Queueing Networks and Markov Chains
|
|
|
- Norah Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Queueing Networks and Markov Chains Modeling and Performance Evaluation with Computer Science Applications Gunter Bolch, Stefan Greiner, Hermann de Meer, and Kishor S. Trivedi A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane / Singapore / Toronto
2 Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction \ 1.1 Motivation Basics of Probabihty and Statistics Random Variables Discrete Random Variables Continuous Random, Variables Multiple Random Variables Independence Condiüonal ProbaHUty Irnportant Relations The Central Limit Theorem Tmnsforms z-transform Laplace Tra/asform, Parameter Estimation Method of Moments Maximum-Likelihood Estimation Confidance Intervall Order Statistics 30
3 1.2.6 Distribution of Sums 31 Markov Chains Markov Processes Stochastic and Markov Processes Markov Chains Discrete-Time Markov Chains Continuous-Time Markov Chains Recapitulation The Modeling Process Modeling Life-cycle Phases Performance Measures A Simple Example Markov Reward Models A Gase Study Generation Methods Petri Nets Generalized Stochastic Petri Nets Stochastic Reward Nets GSPN/SRN Analysis A Larger Example 98 Steady-State Solutions of Markov Chains Symbolic Solution: Birth-Death Process Hessenberg Matrix: Non-Markovian Queues Non-Exponential Service Times Server with Vacations Polling Systems Analysis Numerical Solution: Direct Methods Gaussian Elimination The Grassm.ann Algorithm Numerical Solution: Iterative Methods Convergence of Iterative Methods Power Method Jacobi's Method Gauss-Seidel Method 139 3J h 5 The Method of Successive Over-Relaxation 140
4 The Relaxation Parameter The Test of Convergence Overflow and Underflow The Algorithm Comparison of Numerical Solution Methods Gase Studies Steady-State Aggregation/Disaggregation Methods 153 J h l Courtois's Approximate Method Decomposition Applicabüity Analysis of the Substructures Aggregation and Unconditioning The Algorithm Takahashi's Iterative Method The Fundamental Equations Applicabüity The Algorithm Application Aggregation Disaggregation Final Remarks Transient Solution of Markov Chains Transient Analysis Using Exact Methods A Pure Birth Process A Two-State CTMC Solution Using Laplace Transforrns I Numerical Solution Using Uniformization The Instantaneous Gase Stiffness Tolerant Uniformization The Cumulaiive Gase Other Numerical Methods Ordinary Differential Equations Weak Lumpability Aggregation of Stiff Markov Chains Outline and Basic Definitions Aggregation of Fast Recurrent Subsets 192
5 5.2.3 Aggregation of Fast Transient Subsets Aggregation of Initial State Probahüities Disaggregations Fast Transient States Fast Recurrent States The Algorühm An Example: Server Breakdown and Repair Single Station Queueing Systems Kendall's Notation Performance Measures The M/M/l System The M/M/oo System The M/M/m System The M/M/l/K Fimte Capacity System Machine Repairman Model Closed Tandem Network The M/G/l System The GI/M/1 System The GI/M/m System The GI/G/1 System The M/G/m System The Gl/G/m System Priority Queueing System without Preemption Conservation Laws System with Preemption System with Time-Dependent Priorities The Asymmetrie System Approximate Analysis Exact Analysis Analysis of M/M/m Loss Systems Extending to Non-Lossy System Exact Analysis of an Asymmetrie System M/M/ Systems with Batch Service Queueing Networks 263
6 ix 7.1 Definitions and Notation Single Class Networks Multiclass Networks Performance Measures Single Class Networks Multiclass Networks Product-Form Queueing Networks Global Balance Local Balance Product-Form Jackson Networks Gordon/Newell Networks BCMP Networks The Concept of Chains BCMP Theorem 300 Algorühms for Product-Form Networks The Convolution Algorithm Single Class Closed Networks Multiclass Closed Networks The Mean Value Analysis Single Class Closed Networks Multiclass Closed Networks Mixed Networks Networks with Load-Dependent Service Closed Networks Mixed Networks The REGAL Method Flow Equivalent Server Method FES Method for a Single Node FES Method for Multiple Nödes Summary 376 Approximation Algorühms for Product-Form Networks Approximations Based on the MVA Bard-Schweitzer Approximation Self-Correcting Approximation Technique Single Server Nödes 385
7 Multiple Server Nödes Extended SC AT Algorithm Summaüon Method Single Class Networks Multiclass Networks Bottapprox Method Initial Value of X Single Class Networks 405 rr Multiclass Networks Bounds Analysis Asymptotic Bounds Analysis 4H Balanced Job Bounds Analysis Networks with Variabiliiies in Workload Summary 4^0 10 Algorithms for Non-Product-Form Networks Non-Exponential Bistributions 4^ Diffusion Approximation 4% Open Networks 4% Closed Networks Maximum Entropy Method Open Networks Closed Networks Decomposition for Open Networks Methods for Closed Networks 448 IO.I.4.I Robustness for Closed Networks 448 IOA.4.2 Marie 's Method Extended SUM and BOTT Closing Method for Mvxed Networks Different Service Times at FCFS Nodes Priority Networks 4^ Extended MVA (PRIOMVA) The Method of Shadow Server 4^ The Original Shadow Techmque Extensions of the Shadow Technique Extended SUM Sirnultaneous Resource Possession 407 IO.4.I Memory Constraints 498
8 xi I/O Subsystems Method of Surrogate Delays 504 IO.4.4 Serialization Programs with Internal Concurrency Parallel Processing Asynchronous Tasks Fork-Join Systems Modeimg Performance Measures Analysis Networks with Asymmetrie Nodes Closed Networks Asymmetrie SUM (ASUM) Asymmetrie MVA (AMVA) ASymmetrie SCAT (ASCA T) Open Networks Networks with Blocking Different Blocking Types Solution for Networks with Two Nodes Optimization Optimization Problems and Cost Functions OptirnizaMon based on the Summaüon Method Maximization of the Throughput Minimization of Cost Minimization of the Response Tim,e Optimization based on the Convolution Algorithm Maximization of the Throughput Optimal Design of Storage HierareMes Performance Analysis Tools PEPSY Structure of PEPSY The Input File The Output File Control Files Different Programs in PEPSY Example of using PEPSY 575
