Surfer 13. Powerful Contouring, Gridding, and 3D Surface Mapping Software for Scientists and Engineers
|
|
|
- Meryl Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surfer 13 Powerful Contouring, Gridding, and 3D Surface Mapping Software for Scientists and Engineers Surfer is a full-function 3D visualization, contouring and surface modeling package that runs under Microsoft Windows. Surfer is used extensively for terrain modeling, bathymetric modeling, landscape visualization, surface analysis, contour mapping, watershed and 3D surface mapping, gridding, volumetrics, and much more. Feature Surfer s sophisticated interpolation engine transforms your XYZ data into publication-quality maps. Surfer provides more gridding methods and more control over gridding parameters, including customized variograms, than any other software package on the market. You can also use grid files obtained from other sources, such as USGS DEM files or ESRI grid files. Display your grid as outstanding contour, 3D surface, 3D wireframe, watershed, vector, image, shaded relief, and post maps. Add base maps and combine map types to create the most informative display possible. Virtually all aspects of your maps can be customized to produce exactly the presentation you want. Generating publication quality maps has never been quicker or easier Contour Maps Surfer contour maps give you full control over all map parameters. You can accept the Surfer intelligent defaults to automatically create a contour map, or double-click a map to easily customize map features. Display contour maps over any contour range and contour interval, or specify only the contour levels you want to display on the map. And with Surfer you can add color fill between contours to produce dazzling displays of your maps, or produce gray scale fills for dramatic black and white printouts. Contour Map Features Create colorful contour maps with custom levels, colors, and a color scale!
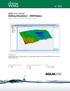
2 3D Surface Map The 3D surface map uses shading and color to emphasize your data features. Change the lighting, display angle and tilt with a click of the mouse. Overlay several surface maps to generate informative block diagrams. Create exciting 3D surface maps from your XYZ data Image Map Surfer image maps use different colors to represent elevations of a grid file. Surfer automatically blends colors between percentage values so you end up with a smooth color gradation over the entire map. You can add color anchors at any percentage point between 0 and 100. Each anchor point can be assigned a unique color, and the colors are automatically blended between adjacent anchor points. This powerful feature allows you to create color maps using any combination of colors. Add a color scale to show the values of the different colors! Image maps can be created independently of other maps, or can be combined with other map layers. They can be scaled, resized, limited and moved.
3 Shaded Relief Map Shaded relief maps are raster images based on grid files. Colors are assigned based on slope orientation relative to a light source. Surfer determines the orientation of each grid cell and calculates reflectance of a point light source on the grid surface. The light source can be thought of as the sun shining on a topographic surface. Surfer automatically blends colors between percentage values so you end up with a smooth color gradation over the map. You can add color anchors so each anchor point can be assigned a unique color, and the colors are automatically blended between adjacent anchor points. This allows you to create color maps using any combination of colors. Shaded relief maps can be created independently of other maps, or can be combined with other layers. Shaded relief maps can be scaled, resized, limited, and moved in the same way as other types of maps. Create spectacular maps in seconds. This map consists of a shaded relief map overlaid with a contour map detailing the salinity of the Atlantic Ocean at 100 meters. Combine a shaded relief map with contour and base map features. Base Maps Surfer can import maps in many different formats to display geographic information. You can combine base maps with other maps in map overlays, or can create stand-alone base maps independent of other maps on the page. You can load any number of base maps on a page. It is easy to overlay a base map on a contour or surface wireframe map, allowing you to display geographic information in combination with the three dimensional data. Display your base maps in Surfer alone or overlay them on other maps.
4 Post maps Post maps show XY locations with fixed size symbols or proportionally scaled symbols of any color. Create post maps independent of other maps on the page, or combined with other map layers. For each posted point, specify the symbol and label type, size, and angle. Also create classed post maps that identify different ranges of data by automatically assigning a different symbol or color to each data range. Post your sample locations, well locations, or original data point locations on a contour map to show the distribution of data points on the map, and to demonstrate the accuracy of the gridding methods you use. Use post maps to display the location of your XY data Watershed Maps Watershed maps automatically calculate and display drainage basins and streams from your grid file. Create colorful watershed maps to display regions draining into a stream, stream system or body of water. Display the catchment basins, streams, or both. Export the basins and streams to any supported file format, including SHP and DXF files, for use in other software! Surfer uses the accurate eight-direction pour point algorithm to calculate the flow direction at each grid node.
5 Detail every aspect of your map from creating watershed boundaries to adding city streets and surrounding elevations Display watershed catchment basins and streams to determine which areas are draining into which streams. Overlay watershed maps on top of aerial photos for a complete picture! 3D Wireframe Maps Surfer wireframe maps provide an impressive three dimensional display of your data. Wireframes are created by connecting Z values along lines of constant X and Y. Use color zones, independent XYZ scaling, orthographic or perspective projections at any tilt or rotation angle, and different combinations of X, Y and Z lines to produce exactly the surface you want. Drape a color-filled contour map over a wireframe map to create the most striking color or black-and-white representations of your data. The possibilities are endless. A wireframe map can be used to display any combination of X,Y, and Z lines. A USGS SDTS DEM file was used to create this map and color zones were defined for the X and Y lines. Vector Maps Instantly create vector maps in Surfer to show direction and magnitude of data at points on a map. You can create vector maps from information in one grid or two separate grids. The two components of the vector map, direction and magnitude, are automatically generated from a single grid by computing the gradient of the represented surface. At any given grid node, the direction of the arrow points in the direction of the steepest descent. The magnitude of the arrow changes depending on the steepness of the descent. Two-grid vector maps use two separate grid files to determine the vector direction and magnitude. The grids can contain Cartesian or polar data. With Cartesian data, one grid consists of X component data and the other grid consists of Y component data. With polar data, one grid consists of angle information and the
6 other grid contains length information. Overlay vector maps on contour or wireframe maps to enhance the presentation! Stacking Maps You can align individual maps horizontally on the page by stacking them. Map stacking was designed to align maps using commensurate coordinate systems. This command is useful for keeping two or more maps separated vertically on the page while keeping relative horizontal positions. Map Layers Adding multiple map layers to your map gives you a way to combine different types of data in one map. For example, you can drape a georeferenced image over a 3D surface map, overlay multiple base maps with a contour map, or plot a post map with contours over a wireframe map. And because you can add any number of map layers to a map, you can show any amount of data on a single map. You are limited only by your imagination!
