A Review of Image- based Rendering Techniques Nisha 1, Vijaya Goel 2 1 Department of computer science, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
|
|
|
- Kristian Hector Spencer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
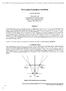
1 A Review of Image- based Rendering Techniques Nisha 1, Vijaya Goel 2 1 Department of computer science, University of Delhi, Delhi, India Keshav Mahavidyalaya, University of Delhi, Delhi, India Abstract In this paper, we survey the techniques for image-based rendering and fundamental principles behind each technique. Image-based rendering is used to create a geometric model in 3D and then projecting it onto a 2D image. Image-based rendering is divided into three categories on the basis of how much geometric information is used. First is rendering without geometry, second is rendering with implicit geometry, and third is rendering with explicit geometry. Image-based modelling and rendering allows the use of multiple two-dimensional images in order to generate directly original twodimensional images without using the manual modelling stage. Image-based rendering has gained attention in graphics to create realistic image. I. INTRODUCTION In recent years image-based rendering get a place in graphics community for creating realistic images. It s one of the important benefit is ability to create real world effects and details of the real world by using collection of images. According to previous work on image based rendering it reveals that it based on the tradeoffs that how many images are needed and how much is known about the scene geometry. Image based rendering techniques are classified into three categories rendering without geometry, rendering with implicit geometry and rendering with explicit geometry. It is shown in diagram. Rendering with no geometry Light field Lumigraph Mosaicking Concentric mosaics Rendering with implicit geometry Transfer methods View morphing View interpolation More Geometry Rendering with explicit geometry LDIs Texture-mapped models 3D warping Viewdependent geometry View-dependent texture Figure 1 Categories of rendering techniques There are three main categories of image based rendering: rendering with no geometry, rendering with implicit geometry and rendering with explicit geometry. Each category is further divided; rendering with no geometry has three categories light field, mosaicking and concentric mosaics. Other categories are also further subdivided which is already shown in above diagram. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Three categories of image-based rendering systems, with no geometry, implicit geometry, and explicit geometric information respectively, are presented in Sections 2, 3, and 4 and concluding remarks are discussed in Section 5. II. RENDERING WITH NO GEOMETRY In this section, we are going to discuss about rendering with no geometry. This technique L is dependent on plenoptic function. e s 2.1 Plenoptic modelling s Image based rendering is a powerful G new approach of generating photorealistic computer e graphics. They can provide animations without oany external geometric representations. Plenoptic function m is given by Adelson and Bergen, is a parametric efunction which describe anything that is visible from a given t point in space. Page 48
2 Plenoptic function is a 7D function to describe light intensity passing through every viewpoint, for every direction, for every wavelength, and for every time instant. The original 7D plenoptic function is defined as the intensity of light rays passing through the camera center at every location (Vx, Vy, Vz) at every possible angle (θ, φ), for every wavelength λ, at every time t, i.e., P7 = P(Vx, Vy, Vz, θ, φ, λ, t). (1) Adelson and Bergen extracted a compact and useful description of the plenoptic function s local properties (e.g., low order derivatives). It was proofed that light source directions can be incorporated into the plenoptic function for illumination control. McMillan and Bishop introduced 5D plenoptic function for plenoptic modelling, by eliminating two variables, time t (static environment) and light wavelength λ (fixed lighting condition). P5 = P(Vx, Vy, Vz, θ, φ). (2) The simplest plenoptic function is a 2D panorama (cylindrical or spherical) when the viewpoint is fixed. P2 = P(θ, φ). Figure 2 Light Field Representations [1] i.e. P4 = P(u,v,s,t) (4) where (u, v) and (s, t) parameterize two parallel planes of the bounding box. Aliasing effect can be reducing in light field by applying pre-filtering before rendering. Vector quantization approach is used to reduce amount of data in light field and on the other hand lumigraph can be constructed from a set of images taken from any viewpoint and after this a re-binning process is required. 2.3 Concentric mosaics Constrain camera motion to planar concentric circle; create concentric mosaics by composing slit images taken at different locations along each circle. It is a 3D parameterization of plenoptic function: radius, rotation angle, vertical elevation. If we want to capture all view point then we need 5D plenoptic functions. If we stay inside the convex hull we have 4D lightfield and if we don t move at all for that we have 2D panorama. And concentric mosaic is a 3D plenoptic function. (3) Image-based rendering becomes one of constructing a continuous representation of the plenoptic function from observed discrete samples. 2.2 Lumigraph and Light field It was seen that if we lie outside the convex hull of an object then we can convert a 5D plenoptic function into 4D plenoptic function for both lumigraph and light field, Page 49
3 Figure 3: Rendering a lobby: rebinned concentric mosaic (a) at the rotation center (b) at the outermost circle (c) at the outermost circle but looking at the opposite direction of (b) [1] (d) a child is occluded in one view but not in the other; [1] (e) parallax change between the plant and the poster [1] Concentric mosaic represents 3D plenoptic function: radius, rotation angle and vertical elevation. Vertical distortion exists in the rendering image, depth correction alleviate vertical distortion. In depth correction rays in the capture plane have no problem, for rays off the plane: Only a small subset of the rays off the plane is stored so have to approximate all rays off the plane from only the slit images. This may cause vertical distortion in the rendered images. Concentric mosaic has good space and high efficiency. In comparison off light field or lumigraph, concentric mosaic has smaller file size. Concentric mosaics are easy to capture except that it require more number of images. It is useful for capturing many virtual reality applications. Rendering a lobby scene is shown in figure 3. A rebinned concentric mosaic at the rotation center is shown in 3 (a), at the outermost circle is shown in 3(b) and at the outermost circle but looking at the opposite direction of (b) is shown in 3(c). In 3(d), a child is occluded in one view but not in the other is shown. In Figure 3(e), strong parallax can be seen between the plant and the poster in the rendered images. 2.4 Image mosaicing Page 50
4 Incomplete sample of images are used to create a complete plenoptic function at fixed point. A panoramic mosaic is constructed by many regular images. For arbitrarily camera motion, first register the images by recovering the camera movement before converting into the cylindrical/spherical map. Now a day s many systems has been built to construct cylindrical panorama by overlapping multiple images. Multiple slits of images are used to construct large panoramic mosaic. By using omnidirectional camera it is easier to capture large panorama. Many transformation operations are applied on set of images to construct a panorama. Transformation matrix is associated with each input image. A rotation mosaic representation associates a rotation matrix with each input image. Figure 4: Tessellated spherical panorama covering the North Pole (constructed from 54 images). [1] III. RENDERING WITH IMPLICIT GEOMETRY Rendering with implicit geometry is a technique that depends on positional correspondence across a small number of images to render new views. In this technique implicit geometry is not directly available but 3D information is computed only using the usual projection calculations. 