Making flow direction data
|
|
|
- Ashlynn McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Step 4. Making flow direction data Training Module 1) The first step in hydrology analysis is making flow direction data. On Arc Toolbox window, click symbol + on Spatial Analyst Tools Hydrology, double click Flow Direction. Next will appear Flow Direction window. 2) On Input surface raster combo box, choose dem_10 layer. 3) On Output flow direction raster combo box, click symbol, save the file into folder: Data source for training/02 Contour data. On Name text box, write flowdir_10. Click Save button. 4) On Flow Direction window, click OK button. 5) Do steps 1 4 above to obtain flow direction data from processing dem_50 data (pixel size 50m). Give the file name with flowdir_50. 21
2 6) Here is a view of flow direction data. Step 5. Making flow accumulation data 1) The next step is making flow accumulation data. Click Flow Accumulation on Hydrology toolbox. Next will appear Flow Accumulation window. 2) On Input flow direction raster combo box, choose flowdir_10 layer. 22
3 3) On Output accumulation flow raster text box, click symbol, save the file into folder: Data source for training/02 Contour data. On text box Name, write flowacc_10. Click Save button. 4) On Flow Accumulation window, click OK button. 5) Do steps 1 4 above to obtain flow accumulation data from processing slope_50 data (pixel size 50m). Give the file name with flowacc_50. 6) Here is a view of flow accumulation data. 7) To save the workspace, click Save button on Standard toolbar, or press Ctrl+S button on computer keyboard. Save the MXD file into folder: Data source for training\02 Contour data, give the name file contour, and then click Save button. 23
4 I.3. Georeferencing geological map and digitations geological elements Step 1. Georeferencing geological map 1) Open/run ArcMap, choose Blank Map. 2) To set the projection and coordinate system of ArcMap workspace, right click Layers in Table of Contents and then click Properties. Next will appear Data Frame Properties window. 3) Click Coordinate System tab. 4) On part Select a coordinate system, click symbol + on Predefined Geographic Coordinate System World, and choose WGS Click OK button on Data Frame Properties window. At this time, ArcMap workspace has had projection system of WGS 1984 and LatLon coordinate system. 24
5 5) Click Add Data button. Enter into folder: Data source for training\04 Geological map, choose file Peta geologi lembar Besuki.jpg, and then click Add button. 6) If data that will be inserted into the ArcMap workspace is a raster data, there will be a confirmation whether we want to create a "pyramid" for this data. Making pyramid is useful to smoothen the process of data loading and zooming. Click the Yes button. 7) Raster file that we will enter, not yet have a geospatial reference, so there will appear a message like below. Click OK button. 8) The following is a geological map that are inserted. 25
6 9) Because the geological map has not georeferenced yet, so for georeferencing purpose we need Georeferencing toolbar. Right click on any empty space on ArcMap workspace and then click Georeferencing. 10) Next, will appear Georeferencing toolbar as below. Place the toolbar on the upper side of ArcMap workspace. 11) On Georeferencing toolbar, make sure that file that is chosen on Layer combo box is the data that will be georeferenced. This should be considerable concern if there are several image layers on the Table of Contents. On this step, layer that should be chosen is Peta geologi lembar Besuki layer. 12) To choose georeference method, click Georeferencing button, and click Auto Adjust. 13) To make this geological map become georeferenced, we will make actual coordinate of fourframe corner of the geological map. Click Zoom In button on Tools toolbar, and then zoom the upper right corner of geological map frame until the corner can be seen clearly. 14) To start georeferencing process, click Add Control Points button on Georeferencing toolbar. 26
7 15) Point the + cursor, as precise as possible to upper right corner of geological map frame, and then click one time. 16) After the + cursor becomes green and attached on the upper right corner of geological map frame, right click on any space. There will appear an option to input the coordinate. Choose Input DMS of Lon and Lat. 17) On Enter Coordinates DMS window, write on the text box the value of Longitude and Latitude according to lat long value of the geological map frame. Click OK button. Because the georeferencing method that we choose is Auto Adjust, so after we press OK button, on Enter Coordinates DMS window, the geological map will move according the actual position of the upper right corner of geological map frame. 18) Right click Peta geologi lembar Besuki layer, then click Zoom To Layer. At this time, the ArcMap workspace will show Peta geologi lembar Besuki layer as a whole. 19) When finished setting the actual coordinates of the upper right corner, next we set the actual coordinates of the lower left corner of the geological map. The procedure according to the step 1:13-1:17 above. Click the Zoom In button on the toolbar Tools, and then zoom the lower left corner of the frame until the corner of the geological map is clearly visible. 27
8 20) Click the Add Control Points button on the Georeferencing toolbar. 21) Move + cursor as precisely as possible with the lower left corner of the geological map frame, then left click one time. 22) Once the green + cursor attached to the frame corner of geological map, right click in any place. There will appear an option to enter the coordinate. Select Input DMS of Lon and Lat. 23) On Enter Coordinates DMS window, fill in the fields of Latitude and Longitude, according to latitude and longitude value of frame corner of the geological map. Then click OK button. 28
9 24) Repeat the procedure according with Stage 1:13 1:17 or Stage 1:18 1:23 for upper left corner and bottom right corner of geological maps frame. The figure below shows the four corners of the geological map frame that has set the actual coordinates. 25) To see the error rate of coordinates setting, click button on Georeferencing toolbar to bring up Link Table window. Column Residual shows the error values contained in each frame corner. We can see the total Root Mean Square (RMS) error on the lower right corner. All units of this value is in degrees. Click OK button to continue. 26) To set the final stage georeference, click Georeferencing button, then click Update Georeferencing. Once this button is pressed, all the red/green + on the four-frame corner, geological map will disappear. 29