7 Map Project Choose from an endless list of coordinate systems for your map to display. Specify the source coordinate system for each of the layers in your map, and choose to display the map in any other coordinate system! For example, load data and grid files in UTM or State Plane coordinates, and display the map in Latitude/Longitude coordinates! It is simply that easy! Create custom coordinate systems by defining projection and datum parameters, and save the coordinate system for future use. You can also assign coordinate system information to your grid or data file and save it as an external file for future reuse. This map was created using ten different data sets in more than five different coordinate systems! No extra effort is required to convert data sets, Surfer works seamlessly with all coordinate systems. Profiles Surfer's automatic profile tool makes it easy to visualize the change in Z value from one point to another. Simply select the map, add a profile, and draw the line on the map. Include as many points as you want in the line; it could be a simple two-point line, or a zig-zag shape. In all cases, the profile is created showing the Z value change along the length of the line. Reshape the line on the map, and the profile automatically updates.
8 Profile Features Title and font properties Setting any areas with missing data to skip, minimum Z value, or a custom value Line and fill properties X and Y scaling Exporting the profile line to a text data file Customize Your Map Make your map look its best by customizing it to fit your needs! Surfer offers numerous map features to enhance the look of your map. Use Surfer s defaults, or customize your map by including scale bars, editing colors, lines and fill styles, showing only portions of a map, adjusting the scale and setting axis properties! Superior Gridding The gridding methods in Surfer allow you to produce accurate contour, surface, wireframe, vector, image, and shaded relief maps from your XYZ data. The data can be randomly dispersed over the map area, and Surfer's gridding will interpolate your data onto a grid. Use Surfer s default settings or choose from twelve different gridding methods. Each gridding method provides complete control over the gridding parameters, so you can produce exactly the map you want. If your data are already collected in a regularly spaced rectangular array, you can create a map directly from your data. Computer generated contour maps have never been more accurate. Gridding Features Interpolate from up to 1 billion XYZ data points (limited by available memory) Produce grids with up to 100 million nodes Specify faults and breaklines when gridding Choose from one of the powerful gridding methods: Inverse Distance, Kriging, Minimum Curvature, Polynomial Regression, Triangulation, Nearest Neighbor, Shepard's Method, Radial Basis Functions, Natural Neighbor, Moving Average, and Local Polynomial Specify isotropic or anisotropic weighting You have full control over the grid line geometry including grid limits, grid spacing, and number of grid lines Customize search options based on user-defined data sector parameters Specify search ellipses at any orientation and scaling Use spline smoothing and grid filtering to alter the grid file Use grid math to perform mathematic operations between grid files Use Nearest Neighbor to create grid files without interpolation Use Triangulation to achieve accuracy with large data sets faster Detrend a surface using Polynomial Regression, generate regression coefficients in a report, and calculate residuals
9 Use data exclusion filters to eliminate unwanted data Use duplicate data resolution techniques Generate a grid of Kriging standard deviations Specify point or block Kriging Generate a report of the gridding statistics and parameters including ANOVA regression statistics Specify scales and range for each variogram model Generate grids from a user-specified function of two variables Calculate grids with Data Metrics including: number of points within search ellipse, distance to nearest and farthest neighbor, median, average and offset distance to points within the search ellipse Use cross-validation to judge the suitability of the gridding method for the particular data set Automatically blank the area outside the convex hull of the data Grid Node Editor Clean up your grid with the grid node editor! Surfer's powerful grid node editor allows you to view and edit each individual grid node in a grid file. You can edit the grid node's Z value simply by selecting a grid node and entering a new Z value in the edit box. Grid nodes are represented by small black +'s, and blanked nodes (null values) are represented by blue x's, so it is easy to see your exact data. Variogram Use the variogram modeling subsystem to quantitatively assess the spatial continuity of data. Variograms may be used to select an appropriate variogram model when gridding with the Kriging algorithm. Surfer uses a variogram grid as a fundamental internal data representation and once this grid is built, any experimental variogram can be computed instantaneously. Variogram Features Virtually unlimited data set sizes Display both the experimental variogram and the variogram model Specify the estimator type: variogram, standardized variogram, auto covariance, or auto correlation Specify the variogram model components: exponential, Gaussian, linear, logarithmic, nugget effect, power, quadratic, rational quadratic, spherical, wave, pentaspherical, and cubic models Customize the variogram to display symbols, variance, and number of pairs for each lag Export the experimental variogram data
10 Faults & Breaklines Define faults and breaklines when gridding your data. Faults act as barriers to the information flow, and data on one side of the fault will not be directly used to calculate grid node values on the other side of the fault. Breaklines include Z values. When Surfer sees a breakline, it uses the Z value of the breakline in combination with nearby data points to calculate the grid node value. Unlike faults, breaklines are not barriers to information flow and the gridding algorithm can cross the breakline to use a point on the other side to calculate a grid node value. Use breaklines to define streamlines, ridges, and other breaks in slopes. The gridding methods that support faults are: Inverse Distance to a Power, Minimum Curvature, Nearest Neighbor, and Data Metrics. The gridding methods that support breaklines are: Inverse Distance to a Power, Kriging, Minimum Curvature, Nearest Neighbor, Radial Basis Function, Moving Average, Data Metrics, and Local Polynomial. Original contour map without faults or breaklines. The same data set gridded with two faults and displayed as a contour map. The same data set gridded with two breaklines and displayed as a contour map. Using USGS and SRTM Data Use USGS Digital Elevation Model (DEM), National Elevation Dataset (NED) and NASA Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) data with any Surfer command that uses grid files. Directly use the files in native format without modification or conversion. Display information about the files, such as X, Y and Z extents or grid statistics. Create contour, vector, shaded relief, image, 3D surface, and 3D wireframe maps from the files. The above contour map was generated from a grid file in BIL format, Worksheet Surfer lets you massage your data in many ways to achieve the exact output you want. Surfer includes a full-featured worksheet for creating, opening, editing, and saving data files. Data files can be up to one billion rows and columns, subject to available memory. You can cut, copy, and paste data within the Surfer worksheet or between applications.
