Implicit Surfaces or Level Sets of Functions *
|
|
|
- Carmella Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Implicit Surfaces or Level Sets of Functions * Surfaces in R 3 are either described as parametrized images F : D 2 R 3 or as implicit surfaces, i.e., as levels of functions f : R 3 R, as the set of points where f has a fixed value v: {x R 3 ; f(x) = v}. One can more easily make images of parametrized surfaces than of implicit surfaces, because every point p D can be mapped with the given function F to obtain explicitly a point F (p) of the surface. Note however that the opposite problem: Given a point in R 3, decide whether it lies on the surface does not have an easy answer. For an implicit surface, on the other hand, it is easy to decide whether a given point in R 3 is on the surface (simply check f(x) = v), but * This file is from the 3D-XplorMath project. Please see:
2 no point is given explicitly, one has to use some algorithm to find points x R 3 which satisfy f(x) = v. And even after one has found many points on the surface, how does one connect them, what is a good way to represent the surface? The method of raytracing has been invented as one solution. Choose some center point C, think of it to be near the eyes of the viewer. Connect each pixel of the screen with C by a line and decide whether this line meets the surface. Of all the intersection points on the line choose the one closest to C, compute the normal of the surface at this point x (i.e. compute grad f(x)) and decide with this information what light (from fixed light sources) will be reflected by the surface at x towards C. Color that pixel accordingly. In this way one produces an image which presents the surface as if it were an illuminated object. The computation used to take very long, but with todays computers such pictures can be computed while you wait, but not quite fast enough for real time rotations. These pictures look very realistic, but of course they show only what is visible from the viewer. In 3D-XplorMath a second method is offered. Imagine that the surface is intersected with random lines until
3 around points have been found on the implicit surface. Then red-green stereo is used to project these points to the screen. When viewing through stereo glasses we see all these points in the correct position in space and our brain interpolates the picture and lets us see a surface in space. In this representation all parts of the surface (within some viewing sphere) can be seen, not just the front most portions. Since it is possible to achieve a fairly uniform distribution of points on level surfaces, one sees many points in the direction towards contours of the surface. This emphasis of the contour points is so strong that one also gets a fair impression of the surface if one does not look through red-green glases. This method is fast enough for real time rotations. What surfaces can one see? Of all the closed surfaces only spheres and tori have explicit parametrizations. Therefore pictures of parametrized surfaces will only show portions of a complicated surface ( patches ) or they will show spheres and tori. By contrast, already fairly simple functions may have level surfaces which are more complicated than tori, are so called bretzel surfaces of genus
4 g > 1. How can one find such functions? As an example, consider two circles of radius r, in the x-y-plane, with midpoints ±1 on the x-axis. This set is described as the intersection of the plane g(x, y, z) := z = 0 with the zero set of the function h(x, y, z) := ((x 1) 2 + y 2 r 2 ) ((x + 1) 2 + y 2 r 2 ). Now define f(x, y, z) := h(x, y, z) 2 + g(x, y, z) 2. Clearly, the zero set of f is the union of the two circles, which is not a surface, because grad f vanishes along this zero set. However, most of the levels {(x, y, z); f(x, y, z) = v > 0} are surfaces without singularities. If the two circles intersect (r > 1), then for very small v the levels are the boundary of a thickening of the two circles, i.e., surfaces of genus 3. As v increases either the middle hole or the two outside holes close first (depending on r). For large v the level surfaces are (not completely round) spheres. Each time such a topological change occurs we observe one special surface, it is not smooth like the other levels, but
5 has one or more cone like singularities. If r < 1 then for very small v the levels are separate tori. Then either the tori grow together to a genus 2 surface, or the holes of the tori close first and later the two sphere like surfaces grow together.
6 Other Functions Supplied in 3D-XplorMath. Note: One should always experiment with the level value v of the function f. For small values of v one will see how the function was designed. Most default morphs vary v = ii. Genus 2, tube around a figure 8: f(x, y, z) :=((1 x 2 )x 2 y 2 ) 2 + z 2. Genus 5, tube around two intersecting ellipses: f(x, y, z) :=((x 2 + y 2 /4 1) (x 2 /4 + y 2 1)) 2 + z 2. Genus 3, tube around circle and orthogonal ellipse: f(x, y, z) :=((x 2 + y 2 1) 2 + (z 1) 2 ) (x 2 /aa + (z tr) 2 1) 2 + y 2 ). Genus 5, tube around three orthogonal circles: f(x, y, z) :=((x 2 + y 2 1) 2 + z 2 ) ((y 2 + z 2 1) 2 + x 2 ) ((z 2 + x 2 1) 2 + y 2 ). Genus 5,13,17, tube around six circles on a cube: f(x, y, z) :=((x 2 + y 2 cc 2 ) 2 + (z 2 1) 2 ) ((y 2 + z 2 cc 2 ) 2 + (x 2 1) 2 ) ((z 2 + x 2 cc 2 ) 2 + (y 2 1) 2 ).
