EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages
|
|
|
- Leon Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Fall 2015 Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to develop methods for using Hardware Description Languages for the design of digital circuits. Part 1: Background Hardware Description Languages (HDL) are widely used for representing digital systems at both the Behavioral and Structural levels. Full functionality of a digital system can ideally be captured in a HDL and the design of digital circuits is often accomplished within the confines of an HDL framework. At the appropriate level in the HDL, CAD tools can take a design down to the mask level for fabrication in silicon with minimal engineering intervention at the Physical Level in the design process. A system appropriately represented in a HDL can be simulated to predict not only the functionality of sequential and combinational logic circuits, but also timing information about how those circuits are predicted to perform when instantiated in silicon. The two most widely used HDLs today are Verilog and VHDL. There is considerable similarity between these two languagees and engineers are expected to be proficient in both. In this laboratory experiment we will limit our discussion to Verilog which has become more popular in US industry today. Specifically we will focus on how a HDL can be used for design and simulation of digital integrated circuits. Appendix A of the Weste and Harris text has a brief discussion of Verilog and students should become familiar with the material in this appendix. There are also numerous books and WEB sites devoted to a discussion of Verilog. Beyond the basic introduction to Verilog discussed in this laboratory experiment, students will be expected to take the initiative to develop their own HDL skills to the level needed to support the digital design component of this course. Part 1.1: Structure of Verilog Representations A Verilog representation of a digital system, be it a small or a very large system, is characterized by a set of modules that describe the system. A large system will be comprised of a large number of nested modules whereas a small system may be comprised of only a single module. As such, the main building block in Verilog is the module. The structure of a module includes statements about input/output variable mappings along with a description about how the input and output variables are related. An example of a module named testcircuit is shown below
2 endmodule module testcircuit (vout, vin); output vout; input vin; assign vout = ~vin; This module has one output, vout, one input, vin, and two bidirectional ports, vdd and vss. The relationship between the input and output for this simple module is defined by the assign statement. The module description is always terminated with an endmodule statement. In Cadence, we can create behavioral modules several ways, two of which will be discussed in this experiment. Symbol-Based Module Creation With the Symbol-based method, a symbol view (that may have been created earlier) is used to generate a behavioral view with the input/output pin and direction information. The user must then enter the remainder of the module to fully define the operation of the circuit. Text-Based Module Creation The user creates a module by creating a text file that includes the module name, pin names and input/output direction information. This text file defines the behavioral view of the module. The user must then enter the remainder of the module to fully define the operation of the circuit. Modules that represent a digital system are simulated by using ModelSim software. ModelSim was looked at in an earlier lab and knowing how to use it is important to successful simulation of a module. To use ModelSim to simulate a module, a testbench for the design under test (DUT) must be created. This is another text file written in Verilog syntax which provides the test inputs to the DUT to check for correct functionality. In this laboratory, you will be asked to create behavioral verilog of an inverter and the gates you used in Lab 4. You will also be asked to simulate each gate as well as the top level Boolean implementation of Lab 4 using individual test benches for each instance. Once the behavioral description of all the gates is complete, you will then simulate your top level design of Lab 4 in Verilog. Part 2: Inverter 2.1 The Verilog File Create a behavioral view of the Boolean Inverter that was created in Lab 2. The following steps create the skeleton of the module from which you can add the functional description. In the Library Manager, select the inverter that you designed in Lab 2 (or the updated version from Lab 4). Click on File New Cell View and in the View
3 Name field, type behavioral. The Tool field should be set to Verilog. When you click OK, an emacs file editor window with the following contents will open: //Verilog HDL for your_library, your_inverter behavioral 3 module your_inverter (vout, vdd, vss, vin); output vout; inout vdd; inout vss; input vin; (Add your code defining the operation of the inverter here) endmodule If you prefer to use another editor, type editor= pico in CIW to choose pico. To use vi, use the command editor= xterm e vi. The change remains valid for the current Cadence session only. To make this choice permanent, add the command to your ~/.cdsinit file. Since you ve already designed, checked and saved this gate in the Cadence environment, the Verilog-Editor will have prior knowledge of how your module looks like, and we only have to add the line that describes the output. To save and exit in the emacs editor, click Ctrl-X Ctrl-C, then when prompted if you want to save, click y. What we just did is write a description of the inverter in a behavioral way. In other words, how do the outputs relate to the inputs, without knowledge of how the operation would be implemented with transistors. Often, an easier way to create the behavioral file for a given module is outside of the Cadence environment. Instead of creating a new cell view, create a.v file using the command gedit and type the module manually. Be sure to save the file as a.v file so later steps work correctly. This file will be simulated in ModelSim and later used in synthesis. 2.2 Simulating Behavioral Code Now we are ready to simulate our file. Be sure to download the ModelSim source file. Create a directory in your EE330 folder to use for simulation. Change to this directory and source the ModelSim text file using the following command in the terminal. source <file_location>/modelsim_env.txt To open ModelSim type: vsim &
4 Before simulating, a test bench for the design under test needs to be written. The test bench is needed to specify the time and value properties of inputs. For given inputs, certain outputs are expected which can be plotted during simulation and compared to expected results. To create a test bench, start by considering the inputs and outputs of the DUT. The test bench should provide the inputs to the DUT so the test bench module will have outputs for the DUT s inputs. Also, outputs of the DUT are to be monitored, so inputs to the test bench are these signals. Thus, the DUT s inputs become the TB s outputs and the DUT s outputs are the TB s inputs. The figure below makes this relationship clear. The TB for a DUT is also a Verilog file with certain syntax for applying inputs to the DUT at specific times. An example test bench for the inverter module is given below. Create the TB file in the same directory as the module it is testing, usually with a similar name such as modulename_tb.v. The # symbol has the simulation wait that many time units (default is nanoseconds) before the line is run. Remember that initial blocks run once at the beginning of the simulation whereas always blocks run continuously, over and over while the simulation is taking place. // Verilog TB file. module inverter_tb(vout, vin); input vout; output vin; reg vin; //Instantiation of DUT with generic name inverter name(vout, vin); //Order of inputs must match original module initial begin vin = 1 b0; end always #20 vin = ~vin; This TB will initially set vin at a (1 bit) value of 0, and after every 20 time units, will invert it. The whole process will last 80 time units. Now we are ready to simulate. In ModelSim, create a new project using the menus and locate the new project in the simulation directory. Add files to the project as was done in Lab 2, including the Verilog files for the DUT and the TB. Now, compile the files using Compile -> Compile All. Once all errors are fixed and compilation completes successfully, run simulation by clicking Simulate -> Start Simulation. In the