9 xii CONTENTS Graphieal User Interface XPEPSY SPNP SPNP Features The CSPL Language ispn MOSES The Model Descnption Language MOSEL Examples Central-Server Model Fault Tolerant Multiprocessor System SHARPE 594 I2.4.I Central-Server Queueing Network 594 T2.4.2 M/M/m/K System M/M/l/K System with Server Failure and Repair Charactertstics of Same Tools Applications Case Studies of Queueing Networks Multiprocessor Systems Tightly Coupled Systems Loosely Coupled Systems Client Server Systems Communication Systems Description of the System Queueing Network Model Model Parameters Results UNIX Kernel Model of the UNIX Kernel Analysis Flexible Production Systems An Open Network Model A Clos ed Network Model Case Studies. of Markov Chains Wafer Production System Polling Systems Client Server Systems 645
10 XIII ISDN Channel The Baseline Model Markov Modutated Poisson Processen ATM Network under Overload Case Studies of Hiemrchical Models A Multiprocessor with Different Cache Strategies Performabüity of a Multiprocessor System 674 Glossary ßjg Bibliography 691 Index
Software Tools for Network Modelling
 6 th International Conference on Applied Informatics Eger, Hungary, January 27 31, 2004. Software Tools for Network Modelling Attila Kuki a, János Sztrik b, Günter Bolch c a Department of Information Technology
6 th International Conference on Applied Informatics Eger, Hungary, January 27 31, 2004. Software Tools for Network Modelling Attila Kuki a, János Sztrik b, Günter Bolch c a Department of Information Technology
MOSEL MOdeling Specification and Evaluation Language
 1 MOdeling Specification and Evaluation Language Jörg Barner and Gunter Bolch University Erlangen / Germany Helmut Herold University of Applied Sciences Nürnberg / Germany Khalid Begain University Bradford
1 MOdeling Specification and Evaluation Language Jörg Barner and Gunter Bolch University Erlangen / Germany Helmut Herold University of Applied Sciences Nürnberg / Germany Khalid Begain University Bradford
Index. ADEPT (tool for modelling proposed systerns),
 Index A, see Arrivals Abstraction in modelling, 20-22, 217 Accumulated time in system ( w), 42 Accuracy of models, 14, 16, see also Separable models, robustness Active customer (memory constrained system),
Index A, see Arrivals Abstraction in modelling, 20-22, 217 Accumulated time in system ( w), 42 Accuracy of models, 14, 16, see also Separable models, robustness Active customer (memory constrained system),
Data Network Protocol Analysis & Simulation
 Module Details Title: Long Title: Data Network PENDING APPROVAL Data Network Module Code: EE509 Credits: 7.5 NFQ Level: 9 Field of Study: Electronic Engineering Valid From: 2017/18 (Sep 2017) Module Delivered
Module Details Title: Long Title: Data Network PENDING APPROVAL Data Network Module Code: EE509 Credits: 7.5 NFQ Level: 9 Field of Study: Electronic Engineering Valid From: 2017/18 (Sep 2017) Module Delivered
Queuing Networks. Renato Lo Cigno. Simulation and Performance Evaluation Queuing Networks - Renato Lo Cigno 1
 Queuing Networks Renato Lo Cigno Simulation and Performance Evaluation 2014-15 Queuing Networks - Renato Lo Cigno 1 Moving between Queues Queuing Networks - Renato Lo Cigno - Interconnecting Queues 2 Moving
Queuing Networks Renato Lo Cigno Simulation and Performance Evaluation 2014-15 Queuing Networks - Renato Lo Cigno 1 Moving between Queues Queuing Networks - Renato Lo Cigno - Interconnecting Queues 2 Moving
Method for Automatic Construction of Queuing System Models
 International Conference on Modelling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (MSAM 215) Method for Automatic Construction of Queuing System Models Eimutis Valakevicius * Department of Mathematical Modeling
International Conference on Modelling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (MSAM 215) Method for Automatic Construction of Queuing System Models Eimutis Valakevicius * Department of Mathematical Modeling
PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS
 PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS RICHARD O. DUDA PETER E. HART Stanford Research Institute, Menlo Park, California A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane
PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS RICHARD O. DUDA PETER E. HART Stanford Research Institute, Menlo Park, California A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane
Stochastic Simulation: Algorithms and Analysis
 Soren Asmussen Peter W. Glynn Stochastic Simulation: Algorithms and Analysis et Springer Contents Preface Notation v xii I What This Book Is About 1 1 An Illustrative Example: The Single-Server Queue 1
Soren Asmussen Peter W. Glynn Stochastic Simulation: Algorithms and Analysis et Springer Contents Preface Notation v xii I What This Book Is About 1 1 An Illustrative Example: The Single-Server Queue 1
Contents. I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1
 page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
THEORY OF LINEAR AND INTEGER PROGRAMMING
 THEORY OF LINEAR AND INTEGER PROGRAMMING ALEXANDER SCHRIJVER Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica, Amsterdam A Wiley-Inter science Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS^ Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore
THEORY OF LINEAR AND INTEGER PROGRAMMING ALEXANDER SCHRIJVER Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica, Amsterdam A Wiley-Inter science Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS^ Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore
Stochastic Processing Networks: What, Why and How? Ruth J. Williams University of California, San Diego
 Stochastic Processing Networks: What, Why and How? Ruth J. Williams University of California, San Diego http://www.math.ucsd.edu/~williams 1 OUTLINE! What is a Stochastic Processing Network?! Applications!
Stochastic Processing Networks: What, Why and How? Ruth J. Williams University of California, San Diego http://www.math.ucsd.edu/~williams 1 OUTLINE! What is a Stochastic Processing Network?! Applications!
