLR), Göttingen, Germany EFFECTIVE VISUALIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER Robert S. Laramee Department of Computer
12TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON FLOW VISUALIZATION September 10-14, 2006, German Aerospace Center (DLR), Göttingen, Germany EFFECTIVE VISUALIZATION OF HEAT TRANSFER Robert S. Laramee Department of Computer
Prof. Fanny Ficuciello Robotics for Bioengineering Visual Servoing
 Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level
Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level
Shape modeling Modeling technique Shape representation! 3D Graphics Modeling Techniques
 D Graphics http://chamilo2.grenet.fr/inp/courses/ensimag4mmgd6/ Shape Modeling technique Shape representation! Part : Basic techniques. Projective rendering pipeline 2. Procedural Modeling techniques Shape
D Graphics http://chamilo2.grenet.fr/inp/courses/ensimag4mmgd6/ Shape Modeling technique Shape representation! Part : Basic techniques. Projective rendering pipeline 2. Procedural Modeling techniques Shape
Hardware-Accelerated Visualization of Time-Varying 2D and 3D Vector Fields by Texture Advection via Programmable Per-Pixel Operations
 Hardware-Accelerated Visualization of Time-Varying 2D and 3D Vector Fields by Texture Advection via Programmable Per-Pixel Operations Daniel Weiskopf Matthias Hopf Thomas Ertl University of Stuttgart,
Hardware-Accelerated Visualization of Time-Varying 2D and 3D Vector Fields by Texture Advection via Programmable Per-Pixel Operations Daniel Weiskopf Matthias Hopf Thomas Ertl University of Stuttgart,
Generation of Accurate Integral Surfaces in Time-Dependent Vector Fields
 Generation of Accurate Integral Surfaces in Time-Dependent Vector Fields Christoph Garth, Hari Krishnan Student Member, IEEE, Xavier Tricoche, Member, IEEE, Tom Bobach Student Member, IEEE and Kenneth
Generation of Accurate Integral Surfaces in Time-Dependent Vector Fields Christoph Garth, Hari Krishnan Student Member, IEEE, Xavier Tricoche, Member, IEEE, Tom Bobach Student Member, IEEE and Kenneth
Scientific Visualization
 Scientific Visualization Dr. Ronald Peikert Summer 2007 Ronald Peikert SciVis 2007 - Introduction 1-1 Introduction to Scientific Visualization Ronald Peikert SciVis 2007 - Introduction 1-2 What is Scientific
Scientific Visualization Dr. Ronald Peikert Summer 2007 Ronald Peikert SciVis 2007 - Introduction 1-1 Introduction to Scientific Visualization Ronald Peikert SciVis 2007 - Introduction 1-2 What is Scientific
Graphics Pipeline 2D Geometric Transformations
 Graphics Pipeline 2D Geometric Transformations CS 4620 Lecture 8 1 Plane projection in drawing Albrecht Dürer 2 Plane projection in drawing source unknown 3 Rasterizing triangles Summary 1 evaluation of
Graphics Pipeline 2D Geometric Transformations CS 4620 Lecture 8 1 Plane projection in drawing Albrecht Dürer 2 Plane projection in drawing source unknown 3 Rasterizing triangles Summary 1 evaluation of
Hardware-Accelerated Lagrangian-Eulerian Texture Advection for 2D Flow Visualization
 Hardware-Accelerated Lagrangian-Eulerian Texture Advection for 2D Flow Visualization Daniel Weiskopf 1 Gordon Erlebacher 2 Matthias Hopf 1 Thomas Ertl 1 1 Visualization and Interactive Systems Group, University
Hardware-Accelerated Lagrangian-Eulerian Texture Advection for 2D Flow Visualization Daniel Weiskopf 1 Gordon Erlebacher 2 Matthias Hopf 1 Thomas Ertl 1 1 Visualization and Interactive Systems Group, University
Many rendering scenarios, such as battle scenes or urban environments, require rendering of large numbers of autonomous characters.
