TRUNCATION SCHEMES FOR RECURSIVE MULTIPLIERS
|
|
|
- Nathan Cobb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 39 th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers TRUNCATION SCHEMES FOR RECURSIVE MULTIPLIERS Pedram Mokrian,, Huapeng Wu, Majid Ahmadi Research Centre for Integrated Microsystems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Windsor Windsor, Ontario, Canada
2 Outline Motivation & Objectives Recursive Digital Multipliers Existing Truncation Methods Proposed Truncation Schemes for Recursive Multipliers Simulation Results Conclusions 1
3 Motivation Constant word size is required throughout arithmetic operations, i.e. DSP applications Rounding circuitry can be complex Various truncations schemes have been presented for multipliers Significant reduction in complexities Most existing schemes target array and tree multipliers The inherent structure of the digital recursive multiplier is very suitable for truncation 2
4 Objectives Error Analysis: Eliminating a portion of the digital recursive multiplier Proposed truncation schemes Gate Complexity Analysis 3
5 Recursive Digital Multipliers Recursive, or divide and conquer multiplication was proposed by Karatsuba and Ofman in 1962 The Karatsuba-Ofman Algorithm (KOA) multiplies two long integers by executing multiplications and additions on their divided parts Fundamental principles of KOA is utilized in the recursive algorithm [Danysh and Swartzlander] 4
6 Recursive Digital Multipliers Mathematically, the recursive algorithm is established around the fact that any 2n x 2n bit multiplication can be carried out through four n x n bit sub-multiplications Considering two unsigned 2n-bit operands: Multiplicand: Multiplier: A = A H 2 n + A L X=X H 2 n + X L Product: Y = A X = (A H 2 n + A L ) (X H 2 n + X L ) = A H X H 2 2n + (A L X H + A H X L ) 2 n + A L X L 5
7 Recursive Digital Multipliers Block diagram representation for multiplication with a single level of recursion Y is the fixed-width rounded product of 2n bits 6
8 Recursive Digital Multipliers Of the 4 sub-multiples, the one contributing the least to the final product is A L X L Truncation schemes to be presented will target this particular component 7
9 Existing Truncation Methods Truncation schemes generally involve not generating the complete partial product matrix in a multiplication, and then applying a scheme to compensate for the error Correction schemes: - Constant Correction [Y. C. Lim] - Variable Correction [E. J. King and E. E. Swartzlander, Jr.] 8
10 Constant Correction Existing Truncation Methods A constant is added to the remaining columns of the partial products matrix based on average value of the bits which are not formed and expected value of rounding error Variable Correction Correction value is data dependent: - If all elements are zeros in the most significant column not formed, there is no correction - If all elements are ones, then a maximum correction value is used Variable correction results in a lower variance in error Constant correction is efficiently implemented with tree multipliers and variable correction with array multipliers 9
11 Proposed Truncation Schemes for Digital Recursive Multipliers Three truncation schemes targeting recursive multipliers involving data-dependent correction terms are proposed Original recursive multiplier can be represented in this way: 2n A H x X L A H x X H A L x X L A L x X H The component A L X L will be truncated 10
12 Proposal #1 Truncation Scheme A H X L or A L X H is simply used to replace the truncated term A L X L : 2n A H x X L A X H L A H x X H A L x X H This correction term is generated at no extra cost 11
13 Proposal #2 Truncation Scheme The average of the two blocks A H X L and A L X H replaces A L X L : A H x X L A X + A X 2 H L L H A H x X H A L x X H High correlation between the truncated term and the replacement term 12
14 Proposal #3 Truncation Scheme Partial product bit a n-1 x n-1 (MSB generated in A L X L ) is added at the least significant bit position of block A H X H : a n-1 x n-1 A L = a n-1 a n-2 a 1 a 0 X L = x n-1 x n-2 x 1 x 0 A H x X L A H x X H A L x X H A 1-bit correction term is generated with little extra cost Simplifies the partial products accumulation step 13
15 Simulation Results Error Statistics: Comparison with existing truncation techniques (6-bit recursive multiplier) Multiplier Type Mean Error Max. Positive Error Max. Negative Error Variance Truncation True Rounding Constant Correction Constant Correction Variable Correction Removal of A L X L Proposal # Proposal # Proposal # Table 1. Error Statistics (2n = 6) 14
16 Simulation Results Complexity Comparison: Savings in number of gates It is assumed that base multiplier for the recursive structure is array multiplier Estimate one full adder as 12 gates, one half adder as 4 gates 2n Original Proposal #1 Proposal #2 Proposal #3 No. of Gates No. of Gates % Savings No. of Gates % Savings No. of Gates % Savings Table 2. Complexity Comparison 15
17 Simulation Results All three proposed schemes show that they have comparatively low errors In terms of complexity, hardware savings are close to 25% when n is large However, gate number is not always a good metric for overall performance For example, Proposal #2 (averaging of two components) involves an addition of 2 more rows to the partial product matrix, increasing the time required for partial products reduction step Further hardware reduction is expected if these correction schemes are applied to multi-level recursive multipliers 16
18 Multi-level Recursive Multiplier Maximum complexity savings after truncation of least significant sub-multiple: Levels of Recursion Projected Maximum Complexity Savings (%)
19 Conclusions Three reduced-hardware truncation schemes have been proposed, targeting the very regular composition of recursive multipliers Examination of hardware overhead and truncation error tradeoff allows for the proper selection of a scheme These are the initial results of an on-going investigation on reduced-hardware truncations schemes with error correction schemes 18
20 Thank you for your attention!
Fixed-Width Recursive Multipliers
 Fixed-Width Recursive Multipliers Presented by: Kevin Biswas Supervisors: Dr. M. Ahmadi Dr. H. Wu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Windsor Motivation & Objectives Outline
Fixed-Width Recursive Multipliers Presented by: Kevin Biswas Supervisors: Dr. M. Ahmadi Dr. H. Wu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Windsor Motivation & Objectives Outline
A High-Speed FPGA Implementation of an RSD- Based ECC Processor
 A High-Speed FPGA Implementation of an RSD- Based ECC Processor Abstract: In this paper, an exportable application-specific instruction-set elliptic curve cryptography processor based on redundant signed
A High-Speed FPGA Implementation of an RSD- Based ECC Processor Abstract: In this paper, an exportable application-specific instruction-set elliptic curve cryptography processor based on redundant signed
Design and Implementation of Signed, Rounded and Truncated Multipliers using Modified Booth Algorithm for Dsp Systems.
