Advanced Computer Networks. Medium Access, WLAN & Bluetooth
|
|
|
- Brett Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advanced Computer Networks Medium Access, WLAN & Bluetooth Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester Tuesday 11 March 2014
2 Last Week Signal Propagation Path loss model Log normal shadowing model Packet reception SINR Theory vs Reality Roofnet Modulation ASK, FSK, PSK Spread Spectrum Frequency Hopping Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum MAC Hidden and Exposed Terminal Space Division Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing Time Divison Multiplexing 2 Tuesday 11 March 2014
3 Today Medium Access (Cont) TDMA CDMA XOR in the AIR BMAC Wireless Networks Bluetooth Low-power MAC 3 Tuesday 11 March 2014
4 Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Same principle as DSSS, but used to multiplex different stations Each station gets its own unique chipping sequence To send 1 bit, station sends chipping sequence To send 0 bit, station sends complement of chipping sequence Remember: this increases the bandwidth required by each stations All stations are in sync, transmitted chip sequences get superimposed Receiver can decode signal of a specific transmitter by multiplying the received signal with the chipping sequence of the transmitter 4 Tuesday 11 March 2014
5 CDMA (2) What are good chipping sequences (codes) for users? A set of codes is optimal for CDMA if the codes are pairwise orthogonal Definition of orthogonal is same as with vectors Two codes S, T are orthogonal if S*T = 0, with S T= 1 m S i T i m=length of codes Bipolar notation: binary 0 is represented as -1 Simplifies calculation (in practice 0,1 model together with XOR) 5 Tuesday 11 March 2014
6 CDMA: Simple example Codes of two senders A and B Ak = (-1,+1,-1,-1,+1+1) is code of sender A Bk = (+1,+1,-1,+1,-1,+1) is code of sender B Sender A wants to send bit Ad = 1 As = +1*(-1,+1,-1,-1,+1+1) = (-1,+1,-1,-1,+1+1) Sender B wants to send bit Bd = 0 Bs = -1*(+1,+1,-1,+1,-1,+1) = (-1,-1,+1,-1,+1,-1) Both signals are superimposed, what is received at a receiver is R = As + Bs = (-2,0,0,-2,+2,0) To decode the signal of sender A R*Ak = 1/6 * (-1,+1,-1,-1,+1+1) * (-2,0,0,-2,+2,0) = 1 To decode the signal of sender B: R*Bk = 0 6 Tuesday 11 March 2014
7 Why does this work R*Ak = (As + Bs + Cs + ) * Ak Ad*Ak*Ak + Bd*Bk*Ak + Cd*Ck*Ak + = pairwise orthogonal codes What if not all signals are equally strong? Assume R' = As + 5*Bs = (-6,-4,+4,-6,+6,-4) Decoding B: R'*Bk = -5 0, A: R'*Ak = 1? Relative differences are smaller, decoding becomes more difficult 7 Tuesday 11 March 2014
8 Near/Far Problem Terminals A and B send, C receives The signal of B hides A's signal C cannot receive A Example: for a path loss exponent of 4, P(new)/P(far)=(1000/50)^4=52dB Common problem in CDMA Solutions: Dynamic power adjustment: close transmitters use less power, far away transmitter use higher power - Affects battery life - Power control runaway problem: terminals increase transmit power in a loop until until transmitters hit a power wall 8 Tuesday 11 March 2014
9 CDMA Near/Far Example Assume B's signal is received 5 times stronger R = As + 5*Bs = (-6,-4,+4,-6,+6,-4) To decode the signal of sender B: R*Bk = -5 Might be detected as 0 To decode the signal of sender A: R*Ak = 1/6 *30 = 1 Value too low: might be detected as 0 (e.g., noise) 9 Tuesday 11 March 2014
10 Comparison SDMA/TDMA/FDMA/CDMA Approach SDMA TDMA FDMA CDMA Idea Segment space into cells Segment time into disjoint timeslots Segment frequency band into disjoint subbands Spread the spectrum using orthogonal codes Terminals Only one terminal can be active in one cell All terminals are active for short periods of time on same frequency Every terminal has its own frequency All terminals can be active at the same place at the same moment Advantages Very simple Established, flexible Simple, robust Flexible, less frequency planning needed Disadvantages Inflexible antennas Synchronization difficult Inflexible, frequencies are scarce resource Needs complicated power control 10 Tuesday 11 March 2014
11 COPE: Wireless Network Coding Consider the following scenario: 11 Tuesday 11 March 2014
12 COPE Approach Increased throughput: saved transmission can be used to send more data 12 Tuesday 11 March 2014
13 Beyond Duplex Flows Source S1 and S2 want to send a data packet to destinations D1 and D2 13 Tuesday 11 March 2014
14 COPE Snooping Every node snoops on all packets A node stores all heard packets for a limited time Node sends Reception Reports to tell its neighbors what packets it heard Reports are piggybacked on packets If no packets to send, periodically send reports 14 Tuesday 11 March 2014
15 COPE Coding To send packet p to neighbor A, XOR p with packets already known to A Thus, A can decode But how can multiple neighbors benefit from a single transmission? 15 Tuesday 11 March 2014
16 COPE Example 16 Tuesday 11 March 2014
17 COPE Example P1 + P2 Bad coding C can decode but A can't 17 Tuesday 11 March 2014
18 COPE Example P1 + P3 Better coding both C and A can decode 18 Tuesday 11 March 2014