Network Performance Analysis
 Network Performance Analysis Network Performance Analysis Thomas Bonald Mathieu Feuillet Series Editor Pierre-Noël Favennec First published 2011 in Great Britain and the United States by ISTE Ltd and
Network Performance Analysis Network Performance Analysis Thomas Bonald Mathieu Feuillet Series Editor Pierre-Noël Favennec First published 2011 in Great Britain and the United States by ISTE Ltd and
Fast Iterative Solvers for Markov Chains, with Application to Google's PageRank. Hans De Sterck
 Fast Iterative Solvers for Markov Chains, with Application to Google's PageRank Hans De Sterck Department of Applied Mathematics University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada joint work with Steve McCormick,
Fast Iterative Solvers for Markov Chains, with Application to Google's PageRank Hans De Sterck Department of Applied Mathematics University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada joint work with Steve McCormick,
Reliability and Dependability in Computer Networks. CS 552 Computer Networks Side Credits: A. Tjang, W. Sanders
 Reliability and Dependability in Computer Networks CS 552 Computer Networks Side Credits: A. Tjang, W. Sanders Outline Overall dependability definitions and concepts Measuring Site dependability Stochastic
Reliability and Dependability in Computer Networks CS 552 Computer Networks Side Credits: A. Tjang, W. Sanders Outline Overall dependability definitions and concepts Measuring Site dependability Stochastic
Teletraffic theory I: Queuing theory
 Teletraffic theory I: Queuing theory Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ 1. Place of the course TLT-2716 is a part of Teletraffic theory five
Teletraffic theory I: Queuing theory Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ 1. Place of the course TLT-2716 is a part of Teletraffic theory five
Mean Value Analysis and Related Techniques
 Mean Value Analysis and Related Techniques 34-1 Overview 1. Analysis of Open Queueing Networks 2. Mean-Value Analysis 3. Approximate MVA 4. Balanced Job Bounds 34-2 Analysis of Open Queueing Networks Used
Mean Value Analysis and Related Techniques 34-1 Overview 1. Analysis of Open Queueing Networks 2. Mean-Value Analysis 3. Approximate MVA 4. Balanced Job Bounds 34-2 Analysis of Open Queueing Networks Used
Queuing Networks Modeling Virtual Laboratory
 Queuing Networks Modeling Virtual Laboratory Dr. S. Dharmaraja Department of Mathematics IIT Delhi http://web.iitd.ac.in/~dharmar Queues Notes 1 1 Outline Introduction Simple Queues Performance Measures
Queuing Networks Modeling Virtual Laboratory Dr. S. Dharmaraja Department of Mathematics IIT Delhi http://web.iitd.ac.in/~dharmar Queues Notes 1 1 Outline Introduction Simple Queues Performance Measures
BROADBAND PACKET SWITCHING TECHNOLOGIES
 BROADBAND PACKET SWITCHING TECHNOLOGIES A Practical Guide to ATM Switches and IP Routers H. JONATHAN CHAO CHEUK H. LAM EMI OKI A Wiley-lnterscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York / Chichester
BROADBAND PACKET SWITCHING TECHNOLOGIES A Practical Guide to ATM Switches and IP Routers H. JONATHAN CHAO CHEUK H. LAM EMI OKI A Wiley-lnterscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York / Chichester
Integer and Combinatorial Optimization
 Integer and Combinatorial Optimization GEORGE NEMHAUSER School of Industrial and Systems Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia LAURENCE WOLSEY Center for Operations Research and
Integer and Combinatorial Optimization GEORGE NEMHAUSER School of Industrial and Systems Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia LAURENCE WOLSEY Center for Operations Research and
F. THOMSON LEIGHTON INTRODUCTION TO PARALLEL ALGORITHMS AND ARCHITECTURES: ARRAYS TREES HYPERCUBES
 F. THOMSON LEIGHTON INTRODUCTION TO PARALLEL ALGORITHMS AND ARCHITECTURES: ARRAYS TREES HYPERCUBES MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS SAN MATEO, CALIFORNIA Contents Preface Organization of the Material Teaching
F. THOMSON LEIGHTON INTRODUCTION TO PARALLEL ALGORITHMS AND ARCHITECTURES: ARRAYS TREES HYPERCUBES MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS SAN MATEO, CALIFORNIA Contents Preface Organization of the Material Teaching
Generalized Additive Models
 :p Texts in Statistical Science Generalized Additive Models An Introduction with R Simon N. Wood Contents Preface XV 1 Linear Models 1 1.1 A simple linear model 2 Simple least squares estimation 3 1.1.1
:p Texts in Statistical Science Generalized Additive Models An Introduction with R Simon N. Wood Contents Preface XV 1 Linear Models 1 1.1 A simple linear model 2 Simple least squares estimation 3 1.1.1
Multigrid Methods for Markov Chains
 Multigrid Methods for Markov Chains Hans De Sterck Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo collaborators Killian Miller Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo, Canada
Multigrid Methods for Markov Chains Hans De Sterck Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo collaborators Killian Miller Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo, Canada
COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS
 COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS THIRD EDITION AHMED A. SHABANA Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Engineering University of Illinois at Chicago A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS COMPUTATIONAL
COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS THIRD EDITION AHMED A. SHABANA Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Engineering University of Illinois at Chicago A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication COMPUTATIONAL DYNAMICS COMPUTATIONAL
The Octave Queueing Package
 The Octave Queueing Package User s Guide, Edition 1 for release 1.2.5 2016-12-06 Moreno Marzolla Copyright c 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2016 Moreno Marzolla (moreno.marzolla@unibo.it). This
The Octave Queueing Package User s Guide, Edition 1 for release 1.2.5 2016-12-06 Moreno Marzolla Copyright c 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2016 Moreno Marzolla (moreno.marzolla@unibo.it). This
Advances in Queueing Theory and Network Applications
 Advances in Queueing Theory and Network Applications Wuyi Yue Yutaka Takahashi Hideaki Takagi Editors Advances in Queueing Theory and Network Applications 123 Editors Wuyi Yue Department of Intelligence
Advances in Queueing Theory and Network Applications Wuyi Yue Yutaka Takahashi Hideaki Takagi Editors Advances in Queueing Theory and Network Applications 123 Editors Wuyi Yue Department of Intelligence
Approximate Analysis of a.. Multi-Class Open Queueing Network with Class Blocking and Push-Out r
 Approximate Analysis of a.. Multi-Class Open Queueing Network with Class Blocking and Push-Out r,tulin Atmaca ~~~}!.HarryG. Perros Yves Dallery Center for Communications and Signal Processing Department
Approximate Analysis of a.. Multi-Class Open Queueing Network with Class Blocking and Push-Out r,tulin Atmaca ~~~}!.HarryG. Perros Yves Dallery Center for Communications and Signal Processing Department
Mean Value Analysis and Related Techniques
 Mean Value Analysis and Related Techniques Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 34-1 Overview
Mean Value Analysis and Related Techniques Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 34-1 Overview
Dependable and Secure Systems Dependability
 Dependable and Secure Systems Dependability Master of Science in Embedded Computing Systems Quantitative Dependability Analysis with Stochastic Activity Networks: the Möbius Tool Andrea Domenici DII, Università
Dependable and Secure Systems Dependability Master of Science in Embedded Computing Systems Quantitative Dependability Analysis with Stochastic Activity Networks: the Möbius Tool Andrea Domenici DII, Università
Dependable and Secure Systems Dependability Master of Science in Embedded Computing Systems
 Dependable and Secure Systems Dependability Master of Science in Embedded Computing Systems Quantitative Dependability Analysis with Stochastic Activity Networks: the Möbius Tool April 2016 Andrea Domenici