7 H.K.
Lagrange multipliers October 2013
 Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 1 1 3/2 Example: Optimization
Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 1 1 3/2 Example: Optimization
Lagrange multipliers 14.8
 Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 Maximum? 1 1 Minimum? 3/2 Idea:
Lagrange multipliers 14.8 14 October 2013 Example: Optimization with constraint. Example: Find the extreme values of f (x, y) = x + 2y on the ellipse 3x 2 + 4y 2 = 3. 3/2 Maximum? 1 1 Minimum? 3/2 Idea:
Lecture 17: Solid Modeling.... a cubit on the one side, and a cubit on the other side Exodus 26:13
 Lecture 17: Solid Modeling... a cubit on the one side, and a cubit on the other side Exodus 26:13 Who is on the LORD's side? Exodus 32:26 1. Solid Representations A solid is a 3-dimensional shape with
Lecture 17: Solid Modeling... a cubit on the one side, and a cubit on the other side Exodus 26:13 Who is on the LORD's side? Exodus 32:26 1. Solid Representations A solid is a 3-dimensional shape with
Surfaces and Integral Curves
 MODULE 1: MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 16 Lecture 3 Surfaces and Integral Curves In Lecture 3, we recall some geometrical concepts that are essential for understanding the nature of solutions of partial
MODULE 1: MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 16 Lecture 3 Surfaces and Integral Curves In Lecture 3, we recall some geometrical concepts that are essential for understanding the nature of solutions of partial
Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4. Mon, Aug 31, 2009
 Model s Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4 World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Aug 31, 2009 Outline Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s 1 2 3 Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window
Model s Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4 World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Aug 31, 2009 Outline Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s 1 2 3 Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window
Create a Rubber Duck. This tutorial shows you how to. Create simple surfaces. Rebuild a surface. Edit surface control points. Draw and project curves
 Page 1 of 24 Create a Rubber Duck This exercise focuses on the free form, squishy aspect. Unlike the flashlight model, the exact size and placement of the objects is not critical. The overall form is the
Page 1 of 24 Create a Rubber Duck This exercise focuses on the free form, squishy aspect. Unlike the flashlight model, the exact size and placement of the objects is not critical. The overall form is the
The University of Calgary
 The University of Calgary Department of Computer Science Final Examination, Questions ENEL/CPSC 555 Computer Graphics Time: 2 Hours Closed Book, calculators are permitted. The questions carry equal weight.
The University of Calgary Department of Computer Science Final Examination, Questions ENEL/CPSC 555 Computer Graphics Time: 2 Hours Closed Book, calculators are permitted. The questions carry equal weight.
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Contours & Implicit Modelling 4
 Brief Recap Contouring & Implicit Modelling Contouring Implicit Functions Visualisation Lecture 8 lecture 6 Marching Cubes lecture 3 visualisation of a Quadric toby.breckon@ed.ac.uk Computer Vision Lab.
Brief Recap Contouring & Implicit Modelling Contouring Implicit Functions Visualisation Lecture 8 lecture 6 Marching Cubes lecture 3 visualisation of a Quadric toby.breckon@ed.ac.uk Computer Vision Lab.
Computer Graphics Ray Casting. Matthias Teschner
 Computer Graphics Ray Casting Matthias Teschner Outline Context Implicit surfaces Parametric surfaces Combined objects Triangles Axis-aligned boxes Iso-surfaces in grids Summary University of Freiburg
Computer Graphics Ray Casting Matthias Teschner Outline Context Implicit surfaces Parametric surfaces Combined objects Triangles Axis-aligned boxes Iso-surfaces in grids Summary University of Freiburg
Quadric Surfaces. Six basic types of quadric surfaces: ellipsoid. cone. elliptic paraboloid. hyperboloid of one sheet. hyperboloid of two sheets
 Quadric Surfaces Six basic types of quadric surfaces: ellipsoid cone elliptic paraboloid hyperboloid of one sheet hyperboloid of two sheets hyperbolic paraboloid (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) 1. For each surface,
Quadric Surfaces Six basic types of quadric surfaces: ellipsoid cone elliptic paraboloid hyperboloid of one sheet hyperboloid of two sheets hyperbolic paraboloid (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) 1. For each surface,
Functions of Several Variables
 . Functions of Two Variables Functions of Several Variables Rectangular Coordinate System in -Space The rectangular coordinate system in R is formed by mutually perpendicular axes. It is a right handed
. Functions of Two Variables Functions of Several Variables Rectangular Coordinate System in -Space The rectangular coordinate system in R is formed by mutually perpendicular axes. It is a right handed
The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 10 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 10 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
Solid Modeling. Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University
 Solid Modeling Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Solids Definition 1. A model which has a well defined inside and outside. 2. For each point, we can in principle determine whether
Solid Modeling Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Solids Definition 1. A model which has a well defined inside and outside. 2. For each point, we can in principle determine whether
CS 130. Scan Conversion. Raster Graphics
 CS 130 Scan Conversion Raster Graphics 2 1 Image Formation Computer graphics forms images, generally two dimensional, using processes analogous to physical imaging systems like: - Cameras - Human visual
CS 130 Scan Conversion Raster Graphics 2 1 Image Formation Computer graphics forms images, generally two dimensional, using processes analogous to physical imaging systems like: - Cameras - Human visual
Hyperbolic Geometry. Thomas Prince. Imperial College London. 21 January 2017
 Hyperbolic Geometry Thomas Prince Imperial College London 21 January 2017 Thomas Prince (Imperial College London) Hyperbolic Planes 21 January 2017 1 / 31 Introducing Geometry What does the word geometry
Hyperbolic Geometry Thomas Prince Imperial College London 21 January 2017 Thomas Prince (Imperial College London) Hyperbolic Planes 21 January 2017 1 / 31 Introducing Geometry What does the word geometry
Assignment 6: Ray Tracing
 Assignment 6: Ray Tracing Programming Lab Due: Monday, April 20 (midnight) 1 Introduction Throughout this semester you have written code that manipulated shapes and cameras to prepare a scene for rendering.