5 window that appears, uncheck the Optimize Design box and select the TB file as the simulation file under the work dropdown. Click OK to start simulation. 2.3 Accessing Simulation Results Now we are ready to view the results. We want to view the waveform of the results to confirm the DUT is operating as expected. To do this, make sure simulation is completed without errors. Select View -> Wave. A waveform viewer will open. Click and drag signals from the object pane to the waveform viewer. Once all desired signals are selected, run simulation by changing simulation time and hitting the Run button next to the time field. Right-click on the waveform and select Zoom Full to view the waveform. Compare again what you expect for the output versus the inputs. Part 3: Behavioral Views of Boolean Gates Create Behavioral Views for all of the gates used in Lab4. Present the simulation results for all of the individual gates in ModelSim. Part 4: Simulation of a Boolean System We will next simulate a system made from gates designed earlier. Create a Verilog behavioral file for the function you created in Lab 4 and a corresponding test bench to test its functionality. Simulate and compare results with those found in Lab 4. They should agree, but one obviously took less time to create and simulate. Name this verilog file boolean_function.v gedit ~/<project_dir>/boolean_function.v Test your verilog code in ModelSim to verify that it compiles and runs correctly. Part 5: Verilog Synthesis with RTL Compiler Introduction The purpose of this section is to develop investigate the concept of synthesis of digital systems from a hardware language description of the system. This is the intermediate step in a three-step design process which starts with the development of a HDL description, followed by synthesis into a set of standard cells. The third step is placing and routing the cells to create a layout of the circuit which can then be fabricated. The generalized digital circuit design flow, with the topics discussed in this tutorial highlighted, can be found below: 1. Design in HDL ( Verilog file ) 2. RTL Compiler ( Verilog file --> Synthesized Verilog file ) 3. Encounter ( Synthesized Verilog file --> Layout ) 4. Cadence (not looked at in this lab) 1. Layout Import ( Encounter --> CIW Import Stream) 2. Netlist Import ( Synthesized Verilog file --> Verilog Import )
6 5. LVS Verification RTL Compiler RTL Compiler is a tool that synthesizes and then optimizes behavioral circuit elements. Logic synthesis translates textual circuit descriptions like Verilog or VHDL into gatelevel representations. Optimization minimizes the area of the synthesized design and improves the design s performance. The HDL description can be synthesized into a gatelevel net-list composed of instances of standard cells. Once the gate-level net-list is finished, it can be imported into Encounter and used to create a layout. Consistency between the layout and schematic can then be verified with an LVS within Cadence. Preliminary Setup To use RTL Compiler and Cadence Encounter tools on the lab computers, the correct location needs to be sourced. Open the ~/.software file from Lab 1 and add the following line to the end of the file. EDI *make sure this is the last line and is all caps Then, the bash setup script needs to run so type bash into the Linux terminal. This will source the correct location where the binaries for both pieces of software are located. If remote connecting or using certain computers in Coover, this step is not required as RTL Compiler may already be installed. If trying to source the location and an error occurs that the location does not exist, try to move on to the next step before seeking further help. Setup Standard Cell Library First, the standard cells in the new OA version of Cadence are needed. They are found on my webpage and can be downloaded from the terminal with the following commands: cd ~/ee330 wget cells_ami05.tar tar -xvf OSU_stdcells_ami05.tar This will download and extract the OSU standard cells for use. Now change the cds.lib file in your ee330 directory by adding the following line. DEFINE OSU_stdcells_ami05 ~/ee330/osu_stdcells_ami05 By opening up Virtuoso, the OSU05 standard cells should now appear. Click around to the different cells to make sure the layout and schematic views can be viewed. The standard cell library should now be available to use. Standard cell files for RTL Compiler and Encounter
7 Now, the necessary files for use in RC and Encounter must be obtained to run the digital design flow. We will be using the OSU05 files in this lab. This cell library uses the same AMI05 process that we should be familiar with from the earlier labs. Use the following commands to download the tar file which contains the LIB, LEF, and Verilog files for the OSU standard cells. Put the downloaded files in the folder where RC will be run. cd ~/ee330/ (or wherever you want to run RC) wget tar -xvf rtl.tar Now the files are downloaded and extracted, which can be confirmed by looking for the lab12_ee330 folder in the location used above. Throughout this lab, carefully watch for path names and make sure they are pointing to the correct directories and files. Now, copy over the Verilog file created (and tested) in Part 4. cp ~/<project_dir>/boolean_funciton.v ~/<project_dir>/lab12_ee330/rtl You should now have a folder named lab12_ee330 that contains folders and files needed for the rest of the tutorial. Change directories to lab12_ee330 and type the following to begin RTL Compiler: cd lab12_ee330/syn rc -gui A GUI will show as well as a command line window..
8 In the command window that has a rc:/> prompt, type the following to load the correct standard cell libraries and run the synthesis script: set OUTPUT_DIR./run_dir set_attribute lib_search_path../libdir set_attribute library {osu05_stdcells.lib} Once the library is set, you need to load and elaborate your Verilog file. In this case, it was placed in the rtl folder and can be processed with the following commands: load -v2001../rtl/boolean_function.v set DESIGN boolean_function elaborate $DESIGN When Verilog is elaborated, each line is evaluated and replaced with a combination of logic gates. The blank GUI screen should be replaced with circuit blocks that represent the input Verilog, which was the following for our boolean function: At this point, RTL Compiler has generated an unoptimized version of the Verilog you provided. The final step is synthesizing the elaborated design, which optimizes the schematic already created and integrates your design with the TSMC standard cell
9 library. While there are many optimization options available to you, we will skip them for this tutorial. The design can be synthesized with the following command: synthesize -to_mapped -eff high -no_incr The GUI window should be updated. Exporting the synthesized Verilog file is done with these two commands: write -mapped > ${DESIGN}_synth.v write_sdc > ${DESIGN}.sdc Import Schematic to Cadence Virtuoso after Synthesis After synthesis, we want to import the gate-level netlist created in RTL Compiler into Cadence Virtuoso. Open Virtuoso and in the CIW (where the errors and other messages appear) select Import -> Verilog. The following screen will appear. Fill it in as is shown in the screen shot except replace the Verilog file with your synthesized Verilog file created by RC and your own library name. This file will end with _synth.v if following the above steps. (*Make sure to use the OSU library name that you defined above in the Reference Library field for example OSU_stdcells_ami05 ) Make sure you filled everything right (be careful of the name of reference libraries. There is no sample basic )
10 The import process should complete and may have a few errors or warnings. Ignore for now. Go to the schematic cell view created by the import process and open in Virtuoso. The synthesized design should appear with the lowest level of hierarchy being the standard digital blocks made of transistors in the AMI06 process. If not something is wrong. Retry the import process or possibly synthesis before asking for help from the TAs.