 Design and Implementation of Signed, Rounded and Truncated Multipliers using Modified Booth Algorithm for Dsp Systems. K. Ram Prakash 1, A.V.Sanju 2 1 Professor, 2 PG scholar, Department of Electronics
Design and Implementation of Signed, Rounded and Truncated Multipliers using Modified Booth Algorithm for Dsp Systems. K. Ram Prakash 1, A.V.Sanju 2 1 Professor, 2 PG scholar, Department of Electronics
Design and Implementation of an Eight Bit Multiplier Using Twin Precision Technique and Baugh-Wooley Algorithm
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013 1 Design and Implementation of an Eight Bit Multiplier Using Twin Precision Technique and Baugh-Wooley Algorithm
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013 1 Design and Implementation of an Eight Bit Multiplier Using Twin Precision Technique and Baugh-Wooley Algorithm
CS 64 Week 1 Lecture 1. Kyle Dewey
 CS 64 Week 1 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Bitwise operation wrap-up Two s complement Addition Subtraction Multiplication (if time) Bitwise Operation Wrap-up Shift Left Move all the bits N positions to
CS 64 Week 1 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Bitwise operation wrap-up Two s complement Addition Subtraction Multiplication (if time) Bitwise Operation Wrap-up Shift Left Move all the bits N positions to
High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit
 High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit Abd-Elrahman G. Qoutb 1, Abdullah M. El-Gunidy 1, Mohammed F. Tolba 1, and Magdy A. El-Moursy 2 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Fayoum
High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit Abd-Elrahman G. Qoutb 1, Abdullah M. El-Gunidy 1, Mohammed F. Tolba 1, and Magdy A. El-Moursy 2 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Fayoum
A novel technique for fast multiplication
 INT. J. ELECTRONICS, 1999, VOL. 86, NO. 1, 67± 77 A novel technique for fast multiplication SADIQ M. SAIT², AAMIR A. FAROOQUI GERHARD F. BECKHOFF and In this paper we present the design of a new high-speed
INT. J. ELECTRONICS, 1999, VOL. 86, NO. 1, 67± 77 A novel technique for fast multiplication SADIQ M. SAIT², AAMIR A. FAROOQUI GERHARD F. BECKHOFF and In this paper we present the design of a new high-speed
Timing for Ripple Carry Adder
 Timing for Ripple Carry Adder 1 2 3 Look Ahead Method 5 6 7 8 9 Look-Ahead, bits wide 10 11 Multiplication Simple Gradeschool Algorithm for 32 Bits (6 Bit Result) Multiplier Multiplicand AND gates 32
Timing for Ripple Carry Adder 1 2 3 Look Ahead Method 5 6 7 8 9 Look-Ahead, bits wide 10 11 Multiplication Simple Gradeschool Algorithm for 32 Bits (6 Bit Result) Multiplier Multiplicand AND gates 32
Rounding. Rounding is a fundamental method to reduce the size of a word, such as after arithmetic operations
 ROUNDING Rounding Rounding is a fundamental method to reduce the size of a word, such as after arithmetic operations For example to maintain the word width for memory storage Mem n-bit words n n+1 n +
ROUNDING Rounding Rounding is a fundamental method to reduce the size of a word, such as after arithmetic operations For example to maintain the word width for memory storage Mem n-bit words n n+1 n +
Binary Multiplication
 inary Multiplication The key to multiplication was memorizing a digit-by-digit table Everything else was just adding 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 3 3 6 9 2 5 8 2 24 27 + You ve got
inary Multiplication The key to multiplication was memorizing a digit-by-digit table Everything else was just adding 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 3 3 6 9 2 5 8 2 24 27 + You ve got
Delay Optimised 16 Bit Twin Precision Baugh Wooley Multiplier
 Delay Optimised 16 Bit Twin Precision Baugh Wooley Multiplier Vivek. V. Babu 1, S. Mary Vijaya Lense 2 1 II ME-VLSI DESIGN & The Rajaas Engineering College Vadakkangulam, Tirunelveli 2 Assistant Professor
Delay Optimised 16 Bit Twin Precision Baugh Wooley Multiplier Vivek. V. Babu 1, S. Mary Vijaya Lense 2 1 II ME-VLSI DESIGN & The Rajaas Engineering College Vadakkangulam, Tirunelveli 2 Assistant Professor
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: , Volume 2, Issue 7, August 2014
 DESIGN OF HIGH SPEED BOOTH ENCODED MULTIPLIER PRAVEENA KAKARLA* *Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECONE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, A.P., India ABSTRACT This paper presents the design and implementation
DESIGN OF HIGH SPEED BOOTH ENCODED MULTIPLIER PRAVEENA KAKARLA* *Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECONE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, A.P., India ABSTRACT This paper presents the design and implementation
Fixed Point Representation And Fractional Math. By Erick L. Oberstar Oberstar Consulting
 Fixed Point Representation And Fractional Math By Erick L. Oberstar 2004-2005 Oberstar Consulting Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Summary... 2 1. Fixed-Point Representation... 2 1.1. Fixed Point
Fixed Point Representation And Fractional Math By Erick L. Oberstar 2004-2005 Oberstar Consulting Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Summary... 2 1. Fixed-Point Representation... 2 1.1. Fixed Point
ECE 341. Lecture # 6
 ECE 34 Lecture # 6 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@pdx.edu October 5, 24 Portland State University Lecture Topics Design of Fast Adders Carry Looakahead Adders (CLA) Blocked Carry-Lookahead Adders Multiplication
ECE 34 Lecture # 6 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@pdx.edu October 5, 24 Portland State University Lecture Topics Design of Fast Adders Carry Looakahead Adders (CLA) Blocked Carry-Lookahead Adders Multiplication
Implementing FIR Filters
 Implementing FIR Filters in FLEX Devices February 199, ver. 1.01 Application Note 73 FIR Filter Architecture This section describes a conventional FIR filter design and how the design can be optimized
Implementing FIR Filters in FLEX Devices February 199, ver. 1.01 Application Note 73 FIR Filter Architecture This section describes a conventional FIR filter design and how the design can be optimized
OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER.
 OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER. A.Anusha 1 R.Basavaraju 2 anusha201093@gmail.com 1 basava430@gmail.com 2 1 PG Scholar, VLSI, Bharath Institute of Engineering
OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER. A.Anusha 1 R.Basavaraju 2 anusha201093@gmail.com 1 basava430@gmail.com 2 1 PG Scholar, VLSI, Bharath Institute of Engineering
Outline. EEL-4713 Computer Architecture Multipliers and shifters. Deriving requirements of ALU. MIPS arithmetic instructions
 Outline EEL-4713 Computer Architecture Multipliers and shifters Multiplication and shift registers Chapter 3, section 3.4 Next lecture Division, floating-point 3.5 3.6 EEL-4713 Ann Gordon-Ross.1 EEL-4713
Outline EEL-4713 Computer Architecture Multipliers and shifters Multiplication and shift registers Chapter 3, section 3.4 Next lecture Division, floating-point 3.5 3.6 EEL-4713 Ann Gordon-Ross.1 EEL-4713
VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier. Guntur(Dt),Pin:522017
 VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier 1 Katakam Hemalatha,(M.Tech),Email Id: hema.spark2011@gmail.com 2 Kundurthi Ravi Kumar, M.Tech,Email Id: kundurthi.ravikumar@gmail.com
VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier 1 Katakam Hemalatha,(M.Tech),Email Id: hema.spark2011@gmail.com 2 Kundurthi Ravi Kumar, M.Tech,Email Id: kundurthi.ravikumar@gmail.com
Sum to Modified Booth Recoding Techniques For Efficient Design of the Fused Add-Multiply Operator
 Sum to Modified Booth Recoding Techniques For Efficient Design of the Fused Add-Multiply Operator D.S. Vanaja 1, S. Sandeep 2 1 M. Tech scholar in VLSI System Design, Department of ECE, Sri VenkatesaPerumal
Sum to Modified Booth Recoding Techniques For Efficient Design of the Fused Add-Multiply Operator D.S. Vanaja 1, S. Sandeep 2 1 M. Tech scholar in VLSI System Design, Department of ECE, Sri VenkatesaPerumal
Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic
 Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic Counting to four billion two fingers at a time What do all those bits mean now? bits (011011011100010...01) instruction R-format I-format... integer data number text
Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic Counting to four billion two fingers at a time What do all those bits mean now? bits (011011011100010...01) instruction R-format I-format... integer data number text
Computer Arithmetic Multiplication & Shift Chapter 3.4 EEC170 FQ 2005
 Computer Arithmetic Multiplication & Shift Chapter 3.4 EEC170 FQ 200 Multiply We will start with unsigned multiply and contrast how humans and computers multiply Layout 8-bit 8 Pipelined Multiplier 1 2
Computer Arithmetic Multiplication & Shift Chapter 3.4 EEC170 FQ 200 Multiply We will start with unsigned multiply and contrast how humans and computers multiply Layout 8-bit 8 Pipelined Multiplier 1 2
9 Multiplication and Division
 9 Multiplication and Division Multiplication is done by doing shifts and additions. Multiplying two (unsigned) numbers of n bits each results in a product of 2n bits. Example: 0110 x 0011 (6x3) At start,
9 Multiplication and Division Multiplication is done by doing shifts and additions. Multiplying two (unsigned) numbers of n bits each results in a product of 2n bits. Example: 0110 x 0011 (6x3) At start,
Automatic VHDL Model Generation of Parameterized FIR Filters
 Automatic VHDL Model Generation of Parameterized FIR Filters E. George Walters III 1, John Glossner 2, and Michael J. Schulte 1 1 Computer Architecture and Arithmetic Laboratory, Computer Science and Engineering
Automatic VHDL Model Generation of Parameterized FIR Filters E. George Walters III 1, John Glossner 2, and Michael J. Schulte 1 1 Computer Architecture and Arithmetic Laboratory, Computer Science and Engineering
Double Precision Floating-Point Multiplier using Coarse-Grain Units
 Double Precision Floating-Point Multiplier using Coarse-Grain Units Rui Duarte INESC-ID/IST/UTL. rduarte@prosys.inesc-id.pt Mário Véstias INESC-ID/ISEL/IPL. mvestias@deetc.isel.ipl.pt Horácio Neto INESC-ID/IST/UTL
Double Precision Floating-Point Multiplier using Coarse-Grain Units Rui Duarte INESC-ID/IST/UTL. rduarte@prosys.inesc-id.pt Mário Véstias INESC-ID/ISEL/IPL. mvestias@deetc.isel.ipl.pt Horácio Neto INESC-ID/IST/UTL
Binary Arithmetic. Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T.
 Binary Arithmetic Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. MIT 6.004 Fall 2018 Reminder: Encoding Positive Integers Bit i in a binary representation (in right-to-left order)
Binary Arithmetic Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. MIT 6.004 Fall 2018 Reminder: Encoding Positive Integers Bit i in a binary representation (in right-to-left order)
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI. Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing
 EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Spring 2017 Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers The two basic operations - generation
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Spring 2017 Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers The two basic operations - generation
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
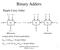 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm
 Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm Abstract: Floating point multiplication is the most usefull in all the computation application like in Arithematic operation, DSP application.
Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm Abstract: Floating point multiplication is the most usefull in all the computation application like in Arithematic operation, DSP application.