Assignment 6: Ray Tracing Programming Lab Due: Monday, April 20 (midnight) 1 Introduction Throughout this semester you have written code that manipulated shapes and cameras to prepare a scene for rendering.
CS 130 Exam I. Fall 2015
 S 3 Exam I Fall 25 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
S 3 Exam I Fall 25 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
Contours & Implicit Modelling 1
 Contouring & Implicit Modelling Visualisation Lecture 8 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Contours & Implicit Modelling 1 Brief Recap Contouring Implicit Functions lecture
Contouring & Implicit Modelling Visualisation Lecture 8 Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Contours & Implicit Modelling 1 Brief Recap Contouring Implicit Functions lecture
CS3621 Midterm Solution (Fall 2005) 150 points
 CS362 Midterm Solution Fall 25. Geometric Transformation CS362 Midterm Solution (Fall 25) 5 points (a) [5 points] Find the 2D transformation matrix for the reflection about the y-axis transformation (i.e.,
CS362 Midterm Solution Fall 25. Geometric Transformation CS362 Midterm Solution (Fall 25) 5 points (a) [5 points] Find the 2D transformation matrix for the reflection about the y-axis transformation (i.e.,
Math background. 2D Geometric Transformations. Implicit representations. Explicit representations. Read: CS 4620 Lecture 6
 Math background 2D Geometric Transformations CS 4620 Lecture 6 Read: Chapter 2: Miscellaneous Math Chapter 5: Linear Algebra Notation for sets, functions, mappings Linear transformations Matrices Matrix-vector
Math background 2D Geometric Transformations CS 4620 Lecture 6 Read: Chapter 2: Miscellaneous Math Chapter 5: Linear Algebra Notation for sets, functions, mappings Linear transformations Matrices Matrix-vector
Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11
 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your
Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your
Dr. Allen Back. Nov. 21, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back of Nov. 21, 2014 The most important thing you should know (e.g. for exams and homework) is how to setup (and perhaps compute if not too hard) surface integrals, triple integrals, etc. But
Dr. Allen Back of Nov. 21, 2014 The most important thing you should know (e.g. for exams and homework) is how to setup (and perhaps compute if not too hard) surface integrals, triple integrals, etc. But
IMAGINARY Proposal for a guided tour of the exhibition
 IMAGINARY Proposal for a guided tour of the exhibition S. Apel, E. Brechmann, A. Matt, A. Caspar, S. Schimpf, H. Grimm-Strele May 7, 2012 1 Introduction and general information 1.1 General rules for the
IMAGINARY Proposal for a guided tour of the exhibition S. Apel, E. Brechmann, A. Matt, A. Caspar, S. Schimpf, H. Grimm-Strele May 7, 2012 1 Introduction and general information 1.1 General rules for the
Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 14!
 Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 14! Student Name:!! Class Account Username:! Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must
Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 14! Student Name:!! Class Account Username:! Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must
Space Curves of Constant Curvature *
 Space Curves of Constant Curvature * 2-11 Torus Knot of constant curvature. See also: About Spherical Curves Definition via Differential Equations. Space Curves that 3DXM can exhibit are mostly given in
Space Curves of Constant Curvature * 2-11 Torus Knot of constant curvature. See also: About Spherical Curves Definition via Differential Equations. Space Curves that 3DXM can exhibit are mostly given in
Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 14 Fall 2016 Prof. James O Brien
 Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 14 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully The exam begins at 3:10pm and ends at 6:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 14 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully The exam begins at 3:10pm and ends at 6:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
16.6. Parametric Surfaces. Parametric Surfaces. Parametric Surfaces. Vector Calculus. Parametric Surfaces and Their Areas
 16 Vector Calculus 16.6 and Their Areas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and Their Areas Here we use vector functions to describe more general
16 Vector Calculus 16.6 and Their Areas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and Their Areas Here we use vector functions to describe more general
Computer Graphics. Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring
 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring Today Environment Mapping Introduction Cubic mapping Sphere mapping refractive mapping Mirroring Introduction reflection first stencil buffer
Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring Today Environment Mapping Introduction Cubic mapping Sphere mapping refractive mapping Mirroring Introduction reflection first stencil buffer
A TESSELLATION FOR ALGEBRAIC SURFACES IN CP 3
 A TESSELLATION FOR ALGEBRAIC SURFACES IN CP 3 ANDREW J. HANSON AND JI-PING SHA In this paper we present a systematic and explicit algorithm for tessellating the algebraic surfaces (real 4-manifolds) F
A TESSELLATION FOR ALGEBRAIC SURFACES IN CP 3 ANDREW J. HANSON AND JI-PING SHA In this paper we present a systematic and explicit algorithm for tessellating the algebraic surfaces (real 4-manifolds) F
3D Design with 123D Design
 3D Design with 123D Design Introduction: 3D Design involves thinking and creating in 3 dimensions. x, y and z axis Working with 123D Design 123D Design is a 3D design software package from Autodesk. A
3D Design with 123D Design Introduction: 3D Design involves thinking and creating in 3 dimensions. x, y and z axis Working with 123D Design 123D Design is a 3D design software package from Autodesk. A
Geometric Representations. Stelian Coros
 Geometric Representations Stelian Coros Geometric Representations Languages for describing shape Boundary representations Polygonal meshes Subdivision surfaces Implicit surfaces Volumetric models Parametric
Geometric Representations Stelian Coros Geometric Representations Languages for describing shape Boundary representations Polygonal meshes Subdivision surfaces Implicit surfaces Volumetric models Parametric
Classification of Surfaces
 Classification of Surfaces 16 April 2014 Classification of Surfaces 16 April 2014 1/29 Last Time On Monday we saw some examples of surfaces and how we can build some by starting with a rectangle and gluing
Classification of Surfaces 16 April 2014 Classification of Surfaces 16 April 2014 1/29 Last Time On Monday we saw some examples of surfaces and how we can build some by starting with a rectangle and gluing
Graphics (INFOGR ): Example Exam
 Graphics (INFOGR 2015-2016): Example Exam StudentID / studentnummer Last name / achternaam First name / voornaam Do not open the exam until instructed to do so! Read the instructions on this page carefully!
Graphics (INFOGR 2015-2016): Example Exam StudentID / studentnummer Last name / achternaam First name / voornaam Do not open the exam until instructed to do so! Read the instructions on this page carefully!
Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 13!
 Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 13! Student Name:!! Class Account Username:! Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 1:10pm and ends at 2:30pm. You must
Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 13! Student Name:!! Class Account Username:! Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 1:10pm and ends at 2:30pm. You must
0. Introduction: What is Computer Graphics? 1. Basics of scan conversion (line drawing) 2. Representing 2D curves
 CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~elf Instructor: Eugene Fiume Office: BA 5266 Phone: 416 978 5472 (not a reliable way) Email:
CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~elf Instructor: Eugene Fiume Office: BA 5266 Phone: 416 978 5472 (not a reliable way) Email:
The exam begins at 5:10pm and ends at 8:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 5:10pm and ends at 8:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 5:10pm and ends at 8:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 Solid Modelling
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 Solid Modelling Welcome to the lectures on computer graphics. We have
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 Solid Modelling Welcome to the lectures on computer graphics. We have
Notes on Spherical Geometry
 Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
TRANSFORMATIONS. The original figure is called the pre-image; the new (copied) picture is called the image of the transformation.
 Quiz Review Sheet A transformation is a correspondence that maps a point. TRANSFORMATIONS The original figure is called the pre-image; the new (copied) picture is called the image of the transformation.
Quiz Review Sheet A transformation is a correspondence that maps a point. TRANSFORMATIONS The original figure is called the pre-image; the new (copied) picture is called the image of the transformation.
