Meysam Taassori. This. and. outpu. sending frequent
|
|
|
- Ronald Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Test of Decompression module Meysam Taassori Abstract Th assay trying explain the process of test of a decompression module. Th module implemented using Verilog and simulated with Modelsim; all other steps from a Verilog code describing the design having a chip have been done by Cadence ols. Th chip fabricated in MOSIS 600nm and tested by Tektronics family called LV500. Th decompression module designed use in memory systems. Since there are a lot of similarities in data going be saved in different hierarchy of memory systems, compression and decompression can be useful for these system tackle one of the most important problems of memory systems, latency of memories. I. INTRODUCTION As technology advances, the designers have more transrs on a chip and in turn theree are more faster cores on one die; therefore, the number of request memory increasing dramatically. On the other hand, memories are implemented and optimized just for capacity and in th situation they cannot cope with th number of fast cores. That, th introduces performance bottleneck in future multicore systems. In new technologies, the contribution of power consumption in memory systems also increasing; th side effect so important servers wheree we need so many memory capacities. These huge numbers of memory so power hungry and th amount of power consumed in memory systems cause other problems including cost, high error rate and so on. Briefly, the gap between CPUs and memory systems going be exacerbated. One approach tackle these problems use data compression in srage of data. According observation, there are a lot of similarities in data pattern resident in memory hierarchy, which make it possible for compression help improve performance. We implemented these compression schemes using Verilog description it in structural level. In next step, th Verilog code synthesized provide us with the gate level of th system. Th step followed by placement and routing in 0.6 micrometer technology using Cadencee ols. The rest of th report organized as follows: First the particular compression and decompression algorithms used in th chip are explained and the of simulation of th module depicted in section 3. Then the method of test of th module dcussed and MSA file used test th module introduced. In section 5, we are going explain difficulties we encountered in the test process. II. COMPRESSION ALGORITHM Frequent Pattern Compression (FPC) one important way of compression sp sring and sending frequent data. Although the frequent dataa differs from program program, it observed thatt all-zero bytes are more frequent than other type of bytes in most of programs. As a result, FPC realized by detecting zero-based patterns and removing redundant parts. More precely, a 64B cache line decomposed sixteen 4B words. Then for each word if it follows the pattern 0000, 000X, 00XY, or XYZT FPC merely keeps 00,01X, 10XY, or 11XYZT, respectively. Note that the underlined numbers represent bits, whereas the other parts showed by alphabets represent bytes, so FPC might lead significant savings with a small overhead. In addition simplifying the decompression process the underlined bits are kept in the first word as metadata. Figure 1 depicts the bitmap in an FPC-based compressed line. Figure 1: Bitmap of FPC Compression Base Delta Intermediate (BDI) a recent proposal that proved be effective for deskp applications. BDI relies on the fact that the difference between words in one cache often limited. As such, BDI keeps the difference (delta) of words with one base value instead of keeping whole words. The base value typically the first word and the delta typicallyy
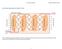
2 valued in the range of [-128,127] fit in a byte. Figure 2 illustrates bitmap for BDI. Figure 2: Bitmap of BDI We use the implementation of FPC and BDI based on proposals in [1] and [2]. Figure 3 shows the block diagram for FPC compression unit. Figure 3: FPC Compression Unit It mainly consts of three important parts: index generar, barrel shifter, and pattern converr. The index generar simply generates an index. The index the position of the first non-zero byte of a word in the compressed cache line, recalling that each word compressed 2-bit metadata kept in the first word and zero or more non-zero bytes. As we have 16 words per line, we need generate 16 indices as well. Since the rate of data arrival 4B per cycle, these indices are generated by one in each cycle. The next important part the barrel shifter. In Cycle i the barrel shifter shifts the cache line, index(i) position, so that the beginning of the non-compressed part of the word matches the LSB position. So zero, one, two, or four least significant bytes are the non- compressed part of Word i. The next component, the pattern converr, decides how many of the first four bytes after shifting belong Word i by checking the metadata associated with th word. It also fills zero bytes when necessary, again based on metadata. In [2] the authors considered complete a barrel shifter in their design. We conclude that th not necessary. In fact, just the first four bytes are needed. Therefore, we modified Barrel shifter shift the line and just keep the first LSB after shift. Th significantly reduced the number of MUXes needed in the barrel shifter. As DBI kept the difference (delta) between each word and the first word, its decompression simply a bunch of adders add up the delta and base find the original word. III. RESULT OF SIMULATION To simulate the structural level model of the design, we use Modelsim. In th stage, we prepare a testbench for th design; our testbench in charge of preparing different input signals such as clock, reset, and data in. Then, the signals willl be get by th testbench and we can check it if they are exactly the same as what we expect. Figure 3 depicts the and input waves of decompression. As shown in figure 3, inputs including reset, clk, ready_in, number, and data_in are set in Modelsim and the ts ncluding data_out get from th simular. Reset in th module would be set for several clock period make sure that circuit gettingg started from reset state. After reset reset, the valid input would be set module in every period of clock. Since, in th step, we are going test the behavior of our circuit, timing has no meaning. It worth mentioning that in th case, no cell has any delay and because of lack of definitionn of delay, timing not d in th step. IV. TEST METHODOLOGY A. Tester The tester we use in th test project from family called LV500 made by Tektronix in Th tester has been designed in order testt of ASIC design. There are two kinds of tester named LV512, and LV514. Both thesee testers have many things in common but the most importantt difference about test head. Test head means the number of input and t pins which are programmable separately. Th tester can test design with a clock whose frequency up 50 MHz. th teset can handle testt vecrs. Another important specification of th system ability connect network upload and download the files. LV512, LV54 have 192 and 128 test channels and 12 and 8 secrs respectively. As shown in figure 4, we design input vecr tests; design of th vecrs so important and we need do it in such a way that th set of vecrs make us sure that th testt as comprehensive as we could and need. The more
3 Figure 3 the result of simulation for decompression module Figure 4 the methodology of test powerful th set of tests, the more reliable our design would be. Th vecrs are given our design as inputs and the real t would be received by tester. On the other hand, we can the ts we are expecting from design. The comparon between real ts and expected another duty of tester. Therefore, if the ts are the same the design working correctly; otherwe, there an error or fault in our circuit. It evident that do th test, we need both input test vecrs and expected ts. Both of these prerequites can be ready just by means of Modelsim. We can prepare a testbench for our design and then inputs as the test vecr; after testing, Modelsim illustrates the expected ts. B. Essential parts of a test Each test we are going conduct needs prerequites; lack of one of these essentials can lead unexpected problem and consequently no result we are expected would be achieved. These parts are mentioned as follows. 1. Wired DUT (Design Under Test) card: th card in charge of connecting the pins of ester input and t of our design called DUT. The mapping between input and t of our design and tester needed. 2. Tester configuration: we need configure voltage, current of tester properly. Moreover, we need set timing of design and tester; it means that we need clarify when inputs should be applied and when the ts need be checked. We need for every channel of tester either it force or compare ; the former for input channel and the latter dedicated t channels. We should notice the point that every channel of a tester might not be active and we are allowed use just active ones. The structure of ester composed of secrs and each secr contains channels; each channel dedicated one input or t of our chip. For example, LV512 has 16 secrs named 0 F and each secr has 16 channel; note that only secrs called 0, 3-B are useable. Figure 5 depicting the card of LV512 and the active secrs are highlighted. Figure 5 DUT Card of Tester LV512