Dependable and Secure Systems Dependability Master of Science in Embedded Computing Systems Quantitative Dependability Analysis with Stochastic Activity Networks: the Möbius Tool April 2016 Andrea Domenici
Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing
 \L\.6 Gw.i Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing A Practical Approach with Examples in Matlab Chris Solomon School of Physical Sciences, University of Kent, Canterbury, UK Toby Breckon School of Engineering,
\L\.6 Gw.i Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing A Practical Approach with Examples in Matlab Chris Solomon School of Physical Sciences, University of Kent, Canterbury, UK Toby Breckon School of Engineering,
Multi-Objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms
 Multi-Objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms Kalyanmoy Deb Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim
Multi-Objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms Kalyanmoy Deb Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim
Discrete Time Batch Arrival Queue with Multiple Vacations
 International Journal of Engineering Research Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 13, Issue 7 (July 2017), PP.49-55 Discrete Time Batch Arrival Queue with Multiple Vacations
International Journal of Engineering Research Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 13, Issue 7 (July 2017), PP.49-55 Discrete Time Batch Arrival Queue with Multiple Vacations
An Introduction to Queueing Systems
 An Introduction to Queueing Systems An lntroduction to Queueing Systems Sanjay K. Bose Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, lndia Springer Science+Business Media, LLC Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication
An Introduction to Queueing Systems An lntroduction to Queueing Systems Sanjay K. Bose Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, lndia Springer Science+Business Media, LLC Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication
Stochastic Petri nets
 Stochastic Petri nets 1 Stochastic Petri nets Markov Chain grows very fast with the dimension of the system Petri nets: High-level specification formalism Markovian Stochastic Petri nets adding temporal
Stochastic Petri nets 1 Stochastic Petri nets Markov Chain grows very fast with the dimension of the system Petri nets: High-level specification formalism Markovian Stochastic Petri nets adding temporal
Statistical Shape Analysis
 Statistical Shape Analysis I. L. Dryden and K. V. Mardia University ofleeds, UK JOHN WILEY& SONS Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto Contents Preface Acknowledgements xv xix 1 Introduction
Statistical Shape Analysis I. L. Dryden and K. V. Mardia University ofleeds, UK JOHN WILEY& SONS Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto Contents Preface Acknowledgements xv xix 1 Introduction
Exam Review TexPoint fonts used in EMF.
 Exam Review Generics Definitions: hard & soft real-time Task/message classification based on criticality and invocation behavior Why special performance measures for RTES? What s deadline and where is
Exam Review Generics Definitions: hard & soft real-time Task/message classification based on criticality and invocation behavior Why special performance measures for RTES? What s deadline and where is
Principles of Network Economics
 Hagen Bobzin Principles of Network Economics SPIN Springer s internal project number, if known unknown Monograph August 12, 2005 Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York Hong Kong London Milan Paris Tokyo Contents
Hagen Bobzin Principles of Network Economics SPIN Springer s internal project number, if known unknown Monograph August 12, 2005 Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York Hong Kong London Milan Paris Tokyo Contents
Simulation Modeling and Analysis
 Simulation Modeling and Analysis FOURTH EDITION Averill M. Law President Averill M. Law & Associates, Inc. Tucson, Arizona, USA www. averill-law. com Boston Burr Ridge, IL Dubuque, IA New York San Francisco
Simulation Modeling and Analysis FOURTH EDITION Averill M. Law President Averill M. Law & Associates, Inc. Tucson, Arizona, USA www. averill-law. com Boston Burr Ridge, IL Dubuque, IA New York San Francisco
QUESTION BANK UNIT I
 QUESTION BANK Subject Name: Operating Systems UNIT I 1) Differentiate between tightly coupled systems and loosely coupled systems. 2) Define OS 3) What are the differences between Batch OS and Multiprogramming?
QUESTION BANK Subject Name: Operating Systems UNIT I 1) Differentiate between tightly coupled systems and loosely coupled systems. 2) Define OS 3) What are the differences between Batch OS and Multiprogramming?
Integration of analytic model and simulation model for analysis on system survivability
 6 Integration of analytic model and simulation model for analysis on system survivability Jang Se Lee Department of Computer Engineering, Korea Maritime and Ocean University, Busan, Korea Summary The objective
6 Integration of analytic model and simulation model for analysis on system survivability Jang Se Lee Department of Computer Engineering, Korea Maritime and Ocean University, Busan, Korea Summary The objective
Contents. Preface xvii Acknowledgments. CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Parallel Computing 1. CHAPTER 2 Parallel Programming Platforms 11
 Preface xvii Acknowledgments xix CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Parallel Computing 1 1.1 Motivating Parallelism 2 1.1.1 The Computational Power Argument from Transistors to FLOPS 2 1.1.2 The Memory/Disk Speed
Preface xvii Acknowledgments xix CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Parallel Computing 1 1.1 Motivating Parallelism 2 1.1.1 The Computational Power Argument from Transistors to FLOPS 2 1.1.2 The Memory/Disk Speed
Structural Mechanics: Graph and Matrix Methods
 Structural Mechanics: Graph and Matrix Methods A. Kaveh Department of Civil Engineering Technical University of Vienna Austria RESEARCH STUDIES PRESS LTD. Taunton, Somerset, England 0 JOHN WILEY & SONS
Structural Mechanics: Graph and Matrix Methods A. Kaveh Department of Civil Engineering Technical University of Vienna Austria RESEARCH STUDIES PRESS LTD. Taunton, Somerset, England 0 JOHN WILEY & SONS
Lecture 5: Performance Analysis I
 CS 6323 : Modeling and Inference Lecture 5: Performance Analysis I Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork Slides: Based on M. Yin (Performability Analysis) Overview
CS 6323 : Modeling and Inference Lecture 5: Performance Analysis I Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork Slides: Based on M. Yin (Performability Analysis) Overview
Module 4: Stochastic Activity Networks
 Module 4: Stochastic Activity Networks Module 4, Slide 1 Stochastic Petri nets Session Outline Places, tokens, input / output arcs, transitions Readers / Writers example Stochastic activity networks Input
Module 4: Stochastic Activity Networks Module 4, Slide 1 Stochastic Petri nets Session Outline Places, tokens, input / output arcs, transitions Readers / Writers example Stochastic activity networks Input
IMAGE ANALYSIS, CLASSIFICATION, and CHANGE DETECTION in REMOTE SENSING
 SECOND EDITION IMAGE ANALYSIS, CLASSIFICATION, and CHANGE DETECTION in REMOTE SENSING ith Algorithms for ENVI/IDL Morton J. Canty с*' Q\ CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC
SECOND EDITION IMAGE ANALYSIS, CLASSIFICATION, and CHANGE DETECTION in REMOTE SENSING ith Algorithms for ENVI/IDL Morton J. Canty с*' Q\ CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC
Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Thread Scheduling Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time
Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Thread Scheduling Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time
Combinatorial Methods in Density Estimation
 Luc Devroye Gabor Lugosi Combinatorial Methods in Density Estimation Springer Contents Preface vii 1. Introduction 1 a 1.1. References 3 2. Concentration Inequalities 4 2.1. Hoeffding's Inequality 4 2.2.