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501
 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design
 CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10122011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Fixed Point Arithmetic Addition/Subtraction
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10122011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Fixed Point Arithmetic Addition/Subtraction
Outline. Introduction to Structured VLSI Design. Signed and Unsigned Integers. 8 bit Signed/Unsigned Integers
 Outline Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Integer Arithmetic and Pipelining Multiplication in the digital domain HW mapping Pipelining optimization Joachim Rodrigues Signed and Unsigned Integers n-1
Outline Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Integer Arithmetic and Pipelining Multiplication in the digital domain HW mapping Pipelining optimization Joachim Rodrigues Signed and Unsigned Integers n-1
How a Digital Binary Adder Operates
 Overview of a Binary Adder How a Digital Binary Adder Operates By: Shawn R Moser A binary adder is a digital electronic component that is used to perform the addition of two binary numbers and return the
Overview of a Binary Adder How a Digital Binary Adder Operates By: Shawn R Moser A binary adder is a digital electronic component that is used to perform the addition of two binary numbers and return the
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI. Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing
 EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6b High-Speed Multiplication - II Spring 2017 Koren Part.6b.1 Accumulating the Partial Products After generating partial
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6b High-Speed Multiplication - II Spring 2017 Koren Part.6b.1 Accumulating the Partial Products After generating partial
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Israel Koren Fall 2010 ECE666/Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Israel Koren Fall 2010 ECE666/Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 8 Division through Multiplication Israel Koren ECE666/Koren Part.8.1 Division by Convergence
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 8 Division through Multiplication Israel Koren ECE666/Koren Part.8.1 Division by Convergence
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 6b High-Speed Multiplication - II Israel Koren ECE666/Koren Part.6b.1 Accumulating the Partial
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 6b High-Speed Multiplication - II Israel Koren ECE666/Koren Part.6b.1 Accumulating the Partial
CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit. A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T
 CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T hurson@mst.edu 1 Outline Motivation Design of a simple ALU How to design
CS 5803 Introduction to High Performance Computer Architecture: Arithmetic Logic Unit A.R. Hurson 323 CS Building, Missouri S&T hurson@mst.edu 1 Outline Motivation Design of a simple ALU How to design
Boolean Unit (The obvious way)
 oolean Unit (The obvious way) It is simple to build up a oolean unit using primitive gates and a mux to select the function. Since there is no interconnection between bits, this unit can be simply replicated
oolean Unit (The obvious way) It is simple to build up a oolean unit using primitive gates and a mux to select the function. Since there is no interconnection between bits, this unit can be simply replicated
Arithmetic Circuits. Nurul Hazlina Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit
 Nurul Hazlina 1 1. Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit Nurul Hazlina 2 Introduction 1. Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations 2. Fundamental
Nurul Hazlina 1 1. Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit Nurul Hazlina 2 Introduction 1. Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations 2. Fundamental
Multi-Operand Addition Ivor Page 1
 Multi-Operand Addition 1 Multi-Operand Addition Ivor Page 1 9.1 Motivation The motivation for multi-operand adders comes from the need for innerproduct calculations and multiplication (summing the partial
Multi-Operand Addition 1 Multi-Operand Addition Ivor Page 1 9.1 Motivation The motivation for multi-operand adders comes from the need for innerproduct calculations and multiplication (summing the partial
Area Efficient, Low Power Array Multiplier for Signed and Unsigned Number. Chapter 3
 Area Efficient, Low Power Array Multiplier for Signed and Unsigned Number Chapter 3 Area Efficient, Low Power Array Multiplier for Signed and Unsigned Number Chapter 3 3.1 Introduction The various sections
Area Efficient, Low Power Array Multiplier for Signed and Unsigned Number Chapter 3 Area Efficient, Low Power Array Multiplier for Signed and Unsigned Number Chapter 3 3.1 Introduction The various sections
MULTIPLE OPERAND ADDITION. Multioperand Addition
 MULTIPLE OPERAND ADDITION Chapter 3 Multioperand Addition Add up a bunch of numbers Used in several algorithms Multiplication, recurrences, transforms, and filters Signed (two s comp) and unsigned Don
MULTIPLE OPERAND ADDITION Chapter 3 Multioperand Addition Add up a bunch of numbers Used in several algorithms Multiplication, recurrences, transforms, and filters Signed (two s comp) and unsigned Don
Reducing Computational Time using Radix-4 in 2 s Complement Rectangular Multipliers
 Reducing Computational Time using Radix-4 in 2 s Complement Rectangular Multipliers Y. Latha Post Graduate Scholar, Indur institute of Engineering & Technology, Siddipet K.Padmavathi Associate. Professor,
Reducing Computational Time using Radix-4 in 2 s Complement Rectangular Multipliers Y. Latha Post Graduate Scholar, Indur institute of Engineering & Technology, Siddipet K.Padmavathi Associate. Professor,
 In this lesson you will learn: how to add and multiply positive binary integers how to work with signed binary numbers using two s complement how fixed and floating point numbers are used to represent
In this lesson you will learn: how to add and multiply positive binary integers how to work with signed binary numbers using two s complement how fixed and floating point numbers are used to represent