Outline. Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete. Noise
 Fundamentals Data Outline Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete Noise 2 Data Data : Function dependent on one or more variables. Example Audio (1D) - depends
Fundamentals Data Outline Visualization Discretization Sampling Quantization Representation Continuous Discrete Noise 2 Data Data : Function dependent on one or more variables. Example Audio (1D) - depends
CPSC / Scan Conversion
 CPSC 599.64 / 601.64 Computer Screens: Raster Displays pixel rasters (usually) square pixels in rectangular raster evenly cover the image problem no such things such as lines, circles, etc. scan conversion
CPSC 599.64 / 601.64 Computer Screens: Raster Displays pixel rasters (usually) square pixels in rectangular raster evenly cover the image problem no such things such as lines, circles, etc. scan conversion
Geometric Modeling Systems
 Geometric Modeling Systems Wireframe Modeling use lines/curves and points for 2D or 3D largely replaced by surface and solid models Surface Modeling wireframe information plus surface definitions supports
Geometric Modeling Systems Wireframe Modeling use lines/curves and points for 2D or 3D largely replaced by surface and solid models Surface Modeling wireframe information plus surface definitions supports
Conic Sections: Parabolas
 Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
The Graphics Pipeline. Interactive Computer Graphics. The Graphics Pipeline. The Graphics Pipeline. The Graphics Pipeline: Clipping
 Interactive Computer Graphics The Graphics Pipeline: The Graphics Pipeline Input: - geometric model - illumination model - camera model - viewport Some slides adopted from F. Durand and B. Cutler, MIT
Interactive Computer Graphics The Graphics Pipeline: The Graphics Pipeline Input: - geometric model - illumination model - camera model - viewport Some slides adopted from F. Durand and B. Cutler, MIT
Intersecting Simple Surfaces. Dr. Scott Schaefer
 Intersecting Simple Surfaces Dr. Scott Schaefer 1 Types of Surfaces Infinite Planes Polygons Convex Ray Shooting Winding Number Spheres Cylinders 2/66 Infinite Planes Defined by a unit normal n and a point
Intersecting Simple Surfaces Dr. Scott Schaefer 1 Types of Surfaces Infinite Planes Polygons Convex Ray Shooting Winding Number Spheres Cylinders 2/66 Infinite Planes Defined by a unit normal n and a point
CS 184, Fall 1996 Midterm #1 Professor: unknown
 CS 184, Fall 1996 Midterm #1 Professor: unknown Problem #1, Transformations (8pts) All questions assume a right handed coordinate system. Circle the correct answer: (2 pts each) a) In 3 space, two rotations
CS 184, Fall 1996 Midterm #1 Professor: unknown Problem #1, Transformations (8pts) All questions assume a right handed coordinate system. Circle the correct answer: (2 pts each) a) In 3 space, two rotations
Character Modeling IAT 343 Lab 6. Lanz Singbeil
 Character Modeling IAT 343 Lab 6 Modeling Using Reference Sketches Start by creating a character sketch in a T-Pose (arms outstretched) Separate the sketch into 2 images with the same pixel height. Make
Character Modeling IAT 343 Lab 6 Modeling Using Reference Sketches Start by creating a character sketch in a T-Pose (arms outstretched) Separate the sketch into 2 images with the same pixel height. Make
CS 428: Fall Introduction to. Raytracing. Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, /18/2009 1
 CS 428: Fall 2009 Introduction to Computer Graphics Raytracing 11/18/2009 1 Forward ray tracing From the light sources Simulate light transport one ray at a time Rays start from lights + bounce around
CS 428: Fall 2009 Introduction to Computer Graphics Raytracing 11/18/2009 1 Forward ray tracing From the light sources Simulate light transport one ray at a time Rays start from lights + bounce around
MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS
 MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT203 covers essentially the same material as MAT201, but is more in depth and theoretical. Exam problems are often more sophisticated in scope and difficulty
MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT203 covers essentially the same material as MAT201, but is more in depth and theoretical. Exam problems are often more sophisticated in scope and difficulty
3D Polygon Rendering. Many applications use rendering of 3D polygons with direct illumination
 Rendering Pipeline 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications use rendering of 3D polygons with direct illumination 3D Polygon Rendering What steps are necessary to utilize spatial coherence while drawing
Rendering Pipeline 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications use rendering of 3D polygons with direct illumination 3D Polygon Rendering What steps are necessary to utilize spatial coherence while drawing
Images from 3D Creative Magazine. 3D Modelling Systems
 Images from 3D Creative Magazine 3D Modelling Systems Contents Reference & Accuracy 3D Primitives Transforms Move (Translate) Rotate Scale Mirror Align 3D Booleans Deforms Bend Taper Skew Twist Squash