11 Part 6: Layout of Digital Circuits with Encounter Introduction In a typical digital design flow, a hardware description language is used to model a design and verify the desired behavior. Once the desired functionality is verified, the HDL description is then taken to a synthesis tool such as RTL compiler. The output of RTL compiler is a gate-level description of the desired circuit. The next step is to take this gate-level description to a place-and-route tool that can convert it to a layout level representation. In this tutorial, you will be introduced to a place-and-route tool called SoC Encounter. For the purposes of this tutorial, it will be assumed that you have a synthesized Verilog file ready to be placed and routed. The generalized digital circuit design flow, with the topics discussed in this tutorial highlighted, can be found below: 1. Design in HDL ( Verilog file ) 2. RTL Compiler ( Verilog file --> Synthesized Verilog file ) 3. Encounter ( Synthesized Verilog file --> Layout ) 4. Cadence 1. Layout Import ( Encounter --> CIW Import Stream ) 2. Netlist Import ( Synthesized Verilog file --> Verilog Import ) 5. LVS Verification SoC Encounter SoC Encounter, in its simplest form, allows a user to create a layout from a synthesized HDL file. Once the synthesized file is imported, Encounter provides a variety of tools to create a floorplan for your design, place standard cells, and automatically connect power rails and local routing. While this tutorial provides a brief overview of Encounter, there are many other optimization and layout options available. Preliminary Setup Before continuing with this tutorial, make sure that you have run through the preliminary setup instructions listed with the RTL Compiler tutorial. We need the LEF, LIB, and Verilog files for the OSU library. You should also confirm that two MAP files are in your libdir directory for the last step. If you haven t done so source the /etc/software/edi location. You may have to do this more than one time if you change directories. Running SoC Encounter In the lab12_ee330 folder, create a folder named encounter and then enter the encounter folder. Encounter can be started from here with the following command: Use old version of encounter
12 PATH=/usr/local/cadence/EDI101/bin:$PATH Encounter You will be presented with a GUI, which has been shown below. Importing Synthesized Verilog Once Encounter is initialized, you need to import your synthesized HDL description file. But first, set the power nets for a later step by typing the following commands in the encounter terminal. set rda_input(ui_pwrnet) {VDD} set rda_input(ui_gndnet) {GND} With that complete, go to File -> Import RTL. Fill in the Verilog Files field with the Verilog files used in the design. Then give a top level name to the design. Under the max timing library field, load the osu05_stdcells.lib. Next, under Timing Constraints, load the SDC file created by RTL Compiler. Move to the Physical tab and load the LEF file for the OSU standard cells called osu05_stdcells.lef which was included in the libdir directory. Finally, in the OA Reference Libraries, add the NCSU_TechLib_ami06 tech library. This will allow the tool to reference the ami06 library for layer information. Click OK and make sure the RTL is successfully imported by looking at the terminal for errors.
13 Should add Ex: home/<username>/ /rtl/fourbitadder.v home/<username>/ /libdir/osu05_stdcells.lib home/<username>/ /syn/
14 Go to File -> RTL Synthesis. Click Customize Options to generate the following figure. Change Incremental to Low and change Synthesis and Mapping to High. These are optimization options. This is performing the same task as RTL Compiler but for the use of the layout tool. When this completes, the floorplan step from Lab 12 can be completed. Floorplanning The Encounter GUI should now display an empty die and the information box in the bottom-right corner should read Design is: In Memory. The next step is to specify a floorplan for your layout. Floorplanning is done to specify the dimensions of your layout and spacing between the core (or area where the standard cells are placed) and power/signal routing. Open up the floorplanning options by clicking on the Floorplan menu and selecting Specify Floorplan. Options that you will need to pay attention to are: Aspect ratio height/width ratio of the core. Suggested: 1.0 Core Utilization the amount of core area used for placing standard cells. A larger value means that your design will be fairly compact but routing may be difficult, if not impossible. Smaller values will drastically increase the design area. Suggested: 0.5 Core Margins by specifies the distance between the core and edge of the die. The margin area needed is proportional to the number of input/output (I/O) pins. Suggested: 10 for core to left, right, top, and bottom Once these values are entered, the layout die/core spacing and aspect ratio should be updated.
15 Power Planning In order to connect your supply voltages to the standard cells, power and ground need to be available on all sides of the die. This is done by adding power rings and specifying global net connections. Select the Power menu and click on Power Planning > Add Rings. A dialog box will pop up and allow you to specify the ring type and configuration. You can plan power in various modes to facilitate various design styles. Since it is preferable to have the routing done inside the power rings, it is a better idea to have them around the I/O boundary so choose this option. If it is not already entered, add GND VDD (without quotes) to the Net(s) field. In the Ring Configuration section, verify that the width and spacing comply with the process design rules and are a multiple of lambda. Once finished, you should see two rings that run inside the I/O boundary. It should look like the following:
16 Connection to the global nets is done automatically if the nets are given the same names as was done in the setting of the power nets above. If all was done correctly, power planning should be finished. Placement Now we are ready to perform the placement. At the end the cells used in the design will be placed so that they don t overlap and there is enough space for routing in between them. Select the Place menu and then Standard Cells. In the dialog box that appears, leave the default settings and hit OK. In the main GUI window, you can verify that the standard cells were placed by selecting the Physical View Icon in the upper-right: You should see the cells placed in the middle of the core. The IO pins have shifted position accordingly as well.
17 If placement fails, it is most likely because Encounter cannot place the cells in the given area without causing gate overlaps. To solve this problem, you must start over by reinitializing the floorplan with relaxed constraints. The best constraint to change is the row utilization factor. By lowering this factor, you can increase the likelihood of placement without overlaps. The final placement should look similar to the following: Routing The built-in routing options within Encounter can now be used to connect the supply nets and create interconnects between the standard cells. Power and ground routing is performed with the Special Route tool. This can be found by selecting the Route menu and then Special Route. In the dialog box that appears, unselect Block pins, Pad pins, and Pad rings. After clicking OK, you should see horizontal and/or vertical metal power routing added to your design.
18 Once power routing is complete, the remaining connections between standard cells and the die I/O can be routed using the NanoRoute tool. Select Route and then NanoRoute and finally Route to enter the dialog box. You do not have to make any changes and can click OK. Your design should now resemble the following: Filler Cells If you import the complete layout from Encounter into Cadence at this point, you may have DRC errors due to nwell layers not being spaced far enough. You can fix these errors by hand in Cadence or you can add pre-designed filler cells with Encounter. These cells provide continuity for nwell layers and power rails between placed cells. Filler cells are placed by selecting the Place menu and then Physcial Cell -> Add Filler. In the dialog box that appears, click Select in the Cell Name(s) field and select the appropriate fill layers. FILLER CELLS IN THE OSU05 LIBRARY ARE JUST
19 CALLED FILL AND THERE IS ONLY ONE OF THEM. You can now click OK to fill in the blank regions in the core of your layout. Verification Before exporting your layout, you need to verify that there are not any geometric errors that occurred during placement or connectivity errors from routing. This can be done by selecting Verify Geometry and Verify Connectivity in the Verify menu. Reports will be generated and placed in the directory that you started Encounter from. You can also look at the terminal used to start Encounter and see the results of the verification. If no errors exist in either geometry or connectivity, the layout is good to fabricate. Save the design by selecting File -> Save Design. Give a name and save. GDS Export of Layout from Encounter Once the layout is complete in Encounter (post-routing and post-filler cells), then you need to perform an export of the layout. This is done in Encounter by going to File -> Save -> GDS/OASIS In the window that appears, select the GDSII radio button. Then type an output file name in Output File field such as design.gds or boolean_function.gds. In the map field select the gds2_encounter.map file located in the libdir directory. In the Library Name, type the Library in Cadence you would like to add the design to. I suggest making up a new library so nothing gets overwritten. Leave all other fields as default making sure the units are 1000 are mode is ALL. Click OK. Look at the terminal and make sure Stream out has finished successfully. Now let s import the design to Cadence. GDS Import of Layout into Virtuoso After creating a layout in Encounter and creating the GDS file, open Virtuoso. Click on the CIW (Virtuoso window where errors and messages appear) and click File -> Import - > Stream. This may produce an error the first time. Try again and it should work and bring up an import window. On the stream in window choose the GDS file created in Encounter as the Stream In file.
