1) People: People are end users who use computers to make them- selves more productive.
|
|
|
- Ellen Jones
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 An information system has 5 parts: 1People: 1) People: People are end users who use computers to make themselves more productive. 2) Procedures: The rules or guidelines for people to follow when using software, hardware, and data are procedures. 3) Software: 4) Hardware: These procedures are typically documented in manuals written by computers specialists. A program consists of the stepbystep instructions that tell the computers how to do its work. Software is another name of program or programs. The purpose of software is to converts data (unprocessed facts) into information (processed facts). The equipment that processes the data to create information is called Hardware. Includes the keyboard, mouse, monitor, system unit and other devices. Hardware is controlled by software. 5) Data: The raw, unprocessed facts, including text, numbers, images, and sounds, are called data. 6) Connectivity: Consider as an additional part to the information system. Typically uses the internet. Allows users to greatly expand the capability and usefulness of their information systems. Allows computers to share information and to connect to the internet. v People are surely the most important part of any information system.
2 2 Software is another name for programs. Programs are the instructions that tell the computers how to process data into the form you want. In most cases, the words software and programs are interchangeable. There are two major kind of software: 1. System software 2. Application software 1. System software: Enables the application software to interact with the computer hardware. System software is background software that helps the computer manage its own internal resources. System software is not a single program. Rather it is a collection of programs including the following: o Operating systems: Programs that coordinate computer resources. Provide an interface between users and the computers, and run application. Windows 7 and Mac OS X are two of the bestknown operating system. o Utilities: Performs specific tasks related to managing computer resources. o Device drivers: Specialized program designed to allow particular input or output devices to communicate with the rest of the computer system. v The user interacts primary with application software. 2. Application software: Might describe as end user software. These programs can be categorized as either basic application or specialized application.
3 3 Basic application: Used widely in nearly all career. One of these basic applications is a browser to navigate, explore, and find information on the Internet. The three most widely used browsers are Microsoft s Internet Explorer, Google chrome and Mozilla s Firefox Specialized application: Include programs that are more narrowly focused on specific disciplines and occupations. Some of the best known are graphics, audio, video, multimedia, web authoring, artificial Intelligence programs, and mobile apps. v Computers are electronic devices that can follow instructions to accept input, process that input, and produce information. There are four 4 types of computers: 1Supercomputers: The most powerful type of computers. Special highcapacity computers used by very large organizations. Fujitsu s K computer (IBM s Blue Gene) is one of the fastest computers in the world. 2Mainframe computers: Occupy specially wired, airconditioned rooms. Not nearly as powerful as supercomputers. Mainframe computers are capable of great processing speeds and data storage. For example : this computers are used by insurance company. 3Minicomputers: Also known as midrange computers. Refrigerator sized machines. Medium size companies or departments of large companies typically use them for specific purpose. 4Microsomputers: The least powerful. Yet the most widely used. Fastestgrowing type of computers. There are 6 types of microcomputers: 1 Desktop computers 2 Media centers 3 Notebook computers (also known as laptop computers) 4 Tablet PC (also known as slate computer) 5 Netbooks 6 Handled computers
4 4 Two of the most widely used handled computers are: 1 Personal Digital Assistants (PDAa) 2 Smartphone v Smartphone are cell phones with wireless connections to the Internet. There are 4 basic categories of microcomputer hardware are: 1 System unit: The system unit is a container that houses most of the electronic components that make up a computer system. Two important components of the system units are: 2 Input/output: 1 Microprocessor: controls and manipulates data to produce information. 2 Memory: Holding area of data, instructions, and information. Input device: Translate data and programs that human can understand into a form that a computer can process. Examples of input device: Keyboard and Mouse. Output device: Translate the processed information from the computers into a form that humans can understand. Examples of output device: Monitor and Printers. 3 Secondary storage: Unlike memory, secondary storage holds data and programs even after electrical power to the computer system has been turned off. The most important kinds of secondary media are: 1 Hard disks: typically used to store programs and very large files. 2 Solidstate storage: Doesn t have any moving parts, is more reliable and requires less power. It saves data and information electronically similar to RAM except that it is not volatile.
5 5 There are 3 types of Solid_ state drives (SSDs): 1 Flash memory cards: widely used in portable device 2 USB drivers :widely used compact storage medium for transporting data and information. 3 Optical disks: Use a laser technology and have the greatest capacity. Have 3 types: Compact discs (CD). Digital Versatile (or video) discs (DVDs). HighDefinition (hi def) discs. 4 Communications: Now using communication devices, a microcomputer can communicate with other computer system located as near as the next office or as far as halfway around the world using the internet. The most widely used communication device is a modem, which: 1 Modify telephone communications into a form that can be processed by a computer. 2 Modify computer output into a form that can be transmitted across standard telephones lines. Data is raw, unprocessed facts, including text, numbers, images, and sounds. There are 4 common types of files are: 1 Document files: created by word processors to save documents, such as memos, terms papers, and letters. 2 Work sheet files: created by electronic spreadsheets to analyze things like budgets and to predict sales. 3 Database files: typically created by database management programs to contain highly structured and organized data. 4 Presentation files: created by presentation graphic programs to save presentation materials. Ø Connectivity is the capacity of your microcomputer to share information with other computers. Many experts predict that these wireless applications are just the beginning of the wireless revolution. Ø Central of the concept of connectivity is network. Ø A network is communications system connection two or more computers. Ø The web provides a multimedia interface to the numerous resources available on the internet. Ø Cloud computing uses the internet and the web to shift many computer activities from a user s computer to computers on the internet.