Images from 3D Creative Magazine 3D Modelling Systems Contents Reference & Accuracy 3D Primitives Transforms Move (Translate) Rotate Scale Mirror Align 3D Booleans Deforms Bend Taper Skew Twist Squash
Central issues in modelling
 Central issues in modelling Construct families of curves, surfaces and volumes that can represent common objects usefully; are easy to interact with; interaction includes: manual modelling; fitting to
Central issues in modelling Construct families of curves, surfaces and volumes that can represent common objects usefully; are easy to interact with; interaction includes: manual modelling; fitting to
A Simple Method of the TEX Surface Drawing Suitable for Teaching Materials with the Aid of CAS
 A Simple Method of the TEX Surface Drawing Suitable for Teaching Materials with the Aid of CAS Masataka Kaneko, Hajime Izumi, Kiyoshi Kitahara 1, Takayuki Abe, Kenji Fukazawa 2, Masayoshi Sekiguchi, Yuuki
A Simple Method of the TEX Surface Drawing Suitable for Teaching Materials with the Aid of CAS Masataka Kaneko, Hajime Izumi, Kiyoshi Kitahara 1, Takayuki Abe, Kenji Fukazawa 2, Masayoshi Sekiguchi, Yuuki
(Refer Slide Time: 00:03:51)
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 17 Scan Converting Lines, Circles and Ellipses Hello and welcome everybody
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 17 Scan Converting Lines, Circles and Ellipses Hello and welcome everybody
CS 130 Exam I. Fall 2015
 CS 130 Exam I Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is
CS 130 Exam I Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is
Homework #2. Hidden Surfaces, Projections, Shading and Texture, Ray Tracing, and Parametric Curves
 Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2013 Homework #2 Hidden Surfaces, Projections, Shading and Texture, Ray Tracing, and Parametric Curves Assigned: Sunday, May 12 th Due: Thursday,
Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2013 Homework #2 Hidden Surfaces, Projections, Shading and Texture, Ray Tracing, and Parametric Curves Assigned: Sunday, May 12 th Due: Thursday,
Ray Tracing. Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16
 Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 Ray Tracing Visible Surface Ray Tracing (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Ray Tracing Determine visibility
Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 Ray Tracing Visible Surface Ray Tracing (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Ray Tracing Determine visibility
Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009
 Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009 Name : Section Leader: Josh Lan Xiannan (Circle one) Genauer Huang Li Section Time: 10:00 11:00 1:15 2:15 (Circle one) This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. No calculators
Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009 Name : Section Leader: Josh Lan Xiannan (Circle one) Genauer Huang Li Section Time: 10:00 11:00 1:15 2:15 (Circle one) This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. No calculators
Rasterization Overview
 Rendering Overview The process of generating an image given a virtual camera objects light sources Various techniques rasterization (topic of this course) raytracing (topic of the course Advanced Computer
Rendering Overview The process of generating an image given a virtual camera objects light sources Various techniques rasterization (topic of this course) raytracing (topic of the course Advanced Computer
Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16
 Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Determine visibility of a surface by tracing rays of light from the viewer s eye
Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Determine visibility of a surface by tracing rays of light from the viewer s eye
Computer Aided Engineering Design Prof. Anupam Saxena Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur.
 (Refer Slide Time: 00:28) Computer Aided Engineering Design Prof. Anupam Saxena Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 6 Hello, this is lecture number 6 of
(Refer Slide Time: 00:28) Computer Aided Engineering Design Prof. Anupam Saxena Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 6 Hello, this is lecture number 6 of
Line Drawing. Foundations of Computer Graphics Torsten Möller
 Line Drawing Foundations of Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Rendering Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism Reading Angel
Line Drawing Foundations of Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Rendering Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism Reading Angel
morphology on binary images
 morphology on binary images Ole-Johan Skrede 10.05.2017 INF2310 - Digital Image Processing Department of Informatics The Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences University of Oslo After original slides
morphology on binary images Ole-Johan Skrede 10.05.2017 INF2310 - Digital Image Processing Department of Informatics The Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences University of Oslo After original slides
Math 126 Final Examination SPR CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems on 8 pages.
