Planing, Cabling, Configuring and Testing Your Network
|
|
|
- Dorothy Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Planing, Cabling, Configuring and Testing Your Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 10, 11 1
2 Obsah Príklad malej siete Návrh HW Realizácia zapojenia a kabeláže Konfigurácia smerovačov Overenie funckionality 2
3 Classless subsieťovanie Vzor firma D (VLSM) ISP Romulus Tristan Fa 0/0 PC S 0/0/0 S 0/0/0 Fa 0/1 Fa 0/1 Fa 0/1 Fa 0/1 Fa 0/2 Fa 0/2 PC Remus Isolda Pridelený adresný rozsah: Maska: / Adresné požiadavky: LAN1: 100 LAN2: 60 Prepoj: 2 Koľko sietí máme v topológii? LAN1 LAN2 3
4 Classless subsieťovanie počiatočná úvaha Pravidlo: Musím uspokojiť požiadavky od najväčších k menším Krok 1 Ktorá sieť má najvyššiu požiadavku na adresný priestor? Lan 1, 100 IP adries Vykonáme subsieťovanie na uspokojenie tejto požiadavky: Koľko bitov musí ostať v host ID? 7 bitov (2 7 =128) Aké adresy podsietí vzniknú? /25 použijeme pre Lan /25 zatiaľ nepoužitá Krok 2 Ktorá sieť má druhú najvyššiu požiadavku na adresný priestor? Lan 2, 60 IP adries Vykonáme subsieťovanie na uspokojenie tejto požiadavky, avšak ostáva nám už len časť nepoužitého adresného priestoru /25 Koľko bitov musí ostať v host ID? 6 bitov (2 6 =64) Aké adresy podsietí vzniknú? /26 použijeme pre Lan /26 zatiaľ nepoužitá 4
5 Classless subsieťovanie počiatočná úvaha Krok 3 Ktorá sieť má tretiu najvyššiu požiadavku na adresný priestor? Prepoje smerovačov, 2 IP adries Vykonáme subsieťovanie na uspokojenie tejto požiadavky, avšak ostáva nám už len časť nepoužitého adresného priestoru /26 Koľko bitov musí ostať v host ID? 2 bitov (2 2 =4) Aké adresy podsietí vzniknú? /30 použijeme pre Core prepoj /30 zatiaľ nepoužitá /30 zatiaľ nepoužitá 5
6 Classless subsieťovanie - výsledok Subsiete vzniknuté subsieťovaním pôvodného adresného rozsahu /24 variabilne Podsieť Adresa podsiete Maska podsiete Prvá použiteľná adresa Posledná použiteľná adresa Broadcastová adresa LAN LAN Prepoj
7 Classless subsieťovanie pridelenie adries ISP Prepoj: k ISP: dodá ISP Fa 0/ Romulus Remus Fa 0/1 Fa 0/ S 0/0/0 S 0/0/0.129 Fa 0/1 Fa 0/1 LAN1: Tristan.2 Fa 0/2 Fa 0/2 Isolda.130 LAN2: PC PC 7
8 Úloha zadanie Vykonajte variabilné subsieťovanie Pridelený adresový rozsah: Maska: Adresové požiadavky: LAN1: LAN2: Prepoj: Vykonajte pridelenie adresového priestoru do sietí Rozdelenie adries sietí Pridelenie IP adries rozhraniam zariadení (smerovačov) Pridelenie IP adries zariadeniam (prepínačom) 8
9 Oboznámenie sa s HW potrebným pre riešenie Smerovače 1841 a 2811 Prepínače TT-L 9
10 Realizácia vyžaduje Prípravu, plánovanie, dokumentáciu (PPDIOO) Výber vhodného hardvéru pre LAN a WAN, vrátane realizácie kabeláže 10
11 Výber hardvéru Pri výbere HW je potrebné zvážiť Vlastnosti zariadenia IOS features (PPPoE, smerovanie-protokoly, NAT, QOS, VoIP, bezpečnosť) Cenu Počet, typ a rýchlosť portov/rozhraní Rozšíriteľnosť (modularita) Manažovateľnosť Veľkosť (form factor) Špeciálne fcie (PoE) 11
12 Cisco prístupový smerovač 1841 predný pohľad Konzolový port 12
13 Cisco prístupový smerovač 1841 zadný pohľad 13
14 Cisco prístupový smerovač 2811 zadný pohľad NM-ESW- 16 modul (prepínač 16xFastEth ernet) 1x NM slot (Network module) 4x WIC sloty, poskytujúc e modularitu 1x WIC2T modul e (2x E1) 2x - 10/100Mbps FastEthernet fixné porty 14
15 Sieťové moduly - WIC 2T module 15
16 Príklady iných sieťových rozhraní pre modulárne smerovače 18xx/28xx 3-port FastEthernet HWIC 4 portový prepínač -WIC- 4ESW ADLS WIC WiFI AP modul 16
17 Smerovače Service provider 7600 series routes Carrier Routing System CRS-3 17
18 HW pre LAN 18
19 Kritéria pre výber LAN prepínačov Ako všeobecne pre sieťový HW cena, port, rýchlosť vlastnosti a pod. Okrem toho dizajnový pohľad počet a umiestnenie HW 19