Outline. CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L15. Files. Files
 Outline CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L15 Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville VHDL What we know (additional topics) Attributes Transport and Inertial Delays Operator
Outline CPE/EE 422/522 Advanced Logic Design L15 Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville VHDL What we know (additional topics) Attributes Transport and Inertial Delays Operator
Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays Lecture 2/3 CERN Accelerator School on Digital Signal Processing Sigtuna, Sweden, 31 May 9 June 2007 Javier Serrano, CERN AB-CO-HT Outline Digital Signal
Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays Lecture 2/3 CERN Accelerator School on Digital Signal Processing Sigtuna, Sweden, 31 May 9 June 2007 Javier Serrano, CERN AB-CO-HT Outline Digital Signal
32-bit Signed and Unsigned Advanced Modified Booth Multiplication using Radix-4 Encoding Algorithm
 2016 IJSRSET Volume 2 Issue 3 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology 32-bit Signed and Unsigned Advanced Modified Booth Multiplication using Radix-4 Encoding
2016 IJSRSET Volume 2 Issue 3 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology 32-bit Signed and Unsigned Advanced Modified Booth Multiplication using Radix-4 Encoding
Divide and Conquer 1
 Divide and Conquer A Useful Recurrence Relation Def. T(n) = number of comparisons to mergesort an input of size n. Mergesort recurrence. T(n) if n T n/2 T n/2 solve left half solve right half merging n
Divide and Conquer A Useful Recurrence Relation Def. T(n) = number of comparisons to mergesort an input of size n. Mergesort recurrence. T(n) if n T n/2 T n/2 solve left half solve right half merging n
MIPS Integer ALU Requirements
 MIPS Integer ALU Requirements Add, AddU, Sub, SubU, AddI, AddIU: 2 s complement adder/sub with overflow detection. And, Or, Andi, Ori, Xor, Xori, Nor: Logical AND, logical OR, XOR, nor. SLTI, SLTIU (set
MIPS Integer ALU Requirements Add, AddU, Sub, SubU, AddI, AddIU: 2 s complement adder/sub with overflow detection. And, Or, Andi, Ori, Xor, Xori, Nor: Logical AND, logical OR, XOR, nor. SLTI, SLTIU (set
Homework 3. Assigned on 02/15 Due time: midnight on 02/21 (1 WEEK only!) B.2 B.11 B.14 (hint: use multiplexors) CSCI 402: Computer Architectures
 Homework 3 Assigned on 02/15 Due time: midnight on 02/21 (1 WEEK only!) B.2 B.11 B.14 (hint: use multiplexors) 1 CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Arithmetic for Computers (2) Fengguang Song Department
Homework 3 Assigned on 02/15 Due time: midnight on 02/21 (1 WEEK only!) B.2 B.11 B.14 (hint: use multiplexors) 1 CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Arithmetic for Computers (2) Fengguang Song Department
Parallel FIR Filters. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
ADDRESS GENERATION UNIT (AGU)
 nc. SECTION 4 ADDRESS GENERATION UNIT (AGU) MOTOROLA ADDRESS GENERATION UNIT (AGU) 4-1 nc. SECTION CONTENTS 4.1 INTRODUCTION........................................ 4-3 4.2 ADDRESS REGISTER FILE (Rn)............................
nc. SECTION 4 ADDRESS GENERATION UNIT (AGU) MOTOROLA ADDRESS GENERATION UNIT (AGU) 4-1 nc. SECTION CONTENTS 4.1 INTRODUCTION........................................ 4-3 4.2 ADDRESS REGISTER FILE (Rn)............................
Research Article Improving 2D-Log-Number-System Representations by Use of an Optimal Base
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 2008, Article ID 710590, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2008/710590 Research Article Improving 2D-Log-Number-System Representations
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 2008, Article ID 710590, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2008/710590 Research Article Improving 2D-Log-Number-System Representations
Run-Time Reconfigurable multi-precision floating point multiplier design based on pipelining technique using Karatsuba-Urdhva algorithms
 Run-Time Reconfigurable multi-precision floating point multiplier design based on pipelining technique using Karatsuba-Urdhva algorithms 1 Shruthi K.H., 2 Rekha M.G. 1M.Tech, VLSI design and embedded system,
Run-Time Reconfigurable multi-precision floating point multiplier design based on pipelining technique using Karatsuba-Urdhva algorithms 1 Shruthi K.H., 2 Rekha M.G. 1M.Tech, VLSI design and embedded system,
FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multiplier Employing Carry Lookahead Adders in Reduction Phase
 FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multiplier Employing Carry Lookahead Adders in Reduction Phase Abhay Sharma M.Tech Student Department of ECE MNNIT Allahabad, India ABSTRACT Tree Multipliers are frequently
FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multiplier Employing Carry Lookahead Adders in Reduction Phase Abhay Sharma M.Tech Student Department of ECE MNNIT Allahabad, India ABSTRACT Tree Multipliers are frequently
A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm
 455 A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm B. Jeevan, Asst. Professor, Dept. of E&IE, KITS, Warangal. jeevanbs776@gmail.com S. Narender, M.Tech (VLSI&ES), KITS, Warangal. narender.s446@gmail.com
455 A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm B. Jeevan, Asst. Professor, Dept. of E&IE, KITS, Warangal. jeevanbs776@gmail.com S. Narender, M.Tech (VLSI&ES), KITS, Warangal. narender.s446@gmail.com
Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic
 Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic 1 / 126 1 Motivation 2 Arithmetic and Logic Unit 3 Integer representation
Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic 1 / 126 1 Motivation 2 Arithmetic and Logic Unit 3 Integer representation
Array Multipliers. Figure 6.9 The partial products generated in a 5 x 5 multiplication. Sec. 6.5
 Sec. 6.5 Array Multipliers I'r) 1'8 P7 p6 PS f'4 1'3 1'2 1' 1 "0 Figure 6.9 The partial products generated in a 5 x 5 multiplication. called itemrive arrc.ly multipliers or simply cirruy m~illil>liers.
Sec. 6.5 Array Multipliers I'r) 1'8 P7 p6 PS f'4 1'3 1'2 1' 1 "0 Figure 6.9 The partial products generated in a 5 x 5 multiplication. called itemrive arrc.ly multipliers or simply cirruy m~illil>liers.
