ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Flow Control Instructions
|
|
|
- Ami Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Flow Control Instructions Textbook: Chapter 4, Section 4.9 (CMP, TEQ,TST) Chapter 6 ARM Cortex-M Users Manual, Chapter 3 1
2 CPU instruction types Data movement operations memory-to-register and register-to-memory includes different memory addressing options memory includes peripheral function registers register-to-register constant-to-register (or to memory in some CPUs) Arithmetic operations add/subtract/multiply/divide multi-precision operations (more than 32 bits) Logical operations and/or/exclusive-or/complement (between operand bits) shift/rotate bit test/set/reset Flow control operations branch to a location (conditionally or unconditionally) branch to a subroutine/function return from a subroutine/function 2
3 ARM comparison instructions These instructions set flags in the PSR without saving the result. Set Status is implied, and there is no destination register CMP : compare : Op1 Op2 Sets Z, N, V and C flags Use to test for signed and unsigned relationships TST : bit-wise AND : Op1 ^ Op2 Sets Z and N flags; C and V flags are unaffected* Use to check selected bit(s) of a word TEQ : bit-wise XOR : Op1 xor Op2 Sets Z and N flags; C and V flags are unaffected* Use instead of CMP to check for equal condition, if C and V flags are to be preserved (ex. for multi-precisions arithmetic) 3 * C flag affected if shift applied to Op2. Avoid shifting Op2 if C flag must be preserved.
4 ARM flow control operations Unconditional branch: B label Target address = PC ± displacement Displacement embedded in instruction code Target < ±32M(ARM),±2K(Thumb),±16M(Thumb2) Conditional branch (cc = true/false condition): Bcc label (Ex. BNE label) Target < ±32M(ARM), (T),±1M(T2) Conditions that can be tested: EQ, NE, CS, CC, MI, PL, VS, VC, HI, LS, GE, LT, GT, LE (see next slide) 4
5 Condition codes represented by PSR flags or Text: Tables 6-2 to 6-5 (Arithmetic in Chap. 2)
6 Conditional Branch Instructions Unsigned conditional branch follow SUBS or CMP BLO target BLS target BHS target BHI target ; Branch if unsigned less than (if C=0, same as BCC) ; Branch if unsigned less than or equal to (if C=0 or Z=1) ; Branch if unsigned greater than or equal to (if C=1, same as BCS) ; Branch if unsigned greater than (if C=1 and Z=0) CMP R0,R1 BLO R0 R1 Next instruction R0<R1 target Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
7 Conditional Branch Instructions Signed conditional branch follow SUBS, CMP, or CMN BLT target BGE target BGT target BLE target ; if signed less than (if (~N&V N&~V)=1 if N V) ; if signed greater than or equal to (if (~N&V N&~V)=0 if N=V) ; if signed greater than (if (Z ~N&V N&~V)=0 if Z=0 and N=V) ; if signed less than or equal to (if (Z ~N&V N&~V)=1 if Z=1 and N V) CMP R0,R1 BLT R0 R1 Next instruction R0<R1 target Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
8 Equality Test Assembly code LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G == 7? BNE next1 ; if not, skip BL GEqual7 ; G == 7 next1 LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G!= 7? BEQ next2 ; if not, skip BL GNotEqual7 ; G!= 7 next2 C code unsigned long G; if(g2 == 7){ GEqual7(); if(g!= 7){ GNotEqual7(); Program 5.1. Conditional structures that test for equality. Can also use TEQ R0, #7 ; Test if Equal (R0 xor #7 = 0) BNE next1 Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
9 Unsigned Conditional Structures Assembly code LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G > 7? BLS next1 ; if not, skip BL GGreater7 ; G > 7 next1 LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G >= 7? BLO next2 ; if not, skip BL GGreaterEq7 ; G >= 7 next2 LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G < 7? BHS next3 ; if not, skip BL GLess7 ; G < 7 next3 LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G <= 7? BHI next4 ; if not, skip BL GLessEq7 ; G <= 7 next4 C code unsigned long G; if(g > 7){ GGreater7(); if(g >= 7){ GGreaterEq7(); if(g < 7){ GLess7(); if(g <= 7){ GLessEq7(); Program 5.2. Unsigned conditional structures. Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
10 Signed Conditional Structures Assembly code LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G > 7? BLE next1 ; if not, skip BL GGreater7 ; G > 7 next1 LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G >= 7? BLT next2 ; if not, skip BL GGreaterEq7 ; G >= 7 next2 LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G < 7? BGE next3 ; if not, skip BL GLess7 ; G < 7 next3 LDR R2, =G ; R2 = &G LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G CMP R0, #7 ; is G <= 7? BGT next4 ; if not, skip BL GLessEq7 ; G <= 7 next4 C code long G; if(g > 7){ GGreater7(); if(g >= 7){ GGreaterEq7(); if(g < 7){ GLess7(); if(g <= 7){ GLessEq7(); Program 5.4. Signed conditional structures. Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
11 If-then-else G1<=G2 G1>G2 islesseq isgreater LDR R2, =G1 ; R2 = &G1 LDR R0, [R2] ; R0 = G1 LDR R2, =G2 ; R2 = &G2 LDR R1, [R2] ; R1 = G2 CMP R0, R1 ; is G1 > G2? BHI high ; if so, skip to high low BL islesseq ; G1 <= G2 B next ; unconditional high BL isgreater ; G1 > G2 next unsigned long G1,G2; if(g1>g2){ isgreater(); else{ islesseq(); Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
12 Example: if-then-else statement C: if (a > b) { x = 5; y = c + d; else x = c - d; Assembler: ; compute and test condition LDR r4,=a ; get address for a LDR r0,[r4] ; get value of a LDR r4,=b ; get address for b LDR r1,[r4] ; get value for b CMP r0,r1 ; compare a < b BLE fblock ; if a ><= b, branch to false block 12
13 If statement, cont d. ; true block MOV r0,#5 LDR r4,=x STR r0,[r4] LDR r4,=c LDR r0,[r4] LDR r4,=d LDR r1,[r4] ADD r0,r0,r1 LDR r4,=y STR r0,[r4] B after ; generate value for x ; get address for x ; store x ; get address for c ; get value of c ; get address for d ; get value of d ; compute y ; get address for y ; store y ; branch around false block 13
14 If statement, cont d. ; false block fblock LDR r4,=c LDR r0,[r4] LDR r4,=d LDR r1,[r4] SUB r0,r0,r1 LDR r4,=x STR r0,[r4] after... ; get address for c ; get value of c ; get address for d ; get value for d ; compute a-b ; get address for x ; store value of x 14
15 While Loops G2<=G1 G2>G1 Body LDR R4, =G1 ; R4 -> G1 LDR R5, =G2 ; R5 -> G2 loop LDR R0, [R5] ; R0 = G2 LDR R1, [R4] ; R1 = G1 CMP R0, R1 ; is G2 <= G1? BLS next ; if so, skip to next BL Body ; body of the loop B loop next unsigned long G1,G2; while(g2 > G1){ Body(); Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
