PRINCIP KOMUNIKACIJE U BLUETOOTH BEŽIČNOJ PAN MREŽI THE COMMUNICATION PRINCIPLE IN THE BLUETOOTH WIRELLES PAN NETWORK
|
|
|
- Noel Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eng. Rev. 26 (2006) UDK :004.6:004.7 PRINCIP KOMUNIKACIJE U BLUETOOTH BEŽIČNOJ PAN MREŽI THE COMMUNICATION PRINCIPLE IN THE BLUETOOTH WIRELLES PAN NETWORK Vedran KOS Antun SOK Sažetak: U ovom radu objašnjen je princip povezivanja i komunikacije u Bluetooth bežičnoj mreži. Bluetooth bežična tehnologija najpoznatiji je predstavnik mrežnih tehnologija u sve popularnijim osobnim mrežama (PAN). Ključne riječi: - Bluetooth - bežična mreža - pikonet Summary: This paper gives an explanation for connection and communication principles of the Bluetooth wirelles network. Bluetooth wireless technology is the most popular network technology for personal area networking (PAN). Key words: - Bluetooth - wireless network - piconet 1. UVOD Porast broja i funkcionalnosti elektroničkih uređaja uz stalnu potrebu njihove međusobne komunikacije dovodi do još bržeg porasta broja potrebnih kabela. To je poprimilo tolike razmjere da je malo ljudi koji koriste računalo, a da nemaju na stolu i u ladicama nepreglednu šumu kabela za spajanje perifernih uređaja, mobitela, kamera, itd. Uz to, velika se pozornost pridaje i mobilnosti unutar radnog okruženja. U početku je to izvedeno pomoću infracrvene veze, ali ona ima nedostatke koji onemogućavaju mobilnost. To se prvenstveno odnosi na potrebu izravne optičke veze i male udaljenosti među uređajima. Za razliku od infracrvene veze radioveza odnosno radiovalovi prostiru se u svim smjerovima i prolaze kroz zidove i ostale nemetalne prepreke. 2. FREKVENCIJE Bluetooth koristi industrijski, znanstveni i medicinski (ISM) frekvencijski pojas. Taj se pojas nalazi u spektru 2,4 GHz. Može se slobodno i bez licence ili naknade koristiti u većini zemalja pod uvjetom ograničene emitirane snage. ISM pojas ima širinu od 83 MHz i zato pruža dovoljno prostora za izbjegavanje smetnji koje dolaze iz drugih uređaja koji koriste određenu frekvenciju. 1. INTRODUCTION The increase in the number and functionalities of electronic devices in addition their mutual communication leads to an even greater increase of necessary communication cables. This has assumed such proportions that there are few people who use a computer and haven t got a bundle of cables for connecting peripherals, mobile phones, cameras, etc. In addition, lots of attention is being paid to mobility within the workplace. In the beginning, it was done via infrared links, but it has some disadvantages that preclude mobility. This especially refers to the need for a direct optical link and small distances between devices. As opposed to infrared link, radio link is transmits in all directions and passes through walls and other nonmetal obstacles. 2. FREQUENCIES Bluetooth uses the Industrial Scientific and Medical (ISM) frequency band. This band is located in the 2,4 GHz band. It may be used without any licence or fee in most of countries under condition of limited radiation power. The ISM band is 83 MHz wide and thus provides enough room to avoid interfering signals coming from equipment that uses a particular frequency.
2 64 V. Kos, A. Sok:Princip komunikacije u... To može biti WLAN, mikrovalna pećnica ili neki drugi izvor. Kako bi se izbjegli problemi s navedenim izvorima od kojih većina ima fiksne frekvencije, Bluetooth koristi tehniku širokog spektra. To znači da se frekvencija brzo mijenja (do 1600 puta u sekundi) na pseudoslučajni način. Rezultat je dovoljan broj slobodnih frekvencija da bi se postigla željena brzina prijenosa podataka. Taj se proces zove preskakanje frekvencija u širokom spektru (FHSS). Bluetooth koristi 79 frekvencija u rasponu između 2,402 GHz i 2,480 GHz u razmaku od 1 MHz. Slika 1 prikazuje princip preskakanja frekvencija [4]. It can be WLAN, a microwave oven or some other source. In order to avoid problems with the mentioned sources, most of which have fixed frequencies, Bluetooth makes use of the spread-spectrum technique. This means that the frequency is changed rapidly (up to 1600 times per second) in a pseudo-random manner. The result is that enough interference-free frequencies are available to allow the desired data transfer to be achieved. This process is called Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS). Bluetooth uses 79 frequencies in the range between 2,402 GHz and 2,480 GHz, with a separation of 1 MHz. Figure 1 shows the principle of frequency hopping [4]. Slika 1. Preskakanje frekvencija [1] Figure 1. Frequency hopping [1] 3. PIKONET I SKATERNET Uređaji opremljeni Bluetooth modulima mogu nezavisno uspostaviti kontakt jedan s drugim pomoću tehnike preskakanja frekvencija. Radi sprječavanja međusobnog ometanja s ostalim Bluetooth uređajima u istom okruženju, koji bi mogli koristiti istu frekvenciju, redoslijed frekvencija određen je adresom i frekvencijom generatora takta onoga uređaja koji započinje povezivanje. Taj uređaj stoga postaje glavni uređaj u toj radiogrupi, dok su svi ostali sudionici označeni kao podređeni te se moraju sinkronizirati s glavnim uređajem. Do 8 uređaja može koristiti isti kanal. Takva grupa tvori mrežu koja se zove pikonet (Slika 2). 3. PICONET AND SCATTERNET Devices equipped with bluetooth modules can autonomously establish contact with each other, using the frequency-hopping technique. In order to prevent mutual interference with other Bluetooth devices in the same vicinity that might use the same frequencies, the frequency sequence is determined by the address and the clock rate of the device that initiates the connection. This device thus becomes the master device in this radio group, while all other participants are designated as slaves and must synchronize themselves with the master device. Up to 8 devices can use a single channel. Such a group forms a network that is called a piconet (Figure 2).