RADIX-4 AND RADIX-8 MULTIPLIER USING VERILOG HDL
 RADIX-4 AND RADIX-8 MULTIPLIER USING VERILOG HDL P. Thayammal 1, R.Sudhashree 2, G.Rajakumar 3 P.G.Scholar, Department of VLSI, Francis Xavier Engineering College, Tirunelveli 1 P.G.Scholar, Department
RADIX-4 AND RADIX-8 MULTIPLIER USING VERILOG HDL P. Thayammal 1, R.Sudhashree 2, G.Rajakumar 3 P.G.Scholar, Department of VLSI, Francis Xavier Engineering College, Tirunelveli 1 P.G.Scholar, Department
Optimized Modified Booth Recorder for Efficient Design of the Operator
 Optimized Modified Booth Recorder for Efficient Design of the Operator 1 DEEPTHI MALLELA, M.TECH.,VLSI 2 VEERABABU A, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR,DEPT.OF ECE 3 SRINIVASULU K,HOD,DEPT. OF ECE 1,2,3 NARASIMHA REDDY
Optimized Modified Booth Recorder for Efficient Design of the Operator 1 DEEPTHI MALLELA, M.TECH.,VLSI 2 VEERABABU A, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR,DEPT.OF ECE 3 SRINIVASULU K,HOD,DEPT. OF ECE 1,2,3 NARASIMHA REDDY
Digital Computer Arithmetic
 Digital Computer Arithmetic Part 6 High-Speed Multiplication Soo-Ik Chae Spring 2010 Koren Chap.6.1 Speeding Up Multiplication Multiplication involves 2 basic operations generation of partial products
Digital Computer Arithmetic Part 6 High-Speed Multiplication Soo-Ik Chae Spring 2010 Koren Chap.6.1 Speeding Up Multiplication Multiplication involves 2 basic operations generation of partial products
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
 An Efficient Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Booth Algorithm Pallavi Ramteke 1, Dr. N. N. Mhala 2, Prof. P. R. Lakhe M.Tech [IV Sem], Dept. of Comm. Engg., S.D.C.E, [Selukate],
An Efficient Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Booth Algorithm Pallavi Ramteke 1, Dr. N. N. Mhala 2, Prof. P. R. Lakhe M.Tech [IV Sem], Dept. of Comm. Engg., S.D.C.E, [Selukate],
II. MOTIVATION AND IMPLEMENTATION
 An Efficient Design of Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Add-Multiply operator Dhanalakshmi.G Applied Electronics PSN College of Engineering and Technology Tirunelveli dhanamgovind20@gmail.com Prof.V.Gopi
An Efficient Design of Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Add-Multiply operator Dhanalakshmi.G Applied Electronics PSN College of Engineering and Technology Tirunelveli dhanamgovind20@gmail.com Prof.V.Gopi
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering
 ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #6 Spring 2015 1. With x = 1111 1111 1111 1111 1011 0011 0101 0011 2 and y = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 1101 0111 2 representing two s
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #6 Spring 2015 1. With x = 1111 1111 1111 1111 1011 0011 0101 0011 2 and y = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 1101 0111 2 representing two s
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF EFFCIENT MODIFIED BOOTH ENCODER MULTIPLIER FOR SIGNED AND UNSIGNED NUMBERS
 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF EFFCIENT MODIFIED BOOTH ENCODER MULTIPLIER FOR SIGNED AND UNSIGNED NUMBERS NUNAVATH.VENNELA (1), A.VIKAS (2) P.G.Scholor (VLSI SYSTEM DESIGN),TKR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (1) M.TECHASSISTANT
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF EFFCIENT MODIFIED BOOTH ENCODER MULTIPLIER FOR SIGNED AND UNSIGNED NUMBERS NUNAVATH.VENNELA (1), A.VIKAS (2) P.G.Scholor (VLSI SYSTEM DESIGN),TKR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (1) M.TECHASSISTANT
A Simple Method to Improve the throughput of A Multiplier
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 9-16 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com A Simple Method to
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 9-16 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com A Simple Method to
Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Module 2: Computer Arithmetic
 Module 2: Computer Arithmetic 1 B O O K : C O M P U T E R O R G A N I Z A T I O N A N D D E S I G N, 3 E D, D A V I D L. P A T T E R S O N A N D J O H N L. H A N N E S S Y, M O R G A N K A U F M A N N
Module 2: Computer Arithmetic 1 B O O K : C O M P U T E R O R G A N I Z A T I O N A N D D E S I G N, 3 E D, D A V I D L. P A T T E R S O N A N D J O H N L. H A N N E S S Y, M O R G A N K A U F M A N N
Implementation of a High Speed Binary Floating point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm in FPGA
 Implementation of a High Speed Binary Floating point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm in FPGA Ms.Komal N.Batra 1, Prof. Ashish B. Kharate 2 1 PG Student, ENTC Department, HVPM S College of Engineering
Implementation of a High Speed Binary Floating point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm in FPGA Ms.Komal N.Batra 1, Prof. Ashish B. Kharate 2 1 PG Student, ENTC Department, HVPM S College of Engineering
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 3. Arithmetic for Computers Implementation
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers Implementation Today Review representations (252/352 recap) Floating point Addition: Ripple
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers Implementation Today Review representations (252/352 recap) Floating point Addition: Ripple
Floating-point to Fixed-point Conversion. Digital Signal Processing Programs (Short Version for FPGA DSP)
 Floating-point to Fixed-point Conversion for Efficient i Implementation ti of Digital Signal Processing Programs (Short Version for FPGA DSP) Version 2003. 7. 18 School of Electrical Engineering Seoul
Floating-point to Fixed-point Conversion for Efficient i Implementation ti of Digital Signal Processing Programs (Short Version for FPGA DSP) Version 2003. 7. 18 School of Electrical Engineering Seoul
A New Architecture for 2 s Complement Gray Encoded Array Multiplier
 A New Architecture for s Complement Gray Encoded Array Multiplier Eduardo Costa Sergio Bampi José Monteiro UCPel, Pelotas, Brazil UFRGS, P. Alegre, Brazil IST/INESC, Lisboa, Portugal ecosta@atlas.ucpel.tche.br
A New Architecture for s Complement Gray Encoded Array Multiplier Eduardo Costa Sergio Bampi José Monteiro UCPel, Pelotas, Brazil UFRGS, P. Alegre, Brazil IST/INESC, Lisboa, Portugal ecosta@atlas.ucpel.tche.br
Design and Implementation of CVNS Based Low Power 64-Bit Adder
 Design and Implementation of CVNS Based Low Power 64-Bit Adder Ch.Vijay Kumar Department of ECE Embedded Systems & VLSI Design Vishakhapatnam, India Sri.Sagara Pandu Department of ECE Embedded Systems
Design and Implementation of CVNS Based Low Power 64-Bit Adder Ch.Vijay Kumar Department of ECE Embedded Systems & VLSI Design Vishakhapatnam, India Sri.Sagara Pandu Department of ECE Embedded Systems
By, Ajinkya Karande Adarsh Yoga
 By, Ajinkya Karande Adarsh Yoga Introduction Early computer designers believed saving computer time and memory were more important than programmer time. Bug in the divide algorithm used in Intel chips.