16 For Loops for(i=0; i<100; i++){ Process(); i = 0 i i < 100 Count up MOV R4, #0 ; R4 = 0 loop CMP R4, #100 ; index >= 100? BHS done ; if so, skip to done BL Process ; process function* ADD R4, R4, #1 ; R4 = R4 + 1 B loop done i >= 100 Process i = i+1 Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
17 For Loops Count down for(i=100; i!=0; i--){ Process(); i = 100 MOV R4, #100 ; R4 = 0 loop BL Process ; process function SUBS R4, R4, #1 ; R4 = R4-1 BNE loop done i i!= 0 i == 0 Process i = i-1 Bard, Gerstlauer, Valvano, Yerraballi
18 Thumb2 conditional execution (IF-THEN) instruction, IT, supports conditional execution in Thumb2 of up to 4 instructions in a block Designate instructions to be executed for THEN and ELSE Format: ITxyz condition, where x,y,z are T/E/blank if (r0 > r1) { cmp r0,r1 ;set flags add r2,r3,r4 ITTEE GT ;condition 4 instr sub r3,r4,r5 addgt r2,r3,r4 ;do if r0>r1 else { subgt r3,r4,r5 ;do if r0>r1 and r2,r3,r4 andle r2,r3,r4 ;do if r0<=r1 orr r3,r4,r5 orrle r3,r4,f5 ;do if r0<=r1 Thumb2 code Pseudo-C 18
19 Example: C switch statement C: switch (test) { case 0: break; case 1: Assembler: LDR r2,=test LDR r0,[r2] ADR r1,switchtab ; get address for test ; load value for test ; load switch table address LDR r15,[r1,r0,lsl #2] ; index switch table switchtab DCD case0 DCD case1... ;address of case0 routine ;address of case1 routine 19
20 Finite impulse response (FIR) filter Σ f = c i x i c 1 c2 c 3 c 4 1 i n x Δ 1 x Δ 2 x Δ 3 x Δ 4 X i s are data samples C i s are constants 20
21 Example: FIR filter C: for (i=0, f=0; i<n; i++) f = f + c[i]*x[i]; Assembler ; loop initiation code MOV r0,#0 ; use r0 for I MOV r8,#0 ; use separate index for arrays LDR r2,=n ; get address for N LDR r1,[r2] ; get value of N MOV r2,#0 ; use r2 for f LDR r3,=c ; load r3 with base of c LDR r5,=x ; load r5 with base of x 21
22 FIR filter, cont.d ; loop body loop LDR r4,[r3,r8] ; get c[i] LDR r6,[r5,r8] ; get x[i] MUL r4,r4,r6 ; compute c[i]*x[i] ADD r2,r2,r4 ; add into running sum f ADD r8,r8,#4 ; add word offset to array index ADD r0,r0,#1 ; add 1 to i CMP r0,r1 ; exit? BLT loop ; if i < N, continue 22
23 FIR filter with MLA & auto-index AREA TestProg, CODE, READONLY ENTRY mov r0,#0 ;accumulator mov r1,#3 ;number of iterations ldr r2,=carray ;pointer to constants ldr r3,=xarray ;pointer to variables loop ldr r4,[r2],#4 ;get c[i] and move pointer ldr r5,[r3],#4 ;get x[i] and move pointer mla r0,r4,r5,r0 ;sum = sum + c[i]*x[i] subs r1,r1,#1 ;decrement iteration count bne loop ;repeat until count=0 here b here carray dcd 1,2,3 xarray dcd 10,20,30 END Also, need time delay to prepare x array for next sample 23
Chapter 2 Instructions Sets. Hsung-Pin Chang Department of Computer Science National ChungHsing University
 Chapter 2 Instructions Sets Hsung-Pin Chang Department of Computer Science National ChungHsing University Outline Instruction Preliminaries ARM Processor SHARC Processor 2.1 Instructions Instructions sets
Chapter 2 Instructions Sets Hsung-Pin Chang Department of Computer Science National ChungHsing University Outline Instruction Preliminaries ARM Processor SHARC Processor 2.1 Instructions Instructions sets
ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Arithmetic Instructions. References: Textbook Chapter 4, Chapter ARM Cortex-M Users Manual, Chapter 3
 ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Arithmetic Instructions References: Textbook Chapter 4, Chapter 9.1 9.2 ARM Cortex-M Users Manual, Chapter 3 1 CPU instruction types Data movement operations (Chapter 5)
ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Arithmetic Instructions References: Textbook Chapter 4, Chapter 9.1 9.2 ARM Cortex-M Users Manual, Chapter 3 1 CPU instruction types Data movement operations (Chapter 5)
ARM Instruction Set Architecture. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 ARM Instruction Set Architecture Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Condition Field (1) Most ARM instructions can be conditionally
ARM Instruction Set Architecture Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Condition Field (1) Most ARM instructions can be conditionally
Comparison InstruCtions
 Status Flags Now it is time to discuss what status flags are available. These five status flags are kept in a special register called the Program Status Register (PSR). The PSR also contains other important
Status Flags Now it is time to discuss what status flags are available. These five status flags are kept in a special register called the Program Status Register (PSR). The PSR also contains other important
Control Flow. September 2, Indiana University. Geoffrey Brown, Bryce Himebaugh 2015 September 2, / 21
 Control Flow Geoffrey Brown Bryce Himebaugh Indiana University September 2, 2016 Geoffrey Brown, Bryce Himebaugh 2015 September 2, 2016 1 / 21 Outline Condition Codes C Relational Operations C Logical
Control Flow Geoffrey Brown Bryce Himebaugh Indiana University September 2, 2016 Geoffrey Brown, Bryce Himebaugh 2015 September 2, 2016 1 / 21 Outline Condition Codes C Relational Operations C Logical
ARM Shift Operations. Shift Type 00 - logical left 01 - logical right 10 - arithmetic right 11 - rotate right. Shift Amount 0-31 bits
 ARM Shift Operations A novel feature of ARM is that all data-processing instructions can include an optional shift, whereas most other architectures have separate shift instructions. This is actually very
ARM Shift Operations A novel feature of ARM is that all data-processing instructions can include an optional shift, whereas most other architectures have separate shift instructions. This is actually very
Flow Control In Assembly
 Chapters 6 Flow Control In Assembly Embedded Systems with ARM Cortext-M Updated: Monday, February 19, 2018 Overview: Flow Control Basics of Flowcharting If-then-else While loop For loop 2 Flowcharting
Chapters 6 Flow Control In Assembly Embedded Systems with ARM Cortext-M Updated: Monday, February 19, 2018 Overview: Flow Control Basics of Flowcharting If-then-else While loop For loop 2 Flowcharting
Unsigned and signed integer numbers
 Unsigned and signed integer numbers Binary Unsigned Signed 0000 0 0 0001 1 1 0010 2 2 0011 3 3 0100 4 4 Subtraction sets C flag opposite of carry (ARM specialty)! - if (carry = 0) then C=1 - if (carry