3.1 View interpolation View interpolation is one of the algorithms for image based rendering. This method was given by Chen and Williams. In this method we need sample number of depth images, by this sample make adjacent graph in which images are nodes and edges are mapping between them and after that interpolate pixels to construct in between images. This method works well when all the input images have same gaze direction and all the output images have restriction to gaze angle less than 90 degree. [1] 3.2 View morphing By using this technique we can reconstruct any viewpoint on the line linking two optical centres of the original image from two input images. If the camera motions of the intermediate views are perpendicular to the camera viewing direction then intermediate views are exactly linear combinations of two views. A pre-warp stage can be employed to rectify two input images so that corresponding scan lines are parallel only if the two input images are not parallel [1]. Accordingly, a post-warp stage can be used to un-rectify the intermediate images. 3.3 Transfer methods Transfer methods use small number of images with the application of geometry constraints to reproject image pixels at a given virtual camera viewpoint. Geometric constraints can be of the forms of known depth value at image pixels. View interpolation and view morphing methods are specific instances of transfer method. For generating novel view from two or three reference images, first the reference trilinear tensor (that link correspondences between triplets of images) is calculated from the point correspondences between reference images. In the case of two images, one of the images is replicated as third image. IV. Rendering with explicit geometry This technique has 3D information encoded in it in the form of depth along known line-of-sight or in 3D coordinates D warping 3D image warping is a process of generating a novel view on the scene based on depth information from one or more images. An image can be rendered by any near view point information by projecting the pixels of original image into 3D location and then re-projecting them into new image. Many holes are generated in wrap an image that is the main problem and this is happened because of sampling resolution difference in input and output image. For filling the holes, the method used is to splat a pixel in the input image to several pixels size in the output image. To improve the rendering speed of 3D warping, there are two steps firstly pre-warping step and then texture mapping step. Texture mapping step can be performed by graphics hardware. 3D warping technique can also be applied on multi-perspective images. 4.2 Layered depth images By storing not only what is visible in image but also what is behind the visible surface we can deal with disocclusion artifacts in 3D warping in LDI. In LDI, each pixel in input image store level of depth and colour information where ray from pixel intersect the environment. LDI is the simplest method of warping a single image. 4.3 View-dependent texture maps Page 51
5 In computer graphics texture mapping are used to generate photo realistic environment. Texture mapping models for real environments can be generated using 3D scanner. Vision techniques are not enough robust to recover accurate 3D models. It is difficult to capture visual effects such as highlights, reflections, and transparency using a single texture-mapped model. V. CONCLUDING REMARKS We have surveyed recent development in image based rendering techniques and, categorize them on the basis of how much geometry information is needed. Geometry information is used as compressing representation for rendering. Image based rendering representation have advantage of photorealistic rendering but have high cost for storing information. IBR and 3D model based rendering techniques have many commendatory characteristics that can be exploit that is clear by our survey. In future rendering hardware customization should be done to handle both 3D modelbased rendering and IBR. REFRENCES [1] Heung-Yeung Shum and Sing Bing Kang. A Review of Image-based Rendering Techniques, Proc. SPIE 4067, Visual Communications and Image Processing 2000, 2 (May 30, 2000); [2] [3] [4] Manuel M. Oliveira1.Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Techniques: A Survey, RITA, inf.ufrgs.br [5] John Amanatides. Realism in Computer Graphics: A Survey Page 52
Image-Based Rendering
 Image-Based Rendering COS 526, Fall 2016 Thomas Funkhouser Acknowledgments: Dan Aliaga, Marc Levoy, Szymon Rusinkiewicz What is Image-Based Rendering? Definition 1: the use of photographic imagery to overcome
Image-Based Rendering COS 526, Fall 2016 Thomas Funkhouser Acknowledgments: Dan Aliaga, Marc Levoy, Szymon Rusinkiewicz What is Image-Based Rendering? Definition 1: the use of photographic imagery to overcome
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering. Image-Based Modeling and Rendering. Final projects IBMR. What we have learnt so far. What IBMR is about
 Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Image-Based Modeling and Rendering MIT EECS 6.837 Frédo Durand and Seth Teller 1 Some slides courtesy of Leonard McMillan, Wojciech Matusik, Byong Mok Oh, Max Chen 2
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Image-Based Modeling and Rendering MIT EECS 6.837 Frédo Durand and Seth Teller 1 Some slides courtesy of Leonard McMillan, Wojciech Matusik, Byong Mok Oh, Max Chen 2
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering
 Traditional Computer Graphics Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University COS 426 Guest Lecture Spring 2003 How would you model and render this scene? (Jensen) How about this
Traditional Computer Graphics Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University COS 426 Guest Lecture Spring 2003 How would you model and render this scene? (Jensen) How about this
Image-Based Rendering. Johns Hopkins Department of Computer Science Course : Rendering Techniques, Professor: Jonathan Cohen
 Image-Based Rendering Image-Based Rendering What is it? Still a difficult question to answer Uses images (photometric( info) as key component of model representation What s Good about IBR Model acquisition
Image-Based Rendering Image-Based Rendering What is it? Still a difficult question to answer Uses images (photometric( info) as key component of model representation What s Good about IBR Model acquisition
Image Base Rendering: An Introduction
 Image Base Rendering: An Introduction Cliff Lindsay CS563 Spring 03, WPI 1. Introduction Up to this point, we have focused on showing 3D objects in the form of polygons. This is not the only approach to
Image Base Rendering: An Introduction Cliff Lindsay CS563 Spring 03, WPI 1. Introduction Up to this point, we have focused on showing 3D objects in the form of polygons. This is not the only approach to
But, vision technology falls short. and so does graphics. Image Based Rendering. Ray. Constant radiance. time is fixed. 3D position 2D direction
 Computer Graphics -based rendering Output Michael F. Cohen Microsoft Research Synthetic Camera Model Computer Vision Combined Output Output Model Real Scene Synthetic Camera Model Real Cameras Real Scene
Computer Graphics -based rendering Output Michael F. Cohen Microsoft Research Synthetic Camera Model Computer Vision Combined Output Output Model Real Scene Synthetic Camera Model Real Cameras Real Scene
IMAGE-BASED RENDERING TECHNIQUES FOR APPLICATION IN VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS
 IMAGE-BASED RENDERING TECHNIQUES FOR APPLICATION IN VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS Xiaoyong Sun A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
IMAGE-BASED RENDERING TECHNIQUES FOR APPLICATION IN VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS Xiaoyong Sun A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
Image-Based Rendering. Johns Hopkins Department of Computer Science Course : Rendering Techniques, Professor: Jonathan Cohen
 Image-Based Rendering Image-Based Rendering What is it? Still a difficult question to answer Uses images (photometric( info) as key component of model representation What s Good about IBR Model acquisition
Image-Based Rendering Image-Based Rendering What is it? Still a difficult question to answer Uses images (photometric( info) as key component of model representation What s Good about IBR Model acquisition
Image-Based Rendering. Image-Based Rendering
 Image-Based Rendering Image-Based Rendering What is it? Still a difficult question to answer Uses images (photometric info) as key component of model representation 1 What s Good about IBR Model acquisition
Image-Based Rendering Image-Based Rendering What is it? Still a difficult question to answer Uses images (photometric info) as key component of model representation 1 What s Good about IBR Model acquisition
Image or Object? Is this real?