20 Under library, type the name of the library you would like to save the module in. Then give a name to the top level cell once it is imported. Attach the NCSU_TechLib_ami06 technology library. Select Show Options and click the following Tabs with the following options: General Tab: View Name should be layout. Check the box that says Replace [] with <>
21 Geometry Tab: Check Snap to Grid Layers Tab: Select Load under Map File - Choose gds2_icfb.map and click ok to load the layers map. The screen should now appear as below.
22 Libraries Tab: Select the two libraries NCSU_TechLib_ami06 and the OSU_stdcells_ami05 library to obtain the reference cells. This setting must be saved by hitting Save As and then typing a name such as import.map ***Make sure to add the OSU cells. Now we are ready to translate the file and import the design. Click Translate. If a box to save the libraries comes up make sure to save the libraries as something. The process will take a little bit. When complete there should be a log file and a message box that appears. This should have 0 errors and only a few warnings if not 0. Go to the library created in the Library Manager and try to open the layout of the design. The standard cells should appear. Hit Ctrl+F to see the layout view. At this point, the synthesized schematic and layout from Encounter have been imported into Virtuoso. Opening the layout allows DRC to be run. Some errors may exist due to the pins but they can be fixed manually by changing the layer information from text to the correct level of metal. This is done by changing the properties of the TEXT itself
23 from a layer of metal to one of text. Once DRC returns zero errors, run LVS to compare to the schematic. Zero errors should exist if the lab has been followed closely. NOTE: The steps below do NOT need to be completed, but they will eliminate DRC error. LVS will still pass without these steps When the importation was done, we could open the layout view of our circuit in the new library, and we had, after hitting Shift+f to see the entire layout,. Now it should have been alright, and we should simply have veri_ed the DRC and LVS, but first we had some errors with the DRC: ********* Summary of rule violations for cell "FourBitAdder layout" ********* # errors Violated Rules 2 dubiousdata(("metal1" "drawing") "Improperly formed shape - metal1") 5 dubiousdata(("metal2" "drawing") "Improperly formed shape - metal2") 9 dubiousdata(("metal3" "drawing") "Improperly formed shape - metal3") 16 Total errors found These errors were due to some text that was interpreted as metal1, metal2 and metal3 layers instead of text layer. To solve these issues, we had to select a view with only these 3 layers, then select everything and press Q to have the properties of every visible layer, and then search with the next button for the text layers that had a metal layer as property, and change this property to text.
24 Congrats on completing this tutorial. Please provide a summary of the steps required for synthesizing and performing layout with Cadence RTL Compiler and SoC Encounter. Explain what the main steps do and provide screen shots of major steps as well as the two verification steps at the end. References Verilog HDL Quick Reference Guide:
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11
 EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Fall 2017 Contents Purpose:... 3 Background... 3 Part 1: Inverter... 4 1.1 Simulating
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Fall 2017 Contents Purpose:... 3 Background... 3 Part 1: Inverter... 4 1.1 Simulating
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design, Simulation and Layout of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages
 EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design, Simulation and Layout of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to develop methods for using Hardware
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design, Simulation and Layout of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to develop methods for using Hardware
Place & Route: Using Silicon Ensemble
 Place & Route: Using Silicon Ensemble Introduction In a typical digital design flow, hardware description language is used to model a design and verify desired behavior. Once the desired functionality
Place & Route: Using Silicon Ensemble Introduction In a typical digital design flow, hardware description language is used to model a design and verify desired behavior. Once the desired functionality
EE 330 Spring Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits
 EE 330 Spring 2013 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Objective: The objective of this experiment is to investigate methods for evaluating the performance of Boolean circuits. Emphasis will be placed
EE 330 Spring 2013 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Objective: The objective of this experiment is to investigate methods for evaluating the performance of Boolean circuits. Emphasis will be placed
Laboratory 6. - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route. By Mulong Li, 2013
 CME 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) Laboratory 6 - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route By Mulong Li, 2013 Reference: Digital VLSI Chip Design with Cadence and Synopsys CAD Tools, Erik Brunvand Background
CME 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) Laboratory 6 - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route By Mulong Li, 2013 Reference: Digital VLSI Chip Design with Cadence and Synopsys CAD Tools, Erik Brunvand Background
Tutorial for Cadence SOC Encounter Place & Route
 Tutorial for Cadence SOC Encounter Place & Route For Encounter RTL-to-GDSII System 13.15 T. Manikas, Southern Methodist University, 3/9/15 Contents 1 Preliminary Setup... 1 1.1 Helpful Hints... 1 2 Starting
Tutorial for Cadence SOC Encounter Place & Route For Encounter RTL-to-GDSII System 13.15 T. Manikas, Southern Methodist University, 3/9/15 Contents 1 Preliminary Setup... 1 1.1 Helpful Hints... 1 2 Starting
ECE425: Introduction to VLSI System Design Machine Problem 3 Due: 11:59pm Friday, Dec. 15 th 2017
 ECE425: Introduction to VLSI System Design Machine Problem 3 Due: 11:59pm Friday, Dec. 15 th 2017 In this MP, you will use automated tools to synthesize the controller module from your MP2 project into
ECE425: Introduction to VLSI System Design Machine Problem 3 Due: 11:59pm Friday, Dec. 15 th 2017 In this MP, you will use automated tools to synthesize the controller module from your MP2 project into
Tutorial for Encounter
 Tutorial for Encounter STEP 1: Login to the Linux system on Linuxlab server. Start a terminal (the shell prompt). (If you don t know how to login to Linuxlab server, look at here) Click here to open a
Tutorial for Encounter STEP 1: Login to the Linux system on Linuxlab server. Start a terminal (the shell prompt). (If you don t know how to login to Linuxlab server, look at here) Click here to open a
VLSI Lab Tutorial 3. Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction
 VLSI Lab Tutorial 3 Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of this lab tutorial is to guide you through the design process in creating a custom IC layout for your CMOS inverter
VLSI Lab Tutorial 3 Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of this lab tutorial is to guide you through the design process in creating a custom IC layout for your CMOS inverter
Virtuoso Layout Editor
 This tutorial will cover the basic steps involved in using the Cadence layout editor called Virtuoso, extracting layout, and running simulation on the layout. The inverter layout is used as an example
This tutorial will cover the basic steps involved in using the Cadence layout editor called Virtuoso, extracting layout, and running simulation on the layout. The inverter layout is used as an example
Design rule illustrations for the AMI C5N process can be found at:
 Cadence Tutorial B: Layout, DRC, Extraction, and LVS Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revised by C Young & Waqar A Qureshi -FS08 Document Contents Introduction
Cadence Tutorial B: Layout, DRC, Extraction, and LVS Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revised by C Young & Waqar A Qureshi -FS08 Document Contents Introduction
EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits
 EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1: Introduction... 2 Part 2 Simulation of a CMOS Inverter... 3 Part 2.1 Attaching technology information... 3 Part
EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1: Introduction... 2 Part 2 Simulation of a CMOS Inverter... 3 Part 2.1 Attaching technology information... 3 Part
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015
 EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 Creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC Early and Often... 2 1.2 Create N active and connect the transistors... 3 1.3 Vias...