Unsigned and signed integer numbers Binary Unsigned Signed 0000 0 0 0001 1 1 0010 2 2 0011 3 3 0100 4 4 Subtraction sets C flag opposite of carry (ARM specialty)! - if (carry = 0) then C=1 - if (carry
ARM Assembly Language. Programming
 Outline: ARM Assembly Language the ARM instruction set writing simple programs examples Programming hands-on: writing simple ARM assembly programs 2005 PEVE IT Unit ARM System Design ARM assembly language
Outline: ARM Assembly Language the ARM instruction set writing simple programs examples Programming hands-on: writing simple ARM assembly programs 2005 PEVE IT Unit ARM System Design ARM assembly language
Writing ARM Assembly. Steven R. Bagley
 Writing ARM Assembly Steven R. Bagley Hello World B main hello DEFB Hello World\n\0 goodbye DEFB Goodbye Universe\n\0 ALIGN main ADR R0, hello ; put address of hello string in R0 SWI 3 ; print it out ADR
Writing ARM Assembly Steven R. Bagley Hello World B main hello DEFB Hello World\n\0 goodbye DEFB Goodbye Universe\n\0 ALIGN main ADR R0, hello ; put address of hello string in R0 SWI 3 ; print it out ADR
STEVEN R. BAGLEY ARM: PROCESSING DATA
 STEVEN R. BAGLEY ARM: PROCESSING DATA INTRODUCTION CPU gets instructions from the computer s memory Each instruction is encoded as a binary pattern (an opcode) Assembly language developed as a human readable
STEVEN R. BAGLEY ARM: PROCESSING DATA INTRODUCTION CPU gets instructions from the computer s memory Each instruction is encoded as a binary pattern (an opcode) Assembly language developed as a human readable
Cortex M3 Programming
 Cortex M3 Programming EE8205: Embedded Computer Systems http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~courses/ee8205/ Dr. Gul N. Khan http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~gnkhan Electrical and Computer Engineering Ryerson University
Cortex M3 Programming EE8205: Embedded Computer Systems http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~courses/ee8205/ Dr. Gul N. Khan http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~gnkhan Electrical and Computer Engineering Ryerson University
Arm Processor. Arm = Advanced RISC Machines, Ltd.
 Arm Processor Arm = Advanced RISC Machines, Ltd. References: Computers as Components, 4 th Ed., by Marilyn Wolf ARM Cortex-M4 User Guide (link on course web page) ARM Architecture Reference Manual (link
Arm Processor Arm = Advanced RISC Machines, Ltd. References: Computers as Components, 4 th Ed., by Marilyn Wolf ARM Cortex-M4 User Guide (link on course web page) ARM Architecture Reference Manual (link
ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Logical and Shift Instructions
 ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Logical and Shift Instructions References: Textbook Chapter 4, Sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.5, 4.6, 4.9 ARM Cortex-M Users Manual, Chapter 3 1 CPU instruction types Data movement
ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Logical and Shift Instructions References: Textbook Chapter 4, Sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.5, 4.6, 4.9 ARM Cortex-M Users Manual, Chapter 3 1 CPU instruction types Data movement
Control Flow Instructions
 Control Flow Instructions CSE 30: Computer Organization and Systems Programming Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 1 So Far... v All instructions have
Control Flow Instructions CSE 30: Computer Organization and Systems Programming Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 1 So Far... v All instructions have
Branch Instructions. R type: Cond
 Branch Instructions Standard branch instructions, B and BL, change the PC based on the PCR. The next instruction s address is found by adding a 24-bit signed 2 s complement immediate value
Branch Instructions Standard branch instructions, B and BL, change the PC based on the PCR. The next instruction s address is found by adding a 24-bit signed 2 s complement immediate value
ARM Processor. Based on Lecture Notes by Marilyn Wolf
 ARM Processor ARM = Advanced RISC Machines, Ltd. ARM licenses IP to other companies (ARM does not fabricate chips) 2005: ARM had 75% of embedded RISC market, with 2.5 billion processors ARM available as
ARM Processor ARM = Advanced RISC Machines, Ltd. ARM licenses IP to other companies (ARM does not fabricate chips) 2005: ARM had 75% of embedded RISC market, with 2.5 billion processors ARM available as
The ARM processor. Morgan Kaufman ed Overheads for Computers as Components
 The ARM processor Born in Acorn on 1983, after the success achieved by the BBC Micro released on 1982. Acorn is a really smaller company than most of the USA competitors, therefore it initially develops
The ARM processor Born in Acorn on 1983, after the success achieved by the BBC Micro released on 1982. Acorn is a really smaller company than most of the USA competitors, therefore it initially develops
ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Memory Addressing Instructions
 ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Memory Addressing Instructions References: Textbook Chapter 4, Sections 4.1-4.5 Chapter 5, Sections 5.1-5.4 ARM Cortex-M Users Manual, Chapter 3 2 CPU instruction types
ARM Cortex-M4 Programming Model Memory Addressing Instructions References: Textbook Chapter 4, Sections 4.1-4.5 Chapter 5, Sections 5.1-5.4 ARM Cortex-M Users Manual, Chapter 3 2 CPU instruction types
Processor Status Register(PSR)
 ARM Registers Register internal CPU hardware device that stores binary data; can be accessed much more rapidly than a location in RAM ARM has 13 general-purpose registers R0-R12 1 Stack Pointer (SP) R13
ARM Registers Register internal CPU hardware device that stores binary data; can be accessed much more rapidly than a location in RAM ARM has 13 general-purpose registers R0-R12 1 Stack Pointer (SP) R13
Overview COMP Microprocessors and Embedded Systems. Lectures 14: Making Decisions in C/Assembly Language II
 OMP 3221 Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 14: Making Decisions in /Assembly Language II Overview ompare instruction mechanism Flag setting Instructions onditional Instructions onclusion http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3221
OMP 3221 Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 14: Making Decisions in /Assembly Language II Overview ompare instruction mechanism Flag setting Instructions onditional Instructions onclusion http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3221
Introduction to C. Write a main() function that swaps the contents of two integer variables x and y.