20 Realizácia LAN Cisco prístupový prepínač TT-L predný pohľad LED indikátory stavu prepínača 24x - Fyzické downlink rozhrania 10/100Mbps s LED indikátormi 2x - Fyzické uplink rozhrania 10/100/1000 Mbps 20
21 Cisco prístupový prepínač TT-L zadný pohľad 21
22 Zapnutie prepínača Prepínače zvyčajne nemajú napájacie tlačidlo Zapínajú a vypínajú sa pripojením napájacieho kábla do napätia 22
23 Prepínače LAN Core Catalyst 6500 Catalyst 4500E 23
24 Média a pripojenie - Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) 24
25 Typy spojení v LAN/WAN 25
26 Kabeláž v LAN 26
27 Priamy a krížený UTP kábel - pinout 27
28 UTP konzolový kábel (rollover) 28
29 UTP konzolový kábel (rollover) RJ-45 to RJ-45 UTP rollover PC serial port DB9 to RJ-45 adapter 29
30 WAN spojenia 30
31 Základy konfigurácie smerovačov 31
32 Pripojenie na konzolu prenosová cesta Prenosová cesta Schématický nákres 32
33 Pripojenie na konzolu cez HyperTerminál - pokyny Založ fyzickú prenosovú cestu Zapni zariadenie (smerovač / prepínač) Spusti HT Start > Programs > Accessories > Communications > HyperTerminal Pomenuj reláciu v poli Name 33
34 Konfigurácia HT Vyber komunikačné rozhranie Nastav jeho parametre 34
35 Pripojenie na konzolu cez Putty - pokyny Založ fyzickú prenosovú cestu Zapni zariadenie (smerovač / prepínač) Spusti Putty / špecifikuj cieľ Vyber z Category vľavo dole Connection Serial Nastav parametre spojenia 35
36 Základná konfigurácia smerovača 36
37 Príkazový riadok Cisco IOS Cisco zariadenia sa spravujú obvykle prostredníctvom textového príkazového riadku CLI Command Line Interface Cisco má vlastný jazyk a sadu príkazov Podporované príkazy závisia od verzie operačného systému IOS a od samotného zariadenia Typ: smerovač, prepínač... Technické vlastnosti: rozhrania, moduly, rozširujúce karty... 37
38 Príkazový riadok Cisco IOS CLI sa sčasti podobá príkazovému riadku operačného systému Má prompt (úvodnú výzvu) Router> Informuje nás o aktuálnej polohe v prostredí operačného systému IOS Router(config-if)# Spracúva naše príkazy a poskytuje výsledky, prípadne informuje o chybe 38
39 Prístupové práva v CLI V CLI existujú prístupové práva, štandardne Používateľský prístup Privilegovaný prístup Používateľský prístup obsahuje prístup len k obmedzenej sade príkazov Je charakteristický výzvou, ktorá končí znakom > Router> Pre nastavovanie zariadenia je potrebný privilegovaný režim Prístup do používateľského režimu je možné zabezpečiť heslom 39
40 Privilegovaný režim CLI Prechod do privilegovaného režimu sa realizuje zadaním príkazu enable Router> enable Router# Privilegovaný režim je charakteristický vo výzve znakom # Prechod do privilegovaného režimu je možné (a potrebné) neskôr zabezpečiť heslom 40
41 Nápoveda CLI CLI obsahuje veľké množstvo príkazov Zoznam príkazov, ktoré sú v momentálnom stave prípustné, je možné zobraziť zadaním znaku? Router#? Exec commands: access-enable Create a temporary Access-List entry access-profile Apply user-profile to interface access-template Create a temporary Access-List entry archive manage archive files bfe For manual emergency modes setting cd Change current directory clear Reset functions clock Manage the system clock 41
42 Nápoveda CLI Príkazy môžu byť viacslovné (viac argumentové) Znak? zadaný za príkazom zobrazí zoznam slov, ktorými môže príkaz pokračovať na mieste znaku? Router#configure? memory network terminal <cr> Router#configure Configure from NV memory Configure from a TFTP network host Configure from the terminal 42
43 Nápoveda CLI Príkazy nie je potrebné písať celými slovami Stačí napísať začiatočné písmená, ktorými slovo začína, a stlačiť <TAB> Router#conf<TAB> Router#configure Môže sa stať, že zadanými písmenami začína niekoľko príkazov v takom prípade <TAB> nevie slovo doplniť Router#con<TAB> Router#con 43
