Fundamentals of Spherical Parameterization for 3D Meshes
|
|
|
- Edward Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
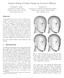
1 Fundamentals of Sphercal Parameterzaton for 3D Meshes Crag Gotsman Xanfeng Gu Alla Sheffer Technon Israel Inst. of Tech. Harvard Unversty Technon Israel Inst. of Tech. Abstract Parameterzaton of 3D mesh data s mportant for many graphcs applcatons, n partcular for texture mappng, remeshng and morphng. Closed manfold genus-0 meshes are topologcally equvalent to a sphere, hence ths s the natural parameter doman for them. Parameterzng a trangle mesh onto the sphere means assgnng a 3D poston on the unt sphere to each of the mesh vertces, such that the sphercal trangles nduced by the mesh connectvty are not too dstorted and do not overlap. Satsfyng the non-overlappng requrement s the most dffcult and crtcal component of ths process. We descrbe a generalzaton of the method of barycentrc coordnates for planar parameterzaton whch solves the sphercal parameterzaton problem, prove ts correctness by establshng a connecton to spectral graph theory and show how to compute these parameterzatons. CR Categores: I.3.5 [Computer Graphcs] Computatonal Geometry and Object Modelng Curve, Surface and Sold and Object Representatons. Keywords: Trangle mesh, parameterzaton, embeddng. 1. Introducton Parameterzaton of 3D mesh data s mportant for many graphcs applcatons, n partcular for texture mappng, remeshng and morphng. To date, mostly planar parameterzatons have been consdered. The man challenge s to produce a planar trangulaton that best matches the geometry of the 3D mesh, mnmzng some measure of dstorton, yet s stll vald. In ths context, vald means that the ndvdual planar trangles do not overlap. Most of the recent works on the subject of parameterzaton (e.g. [Desbrun et al. 2002; Floater 1997; Levy et al. 2002; Sander et al. 2001; Sheffer and de Sturler 2001]) have focused on defnng the dstorton, and showng how to mnmze t. Whle parameterzng to the plane s the most natural way to perform texture-mappng, ths s less natural for other mesh processng operatons whch also requre a parameterzaton. For applcatons such as morphng [Alexa 2000; Kana et al. 2000; Shapro and Tal 1998] and remeshng [Gu et al. 2002; Kobbelt 1999] t s best to parameterze the mesh over a doman whch s topologcally equvalent to t. Ths sgnfcantly reduces the dstorton ntroduced by the parameterzaton wthout resortng to methods whch ntroduce other artfacts, such as cuttng seams. If the mesh has the topology of a sphere, t s best to use a sphercal parameter doman. Parameterzng a 3D trangle mesh over the sphere s equvalent to embeddng ts connectvty graph on the sphere, such that the resultng sphercal trangles partton the sphere (ther unon s the sphere, and they are dsjont). A classcal result due to Stentz s that a graph may be embedded on the sphere f and only f t s planar and 3-connected. Thus a closed manfold genus-0 trangulaton can always be mapped to a sphercal trangulaton. The smplest way to map a closed trangle mesh to the sphere s to reduce the problem to the planar case. Frst cut out one trangle to serve as a boundary. Then parameterze the resultng open mesh over the unt trangle usng any planar parameterzaton method, and fnally use the nverse stereo projecton to map the plane to the sphere [Haker et al. 2000]. See Fg. 1(b). The man problem wth ths method s severe dstorton, and although the nverse stereo projecton s conformal, namely, preserves angles n the contnuous case, t does not preserve angles (or any other geometrc propertes) n the dscrete case. The projecton also does not guarantee that the result wll be a sphercal trangulaton. Another straghtforward method to parameterze to the sphere s to cut the mesh nto two peces, each topologcally equvalent to a dsk, parameterze each over a planar dsk wth a common boundary, and then map each dsk to a hemsphere (by addng an approprate z component to each vertex). The common boundary guarantees that the two hemspheres ft together at the equator. See Fg. 1(c). Snce ths boundary wll presumably contan more than just three vertces, each of the two dsk parameterzatons wll be less dstorted than the one obtaned by usng a sngle trangle as the boundary, so the sphercal result wll also be less dstorted. However, the result wll depend strongly on the specfc cut used to obtan the two dsks. It s more natural to parameterze a mesh drectly on the sphere wthout gong back and forth to the plane. Several methods for drect parameterzaton on the sphere exst. The only one to date that seems to guarantee a vald sphercal trangulaton (.e. wth no trangle foldovers) s that of Shapro and Tal [1998], smlar to that of Das and Goodrch [1997]. Ths method works by smplfyng the mesh by vertex removal untl only a tetrahedron remans. Permsson to make dgtal/hard copy of part of all of ths work for personal or classroom use s granted wthout fee provded that the copes are not made or dstrbuted for proft or commercal advantage, the copyrght notce, the ttle of the publcaton, and ts date appear, and notce s gven that copyng s by permsson of ACM, Inc. To copy otherwse, to republsh, to post on servers, or to redstrbute to lsts, requres pror specfc permsson and/or a fee ACM /03/ $5.00 (a) (b) (c) Fgure 1: Parameterzng the (a) rabbt by (b) nverse stereo mappng (c) two hemspheres. Colored dots mark correspondng vertces. 358
2 The tetrahedron s easly embedded on the sphere, and then the vertces are nserted back one by one, so that the valdty of the trangulaton s preserved throughout the process. Whle ths s qute an effcent process, t s dffcult to optmze the parameterzaton, due to ts greedy nature, and mpossble to steer t to have any desrable mathematcal propertes. Other drect parameterzaton methods were proposed by Kobbelt et al [1999] and Alexa [2000]. These are heurstc teratve procedures, attemptng to converge to a vald parameterzaton by applyng local mprovement (relaxaton) rules. These work well n many cases, but there s no guarantee that they wll termnate, and, even f they do, that the resultng embeddng wll be vald, or have any desrable mathematcal propertes. A method whch guarantees a vald embeddng was recently proposed by Sheffer et al. [2003]. Ths s a hghly non-lnear optmzaton procedure, workng wth the angles of the sphercal trangulaton (as opposed to the vertex postons), nspred by the angle-based method of Sheffer and de Sturler [2001] for planar parameterzatons. So far t lacks an effcent numercal computaton procedure, so t s not very practcal. 1.1 Our contrbuton The problem of mesh parameterzaton s that of mappng a pecewse lnear surface wth a dscrete representaton onto a contnuous sphercal surface. The theory of mappngs between varous Remann surfaces s well understood n the contnuous case usng classcal dfferental geometry [Do Carmo 1976]. Probably the most notable example of ths s the so-called conformal mappng theory whch shows how to map any contnuous Remann surface to another such that angles are preserved. However, the dscrete case of meshes s much less understood. In the lmt t obvously converges to the contnuous case, but n practcal applcatons the meshes nvolved may be far from ths lmt. Hence there s a need to treat the dscrete case separately n a combnatoral manner, albet nspred by the classcal theory. Ths paper ntroduces a precse mathematcal characterzaton of all possble sphercal parameterzatons of a closed manfold genus-0 trangle mesh. We show that t s a natural non-lnear extenson of the lnear theory of barycentrc coordnates used n the planar case. The correctness of ths methodology s proved by establshng a lnk to the so-called Coln de Verdere matrces assocated wth planar graphs. We also descrbe a computatonal method for generatng and controllng these parameterzatons. These contrbutons are concentrated n Secton 4, after establshng the theory n Secton The Method of Barycentrc Coordnates 2.1 The planar case Floater [1997] descrbed a generc method to embed a manfold 3D mesh wth a boundary n the plane wthout foldovers. Floater's method s a generalzaton of the basc procedure orgnally proposed by Tutte [1963] for a planar graph, whch can be traced back as far as I. Fary n 1948 and J.C. Maxwell n Ths method makes use of so-called barycentrc coordnates (or convex combnatons) and proceeds as follows: 1. To each nteror (drected) edge e = (,, assgn a postve weght w j, such that = 1 w j j N ( ) where N() s the lst of vertces neghborng the 'th vertex. 2. To all other entres (,, assgn w j = Embed the boundary vertces n the plane such that they form a closed convex polygon. 4. Solve the followng two lnear systems for the x and y coordnates of the n nteror vertces: ( I W) x = bx, ( I W ) y = b y, where W s a nxn matrx contanng w j, and b x and b y vectors wth non-zero entres correspondng to vertces adjacent to the boundary. The cornerstone of ths theory s the followng theorem, frst proven by Tutte [1963], and reproven over the years n dfferent ways (e.g. [Floater 2003b, Rchter-Gebert 1996, Chap 3]): Theorem 1: Gven a planar 3-connected graph wth a boundary fxed to a convex shape n R 2, the postons of the nteror vertces form a planar trangulaton (.e. none of the trangles overlap) f and only f each vertex poston s some convex combnaton of ts neghbor's postons. Theorem 1 mples that the method of barycentrc coordnates generates all possble vald embeddngs of the graph n the plane, gven the (convex) postons of the boundary. Tutte proposed usng w j =1/deg() for all edges (,, n effect placng each nteror vertex at the centrod of ts neghbors (deg() s the degree, or valence of the 'th vertex). Ths choce of W does not take nto account the geometry of the mesh, just ts connectvty. When the mesh s gven wth 3D geometry, a number of recpes for W have been proposed, each amng for some effect related to reflectng the geometry of the mesh n the parameterzaton, namely, mnmzng ts metrc dstorton when flattened to the plane. The most popular methods seem to be the shape-preservng method [Floater 1997], the conformal, or harmonc method [Haker et al. 2000; Levy et al. 2002; Pnkall and Polther 1993] and the mean-value method [Floater 2003a]. These methods all have the desrable 2D reproducton property [Floater 1997], namely that when appled to a 2D trangulaton, the embeddng procedure wll produce an output dentcal to the nput. However, some of the methods, most notably the conformal method, do not always result n postve weghts, hence cannot guarantee a vald embeddng. In general, the method of barycentrc coordnates may be formulated as the soluton to the 2D vector Laplace equaton on the nteror vertces: (1) L W x = b wth boundary condtons derved from the convex boundary vertex postons, whch prevents the trval zero soluton. Ths s a lnear system. L W = I-W s the general normalzed Laplacan operator, general because the weghts of W are arbtrary postve values, and normalzed because the rows of W all sum to unty. The specal case of w j =1/deg() proposed by Tutte wll be called the normalzed Tutte Laplacan. A smple numercal procedure to solve (1) s a relaxaton procedure, where the boundary vertces are placed on a convex boundary, and the nteror vertces are repeatedly updated to be at the weghted average of ther neghborng vertex postons, as dctated by W. Snce L W s dagonally domnant, ths Gauss-Sedel procedure s guaranteed to converge. 359