11 Supported File Formats Surfer supports many data, grid, and import/export formats. Data Files Grid Files Import/Export Open Data: Access Database (ACCDB, MDB) ASCII Data (DAT) Atlas Boundary (BNA) Comma Separated Variables (CSV) Database (DBF) Excel Spreadsheet (XLS, XLSX) Golden Software Blanking (BLN) LiDAR Data Worksheet (LAS) ODBC Database Connection Sylk Spreadsheet (SLK) Text Data (TXT) Save Data: ASCII Data (DAT) Atlas Boundary (BNA) Comma Separated Variables (CSV) Excel Spreadsheet (XLS, XLSX) Golden Software Blanking (BLN) Sylk Spreadsheet (SLK) Text Data (TXT) Open Grids: ACR-NEMA Medical Image (AN1, AN2) Amira Mesh (AM, COL) Amira Stacked Images (ASI) Analyze 7.5 Medical Image (IMG) Arc/Info ASCII Grid (ASC, AIG, AGR, GRD) Arc/Info Binary Grid (ADF) AVS Field (FLD) AVS X-Image (X, XIMG) Banded Grid (BIL, BIP, BSQ) Compressed Bitmap (JPG) CPS-3 Grid Format (ASC, DAT, GRD, CPS, CPS3) DICOM3 Medical Image (DIC, DCM) DTED (DT?) Edition 1 Grid Format (GRB, GRIB) ER Mapper Grid Format (ERS) ER Mapper (ECW) ESRI ArcInfo Export Format (Grid) (E00) ESRI Float Grid Format (FLT) ETOPO-5 (DOS, DAT) Geosoft Binary Grid (GRD) GIF Image (GIF) GLOBE DEM (?10g) Grid exchange Format (GXF) GTOPO-30 (HDR) Hierarchical Data Format (HDF) Idrisi Raster Format (RST, IMG) Iris Explorer (LAT) Leica Confocal Raw Slices (INFO) LizardTech MrSID Image (SID) Metamorph (STK) PNM/PPM/PGM/PBM Image (PNM, PPM, PGM, PBM) Portable Network Graphics (PNG) RAW Binary Grid (RAW, BIN) SDTS DEM (CATD.DFF, TAR.GZ, TAR, ZIP, TGZ) SGI-RGB Image (RGB, RGBA, BW) Sun Raster Image (SUN, RAS) Surfer Grid (GRD) Tagged Image (TIF) USGS DEM (DEM) Visualization Toolkit (VTK) Windows Bitmap (BMP) Z-MAP Plus Grid Format (ASC, DAT, GRD, XYZ, ZMAP, ZYC, ZYCOR) Save Grids: Amira Mesh (AM, COL) Analyze 7.5 Medical Image (IMG) Arc/Info ASCII Grid (ASC, AIG, AGR, GRD) Arc/Info Binary Grid (ADF) AVS Field (FLD) Banded Interleave By Line (BIL) Banded Interleave By Pixel (BIP) Banded Sequential (BSQ) CPS-3 Grid Format (CPS, CPS3, ASC, DAT, GRD) ER Mapper Grid Format (ERS) ESRI Float Grid Format (FLT) Geosoft Binary Grid (GRD, GGF) Grid exchange Format (GXF) Hierarchical Data Format (HDF) Import: ACR-NEMA Medical Image (AN1, AN2) Atlas Boundary (BNA) AutoCAD Drawing (DXF) AVS X-Image (X, XIMG) Compressed Bitmap (JPG) DICOM3 Medical Image (DIC, DCM) ER Mapper (ECW) ESRI ArcInfo Export Format (E00) ESRI Shapefile (SHP) GeoTIFF (TIF) GIF Image (GIF) Golden Software Blanking (BLN) Golden Software Boundary (GSB) Golden Software Interchange (GSI) Golden Software PlotCall (PLT) GPS Exchange Format (GPX) LizardTech MrSID Image (SID) MapInfo Interchange Format (MIF) PNM/PPM/PGM/PBM Image (PNM, PPM, PGM, PBM) Portable Network Graphics (PNG) SDTS TVP (CATD.DDF, TAR.GZ, ZIP, TGZ) SGI-RGB Image (RGB, RGBA, BW) Stanford PLY (PLY) Sun Raster Image (SUN, RAS) Tagged Image (TIF) Targa (TrueVision) (TGA) USGS Digital Line Graph (DLG, LGO, LGS) Visualization Toolkit (VTK) Windows Bitmap (BMP) Windows Enhanced Metafile (EMF) Windows Metafile (WMF) Export: 3D ESRI Shapefile (SHP) Atlas Boundary (BNA) AutoCAD DXF Drawing (DXF) AVS X-Image (X, XIMG) Encapsulated Postscript (EPS) ESRI Shapefile (SHP) GeoTIFF (TIF) GIF Image (GIF) Golden Software Blanking (BLN) Golden Software Boundary (GSB) Golden Software Interchange (GSI) Google Earth (KML, KMZ) JPEG Compressed Bitmap (JPG) MapInfo Interchange Format (MIF)
12 Iris Explorer (LAT) RAW Binary Grid (RAW, BIN) Surfer 6 Binary Grid (GRD) Surfer 6 Text Grid (GRD) Surfer 7 Binary Grid (GRD) USGS DEM (DEM) Visualization Toolkit (VTK) XYZ Data (DAT) Z-MAP Plus Grid Format (ASC, DAT, GRD, XYZ, ZMAP, ZYC, ZYCOR) PDF (Raster) (PDF) PDF (Vector) (PDF) PNM Image (PNM) Portable Network Graphics (PNG) SGI-RGB Image (RGB, RGBA) Sun Raster Image (RAS, SUN) Tagged Image (TIF) Targa (TrueVision) (TGA) Windows Bitmap (BMP) Windows Enhanced Metafile (EMF) Windows Metafile (WMF)
Surfer 11. Powerful Contouring, Gridding, and 3D Surface Mapping Software for Scientists and Engineers
 Surfer 11 Powerful Contouring, Gridding, and 3D Surface Mapping Software for Scientists and Engineers Surfer is a full-function 3D visualization, contouring and surface modeling package that runs under
Surfer 11 Powerful Contouring, Gridding, and 3D Surface Mapping Software for Scientists and Engineers Surfer is a full-function 3D visualization, contouring and surface modeling package that runs under
Surfer 8 Overview. Which Surfer Features Would You Like to Learn About? Contour Maps
 Surfer 8 Overview Surfer is a contouring and 3D surface mapping program that runs under Microsoft Windows. It quickly and easily converts your data into outstanding contour, surface, wireframe, vector,
Surfer 8 Overview Surfer is a contouring and 3D surface mapping program that runs under Microsoft Windows. It quickly and easily converts your data into outstanding contour, surface, wireframe, vector,
The Industry Standard in Mapping Solutions. Contouring and 3D Surface Mapping for Scientists and Engineers
 The Industry Standard in Mapping Solutions Only $599! Contouring and 3D Surface Mapping for Scientists and Engineers w w w. g o l d e n s o f t w a r e. c o m The software of choice for creating contour
The Industry Standard in Mapping Solutions Only $599! Contouring and 3D Surface Mapping for Scientists and Engineers w w w. g o l d e n s o f t w a r e. c o m The software of choice for creating contour
GRAPHER. Grapher Overview
 GRAPHER Grapher Overview Grapher is the ultimate technical graphing package available. This easy-to-use, powerful, dynamic program will help you create superior publication-quality professional graphs
GRAPHER Grapher Overview Grapher is the ultimate technical graphing package available. This easy-to-use, powerful, dynamic program will help you create superior publication-quality professional graphs
Surfer 10 Self-Paced Training Guide
 Surfer 10 Self-Paced Training Guide I. Introduction to Surfer 1 What Surfer can do Types of files that can be imported Types of files that can be exported Setting options II. Preparing a Base and Post
Surfer 10 Self-Paced Training Guide I. Introduction to Surfer 1 What Surfer can do Types of files that can be imported Types of files that can be exported Setting options II. Preparing a Base and Post
Golden Software, Inc.