Luc Devroye Gabor Lugosi Combinatorial Methods in Density Estimation Springer Contents Preface vii 1. Introduction 1 a 1.1. References 3 2. Concentration Inequalities 4 2.1. Hoeffding's Inequality 4 2.2.
Web application performance
 Web application performance A Lecture for LinuxDays 2017 by Ing. Tomáš Vondra Cloud Architect at Capacity planning Marketing gives you: estimate of the number of customers and its trend > You need to translate
Web application performance A Lecture for LinuxDays 2017 by Ing. Tomáš Vondra Cloud Architect at Capacity planning Marketing gives you: estimate of the number of customers and its trend > You need to translate
Programming with POSIX Threads
 Programming with POSIX Threads David R. Butenhof :vaddison-wesley Boston San Francisco New York Toronto Montreal London Munich Paris Madrid Capetown Sidney Tokyo Singapore Mexico City Contents List of
Programming with POSIX Threads David R. Butenhof :vaddison-wesley Boston San Francisco New York Toronto Montreal London Munich Paris Madrid Capetown Sidney Tokyo Singapore Mexico City Contents List of
Degrees of Freedom in Cached Interference Networks with Limited Backhaul
 Degrees of Freedom in Cached Interference Networks with Limited Backhaul Vincent LAU, Department of ECE, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (A) Motivation Interference Channels 3 No side information
Degrees of Freedom in Cached Interference Networks with Limited Backhaul Vincent LAU, Department of ECE, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (A) Motivation Interference Channels 3 No side information
f xx + f yy = F (x, y)
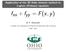 Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Multi-Objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms
 Multi-Objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms Kalyanmoy Deb Department ofmechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim
Multi-Objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms Kalyanmoy Deb Department ofmechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim
Buffer_1 Machine_1 Buffer_2 Machine_2. Arrival. Served
 Modeling and Performance Evaluation of Production Lines Using the Modeling Language MOSEL G. Bolch, S. Greiner IMMD IV { University Erlangen-Nuremberg Martensstrae 1, D { 91058 Erlangen, Germany E-mail:
Modeling and Performance Evaluation of Production Lines Using the Modeling Language MOSEL G. Bolch, S. Greiner IMMD IV { University Erlangen-Nuremberg Martensstrae 1, D { 91058 Erlangen, Germany E-mail:
Calculating Call Blocking, Preemption Probabilities, and Bandwidth Utilization for Satellite Communication Systems.
 Calculating Call Blocking, Preemption Probabilities, and Bandwidth Utilization for Satellite Communication Systems. Aero RIPS 2011 Leah Rosenbaum, Mohit Agrawal, Leah Birch, and Yacoub Kureh Academic Mentor
Calculating Call Blocking, Preemption Probabilities, and Bandwidth Utilization for Satellite Communication Systems. Aero RIPS 2011 Leah Rosenbaum, Mohit Agrawal, Leah Birch, and Yacoub Kureh Academic Mentor
Analysis of Computer and Communication Networks
 Fayez Gebali Analysis of Computer and Communication Networks Sprin er Contents 1 Probability 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Applying Set Theory to Probability 2 1.3 Counting Sample Space Points 4 1.4 The Multiplication
Fayez Gebali Analysis of Computer and Communication Networks Sprin er Contents 1 Probability 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Applying Set Theory to Probability 2 1.3 Counting Sample Space Points 4 1.4 The Multiplication
LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS
 LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS A Computer Science Perspective WINFRIED KARL GRASSMANN Department of Computer Science University of Saskatchewan JEAN-PAUL TREMBLAY Department of Computer Science University
LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS A Computer Science Perspective WINFRIED KARL GRASSMANN Department of Computer Science University of Saskatchewan JEAN-PAUL TREMBLAY Department of Computer Science University
TELCOM 2130 Queueing Theory. David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program. University of Pittsburgh
 TELCOM 2130 Queueing Theory David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Learning Objective To develop the modeling and mathematical skills
TELCOM 2130 Queueing Theory David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Learning Objective To develop the modeling and mathematical skills
Analysis of Replication Control Protocols
 Analysis of Replication Control Protocols Darrell D. E. Long University of California, Santa Cruz darrell@cis.ucsc.edu June 22, 2003 Abstract In recent years many replication control protocols have been
Analysis of Replication Control Protocols Darrell D. E. Long University of California, Santa Cruz darrell@cis.ucsc.edu June 22, 2003 Abstract In recent years many replication control protocols have been
Queuing Systems. 1 Lecturer: Hawraa Sh. Modeling & Simulation- Lecture -4-21/10/2012
 Queuing Systems Queuing theory establishes a powerful tool in modeling and performance analysis of many complex systems, such as computer networks, telecommunication systems, call centers, manufacturing
Queuing Systems Queuing theory establishes a powerful tool in modeling and performance analysis of many complex systems, such as computer networks, telecommunication systems, call centers, manufacturing
Epipolar Geometry in Stereo, Motion and Object Recognition
 Epipolar Geometry in Stereo, Motion and Object Recognition A Unified Approach by GangXu Department of Computer Science, Ritsumeikan University, Kusatsu, Japan and Zhengyou Zhang INRIA Sophia-Antipolis,
Epipolar Geometry in Stereo, Motion and Object Recognition A Unified Approach by GangXu Department of Computer Science, Ritsumeikan University, Kusatsu, Japan and Zhengyou Zhang INRIA Sophia-Antipolis,