Information Technology, the Internet, and You. Information Technology, the Internet, and You 1-2
 Explain the five parts of an information system: people, procedures, software, hardware, and data. Distinguish between system software and application software. Discuss the three kinds of system software
Explain the five parts of an information system: people, procedures, software, hardware, and data. Distinguish between system software and application software. Discuss the three kinds of system software
VISUAL SUMMARY PEOPLE INFORMATION SYSTEMS. Information Technology, the Internet, and You. Rev.Confirming Pages
 Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY Information Technology, the Internet, and You INFORMATION SYSTEMS The way to think about a microcomputer is to realize that it is one part of an information system.
Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY Information Technology, the Internet, and You INFORMATION SYSTEMS The way to think about a microcomputer is to realize that it is one part of an information system.
Software is a computer that tells the computer how to perform particular.
 Name: A is a device that accepts, processes, stores, and produces, all according to a series of stored instructions. _ includes the physical electronic and mechanical devices that process the data. Peripheral
Name: A is a device that accepts, processes, stores, and produces, all according to a series of stored instructions. _ includes the physical electronic and mechanical devices that process the data. Peripheral
INFORMATION SYSTEM PARTS AND COMPUTER TYPES
 INFORMATION SYSTEM PARTS AND COMPUTER TYPES PARTS OF INFORMATION SYSTEM People are end users who use computers to make themselves more productive. Hardware refers to the physical components of your computer
INFORMATION SYSTEM PARTS AND COMPUTER TYPES PARTS OF INFORMATION SYSTEM People are end users who use computers to make themselves more productive. Hardware refers to the physical components of your computer
Information Technology, the Internet, and You The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Click the mouse to advance the slides Click the hyperlink to directly advance to the slide associated with the link; click Return to go back to the calling slide associated with the hyperlink All key terms
Click the mouse to advance the slides Click the hyperlink to directly advance to the slide associated with the link; click Return to go back to the calling slide associated with the hyperlink All key terms
Parts of the Computer System. Parts of the Computer System. Parts of the Computer System. Essential Computer Hardware. Information Processing Cycle
 Looking Inside the Computer System NOS 116, 118, 218, 222 Handout 10 Hardware & Software Computer systems have four parts Hardware Software Data User 1 1B-2 Hardware Mechanical devices in the computer
Looking Inside the Computer System NOS 116, 118, 218, 222 Handout 10 Hardware & Software Computer systems have four parts Hardware Software Data User 1 1B-2 Hardware Mechanical devices in the computer
Introduction to Computers. Joslyn A. Smith
 Introduction to Computers Joslyn A. Smith March 9, 2010 5/18/2011 1 What is a Computer? An electronic device that has the capability of performing the following tasks: Responds to input. Processes the
Introduction to Computers Joslyn A. Smith March 9, 2010 5/18/2011 1 What is a Computer? An electronic device that has the capability of performing the following tasks: Responds to input. Processes the
Introduction to Computers and Applications
 A World of Computers Introduction to Computers and Applications What is computer literacy? Knowledge and understanding of computers and their uses Computers are everywhere What Is a Computer? How is a
A World of Computers Introduction to Computers and Applications What is computer literacy? Knowledge and understanding of computers and their uses Computers are everywhere What Is a Computer? How is a
Lesson 1: Computer Concepts
 Lesson 1: Computer Concepts Learning Objectives After studying this lesson, you will be able to: Identify the basic parts of a computer system Describe the difference between random access memory and storage
Lesson 1: Computer Concepts Learning Objectives After studying this lesson, you will be able to: Identify the basic parts of a computer system Describe the difference between random access memory and storage
Chapter 2 Basic Computer Configuration
 CSCA0101 COMPUTING BASICS Chapter 2 1 Topics: Basic Operations Computer Components Computer Categories 2 Computing Terminology Data Data is anything in a form suitable for use with a computer. Information
CSCA0101 COMPUTING BASICS Chapter 2 1 Topics: Basic Operations Computer Components Computer Categories 2 Computing Terminology Data Data is anything in a form suitable for use with a computer. Information
A utility program included with the many versions of Windows that makes a copy of all files or selected files that have been saved onto a disk.
 A utility program included with the many versions of Windows that makes a copy of all files or selected files that have been saved onto a disk. A. Anti virus B. Backup and restore C. Clean up D. Compressing
A utility program included with the many versions of Windows that makes a copy of all files or selected files that have been saved onto a disk. A. Anti virus B. Backup and restore C. Clean up D. Compressing
Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited NEW DELHI
 Prelims English.qxd 9/29/08 4:57 PM Page 1 Computing Essentials 2008 Edition Timothy J. O Leary Arizona State University Linda I. O Leary Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited NEW DELHI McGraw-Hill
Prelims English.qxd 9/29/08 4:57 PM Page 1 Computing Essentials 2008 Edition Timothy J. O Leary Arizona State University Linda I. O Leary Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited NEW DELHI McGraw-Hill
Unit A: Computer and Internet Basics
 Unit A: Computer and Internet Basics TRUE/FALSE 1. Cars and appliances include digital electronics. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: Concepts 2 2. Usually when people talk about computers, they are talking about a PC.
Unit A: Computer and Internet Basics TRUE/FALSE 1. Cars and appliances include digital electronics. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: Concepts 2 2. Usually when people talk about computers, they are talking about a PC.
Terminology, Types of Computers & Computer Hardware
 Terminology, Types of Computers & Computer Hardware Basic Terminology 1.Computer A device that accepts input, processes data, stores data, and produces output, all according to a series of stored instructions.