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 Creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC Early and Often... 2 1.2 Create N active and connect the transistors... 3 1.3 Vias...
EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems. From Layout to SPICE Simulation (Virtuoso, Calibre, HSpice) Spring 2017 Dae Hyun Kim
 EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems From Layout to SPICE Simulation (Virtuoso, Calibre, HSpice) Spring 2017 Dae Hyun Kim daehyun@eecs.wsu.edu 1 Preparation for Lab2 Download the following file into your working
EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems From Layout to SPICE Simulation (Virtuoso, Calibre, HSpice) Spring 2017 Dae Hyun Kim daehyun@eecs.wsu.edu 1 Preparation for Lab2 Download the following file into your working
Synthesis and APR Tools Tutorial
 Synthesis and APR Tools Tutorial (Last updated: Oct. 26, 2008) Introduction This tutorial will get you familiarized with the design flow of synthesizing and place and routing a Verilog module. All the
Synthesis and APR Tools Tutorial (Last updated: Oct. 26, 2008) Introduction This tutorial will get you familiarized with the design flow of synthesizing and place and routing a Verilog module. All the
Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial
 Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial 1 Table of Contents Design Flow in Libero TM IDE v2.3 Step 1 - Design Creation 3 Step 2 - Design Verification
Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial 1 Table of Contents Design Flow in Libero TM IDE v2.3 Step 1 - Design Creation 3 Step 2 - Design Verification
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #4, Standard cell design flow (from verilog to layout, 8-bit accumulator)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #4, Standard cell design flow (from verilog to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #4, Standard cell design flow (from verilog to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
EECE 285 VLSI Design. Cadence Tutorial EECE 285 VLSI. By: Kevin Dick Co-author: Jeff Kauppila Co-author: Dr. Arthur Witulski
 Cadence Tutorial EECE 285 VLSI By: Kevin Dick Co-author: Jeff Kauppila Co-author: Dr. Arthur Witulski 1 Table of Contents Purpose of Cadence 1) The Purpose of Cadence pg. 4 Linux 1) The Purpose of Linux
Cadence Tutorial EECE 285 VLSI By: Kevin Dick Co-author: Jeff Kauppila Co-author: Dr. Arthur Witulski 1 Table of Contents Purpose of Cadence 1) The Purpose of Cadence pg. 4 Linux 1) The Purpose of Linux
Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for single transistor analysis. Based on existing schematic entry tutorial developed for ECE410
 Cadence Analog Tutorial 1: Schematic Entry and Transistor Characterization Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for
Cadence Analog Tutorial 1: Schematic Entry and Transistor Characterization Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS
 EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Spring 2018 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC... 2 1.2 Stick Diagram to Physical Layer... 3 1.3 Bulk Connections... 3 1.4 Pins...
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Spring 2018 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC... 2 1.2 Stick Diagram to Physical Layer... 3 1.3 Bulk Connections... 3 1.4 Pins...
Cadence IC Design Manual
 Cadence IC Design Manual For EE5518 ZHENG Huan Qun Lin Long Yang Revised on May 2017 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering National University of Singapore 1 P age Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...
Cadence IC Design Manual For EE5518 ZHENG Huan Qun Lin Long Yang Revised on May 2017 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering National University of Singapore 1 P age Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
EE 330 Fall 2017 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools - Setup, Schematic capture and simulation
 EE 330 Fall 2017 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools - Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Table of Contents Objective... 2 1. Setup... 2 Set Bash Shell for the account... 2 2. Starting Cadence Custom
EE 330 Fall 2017 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools - Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Table of Contents Objective... 2 1. Setup... 2 Set Bash Shell for the account... 2 2. Starting Cadence Custom
EE 330 Spring 2018 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools Setup, Schematic capture and simulation
 EE 330 Spring 2018 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Table of Contents Objective... 2 1. Setup... 2 Set Bash Shell for the account... 2 2. Starting Cadence Custom
EE 330 Spring 2018 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Table of Contents Objective... 2 1. Setup... 2 Set Bash Shell for the account... 2 2. Starting Cadence Custom
Tutorial 2 Automatic Placement & Routing
 Tutorial 2 Automatic Placement & Routing Please follow the instructions found under Setup on the CADTA main page before starting this tutorial. 1.1. Start Encounter Log on to a VLSI server using your EE
Tutorial 2 Automatic Placement & Routing Please follow the instructions found under Setup on the CADTA main page before starting this tutorial. 1.1. Start Encounter Log on to a VLSI server using your EE
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation NTU IC541CA 1 Assumed Knowledge This lab assumes use of the Electric
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation NTU IC541CA 1 Assumed Knowledge This lab assumes use of the Electric
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group.
 Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Aug. 2003 update and edit A. Mason add intro/revision/contents
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Aug. 2003 update and edit A. Mason add intro/revision/contents
Physical Placement with Cadence SoCEncounter 7.1
 Physical Placement with Cadence SoCEncounter 7.1 Joachim Rodrigues Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Lund, Sweden November 2008 Address for correspondence: Joachim Rodrigues
Physical Placement with Cadence SoCEncounter 7.1 Joachim Rodrigues Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Lund, Sweden November 2008 Address for correspondence: Joachim Rodrigues
ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS)
 ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS) Objective Part A: To become acquainted with Spectre (or HSpice) by simulating an inverter,
ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS) Objective Part A: To become acquainted with Spectre (or HSpice) by simulating an inverter,
EECS 627, Lab Assignment 3
 EECS 627, Lab Assignment 3 1 Introduction In this lab assignment, we will use Cadence ICFB and Calibre to become familiar with the process of DRC/LVS checks on a design. So far, we have placed and routed
EECS 627, Lab Assignment 3 1 Introduction In this lab assignment, we will use Cadence ICFB and Calibre to become familiar with the process of DRC/LVS checks on a design. So far, we have placed and routed
Creating LEF File. Abstract Generation: Creating LEF Tutorial File Release Date: 01/13/2004. Export GDS:
 Creating LEF Tutorial 1-1 - Creating LEF File Abstract Generation: Export GDS: Abstract generator comes as a part of the Silicon Ensemble package. As such, it cannot directly read ICFB library databases.