 Image or Object? Michael F. Cohen Microsoft Is this real? Photo by Patrick Jennings (patrick@synaptic.bc.ca), Copyright 1995, 96, 97 Whistler B. C. Canada Modeling, Rendering, and Lighting 1 A mental model?
Image or Object? Michael F. Cohen Microsoft Is this real? Photo by Patrick Jennings (patrick@synaptic.bc.ca), Copyright 1995, 96, 97 Whistler B. C. Canada Modeling, Rendering, and Lighting 1 A mental model?
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering
 Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Richard Szeliski Microsoft Research IPAM Graduate Summer School: Computer Vision July 26, 2013 How far have we come? Light Fields / Lumigraph - 1996 Richard Szeliski
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Richard Szeliski Microsoft Research IPAM Graduate Summer School: Computer Vision July 26, 2013 How far have we come? Light Fields / Lumigraph - 1996 Richard Szeliski
Real-time Generation and Presentation of View-dependent Binocular Stereo Images Using a Sequence of Omnidirectional Images
 Real-time Generation and Presentation of View-dependent Binocular Stereo Images Using a Sequence of Omnidirectional Images Abstract This paper presents a new method to generate and present arbitrarily
Real-time Generation and Presentation of View-dependent Binocular Stereo Images Using a Sequence of Omnidirectional Images Abstract This paper presents a new method to generate and present arbitrarily
Rendering by Manifold Hopping
 International Journal of Computer Vision 50(2), 185 201, 2002 c 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Rendering by Manifold Hopping HEUNG-YEUNG SHUM, LIFENG WANG, JIN-XIANG
International Journal of Computer Vision 50(2), 185 201, 2002 c 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Rendering by Manifold Hopping HEUNG-YEUNG SHUM, LIFENG WANG, JIN-XIANG
Re-live the Movie Matrix : From Harry Nyquist to Image-Based Rendering. Tsuhan Chen Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, USA
 Re-live the Movie Matrix : From Harry Nyquist to Image-Based Rendering Tsuhan Chen tsuhan@cmu.edu Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, USA Some History IEEE Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP) Technical
Re-live the Movie Matrix : From Harry Nyquist to Image-Based Rendering Tsuhan Chen tsuhan@cmu.edu Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, USA Some History IEEE Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP) Technical
Hybrid Rendering for Collaborative, Immersive Virtual Environments
 Hybrid Rendering for Collaborative, Immersive Virtual Environments Stephan Würmlin wuermlin@inf.ethz.ch Outline! Rendering techniques GBR, IBR and HR! From images to models! Novel view generation! Putting
Hybrid Rendering for Collaborative, Immersive Virtual Environments Stephan Würmlin wuermlin@inf.ethz.ch Outline! Rendering techniques GBR, IBR and HR! From images to models! Novel view generation! Putting
Image Based Rendering
 Image Based Rendering an overview Photographs We have tools that acquire and tools that display photographs at a convincing quality level 2 1 3 4 2 5 6 3 7 8 4 9 10 5 Photographs We have tools that acquire
Image Based Rendering an overview Photographs We have tools that acquire and tools that display photographs at a convincing quality level 2 1 3 4 2 5 6 3 7 8 4 9 10 5 Photographs We have tools that acquire
Rendering with Concentric Mosaics
 Rendering with Concentric Mosaics Heung-Yeung Shum Microsoft Research, China Li-Wei He Microsoft Research Abstract This paper presents a novel 3D plenoptic function, which we call concentric mosaics. We
Rendering with Concentric Mosaics Heung-Yeung Shum Microsoft Research, China Li-Wei He Microsoft Research Abstract This paper presents a novel 3D plenoptic function, which we call concentric mosaics. We
Modeling Light. Michal Havlik : Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007
 Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 The Plenoptic Function Figure by Leonard McMillan Q: What is the set of all things that we can ever see? A: The
Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 The Plenoptic Function Figure by Leonard McMillan Q: What is the set of all things that we can ever see? A: The
PAPER Three-Dimensional Scene Walkthrough System Using Multiple Acentric Panorama View (APV) Technique
 IEICE TRANS. INF. & SYST., VOL.E86 D, NO.1 JANUARY 2003 117 PAPER Three-Dimensional Scene Walkthrough System Using Multiple Acentric Panorama View (APV) Technique Ping-Hsien LIN and Tong-Yee LEE, Nonmembers
IEICE TRANS. INF. & SYST., VOL.E86 D, NO.1 JANUARY 2003 117 PAPER Three-Dimensional Scene Walkthrough System Using Multiple Acentric Panorama View (APV) Technique Ping-Hsien LIN and Tong-Yee LEE, Nonmembers
Image-based modeling (IBM) and image-based rendering (IBR)
 Image-based modeling (IBM) and image-based rendering (IBR) CS 248 - Introduction to Computer Graphics Autumn quarter, 2005 Slides for December 8 lecture The graphics pipeline modeling animation rendering
Image-based modeling (IBM) and image-based rendering (IBR) CS 248 - Introduction to Computer Graphics Autumn quarter, 2005 Slides for December 8 lecture The graphics pipeline modeling animation rendering
Image-based Modeling and Rendering: 8. Image Transformation and Panorama
 Image-based Modeling and Rendering: 8. Image Transformation and Panorama I-Chen Lin, Assistant Professor Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung Univ, Taiwan Outline Image transformation How to represent the
Image-based Modeling and Rendering: 8. Image Transformation and Panorama I-Chen Lin, Assistant Professor Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung Univ, Taiwan Outline Image transformation How to represent the
Modeling Light. On Simulating the Visual Experience