4 3. A complete set of test vecrs: we need apply these vecrs and check if the ts are equal what we are expected. C. Configuration of test In th sub chapter, we are going explain entire configuration we need consider before starting a test. 1. Mapping the t and input of our circuit the secr and channel of tester. In th step, we need groups including all pins of our design. In fact, all pins which needs a same timing can be considered as a group; for instance, we can consider a group named data_in for all pins of data and another group called data_out consider all t pins of data. In each group we need map the pins of that group channels of ester. For example, data_out0 mapped 9 th channel of secr A as follows signal "data_out0" { dut = "j10"; secr = 0hA; channel = 0h9; } Each group d in first step has specifications including phase, when data should be compared, when data should be forced or even ignored. 2. Defining phase for every group. We can one phase for every group of pins. Each phase has a delay showing when signal getting up, another parameter width depicting how long it would be up, and cycle length showing how long each period takes. 3. Defining the force format: if signal input, we need force format for its group. Th format can be chosen from the set of R1, R0, DNRZL, and DNRZT. Th format along with the phase we d in step 2 can signals precely. 4. Defining the compare format: if signal t we need compare it with what we expect. Compare format we can choose compare edge T, edge L, and window; 5. In th step we need a templatee where we set phases and function of each group. 6. Finally, we need pattern; the patterns are just different inputs and different ts based on behavior of our chip, meaning that we need show what we expect from th system under test. All these parts of configuration can be mentioned in a file with extension of.msa. When we run th file in tester all these configuration parts would be done aumatically. V. RESULT OF TEST After preparing msa file, we can start running the appropriate test. The result of tester mentioned in th chapter. We got the result in two different cases, using logic analyzer, and using software of tester. A. Using logic Analyzer In th case, we connect the digital analyzer the input and tt ports of our chip which are connected different channels and secrs of tester. Therefore, we have th opportunity monir all input ports and all t ports make sure that what we have d in msa file working well. We assume different force formats for signal of clock and in turn we got different t signals. In the following figures, channel 0, 1, 2-9, are dedicated clock, reset, t signals and input signals respectively. 1. Clock format NRZL Figure 6 t of logic analyzer in case 1 2. Clock R0 and in pattern it 0 Figure 7 t of logic analyzer in case 1 Figure 6 and 7 shows that t of th chip strange and it not what we expected. Although the inputs of th circuit seem be correct, the ts are getting stuck at zero or we can see sparks on that t. B. Using software of tester After entering the msa file, we configure the tester in such a way that all our patterns have been entered and we can startt testing. When we changed the format of clock as mentioned in previous section, theree were differences in the t of system.
5 Figure 8 t of file sent fabrication When we assume that the format of clock NRZL, all t pins get stuck at 0 and there no change when the input pins change in our pattern. These two method of test, using software and logic analyzer, made us sure that the problem might be searched in our design not in configuration of tester. However, all other cases also were tested make quite sure that th not because of wrong in configuration. Finally, after investigating the files that we have sent fabrication have our chip fabricated, I found that mtakenly in those files there are many flip flops that are not connected either reset or any function of reset. Therefore, we have many flip flops whose reset state not known and they are starting from unknown state. To make sure that our guess right, we have conducted a simulation using NC-Verilog with the file we have sent fabrication. The result of th simulation indicates that our guess unfortunately was right and there are serious problems in our original file. Figure 8 shows the result of th last experiment using. It indicates that even after reset high for enough period of time, ts of our design are still unknown shown with red wave in figure 8. th problem not about our tester or any configuration we have set, we conducted another test using NC-Verilog; the result of th test also confirmed that our chip has serious problems and does not work correctly. Our guess that th problem about the file we have sent for fabricating fabrication. VII. REFERENCES [1] B. Abali, H. Franke, D. E. Poff, R. A. Saccone, C. O. Schulz, L. M. Herger, and T. B. Smith. Memory expansion technology (MXT): software support and performance. IBM JRD, [2] A. R. Alameldeen and D. A. Wood. Adaptive cache compression for high performance processors. In ISCA-31, VI. CONCLUSION In th essay, we were explaining how test an VLSI chip. We described our methodology for a complete test. Furthermore, we introduced the tester from family LV500 in th paper and how configure th tester. Finally, we showed the results we earned with th tester in two methods, by means of logic analyzer, and software of tester as well. The results were upsetting and showed that our chip does not work properly. To make sure that
Architecture and Partitioning - Architecture
 Architecture and Partitioning - Architecture Architecture Management, Marketing and Senior Project Engineers work together to define product requirements. The product requirements will set cost, size and
Architecture and Partitioning - Architecture Architecture Management, Marketing and Senior Project Engineers work together to define product requirements. The product requirements will set cost, size and
An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design
 An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design Implementation of the first generation AsAP processor Zhiyi Yu and Tinoosh Mohsenin VCL Laboratory UC Davis Outline Overview of standard cellbased
An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design Implementation of the first generation AsAP processor Zhiyi Yu and Tinoosh Mohsenin VCL Laboratory UC Davis Outline Overview of standard cellbased
Testbench Template. The Big Picture
 Testbench Template Testbench template generated by Cadence The Big Picture 1010010100100 1001000010100 1110101001110 1010100010011 0100100010001 Input Vector Table DUT (Device Under Test) Compare Actual
Testbench Template Testbench template generated by Cadence The Big Picture 1010010100100 1001000010100 1110101001110 1010100010011 0100100010001 Input Vector Table DUT (Device Under Test) Compare Actual
Efficient VLSI Huffman encoder implementation and its application in high rate serial data encoding
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.14, No.21, 1 11 Efficient VLSI Huffman encoder implementation and its application in high rate serial data encoding Rongshan Wei a) and Xingang Zhang College of Physics
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.14, No.21, 1 11 Efficient VLSI Huffman encoder implementation and its application in high rate serial data encoding Rongshan Wei a) and Xingang Zhang College of Physics
System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
 Circuits and Systems, 2013, 4, 293-298 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cs.2013.43040 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
Circuits and Systems, 2013, 4, 293-298 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cs.2013.43040 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
Two HDLs used today VHDL. Why VHDL? Introduction to Structured VLSI Design
 Two HDLs used today Introduction to Structured VLSI Design VHDL I VHDL and Verilog Syntax and ``appearance'' of the two languages are very different Capabilities and scopes are quite similar Both are industrial
Two HDLs used today Introduction to Structured VLSI Design VHDL I VHDL and Verilog Syntax and ``appearance'' of the two languages are very different Capabilities and scopes are quite similar Both are industrial
Don t expect to be able to write and debug your code during the lab session.
 EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
A Low Power DDR SDRAM Controller Design P.Anup, R.Ramana Reddy
 A Low Power DDR SDRAM Controller Design P.Anup, R.Ramana Reddy Abstract This paper work leads to a working implementation of a Low Power DDR SDRAM Controller that is meant to be used as a reference for
A Low Power DDR SDRAM Controller Design P.Anup, R.Ramana Reddy Abstract This paper work leads to a working implementation of a Low Power DDR SDRAM Controller that is meant to be used as a reference for
Addressing Verification Bottlenecks of Fully Synthesized Processor Cores using Equivalence Checkers
 Addressing Verification Bottlenecks of Fully Synthesized Processor Cores using Equivalence Checkers Subash Chandar G (g-chandar1@ti.com), Vaideeswaran S (vaidee@ti.com) DSP Design, Texas Instruments India
Addressing Verification Bottlenecks of Fully Synthesized Processor Cores using Equivalence Checkers Subash Chandar G (g-chandar1@ti.com), Vaideeswaran S (vaidee@ti.com) DSP Design, Texas Instruments India
VHDL. VHDL History. Why VHDL? Introduction to Structured VLSI Design. Very High Speed Integrated Circuit (VHSIC) Hardware Description Language
 VHDL Introduction to Structured VLSI Design VHDL I Very High Speed Integrated Circuit (VHSIC) Hardware Description Language Joachim Rodrigues A Technology Independent, Standard Hardware description Language
VHDL Introduction to Structured VLSI Design VHDL I Very High Speed Integrated Circuit (VHSIC) Hardware Description Language Joachim Rodrigues A Technology Independent, Standard Hardware description Language
ECE Lab 8. Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache. To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache.
 ECE 201 - Lab 8 Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache PURPOSE To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache. EQUIPMENT Simulation Software REQUIREMENTS Electronic copy of your
ECE 201 - Lab 8 Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache PURPOSE To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache. EQUIPMENT Simulation Software REQUIREMENTS Electronic copy of your
Lecture 1: Introduction Course arrangements Recap of basic digital design concepts EDA tool demonstration
 TKT-1426 Digital design for FPGA, 6cp Fall 2011 http://www.tkt.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/1426/ Tampere University of Technology Department of Computer Systems Waqar Hussain Lecture Contents Lecture 1: Introduction
TKT-1426 Digital design for FPGA, 6cp Fall 2011 http://www.tkt.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/1426/ Tampere University of Technology Department of Computer Systems Waqar Hussain Lecture Contents Lecture 1: Introduction
Data Cache Final Project Report ECE251: VLSI Systems Design UCI Spring, 2000
 June 15, 2000 Data Cache Final Project Report ECE251: VLSI Systems Design UCI Spring, 2000 Jinfeng Liu Yi Deng ID: 65547013 (jinfengl@ece.uci.edu) ID: 57434732 (dengy@ece.uci.edu) Project Summary In this
June 15, 2000 Data Cache Final Project Report ECE251: VLSI Systems Design UCI Spring, 2000 Jinfeng Liu Yi Deng ID: 65547013 (jinfengl@ece.uci.edu) ID: 57434732 (dengy@ece.uci.edu) Project Summary In this
Graphics: Alexandra Nolte, Gesine Marwedel, Universität Dortmund. RTL Synthesis
 Graphics: Alexandra Nolte, Gesine Marwedel, 2003 Universität Dortmund RTL Synthesis Purpose of HDLs Purpose of Hardware Description Languages: Capture design in Register Transfer Language form i.e. All
Graphics: Alexandra Nolte, Gesine Marwedel, 2003 Universität Dortmund RTL Synthesis Purpose of HDLs Purpose of Hardware Description Languages: Capture design in Register Transfer Language form i.e. All
Memory Supplement for Section 3.6 of the textbook
 The most basic -bit memory is the SR-latch with consists of two cross-coupled NOR gates. R Recall the NOR gate truth table: A S B (A + B) The S stands for Set to remember, and the R for Reset to remember.
The most basic -bit memory is the SR-latch with consists of two cross-coupled NOR gates. R Recall the NOR gate truth table: A S B (A + B) The S stands for Set to remember, and the R for Reset to remember.
Lab #1: Introduction to Design Methodology with FPGAs part 1 (80 pts)
 Nate Pihlstrom, npihlstr@uccs.edu Lab #1: Introduction to Design Methodology with FPGAs part 1 (80 pts) Objective The objective of this lab assignment is to introduce and use a methodology for designing
Nate Pihlstrom, npihlstr@uccs.edu Lab #1: Introduction to Design Methodology with FPGAs part 1 (80 pts) Objective The objective of this lab assignment is to introduce and use a methodology for designing
Lecture 41: Introduction to Reconfigurable Computing
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 41: Introduction to Reconfigurable Computing Michael Le, Sp07 Head TA April 30, 2007 Slides Courtesy of Hayden So, Sp06 CS61c Head TA Following
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 41: Introduction to Reconfigurable Computing Michael Le, Sp07 Head TA April 30, 2007 Slides Courtesy of Hayden So, Sp06 CS61c Head TA Following
An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design
 An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design With examples taken from the implementation of the 36-core AsAP1 chip and the 1000-core KiloCore chip Zhiyi Yu, Tinoosh Mohsenin, Aaron Stillmaker,
An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design With examples taken from the implementation of the 36-core AsAP1 chip and the 1000-core KiloCore chip Zhiyi Yu, Tinoosh Mohsenin, Aaron Stillmaker,
Hardware Design Environments. Dr. Mahdi Abbasi Computer Engineering Department Bu-Ali Sina University
 Hardware Design Environments Dr. Mahdi Abbasi Computer Engineering Department Bu-Ali Sina University Outline Welcome to COE 405 Digital System Design Design Domains and Levels of Abstractions Synthesis
Hardware Design Environments Dr. Mahdi Abbasi Computer Engineering Department Bu-Ali Sina University Outline Welcome to COE 405 Digital System Design Design Domains and Levels of Abstractions Synthesis
Memory-Link Compression Schemes: A Value Locality Perspective
 Memory-Link Compression Schemes: A Value Locality Perspective Martin Thuresson, Lawrence Spracklen and Per Stenström IEEE Presented by Jean Niklas L orange and Caroline Sæhle, for TDT01, Norwegian University
Memory-Link Compression Schemes: A Value Locality Perspective Martin Thuresson, Lawrence Spracklen and Per Stenström IEEE Presented by Jean Niklas L orange and Caroline Sæhle, for TDT01, Norwegian University
File: 'ReportV37P-CT89533DanSuo.doc' CMPEN 411, Spring 2013, Homework Project 9 chip, 'Tiny Chip' fabricated through MOSIS program
 MOSIS Chip Test Report Dan Suo File: 'ReportV37P-CT89533DanSuo.doc' CMPEN 411, Spring 2013, Homework Project 9 chip, 'Tiny Chip' fabricated through MOSIS program Technology: 0.5um CMOS, ON Semiconductor
MOSIS Chip Test Report Dan Suo File: 'ReportV37P-CT89533DanSuo.doc' CMPEN 411, Spring 2013, Homework Project 9 chip, 'Tiny Chip' fabricated through MOSIS program Technology: 0.5um CMOS, ON Semiconductor
Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado
 Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado Alexander Jäger Computer Architecture Group Heidelberg University, Germany Abstract With shrinking feature sizes in the ASIC manufacturing technology,
Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado Alexander Jäger Computer Architecture Group Heidelberg University, Germany Abstract With shrinking feature sizes in the ASIC manufacturing technology,
Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)
 Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Lecturer: Krébesz, Tamas 1 FPGA in general Reprogrammable Si chip Invented in 1985 by Ross Freeman (Xilinx inc.) Combines the advantages of ASIC and uc-based systems
Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Lecturer: Krébesz, Tamas 1 FPGA in general Reprogrammable Si chip Invented in 1985 by Ross Freeman (Xilinx inc.) Combines the advantages of ASIC and uc-based systems
Choosing an Intellectual Property Core
 Choosing an Intellectual Property Core MIPS Technologies, Inc. June 2002 One of the most important product development decisions facing SOC designers today is choosing an intellectual property (IP) core.