10 27) In total there are four geological maps that should be georeferenced. Therefore do the georeference procedure according with step Phase 1:17. 28) The following is a view of two geological map after going through stages of georeferenced. 29) Save the ArcMap work in the folder: Data source for training\04 Geological map, with the name "Geologi.mxd". Step 2. Digitize geological element 1) There are two types of geological elements that will be digitized from geological map. Those element are lineament and fault. The procedure that will be used is refer to Chapter I.1 Step 2 which is procedure to make data if past landslide data. 2) By using Catalog that is on the right ArcMap workspace, make a new shapefile with the name of lineament, feature type: polyline, and coordinate system WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_49S. 3) On Editor toolbar, click Editor button and click Start Editing. 4) Next will appear Start Editing window that give information that the coordinate system of lineament (UTM 49) is different with the coordinate system of ArcMap workspace (lat-long). This is no problem because both still in the same projection system (WGS 84). Click Continue button to continue. 30
11 5) On Create Features window, click lineament; and on Construction Tools window, click Line. 6) Zoom-in in such a way the geological map so the objects on the map such as lineament and fault can be seen clearly. 7) Find the lineament object, and begin the digitization process by following the lineament object. After completion of the digitized object, press F2 key. Find another lineament object on the study area, and start again the digitations process. 8) Once all the lineament objects of the study area has been completed digitized, on Editor toolbar, click Editor button, click Save edits, and click Stop Editing. 9) According to the geological map, the areas covered in the study area does not have fault data, so the fault data can be skipped. 10) For the purposes of this training, we use the file "kelurusan ref.shp" contained in the folder: Ref. 11) Save the ArcMap workspace into folders: Data source for training\04 Geological map. Give it the name "Geologi.mxd". 31
12 I.4. Making basin, Catchment area and sub-area Training Module Catchment area is an area of land, which is a unity with the river and its tributaries, which serve to accommodate, store, and stream water originating from rainfall to the lake or the sea naturally, where the boundary on land is topographical separators and the boundary at sea until the waters are still affected land activities. Basin or micro-watershed is a hollow in the landscape where the water flows in a ditch. Catchment area is an amalgamation from several basin. Step 1. Making basin data 1) Open/run ArcMap, choose Blank Map. 2) Enter flowdir_10 data from the folder: Data source for training/02 Contour data. 3) On Arc Toolbox window, click + symbol on Spatial Analyst Tools Hydrology, then double click Basin. Next will appear Basin window. 4) On combo box Input flow direction raster, choose layer flowdir_10. 5) On text box Output raster, click symbol, save the file into the folder: Data source for training/02 Contour data. On text box Name, fill in with the name of basin. Click Save button. 32
13 6) Click OK button on Basin window. 7) The figure below is a view of basin data. This data will be used for analysis of watershed determination. Step 2. Choosing basin for making catchment area 1) On ArcToolbox, click + symbol on Conversion Tool From Raster, then double click Raster to Polygon. Next will appear Raster to Polygon window. 33
14 2) On Input raster combo box, choose basin. On Field combo box, choose Value. Save the data into folder: Data source for training\05 Creating catchment area, and give the name of basin.shp. Give check sign on Simplify polygons check box. Click OK button. Once the process is complete, automatically there will be a new layer named "basin" (polygon). 3) Add sungai utama.shp and anak sungai.shp data from the folder: Data source for training\03 River vector data. 4) To determine the boundary of catchment area manually, focus on one of the main river that has flow from upstream to downstream. And then focus on the seasonal river that connect to the main river. The first step, focus the one of main river object. To choose/select the object that we want, right click sungai utama layer -- > Selection, click Make This Only Selectable Layer 5) To make continuous selection, click Selection on ArcMap main menu Interactive Selection Method, click Add to Current Selection. 34
15 6) Click Select Features by Rectangle button on Tools toolbar. 7) Select one of the main river object. Zoom-in or zoom out the view to ease the selection process. 8) Right-click on layer "sungai utama", point the mouse cursor to Selection, then click Create Layer From Selected Features. 9) Automatically, will form a new layer called "sungai utama selection". 10) Press Clear Selected Features button on Tools toolbar to clear the previous selected object. 11) To clarify the view of "sungai utama selection" layer, uncheck or turn off the sungai utama layer. 12) The second phase, focus on the seasonal river object which is a tributary branch of the main rivers of the previous selection ("sungai utama selection" layer). To assist in selecting an object which is a tributary branch of the main river, click Selection in ArcMap main menu, then click Select By Location. The next window will appear Select By Location. 35
16 13) On Selection method combo box, choose select features from. On part of Target layer(s), choose anak sungai. On Source layer combo box, choose sungai utama selection layer. On Spatial selection method combo box, choose Target layer(s) features intersect the Source layer feature. Click OK button. 14) The selected tributary is the objects that connect or intersect the main river object. There will be tributary object that wasn t not selected, one of the cause is that object is a second branch (the position was not intersect with main river, but still is branch of main river. We can select the tributary objects by manually regarding process on previous step 4 7. Tributaries objects that are not selected The boundaries of the basin of the previous process Main river objects Objects selected tributaries 36