By, Ajinkya Karande Adarsh Yoga Introduction Early computer designers believed saving computer time and memory were more important than programmer time. Bug in the divide algorithm used in Intel chips.
CHAPTER 1 Numerical Representation
 CHAPTER 1 Numerical Representation To process a signal digitally, it must be represented in a digital format. This point may seem obvious, but it turns out that there are a number of different ways to
CHAPTER 1 Numerical Representation To process a signal digitally, it must be represented in a digital format. This point may seem obvious, but it turns out that there are a number of different ways to
EE 109 Unit 6 Binary Arithmetic
 EE 109 Unit 6 Binary Arithmetic 1 2 Semester Transition Point At this point we are going to start to transition in our class to look more at the hardware organization and the low-level software that is
EE 109 Unit 6 Binary Arithmetic 1 2 Semester Transition Point At this point we are going to start to transition in our class to look more at the hardware organization and the low-level software that is
Floating Point Square Root under HUB Format
 Floating Point Square Root under HUB Format Julio Villalba-Moreno Dept. of Computer Architecture University of Malaga Malaga, SPAIN jvillalba@uma.es Javier Hormigo Dept. of Computer Architecture University
Floating Point Square Root under HUB Format Julio Villalba-Moreno Dept. of Computer Architecture University of Malaga Malaga, SPAIN jvillalba@uma.es Javier Hormigo Dept. of Computer Architecture University
OPTIMIZING THE POWER USING FUSED ADD MULTIPLIER
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 11, November 2014,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 11, November 2014,
LOW POWER PROBABILISTIC FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER DESIGN
 LOW POWER PROBABILISTIC FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER DESIGN Aman Gupta,,*, Satyam Mandavalli, Vincent J. Mooney $,,*,, Keck-Voon Ling,*, Arindam Basu, Henry Johan $,* and Budianto Tandianus $,* International
LOW POWER PROBABILISTIC FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER DESIGN Aman Gupta,,*, Satyam Mandavalli, Vincent J. Mooney $,,*,, Keck-Voon Ling,*, Arindam Basu, Henry Johan $,* and Budianto Tandianus $,* International
Floating-Point Matrix Product on FPGA
 Floating-Point Matrix Product on FPGA Faycal Bensaali University of Hertfordshire f.bensaali@herts.ac.uk Abbes Amira Brunel University abbes.amira@brunel.ac.uk Reza Sotudeh University of Hertfordshire
Floating-Point Matrix Product on FPGA Faycal Bensaali University of Hertfordshire f.bensaali@herts.ac.uk Abbes Amira Brunel University abbes.amira@brunel.ac.uk Reza Sotudeh University of Hertfordshire
COMPUTER ARITHMETIC (Part 1)
 Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture COMPUTER ARITHMETIC (Part 1) Introduction The two principal concerns for computer arithmetic
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture COMPUTER ARITHMETIC (Part 1) Introduction The two principal concerns for computer arithmetic
International Journal of Research in Computer and Communication Technology, Vol 4, Issue 11, November- 2015
 Design of Dadda Algorithm based Floating Point Multiplier A. Bhanu Swetha. PG.Scholar: M.Tech(VLSISD), Department of ECE, BVCITS, Batlapalem. E.mail:swetha.appari@gmail.com V.Ramoji, Asst.Professor, Department
Design of Dadda Algorithm based Floating Point Multiplier A. Bhanu Swetha. PG.Scholar: M.Tech(VLSISD), Department of ECE, BVCITS, Batlapalem. E.mail:swetha.appari@gmail.com V.Ramoji, Asst.Professor, Department
IMPLEMENTATION OF TWIN PRECISION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTIPLICATION
 IMPLEMENTATION OF TWIN PRECISION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTIPLICATION SUNITH KUMAR BANDI #1, M.VINODH KUMAR *2 # ECE department, M.V.G.R College of Engineering, Vizianagaram, Andhra Pradesh, INDIA. 1 sunithjc@gmail.com
IMPLEMENTATION OF TWIN PRECISION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTIPLICATION SUNITH KUMAR BANDI #1, M.VINODH KUMAR *2 # ECE department, M.V.G.R College of Engineering, Vizianagaram, Andhra Pradesh, INDIA. 1 sunithjc@gmail.com
CPE 323 REVIEW DATA TYPES AND NUMBER REPRESENTATIONS IN MODERN COMPUTERS
 CPE 323 REVIEW DATA TYPES AND NUMBER REPRESENTATIONS IN MODERN COMPUTERS Aleksandar Milenković The LaCASA Laboratory, ECE Department, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Email: milenka@uah.edu Web:
CPE 323 REVIEW DATA TYPES AND NUMBER REPRESENTATIONS IN MODERN COMPUTERS Aleksandar Milenković The LaCASA Laboratory, ECE Department, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Email: milenka@uah.edu Web:
Addition and multiplication
 Addition and multiplication Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer, but it s not as easy as you might expect! These next few lectures focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication
Addition and multiplication Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer, but it s not as easy as you might expect! These next few lectures focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication
CPE 323 REVIEW DATA TYPES AND NUMBER REPRESENTATIONS IN MODERN COMPUTERS
 CPE 323 REVIEW DATA TYPES AND NUMBER REPRESENTATIONS IN MODERN COMPUTERS Aleksandar Milenković The LaCASA Laboratory, ECE Department, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Email: milenka@uah.edu Web:
CPE 323 REVIEW DATA TYPES AND NUMBER REPRESENTATIONS IN MODERN COMPUTERS Aleksandar Milenković The LaCASA Laboratory, ECE Department, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Email: milenka@uah.edu Web:
A New Pipelined Array Architecture for Signed Multiplication
 A New Pipelined Array Architecture for Signed Multiplication Eduardo Costa, Sergio Bampi José Monteiro UCPel, Pelotas, Brazil UFRGS, P. Alegre, Brazil IST/INESC, Lisboa, Portugal ecosta@ucpel.tche.br bampi@inf.ufrgs.br
A New Pipelined Array Architecture for Signed Multiplication Eduardo Costa, Sergio Bampi José Monteiro UCPel, Pelotas, Brazil UFRGS, P. Alegre, Brazil IST/INESC, Lisboa, Portugal ecosta@ucpel.tche.br bampi@inf.ufrgs.br