3 2.2 The sphercal case The Laplacan L W has a unt dagonal, negatve entres for each mesh edge, and vanshes otherwse. Also, all rows sum to zero, hence L W s sngular. L W s, however, not symmetrc. In what follows, we restrct the dscusson to the class of symmetrc Laplacans, whch corresponds to sets of barycentrc coordnates whch are edge-symmetrc up to normalzaton of each row. These are: negatve number (, E LW (, = LW (, k) = j k (, E 0 Note that the symmetrc Tutte Laplacan has -1's at entres correspondng to edges, and the vertex degrees along the dagonal. Symmetrc systems such as these can be gven the physcal nterpretaton of a mass-sprng system at rest, where the vertces are pont masses joned by sprngs along the edges. In ths case, the Laplace equatons are just the normal equatons for mnmzng the quadratc sprng energy. Tutte and conformal barycentrc coordnates have the symmetry property, but mean value coordnates unfortunately do not. Generalzng the barycentrc coordnates theory to sphercal embeddngs s not straghtforward. Beng non-planar, t wll be mpossble n general to express a vertex on the sphere as a convex combnaton of ts neghbors (e.g. f a vertex's neghbors are all co-planar, ths wll mply that the vertex should also be on the same plane). Inspred by classcal dfferental geometry operator theory, Gu and Yau [2002] proposed to embed on a curved 3D surface usng the generalzaton of the Laplacan to the Laplace-Beltram operator. Intutvely, ths s just the tangental component of the Laplacan at that pont of the surface, and mples the followng nonlnear system: (2) LW x = 0 s.t. x = 1, = 1,.., n where L s the tangental component of L. The rght hand sde of (2) s zero, as opposed to the non-zero b n (1), because there s no boundary. Whle Gu and Yau showed that solvng (2) results n a bjectve embeddng of a contnuous Remann surface on the sphere, they dd not show that ths also holds for the dscrete case of a pecewse-lnear mesh, n the sense that the result s a vald sphercal trangulaton. In the next secton we show how some recent deep results n spectral graph theory may be appled to establsh ths. 3. Connecton to Spectral Graph Theory We would lke to prove the followng analog of Theorem 1: Theorem 2: Gven a planar 3-connected graph embedded n R 3, the postons of the vertces form a sphercal trangulaton (.e. none of the sphercal trangles overlap) f and only f each vertex poston s some convex combnaton of the postons of ts neghbors, whch s then projected on the sphere. Theorem 2 means that the barycentrc coordnate theory holds also on the sphere up to a radal resdual, consstent wth (2). In Secton 4 we wll prove ths theorem. We start wth some theory. 3.1 The Coln de Verdere number In 1990, Coln de Verdere [1990] establshed an algebrac nvarant for certan famles of graphs. Gven a n-vertex graph G = <V,E>, consder the class M(G) of symmetrc matrces wth element M j such that: negatve number (, E M j = anythng = j 0 (, E Note that M(G) s a superset of the symmetrc Laplacans for G, allowng the dagonal entres to assume arbtrary values (so that the rows do not necessarly sum to zero). Denote by λ(m) = {λ 0,.., λ n-1 } the spectrum of M wth correspondng egenvectors {ξ 0,.., ξ n-1 }. Let r = r(g) be the maxmal nteger such that λ 1 =λ 2 =..=λ r over all matrces n M(G). Let M be a matrx whch attans ths maxmum. Ths r(g) s called the Coln de Verdere (CdV) number of G, the matrx M a CdV matrx for G, ts r dentcal egenvalues CdV egenvalues, and the correspondng egenvectors CdV egenvectors. Coln de Verdere showed that: G s a 3-connected planar graph f and only f r(g) Nullspace embeddng An mportant extenson of the results of Coln de Verdere was obtaned by Lovasz and Schrjver [1999], who showed that CdV egenvectors of a graph G may be used to embed G n R r. For the specal case r(g) = 3, ths translates to: G descrbes the edges of a convex polyhedron n R 3 contanng the orgn f the three egenvectors ξ 1, ξ 2 and ξ 3 of a CdV matrx of G are used as coordnate vectors for ts vertces. The fact that the polyhedron s convex and contans the orgn s a key fact, snce convexty mples star-shapedness. Ths n turn mples that by normalzng the vertces, the polyhedron may be projected onto the unt sphere to form a (vald) sphercal trangulaton. Snce the spectrum of a matrx may be shfted arbtrarly by addng an approprate constant to the dagonal entres, we may assume, wthout loss of generalty, that the three CdV egenvalues are zero. Thus the correspondng CdV matrx has just one negatve egenvalue and co-rank 3. In ths case the three CdV egenvectors are ndependent non-trval solutons to what looks lke Laplace equatons: Mx = 0, or a bass of the nullspace of M. Hence x s called the nullspace embeddng of G. Usng egenvectors of matrces as coordnate vectors for embeddng graphs s not new. The tradtonal way of dong ths s takng the egenvectors correspondng to the smallest postve egenvalues of the Tutte Laplacan (the smallest egenvalue s zero, due to ths matrx beng sngular). Ths dates back to Fedler [1975] and Hall [1970]. See [Koren 2002] for a dscusson of the dfferent ways of usng the Laplacan for "drawng" graphs. Egenvalues and egenvectors of the Tutte Laplacan of a graph are the cornerstone of spectral graph theory [Chung 1997], and have also been used for codng 3D mesh geometry [Karn and Gotsman 2000]. However, the embeddngs resultng from egenvectors of ths Laplacan do not have very appealng geometrc propertes, and, specfcally, the trangles overlap. The Coln de Verdere theory reveals that more powerful generalzatons of the Laplacan must 360
4 be used, yeldng egenvectors whch are more symmetrc, snce they correspond to dentcal egenvalues. On an ntutve level, ths symmetry s what guarantees the valdty of the embeddng. 4. Generatng Sphercal Nullspace Embeddngs It s dffcult to use the Coln de Verdere theory drectly to embed on a sphere, snce, gven a 3-connected planar graph G, nether Coln de Verdere nor Lovasz and Schrjver provded any recpe to generate a CdV matrx for G. In the planar case, once the boundary of the trangulaton has been fxed and the barycentrc coordnates chosen, the postons of the nteror vertces are unquely determned by solvng a lnear system. Ths s not the case for the sphercal scenaro. However, we propose to use a symmetrc Laplacan as the startng pont for constructng a CdV matrx. The off-dagonal values wll not change, but the dagonal of the matrx s stll lackng, and must be corrected. Only then can the embeddng (the nullspace of the CdV matrx) be obtaned. The key observaton of ths paper s that we may solve for the dagonal of the CdV matrx and ts nullspace smultaneously. We also force the resultng nullspace vectors to le vertex-wse on the 3D sphere. Ths may be posed as the followng set of 4n quadratc equatons on the 3n postons of the vertces (x, y, z ) and the n auxlary varables α : (3) x + y + z = 1 α x LW [ ] x = 0 α y LW [ ] y = 0 α z L [ ] z = 0 W = 1,.., n = 1,.., n = 1,.., n = 1,.., n L W [] denotes the 'th row of the matrx L W, and x, y, and z are column vectors. The number of vertces n the mesh s n. Fg. 2 llustrates the geometrc nterpretaton of (3): the vector dfference between the 'th vertex and the weghted average (as dctated by L W ) of ts neghbors s collnear wth the vector dfference between the vertex and the sphere's center. To prove that ths procedure s correct, assume that L s a symmetrc Laplacan for G and that (3) has been solved for column n- vectors x, y, z and α. Ths means that the 'th row L[] of L satsfes L[](x, y, z) = α (x, y, z ). Defne the matrx M as: Lj j M =, j L α = j obtanng M(x, y, z) = 0. Hence M s a CdV matrx for G wth vanshng CdV egenvalue and nullspace spanned by x, y and z, mplyng that x,y,z form a vald sphercal trangulaton when used as coordnate vectors. A smlar argument shows the converse: If the three vectors (x,y,z) are a sphercal trangulaton of a 3-connected planar graph G, then these three vectors span the nullspace of a sutable CdV matrx M, whch may easly be translated nto L W and α satsfyng (3). Ths completes the proof of Theorem 2. Fgure 2: A sphercal trangulaton based on the Tutte Laplacan: The average of the neghbors of vertex V (A, B, C and D) s the pont M, whch s collnear wth the sphere center O and the vertex V: M-O = c(v-o). A smlar relatonshp between a vertex and ts neghbors holds for all mesh vertces. 