Creating LEF Tutorial 1-1 - Creating LEF File Abstract Generation: Export GDS: Abstract generator comes as a part of the Silicon Ensemble package. As such, it cannot directly read ICFB library databases.
TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION
 TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION After finishing a schematic of your design (Tutorial-I), the next step is creating masks which are for
TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION After finishing a schematic of your design (Tutorial-I), the next step is creating masks which are for
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits. Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL)
 EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL) This tutorial will demonstrate schematic-driven layout on the example of a 2-input NAND gate. Simple Layout (that won
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL) This tutorial will demonstrate schematic-driven layout on the example of a 2-input NAND gate. Simple Layout (that won
Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools- Setup, Schematic capture and simulation
 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools- Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Brittany Duffy EE 330- Integrated Electronics Lab Section B Professor Randy Geiger 1/24/13 Introduction The main goal of this
Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools- Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Brittany Duffy EE 330- Integrated Electronics Lab Section B Professor Randy Geiger 1/24/13 Introduction The main goal of this
CPEN 230L: Introduction to Digital Logic Laboratory Lab #6: Verilog and ModelSim
 CPEN 230L: Introduction to Digital Logic Laboratory Lab #6: Verilog and ModelSim Purpose Define logic expressions in Verilog using register transfer level (RTL) and structural models. Use Quartus II to
CPEN 230L: Introduction to Digital Logic Laboratory Lab #6: Verilog and ModelSim Purpose Define logic expressions in Verilog using register transfer level (RTL) and structural models. Use Quartus II to
VLSI Lab Tutorial 1. Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction
 VLSI Lab Tutorial 1 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of the first lab tutorial is to help you become familiar with the schematic editor, Virtuoso Schematic
VLSI Lab Tutorial 1 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of the first lab tutorial is to help you become familiar with the schematic editor, Virtuoso Schematic
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 1: Introduction to Quartus II Schematic Capture and ModelSim Simulation This
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 1: Introduction to Quartus II Schematic Capture and ModelSim Simulation This
ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018
 ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018 Introduction This project will first walk you through the setup
ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018 Introduction This project will first walk you through the setup
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY LAB SHEET DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY LAB SHEET DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DIC1: Schematic Design Entry, Simulation & Verification DIC2: Schematic Driven Layout Drawing (SDL) Design Rule Check (DRC)
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY LAB SHEET DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DIC1: Schematic Design Entry, Simulation & Verification DIC2: Schematic Driven Layout Drawing (SDL) Design Rule Check (DRC)
CMOS Design Lab Manual
 CMOS Design Lab Manual Developed By University Program Team CoreEl Technologies (I) Pvt. Ltd. 1 Objective Objective of this lab is to learn the Mentor Graphics HEP2 tools as well learn the flow of the
CMOS Design Lab Manual Developed By University Program Team CoreEl Technologies (I) Pvt. Ltd. 1 Objective Objective of this lab is to learn the Mentor Graphics HEP2 tools as well learn the flow of the
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO UW ASIC DESIGN TEAM: Cadence Tutorial Description: Part I: Layout & DRC of a CMOS inverter. Part II: Extraction & LVS of a CMOS inverter. Part III: Post-Layout Simulation. The Cadence
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO UW ASIC DESIGN TEAM: Cadence Tutorial Description: Part I: Layout & DRC of a CMOS inverter. Part II: Extraction & LVS of a CMOS inverter. Part III: Post-Layout Simulation. The Cadence
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics
 Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics Introduction This tutorial describes how to generate a mask layout in the Cadence Virtuoso Layout Editor. Use of DIVA
Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics Introduction This tutorial describes how to generate a mask layout in the Cadence Virtuoso Layout Editor. Use of DIVA
Verilog Design Entry, Synthesis, and Behavioral Simulation
 ------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
and 32 bit for 32 bit. If you don t pay attention to this, there will be unexpected behavior in the ISE software and thing may not work properly!
 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE 14.7 Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Simulate the schematic circuit using ISim Part IV: Constraint, Synthesize,
This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE 14.7 Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Simulate the schematic circuit using ISim Part IV: Constraint, Synthesize,
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #1, Full Custom VLSI (inverter layout)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #1, Full Custom VLSI (inverter layout) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville Adapted from Virginia Tech, Dept.
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #1, Full Custom VLSI (inverter layout) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville Adapted from Virginia Tech, Dept.
Select the technology library: NCSU_TechLib_ami06, then press OK.
 ECE 126 Inverter Tutorial: Schematic & Symbol Creation Created for GWU by Anis Nurashikin Nordin & Thomas Farmer Tutorial adapted from: http://www.ee.ttu.edu/ee/cadence/commondirectory/final%20tutorials/digitalcircuitsimulationusingvirtuoso.doc
ECE 126 Inverter Tutorial: Schematic & Symbol Creation Created for GWU by Anis Nurashikin Nordin & Thomas Farmer Tutorial adapted from: http://www.ee.ttu.edu/ee/cadence/commondirectory/final%20tutorials/digitalcircuitsimulationusingvirtuoso.doc
Cell-Based IC Physical Design & Verification SOC Encounter. Advisor : 李昆忠 Presenter : 蕭智元
 Cell-Based IC Physical Design & Verification SOC Encounter Advisor : 李昆忠 Presenter : 蕭智元 Reference: SOC Encounter Training Manual, 2007, edited by CIC. Introduction We ll use some EDA tools to transform
Cell-Based IC Physical Design & Verification SOC Encounter Advisor : 李昆忠 Presenter : 蕭智元 Reference: SOC Encounter Training Manual, 2007, edited by CIC. Introduction We ll use some EDA tools to transform
The IIT standard cell library Version 2.1
 The IIT standard cell library Version 2.1 Highlights - Support for AMI 0.35um library, including pads - Added Primetime and Pathmill support to IIT ASIC Flow - Support for stacked vias (for Virtuoso and
The IIT standard cell library Version 2.1 Highlights - Support for AMI 0.35um library, including pads - Added Primetime and Pathmill support to IIT ASIC Flow - Support for stacked vias (for Virtuoso and
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial
 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial Introduction This tutorial is an introduction to schematic capture and circuit simulation for ENGN1600 using Cadence Virtuoso. These courses
Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial Introduction This tutorial is an introduction to schematic capture and circuit simulation for ENGN1600 using Cadence Virtuoso. These courses
