Prediction of Sea Ice Edge in the Antarctic Using GVF Snake Model
|
|
|
- Prosper Jackson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL GEOLOGICAL SOCIETY OF INDIA Vol.78, August 2011, pp Prediction of Se Ice Edge in the Antrctic Using GVF Snke Model PRAVIN K. RANA +, MIHIR K. DASH*, A. ROUTRAY* nd P. C. PANDEY* + Royl Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden * Indin Institute of Technology, Khrgpur, Indi Emil: mihir@corl.iikgp.ernet.in Astrct: Antrctic se ice cover plys n importnt role in shping the erth s climte, primrily y insulting the ocen from the tmosphere nd incresing the surfce ledo. The convective processes ccompnied with the se ice formtion result ottom wter formtion. The cold nd dense ottom wter moves towrds the equtor long the ocen sins nd tkes prt in the glol thermohline circultion. Se ice edge is potentil indictor of climte chnge. Additionlly, fishing nd commercil shipping ctivities s well s militry sumrine opertions in the polr ses need relile ice edge informtion. However, s the se ice edge is unstle in time, the temporl vlidity of the estimted ice edge is often shorter thn the time required to trnsfer the informtion to the opertionl user. Hence, n ccurte se ice edge prediction s well s determintion is crucil for fine-scle geophysicl modeling nd for ner-rel-time opertions. In this study, ctive contour modelling (known s Snke model) nd non-rigid motion estimtion techniques hve een used for predicting the se ice edge (SIE) in the Antrctic. For this purpose the SIE hs een detected from se ice concentrtion derived using specil sensor microwve imger (SSM/I) oservtions. The 15% se ice concentrtion pixels re eing tken s the edge pixel etween ice nd wter. The externl force, grdient vector flow (GVF), of SIE for totl the Antrctic region is prmeterised for dily s well s weekly dt set. The SIE is predicted t certin points using sttisticl technique. These predicted points hve een used to constitute SIE using rtificil intelligence technique, the grdient vector flow (GVF). The predicted edge hs een vlidted with tht of SSM/I. It is found tht ll the mjor curvtures hve een cptured y the predicted edge nd it is in good greement with tht of the SSM/I oservtion. Keywords: Se ice modelling, Se ice edge, Snke model, Antrctic. INTRODUCTION Antrctic, the southernmost icy continent, remins prdise to the reserchers for its vst ice sheet, extremely dynmic se ice environment nd ove ll its extreme wether nd climte. Antrctic is often clled pulsting continent ecuse its ice pck (i.e. se ice) grows from n re of 1.8 million km 2 y the end of ustrl summer, to out 20 million km 2 y the end of ustrl winter (Vys et l. 2003). The totl se ice re in the Southern Hemisphere is nerly 10 times greter in the ustrl spring thn in the ustrl fll. On verge the dvncement of ice is most rpid in the utumn from April to June nd continues until lte winter/erly spring. Ice retret is most rpid in the erly summer of the yer with minimum ice extent during Ferury. The chnge in the se ice re is due to (i) the polr loction of the continent which hs n lmost 4 month long winter nd 4 months of continuous summer (ii) the ocenic nd the tmospheric circultion in this region. Extremely dynmic se-ice cover plys n importnt role in the Erth s climte system, primrily y insulting the ocen from the tmosphere nd incresing the surfce ledo. Fresh snow cover on ice hs n ledo of the order 98% (Vowinckell nd Orwing, 1970) compred to 10-15% of tht of open wter (Lm, 1982). Atmospheric het exchnge over se ice is up to two orders of mgnitude less thn tht over Open Ocen. Sesonlly expnding nd contrcting se ice profoundly impedes the exchnge of het, momentum, nd gses etween ocen nd tmosphere. Both the insultion nd the ledo effects provide positive feedck nd influence the locl wether nd climte in long run. Also, the Antrctic se ice zone is hitt for mny species of iot. Regions covered y se ice lso ply n importnt role in specilized humn ctivities in the Antrctic. Antrctic hs no indigenous people, ut severl thousnd people live on Antrctic during prts of the yer, supporting scientific reserch t vrious sttions. Mitri Sttion (70 46'S, 11 45'E), the logistics hu of the Indi s Antrctic Progrm, is resupplied y ships ech yer. Thick se ice delys the re-supply nd costs more money. So, the prediction of se ice edge not only importnt form the / /$ 1.00 GEOL. SOC. INDIA
2 100 PRAVIN K. RANA AND OTHERS climtic study point, ut lso from the point of nvigtion nd the study of Mrine Antrctic iot. Although the stellite system, over the lst four decdes, hve provide us gret del of informtion on the rodscle se ice extent nd its vriility. But difficulties to retrieve n ccurte ice edge from stellite sensor during severe wether condition, need of relile ice edge informtion over the Antrctic for fine-scle geophysicl modelling nd ner-rel-time prediction of se ice edge (SIE) for fishing, for commercil shipping ctivities s well s militry sumrine opertions is very much required. The ice edge is unstle in time, hence the temporl vlidity of the estimted ice edge is often shorter thn the time required to trnsfer the informtion to the opertionl users. For exmple the United Sttes Ntionl Ice Centre provides iweekly informtion out glol se-ice condition (Hrpintner et l. 2004). This pper descries model sed on the rtificil intelligence nd sttisticl nlysis to mp nd predict the Antrctic SIE. This model utilizes the se ice concentrtion informtion over the Southern Ocen otined form the Ntionl Snow nd Ice Dt Center (NSIDC) to predict the SIE. DATA AND METHODOLOGY Our study utilises the se ice concentrtion (SIC) otined from the Ntionl Snow nd Ice Dt Center, USA. These dt sets re generted using the Specil Sensor Microwve/Imger (SSM/I) oservtions using the Bootstrp Algorithm with dily vrying tie-points (Comiso et l. 1997). Dily nd monthly gridded dt re ville on the polr stereogrphic grid with 25km x 25 km resolution pssing plne t 70 ltitude to minimize the error in reduction of re t the polr region. Dily gridded SIC hs een used in our study. 15% SIC hs een considered s the threshold vlue for defining the ice edge (Gloersen et l. 1992). The imge vlues hve een converted into grey scle intensity vlue which contins only two grey level vlues, 255 nd 0. The grey level 255 is ssigned to the lnd pixels nd the pixels hving SIC more thn 15%. The grey level 0 is ssigned to the pixels hving SIC less thn 15%. Output of this processing gives grey level imge dt with lots of noise (Fig.1). Noisy grey level se ice imges for two different periods (i) hving pek se ice extent (1 st Septemer 2006) nd (ii) hving melting of se ice (1 st Ferury 2006) is shown in Fig.1. Noises within ice covered region represent the presence of less concentrtion ice pixel. In order to remove noises s well s the holes inside the foreground imge, the sic concept of reltionship etween pixels nd the imges were studied. The oundries were defined through the connectivity of pixels. The imge filling hs een performed using flood-fill technique y specifying ckground pixel s strting point. The oundries were determined sed on the type of neighourhood pixel specified. The filtered imges for ove periods re shown in Fig.2. Cnny method is used to detect the se ice edge. Figure 3 shows typicl exmples of the Antrctic se ice edges for 1 st Septemer nd 1 st Ferury, These imges were used to prmeterize the Active Contour Model (ACM). ACM required imges with white ckground s well Fig.1. The grey scle of se ice imge over the Antrctic otined fter processing. The noises nd hole re clerly seen in the imge. () for 1 st Septemer 2006 nd () for 1 st Ferury 2006.
3 PREDICTION OF SEA ICE EDGE IN THE ANTARCTIC USING GVF SNAKE MODEL 101 Fig.2. Processed imges of the Antrctic with se ice fter the removl of noise nd holes () for 1 st Septemer 2006 nd () for 1 st Ferury Fig.3. The edge generted using cnny method from the imges given in Fig 2. () for 1 st Septemer 2006 nd () for 1 st Ferury Fig.4. Se ice edge fter ltering the ckground nd foreground of the imges given in Fig.3 for () Septemer 1 st, 2006 nd () for Ferury 1 st, These imges serve s the mster to prmeterize the ctive contours.