44 Nápoveda CLI V takom prípade je opäť užitočné použiť znak? Ak sa znak? napíše priamo bez medzery za slovo alebo jeho začiatok... Zobrazí zoznam všetkých príkazov, ktoré začínajú danými písmenami Router#con? configure connect Router# 44
45 Zadávanie a úprava príkazov v CLI Po rozpísanom príkaze je možné pohybovať sa doľava a doprava kurzorovými šípkami Vhodné pre opravu chýb Bežne nefunguje kláves <Del>, namiesto neho treba použiť klávesovú kombináciu <Ctrl><D> Kláves <Backspace> funguje normálne Klávesy <Home> a <End> nefungujú, namiesto nich je možné použiť kombinácie <Ctrl><A> a <Ctrl><E> Príkaz je možné odoslať klávesom <Enter> nezávisle na tom, v ktorom mieste riadku sa nachádza kurzor Nie je potrebné presunúť kurzor na koniec riadku pred odoslaním príkazu 45
46 Zadávanie a úprava príkazov v CLI CLI si pamätá históriu príkazov zadaných od posledného prihlásenia sa k zariadeniu Tieto príkazy je možné spätne vyvolať kurzorovými šípkami nahor a nadol Vyvolaný príkaz je možné bežným spôsobom upraviť, ak je to potrebné, a odoslať 46
47 Úloha zadanie Skúste len s využitím nápovedy nájsť a správne použiť príkaz privilegovaného režimu, ktorý nastavuje systémový čas 47
48 Príkazy show Existuje veľké množstvo príkazov, ktoré začínajú slovom show Zobrazenie rôznych informácií o smerovači, jeho komponentoch, stave a konfigurácii 48
49 Konfiguračný režim CLI V privilegovanom režime CLI máme nad zariadením neobmedzenú moc Privilegovaný režim je ale stále režim príkazový Priamo v ňom sa ešte konfigurácia nedá upravovať Ak je potrebné upraviť konfiguráciu zariadenia, je potrebné v privilegovanom režime zadať príkaz, ktorým sa spúšťa editor konfigurácie Režim, v ktorom sa konfigurácia upravuje, sa nazýva konfiguračný režim 49
50 Konfiguračný režim CLI Do konfiguračného režimu sa vstupuje príkazom configure terminal Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)# V konfiguračnom režime nie je možné priamo použiť príkazy (ne)privilegovaného režimu Konfiguračný režim má vlastnú sadu príkazov Samozrejme aj v ňom sú použiteľné všetky pomôcky <TAB>,?, kurzorové šípky... 50
51 Konfiguračný režim CLI Konfiguračný režim, do ktorého sa dostaneme hneď po príkaze configure terminal, sa nazýva globálny konfiguračný režim (GKR) V GKR sa zadávajú príkazy so všeobecnou platnosťou pre celé zariadenie Z GKR je možné prejsť do mnohých podrežimov, v ktorých sa konfiguruje istá konkrétna súčasť zariadenia Sieťové alebo manažmentové rozhranie Smerovací protokol DHCP server Konfiguračný režim má teda hierarchickú štruktúru na najvyššej úrovni je GKR, pod ním sú jednotlivé podrežimy Konfiguračný režim je možné na ktorejkoľvek úrovni ukončiť príkazom end alebo kombináciou <Ctrl><Z> 51
52 Konfigurácia smerovača Odporúčaný postup pre konfiguráciu smerovača 1. Nastavenie mena zariadenia 2. Zabezpečenie prístupu k smerovaču pomocou hesiel 3. Konfigurácia sieťových rozhraní 4. Konfigurácia smerovania Tento postup nie je záväzný, ale je osvedčený 52
53 Nastavenie mena smerovača Meno smerovača sa nastavuje v GKR príkazom hostname Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#hostname Romulus Romulus(config)# Meno môže byť ľubovoľné Nemôže obsahovať medzery Odporúča sa, aby malo aspoň dve písmená 53
54 Zabezpečenie prístupu k smerovaču pomocou hesiel Nenakonfigurovaný smerovač nevyžaduje heslo ani pre prihlásenie k používateľskému režimu, ani pre prechod do privilegovaného režimu Kvôli bezpečnosti je preto potrebné obe tieto činnosti ochrániť heslom Heslo pre prechod do privilegovaného režimu sa konfiguruje v GKR príkazom enable secret Romulus(config)#enable secret TajneHeslo456 Romulus(config)# 54
55 Zabezpečenie prístupu k smerovaču pomocou hesiel Od tohto momentu je použitie príkazu enable chránené zadaným heslom Romulus(config)#end Romulus# *Mar 1 19:22:24.079: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console Romulus#disable Romulus>enable Password: TajneHeslo456 Romulus# 55