Choosing an Intellectual Property Core MIPS Technologies, Inc. June 2002 One of the most important product development decisions facing SOC designers today is choosing an intellectual property (IP) core.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PROFESSIONAL ENGINEERING STUDIES Volume 9 /Issue 3 / OCT 2017
 Design of Low Power Adder in ALU Using Flexible Charge Recycling Dynamic Circuit Pallavi Mamidala 1 K. Anil kumar 2 mamidalapallavi@gmail.com 1 anilkumar10436@gmail.com 2 1 Assistant Professor, Dept of
Design of Low Power Adder in ALU Using Flexible Charge Recycling Dynamic Circuit Pallavi Mamidala 1 K. Anil kumar 2 mamidalapallavi@gmail.com 1 anilkumar10436@gmail.com 2 1 Assistant Professor, Dept of
COMP12111 Fundamentals of Computer Engineering Paul Nutter Vasilis Pavlidis Comments
 Fundamentals of Computer Engineering Paul Nutter Vasilis Pavlidis Comments Please see the attached report. 12 February 2016 Page 2 of 7 Exam Feedback 2015/16 Q1 set by Paul Nutter Q2 set by Vasilis Pavlidis
Fundamentals of Computer Engineering Paul Nutter Vasilis Pavlidis Comments Please see the attached report. 12 February 2016 Page 2 of 7 Exam Feedback 2015/16 Q1 set by Paul Nutter Q2 set by Vasilis Pavlidis
INTERCONNECT TESTING WITH BOUNDARY SCAN
 INTERCONNECT TESTING WITH BOUNDARY SCAN Paul Wagner Honeywell, Inc. Solid State Electronics Division 12001 State Highway 55 Plymouth, Minnesota 55441 Abstract Boundary scan is a structured design technique
INTERCONNECT TESTING WITH BOUNDARY SCAN Paul Wagner Honeywell, Inc. Solid State Electronics Division 12001 State Highway 55 Plymouth, Minnesota 55441 Abstract Boundary scan is a structured design technique
ECE 459/559 Secure & Trustworthy Computer Hardware Design
 ECE 459/559 Secure & Trustworthy Computer Hardware Design VLSI Design Basics Garrett S. Rose Spring 2016 Recap Brief overview of VHDL Behavioral VHDL Structural VHDL Simple examples with VHDL Some VHDL
ECE 459/559 Secure & Trustworthy Computer Hardware Design VLSI Design Basics Garrett S. Rose Spring 2016 Recap Brief overview of VHDL Behavioral VHDL Structural VHDL Simple examples with VHDL Some VHDL
Power-Mode-Aware Buffer Synthesis for Low-Power Clock Skew Minimization
 This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Power-Mode-Aware Buffer Synthesis for Low-Power
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Power-Mode-Aware Buffer Synthesis for Low-Power
101-1 Under-Graduate Project Digital IC Design Flow
 101-1 Under-Graduate Project Digital IC Design Flow Speaker: Ming-Chun Hsiao Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu Date: 2012/9/25 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Introduction to Integrated Circuit IC Design Flow Verilog HDL
101-1 Under-Graduate Project Digital IC Design Flow Speaker: Ming-Chun Hsiao Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu Date: 2012/9/25 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Introduction to Integrated Circuit IC Design Flow Verilog HDL
Marching Memory マーチングメモリ. UCAS-6 6 > Stanford > Imperial > Verify 中村維男 Based on Patent Application by Tadao Nakamura and Michael J.
 UCAS-6 6 > Stanford > Imperial > Verify 2011 Marching Memory マーチングメモリ Tadao Nakamura 中村維男 Based on Patent Application by Tadao Nakamura and Michael J. Flynn 1 Copyright 2010 Tadao Nakamura C-M-C Computer
UCAS-6 6 > Stanford > Imperial > Verify 2011 Marching Memory マーチングメモリ Tadao Nakamura 中村維男 Based on Patent Application by Tadao Nakamura and Michael J. Flynn 1 Copyright 2010 Tadao Nakamura C-M-C Computer
Defect Tolerance in VLSI Circuits
 Defect Tolerance in VLSI Circuits Prof. Naga Kandasamy We will consider the following redundancy techniques to tolerate defects in VLSI circuits. Duplication with complementary logic (physical redundancy).
Defect Tolerance in VLSI Circuits Prof. Naga Kandasamy We will consider the following redundancy techniques to tolerate defects in VLSI circuits. Duplication with complementary logic (physical redundancy).
ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design
 ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design for APEX II Devices December 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 183 Introduction As communication systems require more low-latency, high-bandwidth interfaces for peripheral
ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design for APEX II Devices December 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 183 Introduction As communication systems require more low-latency, high-bandwidth interfaces for peripheral
Scan Chain Operation for Stuck at Test
 Scan Chain Operation for Stuck at Test Scan Enable Here is an example design under test (DUT). I have shown a single scan chain (in red color) in the circuit, with and ports. Assume that all scan flip
Scan Chain Operation for Stuck at Test Scan Enable Here is an example design under test (DUT). I have shown a single scan chain (in red color) in the circuit, with and ports. Assume that all scan flip
FPGA Matrix Multiplier
 FPGA Matrix Multiplier In Hwan Baek Henri Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science University of California Los Angeles Los Angeles, California Email: chris.inhwan.baek@gmail.com David Boeck Henri
FPGA Matrix Multiplier In Hwan Baek Henri Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science University of California Los Angeles Los Angeles, California Email: chris.inhwan.baek@gmail.com David Boeck Henri
Leso Martin, Musil Tomáš
 SAFETY CORE APPROACH FOR THE SYSTEM WITH HIGH DEMANDS FOR A SAFETY AND RELIABILITY DESIGN IN A PARTIALLY DYNAMICALLY RECON- FIGURABLE FIELD-PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY (FPGA) Leso Martin, Musil Tomáš Abstract:
SAFETY CORE APPROACH FOR THE SYSTEM WITH HIGH DEMANDS FOR A SAFETY AND RELIABILITY DESIGN IN A PARTIALLY DYNAMICALLY RECON- FIGURABLE FIELD-PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY (FPGA) Leso Martin, Musil Tomáš Abstract:
Lab 2 Designing with Verilog
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 2 Designing with Verilog 1.0 Motivation In this lab you will learn how to express
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 2 Designing with Verilog 1.0 Motivation In this lab you will learn how to express
ARM 64-bit Register File
 ARM 64-bit Register File Introduction: In this class we will develop and simulate a simple, pipelined ARM microprocessor. Labs #1 & #2 build some basic components of the processor, then labs #3 and #4
ARM 64-bit Register File Introduction: In this class we will develop and simulate a simple, pipelined ARM microprocessor. Labs #1 & #2 build some basic components of the processor, then labs #3 and #4
A Novel Design of High Speed and Area Efficient De-Multiplexer. using Pass Transistor Logic
 A Novel Design of High Speed and Area Efficient De-Multiplexer Using Pass Transistor Logic K.Ravi PG Scholar(VLSI), P.Vijaya Kumari, M.Tech Assistant Professor T.Ravichandra Babu, Ph.D Associate Professor
A Novel Design of High Speed and Area Efficient De-Multiplexer Using Pass Transistor Logic K.Ravi PG Scholar(VLSI), P.Vijaya Kumari, M.Tech Assistant Professor T.Ravichandra Babu, Ph.D Associate Professor
A True Single Cycle RISC Processor without Pipelining
 1 A True Single Cycle RISC Processor without Pipelining Robert S. Plachno, VP of Audio Abstract This paper details the design of a embedded RISC controller used for mixed signal audio integrated circuits.