Terminology, Types of Computers & Computer Hardware Basic Terminology 1.Computer A device that accepts input, processes data, stores data, and produces output, all according to a series of stored instructions.
Computer Basics. Lesson 1 Introduction to Computers. Edited by C. Rhodes 08/11
 Computer Basics Lesson 1 Introduction to Computers Edited by C. Rhodes 08/11 ESSENTIAL STANDARD Computer Basics ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the parts and features of a computer? What are the functions
Computer Basics Lesson 1 Introduction to Computers Edited by C. Rhodes 08/11 ESSENTIAL STANDARD Computer Basics ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the parts and features of a computer? What are the functions
Introduction to Computer World Fall 2016
 Introduction to Computer World Fall 2016 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102 Email: mehwish.fatima@ciitlahore.edu.pk Website: https://sites.google.com/a/ciitlahore.edu.pk/ict/
Introduction to Computer World Fall 2016 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102 Email: mehwish.fatima@ciitlahore.edu.pk Website: https://sites.google.com/a/ciitlahore.edu.pk/ict/
ABC Atanasoff-Berry Computer
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers A Brief History of Computers First Generation computers 1939-1959 Use vacuum tubes and wire circuits 1939 ABC computer completed, clock speed of 60 Hz, uses punch cards
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers A Brief History of Computers First Generation computers 1939-1959 Use vacuum tubes and wire circuits 1939 ABC computer completed, clock speed of 60 Hz, uses punch cards
COMPUTER HARDWARE RAYMOND ROSE
 COMPUTER HARDWARE RAYMOND ROSE LEARNING OUTCOMES 1.1 Identify types of computer how they process information, and the purpose and function of different hardware components. Understanding the computer and
COMPUTER HARDWARE RAYMOND ROSE LEARNING OUTCOMES 1.1 Identify types of computer how they process information, and the purpose and function of different hardware components. Understanding the computer and
Cambridge Nationals R001. Revision help (LO1)
 Cambridge Nationals R001 Revision help (LO1) Portable devices These are electronic devices that can be carried easily. Examples include: Laptops Netbooks Mobile phones Tablets (Ipad, Android Tablet) handheld
Cambridge Nationals R001 Revision help (LO1) Portable devices These are electronic devices that can be carried easily. Examples include: Laptops Netbooks Mobile phones Tablets (Ipad, Android Tablet) handheld
Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class
 Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class Lecture 2: Computer Concepts (Part A) Lecturer: Objectives Hardware Concepts Types of Computer Components of a Computer System Computer Performance
Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class Lecture 2: Computer Concepts (Part A) Lecturer: Objectives Hardware Concepts Types of Computer Components of a Computer System Computer Performance
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers Chapter 1 Objectives Recognize the importance of computer literacy Discuss the uses of the Internet and World Wide Web Define the term, computer Describe the categories
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers Chapter 1 Objectives Recognize the importance of computer literacy Discuss the uses of the Internet and World Wide Web Define the term, computer Describe the categories
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers
 Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers Chapter 1 Objectives Recognize the importance of computer literacy Define the term, computer Identify the components of a computer Discuss
Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers Chapter 1 Objectives Recognize the importance of computer literacy Define the term, computer Identify the components of a computer Discuss
Introduction to Computers
 Introduction to Computers Considers: Definition of computer Computer system devices Central Processing Unit Introduction to software What Is A Computer? A computer is an electronic device, operating under
Introduction to Computers Considers: Definition of computer Computer system devices Central Processing Unit Introduction to software What Is A Computer? A computer is an electronic device, operating under
SECTION 2 (Part B) Types And Components Of Computer Systems. Sophia Pratzioti
 SECTION 2 (Part B) Types And Components Of Computer Systems 2 Hardware & Software Hardware: is the physical parts of the computer system the part that you can touch and see. Hardware can be either external
SECTION 2 (Part B) Types And Components Of Computer Systems 2 Hardware & Software Hardware: is the physical parts of the computer system the part that you can touch and see. Hardware can be either external
Computer Programming for Engineering
 Chapter 1 213301 Computer Programming for Engineering Introduction to Computer The Amazing Computer What will be known :- List a few profession in which computers are routinely used and the way computers
Chapter 1 213301 Computer Programming for Engineering Introduction to Computer The Amazing Computer What will be known :- List a few profession in which computers are routinely used and the way computers
16/06/56. Secondary Storage. Secondary Storage. Secondary Storage The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Distinguish between primary and secondary storage. Discuss the important characteristics of secondary storage, including media, capacity, storage devices, and access speed. Describe hard disk platters,
Distinguish between primary and secondary storage. Discuss the important characteristics of secondary storage, including media, capacity, storage devices, and access speed. Describe hard disk platters,
What is Information Technology. Chapter 1: Computer System. Why use Information Technology? What is Data?