5. Implementaton Detals Stentz's theorem guarantees that any planar 3-connected mesh admts a vald sphercal trangulaton. The theory of Coln de Verdere guarantees that f a vald sphercal trangulaton exsts, then t can be found by solvng a system of the form (3) for some symmetrc Laplacan L W. However, there s no guarantee that an arbtrary symmetrc Laplacan, when used n (3), wll result n a non-degenerate trangulaton. Degenerate solutons always exst. The case α 0 s the trval soluton when all vertces collapse to one pont on the sphere. Gu and Yau [2002] tred to prevent ths by requrng that the vertces average to zero. However, ths s damagng and can prevent other solutons. Another degenerate soluton can occur when the vertces are mapped to two antpodal ponts on the sphere. In ths case, the vertces are parttoned nto two sets such that the weghted average of the neghbors of a vertex n each set s stll n the same hemsphere as the vertex. A more nterestng stuaton can occur f the connectvty graph contans a Hamltonan cycle. The cycle of vertces may then be mapped to the equator. Beyond the degenerate solutons, a soluton to (3) s not unque, snce any sphercal trangulaton s certanly nvarant to the rotaton group SO(3), whch mmedately gves three degrees of freedom. However, there are more. Ths can be seen by examnng the smple specal case of a tetrahedral mesh connectvty combned wth the Tutte Laplacan. Observe that any rectangular parallelpped crcumscrbed by the unt sphere defnes an equfaced tetrahedron (.e. a tetrahedron whose four faces are dentcal), by takng ts edges to be the opposte dagonals of the sx faces of the parallelpped. It s easy to see that any vertex of the tetrahedron s collnear wth the orgn and the centrod of the three opposte vertces. Ths means that the vertex locatons on the sphere satsfy (3) wth L W = the Tutte Laplacan and α = 4 for 1 4. The CdV matrx s a 4x4 matrx whose entres are all -1's. There are two degrees of freedom n constructng such a rectangular parallelpped, so all together there are fve degrees of freedom. To solve the nonlnear set of equatons (3) for very large meshes, t s mportant to have a stable and effcent numercal procedure. A relaxaton procedure where each vertex s updated to be the weghted average of ts neghbors, and then projected onto the sphere, wll not converge to the desred result, rather collapse to some degenerate confguraton. 361
5 conformal angle-preservng mappng (although these can be negatve), nverse edge lengths for a trangulaton preservng edge lengths, and the prescrpton of Desbrun et al. [2002] for an areapreservng trangulaton. We use the fsolve procedure of MATLAB, a subspace trust regon procedure [Coleman and L 1996]. To better condton the system, t s useful to anchor an arbtrary vertex to a fxed poston on the sphere. Ths elmnates only two degrees of freedom from SO(3), so s not damagng. It appears that anchorng two arbtrary vertces lmts the soluton. Anchorng three vertces s damagng, snce n the case of the equfaced tetrahedron there does not always exst a fourth vertex on the sphere formng the tetrahedron. Fg. 3 shows some sphercal embeddngs generated by our procedure on three sample meshes, and compares them to those generated by the procedure of Alexa [2000], and those based on reducton to the planar case by nverse stereo projecton. The Tutte Laplacan produces an equ-angular trangulaton, whch s smlar n some cases to that generated by Alexa's algorthm. Alexa's algorthm, though, sometmes tends to spread the vertces out over the sphere (as n the Trceratops model). The conformal embeddng preserves many of the features of the 3D geometry, so the eyes and ears of the Rabbt are stll notceable n the result. The stereo embeddng tends to lose most of the geometrc structure. 6. Expermental Results We have used our methodology to generate a varety of embeddngs of closed manfold genus-0 meshes on the unt sphere. The characterstcs of the embeddng may be controlled by the weghts n the Laplacan matrx, smlarly to the planar case. For example, unform (Tutte) weghts should be used f the sphercal trangulaton s requred to be equ-angular, cotangental weghts for a Pawn (154 vertces) Rabbt (543 vertces) Trceratops (1,727 vertces) Tutte Laplacan Conformal Laplacan Stereo Alexa Fgure 3: Some 3D models and ther sphercal parameterzatons. Colored dots mark correspondng vertces. 362
6 In terms of runtmes, solvng (2) usng the MATLAB procedure requred anywhere between a few seconds for the Pawn model of 154 vertces, and a few mnutes for the Trceratops model (1,727 vertces) on a Xeon 2.8 GHz PC wth 1GB RDRAM. 7. Concluson Parameterzng a closed manfold genus-0 mesh to the sphere s of paramount mportance n dgtal geometry processng. It s a fundamental operaton requred for remeshng, morphng, flterng and texture mappng. Whle mappng between Remann surfacees s well understood n the contnuous case, the dscrete case has not receved satsfactory treatment to date. Ths paper has closed ths gap, provdng precse characterzatons of dscrete sphercal parameterzatons and methods to compute them. We have shown that there s a natural extenson of the barycentrc coordnate theory from planar trangulatons to sphercal trangulatons, correspondng to the extenson of the Laplacan operator to the Laplace-Beltram operator n dfferental geometry. Unfortunately, the extenson nvolves a transton from a lnear theory to a non-lnear theory, so s much more dffcult to analyze and compute. The extenson of the theory of contnuous Remann surfaces to a combnatoral treatment of dscrete trangle meshes has been made based on recent results n algebrac and spectral graph theory. Ths translates to a set of equatons whch may be solved wth not too much dffculty. A few questons reman open, most notably on the exstence of non-degenerate solutons and the analyss of the degrees of freedom n the varous sphercal embeddngs, and how to control (or elmnate) them. Extensons to hgher genus s also nterestng. Acknowledgements Thanks to Zach Karn for helpful dscussons on CdV matrces. Ths research was partally funded by European grant HPRN-CT (MINGLE), German-Israel Fund grant I /1999 and Israel Mnstry of Scence grant References ALEXA, M Mergng Polyhedral Shapes wth Scattered Features. The Vsual Computer 16, 1, CHUNG, F.R.K Spectral Graph Theory. CBMS 92, AMS. COLEMAN, T.F., AND LI, Y An Interor Trust Regon Approach for Nonlnear Mnmzaton Subject to Bounds. SIAM Journal on Optmzaton, 6, COLIN DE VERDIERE, Y Sur un Nouvel Invarant des Graphes et un Crtere de Planarte. Journal of Combnatoral Theory B 50, [Englsh translaton: On a New Graph Invarant and a Crteron for Planarty. In Graph Structure Theory (N. Robertson, P. Seymour, Eds.) Contemporary Mathematcs, AMS, ] DAS, G., AND GOODRICH, M.T On the Complexty of Optmzaton Problems for 3-Dmensonal Convex Polyhedra and Decson Trees. Computatonal Geometry, 8, DESBRUN, M., MEYER, M., AND ALLIEZ, P Intrnsc Parameterzatons of Surface Meshes. Computer Graphcs Forum, 21, 3, DO CARMO, M.P Dfferental Geometry of Curves and Surfaces. Prentce-Hall. FIEDLER, M A Property of Egenvectors of Nonnegatve Symmetrc Matrces and Its Applcaton to Graph Theory. Czechoslovak Math. Journal, 25, FLOATER, M.S Parameterzaton and Smooth Approxmaton of Surface Trangulatons. Computer Aded Geometrc Desgn, 14, FLOATER, M.S Mean-value Coordnates. Computer Aded Geometrc Desgn, 20, FLOATER, M.S One-to-one Pecewse Lnear Mappngs Over Trangulatons. Mathematcs of Computaton 2, GU, X., AND YAU, S.-T Computng Conformal Structures of Surfaces. Communcatons n Informaton and Systems, 2, 2, GU, X., GORTLER, S., AND HOPPE, H Geometry Images. ACM Transactons on Graphcs, 21, 3, GUSKOV, I., VIDIMCE, K., SWELDENS, W., AND SCHROEDER, P Normal Meshes. In Proceedngs of ACM SIGGRAPH 2000, ACM Press/ ACM SIGGRAPH, New York, K. Akeley, Ed., Computer Graphcs Proceedngs, Annual Conferences Seres, ACM, HAKER, S., ANGENENT, S., TANNENBAUM, A., KIKINIS, R., AND SAPIRO, G Conformal Surface Parameterzaton for Texture Mappng. IEEE Transactons on Vsualzaton and Computer Graphcs, 6, 2, 1-9. HALL, K.M An r-dmensonal Quadratc Placement Algorthm. Management Scence, 17, KANAI, T., SUZUKI, H., AND KIMURA, F Metamorphoss of Arbtrary Trangular Meshes. IEEE Computer Graphcs and Applcatons, 20, 2, KARNI, Z., AND GOTSMAN, C. Spectral Compresson of Mesh Geometry. In Proceedngs of ACM SIGGRAPH 2000, ACM Press / ACM SIG- GRAPH, New York, K. Ackley, Ed., Computer Graphcs Proceedngs, Annual Conference Seres, ACM, KOBBELT, L.P., VORSATZ, J., LABISK, U., AND SEIDEL, H.-P A Shrnk-wrappng Approach to Remeshng Polygonal Surfaces. Computer Graphcs Forum, 18, 3, KOREN, Y On Spectral Graph Drawng. Preprnt, Wezmann Insttute of Scence. LEVY, B., PETITJEAN, S., RAY, N., AND MAILLOT, J Least Squares Conformal Maps for Automatc Texture Atlas Generaton. ACM Transactons on Graphcs, 21, 3, LOVASZ, L., AND SCHRIJVER, A On the Nullspace of a Coln de Verdere Matrx. Annales de l'insttute Fourer 49, PINKALL, U., AND POLTHIER, K Computng Dscrete Mnmal Surfaces and Ther Conjugates. Expermental Mathematcs, 2, RICHTER-GEBERT, J Realzaton Spaces of Polytopes. Lecture Notes n Math #1643, Sprnger. SANDER, P.V., SNYDER, J., GORTLER S.J., AND HOPPE, H Texture Mappng Progressve Meshes. In Proceedngs of ACM SIGGRAPH 2001, ACM Press/ ACM SIGGRAPH, New York, E. Fume, Ed., Computer Graphcs Proceedngs, Annual Conferences Seres, ACM, SHAPIRO A., AND TAL, A Polygon Realzaton for Shape Transformaton. The Vsual Computer, 14, 8-9, SHEFFER, A., GOTSMAN C., AND DYN, N Robust Sphercal Parameterzaton of Trangular Meshes. In Proceedngs of 4 th Israel-Korea Bnatonal Workshop on Computer Graphcs and Geometrc Modelng, Tel Avv, SHEFFER, A. AND DE STURLER, E Parameterzaton of Faceted Surfaces for Meshng Usng Angle Based Flattenng. Engneerng wth Computers, 17, 3, TUTTE. W.T How to Draw a Graph. Proc. London Math. Soc. 13, 3,
Parameterization of Quadrilateral Meshes
 Parameterzaton of Quadrlateral Meshes L Lu 1, CaMng Zhang 1,, and Frank Cheng 3 1 School of Computer Scence and Technology, Shandong Unversty, Jnan, Chna Department of Computer Scence and Technology, Shandong
Parameterzaton of Quadrlateral Meshes L Lu 1, CaMng Zhang 1,, and Frank Cheng 3 1 School of Computer Scence and Technology, Shandong Unversty, Jnan, Chna Department of Computer Scence and Technology, Shandong
Hermite Splines in Lie Groups as Products of Geodesics
 Hermte Splnes n Le Groups as Products of Geodescs Ethan Eade Updated May 28, 2017 1 Introducton 1.1 Goal Ths document defnes a curve n the Le group G parametrzed by tme and by structural parameters n the
Hermte Splnes n Le Groups as Products of Geodescs Ethan Eade Updated May 28, 2017 1 Introducton 1.1 Goal Ths document defnes a curve n the Le group G parametrzed by tme and by structural parameters n the
Barycentric Coordinates. From: Mean Value Coordinates for Closed Triangular Meshes by Ju et al.