 Introduction to C Write a main() function that swaps the contents of two integer variables x and y. void main(void){ int a = 10; int b = 20; a = b; b = a; } 1 Introduction to C Write a main() function
Introduction to C Write a main() function that swaps the contents of two integer variables x and y. void main(void){ int a = 10; int b = 20; a = b; b = a; } 1 Introduction to C Write a main() function
ARM Cortex M3 Instruction Set Architecture. Gary J. Minden March 29, 2016
 ARM Cortex M3 Instruction Set Architecture Gary J. Minden March 29, 2016 1 Calculator Exercise Calculate: X = (45 * 32 + 7) / (65 2 * 18) G. J. Minden 2014 2 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) ISAs define
ARM Cortex M3 Instruction Set Architecture Gary J. Minden March 29, 2016 1 Calculator Exercise Calculate: X = (45 * 32 + 7) / (65 2 * 18) G. J. Minden 2014 2 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) ISAs define
Outline. ARM Introduction & Instruction Set Architecture. ARM History. ARM s visible registers
 Outline ARM Introduction & Instruction Set Architecture Aleksandar Milenkovic E-mail: Web: milenka@ece.uah.edu http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka ARM Architecture ARM Organization and Implementation ARM Instruction
Outline ARM Introduction & Instruction Set Architecture Aleksandar Milenkovic E-mail: Web: milenka@ece.uah.edu http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka ARM Architecture ARM Organization and Implementation ARM Instruction
MNEMONIC OPERATION ADDRESS / OPERAND MODES FLAGS SET WITH S suffix ADC
 ECE425 MNEMONIC TABLE MNEMONIC OPERATION ADDRESS / OPERAND MODES FLAGS SET WITH S suffix ADC Adds operands and Carry flag and places value in destination register ADD Adds operands and places value in
ECE425 MNEMONIC TABLE MNEMONIC OPERATION ADDRESS / OPERAND MODES FLAGS SET WITH S suffix ADC Adds operands and Carry flag and places value in destination register ADD Adds operands and places value in
EE319K Spring 2016 Exam 1 Solution Page 1. Exam 1. Date: Feb 25, UT EID: Solution Professor (circle): Janapa Reddi, Tiwari, Valvano, Yerraballi
 EE319K Spring 2016 Exam 1 Solution Page 1 Exam 1 Date: Feb 25, 2016 UT EID: Solution Professor (circle): Janapa Reddi, Tiwari, Valvano, Yerraballi Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise
EE319K Spring 2016 Exam 1 Solution Page 1 Exam 1 Date: Feb 25, 2016 UT EID: Solution Professor (circle): Janapa Reddi, Tiwari, Valvano, Yerraballi Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise
ARM Assembly Programming
 Introduction ARM Assembly Programming The ARM processor is very easy to program at the assembly level. (It is a RISC) We will learn ARM assembly programming at the user level and run it on a GBA emulator.
Introduction ARM Assembly Programming The ARM processor is very easy to program at the assembly level. (It is a RISC) We will learn ARM assembly programming at the user level and run it on a GBA emulator.
The PAW Architecture Reference Manual
 The PAW Architecture Reference Manual by Hansen Zhang For COS375/ELE375 Princeton University Last Update: 20 September 2015! 1. Introduction The PAW architecture is a simple architecture designed to be
The PAW Architecture Reference Manual by Hansen Zhang For COS375/ELE375 Princeton University Last Update: 20 September 2015! 1. Introduction The PAW architecture is a simple architecture designed to be
Exam 1. Date: Oct 4, 2018
 Exam 1 Date: Oct 4, 2018 UT EID: Professor: Valvano Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will you help others to cheat
Exam 1 Date: Oct 4, 2018 UT EID: Professor: Valvano Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will you help others to cheat
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 03: Instruction Set Architecture Design
 ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 03: Instruction Set Architecture Design Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2016 1 ISA is the HW/SW
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 03: Instruction Set Architecture Design Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2016 1 ISA is the HW/SW
(2) Part a) Registers (e.g., R0, R1, themselves). other Registers do not exists at any address in the memory map
 (14) Question 1. For each of the following components, decide where to place it within the memory map of the microcontroller. Multiple choice select: RAM, ROM, or other. Select other if the component is
(14) Question 1. For each of the following components, decide where to place it within the memory map of the microcontroller. Multiple choice select: RAM, ROM, or other. Select other if the component is
ARM Architecture and Instruction Set
 AM Architecture and Instruction Set Ingo Sander ingo@imit.kth.se AM Microprocessor Core AM is a family of ISC architectures, which share the same design principles and a common instruction set AM does
AM Architecture and Instruction Set Ingo Sander ingo@imit.kth.se AM Microprocessor Core AM is a family of ISC architectures, which share the same design principles and a common instruction set AM does
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems ARM Assembly Programming: Translating C Control Statements and Function Calls
 CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems ARM Assembly Programming: Translating C Control Statements and Function Calls Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones 1 Announcements Final Projects Projects: Mandatory
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems ARM Assembly Programming: Translating C Control Statements and Function Calls Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones 1 Announcements Final Projects Projects: Mandatory
3 Assembly Programming (Part 2) Date: 07/09/2016 Name: ID:
 3 Assembly Programming (Part 2) 43 Date: 07/09/2016 Name: ID: Name: ID: 3 Assembly Programming (Part 2) This laboratory session discusses about Secure Shell Setup and Assembly Programming. The students
3 Assembly Programming (Part 2) 43 Date: 07/09/2016 Name: ID: Name: ID: 3 Assembly Programming (Part 2) This laboratory session discusses about Secure Shell Setup and Assembly Programming. The students
NET3001. Advanced Assembly
 NET3001 Advanced Assembly Arrays and Indexing supposed we have an array of 16 bytes at 0x0800.0100 write a program that determines if the array contains the byte '0x12' set r0=1 if the byte is found plan:
NET3001 Advanced Assembly Arrays and Indexing supposed we have an array of 16 bytes at 0x0800.0100 write a program that determines if the array contains the byte '0x12' set r0=1 if the byte is found plan:
ARM Cortex-M4 Architecture and Instruction Set 2: General Data Processing Instructions
 ARM Cortex-M4 Architecture and Instruction Set 2: General Data Processing Instructions M J Brockway January 31, 2016 Cortex-M4 Machine Instructions - simple example... main FUNCTION ; initialize registers
ARM Cortex-M4 Architecture and Instruction Set 2: General Data Processing Instructions M J Brockway January 31, 2016 Cortex-M4 Machine Instructions - simple example... main FUNCTION ; initialize registers
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Course Review for Exam 3. Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones
 CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Course Review for Exam 3 Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones 1 Announcements Exam 3: See course website for day/time. Exam 3 location: Our regular classroom Allowed