 What is Information Technology Chapter 1: Computer System Information Technology is the direct use of technology to process data. A more formal definition of IT would be: The acquisition, processing, storage
What is Information Technology Chapter 1: Computer System Information Technology is the direct use of technology to process data. A more formal definition of IT would be: The acquisition, processing, storage
VISUAL SUMMARY. The System Unit
 Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY The System Unit SYSTEM UNIT System unit (system chassis) contains electronic components. There are four basic categories of system units: desktop, notebook (laptop),
Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY The System Unit SYSTEM UNIT System unit (system chassis) contains electronic components. There are four basic categories of system units: desktop, notebook (laptop),
CHAPTER 1 TYPES & COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1 TYPES & COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSTEM 1.1 Hardware and Software Q.1) Define hardware and software: a) Hardware Hardware is a general term used for the physical components (parts) that make up
CHAPTER 1 TYPES & COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSTEM 1.1 Hardware and Software Q.1) Define hardware and software: a) Hardware Hardware is a general term used for the physical components (parts) that make up
Intentionally Blank 0
 Intentionally Blank 0 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1 Understanding Your Computer: Computers are Data Processing Devices Perform four major functions Input:
Intentionally Blank 0 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1 Understanding Your Computer: Computers are Data Processing Devices Perform four major functions Input:
Programming Principles and Techniques
 Aptech Ltd Version 1.0 Page 1 of 11 Table of Contents Aptech Ltd Version 1.0 Page 2 of 11 Application Software Assembler American Standard Code for Information Interchange Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Algorithm
Aptech Ltd Version 1.0 Page 1 of 11 Table of Contents Aptech Ltd Version 1.0 Page 2 of 11 Application Software Assembler American Standard Code for Information Interchange Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Algorithm
Computer chip: A very small pieces of silicon or other semi-conducting material onto which integrated circuits are embedded Circuit board: A thin
 INTRODUCTION We can divide the parts that make up a computer into three broad categories or subsystem: the central processing unit (CPU), the main memory, and the input/output subsystem. The next three
INTRODUCTION We can divide the parts that make up a computer into three broad categories or subsystem: the central processing unit (CPU), the main memory, and the input/output subsystem. The next three
An Overview of the Computer System. Kafui A. Prebbie 24
 An Overview of the Computer System Kafui A. Prebbie -kafui@kafui.com 24 The Parts of a Computer System What is a Computer? Hardware Software Data Users Kafui A. Prebbie -kafui@kafui.com 25 The Parts of
An Overview of the Computer System Kafui A. Prebbie -kafui@kafui.com 24 The Parts of a Computer System What is a Computer? Hardware Software Data Users Kafui A. Prebbie -kafui@kafui.com 25 The Parts of
What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1
 What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did the computer become known as the stored-program computer? Do they all have the same
What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did the computer become known as the stored-program computer? Do they all have the same
SISTEM INFORMASI. Oleh Iwan Sidharta, MM STMIK Mardira Indonesia, Bandung NFORMASI
 SISTEM INFORMASI Oleh Iwan Sidharta, MM STMIK Mardira Indonesia, Bandung NFORMASI Materi Recognize the importance of computer literacy Identify the components of a computer Discuss the uses of the Internet
SISTEM INFORMASI Oleh Iwan Sidharta, MM STMIK Mardira Indonesia, Bandung NFORMASI Materi Recognize the importance of computer literacy Identify the components of a computer Discuss the uses of the Internet
Computer Technology Flash Card 2
 Computer Technology Flash Card 2 Mouse An input device that allows the user to manipulate objects on the screen by moving the mouse along the surface of a desk. Data Refers to the symbols that represent
Computer Technology Flash Card 2 Mouse An input device that allows the user to manipulate objects on the screen by moving the mouse along the surface of a desk. Data Refers to the symbols that represent
VISUAL SUMMARY SYSTEM SOFTWARE OPERATING SYSTEMS. System Software
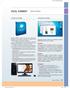 Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY System Software SYSTEM SOFTWARE System software works with end users, application programs, and computer hardware to handle many details relating to computer operations.
Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY System Software SYSTEM SOFTWARE System software works with end users, application programs, and computer hardware to handle many details relating to computer operations.
Parts of Computer hardware Software
 Parts of Computer Parts of Computer If you use a desktop computer, you might already know that there is not any single part called the "computer." A computer is really a system of many parts working together.
Parts of Computer Parts of Computer If you use a desktop computer, you might already know that there is not any single part called the "computer." A computer is really a system of many parts working together.
4) Apple's OS X and Microsoft Windows are examples of software. A) utility B) application C) operating system D) communication
 Technology in Action Complete, 13e (Evans et al.) Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1) Computers use language consisting of 0s and 1s. A) symbol B) binary C) byte D) system 2) In
Technology in Action Complete, 13e (Evans et al.) Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1) Computers use language consisting of 0s and 1s. A) symbol B) binary C) byte D) system 2) In
4.03 IT PowerPoint. Objective 4.03 Understand Information Technology activities and careers.
 4.03 IT PowerPoint Objective 4.03 Understand Information Technology activities and careers. What Is A Computer? An electronic device that receives data, processes data, stores data, and produces a result
4.03 IT PowerPoint Objective 4.03 Understand Information Technology activities and careers. What Is A Computer? An electronic device that receives data, processes data, stores data, and produces a result
Define each of the following computer terms. 1 Period 7 Lesson Computer Terms 1 Wallpaper 2 URL 3 Mainframe 4 Function Keys 5 Font 6 Paste 7 Paint
 1 Period 7 1 Wallpaper 2 URL 3 Mainframe 4 Function Keys 5 Font 6 Paste 7 Paint 8.pcx 9 External hard drive 10 Programmer 11 Power Supply 12 LAN 13 Operating system 14 CAD 15 Crash 16 Power Supply 17 Enable
1 Period 7 1 Wallpaper 2 URL 3 Mainframe 4 Function Keys 5 Font 6 Paste 7 Paint 8.pcx 9 External hard drive 10 Programmer 11 Power Supply 12 LAN 13 Operating system 14 CAD 15 Crash 16 Power Supply 17 Enable
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers
 Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers Chapter 1 Objectives Recognize the importance of computer literacy Define the term, computer Identify the components of a computer Discuss
Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers Chapter 1 Objectives Recognize the importance of computer literacy Define the term, computer Identify the components of a computer Discuss
Introducing the Computer
 Introducing the Computer Lecture Outline 9 Instructor: Kevin Robertson Computer Components and Processing Functions Introduction to the Computer* Information processor capable of performing electronically
Introducing the Computer Lecture Outline 9 Instructor: Kevin Robertson Computer Components and Processing Functions Introduction to the Computer* Information processor capable of performing electronically
Computer Overview. A computer item you can physically see or touch. A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate.