 Barycentrc Coordnates From: Mean Value Coordnates for Closed Trangular Meshes by Ju et al. Motvaton Data nterpolaton from the vertces of a boundary polygon to ts nteror Boundary value problems Shadng Space
Barycentrc Coordnates From: Mean Value Coordnates for Closed Trangular Meshes by Ju et al. Motvaton Data nterpolaton from the vertces of a boundary polygon to ts nteror Boundary value problems Shadng Space
An Optimal Algorithm for Prufer Codes *
 J. Software Engneerng & Applcatons, 2009, 2: 111-115 do:10.4236/jsea.2009.22016 Publshed Onlne July 2009 (www.scrp.org/journal/jsea) An Optmal Algorthm for Prufer Codes * Xaodong Wang 1, 2, Le Wang 3,
J. Software Engneerng & Applcatons, 2009, 2: 111-115 do:10.4236/jsea.2009.22016 Publshed Onlne July 2009 (www.scrp.org/journal/jsea) An Optmal Algorthm for Prufer Codes * Xaodong Wang 1, 2, Le Wang 3,
Analysis of Continuous Beams in General
 Analyss of Contnuous Beams n General Contnuous beams consdered here are prsmatc, rgdly connected to each beam segment and supported at varous ponts along the beam. onts are selected at ponts of support,
Analyss of Contnuous Beams n General Contnuous beams consdered here are prsmatc, rgdly connected to each beam segment and supported at varous ponts along the beam. onts are selected at ponts of support,
Mesh Editing in ROI with Dual Laplacian
 Mesh Edtng n ROI wth Dual Laplacan Luo Qong, Lu Bo, Ma Zhan-guo, Zhang Hong-bn College of Computer Scence, Beng Unversty of Technology, Chna lqngng@sohu.com, lubo@but.edu.cn,mzgsy@63.com,zhb@publc.bta.net.cn
Mesh Edtng n ROI wth Dual Laplacan Luo Qong, Lu Bo, Ma Zhan-guo, Zhang Hong-bn College of Computer Scence, Beng Unversty of Technology, Chna lqngng@sohu.com, lubo@but.edu.cn,mzgsy@63.com,zhb@publc.bta.net.cn
 Chapter 6 Programmng the fnte element method Inow turn to the man subject of ths book: The mplementaton of the fnte element algorthm n computer programs. In order to make my dscusson as straghtforward
Chapter 6 Programmng the fnte element method Inow turn to the man subject of ths book: The mplementaton of the fnte element algorthm n computer programs. In order to make my dscusson as straghtforward
LECTURE : MANIFOLD LEARNING
 LECTURE : MANIFOLD LEARNING Rta Osadchy Some sldes are due to L.Saul, V. C. Raykar, N. Verma Topcs PCA MDS IsoMap LLE EgenMaps Done! Dmensonalty Reducton Data representaton Inputs are real-valued vectors
LECTURE : MANIFOLD LEARNING Rta Osadchy Some sldes are due to L.Saul, V. C. Raykar, N. Verma Topcs PCA MDS IsoMap LLE EgenMaps Done! Dmensonalty Reducton Data representaton Inputs are real-valued vectors
Accounting for the Use of Different Length Scale Factors in x, y and z Directions
 1 Accountng for the Use of Dfferent Length Scale Factors n x, y and z Drectons Taha Soch (taha.soch@kcl.ac.uk) Imagng Scences & Bomedcal Engneerng, Kng s College London, The Rayne Insttute, St Thomas Hosptal,
1 Accountng for the Use of Dfferent Length Scale Factors n x, y and z Drectons Taha Soch (taha.soch@kcl.ac.uk) Imagng Scences & Bomedcal Engneerng, Kng s College London, The Rayne Insttute, St Thomas Hosptal,
Solving two-person zero-sum game by Matlab
 Appled Mechancs and Materals Onlne: 2011-02-02 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 50-51, pp 262-265 do:10.4028/www.scentfc.net/amm.50-51.262 2011 Trans Tech Publcatons, Swtzerland Solvng two-person zero-sum game by
Appled Mechancs and Materals Onlne: 2011-02-02 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vols. 50-51, pp 262-265 do:10.4028/www.scentfc.net/amm.50-51.262 2011 Trans Tech Publcatons, Swtzerland Solvng two-person zero-sum game by
S1 Note. Basis functions.
 S1 Note. Bass functons. Contents Types of bass functons...1 The Fourer bass...2 B-splne bass...3 Power and type I error rates wth dfferent numbers of bass functons...4 Table S1. Smulaton results of type
S1 Note. Bass functons. Contents Types of bass functons...1 The Fourer bass...2 B-splne bass...3 Power and type I error rates wth dfferent numbers of bass functons...4 Table S1. Smulaton results of type
6.854 Advanced Algorithms Petar Maymounkov Problem Set 11 (November 23, 2005) With: Benjamin Rossman, Oren Weimann, and Pouya Kheradpour
 6.854 Advanced Algorthms Petar Maymounkov Problem Set 11 (November 23, 2005) Wth: Benjamn Rossman, Oren Wemann, and Pouya Kheradpour Problem 1. We reduce vertex cover to MAX-SAT wth weghts, such that the
6.854 Advanced Algorthms Petar Maymounkov Problem Set 11 (November 23, 2005) Wth: Benjamn Rossman, Oren Wemann, and Pouya Kheradpour Problem 1. We reduce vertex cover to MAX-SAT wth weghts, such that the
R s s f. m y s. SPH3UW Unit 7.3 Spherical Concave Mirrors Page 1 of 12. Notes
 SPH3UW Unt 7.3 Sphercal Concave Mrrors Page 1 of 1 Notes Physcs Tool box Concave Mrror If the reflectng surface takes place on the nner surface of the sphercal shape so that the centre of the mrror bulges
SPH3UW Unt 7.3 Sphercal Concave Mrrors Page 1 of 1 Notes Physcs Tool box Concave Mrror If the reflectng surface takes place on the nner surface of the sphercal shape so that the centre of the mrror bulges
Lecture 4: Principal components
 /3/6 Lecture 4: Prncpal components 3..6 Multvarate lnear regresson MLR s optmal for the estmaton data...but poor for handlng collnear data Covarance matrx s not nvertble (large condton number) Robustness
/3/6 Lecture 4: Prncpal components 3..6 Multvarate lnear regresson MLR s optmal for the estmaton data...but poor for handlng collnear data Covarance matrx s not nvertble (large condton number) Robustness
High-Boost Mesh Filtering for 3-D Shape Enhancement
 Hgh-Boost Mesh Flterng for 3-D Shape Enhancement Hrokazu Yagou Λ Alexander Belyaev y Damng We z Λ y z ; ; Shape Modelng Laboratory, Unversty of Azu, Azu-Wakamatsu 965-8580 Japan y Computer Graphcs Group,
Hgh-Boost Mesh Flterng for 3-D Shape Enhancement Hrokazu Yagou Λ Alexander Belyaev y Damng We z Λ y z ; ; Shape Modelng Laboratory, Unversty of Azu, Azu-Wakamatsu 965-8580 Japan y Computer Graphcs Group,
An Application of the Dulmage-Mendelsohn Decomposition to Sparse Null Space Bases of Full Row Rank Matrices
 Internatonal Mathematcal Forum, Vol 7, 2012, no 52, 2549-2554 An Applcaton of the Dulmage-Mendelsohn Decomposton to Sparse Null Space Bases of Full Row Rank Matrces Mostafa Khorramzadeh Department of Mathematcal
Internatonal Mathematcal Forum, Vol 7, 2012, no 52, 2549-2554 An Applcaton of the Dulmage-Mendelsohn Decomposton to Sparse Null Space Bases of Full Row Rank Matrces Mostafa Khorramzadeh Department of Mathematcal
Proper Choice of Data Used for the Estimation of Datum Transformation Parameters
 Proper Choce of Data Used for the Estmaton of Datum Transformaton Parameters Hakan S. KUTOGLU, Turkey Key words: Coordnate systems; transformaton; estmaton, relablty. SUMMARY Advances n technologes and
Proper Choce of Data Used for the Estmaton of Datum Transformaton Parameters Hakan S. KUTOGLU, Turkey Key words: Coordnate systems; transformaton; estmaton, relablty. SUMMARY Advances n technologes and
Parallelism for Nested Loops with Non-uniform and Flow Dependences
 Parallelsm for Nested Loops wth Non-unform and Flow Dependences Sam-Jn Jeong Dept. of Informaton & Communcaton Engneerng, Cheonan Unversty, 5, Anseo-dong, Cheonan, Chungnam, 330-80, Korea. seong@cheonan.ac.kr
Parallelsm for Nested Loops wth Non-unform and Flow Dependences Sam-Jn Jeong Dept. of Informaton & Communcaton Engneerng, Cheonan Unversty, 5, Anseo-dong, Cheonan, Chungnam, 330-80, Korea. seong@cheonan.ac.kr
Compiler Design. Spring Register Allocation. Sample Exercises and Solutions. Prof. Pedro C. Diniz
 Compler Desgn Sprng 2014 Regster Allocaton Sample Exercses and Solutons Prof. Pedro C. Dnz USC / Informaton Scences Insttute 4676 Admralty Way, Sute 1001 Marna del Rey, Calforna 90292 pedro@s.edu Regster
Compler Desgn Sprng 2014 Regster Allocaton Sample Exercses and Solutons Prof. Pedro C. Dnz USC / Informaton Scences Insttute 4676 Admralty Way, Sute 1001 Marna del Rey, Calforna 90292 pedro@s.edu Regster
Range images. Range image registration. Examples of sampling patterns. Range images and range surfaces
 Range mages For many structured lght scanners, the range data forms a hghly regular pattern known as a range mage. he samplng pattern s determned by the specfc scanner. Range mage regstraton 1 Examples
Range mages For many structured lght scanners, the range data forms a hghly regular pattern known as a range mage. he samplng pattern s determned by the specfc scanner. Range mage regstraton 1 Examples
Harmonic Coordinates for Character Articulation PIXAR
 Harmonc Coordnates for Character Artculaton PIXAR Pushkar Josh Mark Meyer Tony DeRose Bran Green Tom Sanock We have a complex source mesh nsde of a smpler cage mesh We want vertex deformatons appled to
Harmonc Coordnates for Character Artculaton PIXAR Pushkar Josh Mark Meyer Tony DeRose Bran Green Tom Sanock We have a complex source mesh nsde of a smpler cage mesh We want vertex deformatons appled to
On the Optimality of Spectral Compression of Meshes
 On the Optmalty of Spectral Compresson of Meshes MIRELA BEN-CHEN AND CRAIG GOTSMAN Center for Graphcs and Geometrc Computng Technon Israel Insttute of Technology Spectral compresson of trangle meshes has
On the Optmalty of Spectral Compresson of Meshes MIRELA BEN-CHEN AND CRAIG GOTSMAN Center for Graphcs and Geometrc Computng Technon Israel Insttute of Technology Spectral compresson of trangle meshes has
y and the total sum of
 Lnear regresson Testng for non-lnearty In analytcal chemstry, lnear regresson s commonly used n the constructon of calbraton functons requred for analytcal technques such as gas chromatography, atomc absorpton
Lnear regresson Testng for non-lnearty In analytcal chemstry, lnear regresson s commonly used n the constructon of calbraton functons requred for analytcal technques such as gas chromatography, atomc absorpton
2x x l. Module 3: Element Properties Lecture 4: Lagrange and Serendipity Elements
 Module 3: Element Propertes Lecture : Lagrange and Serendpty Elements 5 In last lecture note, the nterpolaton functons are derved on the bass of assumed polynomal from Pascal s trangle for the fled varable.