 1 2 Many rendering scenarios, such as battle scenes or urban environments, require rendering of large numbers of autonomous characters. Crowd rendering in large environments presents a number of challenges,
1 2 Many rendering scenarios, such as battle scenes or urban environments, require rendering of large numbers of autonomous characters. Crowd rendering in large environments presents a number of challenges,
HPC Computer Aided CINECA
 HPC Computer Aided Engineering @ CINECA Raffaele Ponzini Ph.D. CINECA SuperComputing Applications and Innovation Department SCAI 16-18 June 2014 Segrate (MI), Italy Outline Open-source CAD and Meshing
HPC Computer Aided Engineering @ CINECA Raffaele Ponzini Ph.D. CINECA SuperComputing Applications and Innovation Department SCAI 16-18 June 2014 Segrate (MI), Italy Outline Open-source CAD and Meshing
11/1/13. Visualization. Scientific Visualization. Types of Data. Height Field. Contour Curves. Meshes
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26 Visualization Height Fields and Contours Scalar Fields Volume Rendering Vector Fields [Angel Ch. 2.11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scientific Visualization
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26 Visualization Height Fields and Contours Scalar Fields Volume Rendering Vector Fields [Angel Ch. 2.11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scientific Visualization
Visualization. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26 Visualization Height Fields and Contours Scalar Fields Volume Rendering Vector Fields [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Scientific Visualization
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26 Visualization Height Fields and Contours Scalar Fields Volume Rendering Vector Fields [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Scientific Visualization
3D Modeling: Surfaces
 CS 430/536 Computer Graphics I 3D Modeling: Surfaces Week 8, Lecture 16 David Breen, William Regli and Maxim Peysakhov Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Computer Science Drexel
CS 430/536 Computer Graphics I 3D Modeling: Surfaces Week 8, Lecture 16 David Breen, William Regli and Maxim Peysakhov Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Computer Science Drexel
A Level-Set Method for Flow Visualization
 A Level-Set Method for Flow Visualization Rüdiger Westermann, Christopher Johnson, and Thomas Ertl Scientific Computing and Visualization Group, University of Technology Aachen Scientific Computing and
A Level-Set Method for Flow Visualization Rüdiger Westermann, Christopher Johnson, and Thomas Ertl Scientific Computing and Visualization Group, University of Technology Aachen Scientific Computing and
A Texture-Based Framework for Spacetime-Coherent Visualization of Time-Dependent Vector Fields
 A Texture-Based Framework for Spacetime-Coherent Visualization of Time-Dependent Vector Fields Daniel Weiskopf 1 Gordon Erlebacher 2 Thomas Ertl 1 1 Institute of Visualization and Interactive Systems,
A Texture-Based Framework for Spacetime-Coherent Visualization of Time-Dependent Vector Fields Daniel Weiskopf 1 Gordon Erlebacher 2 Thomas Ertl 1 1 Institute of Visualization and Interactive Systems,
2.11 Particle Systems
 2.11 Particle Systems 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 152 Particle Systems Lagrangian method not mesh-based set of particles to model time-dependent phenomena such as snow fire smoke 320491: Advanced
2.11 Particle Systems 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 152 Particle Systems Lagrangian method not mesh-based set of particles to model time-dependent phenomena such as snow fire smoke 320491: Advanced
Chapter 4 FLUID KINEMATICS
 Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2010 Chapter 4 FLUID KINEMATICS Lecture slides by Hasan Hacışevki Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2010 Chapter 4 FLUID KINEMATICS Lecture slides by Hasan Hacışevki Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
About Phoenix FD PLUGIN FOR 3DS MAX AND MAYA. SIMULATING AND RENDERING BOTH LIQUIDS AND FIRE/SMOKE. USED IN MOVIES, GAMES AND COMMERCIALS.
 About Phoenix FD PLUGIN FOR 3DS MAX AND MAYA. SIMULATING AND RENDERING BOTH LIQUIDS AND FIRE/SMOKE. USED IN MOVIES, GAMES AND COMMERCIALS. Phoenix FD core SIMULATION & RENDERING. SIMULATION CORE - GRID-BASED
About Phoenix FD PLUGIN FOR 3DS MAX AND MAYA. SIMULATING AND RENDERING BOTH LIQUIDS AND FIRE/SMOKE. USED IN MOVIES, GAMES AND COMMERCIALS. Phoenix FD core SIMULATION & RENDERING. SIMULATION CORE - GRID-BASED
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering. Image-Based Modeling and Rendering. Final projects IBMR. What we have learnt so far. What IBMR is about
 Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Image-Based Modeling and Rendering MIT EECS 6.837 Frédo Durand and Seth Teller 1 Some slides courtesy of Leonard McMillan, Wojciech Matusik, Byong Mok Oh, Max Chen 2
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Image-Based Modeling and Rendering MIT EECS 6.837 Frédo Durand and Seth Teller 1 Some slides courtesy of Leonard McMillan, Wojciech Matusik, Byong Mok Oh, Max Chen 2
Manipulating the Boundary Mesh
 Chapter 7. Manipulating the Boundary Mesh The first step in producing an unstructured grid is to define the shape of the domain boundaries. Using a preprocessor (GAMBIT or a third-party CAD package) you
Chapter 7. Manipulating the Boundary Mesh The first step in producing an unstructured grid is to define the shape of the domain boundaries. Using a preprocessor (GAMBIT or a third-party CAD package) you
Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science
 Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science Lecture 16: Models of Object Recognition Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk February 23, 2010 Frank Keller Computational
Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science Lecture 16: Models of Object Recognition Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk February 23, 2010 Frank Keller Computational
Shape Modeling with Point-Sampled Geometry
 Shape Modeling with Point-Sampled Geometry Mark Pauly Richard Keiser Leif Kobbelt Markus Gross ETH Zürich ETH Zürich RWTH Aachen ETH Zürich Motivation Surface representations Explicit surfaces (B-reps)
Shape Modeling with Point-Sampled Geometry Mark Pauly Richard Keiser Leif Kobbelt Markus Gross ETH Zürich ETH Zürich RWTH Aachen ETH Zürich Motivation Surface representations Explicit surfaces (B-reps)