19 COPE Example P1 + P3 + P4 Best coding Nodes A, C, D can decode 19 Tuesday 11 March 2014
20 Overview of Wireless Networks Wireless Personal Area Networks IEEE (Bluetooth), IrDa, Zigbee, sensor networks, etc. Wireless Local Area Networks IEEE , a, b, g, etc. (infrastructure and ad hoc) Cellular Area Network GSM, UMTS, LTE, WiMAX 20 Tuesday 11 March 2014
21 Ingredients of Wireless Systems Physical Layer: FSK, BFSK, DSSS, OFDM, QPSK,... Media Access: FDMA, TDMA, CDMA,... Wireless System: , Bluetooth, GSM, 3G, LTE, Network Architecture, Mobility, Network Management, etc. Tuesday 11 March 2014
22 IEEE Personal Area Networks 22 Tuesday 11 March 2014
23 The Family Target deployment environment: communication of personal devices working together Short range Low power Low cost Small number of devices Four standards: IEEE Bluetooth IEEE Interoperability (e.g., Wifi) IEEE High Data Rate WPAN IEEE Low Data Rate WPAN (ZigBee) 23 Tuesday 11 March 2014
24 Bluetooth - Overview First Bluetooth Specification 1994 by Ericsson Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting mobile phones, handset, laptops, bar code readers, GPS receivers, printers, etc.. Cheap, low power, short range (up to 100m) Physical layer: 2.4 GHz band FHSS, 79 Channels (1 Mhz Wide) Medium Access: TDMA Data rates available to applications: Up to specificiation version 1.2: 0.7 Mbit/s Specification 2.0: 2.1 Mbit/s Specification 3.0: 24 Mbit/s (Bluetooth link only used for negation, data over ) Specification 4.0: Added Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), new protocol stack Range: Up to 100m 24 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 24
25 Bluetooth Protocol Stack Service Discovery Logical Channels Radio Access Above Host Controller Interface (HCI): implemented in Software 25 Connection Management Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 25
26 Piconet Piconet = Collection of BT devices connected in an ad hoc fashion One unit acts as master and the others as slaves for the lifetime of the piconet Each piconet has a unique hopping S P M S P pattern determined by the master SB S Participation in a piconet = synchronization to hopping sequence P SB Each piconet has one master and up to 7 simultaneous active slaves (> 200 could be parked) 26 M=Master S=Slave P=Parked SB=Standby Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 26
27 Forming a Piconet Any two or more device can form a piconet The device establishing the piconet becomes the master Master sends its clock and device ID to the slaves Hopping pattern determined by the device ID, the phase is determined by the clock of the master Adressing: Active Member Address (AMA, 3 bit) Parked Member Address (PMA, 8 bit) 27 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 27
28 Scatternets Scatternet = group of piconets Device can participate multiple piconets Jumping between the hopping sequences of the different piconets Before leaving a device informs the current master that it will be unavailable for a certain amount of time P S S M=Master S=Slave P=Parked SB=Standby S SB P M SB 28 S P S M P SB Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 28
29 Baseband Layer Frequency Selection 625 µs f k f k+1 f k+2 f k+3 f k+4 f k+5 f k+6 M S M S M S M t f k f k+3 f k+4 f k+5 f k+6 M S M S M t f k f k+1 f k+6 M S M t Master sends in all odd slots, slaves share even slots 1-slot, 3-slot or 5-slot packets possible Frequency pattern remains regardless 29of packet size (why?) Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 29
30 Link Types SCO (Synchronous connection-oriented) Mostly used for voice The master reserves two consecutive slots (forward and return slots) at fixed intervals A master can support up to 3 SCO links to the same slave or to different slaves ACL (Asynchronous connectionless) Typically used for data Variable frame size (1,3,5 slots) Master uses polling, a slave may only answer if addressed in the preceding slot Maximum of 1 ACL link per master/slave No direct slave to slave communication, packet transmission only between master and slave 30 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 30
31 Link Types - Example Every sixth slot used for SCO link between master and slave 1 ACL links use single or multiple slots (note: hopping sequence is independent of the transmission of packets) 31 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 31
32 Robustness ACL links can be protected with ARQ scheme (Automatic Repeat Request) One extra bit (ACK, NAK) is enough because master/slave have to send alternating 32 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 32
33 Link Manager Connection Establishment Bluetooth link manager is responsible for authentication, synchronization, power control and device state switching A Bluetooth device can be in one of several states: Standby: - Each 2048th slot a device listens on 32 of the 79 channels Process connection establishement consists of three states Inquiry: search for other devices Page: set up connections (e.g., hopping sequence) When device is connected Device is either in the transmit or the connected state Extra low-power states Sniff: listen to the piconet at a reduced rate (custom) Hold: device stops ACL transmission Park: device relases AMA address, device still 33 synchronized Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 33