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Course Review for Exam 3 Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones 1 Announcements Exam 3: See course website for day/time. Exam 3 location: Our regular classroom Allowed
Introduction to Embedded Systems EE319K (Gerstlauer), Spring 2013
 The University of Texas at Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Introduction to Embedded Systems EE319K (Gerstlauer), Spring 2013 Midterm 1 Solutions Date: February 21, 2013 UT EID:
The University of Texas at Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Introduction to Embedded Systems EE319K (Gerstlauer), Spring 2013 Midterm 1 Solutions Date: February 21, 2013 UT EID:
EE319K Exam 1 Summer 2014 Page 1. Exam 1. Date: July 9, Printed Name:
 EE319K Exam 1 Summer 2014 Page 1 Exam 1 Date: July 9, 2014 UT EID: Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will you help
EE319K Exam 1 Summer 2014 Page 1 Exam 1 Date: July 9, 2014 UT EID: Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will you help
Introduction to Embedded Microcomputer Systems Lecture 8.1. Computers in the future may weigh no more than 1.5 tons Popular Science, 1949
 Introduction to Embedded Microcomputer Systems Lecture 8.1 Computers in the future may weigh no more than 1.5 tons Popular Science, 1949 Recap Debugging: Monitor, dump TExaS Real 9S12DG Overview Addition
Introduction to Embedded Microcomputer Systems Lecture 8.1 Computers in the future may weigh no more than 1.5 tons Popular Science, 1949 Recap Debugging: Monitor, dump TExaS Real 9S12DG Overview Addition
EE319K Spring 2015 Exam 1 Page 1. Exam 1. Date: Feb 26, 2015
 EE319K Spring 2015 Exam 1 Page 1 Exam 1 Date: Feb 26, 2015 UT EID: Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will you help
EE319K Spring 2015 Exam 1 Page 1 Exam 1 Date: Feb 26, 2015 UT EID: Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will you help
EE319K Fall 2013 Exam 1B Modified Page 1. Exam 1. Date: October 3, 2013
 EE319K Fall 2013 Exam 1B Modified Page 1 Exam 1 Date: October 3, 2013 UT EID: Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will
EE319K Fall 2013 Exam 1B Modified Page 1 Exam 1 Date: October 3, 2013 UT EID: Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will
F28HS2 Hardware-Software Interfaces. Lecture 6: ARM Assembly Language 1
 F28HS2 Hardware-Software Interfaces Lecture 6: ARM Assembly Language 1 CISC & RISC CISC: complex instruction set computer original CPUs very simple poorly suited to evolving high level languages extended
F28HS2 Hardware-Software Interfaces Lecture 6: ARM Assembly Language 1 CISC & RISC CISC: complex instruction set computer original CPUs very simple poorly suited to evolving high level languages extended
ARM Cortex-M4 Architecture and Instruction Set 3: Branching; Data definition and memory access instructions
 ARM Cortex-M4 Architecture and Instruction Set 3: Branching; Data definition and memory access instructions M J Brockway February 17, 2016 Branching To do anything other than run a fixed sequence of instructions,
ARM Cortex-M4 Architecture and Instruction Set 3: Branching; Data definition and memory access instructions M J Brockway February 17, 2016 Branching To do anything other than run a fixed sequence of instructions,
18-349: Introduction to Embedded Real- Time Systems Lecture 3: ARM ASM
 18-349: Introduction to Embedded Real- Time Systems Lecture 3: ARM ASM Anthony Rowe Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Mellon University Lecture Overview Exceptions Overview (Review) Pipelining
18-349: Introduction to Embedded Real- Time Systems Lecture 3: ARM ASM Anthony Rowe Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Mellon University Lecture Overview Exceptions Overview (Review) Pipelining
ARM Assembly Language
 ARM Assembly Language Introduction to ARM Basic Instruction Set Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Course Isfahan University of Technology, Dec. 2010 1 Main References The ARM Architecture Presentation
ARM Assembly Language Introduction to ARM Basic Instruction Set Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Course Isfahan University of Technology, Dec. 2010 1 Main References The ARM Architecture Presentation
The ARM Instruction Set Architecture
 The ARM Instruction Set Architecture Mark McDermott With help from our good friends at ARM Fall 008 Main features of the ARM Instruction Set All instructions are 3 bits long. Most instructions execute
The ARM Instruction Set Architecture Mark McDermott With help from our good friends at ARM Fall 008 Main features of the ARM Instruction Set All instructions are 3 bits long. Most instructions execute
ARM Instruction Set. Computer Organization and Assembly Languages Yung-Yu Chuang. with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen
 ARM Instruction Set Computer Organization and Assembly Languages g Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen Introduction The ARM processor is easy to program at the assembly level. (It is a RISC)
ARM Instruction Set Computer Organization and Assembly Languages g Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen Introduction The ARM processor is easy to program at the assembly level. (It is a RISC)
ARM Instruction Set. Introduction. Memory system. ARM programmer model. The ARM processor is easy to program at the
 Introduction ARM Instruction Set The ARM processor is easy to program at the assembly level. (It is a RISC) We will learn ARM assembly programming at the user level l and run it on a GBA emulator. Computer
Introduction ARM Instruction Set The ARM processor is easy to program at the assembly level. (It is a RISC) We will learn ARM assembly programming at the user level l and run it on a GBA emulator. Computer
Exam 1 Fun Times. EE319K Fall 2012 Exam 1A Modified Page 1. Date: October 5, Printed Name:
 EE319K Fall 2012 Exam 1A Modified Page 1 Exam 1 Fun Times Date: October 5, 2012 Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will
EE319K Fall 2012 Exam 1A Modified Page 1 Exam 1 Fun Times Date: October 5, 2012 Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will
Elements of CPU performance
 Elements of CPU performance Cycle time. CPU pipeline. Superscalar design. Memory system. Texec = instructions ( )( program cycles instruction seconds )( ) cycle ARM7TDM CPU Core ARM Cortex A-9 Microarchitecture
Elements of CPU performance Cycle time. CPU pipeline. Superscalar design. Memory system. Texec = instructions ( )( program cycles instruction seconds )( ) cycle ARM7TDM CPU Core ARM Cortex A-9 Microarchitecture
Assembler: Basics. Alberto Bosio October 20, Univeristé de Montpellier
 Assembler: Basics Alberto Bosio bosio@lirmm.fr Univeristé de Montpellier October 20, 2017 Assembler Program Template. t e x t / S t a r t o f the program code s e c t i o n /.data / V a r i a b l e s /
Assembler: Basics Alberto Bosio bosio@lirmm.fr Univeristé de Montpellier October 20, 2017 Assembler Program Template. t e x t / S t a r t o f the program code s e c t i o n /.data / V a r i a b l e s /
The Assembly Language of the Boz 5
 The Assembly Language of the Boz 5 The Boz 5 uses bits 31 27 of the IR as a five bit opcode. Of the possible 32 opcodes, only 26 are implemented. Op-Code Mnemonic Description 00000 HLT Halt the Computer
The Assembly Language of the Boz 5 The Boz 5 uses bits 31 27 of the IR as a five bit opcode. Of the possible 32 opcodes, only 26 are implemented. Op-Code Mnemonic Description 00000 HLT Halt the Computer
The ARM Cortex-M0 Processor Architecture Part-2