Module 3: Element Propertes Lecture : Lagrange and Serendpty Elements 5 In last lecture note, the nterpolaton functons are derved on the bass of assumed polynomal from Pascal s trangle for the fled varable.
Type-2 Fuzzy Non-uniform Rational B-spline Model with Type-2 Fuzzy Data
 Malaysan Journal of Mathematcal Scences 11(S) Aprl : 35 46 (2017) Specal Issue: The 2nd Internatonal Conference and Workshop on Mathematcal Analyss (ICWOMA 2016) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES
Malaysan Journal of Mathematcal Scences 11(S) Aprl : 35 46 (2017) Specal Issue: The 2nd Internatonal Conference and Workshop on Mathematcal Analyss (ICWOMA 2016) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES
Cluster Analysis of Electrical Behavior
 Journal of Computer and Communcatons, 205, 3, 88-93 Publshed Onlne May 205 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/ournal/cc http://dx.do.org/0.4236/cc.205.350 Cluster Analyss of Electrcal Behavor Ln Lu Ln Lu, School
Journal of Computer and Communcatons, 205, 3, 88-93 Publshed Onlne May 205 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/ournal/cc http://dx.do.org/0.4236/cc.205.350 Cluster Analyss of Electrcal Behavor Ln Lu Ln Lu, School
Quality Improvement Algorithm for Tetrahedral Mesh Based on Optimal Delaunay Triangulation
 Intellgent Informaton Management, 013, 5, 191-195 Publshed Onlne November 013 (http://www.scrp.org/journal/m) http://dx.do.org/10.36/m.013.5601 Qualty Improvement Algorthm for Tetrahedral Mesh Based on
Intellgent Informaton Management, 013, 5, 191-195 Publshed Onlne November 013 (http://www.scrp.org/journal/m) http://dx.do.org/10.36/m.013.5601 Qualty Improvement Algorthm for Tetrahedral Mesh Based on
Feature Reduction and Selection
 Feature Reducton and Selecton Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engneerng TongJ Unversty Fall, 2012 Today s Topcs Introducton Problems of Dmensonalty Feature Reducton Statstc methods Prncpal Components
Feature Reducton and Selecton Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engneerng TongJ Unversty Fall, 2012 Today s Topcs Introducton Problems of Dmensonalty Feature Reducton Statstc methods Prncpal Components
Machine Learning: Algorithms and Applications
 14/05/1 Machne Learnng: Algorthms and Applcatons Florano Zn Free Unversty of Bozen-Bolzano Faculty of Computer Scence Academc Year 011-01 Lecture 10: 14 May 01 Unsupervsed Learnng cont Sldes courtesy of
14/05/1 Machne Learnng: Algorthms and Applcatons Florano Zn Free Unversty of Bozen-Bolzano Faculty of Computer Scence Academc Year 011-01 Lecture 10: 14 May 01 Unsupervsed Learnng cont Sldes courtesy of
Assignment # 2. Farrukh Jabeen Algorithms 510 Assignment #2 Due Date: June 15, 2009.
 Farrukh Jabeen Algorthms 51 Assgnment #2 Due Date: June 15, 29. Assgnment # 2 Chapter 3 Dscrete Fourer Transforms Implement the FFT for the DFT. Descrbed n sectons 3.1 and 3.2. Delverables: 1. Concse descrpton
Farrukh Jabeen Algorthms 51 Assgnment #2 Due Date: June 15, 29. Assgnment # 2 Chapter 3 Dscrete Fourer Transforms Implement the FFT for the DFT. Descrbed n sectons 3.1 and 3.2. Delverables: 1. Concse descrpton
Subspace clustering. Clustering. Fundamental to all clustering techniques is the choice of distance measure between data points;
 Subspace clusterng Clusterng Fundamental to all clusterng technques s the choce of dstance measure between data ponts; D q ( ) ( ) 2 x x = x x, j k = 1 k jk Squared Eucldean dstance Assumpton: All features
Subspace clusterng Clusterng Fundamental to all clusterng technques s the choce of dstance measure between data ponts; D q ( ) ( ) 2 x x = x x, j k = 1 k jk Squared Eucldean dstance Assumpton: All features
An Accurate Evaluation of Integrals in Convex and Non convex Polygonal Domain by Twelve Node Quadrilateral Finite Element Method
 Internatonal Journal of Computatonal and Appled Mathematcs. ISSN 89-4966 Volume, Number (07), pp. 33-4 Research Inda Publcatons http://www.rpublcaton.com An Accurate Evaluaton of Integrals n Convex and
Internatonal Journal of Computatonal and Appled Mathematcs. ISSN 89-4966 Volume, Number (07), pp. 33-4 Research Inda Publcatons http://www.rpublcaton.com An Accurate Evaluaton of Integrals n Convex and
Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for Computational Expensive Optimization
 Problem efntons and Evaluaton Crtera for Computatonal Expensve Optmzaton B. Lu 1, Q. Chen and Q. Zhang 3, J. J. Lang 4, P. N. Suganthan, B. Y. Qu 6 1 epartment of Computng, Glyndwr Unversty, UK Faclty
Problem efntons and Evaluaton Crtera for Computatonal Expensve Optmzaton B. Lu 1, Q. Chen and Q. Zhang 3, J. J. Lang 4, P. N. Suganthan, B. Y. Qu 6 1 epartment of Computng, Glyndwr Unversty, UK Faclty
An Approach in Coloring Semi-Regular Tilings on the Hyperbolic Plane
 An Approach n Colorng Sem-Regular Tlngs on the Hyperbolc Plane Ma Louse Antonette N De Las Peñas, mlp@mathscmathadmueduph Glenn R Lago, glago@yahoocom Math Department, Ateneo de Manla Unversty, Loyola
An Approach n Colorng Sem-Regular Tlngs on the Hyperbolc Plane Ma Louse Antonette N De Las Peñas, mlp@mathscmathadmueduph Glenn R Lago, glago@yahoocom Math Department, Ateneo de Manla Unversty, Loyola
12/2/2009. Announcements. Parametric / Non-parametric. Case-Based Reasoning. Nearest-Neighbor on Images. Nearest-Neighbor Classification
 Introducton to Artfcal Intellgence V22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 24: Nearest-Neghbors & Support Vector Machnes Rob Fergus Dept of Computer Scence, Courant Insttute, NYU Sldes from Danel Yeung, John DeNero
Introducton to Artfcal Intellgence V22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 24: Nearest-Neghbors & Support Vector Machnes Rob Fergus Dept of Computer Scence, Courant Insttute, NYU Sldes from Danel Yeung, John DeNero
Lecture 5: Multilayer Perceptrons
 Lecture 5: Multlayer Perceptrons Roger Grosse 1 Introducton So far, we ve only talked about lnear models: lnear regresson and lnear bnary classfers. We noted that there are functons that can t be represented
Lecture 5: Multlayer Perceptrons Roger Grosse 1 Introducton So far, we ve only talked about lnear models: lnear regresson and lnear bnary classfers. We noted that there are functons that can t be represented
The Erdős Pósa property for vertex- and edge-disjoint odd cycles in graphs on orientable surfaces
 Dscrete Mathematcs 307 (2007) 764 768 www.elsever.com/locate/dsc Note The Erdős Pósa property for vertex- and edge-dsjont odd cycles n graphs on orentable surfaces Ken-Ich Kawarabayash a, Atsuhro Nakamoto
Dscrete Mathematcs 307 (2007) 764 768 www.elsever.com/locate/dsc Note The Erdős Pósa property for vertex- and edge-dsjont odd cycles n graphs on orentable surfaces Ken-Ich Kawarabayash a, Atsuhro Nakamoto
Reading. 14. Subdivision curves. Recommended:
 eadng ecommended: Stollntz, Deose, and Salesn. Wavelets for Computer Graphcs: heory and Applcatons, 996, secton 6.-6., A.5. 4. Subdvson curves Note: there s an error n Stollntz, et al., secton A.5. Equaton
eadng ecommended: Stollntz, Deose, and Salesn. Wavelets for Computer Graphcs: heory and Applcatons, 996, secton 6.-6., A.5. 4. Subdvson curves Note: there s an error n Stollntz, et al., secton A.5. Equaton
Simplification of 3D Meshes
 Smplfcaton of 3D Meshes Addy Ngan /4/00 Outlne Motvaton Taxonomy of smplfcaton methods Hoppe et al, Mesh optmzaton Hoppe, Progressve meshes Smplfcaton of 3D Meshes 1 Motvaton Hgh detaled meshes becomng
Smplfcaton of 3D Meshes Addy Ngan /4/00 Outlne Motvaton Taxonomy of smplfcaton methods Hoppe et al, Mesh optmzaton Hoppe, Progressve meshes Smplfcaton of 3D Meshes 1 Motvaton Hgh detaled meshes becomng
A Unified, Integral Construction For Coordinates Over Closed Curves
 A Unfed, Integral Constructon For Coordnates Over Closed Curves Schaefer S., Ju T. and Warren J. Abstract We propose a smple generalzaton of Shephard s nterpolaton to pecewse smooth, convex closed curves
A Unfed, Integral Constructon For Coordnates Over Closed Curves Schaefer S., Ju T. and Warren J. Abstract We propose a smple generalzaton of Shephard s nterpolaton to pecewse smooth, convex closed curves
A Five-Point Subdivision Scheme with Two Parameters and a Four-Point Shape-Preserving Scheme
 Mathematcal and Computatonal Applcatons Artcle A Fve-Pont Subdvson Scheme wth Two Parameters and a Four-Pont Shape-Preservng Scheme Jeqng Tan,2, Bo Wang, * and Jun Sh School of Mathematcs, Hefe Unversty
Mathematcal and Computatonal Applcatons Artcle A Fve-Pont Subdvson Scheme wth Two Parameters and a Four-Pont Shape-Preservng Scheme Jeqng Tan,2, Bo Wang, * and Jun Sh School of Mathematcs, Hefe Unversty
5 The Primal-Dual Method
 5 The Prmal-Dual Method Orgnally desgned as a method for solvng lnear programs, where t reduces weghted optmzaton problems to smpler combnatoral ones, the prmal-dual method (PDM) has receved much attenton
5 The Prmal-Dual Method Orgnally desgned as a method for solvng lnear programs, where t reduces weghted optmzaton problems to smpler combnatoral ones, the prmal-dual method (PDM) has receved much attenton
Support Vector Machines
 /9/207 MIST.6060 Busness Intellgence and Data Mnng What are Support Vector Machnes? Support Vector Machnes Support Vector Machnes (SVMs) are supervsed learnng technques that analyze data and recognze patterns.