 Modeling Light 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros On Simulating the Visual Experience Just feed the eyes the right data No one will know the difference! Philosophy: Ancient question: Does
Modeling Light 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros On Simulating the Visual Experience Just feed the eyes the right data No one will know the difference! Philosophy: Ancient question: Does
Volumetric Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Views
 Volumetric Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Views Chuck Dyer University of Wisconsin dyer@cs cs.wisc.edu www.cs cs.wisc.edu/~dyer Image-Based Scene Reconstruction Goal Automatic construction of photo-realistic
Volumetric Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Views Chuck Dyer University of Wisconsin dyer@cs cs.wisc.edu www.cs cs.wisc.edu/~dyer Image-Based Scene Reconstruction Goal Automatic construction of photo-realistic
Image-Based Rendering and Light Fields
 CS194-13: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture #9 Image-Based Rendering University of California Berkeley Image-Based Rendering and Light Fields Lecture #9: Wednesday, September 30th 2009 Lecturer: Ravi
CS194-13: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture #9 Image-Based Rendering University of California Berkeley Image-Based Rendering and Light Fields Lecture #9: Wednesday, September 30th 2009 Lecturer: Ravi
Announcements. Mosaics. How to do it? Image Mosaics
 Announcements Mosaics Project artifact voting Project 2 out today (help session at end of class) http://www.destination36.com/start.htm http://www.vrseattle.com/html/vrview.php?cat_id=&vrs_id=vrs38 Today
Announcements Mosaics Project artifact voting Project 2 out today (help session at end of class) http://www.destination36.com/start.htm http://www.vrseattle.com/html/vrview.php?cat_id=&vrs_id=vrs38 Today
Computational Photography
 Computational Photography Matthias Zwicker University of Bern Fall 2010 Today Light fields Introduction Light fields Signal processing analysis Light field cameras Application Introduction Pinhole camera
Computational Photography Matthias Zwicker University of Bern Fall 2010 Today Light fields Introduction Light fields Signal processing analysis Light field cameras Application Introduction Pinhole camera
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 7: Image Alignment and Panoramas What s inside your fridge? http://www.cs.washington.edu/education/courses/cse590ss/01wi/ Projection matrix intrinsics projection
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 7: Image Alignment and Panoramas What s inside your fridge? http://www.cs.washington.edu/education/courses/cse590ss/01wi/ Projection matrix intrinsics projection
Image-Based Rendering Methods
 Image-Based Rendering Methods for 3D Video-communications Andrea Fusiello http://profs.sci.univr.it/~fusiello Brixen, July 5 2007 c Copyright by Andrea Fusiello. This work is licensed under the Creative
Image-Based Rendering Methods for 3D Video-communications Andrea Fusiello http://profs.sci.univr.it/~fusiello Brixen, July 5 2007 c Copyright by Andrea Fusiello. This work is licensed under the Creative
FLY THROUGH VIEW VIDEO GENERATION OF SOCCER SCENE
 FLY THROUGH VIEW VIDEO GENERATION OF SOCCER SCENE Naho INAMOTO and Hideo SAITO Keio University, Yokohama, Japan {nahotty,saito}@ozawa.ics.keio.ac.jp Abstract Recently there has been great deal of interest
FLY THROUGH VIEW VIDEO GENERATION OF SOCCER SCENE Naho INAMOTO and Hideo SAITO Keio University, Yokohama, Japan {nahotty,saito}@ozawa.ics.keio.ac.jp Abstract Recently there has been great deal of interest
calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates
 1 calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates 2 Calibration with a rig Uncalibrated epipolar geometry Ambiguities in image formation Stratified reconstruction Autocalibration with partial
1 calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates 2 Calibration with a rig Uncalibrated epipolar geometry Ambiguities in image formation Stratified reconstruction Autocalibration with partial
A Survey of Image-based Rendering Techniques. Sing Bing Kang. CRL 97/4 August 1997
 TM A Survey of Image-based Rendering Techniques Sing Bing Kang CRL 97/4 August 1997 Cambridge Research Laboratory The Cambridge Research Laboratory was founded in 1987 to advance the state of the art in
TM A Survey of Image-based Rendering Techniques Sing Bing Kang CRL 97/4 August 1997 Cambridge Research Laboratory The Cambridge Research Laboratory was founded in 1987 to advance the state of the art in
Projective Texture Mapping with Full Panorama
 EUROGRAPHICS 2002 / G. Drettakis and H.-P. Seidel Volume 21 (2002), Number 3 (Guest Editors) Projective Texture Mapping with Full Panorama Dongho Kim and James K. Hahn Department of Computer Science, The
EUROGRAPHICS 2002 / G. Drettakis and H.-P. Seidel Volume 21 (2002), Number 3 (Guest Editors) Projective Texture Mapping with Full Panorama Dongho Kim and James K. Hahn Department of Computer Science, The
A Survey on Image-Based Rendering
 A Survey on Image-Based Rendering - Representation, Sampling and Compression Cha Zhang and Tsuhan Chen Advanced Multimedia Processing Lab M s 2 1 u v 1 2 L t Technical Report AMP 03-03 June 2003 Electrical
A Survey on Image-Based Rendering - Representation, Sampling and Compression Cha Zhang and Tsuhan Chen Advanced Multimedia Processing Lab M s 2 1 u v 1 2 L t Technical Report AMP 03-03 June 2003 Electrical
An Algorithm for Seamless Image Stitching and Its Application
 An Algorithm for Seamless Image Stitching and Its Application Jing Xing, Zhenjiang Miao, and Jing Chen Institute of Information Science, Beijing JiaoTong University, Beijing 100044, P.R. China Abstract.
An Algorithm for Seamless Image Stitching and Its Application Jing Xing, Zhenjiang Miao, and Jing Chen Institute of Information Science, Beijing JiaoTong University, Beijing 100044, P.R. China Abstract.