 The ARM Cortex-M0 Processor Architecture Part-2 1 Module Syllabus ARM Cortex-M0 Processor Instruction Set ARM and Thumb Instruction Set Cortex-M0 Instruction Set Data Accessing Instructions Arithmetic
The ARM Cortex-M0 Processor Architecture Part-2 1 Module Syllabus ARM Cortex-M0 Processor Instruction Set ARM and Thumb Instruction Set Cortex-M0 Instruction Set Data Accessing Instructions Arithmetic
EE 3170 Microcontroller Applications
 Lecture Overview EE 3170 Microcontroller Applications Lecture 7 : Instruction Subset & Machine Language: Conditions & Branches in Motorola 68HC11 - Miller 2.2 & 2.3 & 2.4 Based on slides for ECE3170 by
Lecture Overview EE 3170 Microcontroller Applications Lecture 7 : Instruction Subset & Machine Language: Conditions & Branches in Motorola 68HC11 - Miller 2.2 & 2.3 & 2.4 Based on slides for ECE3170 by
Basic ARM InstructionS
 Basic ARM InstructionS Instructions include various fields that encode combinations of Opcodes and arguments special fields enable extended functions (more in a minute) several 4-bit OPERAND fields, for
Basic ARM InstructionS Instructions include various fields that encode combinations of Opcodes and arguments special fields enable extended functions (more in a minute) several 4-bit OPERAND fields, for
ECE251: Tuesday September 12
 ECE251: Tuesday September 12 Finish Branch related instructions Stack Subroutines Note: Lab 3 is a 2 week lab, starting this week and covers the Stack and Subroutines. Labs: Lab #2 is due this week. Lab
ECE251: Tuesday September 12 Finish Branch related instructions Stack Subroutines Note: Lab 3 is a 2 week lab, starting this week and covers the Stack and Subroutines. Labs: Lab #2 is due this week. Lab
Interrupt-Driven Input/Output
 Interrupt-Driven Input/Output Textbook: Chapter 11 (Interrupts) ARM Cortex-M4 User Guide (Interrupts, exceptions, NVIC) Sections 2.1.4, 2.3 Exceptions and interrupts Section 4.2 Nested Vectored Interrupt
Interrupt-Driven Input/Output Textbook: Chapter 11 (Interrupts) ARM Cortex-M4 User Guide (Interrupts, exceptions, NVIC) Sections 2.1.4, 2.3 Exceptions and interrupts Section 4.2 Nested Vectored Interrupt
Lecture 15 ARM Processor A RISC Architecture
 CPE 390: Microprocessor Systems Fall 2017 Lecture 15 ARM Processor A RISC Architecture Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken, NJ 07030
CPE 390: Microprocessor Systems Fall 2017 Lecture 15 ARM Processor A RISC Architecture Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken, NJ 07030
Chapter 15. ARM Architecture, Programming and Development Tools
 Chapter 15 ARM Architecture, Programming and Development Tools Lesson 4 ARM CPU 32 bit ARM Instruction set 2 Basic Programming Features- ARM code size small than other RISCs 32-bit un-segmented memory
Chapter 15 ARM Architecture, Programming and Development Tools Lesson 4 ARM CPU 32 bit ARM Instruction set 2 Basic Programming Features- ARM code size small than other RISCs 32-bit un-segmented memory
The ARM instruction set
 Outline: The ARM instruction set privileged modes and exceptions instruction set details system code example hands-on: system software - SWI handler 2005 PEVE IT Unit ARM System Design Instruction set
Outline: The ARM instruction set privileged modes and exceptions instruction set details system code example hands-on: system software - SWI handler 2005 PEVE IT Unit ARM System Design Instruction set
ARM Cortex-A9 ARM v7-a. A programmer s perspective Part 2
 ARM Cortex-A9 ARM v7-a A programmer s perspective Part 2 ARM Instructions General Format Inst Rd, Rn, Rm, Rs Inst Rd, Rn, #0ximm 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7
ARM Cortex-A9 ARM v7-a A programmer s perspective Part 2 ARM Instructions General Format Inst Rd, Rn, Rm, Rs Inst Rd, Rn, #0ximm 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7
Who am I and what am I doing?
 Who am I and what am I doing? Airscanner.com Mobile Security (AV, firewall, sniffer) Dissemination of Information Reverse-engineering is a tool not a weapon Knowing your computer Don t steal pay the programmers
Who am I and what am I doing? Airscanner.com Mobile Security (AV, firewall, sniffer) Dissemination of Information Reverse-engineering is a tool not a weapon Knowing your computer Don t steal pay the programmers
VE7104/INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS UNIT III ARM BASED MICROCONTROLLERS
 VE7104/INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS UNIT III ARM BASED MICROCONTROLLERS Introduction to 32 bit Processors, ARM Architecture, ARM cortex M3, 32 bit ARM Instruction set, Thumb Instruction set, Exception
VE7104/INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS UNIT III ARM BASED MICROCONTROLLERS Introduction to 32 bit Processors, ARM Architecture, ARM cortex M3, 32 bit ARM Instruction set, Thumb Instruction set, Exception
Architecture. Digital Computer Design
 Architecture Digital Computer Design Architecture The architecture is the programmer s view of a computer. It is defined by the instruction set (language) and operand locations (registers and memory).
Architecture Digital Computer Design Architecture The architecture is the programmer s view of a computer. It is defined by the instruction set (language) and operand locations (registers and memory).
Assembly language Simple, regular instructions building blocks of C, Java & other languages Typically one-to-one mapping to machine language
 Assembly Language Readings: 2.1-2.7, 2.9-2.10, 2.14 Green reference card Assembly language Simple, regular instructions building blocks of C, Java & other languages Typically one-to-one mapping to machine
Assembly Language Readings: 2.1-2.7, 2.9-2.10, 2.14 Green reference card Assembly language Simple, regular instructions building blocks of C, Java & other languages Typically one-to-one mapping to machine
Assembly language Simple, regular instructions building blocks of C, Java & other languages Typically one-to-one mapping to machine language
 Assembly Language Readings: 2.1-2.7, 2.9-2.10, 2.14 Green reference card Assembly language Simple, regular instructions building blocks of C, Java & other languages Typically one-to-one mapping to machine
Assembly Language Readings: 2.1-2.7, 2.9-2.10, 2.14 Green reference card Assembly language Simple, regular instructions building blocks of C, Java & other languages Typically one-to-one mapping to machine
3. The Instruction Set
 3. The Instruction Set We now know what the ARM provides by way of memory and registers, and the sort of instructions to manipulate them.this chapter describes those instructions in great detail. As explained
3. The Instruction Set We now know what the ARM provides by way of memory and registers, and the sort of instructions to manipulate them.this chapter describes those instructions in great detail. As explained
ECE 372 Microcontroller Design Assembly Programming. ECE 372 Microcontroller Design Assembly Programming
 Assembly Programming HCS12 Assembly Programming Basic Assembly Programming Top Assembly Instructions (Instruction You Should Know!) Assembly Programming Concepts Assembly Programming HCS12 Assembly Instructions
Assembly Programming HCS12 Assembly Programming Basic Assembly Programming Top Assembly Instructions (Instruction You Should Know!) Assembly Programming Concepts Assembly Programming HCS12 Assembly Instructions
Embedded assembly is more useful. Embedded assembly places an assembly function inside a C program and can be used with the ARM Cortex M0 processor.