 Math 126 Final Examination SPR 2018 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems on 8 pages. This exam is closed book. You may
Math 126 Final Examination SPR 2018 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems on 8 pages. This exam is closed book. You may
Polygon Meshes and Implicit Surfaces
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Polygon Meshes and Implicit Surfaces Polygon Meshes Implicit Surfaces Constructive Solid Geometry [Angel Ch. 10] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Modeling
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Polygon Meshes and Implicit Surfaces Polygon Meshes Implicit Surfaces Constructive Solid Geometry [Angel Ch. 10] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Modeling
Line Drawing. Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller / Mike Phillips. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 Line Drawing Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller / Mike Phillips Rendering Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Color Interaction Texture/ Realism
Line Drawing Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller / Mike Phillips Rendering Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Color Interaction Texture/ Realism
Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces A cylinder is a three dimensional shape that is determined by
 Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces A cylinder is a three dimensional shape that is determined by a two dimensional (plane) curve C in three dimensional space a line L in a plane not parallel to the one in
Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces A cylinder is a three dimensional shape that is determined by a two dimensional (plane) curve C in three dimensional space a line L in a plane not parallel to the one in
CSG obj. oper3. obj1 obj2 obj3. obj5. obj4
 Solid Modeling Solid: Boundary + Interior Volume occupied by geometry Solid representation schemes Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) Boundary representations (B-reps) Space-partition representations Operations
Solid Modeling Solid: Boundary + Interior Volume occupied by geometry Solid representation schemes Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) Boundary representations (B-reps) Space-partition representations Operations
AP * Calculus Review. Area and Volume
 AP * Calculus Review Area and Volume Student Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production of,
AP * Calculus Review Area and Volume Student Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production of,
Two Optimization Methods for Raytracing. W. Sturzlinger and R. F. Tobler
 Two Optimization Methods for Raytracing by W. Sturzlinger and R. F. Tobler Johannes Kepler University of Linz Institute for Computer Science Department for graphical and parallel Processing Altenbergerstrae
Two Optimization Methods for Raytracing by W. Sturzlinger and R. F. Tobler Johannes Kepler University of Linz Institute for Computer Science Department for graphical and parallel Processing Altenbergerstrae
Geometric Modeling in Graphics
 Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Polygon Meshes and Implicit Surfaces
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 and Constructive Solid Geometry [Angel Ch. 10] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Modeling Complex Shapes An equation for a sphere is possible, but how
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 and Constructive Solid Geometry [Angel Ch. 10] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Modeling Complex Shapes An equation for a sphere is possible, but how
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into
 2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
Volume
 Volume Volume is a measure of how much space a three-dimensional object takes up. Area only looked at surface; we counted how many little flat squares could fit on a surface. Volume measures how many 1
Volume Volume is a measure of how much space a three-dimensional object takes up. Area only looked at surface; we counted how many little flat squares could fit on a surface. Volume measures how many 1
CS354 Computer Graphics Surface Representation IV. Qixing Huang March 7th 2018
 CS354 Computer Graphics Surface Representation IV Qixing Huang March 7th 2018 Today s Topic Subdivision surfaces Implicit surface representation Subdivision Surfaces Building complex models We can extend
CS354 Computer Graphics Surface Representation IV Qixing Huang March 7th 2018 Today s Topic Subdivision surfaces Implicit surface representation Subdivision Surfaces Building complex models We can extend
4) Finish the spline here. To complete the spline, double click the last point or select the spline tool again.
 1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
16.7 Surface Integrals
 16 Vector Calculus 16.7 Surface Integrals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Surface Integrals The relationship between surface integrals
16 Vector Calculus 16.7 Surface Integrals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Surface Integrals The relationship between surface integrals
Ansoft HFSS Solids Menu
 Ansoft HFSS Use the commands on the Solids menu to: Draw simple 3D objects such as cylinders, boxes, cones, and spheres. Draw a spiral or helix. Sweep a 2D object to create a 3D object. 2D objects can
Ansoft HFSS Use the commands on the Solids menu to: Draw simple 3D objects such as cylinders, boxes, cones, and spheres. Draw a spiral or helix. Sweep a 2D object to create a 3D object. 2D objects can
CSCI 4620/8626. Coordinate Reference Frames
 CSCI 4620/8626 Computer Graphics Graphics Output Primitives Last update: 2014-02-03 Coordinate Reference Frames To describe a picture, the world-coordinate reference frame (2D or 3D) must be selected.
CSCI 4620/8626 Computer Graphics Graphics Output Primitives Last update: 2014-02-03 Coordinate Reference Frames To describe a picture, the world-coordinate reference frame (2D or 3D) must be selected.
Worksheet 2.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Independent Variables)
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 2.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Independent Variables) From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know the meaning
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 2.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Independent Variables) From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know the meaning
An object in 3D space
 An object in 3D space An object's viewpoint Every Alice object has a viewpoint. The viewpoint of an object is determined by: The position of the object in 3D space. The orientation of the object relative
An object in 3D space An object's viewpoint Every Alice object has a viewpoint. The viewpoint of an object is determined by: The position of the object in 3D space. The orientation of the object relative
Dr. Allen Back. Nov. 19, 2014
 Why of Dr. Allen Back Nov. 19, 2014 Graph Picture of T u, T v for a Lat/Long Param. of the Sphere. Why of Graph Basic Picture Why of Graph Why Φ(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)) Tangents T u = (x u,
Why of Dr. Allen Back Nov. 19, 2014 Graph Picture of T u, T v for a Lat/Long Param. of the Sphere. Why of Graph Basic Picture Why of Graph Why Φ(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)) Tangents T u = (x u,
Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus
 Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus by Sacha Nandlall T.A. for MATH 264, McGill University Email: sacha.nandlall@mail.mcgill.ca Website: http://www.resanova.com/teaching/calculus/ Fall 2006,
Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus by Sacha Nandlall T.A. for MATH 264, McGill University Email: sacha.nandlall@mail.mcgill.ca Website: http://www.resanova.com/teaching/calculus/ Fall 2006,
Math League SCASD. Meet #5. Self-study Packet. Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets):
 Math League SCASD Meet #5 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : Solid (Volume and Surface Area) 3. Number Theory:
Math League SCASD Meet #5 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : Solid (Volume and Surface Area) 3. Number Theory:
form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, and are graphed in Cartesian coordinates.