1 A True Single Cycle RISC Processor without Pipelining Robert S. Plachno, VP of Audio Abstract This paper details the design of a embedded RISC controller used for mixed signal audio integrated circuits.
FPGA: FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY Verilog: a hardware description language. Reference: [1]
![FPGA: FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY Verilog: a hardware description language. Reference: [1] FPGA: FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY Verilog: a hardware description language. Reference: [1]](/thumbs/80/81661285.jpg) FPGA: FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY Verilog: a hardware description language Reference: [] FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY FPGA is a hardware logic device that is programmable Logic functions may be programmed
FPGA: FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY Verilog: a hardware description language Reference: [] FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY FPGA is a hardware logic device that is programmable Logic functions may be programmed
Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web:
 Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web: www.vhdl.us Appendix C Xilinx ISE Tutorial (ISE 11.1) This tutorial is based on ISE 11.1 WebPack (free at
Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web: www.vhdl.us Appendix C Xilinx ISE Tutorial (ISE 11.1) This tutorial is based on ISE 11.1 WebPack (free at
Application of Power-Management Techniques for Low Power Processor Design
 1 Application of Power-Management Techniques for Low Power Processor Design Sivaram Gopalakrishnan, Chris Condrat, Elaine Ly Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Utah, UT 84112
1 Application of Power-Management Techniques for Low Power Processor Design Sivaram Gopalakrishnan, Chris Condrat, Elaine Ly Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Utah, UT 84112
A Brief Introduction to Verilog Hardware Definition Language (HDL)
 www.realdigital.org A Brief Introduction to Verilog Hardware Definition Language (HDL) Forward Verilog is a Hardware Description language (HDL) that is used to define the structure and/or behavior of digital
www.realdigital.org A Brief Introduction to Verilog Hardware Definition Language (HDL) Forward Verilog is a Hardware Description language (HDL) that is used to define the structure and/or behavior of digital
Hardware Description of Multi-Directional Fast Sobel Edge Detection Processor by VHDL for Implementing on FPGA
 Hardware Description of Multi-Directional Fast Sobel Edge Detection Processor by VHDL for Implementing on FPGA Arash Nosrat Faculty of Engineering Shahid Chamran University Ahvaz, Iran Yousef S. Kavian
Hardware Description of Multi-Directional Fast Sobel Edge Detection Processor by VHDL for Implementing on FPGA Arash Nosrat Faculty of Engineering Shahid Chamran University Ahvaz, Iran Yousef S. Kavian
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
Philadelphia University Department of Computer Science. By Dareen Hamoudeh
 Philadelphia University Department of Computer Science By Dareen Hamoudeh 1.REGISTERS WHAT IS REGISTER? register is a quickly accessible location available to a computer's central processing unit (CPU).
Philadelphia University Department of Computer Science By Dareen Hamoudeh 1.REGISTERS WHAT IS REGISTER? register is a quickly accessible location available to a computer's central processing unit (CPU).
ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS)
 ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS) Objective Part A: To become acquainted with Spectre (or HSpice) by simulating an inverter,
ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS) Objective Part A: To become acquainted with Spectre (or HSpice) by simulating an inverter,
ENGN 1630: CPLD Simulation Fall ENGN 1630 Fall Simulating XC9572XLs on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board Using Xilinx ISim
 ENGN 1630 Fall 2018 Simulating XC9572XLs on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board Using Xilinx ISim You will use the Xilinx ISim simulation software for the required timing simulation of the XC9572XL CPLD programmable
ENGN 1630 Fall 2018 Simulating XC9572XLs on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board Using Xilinx ISim You will use the Xilinx ISim simulation software for the required timing simulation of the XC9572XL CPLD programmable
Verilog for Synthesis Ing. Pullini Antonio
 Verilog for Synthesis Ing. Pullini Antonio antonio.pullini@epfl.ch Outline Introduction to Verilog HDL Describing combinational logic Inference of basic combinational blocks Describing sequential circuits
Verilog for Synthesis Ing. Pullini Antonio antonio.pullini@epfl.ch Outline Introduction to Verilog HDL Describing combinational logic Inference of basic combinational blocks Describing sequential circuits
Overview. Memory Classification Read-Only Memory (ROM) Random Access Memory (RAM) Functional Behavior of RAM. Implementing Static RAM
 Memories Overview Memory Classification Read-Only Memory (ROM) Types of ROM PROM, EPROM, E 2 PROM Flash ROMs (Compact Flash, Secure Digital, Memory Stick) Random Access Memory (RAM) Types of RAM Static
Memories Overview Memory Classification Read-Only Memory (ROM) Types of ROM PROM, EPROM, E 2 PROM Flash ROMs (Compact Flash, Secure Digital, Memory Stick) Random Access Memory (RAM) Types of RAM Static
Module 4. Design of Embedded Processors. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 4 Design of Embedded Processors Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 23 Introduction to Hardware Description Languages-III Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives At the end of the
Module 4 Design of Embedded Processors Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 23 Introduction to Hardware Description Languages-III Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives At the end of the
EITF35 - Introduction to the Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2016) Interfacing Keyboard with FPGA Board. (FPGA Interfacing) Teacher: Dr.