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 4: Full Chip Assembly
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 4: Full Chip Assembly In this final lab, you will assemble and simulate your entire MIPS microprocessor! You will build your top level chip cell by connecting the datapath, aludec,
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 4: Full Chip Assembly In this final lab, you will assemble and simulate your entire MIPS microprocessor! You will build your top level chip cell by connecting the datapath, aludec,
CADENCE TUTORIAL. San Diego State University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Amith Dharwadkar and Ashkan Ashrafi
 CADENCE TUTORIAL San Diego State University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Amith Dharwadkar and Ashkan Ashrafi 1 Contents 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Introduction 3 Connecting to the Volta server..4
CADENCE TUTORIAL San Diego State University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Amith Dharwadkar and Ashkan Ashrafi 1 Contents 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Introduction 3 Connecting to the Volta server..4
EE183 LAB TUTORIAL. Introduction. Projects. Design Entry
 EE183 LAB TUTORIAL Introduction You will be using several CAD tools to implement your designs in EE183. The purpose of this lab tutorial is to introduce you to the tools that you will be using, Xilinx
EE183 LAB TUTORIAL Introduction You will be using several CAD tools to implement your designs in EE183. The purpose of this lab tutorial is to introduce you to the tools that you will be using, Xilinx
Cadence Inverter Transistor Sizing Tutorial Cadence Inverter Ocean Introduction Cadence Inverter Corners Tutorial Cadence Inverter VerilogA Tutorial
 Cadence Inverter Transistor Sizing Tutorial Cadence Inverter Ocean Introduction Cadence Inverter Corners Tutorial Cadence Inverter VerilogA Tutorial Alfred Sargezi & Zain Ali AMS Group - San Jose State
Cadence Inverter Transistor Sizing Tutorial Cadence Inverter Ocean Introduction Cadence Inverter Corners Tutorial Cadence Inverter VerilogA Tutorial Alfred Sargezi & Zain Ali AMS Group - San Jose State
Contents. Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2 Page 1 of 14
 Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2 Page 1 of 14 Contents Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2...2 B.1 Getting Started...2 B.1.1 Preparing a Folder for the Project...2 B.1.2 Starting Quartus II...2 B.1.3 Creating
Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2 Page 1 of 14 Contents Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2...2 B.1 Getting Started...2 B.1.1 Preparing a Folder for the Project...2 B.1.2 Starting Quartus II...2 B.1.3 Creating
Tutorial I: Cadence Innovus ECE6133: Physical Design Automation of VLSI Systems Georgia Institute of Technology Prof. Sung Kyu Lim
 Tutorial I: Cadence Innovus ECE6133: Physical Design Automation of VLSI Systems Georgia Institute of Technology Prof. Sung Kyu Lim I. Setup for Cadence Innovus 1. Copy the following files into your working
Tutorial I: Cadence Innovus ECE6133: Physical Design Automation of VLSI Systems Georgia Institute of Technology Prof. Sung Kyu Lim I. Setup for Cadence Innovus 1. Copy the following files into your working
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CS755 CAD TOOL TUTORIAL
 CS755 CAD TOOL TUTORIAL CREATING SCHEMATIC IN CADENCE Shi-Ting Zhou shi-ting@cs.wisc.edu After you have figured out what you want to design, and drafted some pictures and diagrams, it s time to input schematics
CS755 CAD TOOL TUTORIAL CREATING SCHEMATIC IN CADENCE Shi-Ting Zhou shi-ting@cs.wisc.edu After you have figured out what you want to design, and drafted some pictures and diagrams, it s time to input schematics
Cadence Tutorial: Schematic Entry and Circuit Simulation of a CMOS Inverter
 Cadence Tutorial: Schematic Entry and Circuit Simulation of a CMOS Inverter Introduction This tutorial describes the steps involved in the design and simulation of a CMOS inverter using the Cadence Virtuoso
Cadence Tutorial: Schematic Entry and Circuit Simulation of a CMOS Inverter Introduction This tutorial describes the steps involved in the design and simulation of a CMOS inverter using the Cadence Virtuoso
ASIC Physical Design Top-Level Chip Layout
 ASIC Physical Design Top-Level Chip Layout References: M. Smith, Application Specific Integrated Circuits, Chap. 16 Cadence Virtuoso User Manual Top-level IC design process Typically done before individual
ASIC Physical Design Top-Level Chip Layout References: M. Smith, Application Specific Integrated Circuits, Chap. 16 Cadence Virtuoso User Manual Top-level IC design process Typically done before individual
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
Cadence On-Line Document
 Cadence On-Line Document 1 Purpose: Use Cadence On-Line Document to look up command/syntax in SoC Encounter. 2 Cadence On-Line Document An on-line searching system which can be used to inquire about LEF/DEF
Cadence On-Line Document 1 Purpose: Use Cadence On-Line Document to look up command/syntax in SoC Encounter. 2 Cadence On-Line Document An on-line searching system which can be used to inquire about LEF/DEF
Quartus II Tutorial. September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0
 Quartus II Tutorial September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with Modelsim, and downloading
Quartus II Tutorial September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with Modelsim, and downloading
HOMEWORK 9 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/12/ :30pm
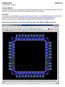 HOMEWORK 9 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/12/2016 11:30pm Learning Objective Complete the full 8 bit RISC microprocessor chip design by placing the processor core design into the 40 pin 'tiny' chip pad frame. Do verify
HOMEWORK 9 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/12/2016 11:30pm Learning Objective Complete the full 8 bit RISC microprocessor chip design by placing the processor core design into the 40 pin 'tiny' chip pad frame. Do verify
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group.
 Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Jan. 2006 Updated for use with spectre simulator
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Jan. 2006 Updated for use with spectre simulator
Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4
 Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Implement a function using
Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Implement a function using
This is a brief tutorial about building a Symbol for a Schematic in Cadence IC design tool environment for hierarchical design of schematics.
 This is a brief tutorial about building a Symbol for a Schematic in Cadence IC design tool environment for hierarchical design of schematics. 1. > cd work035 2. > cadsetup ams035 3. > virtuoso& IMPORTANT:
This is a brief tutorial about building a Symbol for a Schematic in Cadence IC design tool environment for hierarchical design of schematics. 1. > cd work035 2. > cadsetup ams035 3. > virtuoso& IMPORTANT:
More information can be found in the Cadence manuals Virtuoso Layout Editor User Guide and Cadence Hierarchy Editor User Guide.
 Chapter 6 Building with Layout This chapter consists of two parts. The first describes the generation of layout views and the second deals with the various tools used for verifying the layout, both physical
Chapter 6 Building with Layout This chapter consists of two parts. The first describes the generation of layout views and the second deals with the various tools used for verifying the layout, both physical
Cadence SOC Encounter Tutorial for a logic block using the University Of Utah Standard cell Libraries In ON Semiconductor 0.