Anany Levitin 3RD EDITION. Arup Kumar Bhattacharjee. mmmmm Analysis of Algorithms. Soumen Mukherjee. Introduction to TllG DCSISFI &
 Introduction to TllG DCSISFI & mmmmm Analysis of Algorithms 3RD EDITION Anany Levitin Villa nova University International Edition contributions by Soumen Mukherjee RCC Institute of Information Technology
Introduction to TllG DCSISFI & mmmmm Analysis of Algorithms 3RD EDITION Anany Levitin Villa nova University International Edition contributions by Soumen Mukherjee RCC Institute of Information Technology
Discrete, Continuous, and Hybrid Petri Nets
 Discrete, Continuous, and Hybrid Petri Nets Bearbeitet von René David, Hassane Alla 1. Auflage 2004. Buch. XXII, 570 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 22480 8 Format (B x L): 15,5 x 23,5 cm Gewicht: 2080 g Weitere
Discrete, Continuous, and Hybrid Petri Nets Bearbeitet von René David, Hassane Alla 1. Auflage 2004. Buch. XXII, 570 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 22480 8 Format (B x L): 15,5 x 23,5 cm Gewicht: 2080 g Weitere
Contents. I Basics 1. Copyright by SIAM. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
Modeling and Analysis of Computer Communications Networks
 Modeling and Analysis of Computer Communications Networks Applications of Communications Theory Series Editor: R. W. Lucky, Bell Laboratories INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SCIENCE AND SYSTEMS John R. Pierce
Modeling and Analysis of Computer Communications Networks Applications of Communications Theory Series Editor: R. W. Lucky, Bell Laboratories INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SCIENCE AND SYSTEMS John R. Pierce
Programming with the Java Media Framework
 Programming with the Java Media Framework Sean C. Sullivan Loren Winzeler Jeannie Deagen Deanna Brown WILEY COMPUTER PUBLISHING John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto
Programming with the Java Media Framework Sean C. Sullivan Loren Winzeler Jeannie Deagen Deanna Brown WILEY COMPUTER PUBLISHING John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto
Application Programming
 Multicore Application Programming For Windows, Linux, and Oracle Solaris Darryl Gove AAddison-Wesley Upper Saddle River, NJ Boston Indianapolis San Francisco New York Toronto Montreal London Munich Paris
Multicore Application Programming For Windows, Linux, and Oracle Solaris Darryl Gove AAddison-Wesley Upper Saddle River, NJ Boston Indianapolis San Francisco New York Toronto Montreal London Munich Paris
CPU Scheduling: Objectives
 CPU Scheduling: Objectives CPU scheduling, the basis for multiprogrammed operating systems CPU-scheduling algorithms Evaluation criteria for selecting a CPU-scheduling algorithm for a particular system
CPU Scheduling: Objectives CPU scheduling, the basis for multiprogrammed operating systems CPU-scheduling algorithms Evaluation criteria for selecting a CPU-scheduling algorithm for a particular system
7C.l.l ANALYSIS OF A QUEUEING NETWORK MODEL WITH CLASS DEPENDENT WINDOW FLOW CONTROL
 ANALYSIS OF A QUEUEING NETWORK MODEL WITH CLASS DEPENDENT WINDOW FLOW CONTROL H.G. Perrosl Computer Science Department, and Center for Communication and Signal - Processing - North Carolina State University
ANALYSIS OF A QUEUEING NETWORK MODEL WITH CLASS DEPENDENT WINDOW FLOW CONTROL H.G. Perrosl Computer Science Department, and Center for Communication and Signal - Processing - North Carolina State University
OPTIMIZING PRODUCTION WORK FLOW USING OPEMCSS. John R. Clymer
 Proceedings of the 2000 Winter Simulation Conference J. A. Joines, R. R. Barton, K. Kang, and P. A. Fishwick, eds. OPTIMIZING PRODUCTION WORK FLOW USING OPEMCSS John R. Clymer Applied Research Center for
Proceedings of the 2000 Winter Simulation Conference J. A. Joines, R. R. Barton, K. Kang, and P. A. Fishwick, eds. OPTIMIZING PRODUCTION WORK FLOW USING OPEMCSS John R. Clymer Applied Research Center for
A Customized MVA Model for ILP Multiprocessors
 A Customized MVA Model for ILP Multiprocessors Daniel J. Sorin, Mary K. Vernon, Vijay S. Pai, Sarita V. Adve, and David A. Wood Computer Sciences Dept University of Wisconsin - Madison sorin, vernon, david
A Customized MVA Model for ILP Multiprocessors Daniel J. Sorin, Mary K. Vernon, Vijay S. Pai, Sarita V. Adve, and David A. Wood Computer Sciences Dept University of Wisconsin - Madison sorin, vernon, david
The JMT Simulator for Performance Evaluation of Non-Product-Form Queueing Networks
 Politecnico di Milano - DEI Milan, Italy The JMT Simulator for Performance Evaluation of Non-Product-Form Queueing Networks Marco Bertoli, Giuliano Casale, Giuseppe Serazzi Speaker: Giuliano Casale March
Politecnico di Milano - DEI Milan, Italy The JMT Simulator for Performance Evaluation of Non-Product-Form Queueing Networks Marco Bertoli, Giuliano Casale, Giuseppe Serazzi Speaker: Giuliano Casale March
Operating System(16MCA24)
 PESIT- Bangalore South Campus Hosur Road (1km Before Electronic city) Bangalore 560 100 Department of MCA COURSE INFORMATION SHEET Operating System(16MCA24) 1. GENERAL INFORMATION Academic Year: 2017 Semester(s):I
PESIT- Bangalore South Campus Hosur Road (1km Before Electronic city) Bangalore 560 100 Department of MCA COURSE INFORMATION SHEET Operating System(16MCA24) 1. GENERAL INFORMATION Academic Year: 2017 Semester(s):I
Contents. 1 Introduction. 2 Searching and Traversal Techniques. Preface... (vii) Acknowledgements... (ix)
 Contents Preface... (vii) Acknowledgements... (ix) 1 Introduction 1.1 Algorithm 1 1.2 Life Cycle of Design and Analysis of Algorithm 2 1.3 Pseudo-Code for Expressing Algorithms 5 1.4 Recursive Algorithms
Contents Preface... (vii) Acknowledgements... (ix) 1 Introduction 1.1 Algorithm 1 1.2 Life Cycle of Design and Analysis of Algorithm 2 1.3 Pseudo-Code for Expressing Algorithms 5 1.4 Recursive Algorithms
Expectation Propagation
 Expectation Propagation Erik Sudderth 6.975 Week 11 Presentation November 20, 2002 Introduction Goal: Efficiently approximate intractable distributions Features of Expectation Propagation (EP): Deterministic,