 EITF35 - Introduction to the Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2016) Interfacing Keyboard with FPGA Board (FPGA Interfacing) Teacher: Dr. Liang Liu v.1.0.0 1 Abstract This document describes the basic behavior
EITF35 - Introduction to the Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2016) Interfacing Keyboard with FPGA Board (FPGA Interfacing) Teacher: Dr. Liang Liu v.1.0.0 1 Abstract This document describes the basic behavior
DYNAMIC CIRCUIT TECHNIQUE FOR LOW- POWER MICROPROCESSORS Kuruva Hanumantha Rao 1 (M.tech)
 DYNAMIC CIRCUIT TECHNIQUE FOR LOW- POWER MICROPROCESSORS Kuruva Hanumantha Rao 1 (M.tech) K.Prasad Babu 2 M.tech (Ph.d) hanumanthurao19@gmail.com 1 kprasadbabuece433@gmail.com 2 1 PG scholar, VLSI, St.JOHNS
DYNAMIC CIRCUIT TECHNIQUE FOR LOW- POWER MICROPROCESSORS Kuruva Hanumantha Rao 1 (M.tech) K.Prasad Babu 2 M.tech (Ph.d) hanumanthurao19@gmail.com 1 kprasadbabuece433@gmail.com 2 1 PG scholar, VLSI, St.JOHNS
One and a half hours. Section A is COMPULSORY
 One and a half hours Section A is COMPULSORY An additional answersheet is provided for Question 4. Please remember to complete the additional answersheet with your University ID number and attach it to
One and a half hours Section A is COMPULSORY An additional answersheet is provided for Question 4. Please remember to complete the additional answersheet with your University ID number and attach it to
Testability Optimizations for A Time Multiplexed CPLD Implemented on Structured ASIC Technology
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 14, Number 4, 2011, 392 398 Testability Optimizations for A Time Multiplexed CPLD Implemented on Structured ASIC Technology Traian TULBURE
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 14, Number 4, 2011, 392 398 Testability Optimizations for A Time Multiplexed CPLD Implemented on Structured ASIC Technology Traian TULBURE
Laboratory Exercise 3
 Laboratory Exercise 3 Latches, Flip-flops, and egisters The purpose of this exercise is to investigate latches, flip-flops, and registers. Part I Altera FPGAs include flip-flops that are available for
Laboratory Exercise 3 Latches, Flip-flops, and egisters The purpose of this exercise is to investigate latches, flip-flops, and registers. Part I Altera FPGAs include flip-flops that are available for
Project Timing Analysis
 Project Timing Analysis Jacob Schneider, Intel Corp Sanjeev Gokhale, Intel Corp Mark McDermott EE 382M Class Notes Overview Brief overview of global timing Example of extracting AT, RAT, and PASSTHROUGHs
Project Timing Analysis Jacob Schneider, Intel Corp Sanjeev Gokhale, Intel Corp Mark McDermott EE 382M Class Notes Overview Brief overview of global timing Example of extracting AT, RAT, and PASSTHROUGHs
ECE 4514 Digital Design II. Spring Lecture 20: Timing Analysis and Timed Simulation
 ECE 4514 Digital Design II Lecture 20: Timing Analysis and Timed Simulation A Tools/Methods Lecture Topics Static and Dynamic Timing Analysis Static Timing Analysis Delay Model Path Delay False Paths Timing
ECE 4514 Digital Design II Lecture 20: Timing Analysis and Timed Simulation A Tools/Methods Lecture Topics Static and Dynamic Timing Analysis Static Timing Analysis Delay Model Path Delay False Paths Timing
Readings: Storage unit. Can hold an n-bit value Composed of a group of n flip-flops. Each flip-flop stores 1 bit of information.
 Registers Readings: 5.8-5.9.3 Storage unit. Can hold an n-bit value Composed of a group of n flip-flops Each flip-flop stores 1 bit of information ff ff ff ff 178 Controlled Register Reset Load Action
Registers Readings: 5.8-5.9.3 Storage unit. Can hold an n-bit value Composed of a group of n flip-flops Each flip-flop stores 1 bit of information ff ff ff ff 178 Controlled Register Reset Load Action
FPGA briefing Part II FPGA development DMW: FPGA development DMW:
 FPGA briefing Part II FPGA development FPGA development 1 FPGA development FPGA development : Domain level analysis (Level 3). System level design (Level 2). Module level design (Level 1). Academical focus
FPGA briefing Part II FPGA development FPGA development 1 FPGA development FPGA development : Domain level analysis (Level 3). System level design (Level 2). Module level design (Level 1). Academical focus
Chapter 4 Implementation of a Test Circuit
 Chapter 4 Implementation of a Test Circuit We use a simplified cost model (which is the number of transistors) to evaluate the performance of our BIST design methods. Although the simplified cost model
Chapter 4 Implementation of a Test Circuit We use a simplified cost model (which is the number of transistors) to evaluate the performance of our BIST design methods. Although the simplified cost model
A Built-in Self-Test for System-on-Chip
 A Built-in Self-Test for System-on-Chip Rashid Rashidzadeh University of Windsor Digital 1 Objective : Design an intellectual property (IP) core which enables low speed Automatic Test Equipment (ATE) to
A Built-in Self-Test for System-on-Chip Rashid Rashidzadeh University of Windsor Digital 1 Objective : Design an intellectual property (IP) core which enables low speed Automatic Test Equipment (ATE) to
SHA3 Core Specification. Author: Homer Hsing
 SHA3 Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1 January 29, 2013 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1 ii Rev. Date Author Description 0.1 01/29/2013
SHA3 Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1 January 29, 2013 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1 ii Rev. Date Author Description 0.1 01/29/2013
RTL Coding General Concepts
 RTL Coding General Concepts Typical Digital System 2 Components of a Digital System Printed circuit board (PCB) Embedded d software microprocessor microcontroller digital signal processor (DSP) ASIC Programmable
RTL Coding General Concepts Typical Digital System 2 Components of a Digital System Printed circuit board (PCB) Embedded d software microprocessor microcontroller digital signal processor (DSP) ASIC Programmable
Dynamic Phase Alignment for Networking Applications Author: Tze Yi Yeoh
 XAPP7 (v.2) July 2, 25 Application te: Virtex-4 Family Dynamic Phase Alignment for Networking Applications Author: Tze Yi Yeoh Summary This application note describes a dynamic phase alignment (DPA) application
XAPP7 (v.2) July 2, 25 Application te: Virtex-4 Family Dynamic Phase Alignment for Networking Applications Author: Tze Yi Yeoh Summary This application note describes a dynamic phase alignment (DPA) application
A Universal Test Pattern Generator for DDR SDRAM *
 A Universal Test Pattern Generator for DDR SDRAM * Wei-Lun Wang ( ) Department of Electronic Engineering Cheng Shiu Institute of Technology Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C. wlwang@cc.csit.edu.tw used to detect
A Universal Test Pattern Generator for DDR SDRAM * Wei-Lun Wang ( ) Department of Electronic Engineering Cheng Shiu Institute of Technology Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C. wlwang@cc.csit.edu.tw used to detect
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 Memory 2
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 Memory 2 October 22, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec17-mem2 Page 1 SDRAM Recap General Characteristics Optimized for high density and therefore low cost/bit
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 Memory 2 October 22, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec17-mem2 Page 1 SDRAM Recap General Characteristics Optimized for high density and therefore low cost/bit
FPGA for Complex System Implementation. National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 04/14/2011
 FPGA for Complex System Implementation National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 04/14/2011 About FPGA FPGA was invented by Ross Freeman in 1989 SRAM-based FPGA properties Standard parts Allowing multi-level
FPGA for Complex System Implementation National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 04/14/2011 About FPGA FPGA was invented by Ross Freeman in 1989 SRAM-based FPGA properties Standard parts Allowing multi-level
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST
 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST SAKTHIVEL Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Coimbatore Institute of Engineering and Technology Abstract- FPGA is
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST SAKTHIVEL Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Coimbatore Institute of Engineering and Technology Abstract- FPGA is
Programmable Logic Devices
 Programmable Logic Devices INTRODUCTION A programmable logic device or PLD is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike a logic gate, which has a fixed function, a PLD
Programmable Logic Devices INTRODUCTION A programmable logic device or PLD is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike a logic gate, which has a fixed function, a PLD
COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 12. Testing and Design for Testability (focus: processors)
 1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 12 Testing and Design for Testability (focus: processors) Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University 1 Outline Testing
1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 12 Testing and Design for Testability (focus: processors) Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University 1 Outline Testing
LAB 5 Implementing an ALU
 Goals To Do Design a practical ALU LAB 5 Implementing an ALU Learn how to extract performance numbers (area and speed) Draw a block level diagram of the MIPS 32-bit ALU, based on the description in the
Goals To Do Design a practical ALU LAB 5 Implementing an ALU Learn how to extract performance numbers (area and speed) Draw a block level diagram of the MIPS 32-bit ALU, based on the description in the
Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm
 Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm Prof. Kris Gaj Gaurav Doshi, Hiren Shah Outlines Introduction Basic Idea CORDIC Principles Hardware Implementation FPGA & ASIC Results Conclusion Introduction CORDIC
Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm Prof. Kris Gaj Gaurav Doshi, Hiren Shah Outlines Introduction Basic Idea CORDIC Principles Hardware Implementation FPGA & ASIC Results Conclusion Introduction CORDIC
ECE 465, Spring 2010, Instructor: Prof. Shantanu Dutt. Project 2 : Due Fri, April 23, midnight.