17 15) After all of tributary that are the branch of main river are selected, the next step is making a new layer based on this selected tributary. Right click on anak sungai layer Selection, click Create Layer From Selected Features. Automatically, there will form a new layer named anak sungai selection. Figure on below is the view of anak sungai selection layer and sungai utama selection layer. 16) The next step is combining sungai utama selection layer and anak sungai selection layer. On ArcToolbox window, click + symbol on Data Management Tools, General, double click Merge. Next will appear Merge window. 17) On Input Datasets combo box, insert sungai utama selection and anak sungai selection layer. On Output Dataset, save the process result into the folder: Data source for training\03 River vector data. Give the name of sungai selection 01.shp. click OK button. Automatically, will form a new layer on Table of Contents named sungai selection ) Uncheck or turn off the "main stream selection" layer and "selection creeks" layer. 19) Next we will select the basin (sub-das) that are part of this river object. Click Selection on ArcMap main menu, and then click Select By Location. Next will appear Select By Location window. 37
18 20) On Selection method combo box, choose select features from. On Target layer (s) check box, check or choose basin. On Source layer combo box, choose sungai selection 01. On combo box of Spatial selection method, choose Target layer(s) features intersect the source layer feature. Click OK button. We will see the selection result of several basin objects. 21) To make shapefile data based on this selection result, right click basin layer, point the mouse cursor to Data, and then click Export Data. Next will appear Export Data window. 22) Click button on text box of Output feature class. Save the new shapefile into the folder: Data source for training\05 Creating catchment area, with a name of basin 01.shp. 23) If a window appears asking if the exported data will be incorporated into ArcMap as a layer, press the Yes button. 38
19 24) Save the ArcMap workspace into the folder: Data source for training\05 Creating catchment area. Give the name as DAS 1.mxd. Step 3. Determining downstream part of catchment area 1) On this step we will determine the downstream part of a catchment area based on topographic slope. Open/run ArcMap, choose Blank Map. 2) Input sungai selection 01.shp data from the folder: Data source for training\03 River vector data. 3) Input basin_01.shp data from the folder: Data source for training\05 Creating catchment area. 4) Change the symbol view of basin_01 layer, by changing Fill Color become No Color, Outline Width: 1.5, and Outline Color: Blue (Lapis Lazulli). 5) Input the flowdir_10, flowacc_10, and slope_10 data from the folder: Data source for training\02 Contour data. If there are questions to make the Pyramids, click the Yes button. 6) Right click slope_10 layer, and click Properties. 7) On Layer Properties window, click Symbology tab, choose Stretched on part of Show, choose the color gradation green to red on part of Color Ramp, click Invert on part of Stretch, choose Type Stretch Standard Deviation with n: 2. Click OK button. 8) On ArcToolbox window, right click ArcToolbox, choose Add Toolbox. 9) Next will appear Add Toolbox window. Point into the folder: Data source for training\05 Creating catchment area, choose DAS.tbx, click Open button. Automatically, on ArcToolbox window, will add a new Toolbox named DAS. 39
20 10) Right click ArcToolbox and then click Environments. Training Module 11) On Environments window, click Workspace. On text box of Scratch Workspace, click button and point the mouse cursor into the folder: Data source for training\05 Creating catchment area\scratch. Click OK button. 12) Make sure that snapped_pour.shp and watershed.shp file has been erased or there should be no in the folder: Data source for training\05 Creating catchment area\scratch. If these two files are in the folder, using the Catalog, delete both files. 13) Click + symbol on DAS toolbox and then double click Membuat DAS. 14) Next will appear Membuat DAS window. Click Add feature button and then point the cursor to the river flow on the upstream area, that has topographic slope which began sloping. Click the cursor on that position. 40
16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose <None>. Click OK button.
 16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose . Click OK button. 17) The process of TIN making will take some time. Various process
16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose . Click OK button. 17) The process of TIN making will take some time. Various process
I.1. Digitize landslide region and micro-topography using satellite image
 I. Data Preparation At this part, it will be shown the stages of process on preparing all types of data which required in making of landslide potential and banjir bandang hazard map. I.1. Digitize landslide
I. Data Preparation At this part, it will be shown the stages of process on preparing all types of data which required in making of landslide potential and banjir bandang hazard map. I.1. Digitize landslide
GIS LAB 8. Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation
 GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
Lesson 8 : How to Create a Distance from a Water Layer
 Created By: Lane Carter Advisor: Paul Evangelista Date: July 2011 Software: ArcGIS 10 Lesson 8 : How to Create a Distance from a Water Layer Background This tutorial will cover the basic processes involved
Created By: Lane Carter Advisor: Paul Evangelista Date: July 2011 Software: ArcGIS 10 Lesson 8 : How to Create a Distance from a Water Layer Background This tutorial will cover the basic processes involved
15) After appear icon + on the area that we have chosen, click OK button on Membuat DAS window.
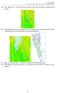 15) After appear icon + on the area that we have chosen, click OK button on Membuat DAS window. 16) Automatically will form two new layer which are snapped_pour layer and Watershed layer. Watershed layer
15) After appear icon + on the area that we have chosen, click OK button on Membuat DAS window. 16) Automatically will form two new layer which are snapped_pour layer and Watershed layer. Watershed layer
Delineating Watersheds from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
 Delineating Watersheds from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) (Using example from the ESRI virtual campus found at http://training.esri.com/courses/natres/index.cfm?c=153) Download locations for additional
Delineating Watersheds from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) (Using example from the ESRI virtual campus found at http://training.esri.com/courses/natres/index.cfm?c=153) Download locations for additional