CS 684 Fall 2005 Image-based Modeling and Rendering. Ruigang Yang
 CS 684 Fall 2005 Image-based Modeling and Rendering Ruigang Yang Administrivia Classes: Monday and Wednesday, 4:00-5:15 PM Instructor: Ruigang Yang ryang@cs.uky.edu Office Hour: Robotics 514D, MW 1500-1600
CS 684 Fall 2005 Image-based Modeling and Rendering Ruigang Yang Administrivia Classes: Monday and Wednesday, 4:00-5:15 PM Instructor: Ruigang Yang ryang@cs.uky.edu Office Hour: Robotics 514D, MW 1500-1600
Plenoptic Stitching: A Scalable Method for Reconstructing 3D Interactive Walkthroughs
 Plenoptic Stitching: A Scalable Method for Reconstructing 3D Interactive Walkthroughs Daniel G. Aliaga aliaga@bell-labs.com Ingrid Carlbom carlbom@bell-labs.com Lucent Technologies Bell Laboratories Abstract
Plenoptic Stitching: A Scalable Method for Reconstructing 3D Interactive Walkthroughs Daniel G. Aliaga aliaga@bell-labs.com Ingrid Carlbom carlbom@bell-labs.com Lucent Technologies Bell Laboratories Abstract
Image Transfer Methods. Satya Prakash Mallick Jan 28 th, 2003
 Image Transfer Methods Satya Prakash Mallick Jan 28 th, 2003 Objective Given two or more images of the same scene, the objective is to synthesize a novel view of the scene from a view point where there
Image Transfer Methods Satya Prakash Mallick Jan 28 th, 2003 Objective Given two or more images of the same scene, the objective is to synthesize a novel view of the scene from a view point where there
Light Field Spring
 Light Field 2015 Spring Recall: Light is Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(l) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) l is wavelength Useful things: Light travels in straight
Light Field 2015 Spring Recall: Light is Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(l) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) l is wavelength Useful things: Light travels in straight
Morphable 3D-Mosaics: a Hybrid Framework for Photorealistic Walkthroughs of Large Natural Environments
 Morphable 3D-Mosaics: a Hybrid Framework for Photorealistic Walkthroughs of Large Natural Environments Nikos Komodakis and Georgios Tziritas Computer Science Department, University of Crete E-mails: {komod,
Morphable 3D-Mosaics: a Hybrid Framework for Photorealistic Walkthroughs of Large Natural Environments Nikos Komodakis and Georgios Tziritas Computer Science Department, University of Crete E-mails: {komod,
Image-Based Rendering using Image-Warping Motivation and Background
 Image-Based Rendering using Image-Warping Motivation and Background Leonard McMillan LCS Computer Graphics Group MIT The field of three-dimensional computer graphics has long focused on the problem of
Image-Based Rendering using Image-Warping Motivation and Background Leonard McMillan LCS Computer Graphics Group MIT The field of three-dimensional computer graphics has long focused on the problem of
A Bayesian Framework for Panoramic Imaging of Complex Scenes
 A Bayesian Framework for Panoramic Imaging of Complex Scenes by Alan Brunton Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies In partial fulfillment of the requirements For the MCS
A Bayesian Framework for Panoramic Imaging of Complex Scenes by Alan Brunton Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies In partial fulfillment of the requirements For the MCS
A Warping-based Refinement of Lumigraphs
 A Warping-based Refinement of Lumigraphs Wolfgang Heidrich, Hartmut Schirmacher, Hendrik Kück, Hans-Peter Seidel Computer Graphics Group University of Erlangen heidrich,schirmacher,hkkueck,seidel@immd9.informatik.uni-erlangen.de
A Warping-based Refinement of Lumigraphs Wolfgang Heidrich, Hartmut Schirmacher, Hendrik Kück, Hans-Peter Seidel Computer Graphics Group University of Erlangen heidrich,schirmacher,hkkueck,seidel@immd9.informatik.uni-erlangen.de
Stereo pairs from linear morphing
 Proc. of SPIE Vol. 3295, Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems V, ed. M T Bolas, S S Fisher, J O Merritt (Apr 1998) Copyright SPIE Stereo pairs from linear morphing David F. McAllister Multimedia
Proc. of SPIE Vol. 3295, Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems V, ed. M T Bolas, S S Fisher, J O Merritt (Apr 1998) Copyright SPIE Stereo pairs from linear morphing David F. McAllister Multimedia
Layered Depth Panoramas
 Layered Depth Panoramas Ke Colin Zheng 1, Sing Bing Kang 2 Michael F. Cohen 2, Richard Szeliski 2 1 University of Washington, Seattle, WA 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA Abstract Representations for
Layered Depth Panoramas Ke Colin Zheng 1, Sing Bing Kang 2 Michael F. Cohen 2, Richard Szeliski 2 1 University of Washington, Seattle, WA 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA Abstract Representations for
Virtual Worlds using Computer Vision
 Virtual Worlds using Computer Vision P. J. Narayanan Centre for Artificial Intelligence & Robotics Raj Bhavan Circle, High Grounds Bangalore, INDIA 560 001. E-mail: pjn@cair.res.in Takeo Kanade Robotics
Virtual Worlds using Computer Vision P. J. Narayanan Centre for Artificial Intelligence & Robotics Raj Bhavan Circle, High Grounds Bangalore, INDIA 560 001. E-mail: pjn@cair.res.in Takeo Kanade Robotics
The Light Field and Image-Based Rendering
 Lecture 11: The Light Field and Image-Based Rendering Visual Computing Systems Demo (movie) Royal Palace: Madrid, Spain Image-based rendering (IBR) So far in course: rendering = synthesizing an image from
Lecture 11: The Light Field and Image-Based Rendering Visual Computing Systems Demo (movie) Royal Palace: Madrid, Spain Image-based rendering (IBR) So far in course: rendering = synthesizing an image from
CSc Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography
 CSc 83010 Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography Tuesdays 11:45-1:45 1:45 Room 3305 Ioannis Stamos istamos@hunter.cuny.edu Office: 1090F, Hunter North (Entrance at 69 th bw/ / Park and Lexington Avenues)
CSc 83010 Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography Tuesdays 11:45-1:45 1:45 Room 3305 Ioannis Stamos istamos@hunter.cuny.edu Office: 1090F, Hunter North (Entrance at 69 th bw/ / Park and Lexington Avenues)
Announcements. Mosaics. Image Mosaics. How to do it? Basic Procedure Take a sequence of images from the same position =
 Announcements Project 2 out today panorama signup help session at end of class Today mosaic recap blending Mosaics Full screen panoramas (cubic): http://www.panoramas.dk/ Mars: http://www.panoramas.dk/fullscreen3/f2_mars97.html
Announcements Project 2 out today panorama signup help session at end of class Today mosaic recap blending Mosaics Full screen panoramas (cubic): http://www.panoramas.dk/ Mars: http://www.panoramas.dk/fullscreen3/f2_mars97.html
FAST ALGORITHM FOR CREATING IMAGE-BASED STEREO IMAGES
 FAST AGRITHM FR CREATING IMAGE-BASED STERE IMAGES Przemysław Kozankiewicz Institute of Computer Science, Warsaw University of Technology, ul. Nowowiejska 15/19, 00-665 Warsaw, Poland pkozanki@ii.pw.edu.pl
FAST AGRITHM FR CREATING IMAGE-BASED STERE IMAGES Przemysław Kozankiewicz Institute of Computer Science, Warsaw University of Technology, ul. Nowowiejska 15/19, 00-665 Warsaw, Poland pkozanki@ii.pw.edu.pl
Model-Based Stereo. Chapter Motivation. The modeling system described in Chapter 5 allows the user to create a basic model of a
 96 Chapter 7 Model-Based Stereo 7.1 Motivation The modeling system described in Chapter 5 allows the user to create a basic model of a scene, but in general the scene will have additional geometric detail