 Hardware Computer Overview A computer item you can physically see or touch. Software A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate. Information Technology (IT) The broad subject related
Hardware Computer Overview A computer item you can physically see or touch. Software A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate. Information Technology (IT) The broad subject related
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 1 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 2 Chapter Topics Functions of a computer Data versus information Bits and bytes Input devices Output devices Processing Storage
1 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 2 Chapter Topics Functions of a computer Data versus information Bits and bytes Input devices Output devices Processing Storage
Zimmer CSCI /24/18. CHAPTER 1 Overview. COMPUTER Programmable devices that can store, retrieve, and process data.
 CHAPTER 1 Overview COMPUTER Programmable devices that can store, retrieve, and process data. COMPUTER DEVELOPMENTS- Smaller size - processors (vacuum tubes -> transistors ->IC chip) Microprocessor - miniaturized
CHAPTER 1 Overview COMPUTER Programmable devices that can store, retrieve, and process data. COMPUTER DEVELOPMENTS- Smaller size - processors (vacuum tubes -> transistors ->IC chip) Microprocessor - miniaturized
There are many types of computers, including:
 Computer Basics There are many types of computers, including: Supercomputers... are used to process very large amounts of information including processing information to predict hurricanes, satellite images
Computer Basics There are many types of computers, including: Supercomputers... are used to process very large amounts of information including processing information to predict hurricanes, satellite images
Types of Data. PE 231 Education Media AND Technology. Information. Assessment. Information Concepts
 Types of Data Data Represented by PE 231 Education Media AND Technology Alphanumeric data Image data Audio data Numbers, letters, and other characters Graphic images or pictures Sound, noise, tones Video
Types of Data Data Represented by PE 231 Education Media AND Technology Alphanumeric data Image data Audio data Numbers, letters, and other characters Graphic images or pictures Sound, noise, tones Video
Chapter 2: Computers: The Machines Behind Computing.
 Chapter 2: Computers: The Machines Behind Computing. TRUEFALSE 1. Computers perform all tasks using a combination of arithmetic and logical operations. 2. Fourth-generation languages (4GLs) are also called
Chapter 2: Computers: The Machines Behind Computing. TRUEFALSE 1. Computers perform all tasks using a combination of arithmetic and logical operations. 2. Fourth-generation languages (4GLs) are also called
Defining Computers. Defining Computers. Understanding Essential Computer Concepts
 Understanding Essential Computer Concepts Defining Computers A high-speed idiot must be told exactly what to do by humans and programs step-by-step instructions An electronic device that accepts input,
Understanding Essential Computer Concepts Defining Computers A high-speed idiot must be told exactly what to do by humans and programs step-by-step instructions An electronic device that accepts input,
Chapter I The System Unit
 Date :../. / Chapter I The System Unit Day :.. Mother Board System Unit Types Desktop System Units Notebook System Units Tablet PC System Units Handheld Computer System Units System Board " Motherboard"
Date :../. / Chapter I The System Unit Day :.. Mother Board System Unit Types Desktop System Units Notebook System Units Tablet PC System Units Handheld Computer System Units System Board " Motherboard"
Introduction to Computers Chapter1
 Introduction to Computers Chapter1 IS-IT-UOB 2013 Topics Covered Computer definition and main parts Computer Hardware Computer Software Computer Strengths Categories of Computers Computer Applications
Introduction to Computers Chapter1 IS-IT-UOB 2013 Topics Covered Computer definition and main parts Computer Hardware Computer Software Computer Strengths Categories of Computers Computer Applications
Lecture 2 Winter 2006 Essentials of Computing
 Information Technology Lecture 2 Winter 2006 Essentials of Computing 1 Objectives Identify the five components of a computer system. Explain the four categories of hardware and their functions. Discuss
Information Technology Lecture 2 Winter 2006 Essentials of Computing 1 Objectives Identify the five components of a computer system. Explain the four categories of hardware and their functions. Discuss
Chapter. IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software
 Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software My First Love! Year: 1985 My Heart Beats Still IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware IT infrastructure: provides platform for supporting all information
Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software My First Love! Year: 1985 My Heart Beats Still IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware IT infrastructure: provides platform for supporting all information
Types of Computers. Computer Technology (S1 Obj 1-1)
 Types of Computers Computer Technology (S1 Obj 1-1) Introduction There are many different types of computers available today. They are categorized into different types depending on their size and processing
Types of Computers Computer Technology (S1 Obj 1-1) Introduction There are many different types of computers available today. They are categorized into different types depending on their size and processing
Chapter 2 Computer Hardware
 Chapter 2 Computer Hardware Computer Concepts 2014 2 Chapter Contents Section A: Personal Computer Basics Section B: Microprocessors and Memory Section C: Storage Devices Section D: Input and Output Devices
Chapter 2 Computer Hardware Computer Concepts 2014 2 Chapter Contents Section A: Personal Computer Basics Section B: Microprocessors and Memory Section C: Storage Devices Section D: Input and Output Devices
2) Computers use a language consisting of 0s and 1s. A) symbol B) binary C) byte D) system
 Technology In Action, Complete, 14e (Evans et al.) Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1) What is the difference between data and information? A) Data represents a fact. Information
Technology In Action, Complete, 14e (Evans et al.) Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1) What is the difference between data and information? A) Data represents a fact. Information
Getting Started. Explorers Guide. Learning about computer basics. Data file: none Objectives:
 Explorers Guide Data file: none Objectives: In this project, you will: learn about computer ergonomics describe computer hardware and software review the Windows desktop and use the mouse work with windows
Explorers Guide Data file: none Objectives: In this project, you will: learn about computer ergonomics describe computer hardware and software review the Windows desktop and use the mouse work with windows
QUESTIONS ABOUT COMPUTERS
 1. What is a computer? QUESTIONS ABOUT COMPUTERS A computer is a machine that processes information, in other words, it receives and stores data, performs calculations with this data and presents the results
1. What is a computer? QUESTIONS ABOUT COMPUTERS A computer is a machine that processes information, in other words, it receives and stores data, performs calculations with this data and presents the results
Introduction To Computers. About the Course
 Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
CMSC 1513 Lecture 1.2
 Key Point: A computer is an electronic device that stores and processes data. Hardware Software Hardware comprises the visible, physical elements of the computer. Software provides the invisible instructions
Key Point: A computer is an electronic device that stores and processes data. Hardware Software Hardware comprises the visible, physical elements of the computer. Software provides the invisible instructions
Computer Concepts and C Programming. Unit I 06CCP13
 Computer Concepts and C Programming () Unit I Unit Division Unit-I Introducing Computer Systems Interacting with Computer Unit-II Processing Data Storing Data Unit-III Using Operating Systems Networks
Computer Concepts and C Programming () Unit I Unit Division Unit-I Introducing Computer Systems Interacting with Computer Unit-II Processing Data Storing Data Unit-III Using Operating Systems Networks
Community Development and Training Centre Semester IT 245 Management Information Systems
 Community Development and Training Centre Semester 2 2006 IT 245 Management Information Systems Computer Hardware Chapter Summary Computer Systems. Major types and trends in computer systems are summarized
Community Development and Training Centre Semester 2 2006 IT 245 Management Information Systems Computer Hardware Chapter Summary Computer Systems. Major types and trends in computer systems are summarized
Information Technology Fundamentals. Unit 1: Computer Basics Wrap-up
 Information Technology Fundamentals Unit 1: Computer Basics Wrap-up What is a Computer? A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve,
Information Technology Fundamentals Unit 1: Computer Basics Wrap-up What is a Computer? A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve,
CSC 170 Introduction to Computers and Their Applications. Computers
 CSC 170 Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture #4 Digital Devices Computers At its core, a computer is a multipurpose device that accepts input, processes data, stores data, and produces
CSC 170 Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture #4 Digital Devices Computers At its core, a computer is a multipurpose device that accepts input, processes data, stores data, and produces
Lecture 4 Today s Goal
 Lecture 4 Today s Goal To learn to classify computers according to their capability and targeted applications To find out about the essential building blocks that make up a modern computer Computer Types
Lecture 4 Today s Goal To learn to classify computers according to their capability and targeted applications To find out about the essential building blocks that make up a modern computer Computer Types
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS When we talk about computers, we really are talking about a Computer System. Computer System: It is a combination of Hardware and Software. This combination allows a computer
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS When we talk about computers, we really are talking about a Computer System. Computer System: It is a combination of Hardware and Software. This combination allows a computer
Second Generations Computers( )
 Second Generations Computers(1954-1962) Second Generations Computers(1954-1962) The invention of the transistor greatly changed the computer's development in 1948. The transistor replaced the large, cumbersome
Second Generations Computers(1954-1962) Second Generations Computers(1954-1962) The invention of the transistor greatly changed the computer's development in 1948. The transistor replaced the large, cumbersome
By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali
 Department of Information Networks The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON Evolving Technology of Laptops By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali College of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@itnet.uobabylon.edu.iq
Department of Information Networks The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON Evolving Technology of Laptops By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali College of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@itnet.uobabylon.edu.iq
Components of a personal computer
 Components of a personal computer Computer systems ranging from a controller in a microwave oven to a large supercomputer contain components providing five functions. A typical personal computer has hard,
Components of a personal computer Computer systems ranging from a controller in a microwave oven to a large supercomputer contain components providing five functions. A typical personal computer has hard,
central processing unit (CPU) software operating system (OS) input device output device
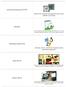 central processing unit (CPU) Brain of the computer that performs instructions defined by software software Set of instructions that tells the hardware what to do. It is what guides the hardware and tells
central processing unit (CPU) Brain of the computer that performs instructions defined by software software Set of instructions that tells the hardware what to do. It is what guides the hardware and tells
File Management. Version: 04_19_04 Developed by: Department of Instructional Technology 2004 Union Institute & University
 File Management Version: 04_19_04 Developed by: Department of Instructional Technology 2004 Union Institute & University Table of Contents FILE MANAGEMENT SCENARIO...2 File Management Terminology...2 FILE
File Management Version: 04_19_04 Developed by: Department of Instructional Technology 2004 Union Institute & University Table of Contents FILE MANAGEMENT SCENARIO...2 File Management Terminology...2 FILE
Introduction to Computers. Chapter1