4 102 PRAVIN K. RANA AND OTHERS s PGM file formt. For this purpose the imge ckground s well s foreground gry level re chnged ccordingly. The resultnt imges with white ckground nd lck foreground for the ove two periods re shown in Fig.4. PARAMETERIZATION OF SEA ICE EDGE USING ACTIVE CONTOUR MODEL Se ice edge is extremely dynmic in nture. Active Contour Model (ACM) or Snke Model is the est tool to simulte se ice edge for prediction. This technique is extensively used in the edge detection prolem nd other computer vision prolem like, shpe recognition, oject trcking nd imge segmenttion. When edge informtion in the imge is insufficient nd corrupted y noise considerle difficulties rise in the ppliction of clssicl edge detection methods for simultion of edge or oundry shpe. As result, clssicl techniques either fil completely or require some kind of post processing step to remove invlid oject oundries in the segmenttion results. ACM promises to provide good solution. Mthemticlly, ctive contour is curve defined s function of rc length, s, is defined s X(s) = [x(s)y(s)], s [0,1] is which moves through the sptil domin of n imge to minimize the following energy functionl: Where α nd β re weighting prmeters tht control the snke s tension nd rigidity, respectively (Kss et l. 1987; Cohen, 1991). The first-term represents the internl energy functionl nd is defined y nd Where, nd denote the first nd second order derivtes of X(s) with respect to s. The externl energy function E ext is derived from imge dt nd tkes smller vlues t oject oundries s well s other feture of interest. Minly there re two different energy functions, (i) edge functionl (E 1 (x,y)) (ii) line functionl ext (E2 (x,y)), which ttrct the ext snke or the contour. Given grey level imge intensity of the imge, I(x, y), viewed s function of continuous position vriles (x, y), typicl externl energy functions designed to led n ctive contour towrd step edge re (1) (2) Where, e is positive weighting prmeter, is twodimensionl Gussin function with stndrd devition is the grdient opertor nd * is the 2D imge convolution opertor (for detiled description of 2 nd 3 plese refer Kss et l. 1987; Xu nd Prince, 1997). Imge with line drwing (lck nd white), eqution 2 nd 3 cn e defined s follows: where l is weighting prmeter. Positive l is used to find lck lines on white ckground, while negtive l is used to find white lines on lck ckground (for detiled description of 4 nd 5 plese refer Xu nd Prince, 1997). For oth edge nd line potentil energies, incresing cn roden its ttrction rnge. However, lrger cn lso cuse shift in the oundry loction, resulting in less ccurte result. INITIALIZING THE CONTOUR For prmeteriztion of se ice edge over Antrctic, initil snke is defined s circle with (166, 158) position in the imge s the origin. Initil snke is tken to e circle, ecuse se ice coverge over Antrctic expnd/contrct lmost rdilly. The edge mp ws otined y convolving the Lplcin with the imge pixels. This edge mp ws single chnnel 8 it imge. This is done ecuse single vlue imge intensity desired to represent the imge energy. Then the Lplcin filter operted on the imge nd the imge is converted into single chnnel grey level imge. The model ws initilised with circle y following eqution x = *cos(t); y = *sin(t); Figure 5 gives the initil circle s position on n imge of Antrctic se ice edge. Here we hve shown the ice edge for 1 st Jnury 2002 which is otined s ove. In order to increse the cpture strength of the edges, the edge mp ws lurred so s to diffuse the effect of strong edges onto nery pixels. As soon s ny contour pixel would come within few pixel of the edge, it would strt experiencing the effects of the edge nd the get pulled towrd the edge. A 5x5 Gussin filter ws used to chieve this lurring. Finlly, rmed with lurred edge mp nd the initil (3) (4) (5)
5 PREDICTION OF SEA ICE EDGE IN THE ANTARCTIC USING GVF SNAKE MODEL 103 GVF SNAKE METHOD Fig.5. A typicl Lplcin filtered single chnnel grey level imge of the se ice edge over the Antrctic with the Initil circulr snke. contour configurtion is invoked which is emedded in the progrm. CHOICE OF,, AND The tension prmeter of the contour is defined t 0.2. It mens tht n verge seprtion of 10 pixels etween two control points should cuse ech to expert n elstic pull of 2 pixel on the other. Now, the ending effect is sutler. A movement of few pixels cn ffect the ending energy gretly. Hence, lower vlue of, the rigidity prmeter is defined s 0. Furthermore, the imge force needs to perform like little stronger force thn the elstic force. It could e surmise s if few points in the contour egin to drift wy from n edge they should not e le to dislodge those points which hve lredy found good strong edge. The presence of ny stry noise pixel my trp one point t flse minimum nd ffect the movement of snke. To void this sitution imge force should e slightly greter thn elstic force. A difference of imge intensity y grey level 255 etween neighouring pixel; is considered s trnsition from pure lck (intensity vlue 0) to pure white (intensity vlue 255), which is the strongest edge possile. But even difference in grey level y 100 represents good visile edge. So we might sy tht n intensity grdient of 128 should exert out the sme level of force s elstic force t 10 pixels prt, which is denoted y. This suggests vlue of 1/64 for. The mjor drw ck of ACM is ssigning vlues to the constnts. After some tril nd error, the vlues = 0.05, = 0, nd = 1 were decided upon. The model strts from the initil contour (circle in this cse) provided to it s input. The grdient vector flow (GVF) snke (Xu nd Prince, 1997) egins with the clcultion of field of forces, clled the GVF forces. The field forces were clculted etween different points on the initil contour nd the finl ice edge in steps. These forces re derived from the diffusion opertions crried out in the imges considering the grey vlues nd tendency to extend very fr wy from the oject. This extends the cpture rnge so tht snkes cn find ojects tht re quite fr wy from the snke s initil position. The typicl exmple of these forces over the entire imge domin for the Antrctic se ice edge is shown in Fig.6. These diffusive forces re normlized (Xu nd Prince, 1997) to give the position of the contour t the end of ech itertion. The output of the (n-1) th itertion is considered s the initil condition for the n th itertion. Figure 7 shows the position of the contours t different itertions. It cn e inferred from the Fig.7 tht the contour intervls re not the sme t ech intervl, ecuse the normlised GVF force (mgnitude nd direction) chnges with itertions. Sine the diffusion property cretes force, the ctive contours cn e pull into concve regions (see Fig.7). The GVF forces ct on oth side of the edge nd try to converse to the oundry (see Fig. 8). The forces inside/outside the contour represent the diffusive forces coming from inside/outside to the contour oundry. Mthemticl expressions for these forces re descried ove. It is oserved tht the GVF field hs much lrger cpture rnge thn trditionl potentil forces. A second oservtion is tht the GVF vectors within the oundry concvity i.e. t the top of the Antrctic se ice edge hve downwrd component. Finlly, it cn e seen in tht the GVF field ehves in n nlogous fshion when viewed from the inside of the oject (see Fig. 8). In prticulr, the GVF vectors re pointing outwrd into Antrctic se ice edge, which represent concvities from this perspective. The performnce of the GVF ctive contour model is studied on 53 weekly (corresponding to one yer) se ice concentrtion imges with the sme initil conditions nd the forcing prmeters (the snke prmeters re chosen s: á = 0.2, â = 0.0, ë =0.3, nd ã =0.4). It is found tht in ll the cses the model fitted to the given edge very nicely. This gives confidence tht using discrete pixel informtion continuous edge cn e simulted using GVF pproch. This potentility hs een explored to predict the se ice edge in the Antrctic.
6 104 PRAVIN K. RANA AND OTHERS Fig.6. GVF externl forces for typicl Antrctic se ice edge imge (the ice edge shown in Fig.5). Fig.7. A view of snke deformtion during run of snke model, fter 230 itertions.
7 PREDICTION OF SEA ICE EDGE IN THE ANTARCTIC USING GVF SNAKE MODEL 105 Fig.8. A close-up GVF externl forces within the oundry concvity. PREDICTION OF SEA ICE EDGE To predict se ice edge over Antrctic, weekly se ice edges hve een computed from the concentrtion imges for the yer The imge is found to e of the form 332 pixel x 316 pixel coordinte system strting from (0, 0) t its left upper corner of the imge. In this coordinte system, the imge is treted s grid of discrete elements, ordered from top to ottom nd left to right. For pixel coordintes, the first component i (the row) increse downwrd, while the second component j (the column) increses to the right. Assuming the expnsion nd contrction of se ice edge is rdil, ech edge pixels re trnsferred to rdil co-ordinte system with the origin of the centre of the co-ordinte system t the pixel loction (166, 158). All the edge pixels hve een trnsformed the rdil co-ordinte system using the following reltion: where, i new-pixel nd j new-pixel re the new trnsformed imge edge pixel in pixel coordinte system of imge. The verged rdius of edge pixels t ech 1 ± 0.2 intervl is clculted for ll 53 weeks. If no ice edge is found then n undefined vlue ( ) is ssigned to the corresponding ngle. In certin cses more thn one solution re found for prticulr ngle. In this cse the edge informtion is verged nd put s single solution. Using the weekly dt sets descried ove time series of ngulr distriution of rdius is generted. Then time series of rdil vrition of the edge corresponding to ech ngle is fitted to four degree polynomil nd mtrix with coefficients of the polynomil is generted. The eqution for the mtrix is given elow (9) i new-pixel = 166 i pixel (6) j new-pixel = j pixel 158 (7) In the trnsformed co-ordinte system the rdil distnce of ech edge pixel (r) nd the ngle covered (θ) with reference to the 158 th row in the nti-clock wise is clculted. The reltion used for the computtion of the ngulr coordinte is given s follows: with, (10) (11) (8) where, r θ is the rdius of the ech pixel loctions, nd = 1,2,3,4, 360, ech vlue of corresponds to n ngles,
8 106 PRAVIN K. RANA AND OTHERS t is the time nd A, B, C, D, E re known polynomil coefficients. Eight smple curves with 4 degree polynomil fit re shown in Fig.9. By using coefficient mtrix of polynomil eqution, the rdil distnce of the se ice edge r t few ngulr positions re predicted for the time step t=55, 56. The rdil components re converted ck to the pixel vlues using the reltion given elow: (12) These pixel vlues otined re with respect to the coordinte system with origin t (166,158). Agin the ove informtion is converted to the originl imge co-ordinte system hving origin t (0,0) loction. The trnsformtion equtions re given elow: (13) Now, we hve few predicted edge pixel position informtion in the imge domin tht cn e given s input to simulte the se ice edge. The informtion re put into GVF snke model nd the se ice edge is simulted using the prmeters descried ove. After 250 itertions, snke simultes the predicted Antrctic SIE imge. Figures 10 nd 11 show typicl GVF Snke model derived SIE imge for 1 st week nd 2 nd week of Jnury, 2005 respectively. The corresponding SSM/I Antrctic se ice edge imge is () θ = 1 () θ = (c) θ = 185 (d) θ = 241 Fig.9. Typicl exmple of 4 th order polynomil curve fitting for 53 weeks, 2004 edge informtion dt for different ngles.