 Golden Software, Inc. Only $299! The most sophisticated graphing package available, providing the professional quality you need with the flexibility you want. Create one of the more than 30 different graph
Golden Software, Inc. Only $299! The most sophisticated graphing package available, providing the professional quality you need with the flexibility you want. Create one of the more than 30 different graph
Surfer. Powerful contouring, gridding & surface mapping system. Full User s Guide
 Surfer Powerful contouring, gridding & surface mapping system Full User s Guide Surfer Registration Information Your Surfer product key is located in the email download instructions and in your account
Surfer Powerful contouring, gridding & surface mapping system Full User s Guide Surfer Registration Information Your Surfer product key is located in the email download instructions and in your account
Chapter 2 Surfer Tutorial
 Chapter 2 Surfer Tutorial Overview This tutorial introduces you to some of Surfer s features and shows you the steps to take to produce maps. In addition, the tutorial will help previous Surfer users learn
Chapter 2 Surfer Tutorial Overview This tutorial introduces you to some of Surfer s features and shows you the steps to take to produce maps. In addition, the tutorial will help previous Surfer users learn
Surfer 8 Version Info
 Surfer 8 Version Info Version 8.09.2391 (May 21, 2008) Fixed a sporadic crash when shutting down Surfer Demo via Automation. Grid Extract on dted file with starting row > 1 crashes. Crash if map is deleted
Surfer 8 Version Info Version 8.09.2391 (May 21, 2008) Fixed a sporadic crash when shutting down Surfer Demo via Automation. Grid Extract on dted file with starting row > 1 crashes. Crash if map is deleted
Surfer Self-Paced Training Guide
 Surfer Self-Paced Training Guide I. Introduction to Surfer 1 What Surfer can do Setting options II. Preparing a Base and Post Map 2 Importing a base map Adding drawing objects to a base map Calculate area
Surfer Self-Paced Training Guide I. Introduction to Surfer 1 What Surfer can do Setting options II. Preparing a Base and Post Map 2 Importing a base map Adding drawing objects to a base map Calculate area
New Features. User Friendly. Image Registration and Processing. Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Page 1 of 5 New Features The following is an overview of some of Didger's new features. User Friendly Install 32-bit or 64-bit version of Didger. Updated to a modern Windows look. Added the Text Editor,
Page 1 of 5 New Features The following is an overview of some of Didger's new features. User Friendly Install 32-bit or 64-bit version of Didger. Updated to a modern Windows look. Added the Text Editor,
Engineering Geology. Engineering Geology is backbone of civil engineering. Topographic Maps. Eng. Iqbal Marie
 Engineering Geology Engineering Geology is backbone of civil engineering Topographic Maps Eng. Iqbal Marie Maps: are a two dimensional representation, of an area or region. There are many types of maps,
Engineering Geology Engineering Geology is backbone of civil engineering Topographic Maps Eng. Iqbal Marie Maps: are a two dimensional representation, of an area or region. There are many types of maps,
Enhance data presentation with summation plots to add additional information to your graph.
 Only $349! Exciting New Features... Display your data as a colorful and informative new stiff diagram! Create the graph you want! Add colors and widths for bar charts directly from the worksheet! Enhance
Only $349! Exciting New Features... Display your data as a colorful and informative new stiff diagram! Create the graph you want! Add colors and widths for bar charts directly from the worksheet! Enhance
Lab 1: Exploring data format
 Geog 458: Map Sources and Errors January 13, 2006 Lab 1: Exploring data format Data format supported by ArcGIS There are many file types supported by ArcGIS, in addition to specific cartographic objects.
Geog 458: Map Sources and Errors January 13, 2006 Lab 1: Exploring data format Data format supported by ArcGIS There are many file types supported by ArcGIS, in addition to specific cartographic objects.
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
New Features. User Friendly. Map Features. This is an overview of some of Surfer 12's new features.
 Page 1 of 5 New Features This is an overview of some of Surfer 12's new features. User Friendly Save in Surfer 11 or Surfer 12.SRF format for easier sharing between versions. Added the Trackball command
Page 1 of 5 New Features This is an overview of some of Surfer 12's new features. User Friendly Save in Surfer 11 or Surfer 12.SRF format for easier sharing between versions. Added the Trackball command
What's New in Voxler 4?
 What's New in Voxler 4? We have compiled a list of some of the top new features in Voxler 4. This list is only a small sampling of the new features added to Voxler 4. Drape GIS Data and Vector Maps over
What's New in Voxler 4? We have compiled a list of some of the top new features in Voxler 4. This list is only a small sampling of the new features added to Voxler 4. Drape GIS Data and Vector Maps over
Quick. Efficient. Versatile. Graphing Software for Scientists and Engineers.
 Quick. GrapherTM 3 Efficient. Versatile. Graphing Discover the easy-to-use and powerful capabilities of Grapher 3! Your graphs are too important not to use the most superior graphing program available.
Quick. GrapherTM 3 Efficient. Versatile. Graphing Discover the easy-to-use and powerful capabilities of Grapher 3! Your graphs are too important not to use the most superior graphing program available.