Stream Network and Watershed Delineation using Spatial Analyst Hydrology Tools
 Stream Network and Watershed Delineation using Spatial Analyst Hydrology Tools Prepared by Venkatesh Merwade School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University vmerwade@purdue.edu January 2018 Objective The
Stream Network and Watershed Delineation using Spatial Analyst Hydrology Tools Prepared by Venkatesh Merwade School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University vmerwade@purdue.edu January 2018 Objective The
STUDENT PAGES GIS Tutorial Treasure in the Treasure State
 STUDENT PAGES GIS Tutorial Treasure in the Treasure State Copyright 2015 Bear Trust International GIS Tutorial 1 Exercise 1: Make a Hand Drawn Map of the School Yard and Playground Your teacher will provide
STUDENT PAGES GIS Tutorial Treasure in the Treasure State Copyright 2015 Bear Trust International GIS Tutorial 1 Exercise 1: Make a Hand Drawn Map of the School Yard and Playground Your teacher will provide
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner December 2015 Revised by Brian Ross July 2016 Exercise Topic: GIS
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner December 2015 Revised by Brian Ross July 2016 Exercise Topic: GIS
A Practical Guide to Using QGIS
 A Practical Guide to Using QGIS 1.1 INTRODUCTION Quantum GIS (QGIS) is a useful mapping software that enables the compilation and displaying of spatial data in the form of a map. Gaining experience in
A Practical Guide to Using QGIS 1.1 INTRODUCTION Quantum GIS (QGIS) is a useful mapping software that enables the compilation and displaying of spatial data in the form of a map. Gaining experience in
Lab 18c: Spatial Analysis III: Clip a raster file using a Polygon Shapefile
 Environmental GIS Prepared by Dr. Zhi Wang, CSUF EES Department Lab 18c: Spatial Analysis III: Clip a raster file using a Polygon Shapefile These instructions enable you to clip a raster layer in ArcMap
Environmental GIS Prepared by Dr. Zhi Wang, CSUF EES Department Lab 18c: Spatial Analysis III: Clip a raster file using a Polygon Shapefile These instructions enable you to clip a raster layer in ArcMap
Introduction to GIS 2011
 Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Lab 6: Transforming Spatial Data
 Lab 6: Transforming Spatial Data Objectives: The primary objectives of this lab are to georeference a raster dataset and to create GIS data by digitizing features from an image as a backdrop. Specifics:
Lab 6: Transforming Spatial Data Objectives: The primary objectives of this lab are to georeference a raster dataset and to create GIS data by digitizing features from an image as a backdrop. Specifics:
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling DEM Delineation Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Read a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Read a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v Introduction to WMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Prerequisite Tutorials None Required Components Data Map
 s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
Exercise Lab: Where is the Himalaya eroding? Using GIS/DEM analysis to reconstruct surfaces, incision, and erosion
 Exercise Lab: Where is the Himalaya eroding? Using GIS/DEM analysis to reconstruct surfaces, incision, and erosion 1) Start ArcMap and ensure that the 3D Analyst and the Spatial Analyst are loaded and
Exercise Lab: Where is the Himalaya eroding? Using GIS/DEM analysis to reconstruct surfaces, incision, and erosion 1) Start ArcMap and ensure that the 3D Analyst and the Spatial Analyst are loaded and
Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
Using LIDAR to Design Embankments in ArcGIS. Written by Scott Ralston U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Windom Wetland Management District
 Using LIDAR to Design Embankments in ArcGIS Written by Scott Ralston U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Windom Wetland Management District This tutorial covers the basics of how to design a dike, embankment
Using LIDAR to Design Embankments in ArcGIS Written by Scott Ralston U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Windom Wetland Management District This tutorial covers the basics of how to design a dike, embankment
Lab.4 & Assignment 2. Lab4. Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map
 EATS4400 GIS Lab.4 & Assignment 2 Lab4 Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map In this lab exercise you will have chance to go through the steps to convert hardcopy map into digital map for ArcGIS. Digitizing
EATS4400 GIS Lab.4 & Assignment 2 Lab4 Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map In this lab exercise you will have chance to go through the steps to convert hardcopy map into digital map for ArcGIS. Digitizing
ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap
 ArcGIS Procedures NUMBER OPERATION APPLICATION: TOOLBAR 1 Import interchange file to coverage 2 Create a new 3 Create a new feature dataset 4 Import Rasters into a 5 Import tables into a PROCEDURE Coverage
ArcGIS Procedures NUMBER OPERATION APPLICATION: TOOLBAR 1 Import interchange file to coverage 2 Create a new 3 Create a new feature dataset 4 Import Rasters into a 5 Import tables into a PROCEDURE Coverage
Georeferencing Imagery in ArcGIS 10.3.x
 Georeferencing Imagery in ArcGIS 10.3.x Georeferencing is the process of aligning imagery (maps, air photos, etc.) with spatial data such as point, lines or polygons (for example, roads and water bodies).
Georeferencing Imagery in ArcGIS 10.3.x Georeferencing is the process of aligning imagery (maps, air photos, etc.) with spatial data such as point, lines or polygons (for example, roads and water bodies).
Tutorial 7: Adding Features and Editing Line and Polygon Layers
 Tutorial 7: Adding Features and Editing Line and Polygon Layers Tutorial Content 7.1. When should I use a line layer to represent data? 7.2. How do I add line features? 7.3. How to use the snapping tool?
Tutorial 7: Adding Features and Editing Line and Polygon Layers Tutorial Content 7.1. When should I use a line layer to represent data? 7.2. How do I add line features? 7.3. How to use the snapping tool?
Display Layers in Geosoft 3D View
 Use the New 2D/3D Workflow features in Target for ArcGIS In Target for ArcGIS version 3.5, there are three new interconnected features that make integrating 2D and 3D data in plan and section maps easier.
Use the New 2D/3D Workflow features in Target for ArcGIS In Target for ArcGIS version 3.5, there are three new interconnected features that make integrating 2D and 3D data in plan and section maps easier.
Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings
 Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings The objective of this analysis is to develop a suitability map for aid in locating helicopter landings in mountainous terrain. The tutorial uses
Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings The objective of this analysis is to develop a suitability map for aid in locating helicopter landings in mountainous terrain. The tutorial uses
Downloading and importing DEM data from ASTER or SRTM (~30m resolution) into ArcMap
 Downloading and importing DEM data from ASTER or SRTM (~30m resolution) into ArcMap Step 1: ASTER or SRTM? There has been some concerns about the quality of ASTER data, nicely exemplified in the following
Downloading and importing DEM data from ASTER or SRTM (~30m resolution) into ArcMap Step 1: ASTER or SRTM? There has been some concerns about the quality of ASTER data, nicely exemplified in the following
Delineating the Stream Network and Watersheds of the Guadalupe Basin
 Delineating the Stream Network and Watersheds of the Guadalupe Basin Francisco Olivera Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University Srikanth Koka Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University
Delineating the Stream Network and Watersheds of the Guadalupe Basin Francisco Olivera Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University Srikanth Koka Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University
Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10
 Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10 Scenario In this exercise, imagine you are a GIS analyst working for Old Dominion University. Construction will begin shortly on renovation of the new
Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10 Scenario In this exercise, imagine you are a GIS analyst working for Old Dominion University. Construction will begin shortly on renovation of the new
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner December 2015 Revised by Brian Ross July 2016 Exercise Topic: Getting
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner December 2015 Revised by Brian Ross July 2016 Exercise Topic: Getting
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3
 Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Field-Scale Watershed Analysis
 Conservation Applications of LiDAR Field-Scale Watershed Analysis A Supplemental Exercise for the Hydrologic Applications Module Andy Jenks, University of Minnesota Department of Forest Resources 2013
Conservation Applications of LiDAR Field-Scale Watershed Analysis A Supplemental Exercise for the Hydrologic Applications Module Andy Jenks, University of Minnesota Department of Forest Resources 2013
A Second Look at DEM s
 A Second Look at DEM s Overview Detailed topographic data is available for the U.S. from several sources and in several formats. Perhaps the most readily available and easy to use is the National Elevation
A Second Look at DEM s Overview Detailed topographic data is available for the U.S. from several sources and in several formats. Perhaps the most readily available and easy to use is the National Elevation
Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader
 Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader Exporting the Yield Data Using SMS Program 1. Data format On Hard Drive. 2. Start program SMS Basic. a. In the File menu choose Open. b. Click on
Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader Exporting the Yield Data Using SMS Program 1. Data format On Hard Drive. 2. Start program SMS Basic. a. In the File menu choose Open. b. Click on
Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data
 Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data Exporting the Yield Data Using JDOffice 1. Data Format On Hard Drive 2. Start program JD Office. a. From the PC Card menu on the left of the screen choose
Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data Exporting the Yield Data Using JDOffice 1. Data Format On Hard Drive 2. Start program JD Office. a. From the PC Card menu on the left of the screen choose
Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
GIS IN ECOLOGY: CREATING RESEARCH MAPS
 GIS IN ECOLOGY: CREATING RESEARCH MAPS Contents Introduction... 2 Elements of Cartography... 2 Course Data Sources... 3 Tasks... 3 Establishing the Map Document... 3 Laying Out the Map... 5 Exporting Your
GIS IN ECOLOGY: CREATING RESEARCH MAPS Contents Introduction... 2 Elements of Cartography... 2 Course Data Sources... 3 Tasks... 3 Establishing the Map Document... 3 Laying Out the Map... 5 Exporting Your
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
Geological mapping using open
 Geological mapping using open source QGIS MOHSEN ALSHAGHDARI -2017- Abstract Geological mapping is very important to display your field work in a map for geologist and others, many geologists face problems
Geological mapping using open source QGIS MOHSEN ALSHAGHDARI -2017- Abstract Geological mapping is very important to display your field work in a map for geologist and others, many geologists face problems
Working with Elevation Data URPL 969 Applied GIS Workshop: Rethinking New Orleans After Hurricane Katrina Spring 2006
 Working with Elevation Data URPL 969 Applied GIS Workshop: Rethinking New Orleans After Hurricane Katrina Spring 2006 This GIS lab exercise will explore Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) data for New
Working with Elevation Data URPL 969 Applied GIS Workshop: Rethinking New Orleans After Hurricane Katrina Spring 2006 This GIS lab exercise will explore Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) data for New
I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10. 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map
 I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10 What is Arc Map? 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map a. Display and manage geo-spatial data (maps, images, points that have a geographic location)
I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10 What is Arc Map? 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map a. Display and manage geo-spatial data (maps, images, points that have a geographic location)
Exporting from GIS 9.0 to AutoCAD
 Exporting from GIS 9.0 to AutoCAD Once a map file is created in GIS with all the desired layers, selected data within a pre-defined boundary can be exported as a AutoCAD.dwg file. Setting up clip boundary
Exporting from GIS 9.0 to AutoCAD Once a map file is created in GIS with all the desired layers, selected data within a pre-defined boundary can be exported as a AutoCAD.dwg file. Setting up clip boundary
ARC HYDRO GROUNDWATER TUTORIALS
 ARC HYDRO GROUNDWATER TUTORIALS details to cross sections Arc Hydro Groundwater (AHGW) is a geodatabase design for representing groundwater datasets within ArcGIS. The data model helps to archive, display,
ARC HYDRO GROUNDWATER TUTORIALS details to cross sections Arc Hydro Groundwater (AHGW) is a geodatabase design for representing groundwater datasets within ArcGIS. The data model helps to archive, display,
CRC Website and Online Book Materials Page 1 of 16
 Page 1 of 16 Appendix 2.3 Terrain Analysis with USGS DEMs OBJECTIVES The objectives of this exercise are to teach readers to: Calculate terrain attributes and create hillshade maps and contour maps. use,
Page 1 of 16 Appendix 2.3 Terrain Analysis with USGS DEMs OBJECTIVES The objectives of this exercise are to teach readers to: Calculate terrain attributes and create hillshade maps and contour maps. use,
WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and bank
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and bank
CE 549 Lab 1 - Linking Streamflow Data to a Gauging Station
 CE 549 Lab 1 - Linking Streamflow Data to a Gauging Station Prepared by Venkatesh Merwade Lyles School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University vmerwade@purdue.edu January 2018 Objective The objective of
CE 549 Lab 1 - Linking Streamflow Data to a Gauging Station Prepared by Venkatesh Merwade Lyles School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University vmerwade@purdue.edu January 2018 Objective The objective of
GIS LAB 1. Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas.