 ECE 465, Spring 2010, Instructor: Prof Shantanu Dutt Project 2 : Due Fri, April 23, midnight 1 Goal The goals of this project are: 1 To design a sequential circuit that meets a given speed requirement
ECE 465, Spring 2010, Instructor: Prof Shantanu Dutt Project 2 : Due Fri, April 23, midnight 1 Goal The goals of this project are: 1 To design a sequential circuit that meets a given speed requirement
CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems. Storage
 CSEE 387: Fundamentals of Computer Systems Storage The big picture General purpose processor (e.g., Power PC, Pentium, MIPS) Internet router (intrusion detection, pacet routing, etc.) WIreless transceiver
CSEE 387: Fundamentals of Computer Systems Storage The big picture General purpose processor (e.g., Power PC, Pentium, MIPS) Internet router (intrusion detection, pacet routing, etc.) WIreless transceiver
Is Power State Table Golden?
 Is Power State Table Golden? Harsha Vardhan #1, Ankush Bagotra #2, Neha Bajaj #3 # Synopsys India Pvt. Ltd Bangalore, India 1 dhv@synopsys.com 2 ankushb@synopsys.com 3 nehab@synopsys.com Abstract: Independent
Is Power State Table Golden? Harsha Vardhan #1, Ankush Bagotra #2, Neha Bajaj #3 # Synopsys India Pvt. Ltd Bangalore, India 1 dhv@synopsys.com 2 ankushb@synopsys.com 3 nehab@synopsys.com Abstract: Independent
IEEE-754 compliant Algorithms for Fast Multiplication of Double Precision Floating Point Numbers
 International Journal of Research in Computer Science ISSN 2249-8257 Volume 1 Issue 1 (2011) pp. 1-7 White Globe Publications www.ijorcs.org IEEE-754 compliant Algorithms for Fast Multiplication of Double
International Journal of Research in Computer Science ISSN 2249-8257 Volume 1 Issue 1 (2011) pp. 1-7 White Globe Publications www.ijorcs.org IEEE-754 compliant Algorithms for Fast Multiplication of Double
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Rapid advances in integrated circuit technology have made it possible to fabricate digital circuits with large number of devices on a single chip. The advantages of integrated circuits
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Rapid advances in integrated circuit technology have made it possible to fabricate digital circuits with large number of devices on a single chip. The advantages of integrated circuits
Programming with HDLs
 Programming with HDLs Paul Chow February 11, 2008 1 Introduction The purpose of this document is to encourage the proper approach or mindset for programming in a hardware description language (HDL), particularly
Programming with HDLs Paul Chow February 11, 2008 1 Introduction The purpose of this document is to encourage the proper approach or mindset for programming in a hardware description language (HDL), particularly
Synthesizable FPGA Fabrics Targetable by the VTR CAD Tool
 Synthesizable FPGA Fabrics Targetable by the VTR CAD Tool Jin Hee Kim and Jason Anderson FPL 2015 London, UK September 3, 2015 2 Motivation for Synthesizable FPGA Trend towards ASIC design flow Design
Synthesizable FPGA Fabrics Targetable by the VTR CAD Tool Jin Hee Kim and Jason Anderson FPL 2015 London, UK September 3, 2015 2 Motivation for Synthesizable FPGA Trend towards ASIC design flow Design
Implementing Tile-based Chip Multiprocessors with GALS Clocking Styles
 Implementing Tile-based Chip Multiprocessors with GALS Clocking Styles Zhiyi Yu, Bevan Baas VLSI Computation Lab, ECE Department University of California, Davis, USA Outline Introduction Timing issues
Implementing Tile-based Chip Multiprocessors with GALS Clocking Styles Zhiyi Yu, Bevan Baas VLSI Computation Lab, ECE Department University of California, Davis, USA Outline Introduction Timing issues
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 7 - Computer Aided Design (CAD) - Part II (Logic Simulation) Finite State Machine Review
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 7 - Computer Aided Design (CAD) - Part II (Logic Simulation) Feb 9, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec7-CAD2 Page 1 Finite State Machine Review State Transition
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 7 - Computer Aided Design (CAD) - Part II (Logic Simulation) Feb 9, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec7-CAD2 Page 1 Finite State Machine Review State Transition
Chapter 1 Overview of Digital Systems Design
 Chapter 1 Overview of Digital Systems Design SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} February 8, 2017 Why Digital Design? Many times, microcontrollers
Chapter 1 Overview of Digital Systems Design SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} February 8, 2017 Why Digital Design? Many times, microcontrollers
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 5 - Verilog Logic Synthesis
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 5 - Verilog Logic Synthesis Jan 31, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec05-verilog_synth Page 1 Outline Quick review of essentials of state elements Finite State
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 5 - Verilog Logic Synthesis Jan 31, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec05-verilog_synth Page 1 Outline Quick review of essentials of state elements Finite State
11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices
 11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices February 2011 SIV51011-3.2 SIV51011-3.2 This chapter describes how to use the error detection cyclical redundancy check (CRC) feature when a Stratix IV device is
11. SEU Mitigation in Stratix IV Devices February 2011 SIV51011-3.2 SIV51011-3.2 This chapter describes how to use the error detection cyclical redundancy check (CRC) feature when a Stratix IV device is
Unique Journal of Engineering and Advanced Sciences Available online: Research Article
 ISSN 2348-375X Unique Journal of Engineering and Advanced Sciences Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article A POWER EFFICIENT CAM DESIGN USING MODIFIED PARITY BIT MATCHING TECHNIQUE Karthik
ISSN 2348-375X Unique Journal of Engineering and Advanced Sciences Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article A POWER EFFICIENT CAM DESIGN USING MODIFIED PARITY BIT MATCHING TECHNIQUE Karthik
An easy to read reference is:
 1. Synopsis: Timing Analysis and Timing Constraints The objective of this lab is to make you familiar with two critical reports produced by the Xilinx ISE during your design synthesis and implementation.