56 Zabezpečenie prístupu k smerovaču pomocou hesiel Zatiaľ však nie je zabezpečený prístup k používateľskému režimu Ktokoľvek môže prísť, zapojiť sa do konzolového portu a hneď získa používateľský režim Je vlastne potrebné zabezpečiť heslom jednotlivé manažmentové rozhrania na smerovači 1. Konzolu (con) 2. Pomocnú konzolu (aux) 3. Možnosť konfigurácie cez sieť (vty) 56
57 Zabezpečenie prístupu k smerovaču pomocou hesiel Zabezpečenie prístupu k príkazovému riadku cez konzolu sa deje v konfigurácii konzoly Vychádzame z GKR a budú potrebné tri príkazy line con 0 Prechod do podrežimu pre konfiguráciu konzoly password Definovanie hesla login Zapne overovanie hesla Romulus(config)#line con 0 Romulus(config-line)#password Heslo123 Romulus(config-line)#login 57
58 Zabezpečenie prístupu k smerovaču pomocou hesiel Z podrežimu pre konfiguráciu konzoly sa vrátime do GKR príkazom exit Romulus(config-line)#exit Romulus(config)# Od tohto momentu bude smerovač už pri novom prístupe cez konzolu vyžadovať zadané heslo Press RETURN to get started. User Access Verification Password: Heslo123 Romulus>enable Password: TajneHeslo456 Romulus# 58
59 Zabezpečenie prístupu k smerovaču pomocou hesiel Takto je zabezpečený port konzoly, no je potrebné zabezpečiť aj aux port, aj možnosti pre správu smerovača cez sieť Príkazy sú prakticky identické, líšia sa iba v názve manažmentového portu, na ktorom nastavujeme heslo Romulus(config)#line aux 0 Romulus(config-line)#password Heslo123 Romulus(config-line)#login Romulus(config-line)#exit Romulus(config)#line vty 0 4 Romulus(config-line)#password Heslo123 Romulus(config-line)#login Romulus(config-line)#exit Romulus(config)# 59
60 Konfigurácia sieťových rozhraní Sieťové rozhrania na smerovačoch majú označenie slovom a číslom Slovo označuje hardvérový typ rozhrania Serial FastEthernet BRI Číslo označuje jeho polohu v smerovači, na nových smerovačoch má tvar X/Y/Z X: shelf číslo zásuvnej dosky Y: slot číslo modulu v shelfe Z: port konkrétne rozhranie na module v danom shelfe a slote 60
61 Konfigurácia sieťových rozhraní Celé meno rozhrania je teda napríklad Serial0/0/1 BRI0/0/0 Niektoré rozhrania (najmä vstavané) a na starších smerovačoch všetky rozhrania môžu mať číselné označenie kratšie Iba Y/Z alebo iba Z Napríklad FastEthernet0/0 Meno rozhrania nie je potrebné písať celé Serial0/0/1 = s0/0/1 FastEthernet0/0 = fa0/0 61
62 Konfigurácia sieťových rozhraní Konfigurácia každého sieťového rozhrania by mala obsahovať tieto súčasti Slovný pomocný popis (description) IP adresu (ip address) Aktiváciu rozhrania (no shutdown) Pri niektorých rozhraniach bude potrebné uviesť aj dodatočné príkazy 62
63 Konfigurácia sieťových rozhraní Do konfiguračného podrežimu pre nastavenie konkrétneho rozhrania sa vstupuje príkazom interface meno číslo Romulus(config)#interface fa0/1 Romulus(config-if)# V konfigurácii rozhrania teraz uvedieme všetky informácie podľa predchádzajúceho slajdu Romulus(config-if)#description LAN1 Romulus(config-if)#ip address Romulus(config-if)#no shutdown Romulus(config-if)# *Mar 1 00:04:18.003: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:04:19.003: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up Romulus(config-if)#exit Romulus(config)# 63
64 Konfigurácia WAN sieťových rozhraní DCE je zariadenie, ktoré ukončuje dátový okruh (pevnú linku, vytáčanú linku apod.) Na synchrónnych rozhraniach je DCE zodpovedné za generovanie hodinového signálu, ktorým sa riadi prenos bitov Konfigurácia DCE sériového rozhrania má preto takýto tvar Konfigurácia DTE akurát neobsahuje clock rate Romulus(config)#interface s0/0/0 Romulus(config-if)#description Spoj na router Remus Romulus(config-if)#clock rate Romulus(config-if)#ip address Romulus(config-if)#no shutdown Romulus(config-if)# *Mar 1 00:20:53.311: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:20:54.311: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to up Romulus(config-if)#exit Romulus(config)# 64