Expectation Propagation Erik Sudderth 6.975 Week 11 Presentation November 20, 2002 Introduction Goal: Efficiently approximate intractable distributions Features of Expectation Propagation (EP): Deterministic,
Abstract. A Simde Exam& of Deadlock and Deadlock
 Performance Analysis of Aut~mated Manufacturing Systems with Blocking and Deadlock N. Viswanadham T.L. Johnson Y. Narahari Department of Computer Control Systems Laboratory Department of Computer Science
Performance Analysis of Aut~mated Manufacturing Systems with Blocking and Deadlock N. Viswanadham T.L. Johnson Y. Narahari Department of Computer Control Systems Laboratory Department of Computer Science
The Stochastic Rendezvous Network Model for. Performance of Synchronous Client-Server-like. Distributed Software
 The Stochastic Rendezvous Network Model for Performance of Synchronous Client-Server-like Distributed Software C.M. Woodside J.E. Neilson D.C. Petriu S. Majumdar Telecommunications Research Institute of
The Stochastic Rendezvous Network Model for Performance of Synchronous Client-Server-like Distributed Software C.M. Woodside J.E. Neilson D.C. Petriu S. Majumdar Telecommunications Research Institute of
Modelling and Quantitative Methods in Fisheries
 SUB Hamburg A/553843 Modelling and Quantitative Methods in Fisheries Second Edition Malcolm Haddon ( r oc) CRC Press \ y* J Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of
SUB Hamburg A/553843 Modelling and Quantitative Methods in Fisheries Second Edition Malcolm Haddon ( r oc) CRC Press \ y* J Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of
Syllabus for Ph.D Entrance Test, RGPV. Common for CSE/IT/CA
 Syllabus for Ph.D Entrance Test, RGPV. Common for CSE/IT/CA Algorithms: Algorithms and complexity; Combinatorics and graph theory; Geometric Algorithms, Parallel and Distributed Algorithms, Randomized
Syllabus for Ph.D Entrance Test, RGPV. Common for CSE/IT/CA Algorithms: Algorithms and complexity; Combinatorics and graph theory; Geometric Algorithms, Parallel and Distributed Algorithms, Randomized
Comparative Study of CPU Scheduling Algorithms based on Markov Chain
 Comparative Study of CPU Scheduling Algorithms based on Pradeep K. Jatav, Research Scholar, Faculty of Computer Science, Pacific Academy of Higher Education and Research University, Udaipur, INDIA Rahul
Comparative Study of CPU Scheduling Algorithms based on Pradeep K. Jatav, Research Scholar, Faculty of Computer Science, Pacific Academy of Higher Education and Research University, Udaipur, INDIA Rahul
Analytic Performance Models for Bounded Queueing Systems
 Analytic Performance Models for Bounded Queueing Systems Praveen Krishnamurthy Roger D. Chamberlain Praveen Krishnamurthy and Roger D. Chamberlain, Analytic Performance Models for Bounded Queueing Systems,
Analytic Performance Models for Bounded Queueing Systems Praveen Krishnamurthy Roger D. Chamberlain Praveen Krishnamurthy and Roger D. Chamberlain, Analytic Performance Models for Bounded Queueing Systems,
Ludwig Fahrmeir Gerhard Tute. Statistical odelling Based on Generalized Linear Model. íecond Edition. . Springer
 Ludwig Fahrmeir Gerhard Tute Statistical odelling Based on Generalized Linear Model íecond Edition. Springer Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition List of Examples List of Figures
Ludwig Fahrmeir Gerhard Tute Statistical odelling Based on Generalized Linear Model íecond Edition. Springer Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition List of Examples List of Figures
Telecommunications Engineering Course Descriptions
 Telecommunications Engineering Course Descriptions Electrical Engineering Courses EE 5305 Radio Frequency Engineering (3 semester hours) Introduction to generation, transmission, and radiation of electromagnetic
Telecommunications Engineering Course Descriptions Electrical Engineering Courses EE 5305 Radio Frequency Engineering (3 semester hours) Introduction to generation, transmission, and radiation of electromagnetic
10703 Deep Reinforcement Learning and Control
 10703 Deep Reinforcement Learning and Control Russ Salakhutdinov Machine Learning Department rsalakhu@cs.cmu.edu Policy Gradient I Used Materials Disclaimer: Much of the material and slides for this lecture
10703 Deep Reinforcement Learning and Control Russ Salakhutdinov Machine Learning Department rsalakhu@cs.cmu.edu Policy Gradient I Used Materials Disclaimer: Much of the material and slides for this lecture
Analysis of Panel Data. Third Edition. Cheng Hsiao University of Southern California CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Analysis of Panel Data Third Edition Cheng Hsiao University of Southern California CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the ThirdEdition Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition
Analysis of Panel Data Third Edition Cheng Hsiao University of Southern California CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the ThirdEdition Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition
Approximate Linear Programming for Average-Cost Dynamic Programming
 Approximate Linear Programming for Average-Cost Dynamic Programming Daniela Pucci de Farias IBM Almaden Research Center 65 Harry Road, San Jose, CA 51 pucci@mitedu Benjamin Van Roy Department of Management
Approximate Linear Programming for Average-Cost Dynamic Programming Daniela Pucci de Farias IBM Almaden Research Center 65 Harry Road, San Jose, CA 51 pucci@mitedu Benjamin Van Roy Department of Management
the Simulation of Dynamics Using Simulink
 INTRODUCTION TO the Simulation of Dynamics Using Simulink Michael A. Gray CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group an informa business
INTRODUCTION TO the Simulation of Dynamics Using Simulink Michael A. Gray CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group an informa business
Petri Nets ~------~ R-ES-O---N-A-N-C-E-I--se-p-te-m--be-r Applications.