9 PREDICTION OF SEA ICE EDGE IN THE ANTARCTIC USING GVF SNAKE MODEL 107 Fig.10. () Predicted imge of 4 th of Jnury 2005 y points otin y polynomil eqution nd edge simulted y point using GVF snke. () SSM/I imge of the Antrctic se ice edge of 4 th Jnury 2005 used for vlidtion of prediction result. Fig.11. () Predicted imge of 11 th of Jnury 2005 y points otin y polynomil eqution nd edge simulted y point using GVF snke. () SSM/I imge of the Antrctic se ice edge of 11 th Jnury 2005 used for vlidtion of prediction result. lso shown in these figures. This is to note tht the imge domin remins sme s tht of the polr stereogrphic projection imge provided y NSIDC. VALIDATION AND ERROR ANALYSIS The predicted imge vlidted y using Antrctic se ice edge of sme dy which is otin y SSM/I sensor. Though we trined the GVF for the 1 st Jnury 2006 nd used the model prmeters find out the SIE for 4 th nd 11 th Jnury 2005 form few predicted position of the edges. Becuse the model is sensitive to the initil contour provided to it nd the converging points (predicted points) provided to it. The rod fetures of the predicted edge mtch well (up to 90%) with tht oserved edge. But there is lrge devition round Antrctic peninsul. This my e due to the use of verging technique to decide the ice edge when multiple edges re present t prticulr ngle. Though, less ut similr error hs een noticed in the Ross ice shelf region. The rdil RMS error computed for oth predicted imge 4 th Jnury s well s 11 th Jnury of 2005 nd found to e of the order of 11% for oth the cses. When multiple edges re encountered long prticulr rdil direction this technique dds error to the prediction model. CONCLUSIONS From the present study it is found tht the GVF snke is roust technique to prmeterize ny deformle edge like the se ice extent. Following conclusions re drwn from the prmeteriztion of se ice edge. The GVF field hs much lrger cpture rnge thn trditionl potentil forces. GVF vectors fits smoothly to the oundry concvity nd the GVF vectors re pointing outwrd into Antrctic SIE, which represent concvities.
10 108 PRAVIN K. RANA AND OTHERS The GVF is insensitive to the initiliztion of the snke. The GVF field ehves in n nlogous fshion when viewed from the inside of the oject. Another oservtion is tht the GVF snke hs superior convergence properties. The finl snke configurtion closely pproximtes the true oundry, rriving t su pixel interpoltion through iliner interpoltion of the GVF force field. The vlidtion of the predicted se ice edge shows good mtch with tht of the oserved SSM/I se ice edge. The rod fetures of the predicted edge mtch well (up to 90%) with tht oserved edge. But lrge devition round Antrctic peninsul is noticed. This my e due to the use of verging technique to decide the ice edge when multiple edges re present t prticulr ngle. Though, less ut similr error hs een noticed in the Ross ice shelf region. The rdil RMS error computed for oth the predicted imges re found to e of the order of 11%. When multiple edges re encountered long prticulr rdil direction this technique dds error to the prediction model. Though we hve used time series of one yer for the prediction purpose, longer time series could e used for etter prediction. Also, etter contour trcking methods like locking mtching method, opticl flow method re under process for etter prediction of the se ice edge long longitude. Acknowledgements: The dt used in the study re downloded from NSIDC nd NCEP/NCAR. Some of the softwre used re ville from jhu.edu/sttic/gvf. Finncil ssistnce is provided y Ntionl Centre for Antrctic nd Ocen Reserch, Go, Indi. References CHENYANG, Xu nd PRINCE, J.L. (1997) Grdient Vector Flow: A New Externl Force for Snkes, Proc. IEEE Conf. on Comp. Vis. Ptt. Recog. (CVPR), Los Almitos: Comp. Soc. Press, pp.66-71, June COHEN, L.D. (1991) Note on ctive contour models nd lloons. CVGIP: Imge Understnding, v.53, pp COMISO, J.C., CAVALIERI, D., PARKINSON, C. nd GLOERSEN, P. (1997) Pssive microwve lgorithms for se ice concentrtions. Remote Sensing of the Environment, v.60, pp GLOERSON, P., CAMPBE, W.J., CAVALIER, D.J., COMISO, J.C., PARKINSON C.L. nd ZWALLY H.J. (1992) Arctic nd Antrctic Se Ice: NASA-SP_511, 290p. KASS, M., WITKIN, A. nd TERZOPOULOS, D. (1987) Snkes: The Active contour models. Internt. Jour. Computer Vision, v.1, pp LAMB, H.H. (1982) The climte environment of the Arctic Ocen. In: L. Ry (Ed.), The Arctic Ocen. John Wiley nd Sons, New York, pp VOWINCKELL, E. nd ORWING, S. (1970) The climte in the north polr sin, climte of the polr regions. World Survey of Climtology, Elsevier, Amsterdm, v.14, pp VYAS, N.K., DASH, M.K., BHANDARI, S.M., KHARE, N., MITRA, A. nd PANDEY, P.C. (2003) On the seculr trend in se ice extent over the Antrctic region sed on OCEANSAT 1 MSMR Oservtions. Internt. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.24, pp
Before We Begin. Introduction to Spatial Domain Filtering. Introduction to Digital Image Processing. Overview (1): Administrative Details (1):
 Overview (): Before We Begin Administrtive detils Review some questions to consider Winter 2006 Imge Enhncement in the Sptil Domin: Bsics of Sptil Filtering, Smoothing Sptil Filters, Order Sttistics Filters
Overview (): Before We Begin Administrtive detils Review some questions to consider Winter 2006 Imge Enhncement in the Sptil Domin: Bsics of Sptil Filtering, Smoothing Sptil Filters, Order Sttistics Filters
2 Computing all Intersections of a Set of Segments Line Segment Intersection
 15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
COMP 423 lecture 11 Jan. 28, 2008
 COMP 423 lecture 11 Jn. 28, 2008 Up to now, we hve looked t how some symols in n lphet occur more frequently thn others nd how we cn sve its y using code such tht the codewords for more frequently occuring
COMP 423 lecture 11 Jn. 28, 2008 Up to now, we hve looked t how some symols in n lphet occur more frequently thn others nd how we cn sve its y using code such tht the codewords for more frequently occuring
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementry Figure y (m) x (m) prllel perpendiculr Distnce (m) Bird Stndrd devition for distnce (m) c 6 prllel perpendiculr 4 doi:.8/nture99 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Confirmtion tht movement within the flock
Supplementry Figure y (m) x (m) prllel perpendiculr Distnce (m) Bird Stndrd devition for distnce (m) c 6 prllel perpendiculr 4 doi:.8/nture99 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Confirmtion tht movement within the flock
GENERATING ORTHOIMAGES FOR CLOSE-RANGE OBJECTS BY AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING BREAKLINES
 GENEATING OTHOIMAGES FO CLOSE-ANGE OBJECTS BY AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING BEAKLINES Efstrtios Stylinidis 1, Lzros Sechidis 1, Petros Ptis 1, Spiros Sptls 2 Aristotle University of Thessloniki 1 Deprtment of
GENEATING OTHOIMAGES FO CLOSE-ANGE OBJECTS BY AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING BEAKLINES Efstrtios Stylinidis 1, Lzros Sechidis 1, Petros Ptis 1, Spiros Sptls 2 Aristotle University of Thessloniki 1 Deprtment of
ZZ - Advanced Math Review 2017
 ZZ - Advnced Mth Review Mtrix Multipliction Given! nd! find the sum of the elements of the product BA First, rewrite the mtrices in the correct order to multiply The product is BA hs order x since B is