/9/207 MIST.6060 Busness Intellgence and Data Mnng What are Support Vector Machnes? Support Vector Machnes Support Vector Machnes (SVMs) are supervsed learnng technques that analyze data and recognze patterns.
For instance, ; the five basic number-sets are increasingly more n A B & B A A = B (1)
 Secton 1.2 Subsets and the Boolean operatons on sets If every element of the set A s an element of the set B, we say that A s a subset of B, or that A s contaned n B, or that B contans A, and we wrte A
Secton 1.2 Subsets and the Boolean operatons on sets If every element of the set A s an element of the set B, we say that A s a subset of B, or that A s contaned n B, or that B contans A, and we wrte A
CS 534: Computer Vision Model Fitting
 CS 534: Computer Vson Model Fttng Sprng 004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Scence CS 534 Model Fttng - 1 Outlnes Model fttng s mportant Least-squares fttng Maxmum lkelhood estmaton MAP estmaton Robust
CS 534: Computer Vson Model Fttng Sprng 004 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Scence CS 534 Model Fttng - 1 Outlnes Model fttng s mportant Least-squares fttng Maxmum lkelhood estmaton MAP estmaton Robust
Consistent Spherical Parameterization
 Consstent Sphercal Parameterzaton Arul Asrvatham 1, Eml Praun 1, and Hugues Hoppe 2 1 School of Computng - Unversty of Utah, USA {arul, emlp}@cs.utah.edu 2 Mcrosoft Research, Redmond, USA http://research.mcrosoft.com/~hoppe
Consstent Sphercal Parameterzaton Arul Asrvatham 1, Eml Praun 1, and Hugues Hoppe 2 1 School of Computng - Unversty of Utah, USA {arul, emlp}@cs.utah.edu 2 Mcrosoft Research, Redmond, USA http://research.mcrosoft.com/~hoppe
the nber of vertces n the graph. spannng tree T beng part of a par of maxmally dstant trees s called extremal. Extremal trees are useful n the mxed an
 On Central Spannng Trees of a Graph S. Bezrukov Unverstat-GH Paderborn FB Mathematk/Informatk Furstenallee 11 D{33102 Paderborn F. Kaderal, W. Poguntke FernUnverstat Hagen LG Kommunkatonssysteme Bergscher
On Central Spannng Trees of a Graph S. Bezrukov Unverstat-GH Paderborn FB Mathematk/Informatk Furstenallee 11 D{33102 Paderborn F. Kaderal, W. Poguntke FernUnverstat Hagen LG Kommunkatonssysteme Bergscher
3D vector computer graphics
 3D vector computer graphcs Paolo Varagnolo: freelance engneer Padova Aprl 2016 Prvate Practce ----------------------------------- 1. Introducton Vector 3D model representaton n computer graphcs requres
3D vector computer graphcs Paolo Varagnolo: freelance engneer Padova Aprl 2016 Prvate Practce ----------------------------------- 1. Introducton Vector 3D model representaton n computer graphcs requres
Hierarchical clustering for gene expression data analysis
 Herarchcal clusterng for gene expresson data analyss Gorgo Valentn e-mal: valentn@ds.unm.t Clusterng of Mcroarray Data. Clusterng of gene expresson profles (rows) => dscovery of co-regulated and functonally
Herarchcal clusterng for gene expresson data analyss Gorgo Valentn e-mal: valentn@ds.unm.t Clusterng of Mcroarray Data. Clusterng of gene expresson profles (rows) => dscovery of co-regulated and functonally
AP PHYSICS B 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP PHYSICS B 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES General Notes About 2008 AP Physcs Scorng Gudelnes 1. The solutons contan the most common method of solvng the free-response questons and the allocaton of ponts for
AP PHYSICS B 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES General Notes About 2008 AP Physcs Scorng Gudelnes 1. The solutons contan the most common method of solvng the free-response questons and the allocaton of ponts for
Injective Shape Deformations Using Cube-Like Cages
 309 Injectve Shape Deformatons Usng Cube-Lke Cages Jr Kosnka 1 and Mchael Barton 2 1 Unversty of Oslo, jr.kosnka@cma.uo.no 2 Technon, barton@cs.technon.ac.l ABSTRACT The present paper nvestgates an applcaton
309 Injectve Shape Deformatons Usng Cube-Lke Cages Jr Kosnka 1 and Mchael Barton 2 1 Unversty of Oslo, jr.kosnka@cma.uo.no 2 Technon, barton@cs.technon.ac.l ABSTRACT The present paper nvestgates an applcaton
Problem Set 3 Solutions
 Introducton to Algorthms October 4, 2002 Massachusetts Insttute of Technology 6046J/18410J Professors Erk Demane and Shaf Goldwasser Handout 14 Problem Set 3 Solutons (Exercses were not to be turned n,
Introducton to Algorthms October 4, 2002 Massachusetts Insttute of Technology 6046J/18410J Professors Erk Demane and Shaf Goldwasser Handout 14 Problem Set 3 Solutons (Exercses were not to be turned n,
Structure from Motion
 Structure from Moton Structure from Moton For now, statc scene and movng camera Equvalentl, rgdl movng scene and statc camera Lmtng case of stereo wth man cameras Lmtng case of multvew camera calbraton
Structure from Moton Structure from Moton For now, statc scene and movng camera Equvalentl, rgdl movng scene and statc camera Lmtng case of stereo wth man cameras Lmtng case of multvew camera calbraton
Electrical analysis of light-weight, triangular weave reflector antennas
 Electrcal analyss of lght-weght, trangular weave reflector antennas Knud Pontoppdan TICRA Laederstraede 34 DK-121 Copenhagen K Denmark Emal: kp@tcra.com INTRODUCTION The new lght-weght reflector antenna
Electrcal analyss of lght-weght, trangular weave reflector antennas Knud Pontoppdan TICRA Laederstraede 34 DK-121 Copenhagen K Denmark Emal: kp@tcra.com INTRODUCTION The new lght-weght reflector antenna
Mathematics 256 a course in differential equations for engineering students
 Mathematcs 56 a course n dfferental equatons for engneerng students Chapter 5. More effcent methods of numercal soluton Euler s method s qute neffcent. Because the error s essentally proportonal to the
Mathematcs 56 a course n dfferental equatons for engneerng students Chapter 5. More effcent methods of numercal soluton Euler s method s qute neffcent. Because the error s essentally proportonal to the
Smooth Approximation to Surface Meshes of Arbitrary Topology with Locally Blended Radial Basis Functions
 587 Smooth Approxmaton to Surface eshes of Arbtrary Topology wth Locally Blended Radal Bass Functons ngyong Pang 1,, Weyn a 1, Zhgeng Pan and Fuyan Zhang 1 Cty Unversty of Hong Kong, mewma@ctyu.edu.hk
587 Smooth Approxmaton to Surface eshes of Arbtrary Topology wth Locally Blended Radal Bass Functons ngyong Pang 1,, Weyn a 1, Zhgeng Pan and Fuyan Zhang 1 Cty Unversty of Hong Kong, mewma@ctyu.edu.hk
Data Representation in Digital Design, a Single Conversion Equation and a Formal Languages Approach
 Data Representaton n Dgtal Desgn, a Sngle Converson Equaton and a Formal Languages Approach Hassan Farhat Unversty of Nebraska at Omaha Abstract- In the study of data representaton n dgtal desgn and computer
Data Representaton n Dgtal Desgn, a Sngle Converson Equaton and a Formal Languages Approach Hassan Farhat Unversty of Nebraska at Omaha Abstract- In the study of data representaton n dgtal desgn and computer
VISUAL SELECTION OF SURFACE FEATURES DURING THEIR GEOMETRIC SIMULATION WITH THE HELP OF COMPUTER TECHNOLOGIES
 UbCC 2011, Volume 6, 5002981-x manuscrpts OPEN ACCES UbCC Journal ISSN 1992-8424 www.ubcc.org VISUAL SELECTION OF SURFACE FEATURES DURING THEIR GEOMETRIC SIMULATION WITH THE HELP OF COMPUTER TECHNOLOGIES
UbCC 2011, Volume 6, 5002981-x manuscrpts OPEN ACCES UbCC Journal ISSN 1992-8424 www.ubcc.org VISUAL SELECTION OF SURFACE FEATURES DURING THEIR GEOMETRIC SIMULATION WITH THE HELP OF COMPUTER TECHNOLOGIES
Kent State University CS 4/ Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Dept. of Math & Computer Science LECT-16. Dynamic Programming
 CS 4/560 Desgn and Analyss of Algorthms Kent State Unversty Dept. of Math & Computer Scence LECT-6 Dynamc Programmng 2 Dynamc Programmng Dynamc Programmng, lke the dvde-and-conquer method, solves problems
CS 4/560 Desgn and Analyss of Algorthms Kent State Unversty Dept. of Math & Computer Scence LECT-6 Dynamc Programmng 2 Dynamc Programmng Dynamc Programmng, lke the dvde-and-conquer method, solves problems
Constructing Minimum Connected Dominating Set: Algorithmic approach
 Constructng Mnmum Connected Domnatng Set: Algorthmc approach G.N. Puroht and Usha Sharma Centre for Mathematcal Scences, Banasthal Unversty, Rajasthan 304022 usha.sharma94@yahoo.com Abstract: Connected
Constructng Mnmum Connected Domnatng Set: Algorthmc approach G.N. Puroht and Usha Sharma Centre for Mathematcal Scences, Banasthal Unversty, Rajasthan 304022 usha.sharma94@yahoo.com Abstract: Connected
UNIT 2 : INEQUALITIES AND CONVEX SETS
 UNT 2 : NEQUALTES AND CONVEX SETS ' Structure 2. ntroducton Objectves, nequaltes and ther Graphs Convex Sets and ther Geometry Noton of Convex Sets Extreme Ponts of Convex Set Hyper Planes and Half Spaces
UNT 2 : NEQUALTES AND CONVEX SETS ' Structure 2. ntroducton Objectves, nequaltes and ther Graphs Convex Sets and ther Geometry Noton of Convex Sets Extreme Ponts of Convex Set Hyper Planes and Half Spaces
Fair Triangle Mesh Generation with Discrete Elastica
 Far Trangle Mesh Generaton wth Dscrete Elastca Shn Yoshzawa, and Alexander G. Belyaev, Computer Graphcs Group, Max-Planck-Insttut für Informatk, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany Phone: [+49](681)9325-414 Fax:
Far Trangle Mesh Generaton wth Dscrete Elastca Shn Yoshzawa, and Alexander G. Belyaev, Computer Graphcs Group, Max-Planck-Insttut für Informatk, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany Phone: [+49](681)9325-414 Fax:
Adaptive Fairing of Surface Meshes by Geometric Diffusion
 Adaptve Farng of Surface Meshes by Geometrc Dffuson Chandrajt L. Bajaj Department of Computer Scences, Unversty of Texas, Austn, TX 78712 Emal: bajaj@cs.utexas.edu Guolang Xu State Key Lab. of Scentfc
Adaptve Farng of Surface Meshes by Geometrc Dffuson Chandrajt L. Bajaj Department of Computer Scences, Unversty of Texas, Austn, TX 78712 Emal: bajaj@cs.utexas.edu Guolang Xu State Key Lab. of Scentfc
Sum of Linear and Fractional Multiobjective Programming Problem under Fuzzy Rules Constraints
 Australan Journal of Basc and Appled Scences, 2(4): 1204-1208, 2008 ISSN 1991-8178 Sum of Lnear and Fractonal Multobjectve Programmng Problem under Fuzzy Rules Constrants 1 2 Sanjay Jan and Kalash Lachhwan
Australan Journal of Basc and Appled Scences, 2(4): 1204-1208, 2008 ISSN 1991-8178 Sum of Lnear and Fractonal Multobjectve Programmng Problem under Fuzzy Rules Constrants 1 2 Sanjay Jan and Kalash Lachhwan
Very simple computational domains can be discretized using boundary-fitted structured meshes (also called grids)
 Structured meshes Very smple computatonal domans can be dscretzed usng boundary-ftted structured meshes (also called grds) The grd lnes of a Cartesan mesh are parallel to one another Structured meshes
Structured meshes Very smple computatonal domans can be dscretzed usng boundary-ftted structured meshes (also called grds) The grd lnes of a Cartesan mesh are parallel to one another Structured meshes
Parallel Numerics. 1 Preconditioning & Iterative Solvers (From 2016)
 Technsche Unverstät München WSe 6/7 Insttut für Informatk Prof. Dr. Thomas Huckle Dpl.-Math. Benjamn Uekermann Parallel Numercs Exercse : Prevous Exam Questons Precondtonng & Iteratve Solvers (From 6)
Technsche Unverstät München WSe 6/7 Insttut für Informatk Prof. Dr. Thomas Huckle Dpl.-Math. Benjamn Uekermann Parallel Numercs Exercse : Prevous Exam Questons Precondtonng & Iteratve Solvers (From 6)
TN348: Openlab Module - Colocalization
 TN348: Openlab Module - Colocalzaton Topc The Colocalzaton module provdes the faclty to vsualze and quantfy colocalzaton between pars of mages. The Colocalzaton wndow contans a prevew of the two mages
TN348: Openlab Module - Colocalzaton Topc The Colocalzaton module provdes the faclty to vsualze and quantfy colocalzaton between pars of mages. The Colocalzaton wndow contans a prevew of the two mages
F Geometric Mean Graphs
 Avalable at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 10, Issue 2 (December 2015), pp. 937-952 Applcatons and Appled Mathematcs: An Internatonal Journal (AAM) F Geometrc Mean Graphs A.