 GIS LAB 1 Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas. ArcGIS offers some advantages for novice users. The graphical user interface is similar to many Windows packages
GIS LAB 1 Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas. ArcGIS offers some advantages for novice users. The graphical user interface is similar to many Windows packages
GEO 465/565 Lab 6: Modeling Landslide Susceptibility
 1 GEO 465/565 Lab 6: Modeling Landslide Susceptibility This lab will give you more practice in understanding and building a GIS analysis model. Recall from class lecture that a GIS analysis model is a
1 GEO 465/565 Lab 6: Modeling Landslide Susceptibility This lab will give you more practice in understanding and building a GIS analysis model. Recall from class lecture that a GIS analysis model is a
WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and
Workshop Exercises for Digital Terrain Analysis with LiDAR for Clean Water Implementation
 Workshop Exercises for Digital Terrain Analysis with LiDAR for Clean Water Implementation This manual is designed to accompany lecture and handout materials provided at a series of workshops offered in
Workshop Exercises for Digital Terrain Analysis with LiDAR for Clean Water Implementation This manual is designed to accompany lecture and handout materials provided at a series of workshops offered in
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8
 LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0
 CHAPTER 2 Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0 In chapter one, Introduction to ILWIS, you started with ILWIS, and learned the basics of the user interface. This chapter presents some key concepts of ILWIS. In section
CHAPTER 2 Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0 In chapter one, Introduction to ILWIS, you started with ILWIS, and learned the basics of the user interface. This chapter presents some key concepts of ILWIS. In section
Lab 9. Raster Analyses. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lab 9 Raster Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University How to Interpolate Surface Turn on the Spatial Analyst extension: Tools > Extensions >
Lab 9 Raster Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University How to Interpolate Surface Turn on the Spatial Analyst extension: Tools > Extensions >
Lab 11: Terrain Analyses
 Lab 11: Terrain Analyses What You ll Learn: Basic terrain analysis functions, including watershed, viewshed, and profile processing. There is a mix of old and new functions used in this lab. We ll explain
Lab 11: Terrain Analyses What You ll Learn: Basic terrain analysis functions, including watershed, viewshed, and profile processing. There is a mix of old and new functions used in this lab. We ll explain
Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in GMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in GMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
v Getting Started An introduction to GMS GMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial An introduction to GMS Objectives This tutorial introduces GMS and covers the basic elements of the user interface. It is the first tutorial that new users should complete. Prerequisite
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial An introduction to GMS Objectives This tutorial introduces GMS and covers the basic elements of the user interface. It is the first tutorial that new users should complete. Prerequisite
SCIMAP-S: Course Notes. Introducing SCIMAP, what is it and how will I use it?
 SCIMAP-S: Course Notes Sensitive Catchment Integrated Modelling and Analysis Platform - for fine Sediment risks Introducing SCIMAP, what is it and how will I use it? See separate slide handout Platforms
SCIMAP-S: Course Notes Sensitive Catchment Integrated Modelling and Analysis Platform - for fine Sediment risks Introducing SCIMAP, what is it and how will I use it? See separate slide handout Platforms
Geographical Information Systems Institute. Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University. LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap
 Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling HEC-1 Interface Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives This tutorial teaches how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives This tutorial teaches how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters
Georeferencing and Digitizing
 INTRODUCTION There is a great deal of geographic data available in formats that cannot be immediately integrated with other GIS data. In order to use these types of data in GIS it is necessary to align
INTRODUCTION There is a great deal of geographic data available in formats that cannot be immediately integrated with other GIS data. In order to use these types of data in GIS it is necessary to align
Construction of Water Table Maps Using GIS
 Geology 309 Construction of Water Table Maps Using GIS Geographic Information Systems (GIS) provide useful tools that enable easy construction of water table maps. In this exercise you will use lake elevation
Geology 309 Construction of Water Table Maps Using GIS Geographic Information Systems (GIS) provide useful tools that enable easy construction of water table maps. In this exercise you will use lake elevation
Converting AutoCAD Map 2002 Projects to ArcGIS
 Introduction This document outlines the procedures necessary for converting an AutoCAD Map drawing containing topologies to ArcGIS version 9.x and higher. This includes the export of polygon and network
Introduction This document outlines the procedures necessary for converting an AutoCAD Map drawing containing topologies to ArcGIS version 9.x and higher. This includes the export of polygon and network
Geography 104 Instructors: Judd Curran & Mark Goodman. LAB EXERCISE #3 Data Analysis - Buffering (25pts)
 Instructors: Judd Curran & Mark Goodman Name: LAB EXERCISE #3 Data Analysis - Buffering (25pts) Transformations in GIS are methods that transform GIS objects and databases into more useful products using
Instructors: Judd Curran & Mark Goodman Name: LAB EXERCISE #3 Data Analysis - Buffering (25pts) Transformations in GIS are methods that transform GIS objects and databases into more useful products using
Data Assembly, Part II. GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4
 Data Assembly, Part II GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4 Objectives Continuation of effective troubleshooting Create shapefiles for analysis with buffers, union, and dissolve functions Calculate polygon
Data Assembly, Part II GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4 Objectives Continuation of effective troubleshooting Create shapefiles for analysis with buffers, union, and dissolve functions Calculate polygon
Spatial Analysis with Raster Datasets
 Spatial Analysis with Raster Datasets Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., P.E. Srikanth Koka Lauren Walker Aishwarya Vijaykumar Keri Clary Department of Civil Engineering April 21, 2014 Contents Brief Overview of
Spatial Analysis with Raster Datasets Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., P.E. Srikanth Koka Lauren Walker Aishwarya Vijaykumar Keri Clary Department of Civil Engineering April 21, 2014 Contents Brief Overview of
New Media in Landscape Architecture: Advanced GIS
 New Media in Landscape Architecture: Advanced GIS - Projections and Transformations - Version 10.2, English ANHALT UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES Hochschule Anhalt Author: Dr. Matthias Pietsch Tutorial-Version:
New Media in Landscape Architecture: Advanced GIS - Projections and Transformations - Version 10.2, English ANHALT UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES Hochschule Anhalt Author: Dr. Matthias Pietsch Tutorial-Version:
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering. Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner Exercise Topic: Getting started with HEC GeoRAS Objective: Create
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner Exercise Topic: Getting started with HEC GeoRAS Objective: Create
3. Map Overlay and Digitizing
 3. Map Overlay and Digitizing 3.1 Opening Map Files NavviewW/SprayView supports digital map files in ShapeFile format from ArcView, DXF format from AutoCAD, MRK format from AG-NAV, Bitmap and JPEG formats
3. Map Overlay and Digitizing 3.1 Opening Map Files NavviewW/SprayView supports digital map files in ShapeFile format from ArcView, DXF format from AutoCAD, MRK format from AG-NAV, Bitmap and JPEG formats
Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS
 Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS Objectives In this lab you will: 1) Learn the basics of the software package we will be using for the remainder of the semester, and 2) Discover the role that climate and
Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS Objectives In this lab you will: 1) Learn the basics of the software package we will be using for the remainder of the semester, and 2) Discover the role that climate and
Raster: The Other GIS Data
 Raster_The_Other_GIS_Data.Docx Page 1 of 11 Raster: The Other GIS Data Objectives Understand the raster format and how it is used to model continuous geographic phenomena. Understand how projections &
Raster_The_Other_GIS_Data.Docx Page 1 of 11 Raster: The Other GIS Data Objectives Understand the raster format and how it is used to model continuous geographic phenomena. Understand how projections &
1. Preparing the base map. 2. Creating new shapefiles. Collecting Spatial Data by Digitizing
 Topics: 1. Preparing the base map 2. Creating new shapefiles 3. Digitizing Features 4. Modifying Existing Features 5. Adding Data Fields and editing Feature Attributes 6. Displaying and Labelling features
Topics: 1. Preparing the base map 2. Creating new shapefiles 3. Digitizing Features 4. Modifying Existing Features 5. Adding Data Fields and editing Feature Attributes 6. Displaying and Labelling features
GIS Fundamentals: Supplementary Lessons with ArcGIS Pro
 Station Analysis (parts 1 & 2) What You ll Learn: - Practice various skills using ArcMap. - Combining parcels, land use, impervious surface, and elevation data to calculate suitabilities for various uses
Station Analysis (parts 1 & 2) What You ll Learn: - Practice various skills using ArcMap. - Combining parcels, land use, impervious surface, and elevation data to calculate suitabilities for various uses
GEO 465/565 - Lab 7 Working with GTOPO30 Data in ArcGIS 9
 GEO 465/565 - Lab 7 Working with GTOPO30 Data in ArcGIS 9 This lab explains how work with a Global 30-Arc-Second (GTOPO30) digital elevation model (DEM) from the U.S. Geological Survey. This dataset can
GEO 465/565 - Lab 7 Working with GTOPO30 Data in ArcGIS 9 This lab explains how work with a Global 30-Arc-Second (GTOPO30) digital elevation model (DEM) from the U.S. Geological Survey. This dataset can
BAEN 673 Biological and Agricultural Engineering Department Texas A&M University ArcSWAT / ArcGIS 10.1 Example 2
 Before you Get Started BAEN 673 Biological and Agricultural Engineering Department Texas A&M University ArcSWAT / ArcGIS 10.1 Example 2 1. Open ArcCatalog Connect to folder button on tool bar navigate
Before you Get Started BAEN 673 Biological and Agricultural Engineering Department Texas A&M University ArcSWAT / ArcGIS 10.1 Example 2 1. Open ArcCatalog Connect to folder button on tool bar navigate
Watershed Modeling Maricopa Predictive HEC-1 Model. Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF LAND SURVEYING & GEO-INFORMATICS LSGI521 PRINCIPLES OF GIS
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF LAND SURVEYING & GEO-INFORMATICS LSGI521 PRINCIPLES OF GIS Student name: Student ID: Table of Content Working with files, folders, various software and
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF LAND SURVEYING & GEO-INFORMATICS LSGI521 PRINCIPLES OF GIS Student name: Student ID: Table of Content Working with files, folders, various software and
Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
Lab#6: Editing Shapefiles With ArcMap. create a point layer from a text file, then join a table to your point attribute table
 NRM338 Fall 2018 Lab#6 Page#1 of 17 In this lab, you will Lab#6: Editing Shapefiles With ArcMap create a point layer from a text file, then join a table to your point attribute table create hyperlinks
NRM338 Fall 2018 Lab#6 Page#1 of 17 In this lab, you will Lab#6: Editing Shapefiles With ArcMap create a point layer from a text file, then join a table to your point attribute table create hyperlinks
Measuring Area/Length of Organisms with GIS
 Measuring Area/Length of Organisms with GIS These instructions enable you to measure the length and area of microscopic organisms in ArcGIS from digital photographs. The four-step process involves: georeferencing
Measuring Area/Length of Organisms with GIS These instructions enable you to measure the length and area of microscopic organisms in ArcGIS from digital photographs. The four-step process involves: georeferencing
GEO/GY461 Applied GIS: Environmental Geology of the Cheaha Mountain, AL, 7.5' Quadrangle Project
 Figure 1: Reference points spreadsheet for Cheaha Mt. 7.5' quadrangle (LatLongCalc_24k.xls). Page -1- Figure 2: RMS statistic from the Cheaha Mountain field map georeference. Page -2- Figure 3: Appearance
Figure 1: Reference points spreadsheet for Cheaha Mt. 7.5' quadrangle (LatLongCalc_24k.xls). Page -1- Figure 2: RMS statistic from the Cheaha Mountain field map georeference. Page -2- Figure 3: Appearance
Watershed Modeling HEC-HMS Interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION 3 ARCGIS 5 START ARCMAP 11 IMPORT 1: MAP DATA 12 ADD WIND FARM DATA 21 CREATE A MAP TO INSERT IN A REPORT 32
 CONTENTS CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION 3 SCENARIO 3 WHAT WILL I LEARN? 3 WHAT DATA DO I HAVE? 4 ARCGIS 5 ARCMAP 6 ARCCATALOG 8 ARCTOOLBOX 9 START ARCMAP 11 IMPORT 1:250000 MAP DATA 12 CREATE A GROUP LAYER 16
CONTENTS CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION 3 SCENARIO 3 WHAT WILL I LEARN? 3 WHAT DATA DO I HAVE? 4 ARCGIS 5 ARCMAP 6 ARCCATALOG 8 ARCTOOLBOX 9 START ARCMAP 11 IMPORT 1:250000 MAP DATA 12 CREATE A GROUP LAYER 16
Exercise 1: Getting to know ArcGIS
 The Scenario You are working for the California Visitor s Commission. You have been asked to prepare a map of California for several dignitaries from out of the country. Your map will need to include enough
The Scenario You are working for the California Visitor s Commission. You have been asked to prepare a map of California for several dignitaries from out of the country. Your map will need to include enough
Creating Contours using ArcMap
 Creating Contours with ArcMap and ArcScene Digital elevation models (DEMs) are geospatial datasets that contain elevation values sampled according to a regularly spaced rectangular grid. They can be used
Creating Contours with ArcMap and ArcScene Digital elevation models (DEMs) are geospatial datasets that contain elevation values sampled according to a regularly spaced rectangular grid. They can be used
This tutorial shows how to extract longitudinal profiles using ArcMap 10.1 and how to plot them with R, an open-source software.