65 Diagnostika rozhraní Na diagnostiku rozhraní existuje v privilegovanom príkazovom režime okrem zobrazenia bežiacej konfigurácie množstvo príkazov Každý z nich poskytuje rôzne informácie o nastaveniach a vlastnostiach rozhraní Príkaz show protocols Informuje o zariadeniach, ich stave a adresách Romulus#show protocols Global values: Internet Protocol routing is enabled FastEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is /25 Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is /30 65
66 Diagnostika rozhraní Príkaz show ip interface brief Poskytuje podobný výpis v inom formáte Romulus#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/ YES manual up up Serial0/0/ YES manual up up Oba príkazy informujú o IP nastaveniach rozhraní a o ich funkčnom stave Status: funkčnosť z pohľadu Layer1 Protocol: funkčnosť z pohľadu Layer2 66
67 Diagnostika rozhraní Príkaz show interfaces Poskytuje rôzne informácie o rozhraniach Romulus#show interfaces FastEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is AmdFE, address is cc (bia cc ) Description: LAN1 Internet address is /25 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, 100BaseTX/FX ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input never, output 00:00:03, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 67
68 Diagnostika rozhraní Samozrejme, kontrolu nastavenia rozhraní môžeme realizovať aj zobrazením konfigurácie Pri rozsiahlej konfigurácii je však predieranie sa dlhým výpisom nepraktické Je možné nechať si zobraziť len výpis konfiguračného odstavca pre zvolené rozhranie príkazom show run int MENO ČÍSLO Romulus#show run int s0/0/0 Building configuration... Current configuration : 162 bytes! interface Serial0/0/0 description Spoj na router Remus bandwidth 128 ip address serial restart-delay 0 clock rate end 68
69 Smerovanie - routing 69
70 Konfigurácia smerovacieho protokolu RIPv2 Konfigurácia RIPv2 na Cisco smerovačoch má tieto kroky Vstup do podrežimu pre RIPv2 (router rip) Aktiváciu verzie 2 (version 2) Vymenovanie priamo pripojených sietí, ktoré sa majú zaradiť do smerovacieho procesu (network) Romulus(config)#router rip Romulus(config-router)#version 2 Romulus(config-router)#network Romulus(config-router)#network Romulus(config-router)#network Romulus(config-router)#exit Romulus(config)# 70
71 Kontrola smerovacieho protokolu Zobrazenie smerovacej tabuľky príkazom show ip route Romulus#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set C C R /16 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks /25 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ /30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/ /26 [120/1] via , 00:00:04, Serial0/0/0 71
72 Kontrola smerovacieho protokolu Nízkoúrovňové sledovanie činnosti protokolu RIP príkazom privilegovaného režimu debug ip rip Romulus#debug ip rip RIP protocol debugging is on Romulus# *Mar 1 00:52:07.959: RIP: sending v2 update to via FastEthernet0/1 ( ) *Mar 1 00:52:07.959: RIP: build update entries *Mar 1 00:52:07.963: /26 via , metric 2, tag 0 *Mar 1 00:52:07.963: /30 via , metric 1, tag 0 *Mar 1 00:52:16.191: RIP: sending v2 update to via Serial0/0/0 ( ) *Mar 1 00:52:16.191: RIP: build update entries *Mar 1 00:52:16.195: /25 via , metric 1, tag 0 *Mar 1 00:52:20.703: RIP: received v2 update from on Serial0/0/0 *Mar 1 00:52:20.707: /26 via in 1 hops *Mar 1 00:52:35.347: RIP: sending v2 update to via FastEthernet0/1 ( ) Sledovanie sa ukončí príkazom privilegovaného 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights režimu reserved. undebug Cisco Public all 72
73 Implementovanie statického adresovania a nastavenie adries na PC Statické nastavenie IP protokolu a overenie nastavenia na PC (ping, tracert, ipconfig) Sniffovanie ICMP aplikácií Wireshark 73