 EE 354 Fall 2015 ARM Lecture 4 Assembly Language, Floating Point, PWM The ARM Cortex M0 processor supports only the thumb2 assembly language instruction set. This instruction set consists of fifty 16-bit
EE 354 Fall 2015 ARM Lecture 4 Assembly Language, Floating Point, PWM The ARM Cortex M0 processor supports only the thumb2 assembly language instruction set. This instruction set consists of fifty 16-bit
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 3
 ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 3 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 22 January 2013 The ARM Architecture 1 Brief ARM History ACORN Wanted a chip
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 3 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 22 January 2013 The ARM Architecture 1 Brief ARM History ACORN Wanted a chip
ARM Assembly Programming
 ARM Assembly Programming Computer Organization and Assembly Languages g Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen GNU compiler and binutils HAM uses GNU compiler and binutils gcc: GNU C compiler as:
ARM Assembly Programming Computer Organization and Assembly Languages g Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen GNU compiler and binutils HAM uses GNU compiler and binutils gcc: GNU C compiler as:
Hi Hsiao-Lung Chan, Ph.D. Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan
 ARM Programmers Model Hi Hsiao-Lung Chan, Ph.D. Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@maili.cgu.edu.twcgu Current program status register (CPSR) Prog Model 2 Data processing
ARM Programmers Model Hi Hsiao-Lung Chan, Ph.D. Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@maili.cgu.edu.twcgu Current program status register (CPSR) Prog Model 2 Data processing
EE251: Tuesday September 5
 EE251: Tuesday September 5 Shift/Rotate Instructions Bitwise logic and Saturating Instructions A Few Math Programming Examples ARM Assembly Language and Assembler Assembly Process Assembly Structure Assembler
EE251: Tuesday September 5 Shift/Rotate Instructions Bitwise logic and Saturating Instructions A Few Math Programming Examples ARM Assembly Language and Assembler Assembly Process Assembly Structure Assembler
EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 4: ARM Instruction Sets
 EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 4 ARM Instruction Sets Wen-Yen Lin, Ph.D. Department of Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University Email wylin@mail.cgu.edu.tw March 2014 Introduction Embedded
EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 4 ARM Instruction Sets Wen-Yen Lin, Ph.D. Department of Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University Email wylin@mail.cgu.edu.tw March 2014 Introduction Embedded
ARM Assembly Programming
 ARM Assembly Programming Computer Organization and Assembly Languages g Yung-Yu Chuang 2007/12/1 with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen GNU compiler and binutils HAM uses GNU compiler and binutils gcc: GNU C compiler
ARM Assembly Programming Computer Organization and Assembly Languages g Yung-Yu Chuang 2007/12/1 with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen GNU compiler and binutils HAM uses GNU compiler and binutils gcc: GNU C compiler
Reconfigurable Computing Systems ( L) Fall 2012 Tiny Register Machine (TRM)
 Reconfigurable Computing Systems (252-2210-00L) Fall 2012 Tiny Register Machine (TRM) L. Liu Department of Computer Science, ETH Zürich Fall semester, 2012 1 Introduction Jumping up a few levels of abstraction.
Reconfigurable Computing Systems (252-2210-00L) Fall 2012 Tiny Register Machine (TRM) L. Liu Department of Computer Science, ETH Zürich Fall semester, 2012 1 Introduction Jumping up a few levels of abstraction.
University of California, San Diego CSE 30 Computer Organization and Systems Programming Winter 2014 Midterm Dr. Diba Mirza
 Name Student ID University of California, San Diego CSE 30 Computer Organization and Systems Programming Winter 2014 Midterm Dr. Diba Mirza Name of person to your left Name of person to your right Please
Name Student ID University of California, San Diego CSE 30 Computer Organization and Systems Programming Winter 2014 Midterm Dr. Diba Mirza Name of person to your left Name of person to your right Please
ARM Instruction Set 1
 ARM Instruction Set 1 What is an embedded system? Components: Processor(s) Co-processors (graphics, security) Memory (disk drives, DRAM, SRAM, CD/DVD) input (mouse, keyboard, mic) output (display, printer)
ARM Instruction Set 1 What is an embedded system? Components: Processor(s) Co-processors (graphics, security) Memory (disk drives, DRAM, SRAM, CD/DVD) input (mouse, keyboard, mic) output (display, printer)
CMPSCI 201 Fall 2004 Midterm #1 Answers
 CMPSCI 201 Fall 2004 Midterm #1 Answers 10 Points Short Essay Answer The 8088 is primarily a CISC processor design, and the ARM is primarily RISC. The 6502 is such an early design that it is difficult
CMPSCI 201 Fall 2004 Midterm #1 Answers 10 Points Short Essay Answer The 8088 is primarily a CISC processor design, and the ARM is primarily RISC. The 6502 is such an early design that it is difficult
Introduction to the ARM Processor Using Intel FPGA Toolchain. 1 Introduction. For Quartus Prime 16.1
 Introduction to the ARM Processor Using Intel FPGA Toolchain For Quartus Prime 16.1 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the ARM Cortex-A9 processor, which is a processor implemented
Introduction to the ARM Processor Using Intel FPGA Toolchain For Quartus Prime 16.1 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the ARM Cortex-A9 processor, which is a processor implemented
Chapter 04: Instruction Sets and the Processor organizations. Lesson 08: Processor Instructions - Part 1
 Chapter 04: Instruction Sets and the Processor organizations Lesson 08: Processor Instructions - Part 1 1 Objective Understand the load, store instructions and register transfer instructions Understand
Chapter 04: Instruction Sets and the Processor organizations Lesson 08: Processor Instructions - Part 1 1 Objective Understand the load, store instructions and register transfer instructions Understand
F28HS2 Hardware-Software Interface. Lecture 7: ARM Assembly Language 2
 F28HS2 Hardware-Software Interface Lecture 7: ARM Assembly Language 2 Structured programming assembly language requires intricate use of labels & branches easy to produce spaghetti code design assembly
F28HS2 Hardware-Software Interface Lecture 7: ARM Assembly Language 2 Structured programming assembly language requires intricate use of labels & branches easy to produce spaghetti code design assembly
Vorlesung / Course IN2075: Mikroprozessoren / Microprocessors
 Vorlesung / Course IN2075: Mikroprozessoren / Microprocessors Pipelining 20 Nov 2017 Carsten Trinitis (LRR) P Techniques: Pipelining etc. Processor Organisation Tasks of a processor Input: Stream of instructions
Vorlesung / Course IN2075: Mikroprozessoren / Microprocessors Pipelining 20 Nov 2017 Carsten Trinitis (LRR) P Techniques: Pipelining etc. Processor Organisation Tasks of a processor Input: Stream of instructions
CS 310 Embedded Computer Systems CPUS. Seungryoul Maeng
 1 EMBEDDED SYSTEM HW CPUS Seungryoul Maeng 2 CPUs Types of Processors CPU Performance Instruction Sets Processors used in ES 3 Processors used in ES 4 Processors used in Embedded Systems RISC type ARM