34 States of a Bluetooth device (power consumption: sniff > hold > park) 34 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 34
35 L2CAP Logical Link Control and Adaption Protocol Simple data link protocol on top of Baseband ACL link L2CAP provides three different channels Connectionless: typically used to broadcast, master to all slaves Connection-oriented: bi-directional channel between master and slave Signaling: used to exchange control information Segmentation and re-assembly of user data L2CAP accepts up to 64KB packets This needs to be chopped into smaller basedband packets (5 slot ACL link can carry a maximum of 339 bytes per packet) 35 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 35
36 L2CAP (2) Channel identifiers (CID) used to demultiplex L2CAP channels Signaling used CID of 1 Connectionless channels have CID 2 at slave and a dynamically assigned CID at master - Additional protocol/service demultiplexer (PSM) needed for connectionless channels Connection-oriented channels get dynamically assigned CID at both master and slave 36 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 36
37 Higher layer protocols Telephony Control library 802.x Emulation 37 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 37
38 Low Energy MAC Bluetooth is low power, but still not low enough power for coin cells and energy harvesting applications Things have data Web services want this data MAC protocols for extremely low power BMAC/SMAC ZigBee Bluetooth Low Energy 38 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 38
39 Sensor Networks: Applications (1) Monitor temperature of goods in supermarket (attach sensor nodes to fridges) Monitor environment of plants in agriculture (solar radiation, temperature, humidity) 39 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 39
40 Sensor Networks: Applications (2) Earthquake detection Earthquake speed ~5-10km/h, Instant detection can give warning ~30second before the shockwave hits a city 200km from the epicenter Structure Monitoring in buildings Understand interactions between ground motions and structure foundation 40 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 40
41 Concept of operation Form Ad Hoc Network (no fixed Infrastructure) Gather data and Forward it to the user ('sink' or gateway node) 41 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 41
42 S-MAC Main sources of energy waste Re-transmissions Overhearing: node picks up packets destined for other nodes Approach: coarse-grained TDMA-like sleep/awake cycles frame listen sleep listen sleep time All nodes choose and announce awake schedules synchronize to awake schedules of neighboring nodes Uses RTS/CTS to resolve contention during listen intervals And allows interfering nodes to go to sleep during data exchange 42 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 42
43 S-MAC Problem: Nodes may have to follow multiple schedules to avoid network partition Different schedules may increase end-to-end latency Schedule 1+2 Schedule 1 Schedule 2 43 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 43
44 B-MAC Packets transmitted with preamble Nodes periodically wake up and stay awake if they overhear a preamble Shortcomings: Problematic in case of shorter packets: relatively long active period 44 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 44
45 Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) New radio and protocol stack Mostly new PHY: not backward compatible with Bluetooth New advertising mechanism for easy of discovery Extremely low power Bandwidth: 1Mbit/s Common with regular Bluetooth Star topology Frequency hopping Part of Bluetooth 4.0 Dual and single stack implementations: advantage of ZigBee Part of mobile phones (e.g., iphone 4S) Designed to enable the Internet of things 45 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 45
46 BLE Use Cases: Internet of Things Everyday objects can become sensors......and monitor things 46 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 46
47 Internet of Things (2) Things upload data to the cloud using mobile phones as gateway Bluetooth Low Energy has gateway functionally built-in 47 Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 47
48 References XORs in The Air: Practical Wireless Network Coding, Sachin Katti, Hariharan Rahul, Wenjun Hu, Dina Katabi, Muriel Medard, Jon Crowcroft, Sigcomm 2006 Versatile Low Power Media Access for Wireless Sensor Networks, Joseph Polastre, Jason Hill, David Culler, Sensys 2004 Bluetooth Low Energy, Joe Decuir, IEEE Communications Society Tuesday 11 March 2014 Department of Computer Science 48
Advanced Computer Networks
 Advanced Computer Networks Exercise ession 3 Ercan Ucan pring emester 2013 Thursday 14 March 2013 Department of Computer cience 1 IEEE 802.15 ersonal Area Networks Thursday 14 March 2013 The 802.15 Family