Avalable at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 10, Issue 2 (December 2015), pp. 937-952 Applcatons and Appled Mathematcs: An Internatonal Journal (AAM) F Geometrc Mean Graphs A.
Module Management Tool in Software Development Organizations
 Journal of Computer Scence (5): 8-, 7 ISSN 59-66 7 Scence Publcatons Management Tool n Software Development Organzatons Ahmad A. Al-Rababah and Mohammad A. Al-Rababah Faculty of IT, Al-Ahlyyah Amman Unversty,
Journal of Computer Scence (5): 8-, 7 ISSN 59-66 7 Scence Publcatons Management Tool n Software Development Organzatons Ahmad A. Al-Rababah and Mohammad A. Al-Rababah Faculty of IT, Al-Ahlyyah Amman Unversty,
Graph-based Clustering
 Graphbased Clusterng Transform the data nto a graph representaton ertces are the data ponts to be clustered Edges are eghted based on smlarty beteen data ponts Graph parttonng Þ Each connected component
Graphbased Clusterng Transform the data nto a graph representaton ertces are the data ponts to be clustered Edges are eghted based on smlarty beteen data ponts Graph parttonng Þ Each connected component
Helsinki University Of Technology, Systems Analysis Laboratory Mat Independent research projects in applied mathematics (3 cr)
 Helsnk Unversty Of Technology, Systems Analyss Laboratory Mat-2.08 Independent research projects n appled mathematcs (3 cr) "! #$&% Antt Laukkanen 506 R ajlaukka@cc.hut.f 2 Introducton...3 2 Multattrbute
Helsnk Unversty Of Technology, Systems Analyss Laboratory Mat-2.08 Independent research projects n appled mathematcs (3 cr) "! #$&% Antt Laukkanen 506 R ajlaukka@cc.hut.f 2 Introducton...3 2 Multattrbute
Face Recognition University at Buffalo CSE666 Lecture Slides Resources:
 Face Recognton Unversty at Buffalo CSE666 Lecture Sldes Resources: http://www.face-rec.org/algorthms/ Overvew of face recognton algorthms Correlaton - Pxel based correspondence between two face mages Structural
Face Recognton Unversty at Buffalo CSE666 Lecture Sldes Resources: http://www.face-rec.org/algorthms/ Overvew of face recognton algorthms Correlaton - Pxel based correspondence between two face mages Structural
CHAPTER 2 DECOMPOSITION OF GRAPHS
 CHAPTER DECOMPOSITION OF GRAPHS. INTRODUCTION A graph H s called a Supersubdvson of a graph G f H s obtaned from G by replacng every edge uv of G by a bpartte graph,m (m may vary for each edge by dentfyng
CHAPTER DECOMPOSITION OF GRAPHS. INTRODUCTION A graph H s called a Supersubdvson of a graph G f H s obtaned from G by replacng every edge uv of G by a bpartte graph,m (m may vary for each edge by dentfyng
Programming in Fortran 90 : 2017/2018
 Programmng n Fortran 90 : 2017/2018 Programmng n Fortran 90 : 2017/2018 Exercse 1 : Evaluaton of functon dependng on nput Wrte a program who evaluate the functon f (x,y) for any two user specfed values
Programmng n Fortran 90 : 2017/2018 Programmng n Fortran 90 : 2017/2018 Exercse 1 : Evaluaton of functon dependng on nput Wrte a program who evaluate the functon f (x,y) for any two user specfed values
A Binarization Algorithm specialized on Document Images and Photos
 A Bnarzaton Algorthm specalzed on Document mages and Photos Ergna Kavalleratou Dept. of nformaton and Communcaton Systems Engneerng Unversty of the Aegean kavalleratou@aegean.gr Abstract n ths paper, a
A Bnarzaton Algorthm specalzed on Document mages and Photos Ergna Kavalleratou Dept. of nformaton and Communcaton Systems Engneerng Unversty of the Aegean kavalleratou@aegean.gr Abstract n ths paper, a
A MOVING MESH APPROACH FOR SIMULATION BUDGET ALLOCATION ON CONTINUOUS DOMAINS
 Proceedngs of the Wnter Smulaton Conference M E Kuhl, N M Steger, F B Armstrong, and J A Jones, eds A MOVING MESH APPROACH FOR SIMULATION BUDGET ALLOCATION ON CONTINUOUS DOMAINS Mark W Brantley Chun-Hung
Proceedngs of the Wnter Smulaton Conference M E Kuhl, N M Steger, F B Armstrong, and J A Jones, eds A MOVING MESH APPROACH FOR SIMULATION BUDGET ALLOCATION ON CONTINUOUS DOMAINS Mark W Brantley Chun-Hung
GSLM Operations Research II Fall 13/14
 GSLM 58 Operatons Research II Fall /4 6. Separable Programmng Consder a general NLP mn f(x) s.t. g j (x) b j j =. m. Defnton 6.. The NLP s a separable program f ts objectve functon and all constrants are
GSLM 58 Operatons Research II Fall /4 6. Separable Programmng Consder a general NLP mn f(x) s.t. g j (x) b j j =. m. Defnton 6.. The NLP s a separable program f ts objectve functon and all constrants are
SLAM Summer School 2006 Practical 2: SLAM using Monocular Vision
 SLAM Summer School 2006 Practcal 2: SLAM usng Monocular Vson Javer Cvera, Unversty of Zaragoza Andrew J. Davson, Imperal College London J.M.M Montel, Unversty of Zaragoza. josemar@unzar.es, jcvera@unzar.es,
SLAM Summer School 2006 Practcal 2: SLAM usng Monocular Vson Javer Cvera, Unversty of Zaragoza Andrew J. Davson, Imperal College London J.M.M Montel, Unversty of Zaragoza. josemar@unzar.es, jcvera@unzar.es,
Interpolation of the Irregular Curve Network of Ship Hull Form Using Subdivision Surfaces
 7 Interpolaton of the Irregular Curve Network of Shp Hull Form Usng Subdvson Surfaces Kyu-Yeul Lee, Doo-Yeoun Cho and Tae-Wan Km Seoul Natonal Unversty, kylee@snu.ac.kr,whendus@snu.ac.kr,taewan}@snu.ac.kr
7 Interpolaton of the Irregular Curve Network of Shp Hull Form Usng Subdvson Surfaces Kyu-Yeul Lee, Doo-Yeoun Cho and Tae-Wan Km Seoul Natonal Unversty, kylee@snu.ac.kr,whendus@snu.ac.kr,taewan}@snu.ac.kr
U.C. Berkeley CS294: Beyond Worst-Case Analysis Handout 5 Luca Trevisan September 7, 2017
 U.C. Bereley CS294: Beyond Worst-Case Analyss Handout 5 Luca Trevsan September 7, 207 Scrbed by Haars Khan Last modfed 0/3/207 Lecture 5 In whch we study the SDP relaxaton of Max Cut n random graphs. Quc
U.C. Bereley CS294: Beyond Worst-Case Analyss Handout 5 Luca Trevsan September 7, 207 Scrbed by Haars Khan Last modfed 0/3/207 Lecture 5 In whch we study the SDP relaxaton of Max Cut n random graphs. Quc
Optimization Methods: Integer Programming Integer Linear Programming 1. Module 7 Lecture Notes 1. Integer Linear Programming
 Optzaton Methods: Integer Prograng Integer Lnear Prograng Module Lecture Notes Integer Lnear Prograng Introducton In all the prevous lectures n lnear prograng dscussed so far, the desgn varables consdered
Optzaton Methods: Integer Prograng Integer Lnear Prograng Module Lecture Notes Integer Lnear Prograng Introducton In all the prevous lectures n lnear prograng dscussed so far, the desgn varables consdered
Image Representation & Visualization Basic Imaging Algorithms Shape Representation and Analysis. outline
 mage Vsualzaton mage Vsualzaton mage Representaton & Vsualzaton Basc magng Algorthms Shape Representaton and Analyss outlne mage Representaton & Vsualzaton Basc magng Algorthms Shape Representaton and
mage Vsualzaton mage Vsualzaton mage Representaton & Vsualzaton Basc magng Algorthms Shape Representaton and Analyss outlne mage Representaton & Vsualzaton Basc magng Algorthms Shape Representaton and
b * -Open Sets in Bispaces
 Internatonal Journal of Mathematcs and Statstcs Inventon (IJMSI) E-ISSN: 2321 4767 P-ISSN: 2321-4759 wwwjmsorg Volume 4 Issue 6 August 2016 PP- 39-43 b * -Open Sets n Bspaces Amar Kumar Banerjee 1 and
Internatonal Journal of Mathematcs and Statstcs Inventon (IJMSI) E-ISSN: 2321 4767 P-ISSN: 2321-4759 wwwjmsorg Volume 4 Issue 6 August 2016 PP- 39-43 b * -Open Sets n Bspaces Amar Kumar Banerjee 1 and
On Some Entertaining Applications of the Concept of Set in Computer Science Course
 On Some Entertanng Applcatons of the Concept of Set n Computer Scence Course Krasmr Yordzhev *, Hrstna Kostadnova ** * Assocate Professor Krasmr Yordzhev, Ph.D., Faculty of Mathematcs and Natural Scences,
On Some Entertanng Applcatons of the Concept of Set n Computer Scence Course Krasmr Yordzhev *, Hrstna Kostadnova ** * Assocate Professor Krasmr Yordzhev, Ph.D., Faculty of Mathematcs and Natural Scences,