 Plot 3D Introduction Plot 3D graphs objects in three dimensions. It has five basic modes: 1. Cartesian mode, where surfaces defined by equations of the form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, 2. cylindrical
Plot 3D Introduction Plot 3D graphs objects in three dimensions. It has five basic modes: 1. Cartesian mode, where surfaces defined by equations of the form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, 2. cylindrical
2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0.
 Midterm 3 Review Short Answer 2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0. 3. Compute the Riemann sum for the double integral where for the given grid
Midterm 3 Review Short Answer 2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0. 3. Compute the Riemann sum for the double integral where for the given grid
The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 12 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 12 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral
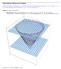 Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral. Set up the integral of a function f x, y, z over the region above the upper nappe of the cone z x y from z to z. Use the following orders of integration: d x
Triple Integrals: Setting up the Integral. Set up the integral of a function f x, y, z over the region above the upper nappe of the cone z x y from z to z. Use the following orders of integration: d x
Geometry. Chapter 5. Types of Curves and Surfaces
 Chapter 5. Geometry Geometry refers to the physical items represented by the model (such as points, curves, and surfaces), independent of their spatial or topological relationships. The ACIS free form
Chapter 5. Geometry Geometry refers to the physical items represented by the model (such as points, curves, and surfaces), independent of their spatial or topological relationships. The ACIS free form
Introduction Ray tracing basics Advanced topics (shading) Advanced topics (geometry) Graphics 2010/2011, 4th quarter. Lecture 11: Ray tracing
 Lecture 11 Ray tracing Introduction Projection vs. ray tracing Projection Ray tracing Rendering Projection vs. ray tracing Projection Ray tracing Basic methods for image generation Major areas of computer
Lecture 11 Ray tracing Introduction Projection vs. ray tracing Projection Ray tracing Rendering Projection vs. ray tracing Projection Ray tracing Basic methods for image generation Major areas of computer
So far, we have considered only local models of illumination; they only account for incident light coming directly from the light sources.
 11 11.1 Basics So far, we have considered only local models of illumination; they only account for incident light coming directly from the light sources. Global models include incident light that arrives
11 11.1 Basics So far, we have considered only local models of illumination; they only account for incident light coming directly from the light sources. Global models include incident light that arrives
There we are; that's got the 3D screen and mouse sorted out.
 Introduction to 3D To all intents and purposes, the world we live in is three dimensional. Therefore, if we want to construct a realistic computer model of it, the model should be three dimensional as
Introduction to 3D To all intents and purposes, the world we live in is three dimensional. Therefore, if we want to construct a realistic computer model of it, the model should be three dimensional as
Math 213 Calculus III Practice Exam 2 Solutions Fall 2002
 Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Spring 2011 Workshop ESSENTIALS OF 3D MODELING IN RHINOCEROS February 10 th 2011 S.R. Crown Hall Lower Core Computer Lab
 [1] Open Rhinoceros. PART 1 INTRODUCTION [4] Click and hold on the Boundary Lines in where they form a crossing and Drag from TOP RIGHT to BOTTOM LEFT to enable only the PERSPECTIVE VIEW. [2] When the
[1] Open Rhinoceros. PART 1 INTRODUCTION [4] Click and hold on the Boundary Lines in where they form a crossing and Drag from TOP RIGHT to BOTTOM LEFT to enable only the PERSPECTIVE VIEW. [2] When the
Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 12!
 Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 12! Student Name:! Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 8:10pm and ends at 10:00pm. You must turn
Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 12! Student Name:! Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 8:10pm and ends at 10:00pm. You must turn
Lesson 2 Constructive Solid Geometry Concept. Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS 2-1
 Lesson 2 Constructive Solid Geometry Concept Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS 2-1 2-2 Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS Introduction In the 1980s, one of the main advancements in Solid Modeling was the development
Lesson 2 Constructive Solid Geometry Concept Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS 2-1 2-2 Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS Introduction In the 1980s, one of the main advancements in Solid Modeling was the development
Morse Theory for Computer Graphics
 Morse Theory for Computer Graphics John C. Hart School of EECS Washington State University Pullman, WA 9964-75 hart@eecs.wsu.edu Technical Report EECS-97- Abstract Morse theory is an area of algebraic
Morse Theory for Computer Graphics John C. Hart School of EECS Washington State University Pullman, WA 9964-75 hart@eecs.wsu.edu Technical Report EECS-97- Abstract Morse theory is an area of algebraic
Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections
 Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
CS Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering
 CS 294-13 Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering Ravi Ramamoorthi This assignment should be done only by those small number of students who have not yet written a raytracer. For those students
CS 294-13 Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering Ravi Ramamoorthi This assignment should be done only by those small number of students who have not yet written a raytracer. For those students