Advanced Computer Networks Exercise ession 3 Ercan Ucan pring emester 2013 Thursday 14 March 2013 Department of Computer cience 1 IEEE 802.15 ersonal Area Networks Thursday 14 March 2013 The 802.15 Family
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Advanced Computer Networks WLAN
 Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Wireless Protocols Overview
 Sami Kiminki Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science sami.kiminki@aalto.fi September 22, 2011 Introduction A primer for wireless IoT topics Brief overview on
Sami Kiminki Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science sami.kiminki@aalto.fi September 22, 2011 Introduction A primer for wireless IoT topics Brief overview on
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview. Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University
 Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University Medium Access Control Topology 3 Simplex and Duplex 4 FDMA TDMA CDMA DSSS FHSS Multiple Access Methods Notice: CDMA and spread spectrum
Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University Medium Access Control Topology 3 Simplex and Duplex 4 FDMA TDMA CDMA DSSS FHSS Multiple Access Methods Notice: CDMA and spread spectrum
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
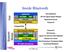 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Wireless Networking: An Introduction. Hongwei Zhang
 Wireless Networking: An Introduction Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Outline Networking as resource allocation A taxonomy of current practice Technical elements Outline Networking as resource
Wireless Networking: An Introduction Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Outline Networking as resource allocation A taxonomy of current practice Technical elements Outline Networking as resource
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
Data Communications. Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs
 Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Mobile Communications Chapter 3 : Media Access
 Mobile Communications Chapter 3 : Media Access 2. Motivation 3. SDMA, FDMA, TDMA 1. Aloha and contention based schemes 4. Reservation schemes 5. Collision avoidance, MACA 6. Polling CDMA (Lecture 6) Prof.
Mobile Communications Chapter 3 : Media Access 2. Motivation 3. SDMA, FDMA, TDMA 1. Aloha and contention based schemes 4. Reservation schemes 5. Collision avoidance, MACA 6. Polling CDMA (Lecture 6) Prof.
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Advanced Computer Networks. WLAN, Cellular Networks
 Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN, Cellular Networks Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2013 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Medium Access COPE Today Last week Short
Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN, Cellular Networks Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2013 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Medium Access COPE Today Last week Short
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei 1393
 Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 Wireless Links, WiFi, Cellular Internet Access, and Mobility Slides derived from those available on the Web site of the book Computer Networking, by Kurose
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 Wireless Links, WiFi, Cellular Internet Access, and Mobility Slides derived from those available on the Web site of the book Computer Networking, by Kurose
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
Wireless and WiFi. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN)
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1
 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
Computer Networks. Wireless LANs
 Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Wireless Local Area Networks. Networks: Wireless LANs 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE W.lan.4
 Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Message acknowledgement and an optional beacon. Channel Access is via Carrier Sense Multiple Access with
 ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
Medium Access Control. MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols
 Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Wireless and Mobile Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-11/
Wireless and Mobile Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-11/
The Importance of Being Opportunistic
 High Performance Switching and Routing Telecom Center Workshop: Sept 4, 1997. The Importance of Being Opportunistic Sachin Katti Dina Katabi, Wenjun Hu, Hariharan Rahul, and Muriel Medard Bandwidth is
High Performance Switching and Routing Telecom Center Workshop: Sept 4, 1997. The Importance of Being Opportunistic Sachin Katti Dina Katabi, Wenjun Hu, Hariharan Rahul, and Muriel Medard Bandwidth is
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer. Computer Networks: Wireless LANs
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Extending or Interconnecting LANS. Physical LAN segment. Virtual LAN. Forwarding Algorithm 11/9/15. segments. VLAN2, Port3. VLAN1, Port1.
 Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
6.9 Summary. 11/20/2013 Wireless and Mobile Networks (SSL) 6-1. Characteristics of selected wireless link standards a, g point-to-point
 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology
 Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Shared Access Networks Wireless. 1/27/14 CS mywireless 1
 Shared Access Networks Wireless 1 Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected devices equals
Shared Access Networks Wireless 1 Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected devices equals
Topic 2b Wireless MAC. Chapter 7. Wireless and Mobile Networks. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach
 Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Chapter 3 MEDIA ACCESS CONTROL
 Chapter 3 MEDIA ACCESS CONTROL Distributed Computing Group Mobile Computing Winter 2005 / 2006 Overview Motivation SDMA, FDMA, TDMA Aloha Adaptive Aloha Backoff protocols Reservation schemes Polling Distributed
Chapter 3 MEDIA ACCESS CONTROL Distributed Computing Group Mobile Computing Winter 2005 / 2006 Overview Motivation SDMA, FDMA, TDMA Aloha Adaptive Aloha Backoff protocols Reservation schemes Polling Distributed
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
CS 332 Computer Networks Wireless Networks
 CS 332 Computer Networks Wireless Networks Professor Szajda Chapter 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers! computer nets:
CS 332 Computer Networks Wireless Networks Professor Szajda Chapter 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers! computer nets:
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8
 MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
04/11/2011. Wireless LANs. CSE 3213 Fall November Overview
 Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee. Dmitri A. Moltchanov kurssit/elt-53306/
 WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
MAC LAYER. Murat Demirbas SUNY Buffalo
 MAC LAYER Murat Demirbas SUNY Buffalo MAC categories Fixed assignment TDMA (Time Division), CDMA (Code division), FDMA (Frequency division) Unsuitable for dynamic, bursty traffic in wireless networks Random
MAC LAYER Murat Demirbas SUNY Buffalo MAC categories Fixed assignment TDMA (Time Division), CDMA (Code division), FDMA (Frequency division) Unsuitable for dynamic, bursty traffic in wireless networks Random
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
CCM 4300 Lecture 16. 3G, 4G, Satellite and Bluetooth Communications. Dr S Rahman. Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communication Systems
 CCM 4300 Lecture 16 Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communication Systems 3G, 4G, Satellite and Bluetooth Communications Dr S Rahman 1 Session Content Recap of last session Lesson Objectives Roadmap
CCM 4300 Lecture 16 Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communication Systems 3G, 4G, Satellite and Bluetooth Communications Dr S Rahman 1 Session Content Recap of last session Lesson Objectives Roadmap
B.E. ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SEMESTER - VII EC WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
 B.E. ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SEMESTER - VII EC2401 - WIRELESS COMMUNICATION Question Bank (ALL UNITS) UNIT-I: SERVICES & TECHNICAL CHALLENGES PART A 1. What are the types of Services? (Nov.
B.E. ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SEMESTER - VII EC2401 - WIRELESS COMMUNICATION Question Bank (ALL UNITS) UNIT-I: SERVICES & TECHNICAL CHALLENGES PART A 1. What are the types of Services? (Nov.