 JESSE S. HILL 2013 UNC-CH This tutorial shows how to extract longitudinal profiles using ArcMap 10.1 and how to plot them with R, an open-source software. R is freely available at: cran.us.r-project.org/
JESSE S. HILL 2013 UNC-CH This tutorial shows how to extract longitudinal profiles using ArcMap 10.1 and how to plot them with R, an open-source software. R is freely available at: cran.us.r-project.org/
Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams.
 GIS LAB 3 Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams. One of the primary goals of this course is to give you some hands-on
GIS LAB 3 Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams. One of the primary goals of this course is to give you some hands-on
v Prerequisite Tutorials GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow GSSHA WMS Basics Creating Feature Objects and Mapping their Attributes to the 2D Grid
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
J.Welhan 5/07. Watershed Delineation Procedure
 Watershed Delineation Procedure 1. Prepare the DEM: - all grids should be in the same projection; if not, then reproject (or define and project); if in UTM, all grids must be in the same zone (if not,
Watershed Delineation Procedure 1. Prepare the DEM: - all grids should be in the same projection; if not, then reproject (or define and project); if in UTM, all grids must be in the same zone (if not,
Importing CDED (Canadian Digital Elevation Data) into ArcGIS 9.x
 Importing CDED (Canadian Digital Elevation Data) into ArcGIS 9.x Related Guides: Obtaining Canadian Digital Elevation Data (CDED) Importing Canadian Digital Elevation Data (CDED) into ArcView 3.x Requirements:
Importing CDED (Canadian Digital Elevation Data) into ArcGIS 9.x Related Guides: Obtaining Canadian Digital Elevation Data (CDED) Importing Canadian Digital Elevation Data (CDED) into ArcView 3.x Requirements:
Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins.
 v. 11.0 HEC-HMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial HEC-HMS Learn how to create multiple sub-basins using HEC-HMS Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins. Prerequisite
v. 11.0 HEC-HMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial HEC-HMS Learn how to create multiple sub-basins using HEC-HMS Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins. Prerequisite
v Overview SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
UNDERSTAND HOW TO SET UP AND RUN A HYDRAULIC MODEL IN HEC-RAS CREATE A FLOOD INUNDATION MAP IN ARCGIS.
 CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
Tutorial 1: Downloading elevation data
 Tutorial 1: Downloading elevation data Objectives In this exercise you will learn how to acquire elevation data from the website OpenTopography.org, project the dataset into a UTM coordinate system, and
Tutorial 1: Downloading elevation data Objectives In this exercise you will learn how to acquire elevation data from the website OpenTopography.org, project the dataset into a UTM coordinate system, and
Practical Manual. Introduction Geo information Science (GRS 10306) B. Kempen, W.TH. ten Haaf (Ed.)
 Laboratory of Geographical Information Science and Remote Sensing Centre for Geo Information Introduction Geo information Science (GRS 10306) Practical Manual B. Kempen, W.TH. ten Haaf (Ed.) September
Laboratory of Geographical Information Science and Remote Sensing Centre for Geo Information Introduction Geo information Science (GRS 10306) Practical Manual B. Kempen, W.TH. ten Haaf (Ed.) September
Using a Geographic Information System (GIS) to look at marine fisheries data
 Using a Geographic Information System (GIS) to look at marine fisheries data Daniel Sheehan GIS Programmer & Analyst Office of Educational Innovation & Technology dsheehan@mit.edu x2-1475 Introduction
Using a Geographic Information System (GIS) to look at marine fisheries data Daniel Sheehan GIS Programmer & Analyst Office of Educational Innovation & Technology dsheehan@mit.edu x2-1475 Introduction
USING CCCR S AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHY IN YOUR OWN GIS
 USING CCCR S AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHY IN YOUR OWN GIS Background: In 2006, the Centre for Catchment and Coastal Research purchased 40 cm resolution aerial photography for the whole of Wales. This product was
USING CCCR S AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHY IN YOUR OWN GIS Background: In 2006, the Centre for Catchment and Coastal Research purchased 40 cm resolution aerial photography for the whole of Wales. This product was
GIS I - Exercise 3 (AV9.2) - Map Rainfall in 3D with Spreadsheets (v2d, Jun 2010)
 GIS I - Exercise 3 (AV9.2) - Map Rainfall in 3D with Spreadsheets (v2d, Jun 2010) Desired Learning Outcomes: Retrieve a set of state boundaries from pre-packaged ESRI data Use the query builder to reduce
GIS I - Exercise 3 (AV9.2) - Map Rainfall in 3D with Spreadsheets (v2d, Jun 2010) Desired Learning Outcomes: Retrieve a set of state boundaries from pre-packaged ESRI data Use the query builder to reduce
Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x
 Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x This guide provides instructions for performing a few basic tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.1, such as adding data to a map document, viewing and changing coordinate system information,
Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x This guide provides instructions for performing a few basic tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.1, such as adding data to a map document, viewing and changing coordinate system information,
BAT Quick Guide 1 / 20
 BAT Quick Guide 1 / 20 Table of contents Quick Guide... 3 Prepare Datasets... 4 Create a New Scenario... 4 Preparing the River Network... 5 Prepare the Barrier Dataset... 6 Creating Soft Barriers (Optional)...
BAT Quick Guide 1 / 20 Table of contents Quick Guide... 3 Prepare Datasets... 4 Create a New Scenario... 4 Preparing the River Network... 5 Prepare the Barrier Dataset... 6 Creating Soft Barriers (Optional)...