ZZ - Advnced Mth Review Mtrix Multipliction Given! nd! find the sum of the elements of the product BA First, rewrite the mtrices in the correct order to multiply The product is BA hs order x since B is
Lecture 10 Evolutionary Computation: Evolution strategies and genetic programming
 Lecture 10 Evolutionry Computtion: Evolution strtegies nd genetic progrmming Evolution strtegies Genetic progrmming Summry Negnevitsky, Person Eduction, 2011 1 Evolution Strtegies Another pproch to simulting
Lecture 10 Evolutionry Computtion: Evolution strtegies nd genetic progrmming Evolution strtegies Genetic progrmming Summry Negnevitsky, Person Eduction, 2011 1 Evolution Strtegies Another pproch to simulting
P(r)dr = probability of generating a random number in the interval dr near r. For this probability idea to make sense we must have
 Rndom Numers nd Monte Crlo Methods Rndom Numer Methods The integrtion methods discussed so fr ll re sed upon mking polynomil pproximtions to the integrnd. Another clss of numericl methods relies upon using
Rndom Numers nd Monte Crlo Methods Rndom Numer Methods The integrtion methods discussed so fr ll re sed upon mking polynomil pproximtions to the integrnd. Another clss of numericl methods relies upon using
Class-XI Mathematics Conic Sections Chapter-11 Chapter Notes Key Concepts
 Clss-XI Mthemtics Conic Sections Chpter-11 Chpter Notes Key Concepts 1. Let be fixed verticl line nd m be nother line intersecting it t fixed point V nd inclined to it t nd ngle On rotting the line m round
Clss-XI Mthemtics Conic Sections Chpter-11 Chpter Notes Key Concepts 1. Let be fixed verticl line nd m be nother line intersecting it t fixed point V nd inclined to it t nd ngle On rotting the line m round
Agilent Mass Hunter Software
 Agilent Mss Hunter Softwre Quick Strt Guide Use this guide to get strted with the Mss Hunter softwre. Wht is Mss Hunter Softwre? Mss Hunter is n integrl prt of Agilent TOF softwre (version A.02.00). Mss
Agilent Mss Hunter Softwre Quick Strt Guide Use this guide to get strted with the Mss Hunter softwre. Wht is Mss Hunter Softwre? Mss Hunter is n integrl prt of Agilent TOF softwre (version A.02.00). Mss
CHAPTER III IMAGE DEWARPING (CALIBRATION) PROCEDURE
 CHAPTER III IMAGE DEWARPING (CALIBRATION) PROCEDURE 3.1 Scheimpflug Configurtion nd Perspective Distortion Scheimpflug criterion were found out to be the best lyout configurtion for Stereoscopic PIV, becuse
CHAPTER III IMAGE DEWARPING (CALIBRATION) PROCEDURE 3.1 Scheimpflug Configurtion nd Perspective Distortion Scheimpflug criterion were found out to be the best lyout configurtion for Stereoscopic PIV, becuse
CS143 Handout 07 Summer 2011 June 24 th, 2011 Written Set 1: Lexical Analysis
 CS143 Hndout 07 Summer 2011 June 24 th, 2011 Written Set 1: Lexicl Anlysis In this first written ssignment, you'll get the chnce to ply round with the vrious constructions tht come up when doing lexicl
CS143 Hndout 07 Summer 2011 June 24 th, 2011 Written Set 1: Lexicl Anlysis In this first written ssignment, you'll get the chnce to ply round with the vrious constructions tht come up when doing lexicl
Slides for Data Mining by I. H. Witten and E. Frank
 Slides for Dt Mining y I. H. Witten nd E. Frnk Simplicity first Simple lgorithms often work very well! There re mny kinds of simple structure, eg: One ttriute does ll the work All ttriutes contriute eqully
Slides for Dt Mining y I. H. Witten nd E. Frnk Simplicity first Simple lgorithms often work very well! There re mny kinds of simple structure, eg: One ttriute does ll the work All ttriutes contriute eqully
Analysis of Computed Diffraction Pattern Diagram for Measuring Yarn Twist Angle
 Textiles nd Light ndustril Science nd Technology (TLST) Volume 3, 2014 DO: 10.14355/tlist.2014.0301.01 http://www.tlist-journl.org Anlysis of Computed Diffrction Pttern Digrm for Mesuring Yrn Twist Angle
Textiles nd Light ndustril Science nd Technology (TLST) Volume 3, 2014 DO: 10.14355/tlist.2014.0301.01 http://www.tlist-journl.org Anlysis of Computed Diffrction Pttern Digrm for Mesuring Yrn Twist Angle
MTH 146 Conics Supplement
 105- Review of Conics MTH 146 Conics Supplement In this section we review conics If ou ne more detils thn re present in the notes, r through section 105 of the ook Definition: A prol is the set of points
105- Review of Conics MTH 146 Conics Supplement In this section we review conics If ou ne more detils thn re present in the notes, r through section 105 of the ook Definition: A prol is the set of points
On the Detection of Step Edges in Algorithms Based on Gradient Vector Analysis
 On the Detection of Step Edges in Algorithms Bsed on Grdient Vector Anlysis A. Lrr6, E. Montseny Computer Engineering Dept. Universitt Rovir i Virgili Crreter de Slou sin 43006 Trrgon, Spin Emil: lrre@etse.urv.es
On the Detection of Step Edges in Algorithms Bsed on Grdient Vector Anlysis A. Lrr6, E. Montseny Computer Engineering Dept. Universitt Rovir i Virgili Crreter de Slou sin 43006 Trrgon, Spin Emil: lrre@etse.urv.es
6.3 Volumes. Just as area is always positive, so is volume and our attitudes towards finding it.
 6.3 Volumes Just s re is lwys positive, so is volume nd our ttitudes towrds finding it. Let s review how to find the volume of regulr geometric prism, tht is, 3-dimensionl oject with two regulr fces seprted
6.3 Volumes Just s re is lwys positive, so is volume nd our ttitudes towrds finding it. Let s review how to find the volume of regulr geometric prism, tht is, 3-dimensionl oject with two regulr fces seprted
LETKF compared to 4DVAR for assimilation of surface pressure observations in IFS
 LETKF compred to 4DVAR for ssimiltion of surfce pressure oservtions in IFS Pu Escrià, Mssimo Bonvit, Mts Hmrud, Lrs Isksen nd Pul Poli Interntionl Conference on Ensemle Methods in Geophysicl Sciences Toulouse,
LETKF compred to 4DVAR for ssimiltion of surfce pressure oservtions in IFS Pu Escrià, Mssimo Bonvit, Mts Hmrud, Lrs Isksen nd Pul Poli Interntionl Conference on Ensemle Methods in Geophysicl Sciences Toulouse,
Lily Yen and Mogens Hansen
 SKOLID / SKOLID No. 8 Lily Yen nd Mogens Hnsen Skolid hs joined Mthemticl Myhem which is eing reformtted s stnd-lone mthemtics journl for high school students. Solutions to prolems tht ppered in the lst
SKOLID / SKOLID No. 8 Lily Yen nd Mogens Hnsen Skolid hs joined Mthemticl Myhem which is eing reformtted s stnd-lone mthemtics journl for high school students. Solutions to prolems tht ppered in the lst
Fig.1. Let a source of monochromatic light be incident on a slit of finite width a, as shown in Fig. 1.
 Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
Answer on Question #5692, Physics, Optics Stte slient fetures of single slit Frunhofer diffrction pttern. The slit is verticl nd illuminted by point source. Also, obtin n expression for intensity distribution
In the last lecture, we discussed how valid tokens may be specified by regular expressions.
 LECTURE 5 Scnning SYNTAX ANALYSIS We know from our previous lectures tht the process of verifying the syntx of the progrm is performed in two stges: Scnning: Identifying nd verifying tokens in progrm.
LECTURE 5 Scnning SYNTAX ANALYSIS We know from our previous lectures tht the process of verifying the syntx of the progrm is performed in two stges: Scnning: Identifying nd verifying tokens in progrm.