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY. Flavia Martelli
 Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Communications & Networks Introduction
 Communications & Networks Introduction Alexander Nelson February 19th, 2018 University of Arkansas - Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering Networking Number of Connected Devices 1 How
Communications & Networks Introduction Alexander Nelson February 19th, 2018 University of Arkansas - Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering Networking Number of Connected Devices 1 How
CDMA-Based MAC Protocol for Wireless Ad Hoc Networks
 CDMA-Based MAC Protocol for Wireless Ad Hoc Networks Alaa Muqattash and Marwan Krunz Presented by: Habibullah Pagarkar for 600.647-Advanced Topics in Wireless Networks. JHU. Spring 04 Today s Presentation
CDMA-Based MAC Protocol for Wireless Ad Hoc Networks Alaa Muqattash and Marwan Krunz Presented by: Habibullah Pagarkar for 600.647-Advanced Topics in Wireless Networks. JHU. Spring 04 Today s Presentation
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
Last Lecture: Data Link Layer
 Last Lecture: Data Link Layer 1. Design goals and issues 2. (More on) Error Control and Detection 3. Multiple Access Control (MAC) 4. Ethernet, LAN Addresses and ARP 5. Hubs, Bridges, Switches 6. Wireless
Last Lecture: Data Link Layer 1. Design goals and issues 2. (More on) Error Control and Detection 3. Multiple Access Control (MAC) 4. Ethernet, LAN Addresses and ARP 5. Hubs, Bridges, Switches 6. Wireless
Wireless LANs/data networks
 RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017
 ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.6: Wireless Networks - MAC Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.6: Wireless Networks - MAC Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527
Wireless networks. Wireless Network Taxonomy
 Wireless networks two components to be considered in deploying applications and protocols wireless links ; mobile computing they are NOT the same thing! wireless vs. wired links lower bandwidth; higher
Wireless networks two components to be considered in deploying applications and protocols wireless links ; mobile computing they are NOT the same thing! wireless vs. wired links lower bandwidth; higher
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Multiple Access in Cellular and Systems
 Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Modulation. Propagation. Typical frequency bands
 References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE
 Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Multiple Access Links and Protocols
 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs
 Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
Mobile Communications Chapter 7: Wireless LANs Characteristics IEEE 802.11 (PHY, MAC, Roaming,.11a, b, g, h, i, n z) Bluetooth / IEEE 802.15.x IEEE 802.16/.20/.21/.22 RFID Comparison Prof. Jó Ueyama courtesy
Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg
 Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing Error Detection Error Correction Media Access Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing
Getting Connected (Chapter 2 Part 4) Networking CS 3470, Section 1 Sarah Diesburg Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing Error Detection Error Correction Media Access Five Problems Encoding/decoding Framing
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Wireless LANs. Characteristics Bluetooth. PHY MAC Roaming Standards
 Wireless LANs Characteristics 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming Standards Bluetooth 1 Significant parts of slides are based on original material by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, FU-Berlin www.jochenschiller.de
Wireless LANs Characteristics 802.11 PHY MAC Roaming Standards Bluetooth 1 Significant parts of slides are based on original material by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, FU-Berlin www.jochenschiller.de
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Medium Access Control in Wireless Networks
 Medium Access Control in Wireless Networks Prof. Congduc Pham http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cpham Université de Pau, France MAC layer Routing protocols Medium Acces Control IEEE 802.X MAC GSM (2G) Channels Downlink
Medium Access Control in Wireless Networks Prof. Congduc Pham http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cpham Université de Pau, France MAC layer Routing protocols Medium Acces Control IEEE 802.X MAC GSM (2G) Channels Downlink
Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society
 Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society Martin Sauter Nortel Networks, Germany John Wiley Si Sons, Ltd Contents Preface List of Figures List of Tables List of Abbreviations xi xiii xix
Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society Martin Sauter Nortel Networks, Germany John Wiley Si Sons, Ltd Contents Preface List of Figures List of Tables List of Abbreviations xi xiii xix
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs. Agenda (1) Agenda (2) Wireless Spectrum (1)
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Data Link Layer Technologies
 Chapter 2.2 La 2 Data Link La Technologies 1 Content Introduction La 2: Frames Error Handling 2 Media Access Control General approaches and terms Aloha Principles CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA / CA Master-Slave
Chapter 2.2 La 2 Data Link La Technologies 1 Content Introduction La 2: Frames Error Handling 2 Media Access Control General approaches and terms Aloha Principles CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA / CA Master-Slave
SENSOR-MAC CASE STUDY
 SENSOR-MAC CASE STUDY Periodic Listen and Sleep Operations One of the S-MAC design objectives is to reduce energy consumption by avoiding idle listening. This is achieved by establishing low-duty-cycle
SENSOR-MAC CASE STUDY Periodic Listen and Sleep Operations One of the S-MAC design objectives is to reduce energy consumption by avoiding idle listening. This is achieved by establishing low-duty-cycle
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
ETSI Project BRAN Hiperlan Type 2 for IEEE 1394 Applications System Overview
 ETSI Project BRAN Hiperlan Type 2 for IEEE 1394 Applications System Overview Source : Jamshid Khun Jush (Ericsson) (THOMSON multimedia) 1 HIPERLAN/2 Standard A new standard developed by the ETSI Project
ETSI Project BRAN Hiperlan Type 2 for IEEE 1394 Applications System Overview Source : Jamshid Khun Jush (Ericsson) (THOMSON multimedia) 1 HIPERLAN/2 Standard A new standard developed by the ETSI Project