Digital Elevation Models
 Digital Elevation Models National Elevation Dataset 1 Data Sets US DEM series 7.5, 30, 1 o for conterminous US 7.5, 15 for Alaska US National Elevation Data (NED) GTOPO30 Global Land One-kilometer Base
Digital Elevation Models National Elevation Dataset 1 Data Sets US DEM series 7.5, 30, 1 o for conterminous US 7.5, 15 for Alaska US National Elevation Data (NED) GTOPO30 Global Land One-kilometer Base
Geographic Surfaces. David Tenenbaum EEOS 383 UMass Boston
 Geographic Surfaces Up to this point, we have talked about spatial data models that operate in two dimensions How about the rd dimension? Surface the continuous variation in space of a third dimension
Geographic Surfaces Up to this point, we have talked about spatial data models that operate in two dimensions How about the rd dimension? Surface the continuous variation in space of a third dimension
Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers
 Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers 3. Representing Maps as Numbers 3.2 Structuring Attributes 3.3 Structuring Maps 3.4 Why Topology Matters 3.5 Formats for GIS Data 3.6 Exchanging Data David Tenenbaum EEOS 265
Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers 3. Representing Maps as Numbers 3.2 Structuring Attributes 3.3 Structuring Maps 3.4 Why Topology Matters 3.5 Formats for GIS Data 3.6 Exchanging Data David Tenenbaum EEOS 265
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY
 LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
Geostatistics 2D GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Contents
 GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS 1 Introduction Two-dimensional geostatistics (interpolation) can be performed in GMS using the 2D Scatter Point module. The module is used to interpolate from sets of 2D scatter points
GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS 1 Introduction Two-dimensional geostatistics (interpolation) can be performed in GMS using the 2D Scatter Point module. The module is used to interpolate from sets of 2D scatter points
ENVI Tutorial: Map Composition
 ENVI Tutorial: Map Composition Table of Contents OVERVIEW OF THIS TUTORIAL...3 MAP COMPOSITION IN ENVI...4 Open and Display Landsat TM Data...4 Build the QuickMap Template...4 MAP ELEMENTS...6 Adding Virtual
ENVI Tutorial: Map Composition Table of Contents OVERVIEW OF THIS TUTORIAL...3 MAP COMPOSITION IN ENVI...4 Open and Display Landsat TM Data...4 Build the QuickMap Template...4 MAP ELEMENTS...6 Adding Virtual
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O
 RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
What's New in Surfer 14?
 What's New in Surfer 14? There are many very exciting new features in Surfer v14! We focused on increasing usability, improving workflows to increase time savings, and including the most popular new features
What's New in Surfer 14? There are many very exciting new features in Surfer v14! We focused on increasing usability, improving workflows to increase time savings, and including the most popular new features
Lecture 06. Raster and Vector Data Models. Part (1) Common Data Models. Raster. Vector. Points. Points. ( x,y ) Area. Area Line.
 Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 13. TERRAIN MAPPING AND ANALYSIS 13.1 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis 13.1.1 DEM 13.1.2 TIN Box 13.1 Terrain Data Format 13.2 Terrain Mapping 13.2.1 Contouring 13.2.2 Vertical Profiling 13.2.3
Chapter 13. TERRAIN MAPPING AND ANALYSIS 13.1 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis 13.1.1 DEM 13.1.2 TIN Box 13.1 Terrain Data Format 13.2 Terrain Mapping 13.2.1 Contouring 13.2.2 Vertical Profiling 13.2.3
The GIS Spatial Data Model
 The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
Accessing Data Where it Lives
 Accessing Data Where it Lives Session 3A Steve Carr TSI Tyson Haverkort Safe Software Session Description We ll discuss many types of data that can be used in MapInfo Professional such as: Business Data
Accessing Data Where it Lives Session 3A Steve Carr TSI Tyson Haverkort Safe Software Session Description We ll discuss many types of data that can be used in MapInfo Professional such as: Business Data
BREEZE 3D Analyst for the Advanced AERMOD Modeler BREEZE Software
 BREEZE 3D Analyst for the Advanced AERMOD Modeler BREEZE Software 12770 Merit Drive Suite 900 Dallas, TX 75251 +1 (972) 661-8881 breeze-software.com BREEZE 3D Analyst Presented by: Name, Title Date For
BREEZE 3D Analyst for the Advanced AERMOD Modeler BREEZE Software 12770 Merit Drive Suite 900 Dallas, TX 75251 +1 (972) 661-8881 breeze-software.com BREEZE 3D Analyst Presented by: Name, Title Date For
Surface Analysis. Data for Surface Analysis. What are Surfaces 4/22/2010
 Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
ENVI Classic Tutorial: Introduction to ENVI Classic 2
 ENVI Classic Tutorial: Introduction to ENVI Classic Introduction to ENVI Classic 2 Files Used in This Tutorial 2 Getting Started with ENVI Classic 3 Loading a Gray Scale Image 3 ENVI Classic File Formats
ENVI Classic Tutorial: Introduction to ENVI Classic Introduction to ENVI Classic 2 Files Used in This Tutorial 2 Getting Started with ENVI Classic 3 Loading a Gray Scale Image 3 ENVI Classic File Formats
DigiTerra Explorer 7 Basic Advanced Professional
 Files Supported map and mapping project formats DigiTerra Explorer Map (.EXP) DigiTerra Map Pack (.DMP) Embedded DigiTerra Map Pack (.DMP in.exp file) Hungarian Digital Base Map (.DAT) OpenGIS KML Map
Files Supported map and mapping project formats DigiTerra Explorer Map (.EXP) DigiTerra Map Pack (.DMP) Embedded DigiTerra Map Pack (.DMP in.exp file) Hungarian Digital Base Map (.DAT) OpenGIS KML Map
SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL
 SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL DIGITAL MAPPING FILES (very efficient/extremely accurate): 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT FILE EXT(S) FORMAT FILE EXT(S) AutoCAD (*.dwg,
SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL DIGITAL MAPPING FILES (very efficient/extremely accurate): 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT FILE EXT(S) FORMAT FILE EXT(S) AutoCAD (*.dwg,
SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL
 SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL DIGITAL MAPPING FILES (very efficient/extremely accurate): 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT FILE EXT(S) FORMAT FILE EXT(S) AutoCAD (*.dwg,
SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL DIGITAL MAPPING FILES (very efficient/extremely accurate): 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT FILE EXT(S) FORMAT FILE EXT(S) AutoCAD (*.dwg,
MARS v Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds and )
 MARS v2018.0 Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds 8302.01 8302.18 and 8350.00 8352.00) Contents New Features:... 2 Enhancements:... 6 List of Bug Fixes... 13 1 New Features: LAS Up-Conversion prompts
MARS v2018.0 Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds 8302.01 8302.18 and 8350.00 8352.00) Contents New Features:... 2 Enhancements:... 6 List of Bug Fixes... 13 1 New Features: LAS Up-Conversion prompts
ENVI Tutorial: Introduction to ENVI
 ENVI Tutorial: Introduction to ENVI Table of Contents OVERVIEW OF THIS TUTORIAL...1 GETTING STARTED WITH ENVI...1 Starting ENVI...1 Starting ENVI on Windows Machines...1 Starting ENVI in UNIX...1 Starting
ENVI Tutorial: Introduction to ENVI Table of Contents OVERVIEW OF THIS TUTORIAL...1 GETTING STARTED WITH ENVI...1 Starting ENVI...1 Starting ENVI on Windows Machines...1 Starting ENVI in UNIX...1 Starting
Gridding and Contouring in Geochemistry for ArcGIS
 Gridding and Contouring in Geochemistry for ArcGIS The Geochemsitry for ArcGIS extension includes three gridding options: Minimum Curvature Gridding, Kriging and a new Inverse Distance Weighting algorithm.