1. Synopsis: Timing Analysis and Timing Constraints The objective of this lab is to make you familiar with two critical reports produced by the Xilinx ISE during your design synthesis and implementation.
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 2: Datapath Design and Verification
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 2: Datapath Design and Verification In this lab, you will begin designing an 8-bit MIPS processor. You will first review and simulate a Verilog model of the overall processor. You
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 2: Datapath Design and Verification In this lab, you will begin designing an 8-bit MIPS processor. You will first review and simulate a Verilog model of the overall processor. You
FPGA Provides Speedy Data Compression for Hyperspectral Imagery
 FPGA Provides Speedy Data Compression for Hyperspectral Imagery Engineers implement the Fast Lossless compression algorithm on a Virtex-5 FPGA; this implementation provides the ability to keep up with
FPGA Provides Speedy Data Compression for Hyperspectral Imagery Engineers implement the Fast Lossless compression algorithm on a Virtex-5 FPGA; this implementation provides the ability to keep up with
SystemC-to-Layout ASIC Flow Walkthrough
 SystemC-to-Layout ASIC Flow Walkthrough 20.6.2015 Running the Demo You can execute the flow automatically by executing the csh shell script: csh run_asic_demo.csh The script runs all tools in a sequence.
SystemC-to-Layout ASIC Flow Walkthrough 20.6.2015 Running the Demo You can execute the flow automatically by executing the csh shell script: csh run_asic_demo.csh The script runs all tools in a sequence.
Design & Implementation of AHB Interface for SOC Application
 Design & Implementation of AHB Interface for SOC Application Sangeeta Mangal M. Tech. Scholar Department of Electronics & Communication Pacific University, Udaipur (India) enggsangeetajain@gmail.com Nakul
Design & Implementation of AHB Interface for SOC Application Sangeeta Mangal M. Tech. Scholar Department of Electronics & Communication Pacific University, Udaipur (India) enggsangeetajain@gmail.com Nakul
Laboratory Exercise 3 Comparative Analysis of Hardware and Emulation Forms of Signed 32-Bit Multiplication
 Laboratory Exercise 3 Comparative Analysis of Hardware and Emulation Forms of Signed 32-Bit Multiplication Introduction All processors offer some form of instructions to add, subtract, and manipulate data.
Laboratory Exercise 3 Comparative Analysis of Hardware and Emulation Forms of Signed 32-Bit Multiplication Introduction All processors offer some form of instructions to add, subtract, and manipulate data.
TEXAS INSTRUMENTS ANALOG UNIVERSITY PROGRAM DESIGN CONTEST MIXED SIGNAL TEST INTERFACE CHRISTOPHER EDMONDS, DANIEL KEESE, RICHARD PRZYBYLA SCHOOL OF
 TEXASINSTRUMENTSANALOGUNIVERSITYPROGRAMDESIGNCONTEST MIXED SIGNALTESTINTERFACE CHRISTOPHEREDMONDS,DANIELKEESE,RICHARDPRZYBYLA SCHOOLOFELECTRICALENGINEERINGANDCOMPUTERSCIENCE OREGONSTATEUNIVERSITY I. PROJECT
TEXASINSTRUMENTSANALOGUNIVERSITYPROGRAMDESIGNCONTEST MIXED SIGNALTESTINTERFACE CHRISTOPHEREDMONDS,DANIELKEESE,RICHARDPRZYBYLA SCHOOLOFELECTRICALENGINEERINGANDCOMPUTERSCIENCE OREGONSTATEUNIVERSITY I. PROJECT
Design Progression With VHDL Helps Accelerate The Digital System Designs
 Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 2006) Breaking Frontiers and Barriers in Engineering: Education, Research and Practice 21-23 June
Overview. Design flow. Principles of logic synthesis. Logic Synthesis with the common tools. Conclusions
 Logic Synthesis Overview Design flow Principles of logic synthesis Logic Synthesis with the common tools Conclusions 2 System Design Flow Electronic System Level (ESL) flow System C TLM, Verification,
Logic Synthesis Overview Design flow Principles of logic synthesis Logic Synthesis with the common tools Conclusions 2 System Design Flow Electronic System Level (ESL) flow System C TLM, Verification,
The University of Alabama in Huntsville ECE Department CPE Final Exam April 28, 2016
 The University of Alabama in Huntsville ECE Department CPE 426 01 Final Exam April 28, 2016 Name: 1. (6 points) Draw the transistor-level diagram of a two input CMOS NAND gate. 2. (5 points) If the NRE
The University of Alabama in Huntsville ECE Department CPE 426 01 Final Exam April 28, 2016 Name: 1. (6 points) Draw the transistor-level diagram of a two input CMOS NAND gate. 2. (5 points) If the NRE
Spiral 1 / Unit 6. Flip-flops and Registers
 1-5.1 Spiral 1 / Unit 6 Flip-flops and Registers 1-5.2 Outcomes I know the difference between combinational and sequential logic and can name examples of each. I understand latency, throughput, and at
1-5.1 Spiral 1 / Unit 6 Flip-flops and Registers 1-5.2 Outcomes I know the difference between combinational and sequential logic and can name examples of each. I understand latency, throughput, and at
CS250 VLSI Systems Design Lecture 9: Memory
 CS250 VLSI Systems esign Lecture 9: Memory John Wawrzynek, Jonathan Bachrach, with Krste Asanovic, John Lazzaro and Rimas Avizienis (TA) UC Berkeley Fall 2012 CMOS Bistable Flip State 1 0 0 1 Cross-coupled
CS250 VLSI Systems esign Lecture 9: Memory John Wawrzynek, Jonathan Bachrach, with Krste Asanovic, John Lazzaro and Rimas Avizienis (TA) UC Berkeley Fall 2012 CMOS Bistable Flip State 1 0 0 1 Cross-coupled
Tradeoff between coverage of a Markov prefetcher and memory bandwidth usage
 Tradeoff between coverage of a Markov prefetcher and memory bandwidth usage Elec525 Spring 2005 Raj Bandyopadhyay, Mandy Liu, Nico Peña Hypothesis Some modern processors use a prefetching unit at the front-end
Tradeoff between coverage of a Markov prefetcher and memory bandwidth usage Elec525 Spring 2005 Raj Bandyopadhyay, Mandy Liu, Nico Peña Hypothesis Some modern processors use a prefetching unit at the front-end