Integer Multiplication and Division
 Integer Multiplication and Division COE 301 Computer Organization Prof. Muhamed Mudawar College of Computer Sciences and Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline
Integer Multiplication and Division COE 301 Computer Organization Prof. Muhamed Mudawar College of Computer Sciences and Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline
Chapter 5 : Computer Arithmetic
 Chapter 5 Computer Arithmetic Integer Representation: (Fixedpoint representation): An eight bit word can be represented the numbers from zero to 255 including = 1 = 1 11111111 = 255 In general if an nbit
Chapter 5 Computer Arithmetic Integer Representation: (Fixedpoint representation): An eight bit word can be represented the numbers from zero to 255 including = 1 = 1 11111111 = 255 In general if an nbit
Design and Analysis of Kogge-Stone and Han-Carlson Adders in 130nm CMOS Technology
 Design and Analysis of Kogge-Stone and Han-Carlson Adders in 130nm CMOS Technology Senthil Ganesh R & R. Kalaimathi 1 Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Info Institute of Engineering,
Design and Analysis of Kogge-Stone and Han-Carlson Adders in 130nm CMOS Technology Senthil Ganesh R & R. Kalaimathi 1 Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Info Institute of Engineering,
Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers (Part 2)
 Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers (Part 2) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Eng ineering, Feng-Chia Unive
Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers (Part 2) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Eng ineering, Feng-Chia Unive
International Journal of Engineering and Techniques - Volume 4 Issue 2, April-2018
 RESEARCH ARTICLE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF RADIX-16 BOOTH PARTIAL PRODUCT GENERATOR FOR 64-BIT BINARY MULTIPLIERS K.Deepthi 1, Dr.T.Lalith Kumar 2 OPEN ACCESS 1 PG Scholar,Dept. Of ECE,Annamacharya Institute
RESEARCH ARTICLE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF RADIX-16 BOOTH PARTIAL PRODUCT GENERATOR FOR 64-BIT BINARY MULTIPLIERS K.Deepthi 1, Dr.T.Lalith Kumar 2 OPEN ACCESS 1 PG Scholar,Dept. Of ECE,Annamacharya Institute
Analysis of Different Multiplication Algorithms & FPGA Implementation
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 4, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 29-35 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 Analysis of Different Multiplication Algorithms & FPGA
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 4, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 29-35 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 Analysis of Different Multiplication Algorithms & FPGA
Review of Last lecture. Review ALU Design. Designing a Multiplier Shifter Design Review. Booth s algorithm. Today s Outline
 Today s Outline San Jose State University EE176-SJSU Computer Architecture and Organization Lecture 5 HDL, ALU, Shifter, Booth Algorithm Multiplier & Divider Instructor: Christopher H. Pham Review of Last
Today s Outline San Jose State University EE176-SJSU Computer Architecture and Organization Lecture 5 HDL, ALU, Shifter, Booth Algorithm Multiplier & Divider Instructor: Christopher H. Pham Review of Last
Lecture 12 Integers. Computer and Network Security 19th of December Computer Science and Engineering Department
 Lecture 12 Integers Computer and Network Security 19th of December 2016 Computer Science and Engineering Department CSE Dep, ACS, UPB Lecture 12, Integers 1/40 Outline Data Types Representation Conversions
Lecture 12 Integers Computer and Network Security 19th of December 2016 Computer Science and Engineering Department CSE Dep, ACS, UPB Lecture 12, Integers 1/40 Outline Data Types Representation Conversions
Carry Prediction and Selection for Truncated Multiplication
 Carry Prediction and Selection for Truncated Multiplication Romain Michard, Arnaud Tisserand and Nicolas Veyrat-Charvillon Arénaire project, LIP (CNRS ENSL INRIA UCBL) Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon
Carry Prediction and Selection for Truncated Multiplication Romain Michard, Arnaud Tisserand and Nicolas Veyrat-Charvillon Arénaire project, LIP (CNRS ENSL INRIA UCBL) Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI. Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing
 EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 4-B Floating-Point Arithmetic - II Spring 2017 Koren Part.4b.1 The IEEE Floating-Point Standard Four formats for floating-point
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 4-B Floating-Point Arithmetic - II Spring 2017 Koren Part.4b.1 The IEEE Floating-Point Standard Four formats for floating-point
Low Power Floating-Point Multiplier Based On Vedic Mathematics
 Low Power Floating-Point Multiplier Based On Vedic Mathematics K.Prashant Gokul, M.E(VLSI Design), Sri Ramanujar Engineering College, Chennai Prof.S.Murugeswari., Supervisor,Prof.&Head,ECE.,SREC.,Chennai-600
Low Power Floating-Point Multiplier Based On Vedic Mathematics K.Prashant Gokul, M.E(VLSI Design), Sri Ramanujar Engineering College, Chennai Prof.S.Murugeswari., Supervisor,Prof.&Head,ECE.,SREC.,Chennai-600
Clocked Sequential System Design. Multiply Example
 Clocked Sequential System Design Example 1 Multipliers (Gradeschool, Modified Gradeschool) Multiply Example (185) (215) 00000000 00000000 ------ 1001101101011111 (39775) 1 0000000000000000
Clocked Sequential System Design Example 1 Multipliers (Gradeschool, Modified Gradeschool) Multiply Example (185) (215) 00000000 00000000 ------ 1001101101011111 (39775) 1 0000000000000000
Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor, EC Department, Bhabha College of Engineering
 A Review: Design of 16 bit Arithmetic and Logical unit using Vivado 14.7 and Implementation on Basys 3 FPGA Board Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor,
A Review: Design of 16 bit Arithmetic and Logical unit using Vivado 14.7 and Implementation on Basys 3 FPGA Board Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor,