Gridding and Contouring in Geochemistry for ArcGIS The Geochemsitry for ArcGIS extension includes three gridding options: Minimum Curvature Gridding, Kriging and a new Inverse Distance Weighting algorithm.
Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
Gravity and Magnetics
 www.geosoft.com Mapping, Modelling, Interpretation Gravity and Magnetics Energy Exploration Solutions Geosoft is still by far the best software for generating gravity and magnetic interpretations, and
www.geosoft.com Mapping, Modelling, Interpretation Gravity and Magnetics Energy Exploration Solutions Geosoft is still by far the best software for generating gravity and magnetic interpretations, and
GeoShow3D. Product Features. Product Information Number: Persona de contacto:
 Product Information Number: 0001 2.7.2004 Persona de contacto: info@geovirtual.com GeoShow3D Rambla de Cataluña 35, principal. E-08007 Barcelona Tel. +34 934 872 144 Fax +34 934 875 809 Spain. www.geovirtual.com
Product Information Number: 0001 2.7.2004 Persona de contacto: info@geovirtual.com GeoShow3D Rambla de Cataluña 35, principal. E-08007 Barcelona Tel. +34 934 872 144 Fax +34 934 875 809 Spain. www.geovirtual.com
GY301 Geomorphology Lab 5 Topographic Map: Final GIS Map Construction
 GY301 Geomorphology Lab 5 Topographic Map: Final GIS Map Construction Introduction This document describes how to take the data collected with the total station for the campus topographic map project and
GY301 Geomorphology Lab 5 Topographic Map: Final GIS Map Construction Introduction This document describes how to take the data collected with the total station for the campus topographic map project and
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007
 Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007 A chart is a pictorial representation of the data you enter in a worksheet. Often, a chart can be a more descriptive way of representing your data. As a result, those
Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007 A chart is a pictorial representation of the data you enter in a worksheet. Often, a chart can be a more descriptive way of representing your data. As a result, those
SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL
 SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL DIGITAL MAPPING FILES (very efficient/extremely accurate): 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT FILE EXT(S) FORMAT FILE EXT(S) AutoCAD (*.dwg,
SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL DIGITAL MAPPING FILES (very efficient/extremely accurate): 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT FILE EXT(S) FORMAT FILE EXT(S) AutoCAD (*.dwg,
Overview of the SMS Interface for the CMS and New CIRP Additions: CIRP Wiki and CMS Discussion List
 Overview of the SMS Interface for the CMS and New Additions: Wiki and CMS Discussion List Mitch Brown Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Engineer Research and Development Center May 20, 2010 US Army Corps
Overview of the SMS Interface for the CMS and New Additions: Wiki and CMS Discussion List Mitch Brown Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Engineer Research and Development Center May 20, 2010 US Army Corps
L7 Raster Algorithms
 L7 Raster Algorithms NGEN6(TEK23) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems by: Abdulghani Hasan, updated Nov 216 by Per-Ola Olsson Background Store and analyze the geographic information: Raster
L7 Raster Algorithms NGEN6(TEK23) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems by: Abdulghani Hasan, updated Nov 216 by Per-Ola Olsson Background Store and analyze the geographic information: Raster
Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst
 Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid Duri Surface Basics Defining the surface Representation of any continuous measurement
Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid Duri Surface Basics Defining the surface Representation of any continuous measurement
3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin
 2nd International Workshop in Geoenvironment and 1 3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin G. Argyris, I. Kapageridis and A. Triantafyllou Department of Geotechnology and Environmental Engineering,
2nd International Workshop in Geoenvironment and 1 3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin G. Argyris, I. Kapageridis and A. Triantafyllou Department of Geotechnology and Environmental Engineering,
Image Services for Elevation Data
 Image Services for Elevation Data Peter Becker Need for Elevation Using Image Services for Elevation Data sources Creating Elevation Service Requirement: GIS and Imagery, Integrated and Accessible Field
Image Services for Elevation Data Peter Becker Need for Elevation Using Image Services for Elevation Data sources Creating Elevation Service Requirement: GIS and Imagery, Integrated and Accessible Field
Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
NEXTMap World 30 Digital Surface Model
 NEXTMap World 30 Digital Surface Model Intermap Technologies, Inc. 8310 South Valley Highway, Suite 400 Englewood, CO 80112 083013v3 NEXTMap World 30 (top) provides an improvement in vertical accuracy
NEXTMap World 30 Digital Surface Model Intermap Technologies, Inc. 8310 South Valley Highway, Suite 400 Englewood, CO 80112 083013v3 NEXTMap World 30 (top) provides an improvement in vertical accuracy
Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics
 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related more than distant places Corollary:
(Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related more than distant places Corollary:
Final project: Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Talk about class project (copy follow_along_data\ch8a_class_ex into U:\ArcGIS\ if needed) Catch up with lecture 20
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Talk about class project (copy follow_along_data\ch8a_class_ex into U:\ArcGIS\ if needed) Catch up with lecture 20
Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data. A story of data, more data and some more data
 Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data A story of data, more data and some more data Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Introduction and Background
Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data A story of data, more data and some more data Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Introduction and Background
Converting AutoCAD Map 2002 Projects to ArcGIS
 Introduction This document outlines the procedures necessary for converting an AutoCAD Map drawing containing topologies to ArcGIS version 9.x and higher. This includes the export of polygon and network
Introduction This document outlines the procedures necessary for converting an AutoCAD Map drawing containing topologies to ArcGIS version 9.x and higher. This includes the export of polygon and network
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Google Earth an introduction
 Luana Valentini InternetGIS course - 2011 Google Earth an introduction Google Earth combines the power of Google Search with satellite imagery, maps, terrain and 3D buildings to put the world's geographic
Luana Valentini InternetGIS course - 2011 Google Earth an introduction Google Earth combines the power of Google Search with satellite imagery, maps, terrain and 3D buildings to put the world's geographic
Objectives Import DEMs from an online database. Set the display options of an imported DEM and view and edit the DEM attributes.