3 Eng. Rev. 26 (2006) Glavni uređaj Master device Glavni/podređeni uređaj Master/slave device Aktivni podređeni uređaj Active slave device Pasivni podređeni uređaj Parked slave device Uređaj na čekanju Standby device Slika 2. Komunikacijska topologija Figure 2. Communication topology U ovom kontekstu pojam kanal znači da svi sudionici pikoneta koriste isti redoslijed preskakanja, što znači da koriste isti redoslijed frekvencija. Budući da je svakom Bluetooth uređaju dodijeljena jedinstvena 48-bitna adresa, nije moguće da dva zasebna kanala imaju istu frekvenciju preskakanja. Ako se nezavisno postave dodatni pikoneti na jednoj lokaciji, moguće je iskoristiti više od 8 Bluetooth uređaja uz velike brzine prijenosa podataka. Podređeni uređaj koji radi u određenom pikonetu adresiran je u jednom vremenskom odsječku, a može se odazvati u sljedećem. Podređeni uređaj slobodan je sudjelovati u nekom drugom pikonetu u preostalim vremenskim odsječcima. Kako bi to učinio, namješta svoj prijamnik na frekvenciju drugog pikoneta odnosno na njegov fizički kanal i sinkronizira se s glavnim uređajem tog pikoneta. Višestruke bežične mreže povezane na taj način nazivaju se skaternet. Sudari su izbjegnuti činjenicom da se podređeni uređaji sinkroniziraju s taktom glavnog uređaja. Skaternet više razine može sadržavati do 10 pikoneta pa je moguće napraviti mrežu od 80 uređaja. Čak i kad je jedan uređaj član svih 10 pikoneta, brzina će prijenosa podataka pasti za maksimalno oko 10% [3]. 4. FIZIČKI KANAL Fizički kanali obilježeni su RF (Radio Frequency) frekvencijom kombiniranom s vremenskim parametrima i ograničenim dometom. Preskakanje frekvencija koristi se za periodično smanjivanje utjecaja interferencija te za regulaciju. In this context, the term channel means that all members of the piconet employ the same hopping sequence, which means that they use the same series of frequencies. Since each Bluetooth device is assigned a unique 48-bit address, it is not possible for two separate channels to have the same hopping sequence. By independently setting up additional piconets in the same vicinity, it is possible to use more than eight bluetooth devices in one location, with high data transfer rates. A slave device operating in a particular piconet is addressed by a master device in one time slot (even numbered) and may respond in a subsequent time slot (odd numbered). The slave is free to participate in another piconet in the remaining time slots. In order to do so, it sets its receiver to the frequency to which the other piconet has just hopped and synchronizes itself to the master device of that piconet. Multiple wirelless networks that are interconnected in this manner are reffered to as scatternet. Collisions are avoided by the fact that the slave devices synchronize themselves to the clock rate of the master. The higher level scatternet can contain up to 10 piconets, so that it is possible to build a network containing up to 80 devices. Even when a single device is a member of all 10 piconets, the data transfer rate is reduced by no more than around 10% [3]. 4. PHYSICAL CHANNELS Physical channels are characterized by an RF Radio Frequency) frequency combined with temporal parameters and restricted by spatial considerations. Frequency hopping is used to change the frequency periodically to reduce the effects of interference and for regulation purposes.
4 66 V. Kos, A. Sok:Princip komunikacije u... Dva Bluetooth uređaja koriste dijeljeni komunikacijski kanal za komunikaciju. Da bi se to postiglo, njihovi primopredajnici moraju biti podešeni na istu frekvenciju u isto vrijeme i moraju biti u dometu. Budući da je broj frekvencija ograničen i da postoji mogućnost prisutnosti drugih uređaja u istom prostornom i vremenskom polju, mogućnost je kolizije velika. Kako bi se izbjegla kolizija, svaki prijenos započinje pristupnim kodom koji služi kao povezni kod uređaja spojenih na fizički kanal. Pristupni kod pripada fizičkom kanalu. Kako bi podržao višestruke konkurentne zadatke, uređaj koristi vremensko multipleksiranje (TDM Time-Division Multiplex) kanala. Na taj način uređaj prividno simultano djeluje među drugim uređajima ili pikonetima i još je pristupačan (može ga se otkriti i spojiti na njega). Preko fizičkih kanala promet se odvija prividno dvosmjerno po TDD (Time-Division Duplex) principu. Master i slave u ovom slučaju koriste svaki drugi vremenski odsječak kako je prikazano na slici 3. Kad god je uređaj sinkroniziran s vremenom, frekvencijom i pristupnim kodom fizičkoga kanala, uređaj je spojen na taj kanal. Pristupni kod nalazi se u podatkovnom paketu [1]. Two Bluetooth devices use a shared physical channel for communication. To achieve this their transceivers need to be tuned to the same frequency at the same time, and they need to be in range of each other. Given that the number of frequencies is limited and that many devices may be operating independently within the same spatial and temporal area, there is strong likelihood of collision. To mitigate the unwanted effects of this collision each transmission starts with an access code that is used as a correlation code by devices tuned to the physical channel. The access code belongs to the physical channel. In order to support multiple concurrent operations the device uses time division multiplexing (TDM) between the channels. In this way a device can appear to operate simultaneously in several piconets, as well as being discoverable and connectable. Traffic over the physical channel takes place apparently in both dirrections using time division duplex (TDD). In this case, master and slave use every second time slot as shown in Figure 3. Whenever the device is synchronized with the time, frequency and the access code of a channel, the device is connected to that channel. The access code is located in data packet [1]. Slika 3. Vremenski dupleks Figure 3. Time-division duplex 5. LOGIČKI PRIJENOS PODATAKA Moguće su dvije osnovne vrste prijenosa podataka u Bluetooth mreži. To su jednostruki, od točke do točke i višestruki, od jedne točke do više točaka. Jednostruki su navedeni kao SCO (Synchronous Connection Oriented). Primarno su namijenjeni za prijenos glasovnih podataka. Potrebna je konekcija. Veza je stoga simetrična, što znači da je brzina prijenosa jednaka u obama smjerovima. 5. LOGICAL DATA TRANSMISSION There are two basic types of data transmission in a Bluetooth network. These are point-to-point and pointto-multipoint. Point-to-point transfers are referred to as SCO (Synchronous Connection Oriented). They are primarily intended to be used for voice data transmission. The link is thus symmetrical, which means that the data rate in both directions is the same.