74 Nastavenie statickej adresy na PC v LAN1 Start Control Panel Network connections right click on an interface Choose properties
75 Zálohovanie konfigurácie - tftp 75
76 Zálohovanie konfigurácie - terminál 76
77 Testovanie konektivity Ping / traceroute / pathping / wireshark 77
VLSM a CIDR. CCNA2 Kapitola Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1
 VLSM a CIDR CCNA2 Kapitola 6 1 Trošku histórie Pred rokom 1981 IP adresy používali na špecifikáciu siete len prvých 8 bitov Rok1981, RFC 791 Zaviedol adresný priestor s tromi triedami adries Polovica 90
VLSM a CIDR CCNA2 Kapitola 6 1 Trošku histórie Pred rokom 1981 IP adresy používali na špecifikáciu siete len prvých 8 bitov Rok1981, RFC 791 Zaviedol adresný priestor s tromi triedami adries Polovica 90
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS. Cisco Lab Øvelse Af Kim Donnerborg / RTS. Side 0 af 8
 KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS
 QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
Module 9, Assignment 7
 Module 9, Assignment 7 7.2.3 Control Router via Console (in Packet Tracer) 1. Prepare a Cisco 1841 Router (see figure 6-9). 2. Prepare a PC for administration. 3. Prepare a console cable and plug the serial
Module 9, Assignment 7 7.2.3 Control Router via Console (in Packet Tracer) 1. Prepare a Cisco 1841 Router (see figure 6-9). 2. Prepare a PC for administration. 3. Prepare a console cable and plug the serial
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic Switch Configuration
 Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Sieťové prepínače. Pavol Sokol / /
 Sieťové prepínače Pavol Sokol 9.5.2018 / 15.5.2018 / 16.5.2018 Sieťový prepínač zariadenie spojovej vrstvy: má aktívnu úlohu ukladá a rozposiela Ethernet rámce (frames) preskúmava MAC adresu prichádzajúcich
Sieťové prepínače Pavol Sokol 9.5.2018 / 15.5.2018 / 16.5.2018 Sieťový prepínač zariadenie spojovej vrstvy: má aktívnu úlohu ukladá a rozposiela Ethernet rámce (frames) preskúmava MAC adresu prichádzajúcich
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Shooting Trouble with IP
 C H A P T E R 3 Shooting Trouble with IP This chapter focuses on a number of objectives falling under the CCNP Troubleshooting guidelines. Understanding basic TCP/IP troubleshooting principles not only
C H A P T E R 3 Shooting Trouble with IP This chapter focuses on a number of objectives falling under the CCNP Troubleshooting guidelines. Understanding basic TCP/IP troubleshooting principles not only
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Registrácia účtu Hik-Connect
 Registrácia účtu Hik-Connect Tento návod popisuje postup registrácie účtu služby Hik-Connect prostredníctvom mobilnej aplikácie a webového rozhrania na stránke www.hik-connect.comg contents in this document
Registrácia účtu Hik-Connect Tento návod popisuje postup registrácie účtu služby Hik-Connect prostredníctvom mobilnej aplikácie a webového rozhrania na stránke www.hik-connect.comg contents in this document
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Table of Contents. co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern
 outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
Lab Viewing Network Device MAC Addresses
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol.
 CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
CS IT ports switch basic configuration. Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee.
 Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control
 hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router (InterVLAN Routing)
 Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
configuring and connecting 24
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Lab: Basic Static Route onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab: Basic Static Route onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