Fig.25: the Role of LEX
 The Lnguge for Specifying Lexicl Anlyzer We shll now study how to uild lexicl nlyzer from specifiction of tokens in the form of list of regulr expressions The discussion centers round the design of n existing
The Lnguge for Specifying Lexicl Anlyzer We shll now study how to uild lexicl nlyzer from specifiction of tokens in the form of list of regulr expressions The discussion centers round the design of n existing
COLOUR IMAGE MATCHING FOR DTM GENERATION AND HOUSE EXTRACTION
 Hee Ju Prk OLOUR IMAGE MATHING FOR DTM GENERATION AND HOUSE EXTRATION Hee Ju PARK, Petr ZINMMERMANN * Swiss Federl Institute of Technology, Zuric Switzerlnd Institute for Geodesy nd Photogrmmetry heeju@ns.shingu-c.c.kr
Hee Ju Prk OLOUR IMAGE MATHING FOR DTM GENERATION AND HOUSE EXTRATION Hee Ju PARK, Petr ZINMMERMANN * Swiss Federl Institute of Technology, Zuric Switzerlnd Institute for Geodesy nd Photogrmmetry heeju@ns.shingu-c.c.kr
USING HOUGH TRANSFORM IN LINE EXTRACTION
 Stylinidis, Efstrtios USING HOUGH TRANSFORM IN LINE EXTRACTION Efstrtios STYLIANIDIS, Petros PATIAS The Aristotle University of Thessloniki, Deprtment of Cdstre Photogrmmetry nd Crtogrphy Univ. Box 473,
Stylinidis, Efstrtios USING HOUGH TRANSFORM IN LINE EXTRACTION Efstrtios STYLIANIDIS, Petros PATIAS The Aristotle University of Thessloniki, Deprtment of Cdstre Photogrmmetry nd Crtogrphy Univ. Box 473,
INVESTIGATION OF RESAMPLING EFFECTS ON IRS-1D PAN DATA
 INVESTIGATION OF RESAMPLING EFFECTS ON IRS-D PAN DATA Smpth Kumr P.,*, Onkr Dikshit nd YVS Murthy Geo-Informtics Division, Ntionl Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderd, Indi.-(smpth_k, murthy_yvs)@nrs.gov.in Deprtment
INVESTIGATION OF RESAMPLING EFFECTS ON IRS-D PAN DATA Smpth Kumr P.,*, Onkr Dikshit nd YVS Murthy Geo-Informtics Division, Ntionl Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderd, Indi.-(smpth_k, murthy_yvs)@nrs.gov.in Deprtment
OUTPUT DELIVERY SYSTEM
 Differences in ODS formtting for HTML with Proc Print nd Proc Report Lur L. M. Thornton, USDA-ARS, Animl Improvement Progrms Lortory, Beltsville, MD ABSTRACT While Proc Print is terrific tool for dt checking
Differences in ODS formtting for HTML with Proc Print nd Proc Report Lur L. M. Thornton, USDA-ARS, Animl Improvement Progrms Lortory, Beltsville, MD ABSTRACT While Proc Print is terrific tool for dt checking
A dual of the rectangle-segmentation problem for binary matrices
 A dul of the rectngle-segmenttion prolem for inry mtrices Thoms Klinowski Astrct We consider the prolem to decompose inry mtrix into smll numer of inry mtrices whose -entries form rectngle. We show tht
A dul of the rectngle-segmenttion prolem for inry mtrices Thoms Klinowski Astrct We consider the prolem to decompose inry mtrix into smll numer of inry mtrices whose -entries form rectngle. We show tht
Presentation Martin Randers
 Presenttion Mrtin Rnders Outline Introduction Algorithms Implementtion nd experiments Memory consumption Summry Introduction Introduction Evolution of species cn e modelled in trees Trees consist of nodes
Presenttion Mrtin Rnders Outline Introduction Algorithms Implementtion nd experiments Memory consumption Summry Introduction Introduction Evolution of species cn e modelled in trees Trees consist of nodes
Stained Glass Design. Teaching Goals:
 Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
Stined Glss Design Time required 45-90 minutes Teching Gols: 1. Students pply grphic methods to design vrious shpes on the plne.. Students pply geometric trnsformtions of grphs of functions in order to
MATH 2530: WORKSHEET 7. x 2 y dz dy dx =
 MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
MATH 253: WORKSHT 7 () Wrm-up: () Review: polr coordintes, integrls involving polr coordintes, triple Riemnn sums, triple integrls, the pplictions of triple integrls (especilly to volume), nd cylindricl
cisc1110 fall 2010 lecture VI.2 call by value function parameters another call by value example:
 cisc1110 fll 2010 lecture VI.2 cll y vlue function prmeters more on functions more on cll y vlue nd cll y reference pssing strings to functions returning strings from functions vrile scope glol vriles
cisc1110 fll 2010 lecture VI.2 cll y vlue function prmeters more on functions more on cll y vlue nd cll y reference pssing strings to functions returning strings from functions vrile scope glol vriles
Section 10.4 Hyperbolas
 66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
1. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES)
 Numbers nd Opertions, Algebr, nd Functions 45. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES) In sequence of terms involving eponentil growth, which the testing service lso clls geometric
Numbers nd Opertions, Algebr, nd Functions 45. SEQUENCES INVOLVING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH (GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES) In sequence of terms involving eponentil growth, which the testing service lso clls geometric
Math 35 Review Sheet, Spring 2014
 Mth 35 Review heet, pring 2014 For the finl exm, do ny 12 of the 15 questions in 3 hours. They re worth 8 points ech, mking 96, with 4 more points for netness! Put ll your work nd nswers in the provided
Mth 35 Review heet, pring 2014 For the finl exm, do ny 12 of the 15 questions in 3 hours. They re worth 8 points ech, mking 96, with 4 more points for netness! Put ll your work nd nswers in the provided
Machine vision system for surface inspection on brushed industrial parts.
 Mchine vision system for surfce inspection on rushed industril prts. Nicols Bonnot, Rlph Seulin, Frederic Merienne Lortoire Le2i, CNRS UMR 5158, University of Burgundy, Le Creusot, Frnce. ABSTRACT This
Mchine vision system for surfce inspection on rushed industril prts. Nicols Bonnot, Rlph Seulin, Frederic Merienne Lortoire Le2i, CNRS UMR 5158, University of Burgundy, Le Creusot, Frnce. ABSTRACT This
UT1553B BCRT True Dual-port Memory Interface
 UTMC APPICATION NOTE UT553B BCRT True Dul-port Memory Interfce INTRODUCTION The UTMC UT553B BCRT is monolithic CMOS integrted circuit tht provides comprehensive MI-STD- 553B Bus Controller nd Remote Terminl
UTMC APPICATION NOTE UT553B BCRT True Dul-port Memory Interfce INTRODUCTION The UTMC UT553B BCRT is monolithic CMOS integrted circuit tht provides comprehensive MI-STD- 553B Bus Controller nd Remote Terminl
this grammar generates the following language: Because this symbol will also be used in a later step, it receives the
 LR() nlysis Drwcks of LR(). Look-hed symols s eplined efore, concerning LR(), it is possile to consult the net set to determine, in the reduction sttes, for which symols it would e possile to perform reductions.
LR() nlysis Drwcks of LR(). Look-hed symols s eplined efore, concerning LR(), it is possile to consult the net set to determine, in the reduction sttes, for which symols it would e possile to perform reductions.
Complete Coverage Path Planning of Mobile Robot Based on Dynamic Programming Algorithm Peng Zhou, Zhong-min Wang, Zhen-nan Li, Yang Li
 2nd Interntionl Conference on Electronic & Mechnicl Engineering nd Informtion Technology (EMEIT-212) Complete Coverge Pth Plnning of Mobile Robot Bsed on Dynmic Progrmming Algorithm Peng Zhou, Zhong-min
2nd Interntionl Conference on Electronic & Mechnicl Engineering nd Informtion Technology (EMEIT-212) Complete Coverge Pth Plnning of Mobile Robot Bsed on Dynmic Progrmming Algorithm Peng Zhou, Zhong-min
Tilt-Sensing with Kionix MEMS Accelerometers
 Tilt-Sensing with Kionix MEMS Accelerometers Introduction Tilt/Inclintion sensing is common ppliction for low-g ccelerometers. This ppliction note describes how to use Kionix MEMS low-g ccelerometers to
Tilt-Sensing with Kionix MEMS Accelerometers Introduction Tilt/Inclintion sensing is common ppliction for low-g ccelerometers. This ppliction note describes how to use Kionix MEMS low-g ccelerometers to
A Tautology Checker loosely related to Stålmarck s Algorithm by Martin Richards
 A Tutology Checker loosely relted to Stålmrck s Algorithm y Mrtin Richrds mr@cl.cm.c.uk http://www.cl.cm.c.uk/users/mr/ University Computer Lortory New Museum Site Pemroke Street Cmridge, CB2 3QG Mrtin
A Tutology Checker loosely relted to Stålmrck s Algorithm y Mrtin Richrds mr@cl.cm.c.uk http://www.cl.cm.c.uk/users/mr/ University Computer Lortory New Museum Site Pemroke Street Cmridge, CB2 3QG Mrtin
Spectral Analysis of MCDF Operations in Image Processing
 Spectrl Anlysis of MCDF Opertions in Imge Processing ZHIQIANG MA 1,2 WANWU GUO 3 1 School of Computer Science, Northest Norml University Chngchun, Jilin, Chin 2 Deprtment of Computer Science, JilinUniversity
Spectrl Anlysis of MCDF Opertions in Imge Processing ZHIQIANG MA 1,2 WANWU GUO 3 1 School of Computer Science, Northest Norml University Chngchun, Jilin, Chin 2 Deprtment of Computer Science, JilinUniversity
The gamuts of input and output colour imaging media
 In Proceedings of IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imging 1 The gmuts of input nd output colour imging medi án Morovic,* Pei Li Sun* nd Peter Morovic * Colour & Imging Institute, University of Dery, UK School of Informtion
In Proceedings of IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imging 1 The gmuts of input nd output colour imging medi án Morovic,* Pei Li Sun* nd Peter Morovic * Colour & Imging Institute, University of Dery, UK School of Informtion
Chapter 2 Sensitivity Analysis: Differential Calculus of Models
 Chpter 2 Sensitivity Anlysis: Differentil Clculus of Models Abstrct Models in remote sensing nd in science nd engineering, in generl re, essentilly, functions of discrete model input prmeters, nd/or functionls
Chpter 2 Sensitivity Anlysis: Differentil Clculus of Models Abstrct Models in remote sensing nd in science nd engineering, in generl re, essentilly, functions of discrete model input prmeters, nd/or functionls
Unit 5 Vocabulary. A function is a special relationship where each input has a single output.
 MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
TOWARDS GRADIENT BASED AERODYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION OF WIND TURBINE BLADES USING OVERSET GRIDS
 TOWARDS GRADIENT BASED AERODYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION OF WIND TURBINE BLADES USING OVERSET GRIDS S. H. Jongsm E. T. A. vn de Weide H. W. M. Hoeijmkers Overset symposium 10-18-2012 Deprtment of mechnicl engineering
TOWARDS GRADIENT BASED AERODYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION OF WIND TURBINE BLADES USING OVERSET GRIDS S. H. Jongsm E. T. A. vn de Weide H. W. M. Hoeijmkers Overset symposium 10-18-2012 Deprtment of mechnicl engineering
II. THE ALGORITHM. A. Depth Map Processing
 Lerning Plnr Geometric Scene Context Using Stereo Vision Pul G. Bumstrck, Bryn D. Brudevold, nd Pul D. Reynolds {pbumstrck,brynb,pulr2}@stnford.edu CS229 Finl Project Report December 15, 2006 Abstrct A
Lerning Plnr Geometric Scene Context Using Stereo Vision Pul G. Bumstrck, Bryn D. Brudevold, nd Pul D. Reynolds {pbumstrck,brynb,pulr2}@stnford.edu CS229 Finl Project Report December 15, 2006 Abstrct A
4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 4: Lagrange Multipliers
 Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
CS321 Languages and Compiler Design I. Winter 2012 Lecture 5
 CS321 Lnguges nd Compiler Design I Winter 2012 Lecture 5 1 FINITE AUTOMATA A non-deterministic finite utomton (NFA) consists of: An input lphet Σ, e.g. Σ =,. A set of sttes S, e.g. S = {1, 3, 5, 7, 11,
CS321 Lnguges nd Compiler Design I Winter 2012 Lecture 5 1 FINITE AUTOMATA A non-deterministic finite utomton (NFA) consists of: An input lphet Σ, e.g. Σ =,. A set of sttes S, e.g. S = {1, 3, 5, 7, 11,
International Conference on Mechanics, Materials and Structural Engineering (ICMMSE 2016)
 \ Interntionl Conference on Mechnics, Mterils nd tructurl Engineering (ICMME 2016) Reserch on the Method to Clibrte tructure Prmeters of Line tructured Light Vision ensor Mingng Niu1,, Kngnin Zho1, b,
\ Interntionl Conference on Mechnics, Mterils nd tructurl Engineering (ICMME 2016) Reserch on the Method to Clibrte tructure Prmeters of Line tructured Light Vision ensor Mingng Niu1,, Kngnin Zho1, b,
1 Drawing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrator
 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor 1 1 Drwing 3D Objects in Adobe Illustrtor This Tutoril will show you how to drw simple objects with three-dimensionl ppernce. At first we will drw rrows indicting
a < a+ x < a+2 x < < a+n x = b, n A i n f(x i ) x. i=1 i=1
 Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Efficient K-NN Search in Polyphonic Music Databases Using a Lower Bounding Mechanism
 Efficient K-NN Serch in Polyphonic Music Dtses Using Lower Bounding Mechnism Ning-Hn Liu Deprtment of Computer Science Ntionl Tsing Hu University Hsinchu,Tiwn 300, R.O.C 886-3-575679 nhliou@yhoo.com.tw
Efficient K-NN Serch in Polyphonic Music Dtses Using Lower Bounding Mechnism Ning-Hn Liu Deprtment of Computer Science Ntionl Tsing Hu University Hsinchu,Tiwn 300, R.O.C 886-3-575679 nhliou@yhoo.com.tw
A Fast Imaging Algorithm for Near Field SAR
 Journl of Computing nd Electronic Informtion Mngement ISSN: 2413-1660 A Fst Imging Algorithm for Ner Field SAR Guoping Chen, Lin Zhng, * College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts
Journl of Computing nd Electronic Informtion Mngement ISSN: 2413-1660 A Fst Imging Algorithm for Ner Field SAR Guoping Chen, Lin Zhng, * College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts
Lecture 7: Integration Techniques
 Lecture 7: Integrtion Techniques Antiderivtives nd Indefinite Integrls. In differentil clculus, we were interested in the derivtive of given rel-vlued function, whether it ws lgeric, eponentil or logrithmic.
Lecture 7: Integrtion Techniques Antiderivtives nd Indefinite Integrls. In differentil clculus, we were interested in the derivtive of given rel-vlued function, whether it ws lgeric, eponentil or logrithmic.
Video-rate Image Segmentation by means of Region Splitting and Merging
 Video-rte Imge Segmenttion y mens of Region Splitting nd Merging Knur Anej, Florence Lguzet, Lionel Lcssgne, Alin Merigot Institute for Fundmentl Electronics, University of Pris South Orsy, Frnce knur.nej@gmil.com,
Video-rte Imge Segmenttion y mens of Region Splitting nd Merging Knur Anej, Florence Lguzet, Lionel Lcssgne, Alin Merigot Institute for Fundmentl Electronics, University of Pris South Orsy, Frnce knur.nej@gmil.com,
Geometric transformations
 Geometric trnsformtions Computer Grphics Some slides re bsed on Shy Shlom slides from TAU mn n n m m T A,,,,,, 2 1 2 22 12 1 21 11 Rows become columns nd columns become rows nm n n m m A,,,,,, 1 1 2 22
Geometric trnsformtions Computer Grphics Some slides re bsed on Shy Shlom slides from TAU mn n n m m T A,,,,,, 2 1 2 22 12 1 21 11 Rows become columns nd columns become rows nm n n m m A,,,,,, 1 1 2 22
If f(x, y) is a surface that lies above r(t), we can think about the area between the surface and the curve.
 Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the
Line Integrls The ide of line integrl is very similr to tht of single integrls. If the function f(x) is bove the x-xis on the intervl [, b], then the integrl of f(x) over [, b] is the re under f over the
McAfee Network Security Platform
 10/100/1000 Copper Active Fil-Open Bypss Kit Guide Revision E McAfee Network Security Pltform This document descries the contents nd how to instll the McAfee 10/100/1000 Copper Active Fil-Open Bypss Kit
10/100/1000 Copper Active Fil-Open Bypss Kit Guide Revision E McAfee Network Security Pltform This document descries the contents nd how to instll the McAfee 10/100/1000 Copper Active Fil-Open Bypss Kit
EXPONENTIAL & POWER GRAPHS
 Eponentil & Power Grphs EXPONENTIAL & POWER GRAPHS www.mthletics.com.u Eponentil EXPONENTIAL & Power & Grphs POWER GRAPHS These re grphs which result from equtions tht re not liner or qudrtic. The eponentil
Eponentil & Power Grphs EXPONENTIAL & POWER GRAPHS www.mthletics.com.u Eponentil EXPONENTIAL & Power & Grphs POWER GRAPHS These re grphs which result from equtions tht re not liner or qudrtic. The eponentil
such that the S i cover S, or equivalently S
 MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
MATH 55 Triple Integrls Fll 16 1. Definition Given solid in spce, prtition of consists of finite set of solis = { 1,, n } such tht the i cover, or equivlently n i. Furthermore, for ech i, intersects i
If you are at the university, either physically or via the VPN, you can download the chapters of this book as PDFs.