96 Chapter 7 Model-Based Stereo 7.1 Motivation The modeling system described in Chapter 5 allows the user to create a basic model of a scene, but in general the scene will have additional geometric detail
Multiview Reconstruction
 Multiview Reconstruction Why More Than 2 Views? Baseline Too short low accuracy Too long matching becomes hard Why More Than 2 Views? Ambiguity with 2 views Camera 1 Camera 2 Camera 3 Trinocular Stereo
Multiview Reconstruction Why More Than 2 Views? Baseline Too short low accuracy Too long matching becomes hard Why More Than 2 Views? Ambiguity with 2 views Camera 1 Camera 2 Camera 3 Trinocular Stereo
Modeling Light. Slides from Alexei A. Efros and others
 Project 3 Results http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/jcmace/ http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/damoreno/ http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/taox/ Stereo
Project 3 Results http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/jcmace/ http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/damoreno/ http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/taox/ Stereo
Modeling Light. Michal Havlik
 Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power
Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power
DECODING COMPLEXITY CONSTRAINED RATE-DISTORTION OPTIMIZATION FOR THE COMPRESSION OF CONCENTRIC MOSAICS
 DECODING COMPLEXITY CONSTRAINED RATE-DISTORTION OPTIMIZATION FOR THE COMPRESSION OF CONCENTRIC MOSAICS Eswar Kalyan Vutukuri, Ingo Bauerman and Eckehard Steinbach Institute of Communication Networks, Media
DECODING COMPLEXITY CONSTRAINED RATE-DISTORTION OPTIMIZATION FOR THE COMPRESSION OF CONCENTRIC MOSAICS Eswar Kalyan Vutukuri, Ingo Bauerman and Eckehard Steinbach Institute of Communication Networks, Media
Image Based Rendering. D.A. Forsyth, with slides from John Hart
 Image Based Rendering D.A. Forsyth, with slides from John Hart Topics Mosaics translating cameras reveal extra information, break occlusion Optical flow for very small movements of the camera Explicit
Image Based Rendering D.A. Forsyth, with slides from John Hart Topics Mosaics translating cameras reveal extra information, break occlusion Optical flow for very small movements of the camera Explicit
A million pixels, a million polygons. Which is heavier? François X. Sillion. imagis* Grenoble, France
 A million pixels, a million polygons. Which is heavier? François X. Sillion imagis* Grenoble, France *A joint research project of CNRS, INRIA, INPG and UJF MAGIS Why this question? Evolution of processing
A million pixels, a million polygons. Which is heavier? François X. Sillion imagis* Grenoble, France *A joint research project of CNRS, INRIA, INPG and UJF MAGIS Why this question? Evolution of processing
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Compositing a bird's eye view mosaic
 Compositing a bird's eye view mosaic Robert Laganiere School of Information Technology and Engineering University of Ottawa Ottawa, Ont KN 6N Abstract This paper describes a method that allows the composition
Compositing a bird's eye view mosaic Robert Laganiere School of Information Technology and Engineering University of Ottawa Ottawa, Ont KN 6N Abstract This paper describes a method that allows the composition
Optimizing an Inverse Warper
 Optimizing an Inverse Warper by Robert W. Marcato, Jr. Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degrees of Bachelor
Optimizing an Inverse Warper by Robert W. Marcato, Jr. Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degrees of Bachelor
Fundamentals of Stereo Vision Michael Bleyer LVA Stereo Vision
 Fundamentals of Stereo Vision Michael Bleyer LVA Stereo Vision What Happened Last Time? Human 3D perception (3D cinema) Computational stereo Intuitive explanation of what is meant by disparity Stereo matching
Fundamentals of Stereo Vision Michael Bleyer LVA Stereo Vision What Happened Last Time? Human 3D perception (3D cinema) Computational stereo Intuitive explanation of what is meant by disparity Stereo matching
Modeling Light. Michal Havlik : Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2011
 Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2011 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power
Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2011 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power
The Plenoptic videos: Capturing, Rendering and Compression. Chan, SC; Ng, KT; Gan, ZF; Chan, KL; Shum, HY.
 Title The Plenoptic videos: Capturing, Rendering and Compression Author(s) Chan, SC; Ng, KT; Gan, ZF; Chan, KL; Shum, HY Citation IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems Proceedings, Vancouver,
Title The Plenoptic videos: Capturing, Rendering and Compression Author(s) Chan, SC; Ng, KT; Gan, ZF; Chan, KL; Shum, HY Citation IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems Proceedings, Vancouver,
IRW: An Incremental Representation for Image-Based Walkthroughs
 IRW: An Incremental Representation for Image-Based Walkthroughs David Gotz gotz@cs.unc.edu Ketan Mayer-Patel kmp@cs.unc.edu University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill CB #3175, Sitterson Hall Chapel Hill,
IRW: An Incremental Representation for Image-Based Walkthroughs David Gotz gotz@cs.unc.edu Ketan Mayer-Patel kmp@cs.unc.edu University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill CB #3175, Sitterson Hall Chapel Hill,
Multiple View Geometry
 Multiple View Geometry Martin Quinn with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Jianbo Shi 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 Our Goal The Plenoptic Function P(θ,φ,λ,t,V
Multiple View Geometry Martin Quinn with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Jianbo Shi 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 Our Goal The Plenoptic Function P(θ,φ,λ,t,V
A Simple Vision System
 Chapter 1 A Simple Vision System 1.1 Introduction In 1966, Seymour Papert wrote a proposal for building a vision system as a summer project [4]. The abstract of the proposal starts stating a simple goal:
Chapter 1 A Simple Vision System 1.1 Introduction In 1966, Seymour Papert wrote a proposal for building a vision system as a summer project [4]. The abstract of the proposal starts stating a simple goal:
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms
 Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Quiz 2 Thursday November 20, :40-4pm One hand-written sheet of notes allowed
 6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Quiz 2 Thursday November 20, 2003 2:40-4pm One hand-written sheet of notes allowed Name: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 / 4 / 15 / 5 / 5 / 12 / 2 / 7 Total / 50 1 Animation [ /4]
6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Quiz 2 Thursday November 20, 2003 2:40-4pm One hand-written sheet of notes allowed Name: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 / 4 / 15 / 5 / 5 / 12 / 2 / 7 Total / 50 1 Animation [ /4]
Linearizing the Plenoptic Space
 Linearizing the Plenoptic Space Grégoire Nieto1, Frédéric Devernay1, James Crowley2 LJK, Université Grenoble Alpes, France 2 LIG, Université Grenoble Alpes, France 1 1 Goal: synthesize a new view Capture/sample
Linearizing the Plenoptic Space Grégoire Nieto1, Frédéric Devernay1, James Crowley2 LJK, Université Grenoble Alpes, France 2 LIG, Université Grenoble Alpes, France 1 1 Goal: synthesize a new view Capture/sample
Automatically Synthesising Virtual Viewpoints by Trinocular Image Interpolation