 Petri Nets 2. Applications Y Narahari Y Narahari is currently an Associate Professor of Computer Science and Automation at the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. His research interests are broadly
Petri Nets 2. Applications Y Narahari Y Narahari is currently an Associate Professor of Computer Science and Automation at the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. His research interests are broadly
CLASSIFICATION AND CHANGE DETECTION
 IMAGE ANALYSIS, CLASSIFICATION AND CHANGE DETECTION IN REMOTE SENSING With Algorithms for ENVI/IDL and Python THIRD EDITION Morton J. Canty CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYork CRC
IMAGE ANALYSIS, CLASSIFICATION AND CHANGE DETECTION IN REMOTE SENSING With Algorithms for ENVI/IDL and Python THIRD EDITION Morton J. Canty CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYork CRC
OPTIMAL DESIGN OF NETWORKS OF GENERAL FINITE MULTI-SERVER QUEUES
 OPTIMAL DESIGN OF NETWORKS OF GENERAL FINITE MULTI-SERVER QUEUES Frederico R. B. Cruz- e-mail: fcruz@est.ufmg.br Federal University of Minas Gerais, Department of Statistics Av. Antônio Carlos, 6627-31270-901
OPTIMAL DESIGN OF NETWORKS OF GENERAL FINITE MULTI-SERVER QUEUES Frederico R. B. Cruz- e-mail: fcruz@est.ufmg.br Federal University of Minas Gerais, Department of Statistics Av. Antônio Carlos, 6627-31270-901
ANALYSIS OF GEOPHYSICAL POTENTIAL FIELDS A Digital Signal Processing Approach
 ADVANCES IN EXPLORATION GEOPHYSICS 5 ANALYSIS OF GEOPHYSICAL POTENTIAL FIELDS A Digital Signal Processing Approach PRABHAKAR S. NAIDU Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India AND M.P. MATHEW
ADVANCES IN EXPLORATION GEOPHYSICS 5 ANALYSIS OF GEOPHYSICAL POTENTIAL FIELDS A Digital Signal Processing Approach PRABHAKAR S. NAIDU Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India AND M.P. MATHEW
The A* traffic process in a queue with feedback
 The A traffic process in a queue with feedback Elizabeth Varki Abstract This paper establishes the A traffic process in queueing networks. The A traffic process links open and closed networks, and explains
The A traffic process in a queue with feedback Elizabeth Varki Abstract This paper establishes the A traffic process in queueing networks. The A traffic process links open and closed networks, and explains
Simulation of Reliability in Multi-server Computer Networks
 Simulation of Reliability in Multi-server Computer Networks SAULIUS MINKEVIČIUS, VU Institute of Mathematics Informatics, Akademijos 4, 08663 Vilnius, Lithuania Vilnius University Mathematics Informatics
Simulation of Reliability in Multi-server Computer Networks SAULIUS MINKEVIČIUS, VU Institute of Mathematics Informatics, Akademijos 4, 08663 Vilnius, Lithuania Vilnius University Mathematics Informatics
Using Queuing theory the performance measures of cloud with infinite servers
 Using Queuing theory the performance measures of cloud with infinite servers A.Anupama Department of Information Technology GMR Institute of Technology Rajam, India anupama.a@gmrit.org G.Satya Keerthi
Using Queuing theory the performance measures of cloud with infinite servers A.Anupama Department of Information Technology GMR Institute of Technology Rajam, India anupama.a@gmrit.org G.Satya Keerthi
MOBILITY MODELS FOR NEXT WIRELESS NETWORKS GENERATION WILEY AD HOC, VEHICULAR AND MESH NETWORKS. Paolo Santi
 MOBILITY MODELS FOR NEXT GENERATION WIRELESS NETWORKS AD HOC, VEHICULAR AND MESH NETWORKS Paolo Santi Istituto di Informatica e Telematica del CNR, Italy WILEY A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents
MOBILITY MODELS FOR NEXT GENERATION WIRELESS NETWORKS AD HOC, VEHICULAR AND MESH NETWORKS Paolo Santi Istituto di Informatica e Telematica del CNR, Italy WILEY A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents
Structured Parallel Programming Patterns for Efficient Computation
 Structured Parallel Programming Patterns for Efficient Computation Michael McCool Arch D. Robison James Reinders ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO
Structured Parallel Programming Patterns for Efficient Computation Michael McCool Arch D. Robison James Reinders ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO
CONTENTS. Computer-System Structures
 CONTENTS PART ONE OVERVIEW Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What Is an Operating System? 3 1.2 Simple Batch Systems 6 1.3 Multiprogrammed Batched Systems 8 1.4 Time-Sharing Systems 9 1.5 Personal-Computer Systems
CONTENTS PART ONE OVERVIEW Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What Is an Operating System? 3 1.2 Simple Batch Systems 6 1.3 Multiprogrammed Batched Systems 8 1.4 Time-Sharing Systems 9 1.5 Personal-Computer Systems
QUEUEING NETWORKS- CUSTOMERS, SIGNALS,
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Stochastic Analysis, 14:4 (2001), 421-426. QUEUEING NETWORKS- CUSTOMERS, SIGNALS, AND PRODUCT FORM SOLUTIONS by X. Chao, M. Miyazawa, and M. Pincdo and INTRODUCTION TO
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Stochastic Analysis, 14:4 (2001), 421-426. QUEUEING NETWORKS- CUSTOMERS, SIGNALS, AND PRODUCT FORM SOLUTIONS by X. Chao, M. Miyazawa, and M. Pincdo and INTRODUCTION TO
Graph Coloring Problems
 Graph Coloring Problems TOMMY R. JENSEN BJARNE TOFT Odense University A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction
Graph Coloring Problems TOMMY R. JENSEN BJARNE TOFT Odense University A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction
GRAPHS: THEORY AND ALGORITHMS
 GRAPHS: THEORY AND ALGORITHMS K. THULASIRAMAN M. N. S. SWAMY Concordia University Montreal, Canada A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York / Chichester / Brisbane / Toronto /
GRAPHS: THEORY AND ALGORITHMS K. THULASIRAMAN M. N. S. SWAMY Concordia University Montreal, Canada A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York / Chichester / Brisbane / Toronto /
these developments has been in the field of formal methods. Such methods, typically given by a
 PCX: A Translation Tool from PROMELA/Spin to the C-Based Stochastic Petri et Language Abstract: Stochastic Petri ets (SPs) are a graphical tool for the formal description of systems with the features of
PCX: A Translation Tool from PROMELA/Spin to the C-Based Stochastic Petri et Language Abstract: Stochastic Petri ets (SPs) are a graphical tool for the formal description of systems with the features of