If this is your first time configuring the switch, you will notice that the Switch IOS is almost identical to Router IOS.
 Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
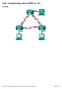 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup
 Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay
 Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE
 Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses
 Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
TP-LINK 150Mbps Wireless AP/Client Router Model TL-WR743ND Rýchly inštalačný sprievodca
 TP-LINK 150Mbps Wireless AP/Client Router Model TL-WR743ND Rýchly inštalačný sprievodca Obsah balenia TL-WR743ND Rýchly inštalačný sprievodca PoE injektor Napájací adaptér CD Ethernet kábel Systémové požiadavky
TP-LINK 150Mbps Wireless AP/Client Router Model TL-WR743ND Rýchly inštalačný sprievodca Obsah balenia TL-WR743ND Rýchly inštalačný sprievodca PoE injektor Napájací adaptér CD Ethernet kábel Systémové požiadavky
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Cisco Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam. Practice Test. Version 2.2. https://certkill.com
 Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
Inverse MUX Application using Multilink PPP
 Inverse MUX Application using Multilink PPP Document ID: 10235 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used Related Products onventions onfigure Network Diagram onfigurations Verify Troubleshoot
Inverse MUX Application using Multilink PPP Document ID: 10235 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used Related Products onventions onfigure Network Diagram onfigurations Verify Troubleshoot
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT
 Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
CCNA Practice test. 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage? A. NTP B. WCCP C. Telnet D. SNMP Answer: D
 1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH
 BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH switch#show running-config ( prikaz trenutne konfiguracije ) switch#show startup-config ( prikaz startne konfiguracije ) switch#configure terminal ( ulaz u global config
BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH switch#show running-config ( prikaz trenutne konfiguracije ) switch#show startup-config ( prikaz startne konfiguracije ) switch#configure terminal ( ulaz u global config
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab Exploring Cisco IOS and Configuring Basic Switch Settings
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Cable
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Cable
Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card
 CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
Switch configuration. By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch.
 By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
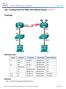 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway Fa0/ N/A. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Felix Rohrer Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.0.9 255.255.255.252
Felix Rohrer Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.0.9 255.255.255.252
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA ( )
 STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
Configuring IRB. Integrated Routing and Bridging CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0 135 points 1.1.1 What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System 1.1.1.2 What does a router connect?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0 135 points 1.1.1 What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System 1.1.1.2 What does a router connect?