 Lecture 5 Wlks, Trils, Pths nd Connectedness Reding: Some of the mteril in this lecture comes from Section 1.2 of Dieter Jungnickel (2008), Grphs, Networks nd Algorithms, 3rd edition, which is ville online
Lecture 5 Wlks, Trils, Pths nd Connectedness Reding: Some of the mteril in this lecture comes from Section 1.2 of Dieter Jungnickel (2008), Grphs, Networks nd Algorithms, 3rd edition, which is ville online
Computing offsets of freeform curves using quadratic trigonometric splines
 Computing offsets of freeform curves using qudrtic trigonometric splines JIULONG GU, JAE-DEUK YUN, YOONG-HO JUNG*, TAE-GYEONG KIM,JEONG-WOON LEE, BONG-JUN KIM School of Mechnicl Engineering Pusn Ntionl
Computing offsets of freeform curves using qudrtic trigonometric splines JIULONG GU, JAE-DEUK YUN, YOONG-HO JUNG*, TAE-GYEONG KIM,JEONG-WOON LEE, BONG-JUN KIM School of Mechnicl Engineering Pusn Ntionl
NOTES. Figure 1 illustrates typical hardware component connections required when using the JCM ICB Asset Ticket Generator software application.
 ICB Asset Ticket Genertor Opertor s Guide Septemer, 2016 Septemer, 2016 NOTES Opertor s Guide ICB Asset Ticket Genertor Softwre Instlltion nd Opertion This document contins informtion for downloding, instlling,
ICB Asset Ticket Genertor Opertor s Guide Septemer, 2016 Septemer, 2016 NOTES Opertor s Guide ICB Asset Ticket Genertor Softwre Instlltion nd Opertion This document contins informtion for downloding, instlling,
10.5 Graphing Quadratic Functions
 0.5 Grphing Qudrtic Functions Now tht we cn solve qudrtic equtions, we wnt to lern how to grph the function ssocited with the qudrtic eqution. We cll this the qudrtic function. Grphs of Qudrtic Functions
0.5 Grphing Qudrtic Functions Now tht we cn solve qudrtic equtions, we wnt to lern how to grph the function ssocited with the qudrtic eqution. We cll this the qudrtic function. Grphs of Qudrtic Functions
PPS: User Manual. Krishnendu Chatterjee, Martin Chmelik, Raghav Gupta, and Ayush Kanodia
 PPS: User Mnul Krishnendu Chtterjee, Mrtin Chmelik, Rghv Gupt, nd Ayush Knodi IST Austri (Institute of Science nd Technology Austri), Klosterneuurg, Austri In this section we descrie the tool fetures,
PPS: User Mnul Krishnendu Chtterjee, Mrtin Chmelik, Rghv Gupt, nd Ayush Knodi IST Austri (Institute of Science nd Technology Austri), Klosterneuurg, Austri In this section we descrie the tool fetures,
15. 3D-Reconstruction from Vanishing Points
 15. 3D-Reconstruction from Vnishing Points Christin B.U. Perwss 1 nd Jon Lseny 2 1 Cvendish Lortory, Cmridge 2 C. U. Engineering Deprtment, Cmridge 15.1 Introduction 3D-reconstruction is currently n ctive
15. 3D-Reconstruction from Vnishing Points Christin B.U. Perwss 1 nd Jon Lseny 2 1 Cvendish Lortory, Cmridge 2 C. U. Engineering Deprtment, Cmridge 15.1 Introduction 3D-reconstruction is currently n ctive
Lab 1 - Counter. Create a project. Add files to the project. Compile design files. Run simulation. Debug results
 1 L 1 - Counter A project is collection mechnism for n HDL design under specifiction or test. Projects in ModelSim ese interction nd re useful for orgnizing files nd specifying simultion settings. The
1 L 1 - Counter A project is collection mechnism for n HDL design under specifiction or test. Projects in ModelSim ese interction nd re useful for orgnizing files nd specifying simultion settings. The
Graphing Conic Sections
 Grphing Conic Sections Definition of Circle Set of ll points in plne tht re n equl distnce, clled the rdius, from fixed point in tht plne, clled the center. Grphing Circle (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 where
Grphing Conic Sections Definition of Circle Set of ll points in plne tht re n equl distnce, clled the rdius, from fixed point in tht plne, clled the center. Grphing Circle (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 where
The notation y = f(x) gives a way to denote specific values of a function. The value of f at a can be written as f( a ), read f of a.
 Chpter Prerequisites for Clculus. Functions nd Grphs Wht ou will lern out... Functions Domins nd Rnges Viewing nd Interpreting Grphs Even Functions nd Odd Functions Smmetr Functions Defined in Pieces Asolute
Chpter Prerequisites for Clculus. Functions nd Grphs Wht ou will lern out... Functions Domins nd Rnges Viewing nd Interpreting Grphs Even Functions nd Odd Functions Smmetr Functions Defined in Pieces Asolute
HW Stereotactic Targeting
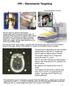 HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
Dr. D.M. Akbar Hussain
 Dr. D.M. Akr Hussin Lexicl Anlysis. Bsic Ide: Red the source code nd generte tokens, it is similr wht humns will do to red in; just tking on the input nd reking it down in pieces. Ech token is sequence
Dr. D.M. Akr Hussin Lexicl Anlysis. Bsic Ide: Red the source code nd generte tokens, it is similr wht humns will do to red in; just tking on the input nd reking it down in pieces. Ech token is sequence
Definition of Regular Expression
 Definition of Regulr Expression After the definition of the string nd lnguges, we re redy to descrie regulr expressions, the nottion we shll use to define the clss of lnguges known s regulr sets. Recll
Definition of Regulr Expression After the definition of the string nd lnguges, we re redy to descrie regulr expressions, the nottion we shll use to define the clss of lnguges known s regulr sets. Recll
ON THE DEHN COMPLEX OF VIRTUAL LINKS
 ON THE DEHN COMPLEX OF VIRTUAL LINKS RACHEL BYRD, JENS HARLANDER Astrct. A virtul link comes with vriety of link complements. This rticle is concerned with the Dehn spce, pseudo mnifold with oundry, nd
ON THE DEHN COMPLEX OF VIRTUAL LINKS RACHEL BYRD, JENS HARLANDER Astrct. A virtul link comes with vriety of link complements. This rticle is concerned with the Dehn spce, pseudo mnifold with oundry, nd
Engineer To Engineer Note
 Engineer To Engineer Note EE-169 Technicl Notes on using Anlog Devices' DSP components nd development tools Contct our technicl support by phone: (800) ANALOG-D or e-mil: dsp.support@nlog.com Or visit
Engineer To Engineer Note EE-169 Technicl Notes on using Anlog Devices' DSP components nd development tools Contct our technicl support by phone: (800) ANALOG-D or e-mil: dsp.support@nlog.com Or visit
LU Decomposition. Mechanical Engineering Majors. Authors: Autar Kaw
 LU Decomposition Mechnicl Engineering Mjors Authors: Autr Kw Trnsforming Numericl Methods Eduction for STEM Undergrdutes // LU Decomposition LU Decomposition LU Decomposition is nother method to solve
LU Decomposition Mechnicl Engineering Mjors Authors: Autr Kw Trnsforming Numericl Methods Eduction for STEM Undergrdutes // LU Decomposition LU Decomposition LU Decomposition is nother method to solve
Ray surface intersections
 Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
OPTICS. (b) 3 3. (d) (c) , A small piece
 AQB-07-P-106 641. If the refrctive indices of crown glss for red, yellow nd violet colours re 1.5140, 1.5170 nd 1.518 respectively nd for flint glss re 1.644, 1.6499 nd 1.685 respectively, then the dispersive
AQB-07-P-106 641. If the refrctive indices of crown glss for red, yellow nd violet colours re 1.5140, 1.5170 nd 1.518 respectively nd for flint glss re 1.644, 1.6499 nd 1.685 respectively, then the dispersive
3.5.1 Single slit diffraction
 3.5.1 Single slit diffrction Wves pssing through single slit will lso diffrct nd produce n interference pttern. The reson for this is to do with the finite width of the slit. We will consider this lter.
3.5.1 Single slit diffrction Wves pssing through single slit will lso diffrct nd produce n interference pttern. The reson for this is to do with the finite width of the slit. We will consider this lter.
PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED COMPUTING
 PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED COMPUTING 2009/2010 1 st Semester Teste Jnury 9, 2010 Durtion: 2h00 - No extr mteril llowed. This includes notes, scrtch pper, clcultor, etc. - Give your nswers in the ville spce
PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED COMPUTING 2009/2010 1 st Semester Teste Jnury 9, 2010 Durtion: 2h00 - No extr mteril llowed. This includes notes, scrtch pper, clcultor, etc. - Give your nswers in the ville spce
Section 9.2 Hyperbolas
 Section 9. Hperols 597 Section 9. Hperols In the lst section, we lerned tht plnets hve pproimtel ellipticl orits round the sun. When n oject like comet is moving quickl, it is le to escpe the grvittionl
Section 9. Hperols 597 Section 9. Hperols In the lst section, we lerned tht plnets hve pproimtel ellipticl orits round the sun. When n oject like comet is moving quickl, it is le to escpe the grvittionl
8.2 Areas in the Plane
 39 Chpter 8 Applictions of Definite Integrls 8. Ares in the Plne Wht ou will lern out... Are Between Curves Are Enclosed Intersecting Curves Boundries with Chnging Functions Integrting with Respect to
39 Chpter 8 Applictions of Definite Integrls 8. Ares in the Plne Wht ou will lern out... Are Between Curves Are Enclosed Intersecting Curves Boundries with Chnging Functions Integrting with Respect to
6.2 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method
 mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
Midterm 2 Sample solution
 Nme: Instructions Midterm 2 Smple solution CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fll 2012 November 28, 2012 This exm contins 9 pges, including this one. Mke sure you hve ll the pges. Write your nme on the
Nme: Instructions Midterm 2 Smple solution CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fll 2012 November 28, 2012 This exm contins 9 pges, including this one. Mke sure you hve ll the pges. Write your nme on the
Unit #9 : Definite Integral Properties, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Summer Review Packet For Algebra 2 CP/Honors
 Summer Review Pcket For Alger CP/Honors Nme Current Course Mth Techer Introduction Alger uilds on topics studied from oth Alger nd Geometr. Certin topics re sufficientl involved tht the cll for some review
Summer Review Pcket For Alger CP/Honors Nme Current Course Mth Techer Introduction Alger uilds on topics studied from oth Alger nd Geometr. Certin topics re sufficientl involved tht the cll for some review
What do all those bits mean now? Number Systems and Arithmetic. Introduction to Binary Numbers. Questions About Numbers
 Wht do ll those bits men now? bits (...) Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school instruction R-formt I-formt... integer dt number text chrs... floting point signed unsigned single
Wht do ll those bits men now? bits (...) Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school instruction R-formt I-formt... integer dt number text chrs... floting point signed unsigned single
1.5 Extrema and the Mean Value Theorem
 .5 Extrem nd the Men Vlue Theorem.5. Mximum nd Minimum Vlues Definition.5. (Glol Mximum). Let f : D! R e function with domin D. Then f hs n glol mximum vlue t point c, iff(c) f(x) for ll x D. The vlue
.5 Extrem nd the Men Vlue Theorem.5. Mximum nd Minimum Vlues Definition.5. (Glol Mximum). Let f : D! R e function with domin D. Then f hs n glol mximum vlue t point c, iff(c) f(x) for ll x D. The vlue
Mobile IP route optimization method for a carrier-scale IP network
 Moile IP route optimiztion method for crrier-scle IP network Tkeshi Ihr, Hiroyuki Ohnishi, nd Ysushi Tkgi NTT Network Service Systems Lortories 3-9-11 Midori-cho, Musshino-shi, Tokyo 180-8585, Jpn Phone:
Moile IP route optimiztion method for crrier-scle IP network Tkeshi Ihr, Hiroyuki Ohnishi, nd Ysushi Tkgi NTT Network Service Systems Lortories 3-9-11 Midori-cho, Musshino-shi, Tokyo 180-8585, Jpn Phone:
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES
 INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
Characteristics of MODIS BRDF shape and its relationship with land cover classes in Australia
 2th Interntionl Congress on Modelling nd imultion, Adelide, Austrli, 1 6 Decemer 213 www.mssnz.org.u/modsim213 Chrcteristics of MODI BRDF shpe nd its reltionship with lnd cover clsses in Austrli F. Li,
2th Interntionl Congress on Modelling nd imultion, Adelide, Austrli, 1 6 Decemer 213 www.mssnz.org.u/modsim213 Chrcteristics of MODI BRDF shpe nd its reltionship with lnd cover clsses in Austrli F. Li,
AI Adjacent Fields. This slide deck courtesy of Dan Klein at UC Berkeley
 AI Adjcent Fields Philosophy: Logic, methods of resoning Mind s physicl system Foundtions of lerning, lnguge, rtionlity Mthemtics Forml representtion nd proof Algorithms, computtion, (un)decidility, (in)trctility
AI Adjcent Fields Philosophy: Logic, methods of resoning Mind s physicl system Foundtions of lerning, lnguge, rtionlity Mthemtics Forml representtion nd proof Algorithms, computtion, (un)decidility, (in)trctility
3.5.1 Single slit diffraction
 3..1 Single slit diffrction ves pssing through single slit will lso diffrct nd produce n interference pttern. The reson for this is to do with the finite width of the slit. e will consider this lter. Tke
3..1 Single slit diffrction ves pssing through single slit will lso diffrct nd produce n interference pttern. The reson for this is to do with the finite width of the slit. e will consider this lter. Tke
The Nature of Light. Light is a propagating electromagnetic waves
 The Nture of Light Light is propgting electromgnetic wves Index of Refrction n: In mterils, light intercts with toms/molecules nd trvels slower thn it cn in vcuum, e.g., vwter The opticl property of trnsprent
The Nture of Light Light is propgting electromgnetic wves Index of Refrction n: In mterils, light intercts with toms/molecules nd trvels slower thn it cn in vcuum, e.g., vwter The opticl property of trnsprent
3 4. Answers may vary. Sample: Reteaching Vertical s are.
 Chpter 7 Answers Alterntive Activities 7-2 1 2. Check students work. 3. The imge hs length tht is 2 3 tht of the originl segment nd is prllel to the originl segment. 4. The segments pss through the endpoints
Chpter 7 Answers Alterntive Activities 7-2 1 2. Check students work. 3. The imge hs length tht is 2 3 tht of the originl segment nd is prllel to the originl segment. 4. The segments pss through the endpoints
Introduction Transformation formulae Polar graphs Standard curves Polar equations Test GRAPHS INU0114/514 (MATHS 1)
 POLAR EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS GEOMETRY INU4/54 (MATHS ) Dr Adrin Jnnett MIMA CMth FRAS Polr equtions nd grphs / 6 Adrin Jnnett Objectives The purpose of this presenttion is to cover the following topics:
POLAR EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS GEOMETRY INU4/54 (MATHS ) Dr Adrin Jnnett MIMA CMth FRAS Polr equtions nd grphs / 6 Adrin Jnnett Objectives The purpose of this presenttion is to cover the following topics:
B. Definition: The volume of a solid of known integrable cross-section area A(x) from x = a
 Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
Mth 176 Clculus Sec. 6.: Volume I. Volume By Slicing A. Introduction We will e trying to find the volume of solid shped using the sum of cross section res times width. We will e driving towrd developing
YMCA Your Mesh Comparison Application
 YMCA Your Mesh Comprison Appliction Johnn Schmidt, Reinhold Preiner, Thoms Auzinger, Michel Wimmer, M. Edurd Gröller, Memer, IEEE CS, nd Stefn Bruckner Memer, IEEE CS Alg. 01 Alg. 02 Alg. 03 Alg. 01 Alg.
YMCA Your Mesh Comprison Appliction Johnn Schmidt, Reinhold Preiner, Thoms Auzinger, Michel Wimmer, M. Edurd Gröller, Memer, IEEE CS, nd Stefn Bruckner Memer, IEEE CS Alg. 01 Alg. 02 Alg. 03 Alg. 01 Alg.
Performance enhancement of IEEE DCF using novel backoff algorithm
 Kuo et l. EURASIP Journl on Wireless Communictions nd Networking 212, 212:274 http://jis.eursipjournls.com/content/212/1/274 RESEARCH Open Access Performnce enhncement of IEEE 82.11 using novel ckoff lgorithm
Kuo et l. EURASIP Journl on Wireless Communictions nd Networking 212, 212:274 http://jis.eursipjournls.com/content/212/1/274 RESEARCH Open Access Performnce enhncement of IEEE 82.11 using novel ckoff lgorithm
A New Learning Algorithm for the MAXQ Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning Method
 A New Lerning Algorithm for the MAXQ Hierrchicl Reinforcement Lerning Method Frzneh Mirzzdeh 1, Bbk Behsz 2, nd Hmid Beigy 1 1 Deprtment of Computer Engineering, Shrif University of Technology, Tehrn,
A New Lerning Algorithm for the MAXQ Hierrchicl Reinforcement Lerning Method Frzneh Mirzzdeh 1, Bbk Behsz 2, nd Hmid Beigy 1 1 Deprtment of Computer Engineering, Shrif University of Technology, Tehrn,
9 Graph Cutting Procedures
 9 Grph Cutting Procedures Lst clss we begn looking t how to embed rbitrry metrics into distributions of trees, nd proved the following theorem due to Brtl (1996): Theorem 9.1 (Brtl (1996)) Given metric
9 Grph Cutting Procedures Lst clss we begn looking t how to embed rbitrry metrics into distributions of trees, nd proved the following theorem due to Brtl (1996): Theorem 9.1 (Brtl (1996)) Given metric