 Introduction to Computers Chapter1 ITBIS105 IS-IT-UOB 2016 IS-IT-UOB 2016 Topics Covered Computer Computer Computer Computer Categories of Computers Computer Applications in Networks definition and main
Introduction to Computers Chapter1 ITBIS105 IS-IT-UOB 2016 IS-IT-UOB 2016 Topics Covered Computer Computer Computer Computer Categories of Computers Computer Applications in Networks definition and main
8 9 Before: Computers are categorized into three main categories from least to most powerful: microcomputers minicomputers mainframe computers Today:
 1 Computer, Internet, and Network Basics 2 Computer Basics A computer system includes a computer, peripheral devices, and software Computer refers to a device that accepts data as input, processes data,
1 Computer, Internet, and Network Basics 2 Computer Basics A computer system includes a computer, peripheral devices, and software Computer refers to a device that accepts data as input, processes data,
About the Presentations
 About the Presentations The presentations cover the objectives found in the opening of each chapter. All chapter objectives are listed in the beginning of each presentation. You may customize the presentations
About the Presentations The presentations cover the objectives found in the opening of each chapter. All chapter objectives are listed in the beginning of each presentation. You may customize the presentations
Lecture -1- By lec. (Eng.) Hind Basil University of technology Department of Materials Engineering
 Lecture -1- By lec. (Eng.) Hind Basil University of technology Department of Materials Engineering What is Computer? Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user
Lecture -1- By lec. (Eng.) Hind Basil University of technology Department of Materials Engineering What is Computer? Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user
Chapter 1. Computer System Organization
 Chapter 1 Computer System Organization Prepared By: Manish Kumar Prajapati PGT (Comp.Sc.) (First Shift) Kendriya Vidyalaya Bailey Road Patna-14 What is Computer? A computer is an electronic device that
Chapter 1 Computer System Organization Prepared By: Manish Kumar Prajapati PGT (Comp.Sc.) (First Shift) Kendriya Vidyalaya Bailey Road Patna-14 What is Computer? A computer is an electronic device that
TECHNOLOGY IN ACTION. Chapter 2. Alan Evans * Kendall Martin * Mary Anne Poatsy. Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts
 TECHNOLOGY IN ACTION Alan Evans * Kendall Martin * Mary Anne Poatsy Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices Output
TECHNOLOGY IN ACTION Alan Evans * Kendall Martin * Mary Anne Poatsy Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices Output
This lesson was made possible with the assistance of the following organisations:
 16 MODULE 4: ICT in Support of Farming LESSON 1: Introduction to Computers TIME: 1 hour 36 minutes AUTHOR: Dalton Ndirangu This lesson was made possible with the assistance of the following organisations:
16 MODULE 4: ICT in Support of Farming LESSON 1: Introduction to Computers TIME: 1 hour 36 minutes AUTHOR: Dalton Ndirangu This lesson was made possible with the assistance of the following organisations:
Computer Concepts - Illustrated Introductory, Ninth Edition
 Computer Concepts - Illustrated Introductory, Ninth Edition Page 1 of 11 Computer Concepts - Illustrated Introductory, Ninth Edition Unit A: Computer and Internet Basics 1. Make sure that you can define
Computer Concepts - Illustrated Introductory, Ninth Edition Page 1 of 11 Computer Concepts - Illustrated Introductory, Ninth Edition Unit A: Computer and Internet Basics 1. Make sure that you can define
CSC 170 Fall 2017 Dr. R. M. Siegfried. Study Guide for Final Exam
 CSC 170 Fall 2017 Dr. R. M. Siegfried Study Guide for Final Exam Definitions to know: Lecture #1 1. Data 2. Digitization 3. Bit 4. Byte 5. Binary Numbers 6. How Are Characters Stored? a. ASCII b. Unicode
CSC 170 Fall 2017 Dr. R. M. Siegfried Study Guide for Final Exam Definitions to know: Lecture #1 1. Data 2. Digitization 3. Bit 4. Byte 5. Binary Numbers 6. How Are Characters Stored? a. ASCII b. Unicode
TODAY AND TOMORROW. Storage CHAPTER
 1 TODAY AND TOMORROW 3 Storage CHAPTER Storage Systems Characteristics All storage systems have specific characteristics Storage medium (what data is stored on) Can be removable or nonremovable from the
1 TODAY AND TOMORROW 3 Storage CHAPTER Storage Systems Characteristics All storage systems have specific characteristics Storage medium (what data is stored on) Can be removable or nonremovable from the
8/25/2016. What Is a Computer? The Components of a Computer
 Discovering Computers & Microsoft Office 2010 Selected Slides from Chapters 1-5 What Is a Computer? A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory
Discovering Computers & Microsoft Office 2010 Selected Slides from Chapters 1-5 What Is a Computer? A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory
Computer is an electronic machine that can receive, store, transform and output data of all kinds (image, text, numeric, graphics and sound).
 ELECTRONIC COMPUTERS THEN AND NOW Computer is an electronic machine that can receive, store, transform and output data of all kinds (image, text, numeric, graphics and sound). In the Past (i.e., during
ELECTRONIC COMPUTERS THEN AND NOW Computer is an electronic machine that can receive, store, transform and output data of all kinds (image, text, numeric, graphics and sound). In the Past (i.e., during
PARTS OF THE COMPUTER. 2nd ESO IES CAP DE LLEVANT
 PARTS OF THE COMPUTER 2nd ESO IES CAP DE LLEVANT 1. COMPUTING OR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY The branch of engineering science that studies (with the aid of computers)the procedure of calculating and information
PARTS OF THE COMPUTER 2nd ESO IES CAP DE LLEVANT 1. COMPUTING OR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY The branch of engineering science that studies (with the aid of computers)the procedure of calculating and information
Chapter 2 Computer Hardware. Computer Concepts 2013
 Chapter 2 Computer Hardware Computer Concepts 2013 2 Chapter Contents Section A: Personal Computer Basics Section B: Microprocessors and Memory Section C: Storage Devices Section D: Input and Output Devices
Chapter 2 Computer Hardware Computer Concepts 2013 2 Chapter Contents Section A: Personal Computer Basics Section B: Microprocessors and Memory Section C: Storage Devices Section D: Input and Output Devices
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing
 INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 6 Storage Technologies Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 6 Storage Technologies Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
Computer and Online Basics.