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
 This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
Management IP Interface
 The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
Lab Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration
 Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network
 CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network 11.1.1 What is the system software in Cisco devices? The Cisco IOS provides devices with what network services? How is the IOS generally accessed?
CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network 11.1.1 What is the system software in Cisco devices? The Cisco IOS provides devices with what network services? How is the IOS generally accessed?
CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0)
 CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0) 1. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function
CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0) 1. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable
 Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
ROUTE Lab Guide Labs powered by
 OUTE Lab Guide 300-101 ii OUTE 300-101 Lab Guide LM20170908/BV1.0 iii 25 C e n tur y Blvd., S te. 5 0 0, N a s hvill e, T N 37214 B o s o n.c o m To perform the labs referenced in this book, please download
OUTE Lab Guide 300-101 ii OUTE 300-101 Lab Guide LM20170908/BV1.0 iii 25 C e n tur y Blvd., S te. 5 0 0, N a s hvill e, T N 37214 B o s o n.c o m To perform the labs referenced in this book, please download
outing and Switching Elective : Le
 Routing and Switching Elective : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapters covered: Cabling Router Configuration
Routing and Switching Elective : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapters covered: Cabling Router Configuration
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
Lab Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity
 Lab 9.2.5 Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252
Lab 9.2.5 Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252
Lab QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
 Lab 8.1.10.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Scenario Step 1 Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC)
Lab 8.1.10.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Scenario Step 1 Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC)
Lab 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 Default Gateway Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 Default Gateway Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay
 Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing
 Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Lab Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to use
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to use
Application Guide. VLANs for improved Q-SYS performance
 Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
RR> RR> RR>en RR# RR# RR# RR# *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 RR#
 RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers
 Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
BGP - duálne prepojenie AS. (primary + backup spoj), s IBGP, cez virtuální L2 linky
 BGP - duálne prepojenie AS (primary + backup spoj), s IBGP, cez virtuální L2 linky Peter Jašica Abstrakt: Cieľom tohto projektu je zhotoviť a otestovať funkčnosť BGP s dvojitým prepojením Autonómnych systémov.
BGP - duálne prepojenie AS (primary + backup spoj), s IBGP, cez virtuální L2 linky Peter Jašica Abstrakt: Cieľom tohto projektu je zhotoviť a otestovať funkčnosť BGP s dvojitým prepojením Autonómnych systémov.
เฉลยแล ป Packet Activity
 เฉลยแล ป Packet Activity CCNA LAB 4-4: IP Routing - EIGRP [ต งค าท Ranet HQ (คล กท เคร อง console)] : (ไปย งแท บ Desktop > คล ก Terminal > กด OK) Ranet-HQ>en Ranet-HQ#conf t Enter configuration commands,
เฉลยแล ป Packet Activity CCNA LAB 4-4: IP Routing - EIGRP [ต งค าท Ranet HQ (คล กท เคร อง console)] : (ไปย งแท บ Desktop > คล ก Terminal > กด OK) Ranet-HQ>en Ranet-HQ#conf t Enter configuration commands,
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks
 Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks Packet Tracer Practice with Dans Sample http://www.danscourses.com/ In this lab, you will learn how to configure the following tasks: IPv4 Addressing
Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks Packet Tracer Practice with Dans Sample http://www.danscourses.com/ In this lab, you will learn how to configure the following tasks: IPv4 Addressing
CCNA Questions/Answers Routing Protocols
 Refer to the exhibit and configuration shown above. Routers R1 and R2 are properly configured with eigrp 976 protocol and are able to ping interfaces fa0/1 and fa0/2, respectively. Which commands are necessary
Refer to the exhibit and configuration shown above. Routers R1 and R2 are properly configured with eigrp 976 protocol and are able to ping interfaces fa0/1 and fa0/2, respectively. Which commands are necessary
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
 Lab 8.9.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is likely to lead
Lab 8.9.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is likely to lead