5 Eng. Rev. 26 (2006) Maksimalan je broj tih veza u pikonetu 3. Podređeni uređaj podržava dvije veze u isto vrijeme koje dolaze od različitih glavnih uređaja. Jedan može koristiti glasovne pakete ili miješane pakete glas/podaci. Brzina uzorkovanja za prijenos glasovnih podataka iznosi 64 kb/s, isto kao i za ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network). Višestruki prijenos podataka asinkron je i ne treba biti uspostavljena konekcija. Baziran je na podatkovnim paketima. Takve su veze navedene kao ACL (Asynchronous Connection Less). Master uređaj koristi tu vrstu prijenosa da bi komunicirao s nekoliko podređenih uređaja u isto vrijeme. Uz slanje paketa svim podređenim uređajima ta se vrsta prijenosa također koristi za slanje paketa specifičnom uređaju. Kako bi se povećala brzina prijenosa podataka, paket može zauzeti ne jedan već 3 ili 5 vremenskih odsječaka kao što je prikazano na slici 4. A piconet has a maximum number of 3 SCO links. The slave device supports two links at the same time, originating from different masters. One can use the voice packets or mixed data/voice packets. The sampling rate for voice data transfers is 64 kb/s, the same as for ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network). Point-to-multipoint transfers are asynchronous and connection-independent. They are based on data packets. Such links are referred to as ACL (Asynchronous Connection Oriented). This type of transfer is used by the master device to communicate with several slave devices at the same time. In addition to being used for sending messages to all slave devices, this type of transfer is also used for sending data packets to a particular slave device. In order to increase the data transfer rate, a packet may use not only one but also 3 or 5 time slots, as shown in Figure 4. Slika 4. Višestruki paketi Figure 4. Multi-slot packets Da bi se to omogućilo, preskakanje frekvencija se zaustavi, a frekvencija na početku prijenosa paketa ostaje ista u trajanju svih 3 ili 5 vremenskih intervala. To omogućava da se rupe između susjednih odsječaka iskoriste za prijenos podataka. Zbog održavanja cjelokupne sinkronizacije preskakanje frekvencija se nastavlja onim redoslijedom koji bi i inače bio korišten. Prijenos podataka odvija se između podređenog i glavnog uređaja ili između podređenih uređaja. Izravna komunikacija između podređenih uređaja nije moguća te se odvija preko glavnog uređaja koji za to šalje dozvole. Zaštita od pogrešaka vrši se isključivo nad ACL paketima. Ako kod rezervacije odsječaka u slučaju SCO veze ostane slobodnih mjesta, glavni uređaj može ta mjesta iskoristiti za slanje prema drugim uređajima. Primjer toga prikazan je na slici 5 [3]. To make this possible, frequency-hopping is suspended and the frequency at the start of the packet transfer is maintained for the duration of 3 or 5 slot intervals. This allows the holes between successive slots to be used for data transfer. In order to maintain overall synchronization, frequency hopping resumes on completion of the transfer with the frequency that would normally be used. Data transfers are carried out between slave and master and between slave devices. Direct communication between slaves isn't possible and is carried out over a master device, which sends permissions to allow that. Error correction works only for ACL packets. If between reserved slots in the case of SCO links a few slots remain free, the master can use them to send data to other devices. an example of this procedure is shown in Figure 5 [3].
6 68 V. Kos, A. Sok:Princip komunikacije u... Slika 5. Komunikacija u rezerviranim i slobodnim odsječcima Figure 5. Communication in reserved and free slots 6. STANJA PIKONETA Bluetooth uređaji koji nisu članovi nijednog pikoneta, rade u pasivnom načinu rada, u kojem traže moguće povezivanje u njegovu najbližem okruženju svakih 1,28 s. To rade ispitujući 32 od mogućih 79 frekvencija koje su označene kao pobudni nosioci. Uređaj koji još nije spojen emitira poziv putem pobudnih nosilaca. Odgovor dobiva od ostalih uređaja u blizini. 6. PICONET STATES Bluetooth devices that are not members of any piconet, operate in the Standby mode in which they search for possible transfers in their immediate environment every 1,28 s. They do this by testing 32 of the possible 79 frequencies, which are designated as wake-up carriers. A device that is not yet connected transmits a call via wakeup carriers. Slika 6. Dijagram stanja Bluetooth uređaja [4] Figure 6. Bluetooth device state diagram [4]
7 Eng. Rev. 26 (2006) Nakon početnog dogovora, dva uređaja stvaraju pikonet, u kojem uređaj koji je započeo poziv uzima ulogu glavnog, te uspostavlja redoslijed skakanja frekvencija za taj pikonet, baziran na njegovoj 48-bitnoj adresi. Podređeni uređaj i bilo koji uređaj koji poslije pristupi tom pikonetu, sinkronizira se poslije s taktom glavnog uređaja. Slika 6 prikazuje dijagram stanja Bluetooth uređaja. Počevši od pasivnog stanja kreće prema Inquiry stanju u kojem se otkriva drugi uređaj. U tom stanju emitira poziv kojem slijedi zahtjev za adresom. Jednom kad je adresa drugog uređaja utvrđena ili je već bila poznata u pasivnom stanju, uređaj prelazi u Page stanje. Nakon karakterističnoga kašnjenja od 0,6 s veza postaje aktivna (povezano stanje). Sada se podaci mogu prenositi (u stanju prijenosa podataka). Nakon uspješnog prijenosa podataka, uređaj se može ili vratiti u pasivno stanje ili ući u jedan od triju načina rada niske potrošnje energije: prvi ekonomični način rada je Hold, u kojem uređaj ostaje aktivni član pikoneta (zadržava adresu aktivnog člana AM_ADDR). Ako je potrebno, uređaj može odmah napustiti Hold način rada kako bi prenosio podatke. Glavni uređaj može prisiliti podređeni da ode u Hold, ali on može dobrovoljno ući u njega. u drugom ekonomičnom načinu rada poznatom kao Sniff, podređeni je uređaj programiran da periodički sluša pikonet komunikaciju ne bi li ustvrdio ima li nekih podataka za njega na čekanju. treći ekonomični način rada zove se Park. U tom načinu rada podređeni uređaj ostavlja pikonet i otpušta svoju AM_ADDR. Poslije toga ostaje pasivan i jedina je moguća aktivnost nastavak sinkronizacije s glavnim uređajem. Uređaj dobiva 8-bitnu adresu pasivnog člana, PM_ADDR. Taj način rada podržava maksimalno 255 uređaja [4]. After an introductory handshake, the two devices set up a piconet, in which the device that first issued the call takes on the roll of master. Based on its 48-bit address, it establishes the hopping sequence for the piconet. The slave device, and any other devices that later join this piconet, synchronize themselves to the clock rate of the master device. Figure 6 shows a diagram of the state of a Bluetooth device. Starting from the Standby mode, it moves to the Inquiry state in detecting a second device. In this state, it transmits a general call followed by an address request. Once the address of the other device has been determined, or if this was already known in the Standby mode, the device transfers to the page mode. After a typical delay of 0,6 s, the connection becomes active (Connected State). Data transmission can now take place (in the Transmit Data State). After a successful data transmission, the device can either return to the Standby mode or enter one of three low-power (energy-saving) modes: - the first low-power mode is the Hold mode, in which the device remains an active member of the piconet (it keeps the address of the active member AM_ADDR). If necessary, the slave can leave the Hold mode in order to transfer data. The master can force a slave into the Hold mode, but a slave can also voluntarily enter the Hold mode. - in the second low-power mode, the Sniff mode, the slave is programmed to periodically listen to the piconet to determine whether there is a data transfer waiting for it. - the third mode is the Park mode. In this mode, the slave drops out of the piconet and frees its AM_ADDR. After this it remains passive, and its only activity is to maintain synchronization with the master. The device gets an 8-bit, passive member address, PM_AADR. This mode supports a maximum of 255 devices [4]. 7. MODULACIJA I ZAŠTITA OD POGREŠAKA Za svaki uskopojasni nosilac frekvencijskog preskakanja koristi se GFSK (Gaussian Frequency-Shift Keying) modulacija. S frekventnom devijacijom od 150 khz širina nosioca uz atenuaciju -3 db je 220 khz. Ta prilično jednostavna modulacijska shema izabrana je da cijena primopredajnih integriranih krugova bude što niža. 1 mw (0 dbm) emitirane snage omogućava barem deset metara efektivnog dometa pod normalnim okolnostima. U nekim određenim slučajevima emitiranje većih snaga (do 100 mw ili +20dBm) dozvoljeno je uz emisije u širokom spektru, što omogućava domet do 100 m [5]. 7. MODULATION AND ERROR HANDLING Gaussian Frequency-Shift Keying (GFSK) modulation is employed for the frequency-hopping narrow-band carrier of each channel. With a frequency deviation of around 150 khz, the -3 db carrier bandwidth is 220 khz. This fairly simple modulation scheme was chosen in order to keep the cost of the transceiver chips as low as possible. The transmitted power, at 1 mw (0 dbm), allows for an effective range of ten meters under normal conditions. In certain special cases, the generation of higher field strengths (up to 100 mw or +20 dbm) is permitted with spread spectrum transmissions, which enables effective ranges of up to 100 m [5].
8 70 V. Kos, A. Sok:Princip komunikacije u... Bluetooth je RF komunikacijski sistem. U lošim RF uvjetima trebao bi se smatrati nepouzdanim. Kako bi se smanjio utjecaj smetnji, na svakoj razini postoji zaštita od smetnji. Zaglavlje podatkovnog paketa koristi FEC (Forward Error Correction) u prijamniku i HEC (Header Error Check) da otkrije pogreške preostale nakon korekcije. Određeni paketi sadrže FEC za sadržaj. Nadalje, neki paketi sadrže CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check). U slučaju ACL logičkog transporta, rezultati dobiveni pomoću FEC koriste se za pokretanje ARQ (Automatic Repeat request) protokola. To pruža poboljšanu pouzdanost retransmisijom paketa koji ne prođu provjeru u prijamniku. Moguće je modificirati te postavke kako bi se podržali paketi osjetljivi na kašnjenje na način da se isključi neuspješno poslani paket ako mu je korisno vrijeme isteklo. Rezultirajuća je pouzdanost toga protokola ovisna o mogućnostima CRC i HEC kodova da otkriju pogreške. U većini slučajeva to je dovoljno. Doduše kod duljih paketa vjerojatnost je neotkrivenih pogrešaka prevelika za prijenos tipičnih aplikacija, pogotovo kod onih s velikom količinom informacija. Broadcast veze zbog jednosmjernog protoka informacija ne mogu koristiti ARQ, ali prijamnici svejedno mogu detektirati pogrešku. Umjesto toga paketi se šalju nekoliko puta u nadi da će prijamnik ispravno primiti barem jednu kopiju. Unatoč tome pristupu nema jamstva sigurnog prijma pa se te veze smatraju nepouzdanima [3]. Bluetooth is a wireless communications system. In poor RF environments, this system should be considered unreliable. To counteract this, the system provides levels of protection at each layer. The packet header uses forward error correcting (FEC) in the receiver and a header error check (HEC) to detect errors remaining after correction. Certain packet types include FEC for the payload. Furthermore, some packet types include a cyclic redundancy error check (CRC). On ACL logical transports the results of the FEC algorithm are used to drive a simple automatic repeat request (ARQ) protocol. This provides an enhanced reliability by retransmitting packets that do not pass the receiver s error checking algorithm. It is possible to modify this scheme to support latency-sensitive packets by discarding an unsuccessfully transmitted packet if the packet s useful life has expired. The resulting reliability gained by this ARQ protocol is only as dependable as the ability of the HEC and CRC codes to detect errors. In most cases this is sufficient. However, for the longer packet types the probability of an undetected error is too high to support typical applications, especially those with a large amount of data being transferred. Broadcast links have no feedback route, and are unable to use the ARQ scheme (although the receiver is still able to detect errors). Instead, each packet is transmitted several times in the hope that the receiver is able to receive at least one of the copies successfully. Despite this approach there are still no guarantees of successful receipt, and so these links are considered unreliable [3]. 8. BLUETOOTH PAKETI Baseband paket sastoji se od pristupnog koda (68 ili 72 bita), zaglavlja (54 bita) i korisnih informacija ( bita). U zaglavlju se nalaze kontrolne informacije o paketu, vezi i adresa odredišta. Korisni dio sadrži poruku (informaciju) o trenutnom stanju, ako se radi o višem sloju protokola ili jednostavno podatke. Sadrži još i CRC bitove. Postoje tri vrste pristupnoga koda. To su CAC (Channel Access Code), DAC (Device Access Code) i IAC (Inquiry Access Code). CAC služi za pristup fizičkom kanalu i izveden je iz 48-bitne adrese Bluetooth uređaja. DAC služi za pristup uređaju te se koristi kod stanja povezivanja (page). IAC se koristi kod pristupa funciji upita (inquiry) [3]. Na slici 7 prikazana je struktura paketa. 8. BLUETOOTH PACKETS The baseband packet consists of an access code (68 or 72- bit), header (54-bit) and payload ( bits). The header contains the packet control information, information about the link and destination address. The payload contains data on current states if this refers to higher protocols, or simply user data. CRC bits are also part of the payload. There are three types of access code. These are the CAC (Channel Access Code), the DAC (Device Access Code) and the IAC (Inquiry Access Code). The CAC serves for accessing the physical channel and it is made of a 48-bit Bluetooth device address. The DAC serves for accessing a device and it is used for paging. IAC is used to access the inquiry function [3]. Figure 7 illustrates the packet structure.
9 Eng. Rev. 26 (2006) Slika 7. Struktura paketa [3] Figure 7. Packet structure [3] 9. PROTOKOLNI STOG Na kraju treba prikazati i sam protokolni stog čije su funkcije odgovorne za funkcioniranje ove tehnologije. Blok shema prikazana je na slici PROTOCOL STACK Finally, there is a need to reveal the protocol stack itself, whose functions are crucial for the functioning of this technology. The block scheme is shown in figure 8. Slika 8. Protokolni stog [5] Figure 8. Protocol stack [5] Radio je najniži sloj. Specifikacije njegova sučelja definiraju izlazne karakteristike, frekvencijske pojaseve, raspored kanala, dopuštene razine izlazne snage i osjetljivost prijamnika. Sljedeći sloj je baseband. On izvršava fizičku obradu podataka i kontrolu pristupa fizičkom mediju. The radio is the lowest layer. Its interface specification defines the characteristics of the radio front end, frequency bands, channel arrangements, permissible transmit power levels, and receiver sensitivity level. The next layer is the baseband. It carries out physical and media access control processing.
10 72 V. Kos, A. Sok:Princip komunikacije u... To uključuje zadatke poput otkrivanja uređaja, formaciju veza i sinkronu i asinkronu komunikaciju sa signalizacijom. Bluetooth signalizacija mora izmijeniti mnoge kontrolne poruke s ciljem konfiguracije i upravljanja baseband konekcijama. Te su kontrolne poruke u sastavu LMP-a (Link Manager Protocol). Funkcijski entitet odgovoran za izvršavanje obrade povezan sa LMP zove se link manager. HCI (Host to Controller Inerface) specifikacija definira metodu komunikacije s Bluetooth kontrolerom neovisnu o sučelju. Programski stog na host procesoru komunicira s Bluetooth sklopovljem koristeći HCI komande. Budući da nije potrebno poznavati rad sklopovlja, programe protokolnog stoga moguće je jednostavno premještati s jednog Bluetooth integriranog kruga na drugi. HCI sloj je dio Bluetooth stoga, ali ne čini komunikaciju među urređajima i njegove se poruke ne prenose preko fizičkih veza. L2CAP (Logical Link And Adaptation Protocol) moguće je promatrati kao sloj veze Bluetooth stoga. Obično su L2CAP i viši slojevi izvedeni programski. L2CAP dostavlja pakete dobivene od viših slojeva na drugi kraj veze. Bluetooth uređaji mogu uspostaviti L2CAP konekciju čim su u dometu. Tada uređaj u ulozi klijenta treba otkriti usluge koje pruža server. SDP (Service Descovery Protocol) definira načine na koje klijent može otkriti usluge i atribute tih usluga. Dizajn SDP-a optimiziran je za Bluetooth. Definira samo mehanizme otkrivanja, ali metode za pristupanje tim uslugama izvan su njegove domene. RFCOMM definira metodu emulacije RS-232 konekcije preko Bluetooth zračne veze. RFCOMM podržava aplikacije koje koriste COM priključak za komunikaciju s hostom. Ostali viši protokoli prikazani na slici 8 manje su bitni za rad samog uređaja i ovisni su o aplikacijama odnosno implementaciji sistema [5]. 10. ZAKLJUČAK Budućnost je komunikacija u bežičnom umrežavanju. Razlog je tomu sve dinamičniji pristup življenju, poslovanju, komuniciranju, itd. Bluetooth bežična tehnologija zbog svojih osnovnih karakteristika, malih dimenzija, niske potrošnje i cijene, može postati sveprisutna u malim elektroničkim uređajima kao što je to danas infracrvena tehnologija. Zbog svojih specifičnosti Bluetooth bežična tehnologija nije izravan konkurent već postojećim i dobro usvojenim tehnologijama. Bluetooth je komplementaran mobilnim mrežama druge i treće generacije i WLAN mrežama. This includes tasks such as device discovery, link formation, and synchronous and asynchronous communication with signalization. Bluetooth signalization must exchange several control messages for the purpose of configuring and managing the baseband connections. These control messages are part of the link manager protocol (LMP). The functional entity responsible for carrying out the processing associated with LMP is called the link manager. The Host to Controller Interface (HCI) specification defines an interface-independent method of communicating with the Bluetooth controller. The software stack on the host processor communicates with the Bluetooth hardware using HCI commands. Since no hardware knowledge is needed, the Bluetooth stack software can easily be ported from one Bluetooth chip to another. The HCI layer is part of the Bluetooth stack, but it doesn t constitute a peer-to-peer communication layer since the HCI command and response messages do not flow over the physical link. The logical link control and adaptation protocol (L2CAP) can be viewed as the Bluetooth s link layer. Usually, L2CAP and layers above it are implemented in software. The L2CAP delivers packets received from higher layers to the other end of the link. Bluetooth devices can establish an L2CAP connection as soon as they are in range of each other. A client device then needs to discover the services provided by the server device. The service discovery protocol (SDP) defines the means by which the client device can discover services as well as their attributes. The SDP design has been optimized for Bluetooth. It defines only the discovery mechanisms but the methods for accessing those services are outside its scope. The RFCOMM defines a method of emulating the RS-232 connection over Bluetooth airlink. RFCOMM supports applications that use the COM port to communicate with the host. Other higher-level protocols shown in Figure 8 are less signifficant for device core operation and they are application and implementation-dependent [5]. 10. CONCLUSION The future of communications is in the wireless approach. The reason for this lies in a more dynamic way of life, business, communication, etc. Because of its basic characteristics, small proportions, low consumption and price, Bluetooth technology can become omnipresent in small electronic devices the way that infrared technology is today. Bluetooth wireless technology isn't a direct competitor to other existing and well-adopted technologies. Bluetooth is complementary to second and third generation mobile networks and WLAN.
11 Eng. Rev. 26 (2006) U širem kontekstu jedne mobilne veze možemo je promatrati kao zadnji bežični korak do korisnika. Bluetooth bežična tehnologija je i najpoznatiji predstavnik tehnologija za umrežavanje u sve popularnijim osobnim mrežama, Personal Area Network (PAN) i u tom području se može očekivati daljnja afirmacija. In the wider context of a mobile network, it can be observed as the last wireless step closer to the user. Bluetooth wireless technology is also the most popular representative for personal area networking and in this field future affirmation can be expected. LITERATURE REFERENCES [1] Nathan J. Muller : Bluetoot Demystified, McGraw-Hill, 2000 [2] D. Kammer, G. McNutt, B. Senesse, J. Bray: Bluetooth Application Developer s Guide, Syngress, 2002 [3] Brent A. Miller, Chatschik Bisdikan : Bluetooth Revealed, Prentice Hall, 2000 [4] [5] Strukovni članak Professional Paper Adrese autora / Author s addresses: Vedran Kos, ing. Prof. v. šk. mr. sc. Antun Sok, dipl. ing. Sveučilište u Rijeci, Tehnički fakultet Vukovarska 58 HR Rijeka, Hrvatska
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
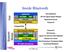 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
VDSL modem Zyxel VMG1312-B10A/B30A
 VDSL modem Zyxel VMG1312-B10A/B30A Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.2.1 User Name user Password 1234 Funkcionalnost lampica Power lampica treperi kratko vrijeme nakon uključivanja modema,
VDSL modem Zyxel VMG1312-B10A/B30A Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.2.1 User Name user Password 1234 Funkcionalnost lampica Power lampica treperi kratko vrijeme nakon uključivanja modema,
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Version 1.01(5/8/2008) BLUETOOTH
 BLUETOOTH Bluetooth tehnologija razvijena je za bežično povezivanje (RF veze kratkog dometa) prijenosnih i stolnih računala, računalnih oprema, mobilnih telefona, kamera i drugih digitalnih uređaja na
BLUETOOTH Bluetooth tehnologija razvijena je za bežično povezivanje (RF veze kratkog dometa) prijenosnih i stolnih računala, računalnih oprema, mobilnih telefona, kamera i drugih digitalnih uređaja na
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
TP-LINK TL-WPA4220 strujni prijenosnik Internet ili IPTV signala s bežičnim modulom. Priručnik za korištenje i brzu instalaciju
 TP-LINK TL-WPA4220 strujni prijenosnik Internet ili IPTV signala s bežičnim modulom Priručnik za korištenje i brzu instalaciju Sadržaj ŠTO JE TP-LINK TL-WPA4220... 3 KAKO KORISITI TP-LINK TL-WPA4220...
TP-LINK TL-WPA4220 strujni prijenosnik Internet ili IPTV signala s bežičnim modulom Priručnik za korištenje i brzu instalaciju Sadržaj ŠTO JE TP-LINK TL-WPA4220... 3 KAKO KORISITI TP-LINK TL-WPA4220...
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
Windows Server 2012, VDI Licenciranje najprodavanijeg servera, što je novo, VDI licenciranje. Office 2013 / Office 365
 Windows 8 Licenciranje, razlike u verzijama Windows Server 2012, VDI Licenciranje najprodavanijeg servera, što je novo, VDI licenciranje Serverski proizvodi Server 2012, System centar 2012, SQL 2012, Sharepoint
Windows 8 Licenciranje, razlike u verzijama Windows Server 2012, VDI Licenciranje najprodavanijeg servera, što je novo, VDI licenciranje Serverski proizvodi Server 2012, System centar 2012, SQL 2012, Sharepoint
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Wireless Local Area Network. Internet Protocol Suite
 Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Računarske osnove Interneta (SI3ROI, IR4ROI)
 Računarske osnove terneta (SI3ROI, IR4ROI) Vežbe MPLS Predavač: 08.11.2011. Dražen Drašković, drazen.draskovic@etf.rs Autori: Dražen Drašković Naučili ste na predavanjima MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching)
Računarske osnove terneta (SI3ROI, IR4ROI) Vežbe MPLS Predavač: 08.11.2011. Dražen Drašković, drazen.draskovic@etf.rs Autori: Dražen Drašković Naučili ste na predavanjima MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching)
BASEBAND SPECIFICATION
 Core System Package [Controller volume] Part B BASEBAND SPECIFICATION This document describes the specification of the Bluetooth link controller which carries out the baseband protocols and other lowlevel
Core System Package [Controller volume] Part B BASEBAND SPECIFICATION This document describes the specification of the Bluetooth link controller which carries out the baseband protocols and other lowlevel
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Upute za VDSL modem BiPAC 8700VNXL R3
 Upute za VDSL modem BiPAC 8700VNXL R3 Default Login Details LAN IP Address User Name Password http://192.168.2.1 user user Funkcionalnost lampica LED Stanje Opis Power LAN 1-4 WLAN WPS USB Crvena svijetli
Upute za VDSL modem BiPAC 8700VNXL R3 Default Login Details LAN IP Address User Name Password http://192.168.2.1 user user Funkcionalnost lampica LED Stanje Opis Power LAN 1-4 WLAN WPS USB Crvena svijetli
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
VRIJEDNOSTI ATRIBUTA
 VRIJEDNOSTI ATRIBUTA Svaki atribut (bilo da je primarni ključ, vanjski ključ ili običan atribut) može i ne mora imati ograničenja na svojim vrijednostima. Neka od ograničenja nad atributima: Null / Not
VRIJEDNOSTI ATRIBUTA Svaki atribut (bilo da je primarni ključ, vanjski ključ ili običan atribut) može i ne mora imati ograničenja na svojim vrijednostima. Neka od ograničenja nad atributima: Null / Not
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN
 Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Unaprjeñenje sigurnosti u mrežama pružatelja
 Unaprjeñenje sigurnosti u mrežama pružatelja usluga Miroslav Šimić miroslav.simic@snt.hr CCIE #19429 Agenda Zaštita mrežne infrastrukture Zaštita na rubovima mreže Uočavanje i sprječavanje napada Agenda
Unaprjeñenje sigurnosti u mrežama pružatelja usluga Miroslav Šimić miroslav.simic@snt.hr CCIE #19429 Agenda Zaštita mrežne infrastrukture Zaštita na rubovima mreže Uočavanje i sprječavanje napada Agenda
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
CSS CSS. selector { property: value; } 3/20/2018. CSS: Cascading Style Sheets
 CSS CSS CSS: Cascading Style Sheets - Opisuje izgled (appearance) i raspored (layout) stranice - Sastoji se od CSS pravila, koji defini[u skup stilova selector { property: value; 1 Font face: font-family
CSS CSS CSS: Cascading Style Sheets - Opisuje izgled (appearance) i raspored (layout) stranice - Sastoji se od CSS pravila, koji defini[u skup stilova selector { property: value; 1 Font face: font-family
BLUETOOTH. Kolegij: Mreže računala Seminarski rad: Martin Žagar U Zagrebu, 1. siječnja 2003.
 Sveučilište u Zagrebu Fakultet elektrotehnike i računarstva Zavod za elektroniku, mikroelektroniku, računalne i inteligentne sustave Kolegij: Mreže računala Seminarski rad: BLUETOOTH Martin Žagar 36374880
Sveučilište u Zagrebu Fakultet elektrotehnike i računarstva Zavod za elektroniku, mikroelektroniku, računalne i inteligentne sustave Kolegij: Mreže računala Seminarski rad: BLUETOOTH Martin Žagar 36374880
A Guide. Wireless Network Library Bluetooth
 A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology
 SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
PREDMET. Osnove Java Programiranja. Čas JAVADOC
 PREDMET Osnove Java Programiranja JAVADOC Copyright 2010 UNIVERZITET METROPOLITAN, Beograd. Sva prava zadržana. Bez prethodne pismene dozvole od strane Univerziteta METROPOLITAN zabranjena je reprodukcija,
PREDMET Osnove Java Programiranja JAVADOC Copyright 2010 UNIVERZITET METROPOLITAN, Beograd. Sva prava zadržana. Bez prethodne pismene dozvole od strane Univerziteta METROPOLITAN zabranjena je reprodukcija,
Bežična topologija. Kategorije bežičnih mreža po površini pokrivanja
 Danas su bežične mreže sastavni deo društva i njegov veliki činilac u delu razmene podataka i informacija. Bežične mreže za razliku od ostalih tipova mreža nemaju ograničenja u smislu vezanosti za mrežne
Danas su bežične mreže sastavni deo društva i njegov veliki činilac u delu razmene podataka i informacija. Bežične mreže za razliku od ostalih tipova mreža nemaju ograničenja u smislu vezanosti za mrežne
Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference
 Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering
Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Case Study Hrvatska pošta: Korisničko iskustvo iz snova. Tomislav Turk Samostalni sistem inženjer, Combis d.o.o. Zagreb,
 Case Study Hrvatska pošta: Korisničko iskustvo iz snova Tomislav Turk Samostalni sistem inženjer, Combis d.o.o. Zagreb, 27.12.2018. Sadržaj Hrvatska pošta prije projekta Izazovi projekta Tehnologije korištene
Case Study Hrvatska pošta: Korisničko iskustvo iz snova Tomislav Turk Samostalni sistem inženjer, Combis d.o.o. Zagreb, 27.12.2018. Sadržaj Hrvatska pošta prije projekta Izazovi projekta Tehnologije korištene
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 radionica EDU IT Pro, Zagreb,
 Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 radionica EDU IT Pro, Zagreb, 13.04.2017. Podešavanje Hyper-V Servera 2016 za RSAT upravljanje Dario Štefek Lokacije za preuzimanje: Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/evalcenter/evaluate-hyper-v-server-2016
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 radionica EDU IT Pro, Zagreb, 13.04.2017. Podešavanje Hyper-V Servera 2016 za RSAT upravljanje Dario Štefek Lokacije za preuzimanje: Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/evalcenter/evaluate-hyper-v-server-2016
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth
 Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth Pravin Bhagwat Networking Research Group AT&T Labs - Research pravin@acm.org ACM Mobicom 2000 Half day tutorial Aug 06, 2000 Boston, MA Bluetooth A cable replacement
Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth Pravin Bhagwat Networking Research Group AT&T Labs - Research pravin@acm.org ACM Mobicom 2000 Half day tutorial Aug 06, 2000 Boston, MA Bluetooth A cable replacement
Lecture Computer Networks
 Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Lecture Computer Networks Networks for Multimedia
Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Lecture Computer Networks Networks for Multimedia
Master. Slave. Master. Slaves. TCP/IP Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology. Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3
 / Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
/ Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic
 Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth
 Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth Martin Connolly, Cormac J. Sreenan University College Cork Department of Computer Science Email: cjs@cs.ucc.ie Abstract The Bluetooth protocol is one of the better-known
Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth Martin Connolly, Cormac J. Sreenan University College Cork Department of Computer Science Email: cjs@cs.ucc.ie Abstract The Bluetooth protocol is one of the better-known
Mrežni koncepti (koncept, skica, nacrt, plan) o Pregled na najvažnije koncepte mreže. Slanje paketa sa Argon-1 prema Neon-u
 Mrežni koncepti (koncept, skica, nacrt, plan) Arhitektura tu protokola o Pregled na najvažnije koncepte mreže Protokol slojevi Encapsulation Uvod u mreže. Mrežna apstrakcija Ova prezentacija koristi primjer
Mrežni koncepti (koncept, skica, nacrt, plan) Arhitektura tu protokola o Pregled na najvažnije koncepte mreže Protokol slojevi Encapsulation Uvod u mreže. Mrežna apstrakcija Ova prezentacija koristi primjer
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
Sadržaj. Verzija 03/2017 Primjenjuje se od 20. novembra godine
 Sadržaj 1 Web hosting 3 2 Registracija domena 3 3 Internet marketing 3 4 E mail paketi 4 5 Virtuoz 4 6 Internet Security servis 5 7 Kolokacija servera 6 8 Cloud usluge 6 9 Aktivni servisi koji nijesu u
Sadržaj 1 Web hosting 3 2 Registracija domena 3 3 Internet marketing 3 4 E mail paketi 4 5 Virtuoz 4 6 Internet Security servis 5 7 Kolokacija servera 6 8 Cloud usluge 6 9 Aktivni servisi koji nijesu u
Osnove programskog jezika C# Čas 5. Delegati, događaji i interfejsi
 Osnove programskog jezika C# Čas 5. Delegati, događaji i interfejsi DELEGATI Bezbedni pokazivači na funkcije Jer garantuju vrednost deklarisanog tipa. Prevodilac prijavljuje grešku ako pokušate da povežete
Osnove programskog jezika C# Čas 5. Delegati, događaji i interfejsi DELEGATI Bezbedni pokazivači na funkcije Jer garantuju vrednost deklarisanog tipa. Prevodilac prijavljuje grešku ako pokušate da povežete
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
Cjenovnik usluga informacionog društva
 Cjenovnik usluga informacionog društva Verzija: 01/2018 Sadržaj 1 Web hosting 3 2 Registracija domena 3 3 Internet marketing 3 4 E mail paketi 4 5 Virtuoz 4 6 Internet Security servis 5 7 Kolokacija servera
Cjenovnik usluga informacionog društva Verzija: 01/2018 Sadržaj 1 Web hosting 3 2 Registracija domena 3 3 Internet marketing 3 4 E mail paketi 4 5 Virtuoz 4 6 Internet Security servis 5 7 Kolokacija servera
RECOGNITION OF BLUETOOTH SIGNALS BASED ON FEATURE DETECTION
 Facoltà di Ingegneria Tesi di Laurea Specialistica in Ingegneria delle Telecomunicazioni RECOGNITION OF BLUETOOTH SIGNALS BASED ON FEATURE DETECTION Candidato Stefano Boldrini Relatore Prof.ssa Maria-
Facoltà di Ingegneria Tesi di Laurea Specialistica in Ingegneria delle Telecomunicazioni RECOGNITION OF BLUETOOTH SIGNALS BASED ON FEATURE DETECTION Candidato Stefano Boldrini Relatore Prof.ssa Maria-
original standard a transmission at 5 GHz bit rate 54 Mbit/s b support for 5.5 and 11 Mbit/s e QoS
 IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
Sberbank Business Online na Mozilla FireFox
 Sberbank Business Online na Mozilla FireFox Verzija 1.6 Srpanj 2016. Sberbank d.d. Stranica 1 SADRŽAJ 1 INSTALACIJA... 2 2 POKRETANJE MOZILLE FIREFOX... 3 2.1 IMPORT SECURITY MODULA... 4 2.2 AUTOMATSKI
Sberbank Business Online na Mozilla FireFox Verzija 1.6 Srpanj 2016. Sberbank d.d. Stranica 1 SADRŽAJ 1 INSTALACIJA... 2 2 POKRETANJE MOZILLE FIREFOX... 3 2.1 IMPORT SECURITY MODULA... 4 2.2 AUTOMATSKI
Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be
 IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
Vežba 3 Mrežni protokoli
 Računarska tehnika i računarske komunikacije Osnovi računarskih mreža 1 2017-2018 Vežba 3 Mrežni protokoli Mrežni protokoli definišu format i redosled poruka koje se razmenjuju između dva ili više komunikacionih
Računarska tehnika i računarske komunikacije Osnovi računarskih mreža 1 2017-2018 Vežba 3 Mrežni protokoli Mrežni protokoli definišu format i redosled poruka koje se razmenjuju između dva ili više komunikacionih
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela
 By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Objectives of the Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a. worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the
 Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the worldwide standard for short-range wireless communication.
Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the worldwide standard for short-range wireless communication.
FAKULTET ELEKTROTEHNIKE I RAČUNARSTVA
 FAKULTET ELEKTROTEHNIKE I RAČUNARSTVA Sustavi za praćenje i vođenje procesa Seminarski rad LOGIČKI ANALIZATOR (PC kao instrument) 26. svibnja 2007. Ivan Grubišić 0036404380 1. Logički analizator Logički
FAKULTET ELEKTROTEHNIKE I RAČUNARSTVA Sustavi za praćenje i vođenje procesa Seminarski rad LOGIČKI ANALIZATOR (PC kao instrument) 26. svibnja 2007. Ivan Grubišić 0036404380 1. Logički analizator Logički
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE W.lan.4
 Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Informatika Uvod u C#,.NET Framework i Visual Studio... nastavak...
 Informatika Uvod u C#,.NET Framework i Visual Studio... nastavak... Prof. dr. sc. Tomislav Pribanić Izv. prof. dr. sc. Vedran Podobnik Doc. dr. sc. Marija Seder Sveučilište u Zagrebu Fakultet elektrotehnike
Informatika Uvod u C#,.NET Framework i Visual Studio... nastavak... Prof. dr. sc. Tomislav Pribanić Izv. prof. dr. sc. Vedran Podobnik Doc. dr. sc. Marija Seder Sveučilište u Zagrebu Fakultet elektrotehnike
CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING
 Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Bluetooth. Bluetooth. WPAN Technologies. HomeRF. Bluetooth. Claudio Casetti. Dipartimento di Elettronica Politecnico di Torino
 Bluetooth Claudio Casetti Dipartimento di Elettronica Politecnico di Torino WPAN Technologies HomeRF Bluetooth Bluetooth A cable replacement technology 1 Mb/s symbol rate Range 10+ meters Single chip radio+baseband
Bluetooth Claudio Casetti Dipartimento di Elettronica Politecnico di Torino WPAN Technologies HomeRF Bluetooth Bluetooth A cable replacement technology 1 Mb/s symbol rate Range 10+ meters Single chip radio+baseband
13 Wireless. Communications Using Bluetooth. Oge Marques and Nitish Barman CONTENTS
 13 Wireless Communications Using Bluetooth Oge Marques and Nitish Barman CONTENTS 13.1 Introduction...308 13.2 Overview...309 13.2.1 Masters and Slaves...310 13.2.2 Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS)
13 Wireless Communications Using Bluetooth Oge Marques and Nitish Barman CONTENTS 13.1 Introduction...308 13.2 Overview...309 13.2.1 Masters and Slaves...310 13.2.2 Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS)
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets
 A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
USLOVI I CENE KORIŠĆENJA ZA TARIFNE PAKETE «PRENESI I SURFUJ+»
 USLOVI I CENE KORIŠĆENJA ZA TARIFNE PAKETE «SURFUJ+» USLUGE U OKVIRU PAKETA pretpl ate sa pdvom pretplate ka mreža ma u Telenor mreži SMS poruka SURFUJ+ S 950 791.67 150 5,000 250 SURFUJ+ M 1,250 1,041.67
USLOVI I CENE KORIŠĆENJA ZA TARIFNE PAKETE «SURFUJ+» USLUGE U OKVIRU PAKETA pretpl ate sa pdvom pretplate ka mreža ma u Telenor mreži SMS poruka SURFUJ+ S 950 791.67 150 5,000 250 SURFUJ+ M 1,250 1,041.67
Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies
 Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies Topics Background What is Bluetooth low energy? Basic concepts Architecture Differentiation and comparison Markets and applications Background Background
Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies Topics Background What is Bluetooth low energy? Basic concepts Architecture Differentiation and comparison Markets and applications Background Background