 Computer and Online Basics www.bcs.org/onlinebasics E Published under Licence from the ECDL Foundation Ltd. All rights reserved, no part of this book may be reproduced without permission of the copyright
Computer and Online Basics www.bcs.org/onlinebasics E Published under Licence from the ECDL Foundation Ltd. All rights reserved, no part of this book may be reproduced without permission of the copyright
Good morning! Hardware: Input, Processing, Output, and Storage Devices
 Good morning! Hardware: Input, Processing, Output, and Storage Devices Computer Systems: Integrating the Power of Technology Hardware components: Central processing unit (CPU): Arithmetic/logic unit, the
Good morning! Hardware: Input, Processing, Output, and Storage Devices Computer Systems: Integrating the Power of Technology Hardware components: Central processing unit (CPU): Arithmetic/logic unit, the
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 : Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
Chapter 1 Introduction to the World of Computers
 Understanding Computers in a Changing Society, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1 Introduction to the World of Computers Learning Objectives Explain why it is essential to learn about computers today and discuss several
Understanding Computers in a Changing Society, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1 Introduction to the World of Computers Learning Objectives Explain why it is essential to learn about computers today and discuss several
FUNCTIONS OF COMPONENTS OF A PERSONAL COMPUTER
 FUNCTIONS OF COMPONENTS OF A PERSONAL COMPUTER Components of a personal computer - Summary Computer Case aluminium casing to store all components. Motherboard Central Processor Unit (CPU) Power supply
FUNCTIONS OF COMPONENTS OF A PERSONAL COMPUTER Components of a personal computer - Summary Computer Case aluminium casing to store all components. Motherboard Central Processor Unit (CPU) Power supply
CSC 101 Questions: Chapter 1: Multiple Choice: 1. When did the World Wide Web become available to users? a. 1960s b. 1970s c. 1980s d.
 CSC 101 Questions: Chapter 1: Multiple Choice: 1. When did the World Wide Web become available to users? a. 1960s b. 1970s c. 1980s d. 2000s 2. When did Web 2.0 sites like MySpace and Flickr become popular?
CSC 101 Questions: Chapter 1: Multiple Choice: 1. When did the World Wide Web become available to users? a. 1960s b. 1970s c. 1980s d. 2000s 2. When did Web 2.0 sites like MySpace and Flickr become popular?
Full file at
 Exam Name Full file at https://fratstock.eu MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) is data that has been organized or presented in a meaningful
Exam Name Full file at https://fratstock.eu MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) is data that has been organized or presented in a meaningful
LOCARNO CLASSIFICATION List of Goods in Class Order
 Class 14 Recording, communication or information retrieval equipment 14-01 EQUIPMENT FOR THE RECORDING OR REPRODUCTION OF SOUNDS OR PICTURES Note(s) Not including photographic or cinematographic apparatus
Class 14 Recording, communication or information retrieval equipment 14-01 EQUIPMENT FOR THE RECORDING OR REPRODUCTION OF SOUNDS OR PICTURES Note(s) Not including photographic or cinematographic apparatus
Microsoft Office and How to Purchase a Personal Computer
 Microsoft Office 2007 Essential Introduction to Computers and How to Purchase a Personal Computer Objectives Define the term computer and discuss the four basic computer operations: input, processing,
Microsoft Office 2007 Essential Introduction to Computers and How to Purchase a Personal Computer Objectives Define the term computer and discuss the four basic computer operations: input, processing,
Downloaded From :
 04-012-2011 Test V Computer Knowledge 201. The operation of combining two cells into a single cell in Excel is referred to as (1) Join Cells (2) Merge Cells (3) Merge Table (4) Join Table 202. Which of
04-012-2011 Test V Computer Knowledge 201. The operation of combining two cells into a single cell in Excel is referred to as (1) Join Cells (2) Merge Cells (3) Merge Table (4) Join Table 202. Which of
Dawood Public School Computer Studies Course Outline for Class VI. Course book- Right Byte 1 Fourth edition (Oxford University Press)
 Dawood Public School Computer Studies Course Outline for 2017-2018 Class VI Course book- Right Byte 1 Fourth edition (Oxford University Press) Month wise Distribution of Course Work August The Evolution
Dawood Public School Computer Studies Course Outline for 2017-2018 Class VI Course book- Right Byte 1 Fourth edition (Oxford University Press) Month wise Distribution of Course Work August The Evolution
Computers Are Your Future
 Computers Are Your Future 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Inside the System Unit 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 2 What You Will Learn... Understand how computers represent
Computers Are Your Future 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Inside the System Unit 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 2 What You Will Learn... Understand how computers represent
5/3/2012. Copyright 2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill. McGraw-Hill. McGraw-Hill. McGraw-Hill
 Chapter 03: Basic Application Software Competencies (Page 1 of 2) Discuss common features of most software applications. Discuss word processors and word processing features. Describe spreadsheets and
Chapter 03: Basic Application Software Competencies (Page 1 of 2) Discuss common features of most software applications. Discuss word processors and word processing features. Describe spreadsheets and