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Import, view, and edit digital elevation models Objectives Import DEMs from an online database. Set the display options of an imported DEM and view and edit the DEM attributes.
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Import, view, and edit digital elevation models Objectives Import DEMs from an online database. Set the display options of an imported DEM and view and edit the DEM attributes.
SPECIFICATIONS FOR G.I.S. DATA/INFORMATION PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL
 SPECIFICATIONS FOR G.I.S. DATA/INFORMATION PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL Digital Mapping Files that we can accept: 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT AutoCad File Latest Releases ESRI Arc/Info
SPECIFICATIONS FOR G.I.S. DATA/INFORMATION PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL Digital Mapping Files that we can accept: 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT AutoCad File Latest Releases ESRI Arc/Info
Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst
 2013 Esri International User Conference July 8 12, 2013 San Diego, California Technical Workshop Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid H. Duri Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop. Why use 3D GIS? Because
2013 Esri International User Conference July 8 12, 2013 San Diego, California Technical Workshop Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid H. Duri Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop. Why use 3D GIS? Because
Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models
 Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models GEOG413/613 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Digital Terrain Modeling Terms: DEM, DTM, DTEM, DSM, DHM not synonyms. The concepts they illustrate are different Digital Terrain Modeling
Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models GEOG413/613 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Digital Terrain Modeling Terms: DEM, DTM, DTEM, DSM, DHM not synonyms. The concepts they illustrate are different Digital Terrain Modeling
Features and Benefits
 CAiCE Visual Survey 10 Features and Benefits CAiCE Visual Survey 10 software enables surveying professionals to import, process, analyze, and present surveying all in one software package. Visual Survey
CAiCE Visual Survey 10 Features and Benefits CAiCE Visual Survey 10 software enables surveying professionals to import, process, analyze, and present surveying all in one software package. Visual Survey
Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/2018
 Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/201 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Distance between pairs of points Lag Mean Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places
Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/201 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Distance between pairs of points Lag Mean Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places
Your MapViewer serial number is located on the CD cover or in the download instructions, depending on how you purchased MapViewer.
 MapViewer TM Registration Information Your MapViewer serial number is located on the CD cover or in the email download instructions, depending on how you purchased MapViewer. Register your MapViewer serial
MapViewer TM Registration Information Your MapViewer serial number is located on the CD cover or in the email download instructions, depending on how you purchased MapViewer. Register your MapViewer serial
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
New File Formats: Open/Import: IMG DEM Export: IMG/IGE (this will support export of DEM s greater than 4GB in size), USGS DEM
 What s New for Quick Terrain Modeler Version 7.1.3 April 15, 2011 (planned release date) New v7.1.3 Features: Quick Terrain Modeler adds significant new capabilities that range from a very fast indexing
What s New for Quick Terrain Modeler Version 7.1.3 April 15, 2011 (planned release date) New v7.1.3 Features: Quick Terrain Modeler adds significant new capabilities that range from a very fast indexing
Creating and Displaying Multi-Layered Cross Sections in Surfer 11
 Creating and Displaying Multi-Layered Cross Sections in Surfer 11 The ability to create a profile in Surfer has always been a powerful tool that many users take advantage of. The ability to combine profiles
Creating and Displaying Multi-Layered Cross Sections in Surfer 11 The ability to create a profile in Surfer has always been a powerful tool that many users take advantage of. The ability to combine profiles
What s New in Desktop 10.1
 What s New in Desktop 10.1 Damian Spangrud Esri Redlands Trip Down Memory Lane ArcGIS A Complete System for Geographic Information Cloud Web Online Mobile Enterprise Desktop Sharing Information sharing
What s New in Desktop 10.1 Damian Spangrud Esri Redlands Trip Down Memory Lane ArcGIS A Complete System for Geographic Information Cloud Web Online Mobile Enterprise Desktop Sharing Information sharing
v TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics SMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
Lab 11: Terrain Analyses
 Lab 11: Terrain Analyses What You ll Learn: Basic terrain analysis functions, including watershed, viewshed, and profile processing. There is a mix of old and new functions used in this lab. We ll explain
Lab 11: Terrain Analyses What You ll Learn: Basic terrain analysis functions, including watershed, viewshed, and profile processing. There is a mix of old and new functions used in this lab. We ll explain
EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015
 EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015 EMIGMA for Gravity EMIGMA for Gravity license is a comprehensive package that offers a wide array of processing, visualization and interpretation tools. The package
EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015 EMIGMA for Gravity EMIGMA for Gravity license is a comprehensive package that offers a wide array of processing, visualization and interpretation tools. The package
Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives This tutorial teaches how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives This tutorial teaches how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters
EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series
 EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series EMIGMA BASIC January 2014 Firstly, EMIGMA Basic describes the tools that are available in every EMIGMA license. Secondly, EMIGMA Basic is the name we use for our free viewing
EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series EMIGMA BASIC January 2014 Firstly, EMIGMA Basic describes the tools that are available in every EMIGMA license. Secondly, EMIGMA Basic is the name we use for our free viewing
product description product capabilities
 product description Geosoft s Airborne Geophy s- ics application for the Oasis montaj software platform provides field geophysicists with the ability to process, filter, grid, and map data from airborne
product description Geosoft s Airborne Geophy s- ics application for the Oasis montaj software platform provides field geophysicists with the ability to process, filter, grid, and map data from airborne
Data Representation From 0s and 1s to images CPSC 101
 Data Representation From 0s and 1s to images CPSC 101 Learning Goals After the Data Representation: Images unit, you will be able to: Recognize and translate between binary and decimal numbers Define bit,
Data Representation From 0s and 1s to images CPSC 101 Learning Goals After the Data Representation: Images unit, you will be able to: Recognize and translate between binary and decimal numbers Define bit,
Gravity and Magnetics
 w w w. g e o s o f t. c o m Mapping, Modeling, Interpretation Gravity and Magnetics Oil and Gas Exploration Solutions Tools to focus all your exploration efforts In today s competitive energy marketplace,
w w w. g e o s o f t. c o m Mapping, Modeling, Interpretation Gravity and Magnetics Oil and Gas Exploration Solutions Tools to focus all your exploration efforts In today s competitive energy marketplace,
City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document
 City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document This document was created to assist in using the new City of La Crosse online mapping sites. When the website is first opened, a map showing the City
City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document This document was created to assist in using the new City of La Crosse online mapping sites. When the website is first opened, a map showing the City
Terrain Analysis. Using QGIS and SAGA
 Terrain Analysis Using QGIS and SAGA Tutorial ID: IGET_RS_010 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial
Terrain Analysis Using QGIS and SAGA Tutorial ID: IGET_RS_010 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial
GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
NEXTMap World 10 Digital Elevation Model
 NEXTMap Digital Elevation Model Intermap Technologies, Inc. 8310 South Valley Highway, Suite 400 Englewood, CO 80112 10012015 NEXTMap (top) provides an improvement in vertical accuracy and brings out greater
NEXTMap Digital Elevation Model Intermap Technologies, Inc. 8310 South Valley Highway, Suite 400 Englewood, CO 80112 10012015 NEXTMap (top) provides an improvement in vertical accuracy and brings out greater
Questions and Answers
 Autodesk AutoCAD Raster Design 2011 Questions and Answers AutoCAD Raster Design 2011 Questions and Answers Make the most of rasterized scanned drawings, maps, aerial photos, satellite imagery, and digital
Autodesk AutoCAD Raster Design 2011 Questions and Answers AutoCAD Raster Design 2011 Questions and Answers Make the most of rasterized scanned drawings, maps, aerial photos, satellite imagery, and digital
Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges
 Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges Objectives In this lab, you will analyze the relief structure of the San Gabriel Mountains in southern California and how it relates to
Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges Objectives In this lab, you will analyze the relief structure of the San Gabriel Mountains in southern California and how it relates to
TCP MDT Digital Terrain Model - V7.5
 TCP MDT Digital Terrain Model - V7.5 Standard Version Introduction The Standard Version is suitable for carrying out all kinds of topographical survey projects, terrain profiles, volume calculations etc.