Solitary and Traveling Wave Solutions to a Model. of Long Range Diffusion Involving Flux with. Stability Analysis
 Internatonal Mathematcal Forum, Vol. 6,, no. 7, 8 Soltary and Travelng Wave Solutons to a Model of Long Range ffuson Involvng Flux wth Stablty Analyss Manar A. Al-Qudah Math epartment, Rabgh Faculty of
Internatonal Mathematcal Forum, Vol. 6,, no. 7, 8 Soltary and Travelng Wave Solutons to a Model of Long Range ffuson Involvng Flux wth Stablty Analyss Manar A. Al-Qudah Math epartment, Rabgh Faculty of
Lecture #15 Lecture Notes
 Lecture #15 Lecture Notes The ocean water column s very much a 3-D spatal entt and we need to represent that structure n an economcal way to deal wth t n calculatons. We wll dscuss one way to do so, emprcal
Lecture #15 Lecture Notes The ocean water column s very much a 3-D spatal entt and we need to represent that structure n an economcal way to deal wth t n calculatons. We wll dscuss one way to do so, emprcal
Ramsey numbers of cubes versus cliques
 Ramsey numbers of cubes versus clques Davd Conlon Jacob Fox Choongbum Lee Benny Sudakov Abstract The cube graph Q n s the skeleton of the n-dmensonal cube. It s an n-regular graph on 2 n vertces. The Ramsey
Ramsey numbers of cubes versus clques Davd Conlon Jacob Fox Choongbum Lee Benny Sudakov Abstract The cube graph Q n s the skeleton of the n-dmensonal cube. It s an n-regular graph on 2 n vertces. The Ramsey
Math Homotopy Theory Additional notes
 Math 527 - Homotopy Theory Addtonal notes Martn Frankland February 4, 2013 The category Top s not Cartesan closed. problem. In these notes, we explan how to remedy that 1 Compactly generated spaces Ths
Math 527 - Homotopy Theory Addtonal notes Martn Frankland February 4, 2013 The category Top s not Cartesan closed. problem. In these notes, we explan how to remedy that 1 Compactly generated spaces Ths
CMPS 10 Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes
 CPS 0 Introducton to Computer Scence Lecture Notes Chapter : Algorthm Desgn How should we present algorthms? Natural languages lke Englsh, Spansh, or French whch are rch n nterpretaton and meanng are not
CPS 0 Introducton to Computer Scence Lecture Notes Chapter : Algorthm Desgn How should we present algorthms? Natural languages lke Englsh, Spansh, or French whch are rch n nterpretaton and meanng are not
Ecient Computation of the Most Probable Motion from Fuzzy. Moshe Ben-Ezra Shmuel Peleg Michael Werman. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
 Ecent Computaton of the Most Probable Moton from Fuzzy Correspondences Moshe Ben-Ezra Shmuel Peleg Mchael Werman Insttute of Computer Scence The Hebrew Unversty of Jerusalem 91904 Jerusalem, Israel Emal:
Ecent Computaton of the Most Probable Moton from Fuzzy Correspondences Moshe Ben-Ezra Shmuel Peleg Mchael Werman Insttute of Computer Scence The Hebrew Unversty of Jerusalem 91904 Jerusalem, Israel Emal:
Circuit Analysis I (ENGR 2405) Chapter 3 Method of Analysis Nodal(KCL) and Mesh(KVL)
 Crcut Analyss I (ENG 405) Chapter Method of Analyss Nodal(KCL) and Mesh(KVL) Nodal Analyss If nstead of focusng on the oltages of the crcut elements, one looks at the oltages at the nodes of the crcut,
Crcut Analyss I (ENG 405) Chapter Method of Analyss Nodal(KCL) and Mesh(KVL) Nodal Analyss If nstead of focusng on the oltages of the crcut elements, one looks at the oltages at the nodes of the crcut,
Intra-Parametric Analysis of a Fuzzy MOLP
 Intra-Parametrc Analyss of a Fuzzy MOLP a MIAO-LING WANG a Department of Industral Engneerng and Management a Mnghsn Insttute of Technology and Hsnchu Tawan, ROC b HSIAO-FAN WANG b Insttute of Industral
Intra-Parametrc Analyss of a Fuzzy MOLP a MIAO-LING WANG a Department of Industral Engneerng and Management a Mnghsn Insttute of Technology and Hsnchu Tawan, ROC b HSIAO-FAN WANG b Insttute of Industral
The Greedy Method. Outline and Reading. Change Money Problem. Greedy Algorithms. Applications of the Greedy Strategy. The Greedy Method Technique
 //00 :0 AM Outlne and Readng The Greedy Method The Greedy Method Technque (secton.) Fractonal Knapsack Problem (secton..) Task Schedulng (secton..) Mnmum Spannng Trees (secton.) Change Money Problem Greedy
//00 :0 AM Outlne and Readng The Greedy Method The Greedy Method Technque (secton.) Fractonal Knapsack Problem (secton..) Task Schedulng (secton..) Mnmum Spannng Trees (secton.) Change Money Problem Greedy
ROBOT KINEMATICS. ME Robotics ME Robotics
 ROBOT KINEMATICS Purpose: The purpose of ths chapter s to ntroduce you to robot knematcs, and the concepts related to both open and closed knematcs chans. Forward knematcs s dstngushed from nverse knematcs.
ROBOT KINEMATICS Purpose: The purpose of ths chapter s to ntroduce you to robot knematcs, and the concepts related to both open and closed knematcs chans. Forward knematcs s dstngushed from nverse knematcs.
A NOTE ON FUZZY CLOSURE OF A FUZZY SET
 (JPMNT) Journal of Process Management New Technologes, Internatonal A NOTE ON FUZZY CLOSURE OF A FUZZY SET Bhmraj Basumatary Department of Mathematcal Scences, Bodoland Unversty, Kokrajhar, Assam, Inda,
(JPMNT) Journal of Process Management New Technologes, Internatonal A NOTE ON FUZZY CLOSURE OF A FUZZY SET Bhmraj Basumatary Department of Mathematcal Scences, Bodoland Unversty, Kokrajhar, Assam, Inda,
Content Based Image Retrieval Using 2-D Discrete Wavelet with Texture Feature with Different Classifiers
 IOSR Journal of Electroncs and Communcaton Engneerng (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 78-834,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume 9, Issue, Ver. IV (Mar - Apr. 04), PP 0-07 Content Based Image Retreval Usng -D Dscrete Wavelet wth
IOSR Journal of Electroncs and Communcaton Engneerng (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 78-834,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume 9, Issue, Ver. IV (Mar - Apr. 04), PP 0-07 Content Based Image Retreval Usng -D Dscrete Wavelet wth
A Geometric Approach for Multi-Degree Spline
 L X, Huang ZJ, Lu Z. A geometrc approach for mult-degree splne. JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 27(4): 84 850 July 202. DOI 0.007/s390-02-268-2 A Geometrc Approach for Mult-Degree Splne Xn L
L X, Huang ZJ, Lu Z. A geometrc approach for mult-degree splne. JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 27(4): 84 850 July 202. DOI 0.007/s390-02-268-2 A Geometrc Approach for Mult-Degree Splne Xn L
Computational Geometry: Theory and Applications
 JID:COMGEO AID:1238 /FLA [m3g; v 1.87; Prn:22/11/2012; 15:16] P.1 (1-25) Computatonal Geometry ( ) Contents lsts avalable at ScVerse ScenceDrect Computatonal Geometry: Theory and Applcatons www.elsever.com/locate/comgeo
JID:COMGEO AID:1238 /FLA [m3g; v 1.87; Prn:22/11/2012; 15:16] P.1 (1-25) Computatonal Geometry ( ) Contents lsts avalable at ScVerse ScenceDrect Computatonal Geometry: Theory and Applcatons www.elsever.com/locate/comgeo
An As-Rigid-As-Possible Approach to Sensor Network Localization. Lei Zhang, Ligang Liu, Craig Gotsman and Steven J.
 An As-Rgd-As-Possble Approach to Sensor Network Localzaton Le Zhang, Lgang Lu, Crag Gotsman and Steven J. Gortler TR-0-09 Computer Scence Group Harvard Unversty Cambrdge, Massachusetts An As-Rgd-As-Possble
An As-Rgd-As-Possble Approach to Sensor Network Localzaton Le Zhang, Lgang Lu, Crag Gotsman and Steven J. Gortler TR-0-09 Computer Scence Group Harvard Unversty Cambrdge, Massachusetts An As-Rgd-As-Possble
Applications of DEC:
 Applcatons of DEC: Flud Mechancs and Meshng Dscrete Dfferental Geometry Overvew Puttng DEC to good use Fluds, fluds, fluds geometrc nterpretaton of classcal models dscrete geometrc nterpretaton new geometry-based
Applcatons of DEC: Flud Mechancs and Meshng Dscrete Dfferental Geometry Overvew Puttng DEC to good use Fluds, fluds, fluds geometrc nterpretaton of classcal models dscrete geometrc nterpretaton new geometry-based