1 EMBEDDED SYSTEM HW CPUS Seungryoul Maeng 2 CPUs Types of Processors CPU Performance Instruction Sets Processors used in ES 3 Processors used in ES 4 Processors used in Embedded Systems RISC type ARM
Lecture 6 Assembly Programming: Branch & Iteration
 CPE 390: Microprocessor Systems Spring 2018 Lecture 6 Assembly Programming: Branch & Iteration Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken, NJ
CPE 390: Microprocessor Systems Spring 2018 Lecture 6 Assembly Programming: Branch & Iteration Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken, NJ
Raspberry Pi / ARM Assembly. OrgArch / Fall 2018
 Raspberry Pi / ARM Assembly OrgArch / Fall 2018 The Raspberry Pi uses a Broadcom System on a Chip (SoC), which is based on an ARM CPU. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/arm_architecture The 64-bit ARM processor
Raspberry Pi / ARM Assembly OrgArch / Fall 2018 The Raspberry Pi uses a Broadcom System on a Chip (SoC), which is based on an ARM CPU. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/arm_architecture The 64-bit ARM processor
LAB 1 Using Visual Emulator. Download the emulator https://salmanarif.bitbucket.io/visual/downloads.html Answer to questions (Q)
 LAB 1 Using Visual Emulator Download the emulator https://salmanarif.bitbucket.io/visual/downloads.html Answer to questions (Q) Load the following Program in Visual Emulator ; The purpose of this program
LAB 1 Using Visual Emulator Download the emulator https://salmanarif.bitbucket.io/visual/downloads.html Answer to questions (Q) Load the following Program in Visual Emulator ; The purpose of this program
ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 5
 ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 5 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 17 September 2013 HW#1 is due Thursday Announcements For next class, at least skim book Chapter
ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 5 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 17 September 2013 HW#1 is due Thursday Announcements For next class, at least skim book Chapter
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Encoding of instructions raises some interesting choices Tradeoffs: performance, compactness, programmability Uniformity. Should different instructions Be the same size
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Encoding of instructions raises some interesting choices Tradeoffs: performance, compactness, programmability Uniformity. Should different instructions Be the same size
Condition Code Register. Microcomputer Architecture and Interfacing Colorado School of Mines Professor William Hoff
 Condition Code Register 1 Topics Condition code register Addition and subtraction instructions Conditional branches 2 Condition Code Register Condition code bits are automatically set by some instructions
Condition Code Register 1 Topics Condition code register Addition and subtraction instructions Conditional branches 2 Condition Code Register Condition code bits are automatically set by some instructions
Assembly Language. CS2253 Owen Kaser, UNBSJ
 Assembly Language CS2253 Owen Kaser, UNBSJ Assembly Language Some insane machine-code programming Assembly language as an alternative Assembler directives Mnemonics for instructions Machine-Code Programming
Assembly Language CS2253 Owen Kaser, UNBSJ Assembly Language Some insane machine-code programming Assembly language as an alternative Assembler directives Mnemonics for instructions Machine-Code Programming
Memory management units
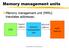 Memory management units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU logical address memory management unit physical address main memory Computers as Components 1 Access time comparison Media
Memory management units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU logical address memory management unit physical address main memory Computers as Components 1 Access time comparison Media
ARM Assembly Programming II
 ARM Assembly Programming II Computer Organization and Assembly Languages Yung-Yu Chuang 2007/11/26 with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen GNU compiler and binutils HAM uses GNU compiler and binutils gcc: GNU C
ARM Assembly Programming II Computer Organization and Assembly Languages Yung-Yu Chuang 2007/11/26 with slides by Peng-Sheng Chen GNU compiler and binutils HAM uses GNU compiler and binutils gcc: GNU C
COMPSCI 313 S Computer Organization. 7 MIPS Instruction Set
 COMPSCI 313 S2 2018 Computer Organization 7 MIPS Instruction Set Agenda & Reading MIPS instruction set MIPS I-format instructions MIPS R-format instructions 2 7.1 MIPS Instruction Set MIPS Instruction
COMPSCI 313 S2 2018 Computer Organization 7 MIPS Instruction Set Agenda & Reading MIPS instruction set MIPS I-format instructions MIPS R-format instructions 2 7.1 MIPS Instruction Set MIPS Instruction
2) [ 2 marks] Both of the following statements cause the value $0300 to be stored in location $1000, but at different times. Explain the difference.
![2) [ 2 marks] Both of the following statements cause the value $0300 to be stored in location $1000, but at different times. Explain the difference. 2) [ 2 marks] Both of the following statements cause the value $0300 to be stored in location $1000, but at different times. Explain the difference.](/thumbs/74/70477363.jpg) 1) [ 9 marks] Write a sequence of directives for an HCS12 assembly language program that performs all of these tasks, in this order: a) Define an array called Measurements starting from memory location
1) [ 9 marks] Write a sequence of directives for an HCS12 assembly language program that performs all of these tasks, in this order: a) Define an array called Measurements starting from memory location
Assembly Language Programming
 Assembly Language Programming ECE 362 https://engineering.purdue.edu/ee362/ Rick Reading and writing arrays Consider this C code again: int array1[100]; int array2[100]; for(n=0; n
Assembly Language Programming ECE 362 https://engineering.purdue.edu/ee362/ Rick Reading and writing arrays Consider this C code again: int array1[100]; int array2[100]; for(n=0; n
ARM-7 ADDRESSING MODES INSTRUCTION SET
 ARM-7 ADDRESSING MODES INSTRUCTION SET Dr. P. H. Zope 1 Assistant Professor SSBT s COET Bambhori Jalgaon North Maharashtra University Jalgaon India phzope@gmail.com 9860631040 Addressing modes When accessing
ARM-7 ADDRESSING MODES INSTRUCTION SET Dr. P. H. Zope 1 Assistant Professor SSBT s COET Bambhori Jalgaon North Maharashtra University Jalgaon India phzope@gmail.com 9860631040 Addressing modes When accessing
Course Administration
 Fall 2017 EE 3613: Computer Organization Chapter 2: Instruction Set Architecture 2/4 Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 45701 E-mail: kodi@ohio.edu
Fall 2017 EE 3613: Computer Organization Chapter 2: Instruction Set Architecture 2/4 Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 45701 E-mail: kodi@ohio.edu
Exam 1. Date: February 23, 2018
 Exam 1 Date: February 23, 2018 UT EID: Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will you help others to cheat on this exam:
Exam 1 Date: February 23, 2018 UT EID: Printed Name: Last, First Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will not cheat on this exam, nor will you help others to cheat on this exam:
