Wireless Protocols for IoT Part I: Bluetooth and Bluetooth Smart
|
|
|
- Oswald Booker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wireless Protocols for IoT Part I: Bluetooth and Bluetooth Smart Raj Jain Professor of CSE Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO Audio/Video recordings of this class lecture are available on-line at: 11-1
2 Overview 1. Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) 2. IEEE Projects 3. Bluetooth: Packet Format, Energy Management 4. Bluetooth Protocol Stack, Application Profiles 5. Bluetooth LE: Protocol Stack, PHY, MAC 6. Bluetooth and WiFi Coexistence Note: This is 1 st in a series of lectures on WPANs. ZigBee and other networks are discussed in subsequent lectures. 11-2
3 Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) 10m or less e Nomadic Mobile Wide Area Network (WAN) Handoff WRAN Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) 2G, 2.5G, 3G Cellular /WiMAX Fixed Wireless MAN Local Area Network (LAN) Wi-Fi Personal Area Network (PAN) Bluetooth ZigBee Body Area Networks 11-3
4 WPAN: Design Challenges Battery powered: Maximize battery life. A few hours to a few years on a coin cell. Dynamic topologies: Short duration connections and then device is turned off or goes to sleep No infrastructure Avoid Interference due to larger powered LAN devices Simple and Extreme Interoperability: Billions of devices. More variety than LAN or MAN Low-cost: A few dollars 11-4
5 IEEE Projects IEEE : Bluetooth 1.2 IEEE : Coexistence Recommended Practice IEEE : High Rate (55 Mbps) Multimedia WPAN IEEE a: Ultra-Wide Band Phy - disbanded IEEE b-2005: MAC Interoperability IEEE c-2009: High Rate (>1Gbps) mm Wave PHY IEEE d: 100 Gbps point-to-point Phy IEEE e: High-Rate close proximity point-to-point MAC and PHY IEEE : Low Rate (250kbps) WPAN - ZigBee IEEE e-2012: MAC Enhancements 11-5
6 IEEE Projects (Cont) IEEE f-2012: PHY for Active RFID IEEE g-2012: PHY for Smart Utility Networks IEEE h: Corrigendum 1 IEEE i: Roll-up to include 15.4a, c & d IEEE j-2013: Medical Body Area Network GHz IEEE k-2013: Low Energy Critical Infrastructure Monitoring PHY IEEE m-2014: TV White Spaces PHY IEEE P n: China Medical Band PHY IEEE P p-2014: Positive Train Control (Rail Communications & Control) PHY IEEE P q: Ultra Low Power PHY 11-6
7 IEEE Projects (Cont) IEEE r: Common Ranging (Distance Measurement) Protocol IEEE s: System resource usage IEEE t: High rate PHY IEEE u: MHz band in India IEEE : Mesh Networking. Full/partial meshes. Range Extension IEEE : Body Area Networking. Medical and entertainment. Low power IEEE : Visible Light Communications IEEE r1: Optical wireless (infrared, ultraviolet, visible light) IEEE P : Peer Aware Communications 11-7
8 IEEE Projects (Cont) IEEE P : Key Management Protocol IEEE P : Layer 2 (Mesh) Routing IEEE SG12: Consolidated Link Layer Control study group IEEE IG6T: Consolidate Link Layer Control interest group IEEE IGdep: Enhanced Dependability interest group IEEE IGguide: Guide for 15.4 use interest group IEEE IGhrrc: High Rate Rail Communications interest group IEEE ITTHz: Terahertz interest group IEEE SCwng: Wireless Next-Generation standing committee IEEE SCmaint: Maintenance standing committee 11-8
9 Li-Fi Optical wireless using light Localized Secure High SNR Dense reuse No electromagnetic interference Good for EMI sensitive environments, e.g., planes Ref: N. Serafimovski, What is Li-Fi?, Jan 2015,
10 Bluetooth Started with Ericsson's Bluetooth Project in 1994 for radiocommunication between cell phones over short distances Named after Danish king Herald Blatand (AD ) who was fond of blueberries Intel, IBM, Nokia, Toshiba, and Ericsson formed Bluetooth SIG in May 1998 Version 1.0A of the specification came out in late IEEE approved in early 2002 is based on Bluetooth Later versions handled by Bluetooth SIG directly Key Features: Lower Power: 10 ma in standby, 50 ma while transmitting Cheap: $5 per device Small: 9 mm 2 single chips 11-10
11 Bluetooth Versions Bluetooth 1.1: IEEE Bluetooth 1.2: IEEE Completed Nov Extended SCO, Higher variable rate retransmission for SCO + Adaptive frequency hopping (avoid frequencies with interference). Bluetooth Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) (Nov 2004): 3 Mbps using DPSK. For video applications. Reduced power due to reduced duty cycle Bluetooth EDR (July 2007): Secure Simple Pairing to speed up pairing Bluetooth 3.0+ High Speed (HS) (April 2009): 24 Mbps using WiFi PHY + Bluetooth PHY for lower rates Bluetooth 4.0 (June 2010): Low energy. Smaller devices requiring longer battery life (several years). New incompatible PHY. Bluetooth Smart or BLE Bluetooth 4.1: Core Specification Amendments (CSA) 1, 2, 3, 4 Bluetooth 4.2 (Dec 2014): Larger packets, security/privacy, IPv6 profile Ref: ITL, Security of Bluetooth Systems and Devices,
12 Bluetooth: Details Frequency Range: MHz (total 79 MHz band) 23 MHz in some countries, e.g., Spain Data Rate: 1 Mbps using 1 MHz (Nominal) 720 kbps (User) Radio Frequency hopping: 1600 times/s 625 ms/hop Security: Challenge/Response Authentication. 128b Encryption TX Output Power: Class 1: 20 dbm Max. (0.1W) 100m Class 2: 4 dbm (2.5 mw) Class 3: 0 dbm (1mW) 10m Frequency Ref: Network 1 Network 2 Time
13 Piconet Piconet is formed by a master and many slaves Up to 7 active slaves. Slaves can only transmit when requested by master Up to 255 Parked slaves Active slaves are polled by master for transmission Each station gets a 8-bit parked address 255 parked slaves/piconet The parked station can join in 2ms. Other stations can join in more time. Scatter net: A device can participate in multiple Pico nets Timeshare and must synchronize to the master of the current piconet. Routing protocol not defined. Ref: P. Bhagwat, Bluetooth Technology for short range wireless Apps, IEEE Internet Computing, May-June 2001, pp , bluetooth.pdf (Must read) 11-13
14 Frequency Hopping Sequences Frequency 1 Frequency 2 Frequency ms slots using a ms clock Time-division duplex (TDD) Downstream and upstream alternate Master starts in even numbered slots only. Slaves start in odd numbered slots only Slaves can transmit in one slot right after receiving a packet from master Packets = 1 slot, 3 slot, or 5 slots long The frequency hop is skipped during a packet
15 Bluetooth Packet Format Access Baseband/Link Data Code Control Header Payload 72b 54b b Packets can be up to five slots long. 5 slots =3125 bits. Access codes: Channel access code identifies the piconet Device access code for paging requests and response Inquiry access code to discover units Header: member address (3b), type code (4b), flow control, ack/nack (1b), sequence number, and header error check (8b) 18b Header is encoded using 1/3 rate FEC resulting in 54b Synchronous traffic has periodic reserved slots. Other slots can be allocated for asynchronous traffic 11-15
16 Bluetooth Operational States Disconnected Standby Connecting Inquiry Page Active Transmit Connected Low Power Park Sniff Hold Standby: Initial state Inquiry: Master sends an inquiry packet. Slaves scan for inquiries and respond with their address and clock after a random delay (CSMA/CA) 11-16
17 Bluetooth Operational States (Cont) Page: Master in page state invites devices to join the piconet. Page message is sent in 3 consecutive slots (3 frequencies). Slave enters page response state and sends page response including its device access code. Master informs slave about its clock and address so that slave can participate in piconet. Slave computes the clock offset. Connected: A short 3-bit logical address is assigned Transmit: Standby Inquiry Page Transmit Connected Park Sniff Hold 11-17
18 Energy Management in Bluetooth Three inactive states: 1. Hold: No Asynchronous Connection List (ACL). Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO) continues. Node can do something else: scan, page, inquire 2. Sniff: Low-power mode. Slave listens after fixed sniff intervals. 3. Park: Very Low-power mode. Gives up its 3-bit active member address and gets an 8-bit parked member address. Wake up periodically and listen to beacons. Master broadcasts a train of beacons periodically Sniff Park 11-18
19 Bluetooth Protocol Stack Application Middleware Audio Transport BNEP Applications (Profiles) TCS RFCOMM SDP L2CAP Link Manager Baseband RF RF: Frequency hopping Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying (GFSK) modulation Baseband: Frequency hop selection, connection, MAC Host Controller Interface Freq Time FSK Freq Time GFSK 11-19
20 Baseband Layer Each device has a 48-bit IEEE MAC address 3 parts: Lower address part (LAP) 24 bits Upper address part (UAP) 8 bits Non-significant address part (NAP) - 16 bits UAP+NAP = Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) from IEEE LAP is used in identifying the piconet and other operations Clock runs at 3200 cycles/sec or ms (twice the hop rate) Upper Address Part Non-sig. Address Part Lower Address Part 8b 16b 24b 11-20
21 Bluetooth Protocol Stack (Cont) Link Manager: Negotiate parameters, Set up connections Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP): Protocol multiplexing Segmentation and reassembly Controls peak bandwidth, latency, and delay variation Host Controller Interface: Chip independent interface to Bluetooth chip. Allows same software to run on all chips. RFCOMM Layer: Presents a virtual serial port Sets up a connection to another RFCOMM Service Discovery Protocol (SDP): Devices can discover the services offered and their parameters Audio Applications (Profiles) BNEP TCS RFCOMM SDP L2CAP Link Manager Baseband Host Controller Interface RF
22 Bluetooth Protocol Stack (Cont) Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol (BNEP): To transport Ethernet/IP packets over Bluetooth IrDA Interoperability protocols: Allow existing IrDA applications to work w/o changes. IrDA object Exchange (IrOBEX) and Infrared Mobile Communication (IrMC) for synchronization Audio is carried over 64 kbps over SCO links over baseband Telephony control specification binary (TCS-BIN): Call control including group management (multiple extensions, call forwarding, and group calls) Application Profiles: Set of algorithms, options, and parameters. Audio Applications (Profiles) BNEP TCS RFCOMM SDP L2CAP Link Manager Baseband Host Controller Interface RF
23 Application Profile Examples Headset Profile Global Navigation Satellite System Profile Hands-Free Profile Phone Book Access Profile SIM Access Profile Synchronization Profile Video Distribution Profile Blood Pressure Profile Cycling Power Profile Find Me Profile Heart Rate Profile Basic Printing Profile Dial-Up Networking Profile File Transfer Profile Ref: Bluetooth SIGn, Adopted Bluetooth Profiles, Services, Protocols and Transports,
24 Bluetooth and WiFi Coexistence Bluetooth frequency hops in 1 MHz carriers over MHz (79 MHz total) WiFi uses OFDM with 52 subcarriers in 20 MHz channels in MHz (3 non-overlapping channels) Most computers have both Bluetooth and WiFi Collaborative Strategies: Two networks on the same device Non-Collaborative Strategies: No common device 11-24
25 Collaborative Coexistence Strategies Both networks on the same equipment (Laptop or IPhone): 1. Time Division: Bluetooth skips slots when WiFi is busy, WiFi reserves time for Bluetooth between Beacons 2. Packet Traffic Arbitration: Packets are prioritized and queued on a common queue for transmission 3. Notch Filter: WiFi OFDM does not use subcarriers to which Bluetooth hops BT WiFi Notch 11-25
26 Non-Collaborative Coexistence Strategies Measure noise level and error rate: Random bit errors Þ Noise 1. Adaptive Packet Selection: Bluetooth uses coding (FEC and Modulation) depending upon interference. Use FEC only if noise. No FEC if interference. 2. Master Delay Policy: Bluetooth keeps track of error rates on various frequencies. Refrains from transmission on frequencies where interference is high 3. Adaptive frequency hoping: Hop over only good frequencies 4. Adaptive Notch Filter on WiFi 11-26
27 State Sensors periodically announce their state 30 F 55 km/hr 23 KwH Small data transfers Event triggered or polled. Gateway devices, e.g., cell phones, can transfer this data to Internet. Sensors do not need to speak IP
28 Bluetooth Smart Low Energy: 1% to 50% of Bluetooth classic For short broadcast: Your body temperature, Heart rate, Wearables, sensors, automotive, industrial. Not for voice/video, file transfers, Small messages: 1Mbps data rate but throughput not critical. Battery life: In years from coin cells Simple: Star topology. No scatter nets, mesh, Lower cost than Bluetooth classic New protocol design based on Nokia s WiBree technology Shares the same 2.4GHz radio as Bluetooth Dual mode chips All new smart phones (iphone, Android, ) have dual-mode chips 11-28
29 2.4 GHz. 150 m open field Star topology Bluetooth Smart PHY 1 Mbps Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying Better range than Bluetooth classic Adaptive Frequency hopping. 40 Channels with 2 MHz spacing. 3 channels reserved for advertizing and 37 channels for data Advertising channels specially selected to avoid interference with WiFi channels Freq Time FSK Freq Time GFSK Ref: J. Decuir, Bluetooth 4.0: Low Energy, 2010, Freq.
30 Bluetooth Smart MAC Two Device Types: Peripherals simpler than central Two PDU Types: Advertising, Data Non-Connectable Advertising: Broadcast data in clear Discoverable Advertising: Central may request more information. Peripheral can send data without connection General Advertising: Broadcast presense wanting to connect. Central may request a short connection. Directed Advertising: Transmit signed data to a previously connected master Peripheral Central Channel 37 Channel 38 Channel 39 Channel Channel Channel Adv_Ind Adv_Ind Adv_Ind Ref: J. Decuir, Bluetooth 4.0: Low Energy, 2010, Scan_Req Scan_Resp Conn_Req
31 Bluetooth Smart MAC (Cont) After connecting, master tells slave about hopping sequence and wake up cycle All subsequent data transfers in 37 data channels Both devices can sleep between transactions Data can be encrypted. ~3 ms per transaction, 15 mw Power = 10 ma using 1.5V Þ 30mAs/transaction Þ 21.6 M transactions using 180 mah battery Þ 41.1 years with 1 transaction/minute Peripheral Advertising Channel Adv_Ind Slave Data Channels Data LL End Central Connect_Req Master Ack Ack Ack 11-31
32 Bluetooth Smart Protocol Stack Applications Generic Access Profile Generic Attribute Profile Attribute Protocol Security Manager Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol Host Controller Interface Link Layer Direct Test Mode Physical Layer Apps Host Controller Ref: J. Decuir, Bluetooth 4.0: Low Energy, 2010,
33 Generic Attribute (GATT) Profile Defines data formats and interfaces with the Attribute Protocol Type-Length-Value (TLV) encoding is used Each attribute has a 16-bit Universally Unique ID (UUID) standardized by Bluetooth SIG 128-bit UUID if assigned by a manufacturer Allows any client to find a server, read/write data Allows servers to talk to generic gateways Allows security up to AES-128 Each to encode in XML Makes profile (application) development easier 11-33
34 Bluetooth Gateway Devices A gateway device helps connect a Bluetooth device to the Internet. Smart phone, Tablets, PC, A generic app can forward the data to the URL sent by the device 11-34
35 Bluetooth Smart Applications Proximity: In car, In room 303, In the mall Locator: Keys, watches, Animals Health devices: Heart rate monitor, physical activities monitors, thermometer Sensors: Temperature, Battery Status, tire pressure Remote control: Open/close locks, turn on lights Ref: E. Vlugt, Bluetooth Low Energy, Beacons and Retail, Verifone White paper, 2013, 12 pp.,
36 Beacons Advertizing based on proximity Peripherals (your phone) broadcasts its presence if Bluetooth is turned on Primary aim of these broadcasts is to allow device discovery Advertising packets consist of a header and max 27B of payload with multiple TLV-encoded data items May include signal strength Þ Distance ios7 iphones can send/received ibeacons Can be used for customized advertising, indoor location, geofencing PayPal uses this to identify you. You can pay using a PIN and your phone
37 Summary 1. Bluetooth basic rate uses frequency hoping over 79 1-MHz channels with 1, 3, 5 slots packets. 2. Three inactive states: hold, sniff, park. Has a fixed set of applications called "Profiles" 3. Bluetooth and WiFi co-exist by time-sharing or adaptive frequency notching 4. Bluetooth Smart is designed for short broadcasts by sensors MHz channels with 3 channels reserved for advertising. One or two-message exchanges 5. Generic attribute profile allows new applications using UUID for data types 11-37
38 Homework 11 Submit answer to the following Problem: Assume that in one slot in Bluetooth 256 bits of payload could be transmitted. How many slots are needed if the payload size is (a) 512 bits, (b) 728 bits, and (c) 1024 bits. Assume that the non-payload portions do not change
39 Reading List: Bluetooth Kevin Townsend, Carles Cufí, Akiba, Robert Davidson, "Getting Started with Bluetooth Low Energy," O'Reilly Media, Inc., May 2014, 180 pp., ISBN: (Safari Book), Chapter 2. J. Decuir, Bluetooth 4.0: Low Energy, 2010, 62 pp., E. Vlugt, Bluetooth Low Energy, Beacons and Retail, Verifone White paper, 2013, 12 pp., P. Bhagwat, "Bluetooth Technology for short range wireless Apps," IEEE Internet Computing, May-June 2001, pp , Logitech, Bluetooth FAQ,
40 References Bluetooth SIG, Bluetooth SIG, BLUETOOTH 4.1 Features and Technical Description, 2013, Bluetooth SIG, "Adopted Bluetooth Profiles, Services, Protocols and Transports," ITL, "Security of Bluetooth Systems and Devices," E. Ferro and F. Potorti, ""Bluetooth and Wi-Fi wireless protocols: a survey and a comparison", Volume: 12 Issue: 1, Pages: 12-26, IEEE Wireless Communications, 2005, &isnumber=
41 References (Cont) P. McDermott-Wells, "What is Bluetooth?", Volume 23, Issue 5, Page(s):33-35, IEEE Potentials, 2005, umber= &isnumber=29958 K.V.S.S.S.S. Sairam, N. Gunasekaran, and S.R. Redd, "Bluetooth in wireless communication" Volume 40, Issue 6, Page(s):90-96, IEEE Communications Magazine, June 2002, umber= &isnumber=21727 B. Chatschik, "An overview of the Bluetooth wireless technology", Volume 39, Issue 12, Page(s):86-94, IEEE Communications Magazine, 2001, umber=
42 Acronyms ACL Asynchronous Connection List AES-128 Advanced Encryption Standard w 128 bit keys BLE Bluetooth Low Energy BNEP Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol CAP Connection Access Profile CSA Core Specification Amendment dbm Deci-bel milli-watt DPSK Differential Phase Shift Keying EDR Enhanced Data Rate, EU European Union FEC Forward Error Correction FSK Frequency Shift Keying GATT Generic Attribute GFSK Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying GHz Giga Hertz GPS Global Positioning System HS High Speed, 11-42
43 Acronyms (Cont) ID Identifier IEEE Institution of Electrical and Electronics Engineers IETF Internet Engineering Task Force IG Interest Group ios Apple's idevices Operating System IP Internet Protocol IPv6 Internet Protocol version 6 IrDA Infrared Data Association IrMC Infrared Mobile Communications IrOBEX Infrared Object Exchange LAN Local Area Network LAP Lower address part LE Low Energy LTE Long Term Evolution MAC Media Access Control MAN Metropolitan Area Network 11-43
44 Acronyms (Cont) MB Mega Byte MHz Mega Hertz mw milli Watt NAP Non-significant address part OFDM Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing OUI Organizationally Unique Identifier PAL Protocol Adaptation Layer PAN Personal Area Network PC Personal Computer PDU Protocol Data Unity PHY Physical Layer PIN Personal Identification Number RF Radio Frequency RFCOMM Radio Frequency Communication RFID Radio Frequency Identifier SC Standing Committee 11-44
45 Acronyms (Cont) SCO Synchronous Connection Oriented SDP Service Discovery Protocol SG Study Group SIG Special Interest Group SIM Subscriber Identity Module TCS Telephony Control Specification TDD Time-division duplex TLV Type-Length-Value TV Television TX Transmit UAP Upper address part UCD Unicast Connectionless Data URL Uniform Resource Locator USB Universal Serial Bus UUID Universally Unique Identifier uw Micro-Watt 11-45
46 Acronyms (Cont) WAN Wide Area Network WBS Wide Band Speed WiFi Wireless Fidelity WiMax Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access WPAN Wireless Personal Area Networks WRAN Wireless Regional Area Network XML Extensible Markup Language 11-46
47 Scan This to Get These Slides 11-47
48 Related Modules Internet of Things, j_10iot.htm Wireless Protocols for IoT Part II: IEEE WPAN, j_12wpn.htm Wireless Protocols for IoT Part III: ZigBee, j_13zgb.htm Low Power WAN Protocols for IoT, j_14ahl.htm Audio/Video Recordings and Podcasts of Professor Raj Jain's Lectures,
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY. Flavia Martelli
 Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies
 Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies Topics Background What is Bluetooth low energy? Basic concepts Architecture Differentiation and comparison Markets and applications Background Background
Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies Topics Background What is Bluetooth low energy? Basic concepts Architecture Differentiation and comparison Markets and applications Background Background
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Bluetooth LE 4.0 and 4.1 (BLE)
 Bluetooth LE 4.0 and 4.1 (BLE) Lab 11 Lunch April 23rd, 2014 Noah Klugman Josh Adkins 1 Outline History of Bluetooth Introduction to BLE Architecture Controller Host Applications Power Topology Example:
Bluetooth LE 4.0 and 4.1 (BLE) Lab 11 Lunch April 23rd, 2014 Noah Klugman Josh Adkins 1 Outline History of Bluetooth Introduction to BLE Architecture Controller Host Applications Power Topology Example:
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Wireless Protocols for IoT Part II: IEEE Wireless Personal Area Networks
 Wireless Protocols for IoT Part II: IEEE 802.15.4 Wireless Personal Area Networks. Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides and audio/video recordings
Wireless Protocols for IoT Part II: IEEE 802.15.4 Wireless Personal Area Networks. Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides and audio/video recordings
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee. Dmitri A. Moltchanov kurssit/elt-53306/
 WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
IEEE Wireless LANs Part I: Basics
 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs Part I: Basics Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this
IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs Part I: Basics Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
Wireless Protocols for IoT Part II: IEEE Wireless Personal Area Networks
 Wireless Protocols for IoT Part II: IEEE 802.15.4 Wireless Personal Area Networks. Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides and audio/video recordings
Wireless Protocols for IoT Part II: IEEE 802.15.4 Wireless Personal Area Networks. Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides and audio/video recordings
Bluetooth SIG Liaison Report May 2009
 Bluetooth SIG Liaison Report May 2009 Authors: Date: 2009-05-12 The Bluetooth word mark and logos are registered trademarks owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc. and any use of such marks by Motorola, Inc. is under
Bluetooth SIG Liaison Report May 2009 Authors: Date: 2009-05-12 The Bluetooth word mark and logos are registered trademarks owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc. and any use of such marks by Motorola, Inc. is under
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
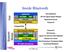 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea
 Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea http://usn.konkuk.ac.kr/~jskim 1 IEEE 802.x Standards 802.11 for Wireless Local Area Network 802.11 legacy clarified 802.11 legacy
Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea http://usn.konkuk.ac.kr/~jskim 1 IEEE 802.x Standards 802.11 for Wireless Local Area Network 802.11 legacy clarified 802.11 legacy
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Introduction to Bluetooth Low Energy
 Introduction to Bluetooth Low Energy Qualcomm Bluetooth Low Energy Terminology clarification In this document you will notice a number of references are made to Qualcomm Bluetooth Low Energy SDK. While
Introduction to Bluetooth Low Energy Qualcomm Bluetooth Low Energy Terminology clarification In this document you will notice a number of references are made to Qualcomm Bluetooth Low Energy SDK. While
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE
 Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Modulation. Propagation. Typical frequency bands
 References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
PM0257. BlueNRG-1, BlueNRG-2 BLE stack v2.x programming guidelines. Programming manual. Introduction
 Programming manual BlueNRG-1, BlueNRG-2 BLE stack v2.x programming guidelines Introduction The main purpose of this document is to provide a developer with some reference programming guidelines about how
Programming manual BlueNRG-1, BlueNRG-2 BLE stack v2.x programming guidelines Introduction The main purpose of this document is to provide a developer with some reference programming guidelines about how
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Wireless and Mobile Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-11/
Wireless and Mobile Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-11/
Wireless and WiFi. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Objectives of the Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth 5 Presenter Tomas O Raghallaigh )
 Bluetooth 5 Presenter Tomas O Raghallaigh (tomas.oraghallaigh@teledyne.com ) Frontline Joins Teledyne Technologies Charlottesville, Virginia, USA April 7, 2016 Frontline Test Equipment, Inc. the worldwide
Bluetooth 5 Presenter Tomas O Raghallaigh (tomas.oraghallaigh@teledyne.com ) Frontline Joins Teledyne Technologies Charlottesville, Virginia, USA April 7, 2016 Frontline Test Equipment, Inc. the worldwide
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
Bluetooth Low Energy. Fillipe Resina Marcela Terakado Ricardo Guimarães. Institute of Mathematics and Statistics - University of São Paulo
 Bluetooth Low Energy Fillipe Resina Marcela Terakado Ricardo Guimarães Institute of Mathematics and Statistics - University of São Paulo Table of contents 1. Introduction 2. History 3. Architecture 4.
Bluetooth Low Energy Fillipe Resina Marcela Terakado Ricardo Guimarães Institute of Mathematics and Statistics - University of São Paulo Table of contents 1. Introduction 2. History 3. Architecture 4.
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology
 SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE W.lan.4
 Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
CS123 - Communication
 CS123 - Communication Programming Your Personal Robot Kyong-Sok KC Chang, David Zhu Fall 2015-16 Course Description An introduction to the programming of a sensor-rich personal robot. This course extends
CS123 - Communication Programming Your Personal Robot Kyong-Sok KC Chang, David Zhu Fall 2015-16 Course Description An introduction to the programming of a sensor-rich personal robot. This course extends
Energy Efficient Mobile Compu4ng Building low power sensing devices with Bluetooth low energy. Simo Veikkolainen Nokia May 2014
 Energy Efficient Mobile Compu4ng Building low power sensing devices with Bluetooth low energy Simo Veikkolainen Nokia May 2014 Bluetooth low energy Short range radio technology and protocol suite designed
Energy Efficient Mobile Compu4ng Building low power sensing devices with Bluetooth low energy Simo Veikkolainen Nokia May 2014 Bluetooth low energy Short range radio technology and protocol suite designed
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
When is Bluetooth not Bluetooth?
 When is Bluetooth not Bluetooth? Mike Anderson Chief Scientist The PTR Group, Inc. http://www.theptrgroup.com Bluetooth variants Sample devices Dealing with broadcast devices Connecting to a Bluetooth
When is Bluetooth not Bluetooth? Mike Anderson Chief Scientist The PTR Group, Inc. http://www.theptrgroup.com Bluetooth variants Sample devices Dealing with broadcast devices Connecting to a Bluetooth
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Seminar: Mobile Systems. Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht
 Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Inside Bluetooth Low Energy
 Inside Bluetooth Low Energy Naresh Gupta BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface Acknowledgments Foreword xix xxiii xxv Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction to Wireless Communication 1 1.2 Data Rates
Inside Bluetooth Low Energy Naresh Gupta BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface Acknowledgments Foreword xix xxiii xxv Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction to Wireless Communication 1 1.2 Data Rates
STA-MU-A0028S (MiniCard-USB version)
 STA-MU-A0028S (MiniCard-USB version) WiFi 802.11 b/g and Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR Combo Mini Card Module Approval Sheet Ver: 1.1 CONTENT 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Features & Benefits...3 1.2 Applications...4
STA-MU-A0028S (MiniCard-USB version) WiFi 802.11 b/g and Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR Combo Mini Card Module Approval Sheet Ver: 1.1 CONTENT 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Features & Benefits...3 1.2 Applications...4
Wireless LANs/data networks
 RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I Raj Jain Professor of CSE Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part I Raj Jain Professor of CSE Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8
 ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
Wireless (NFC, RFID, Bluetooth LE, ZigBee IP, RF) protocols for the Physical- Data Link layer communication technologies
 Wireless (NFC, RFID, Bluetooth LE, ZigBee IP, RF) protocols for the Physical- Data Link layer communication technologies 1 Connected devices communication to the Local Network and Gateway 1 st to i th
Wireless (NFC, RFID, Bluetooth LE, ZigBee IP, RF) protocols for the Physical- Data Link layer communication technologies 1 Connected devices communication to the Local Network and Gateway 1 st to i th
Wireless Protocols Overview
 Sami Kiminki Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science sami.kiminki@aalto.fi September 22, 2011 Introduction A primer for wireless IoT topics Brief overview on
Sami Kiminki Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science sami.kiminki@aalto.fi September 22, 2011 Introduction A primer for wireless IoT topics Brief overview on
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
KW41Z IEEE and BLE Coexistence Performance
 NXP Semiconductors Document Number: AN12231 Application Note Rev. 0, 08/2018 KW41Z IEEE 802.15.4 and BLE Coexistence Performance MWS module 1. About this manual This document aims to evaluate the performance
NXP Semiconductors Document Number: AN12231 Application Note Rev. 0, 08/2018 KW41Z IEEE 802.15.4 and BLE Coexistence Performance MWS module 1. About this manual This document aims to evaluate the performance
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Bluetooth: Technology and Applications. Yang Bo, CTTL SYS, CAICT
 Bluetooth: Technology and Applications Yang Bo, CTTL SYS, CAICT 2017.10.31 Course Objectives Upon completion of this course, you will be able to Know what the Bluetooth technology is and its evolution
Bluetooth: Technology and Applications Yang Bo, CTTL SYS, CAICT 2017.10.31 Course Objectives Upon completion of this course, you will be able to Know what the Bluetooth technology is and its evolution
Lecture Objectives. Lecture and Bluetooth technology. Agenda. IEEE b. Characteristics. Center Frequencies
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and obile ystems Lecture 2 802.11 and Bluetooth technology Discuss the operation of IEEE 802.11 and Bluetooth WLANs/WANs ummarize standardization efforts and recommendations
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and obile ystems Lecture 2 802.11 and Bluetooth technology Discuss the operation of IEEE 802.11 and Bluetooth WLANs/WANs ummarize standardization efforts and recommendations
A Study Wireless Communication Domain
 A Study Wireless Communication Domain Sangram Routray 1, Sanjib k. Nayak 2 Lalit M. Satapathy 1 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engg. KIST,Bhubaneswar 2 Department of Computer science and
A Study Wireless Communication Domain Sangram Routray 1, Sanjib k. Nayak 2 Lalit M. Satapathy 1 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engg. KIST,Bhubaneswar 2 Department of Computer science and
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech. Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, 7.1
 Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
STA-UI-A003D (USB version)
 STA-UI-A003D (USB version) WiFi 802.11 b/g and Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR Combo USB Dongle Module Ver: 1.0 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. CONTENT Introduction...3 1.1Features & Benefits...3 1.2Applications...4 Product
STA-UI-A003D (USB version) WiFi 802.11 b/g and Bluetooth v2.0 + EDR Combo USB Dongle Module Ver: 1.0 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. CONTENT Introduction...3 1.1Features & Benefits...3 1.2Applications...4 Product
6.9 Summary. 11/20/2013 Wireless and Mobile Networks (SSL) 6-1. Characteristics of selected wireless link standards a, g point-to-point
 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Message acknowledgement and an optional beacon. Channel Access is via Carrier Sense Multiple Access with
 ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
DASH7 ALLIANCE PROTOCOL - WHERE RFID MEETS WSN. public
 DASH7 ALLIANCE PROTOCOL - WHERE RFID MEETS WSN public DASH7 ALLIANCE PROTOCOL OPEN STANDARD OF ULTRA LOW POWER MID-RANGE SENSOR AND ACTUATOR COMMUNICATION Wireless Sensor and Actuator Network Protocol
DASH7 ALLIANCE PROTOCOL - WHERE RFID MEETS WSN public DASH7 ALLIANCE PROTOCOL OPEN STANDARD OF ULTRA LOW POWER MID-RANGE SENSOR AND ACTUATOR COMMUNICATION Wireless Sensor and Actuator Network Protocol
What is a personal area network?
 Wireless Personal Area Networks David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Slides 16 Wireless Networks Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs)
Wireless Personal Area Networks David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Slides 16 Wireless Networks Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs)
Wireless Networking: An Introduction. Hongwei Zhang
 Wireless Networking: An Introduction Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Outline Networking as resource allocation A taxonomy of current practice Technical elements Outline Networking as resource
Wireless Networking: An Introduction Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Outline Networking as resource allocation A taxonomy of current practice Technical elements Outline Networking as resource
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Wireless Local Area Network. Internet Protocol Suite
 Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Chapter 1. Uses of Computer Networks Network Hardware Network Software Reference Models Example Networks Network Standardization. Revised: August 2011
 Introduction ti Chapter 1 Uses of Computer Networks Network Hardware Network Software Reference Models Example Networks Network Standardization Metric Units Revised: August 2011 Uses of Computer Networks
Introduction ti Chapter 1 Uses of Computer Networks Network Hardware Network Software Reference Models Example Networks Network Standardization Metric Units Revised: August 2011 Uses of Computer Networks
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets
 A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Low Energy Communication
 SCITECH Volume 7, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION April 28, 2018 Journal of Information Sciences and Computing Technologies www.scitecresearch.com/journals Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Low Energy
SCITECH Volume 7, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION April 28, 2018 Journal of Information Sciences and Computing Technologies www.scitecresearch.com/journals Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Low Energy