 Automatically Synthesising Virtual Viewpoints by Trinocular Image Interpolation Stephen Pollard, Sean Hayes, Maurizio Pilu, Adele Lorusso Digital Media Department HP Laboratories Bristol HPL-98-05 January,
Automatically Synthesising Virtual Viewpoints by Trinocular Image Interpolation Stephen Pollard, Sean Hayes, Maurizio Pilu, Adele Lorusso Digital Media Department HP Laboratories Bristol HPL-98-05 January,
Image Warping and Mosacing
 Image Warping and Mosacing 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski Today Mosacs Image Warping Homographies Programming Assignment
Image Warping and Mosacing 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski Today Mosacs Image Warping Homographies Programming Assignment
Hierarchical Matching Techiques for Automatic Image Mosaicing
 Hierarchical Matching Techiques for Automatic Image Mosaicing C.L Begg, R Mukundan Department of Computer Science, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand clb56@student.canterbury.ac.nz, mukund@cosc.canterbury.ac.nz
Hierarchical Matching Techiques for Automatic Image Mosaicing C.L Begg, R Mukundan Department of Computer Science, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand clb56@student.canterbury.ac.nz, mukund@cosc.canterbury.ac.nz
Modeling Light. Michal Havlik
 Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Spring 2010 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R( ) is EMR, measured in units of
Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Spring 2010 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R( ) is EMR, measured in units of
Capturing and View-Dependent Rendering of Billboard Models
 Capturing and View-Dependent Rendering of Billboard Models Oliver Le, Anusheel Bhushan, Pablo Diaz-Gutierrez and M. Gopi Computer Graphics Lab University of California, Irvine Abstract. In this paper,
Capturing and View-Dependent Rendering of Billboard Models Oliver Le, Anusheel Bhushan, Pablo Diaz-Gutierrez and M. Gopi Computer Graphics Lab University of California, Irvine Abstract. In this paper,
5LSH0 Advanced Topics Video & Analysis
 1 Multiview 3D video / Outline 2 Advanced Topics Multimedia Video (5LSH0), Module 02 3D Geometry, 3D Multiview Video Coding & Rendering Peter H.N. de With, Sveta Zinger & Y. Morvan ( p.h.n.de.with@tue.nl
1 Multiview 3D video / Outline 2 Advanced Topics Multimedia Video (5LSH0), Module 02 3D Geometry, 3D Multiview Video Coding & Rendering Peter H.N. de With, Sveta Zinger & Y. Morvan ( p.h.n.de.with@tue.nl
Chapter 5. Projections and Rendering
 Chapter 5 Projections and Rendering Topics: Perspective Projections The rendering pipeline In order to view manipulate and view a graphics object we must find ways of storing it a computer-compatible way.
Chapter 5 Projections and Rendering Topics: Perspective Projections The rendering pipeline In order to view manipulate and view a graphics object we must find ways of storing it a computer-compatible way.
Towards a Perceptual Method of Blending for Image-Based Models
 Towards a Perceptual Method of Blending for Image-Based Models Gordon Watson, Patrick O Brien and Mark Wright Edinburgh Virtual Environment Centre University of Edinburgh JCMB, Mayfield Road, Edinburgh
Towards a Perceptual Method of Blending for Image-Based Models Gordon Watson, Patrick O Brien and Mark Wright Edinburgh Virtual Environment Centre University of Edinburgh JCMB, Mayfield Road, Edinburgh
Page 1. Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms
 Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Advanced Image Based Rendering Techniques
 Advanced Image Based Rendering Techniques Herbert Grasberger Institute of Computergraphics & Algorithms, TU Vienna, Austria June 13, 2006 Abstract Image Based Rendering is a rendering approach based on
Advanced Image Based Rendering Techniques Herbert Grasberger Institute of Computergraphics & Algorithms, TU Vienna, Austria June 13, 2006 Abstract Image Based Rendering is a rendering approach based on
A Survey and Classification of Real Time Rendering Methods
 Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Cambridge Research Center Technical Report 2000-09 March 29, 2000 A Survey and Classification of Real Time Rendering Methods Matthias Zwicker *, Markus H. Gross
Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Cambridge Research Center Technical Report 2000-09 March 29, 2000 A Survey and Classification of Real Time Rendering Methods Matthias Zwicker *, Markus H. Gross
Image Processing: Motivation Rendering from Images. Related Work. Overview. Image Morphing Examples. Overview. View and Image Morphing CS334
 Motivation Rendering from Images Image rocessing: View and CS334 Given left image right image Create intermediate images simulates camera movement [Seitz96] Related Work anoramas ([Chen95/QuicktimeVR],
Motivation Rendering from Images Image rocessing: View and CS334 Given left image right image Create intermediate images simulates camera movement [Seitz96] Related Work anoramas ([Chen95/QuicktimeVR],
Last week. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 Last week Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Overview of a graphics system Output device Input devices Image formed and stored in frame buffer Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 2 Introduction to CG Torsten Möller 3 Ray tracing:
Last week Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Overview of a graphics system Output device Input devices Image formed and stored in frame buffer Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 2 Introduction to CG Torsten Möller 3 Ray tracing:
Computational Photography
 Computational Photography Photography and Imaging Michael S. Brown Brown - 1 Part 1 Overview Photography Preliminaries Traditional Film Imaging (Camera) Part 2 General Imaging 5D Plenoptic Function (McMillan)
Computational Photography Photography and Imaging Michael S. Brown Brown - 1 Part 1 Overview Photography Preliminaries Traditional Film Imaging (Camera) Part 2 General Imaging 5D Plenoptic Function (McMillan)
Image stitching. Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang. with slides by Richard Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Matthew Brown and Vaclav Hlavac
 Image stitching Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Richard Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Matthew Brown and Vaclav Hlavac Image stitching Stitching = alignment + blending geometrical registration
Image stitching Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Richard Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Matthew Brown and Vaclav Hlavac Image stitching Stitching = alignment + blending geometrical registration
Lecture 15: Image-Based Rendering and the Light Field. Kayvon Fatahalian CMU : Graphics and Imaging Architectures (Fall 2011)
 Lecture 15: Image-Based Rendering and the Light Field Kayvon Fatahalian CMU 15-869: Graphics and Imaging Architectures (Fall 2011) Demo (movie) Royal Palace: Madrid, Spain Image-based rendering (IBR) So
Lecture 15: Image-Based Rendering and the Light Field Kayvon Fatahalian CMU 15-869: Graphics and Imaging Architectures (Fall 2011) Demo (movie) Royal Palace: Madrid, Spain Image-based rendering (IBR) So
Face Cyclographs for Recognition
 Face Cyclographs for Recognition Guodong Guo Department of Computer Science North Carolina Central University E-mail: gdguo@nccu.edu Charles R. Dyer Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin-Madison