TCP MDT Digital Terrain Model - V7.5 Standard Version Introduction The Standard Version is suitable for carrying out all kinds of topographical survey projects, terrain profiles, volume calculations etc.
GY461/GEO461 Computer Mapping & GIS Technology Merging of DEM and Geology Raster Images
 Introduction In this exercise you will merge the geology color fills created for the quadrangle geologic map, with a hill-shade image produced from a digital elevation model (DEM) of the quadrangle. This
Introduction In this exercise you will merge the geology color fills created for the quadrangle geologic map, with a hill-shade image produced from a digital elevation model (DEM) of the quadrangle. This
What can we represent as a Surface?
 Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Tutorial. Exporting Geodata E X P O R T I N G. Exporting Geodata. with. TNTmips and TNTedit. page 1
 E X P O R T I N G Tutorial Exporting Geodata Exporting Geodata with TNTmips and TNTedit page 1 Before Getting Started This booklet introduces the procedures used to export geospatial data from TNTmips
E X P O R T I N G Tutorial Exporting Geodata Exporting Geodata with TNTmips and TNTedit page 1 Before Getting Started This booklet introduces the procedures used to export geospatial data from TNTmips
General GPS TPS ROB X POLE VOL RDN RPL Jobs management System settings (units, precision, parameters, etc.)
 XPAD Survey Modules XPAD Survey GPS TPS XPOLE General GPS TPS ROB XPOLE VOL RDN RPL Jobs management System settings (units, precision, parameters, etc.) Instruments GPS GPS TPS ROB XPOLE VOL RDN RPL Instrument
XPAD Survey Modules XPAD Survey GPS TPS XPOLE General GPS TPS ROB XPOLE VOL RDN RPL Jobs management System settings (units, precision, parameters, etc.) Instruments GPS GPS TPS ROB XPOLE VOL RDN RPL Instrument
Your Prioritized List. Priority 1 Faulted gridding and contouring. Priority 2 Geoprocessing. Priority 3 Raster format
 Your Prioritized List Priority 1 Faulted gridding and contouring Priority 2 Geoprocessing Priority 3 Raster format Priority 4 Raster Catalogs and SDE Priority 5 Expanded 3D Functionality Priority 1 Faulted
Your Prioritized List Priority 1 Faulted gridding and contouring Priority 2 Geoprocessing Priority 3 Raster format Priority 4 Raster Catalogs and SDE Priority 5 Expanded 3D Functionality Priority 1 Faulted
Features available in this release of Encom Discover are: Simplified installation - Discover and Discover 3D are now bundled in the same installer
 EncomTM DiscoverTM v12.0 Pitney Bowes Business Insight s latest release of Encom Discover showcases the ongoing innovative developments that have made Discover the must-have GIS application for geoscientists
EncomTM DiscoverTM v12.0 Pitney Bowes Business Insight s latest release of Encom Discover showcases the ongoing innovative developments that have made Discover the must-have GIS application for geoscientists
Lecture 9. Raster Data Analysis. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 9 Raster Data Analysis Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Raster Data Model The GIS raster data model represents datasets in which square
Lecture 9 Raster Data Analysis Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Raster Data Model The GIS raster data model represents datasets in which square
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation
 Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Data for the exercise are in the L12 subdirectory.
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Data for the exercise are in the L12 subdirectory.
Rasters are: The Raster Data Model. Cell location specified by: Why squares? Raster Data Models 9/25/2014. GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1
 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 5 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 The Raster Data Model Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equalsized,
5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 5 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 The Raster Data Model Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equalsized,
ASSIGNMENT 3 Cobalt data T:\sys502\arcview\projects\Cobalt_2 T:\sys502\arcview\ projects\cobalt_2\cobalt_2.mxd T:\sys502\arcview\projects\Cobalt_2
 ESE 502 Tony E. Smith ASSIGNMENT 3 (1) In this study you will use some of the Cobalt data from Vancouver Island Geochemistry data set in B&G (pp.150, 202) to carry out essentially the same type of analysis
ESE 502 Tony E. Smith ASSIGNMENT 3 (1) In this study you will use some of the Cobalt data from Vancouver Island Geochemistry data set in B&G (pp.150, 202) to carry out essentially the same type of analysis
Tools Menu (Frequently Used Features)
 Tools Menu (Frequently Used Features) Exit VoxelCalc Shop for features Show VoxelCalc User Guide (right click on oither icons shows user guide for that function) Region of Interest (ROI) tool with beam
Tools Menu (Frequently Used Features) Exit VoxelCalc Shop for features Show VoxelCalc User Guide (right click on oither icons shows user guide for that function) Region of Interest (ROI) tool with beam
The Raster Data Model
 The Raster Data Model 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Llano River, Mason Co., TX 9/24/201 GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1 Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed
The Raster Data Model 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Llano River, Mason Co., TX 9/24/201 GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1 Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed
Introduction to GIS 2011
 Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in GMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in GMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
The Raster Data Model
 The Raster Data Model 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Llano River, Mason Co., TX 1 Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equal-sized, square
The Raster Data Model 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Llano River, Mason Co., TX 1 Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equal-sized, square