Face Cyclographs for Recognition Guodong Guo Department of Computer Science North Carolina Central University E-mail: gdguo@nccu.edu Charles R. Dyer Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin-Madison
3-D Shape Reconstruction from Light Fields Using Voxel Back-Projection
 3-D Shape Reconstruction from Light Fields Using Voxel Back-Projection Peter Eisert, Eckehard Steinbach, and Bernd Girod Telecommunications Laboratory, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Cauerstrasse 7,
3-D Shape Reconstruction from Light Fields Using Voxel Back-Projection Peter Eisert, Eckehard Steinbach, and Bernd Girod Telecommunications Laboratory, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Cauerstrasse 7,
Image based Object/Environment Representation for VR and MAR
 Image based Object/Environment Representation for VR and MAR SC 24 WG 9 Seoul, Korea January, 2019 Changhyun Jun, Gerard J. Kim Korea University Image based Rendering Rely on a set of two-dimensional images
Image based Object/Environment Representation for VR and MAR SC 24 WG 9 Seoul, Korea January, 2019 Changhyun Jun, Gerard J. Kim Korea University Image based Rendering Rely on a set of two-dimensional images
Computer Graphics I Lecture 11
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 11 Midterm Review Assignment 3 Movie Midterm Review Midterm Preview February 26, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 11 Midterm Review Assignment 3 Movie Midterm Review Midterm Preview February 26, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/
Tour Into the Picture using a Vanishing Line and its Extension to Panoramic Images
 EUROGRAPHICS 2001 / A. Chalmers and T.-M. Rhyne (Guest Editors) Volume 20 (2001), Number 3 Tour Into the Picture using a Vanishing Line and its Extension to Panoramic Images Hyung Woo Kang, Soon Hyoung
EUROGRAPHICS 2001 / A. Chalmers and T.-M. Rhyne (Guest Editors) Volume 20 (2001), Number 3 Tour Into the Picture using a Vanishing Line and its Extension to Panoramic Images Hyung Woo Kang, Soon Hyoung
Computing Visibility. Backface Culling for General Visibility. One More Trick with Planes. BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz
 Computing Visibility BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz Power of Plane Equations We ve gotten a lot of mileage out of one simple equation. Basis for D outcode-clipping Basis for plane-at-a-time
Computing Visibility BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz Power of Plane Equations We ve gotten a lot of mileage out of one simple equation. Basis for D outcode-clipping Basis for plane-at-a-time
Introduction Ray tracing basics Advanced topics (shading) Advanced topics (geometry) Graphics 2010/2011, 4th quarter. Lecture 11: Ray tracing
 Lecture 11 Ray tracing Introduction Projection vs. ray tracing Projection Ray tracing Rendering Projection vs. ray tracing Projection Ray tracing Basic methods for image generation Major areas of computer
Lecture 11 Ray tracing Introduction Projection vs. ray tracing Projection Ray tracing Rendering Projection vs. ray tracing Projection Ray tracing Basic methods for image generation Major areas of computer
A Framework for 3D Pushbroom Imaging CUCS
 A Framework for 3D Pushbroom Imaging CUCS-002-03 Naoyuki Ichimura and Shree K. Nayar Information Technology Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) Tsukuba,
A Framework for 3D Pushbroom Imaging CUCS-002-03 Naoyuki Ichimura and Shree K. Nayar Information Technology Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) Tsukuba,
Virtual Navigation of Complex Scenes using Clusters of Cylindrical. panoramic images.
 Virtual Navigation of Complex Scenes using Clusters of Cylindrical Panoramic Images Sing Bing Kang a a Digital Equipment Corporation Cambridge Research Lab. One Kendall Square, Bldg. 700 Cambridge, MA
Virtual Navigation of Complex Scenes using Clusters of Cylindrical Panoramic Images Sing Bing Kang a a Digital Equipment Corporation Cambridge Research Lab. One Kendall Square, Bldg. 700 Cambridge, MA
Ray tracing. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1
 Ray tracing Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1 From last time Hidden surface removal Painter s algorithm Clipping algorithms Area subdivision BSP trees Z-Buffer
Ray tracing Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1 From last time Hidden surface removal Painter s algorithm Clipping algorithms Area subdivision BSP trees Z-Buffer
Multi-View Omni-Directional Imaging
 Multi-View Omni-Directional Imaging Tuesday, December 19, 2000 Moshe Ben-Ezra, Shmuel Peleg Abstract This paper describes a novel camera design or the creation o multiple panoramic images, such that each
Multi-View Omni-Directional Imaging Tuesday, December 19, 2000 Moshe Ben-Ezra, Shmuel Peleg Abstract This paper describes a novel camera design or the creation o multiple panoramic images, such that each
Texture. Texture Mapping. Texture Mapping. CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics. Lecture 11 : Texture
 Texture CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics Add surface detail Paste a photograph over a surface to provide detail. Texture can change surface colour or modulate surface colour. Lecture 11 : Texture http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/uv_mapping
Texture CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics Add surface detail Paste a photograph over a surface to provide detail. Texture can change surface colour or modulate surface colour. Lecture 11 : Texture http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/uv_mapping
CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics. Lecture 11 : Texture
 CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics Lecture 11 : Texture Texture Add surface detail Paste a photograph over a surface to provide detail. Texture can change surface colour or modulate surface colour. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/uv_mapping
CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics Lecture 11 : Texture Texture Add surface detail Paste a photograph over a surface to provide detail. Texture can change surface colour or modulate surface colour. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/uv_mapping
Interactive 3D Scene Reconstruction from Images
 Interactive 3D Scene Reconstruction from Images Aaron Hertzmann Media Research Laboratory Department of Computer Science New York University 719 Broadway, 12th Floor New York, NY 10003 hertzman@mrl.nyu.edu
Interactive 3D Scene Reconstruction from Images Aaron Hertzmann Media Research Laboratory Department of Computer Science New York University 719 Broadway, 12th Floor New York, NY 10003 hertzman@mrl.nyu.edu
0. Introduction: What is Computer Graphics? 1. Basics of scan conversion (line drawing) 2. Representing 2D curves
 CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~elf Instructor: Eugene Fiume Office: BA 5266 Phone: 416 978 5472 (not a reliable way) Email:
CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~elf Instructor: Eugene Fiume Office: BA 5266 Phone: 416 978 5472 (not a reliable way) Email:
View Synthesis by Trinocular Edge Matching and Transfer
 View Synthesis by Trinocular Edge Matching and Transfer S. Pollard, M. Pilu, S. Hayes and A. Lorusso Hewlett-Packard Laboratories Bristol (UK) BS12 6QZ [stp mp esh lorusso]@hplb.hpl.hp.com Abstract This
View Synthesis by Trinocular Edge Matching and Transfer S. Pollard, M. Pilu, S. Hayes and A. Lorusso Hewlett-Packard Laboratories Bristol (UK) BS12 6QZ [stp mp esh lorusso]@hplb.hpl.hp.com Abstract This