 Cadence SOC Encounter Tutorial for a logic block using the University Of Utah Standard cell Libraries In ON Semiconductor 0.5 µ C5N CMOS 1. Create a folder called encounter inside of your project folder
Cadence SOC Encounter Tutorial for a logic block using the University Of Utah Standard cell Libraries In ON Semiconductor 0.5 µ C5N CMOS 1. Create a folder called encounter inside of your project folder
ANALOG MICROELECTRONICS ( A)
 ANALOG MICROELECTRONICS (304-534A) IBM 130 nm CMOS Technology An Introduction to Cadence Virtuoso Layout Tool and the Analog Simulation Environment Prepared By - Azhar A. Chowdhury Updated by Ming Yang
ANALOG MICROELECTRONICS (304-534A) IBM 130 nm CMOS Technology An Introduction to Cadence Virtuoso Layout Tool and the Analog Simulation Environment Prepared By - Azhar A. Chowdhury Updated by Ming Yang
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
Verifying the Multiplexer Layout
 4 This chapter introduces you to interactive verification. You will perform two different tests in the Virtuoso layout editor while using Assura interactive verification products. One test uses the Design
4 This chapter introduces you to interactive verification. You will perform two different tests in the Virtuoso layout editor while using Assura interactive verification products. One test uses the Design
Abstract Editor (Last updated: Oct. 23, 2008)
 Abstract Editor (Last updated: Oct. 23, 2008) Abstract Editor Tutorial This tutorial has been created to discuss all of the steps needed to create an abstract Library Exchange Format (LEF) file for custom
Abstract Editor (Last updated: Oct. 23, 2008) Abstract Editor Tutorial This tutorial has been created to discuss all of the steps needed to create an abstract Library Exchange Format (LEF) file for custom
Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences 1. Motivation Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping In this lab you will learn how to use
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences 1. Motivation Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping In this lab you will learn how to use
ELEC451 Integrated Circuit Engineering Using Cadence's Virtuoso Layout Editing Tool
 ELEC451 Integrated Circuit Engineering Using Cadence's Virtuoso Layout Editing Tool Contents Contents 1. General 2. Creating and Working On a Layout o 2.1 Undoing/Re-doing an Action o 2.2 Display Options
ELEC451 Integrated Circuit Engineering Using Cadence's Virtuoso Layout Editing Tool Contents Contents 1. General 2. Creating and Working On a Layout o 2.1 Undoing/Re-doing an Action o 2.2 Display Options
Pipelined MIPS CPU Synthesis and On-Die Representation ECE472 Joseph Crop Stewart Myers
 Pipelined MIPS CPU Synthesis and On-Die Representation ECE472 Joseph Crop Stewart Myers 2008 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Steps Taken and Simulation... 3 Pitfalls... 8 Simulated Delay... 9 APPENDIX
Pipelined MIPS CPU Synthesis and On-Die Representation ECE472 Joseph Crop Stewart Myers 2008 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Steps Taken and Simulation... 3 Pitfalls... 8 Simulated Delay... 9 APPENDIX
Microelectronica. Full-Custom Design with Cadence Tutorial
 Área Científica de Electrónica Microelectronica Full-Custom Design with Cadence Tutorial AustriaMicroSystems C35B3 (HIT-Kit 3.70) Marcelino Santos Table of contends 1. Starting Cadence... 3 Starting Cadence
Área Científica de Electrónica Microelectronica Full-Custom Design with Cadence Tutorial AustriaMicroSystems C35B3 (HIT-Kit 3.70) Marcelino Santos Table of contends 1. Starting Cadence... 3 Starting Cadence
University of Florida EEL 3701 Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Revision 0 12-Jun-16
 Page 1/14 Quartus Tutorial with Basic Graphical Gate Entry and Simulation Example Problem Given the logic equation Y = A*/B + /C, implement this equation using a two input AND gate, a two input OR gate
Page 1/14 Quartus Tutorial with Basic Graphical Gate Entry and Simulation Example Problem Given the logic equation Y = A*/B + /C, implement this equation using a two input AND gate, a two input OR gate
An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design
 An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design With examples taken from the implementation of the 36-core AsAP1 chip and the 1000-core KiloCore chip Zhiyi Yu, Tinoosh Mohsenin, Aaron Stillmaker,
An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design With examples taken from the implementation of the 36-core AsAP1 chip and the 1000-core KiloCore chip Zhiyi Yu, Tinoosh Mohsenin, Aaron Stillmaker,
DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 3.0
 DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 3.0 Start virtuoso l l Open a virtuoso session in the directory which contains the required cds.lib and lib.def files. Command : virtuoso & Open the layout
DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 3.0 Start virtuoso l l Open a virtuoso session in the directory which contains the required cds.lib and lib.def files. Command : virtuoso & Open the layout
Step 1: Downloading the source files
 Introduction: In this lab and in the remainder of the ELEC 2607 labs, you will be using the Xilinx ISE to enter and simulate the designs for your circuits. In labs 3 and 4, you will use ISE to compile
Introduction: In this lab and in the remainder of the ELEC 2607 labs, you will be using the Xilinx ISE to enter and simulate the designs for your circuits. In labs 3 and 4, you will use ISE to compile
ECE471/571 Energy Ecient VLSI Design
 ECE471/571 Energy Ecient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30pm on Friday, January 30 th 2015 Introduction This project will rst walk you through the setup for
ECE471/571 Energy Ecient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30pm on Friday, January 30 th 2015 Introduction This project will rst walk you through the setup for
TUTORIAL SESSION Technical Group Hoda Najafi & Sunita Bhide
 TUTORIAL SESSION 2014 Technical Group Hoda Najafi & Sunita Bhide SETUP PROCEDURE Start the Altium Designer Software. (Figure 1) Ensure that the Files and Projects tabs are located somewhere on the screen.
TUTORIAL SESSION 2014 Technical Group Hoda Najafi & Sunita Bhide SETUP PROCEDURE Start the Altium Designer Software. (Figure 1) Ensure that the Files and Projects tabs are located somewhere on the screen.
CS 4120 Hardware Description Languages and Synthesis Homework 6: Introduction to Cadence Silicon Ensemble
 CS 4120 Hardware Description Languages and Synthesis Homework 6: Introduction to Cadence Silicon Ensemble 0. Introduction In this homework, you will be introduced to a Place and Route tool called Silicon
CS 4120 Hardware Description Languages and Synthesis Homework 6: Introduction to Cadence Silicon Ensemble 0. Introduction In this homework, you will be introduced to a Place and Route tool called Silicon
EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #1 Cadence Schematic Capture and Layout Tutorial
 EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #1 Cadence Schematic Capture and Layout Tutorial Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis September 26, 2011 Reading: Rabaey Chapters 1, 2, A,
EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #1 Cadence Schematic Capture and Layout Tutorial Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis September 26, 2011 Reading: Rabaey Chapters 1, 2, A,
Alfred Sargezi & Zain Ali. AMS Group - San Jose State University ams.sjsu.edu
 Cadence Inverter Transistor Sizing Tutorial Cadence Inverter Ocean Introduction Cadence Inverter Corners Tutorial Cadence Inverter VerilogA Tutorial Cadence Inverter Vout vs Vin Tutorial Alfred Sargezi
Cadence Inverter Transistor Sizing Tutorial Cadence Inverter Ocean Introduction Cadence Inverter Corners Tutorial Cadence Inverter VerilogA Tutorial Cadence Inverter Vout vs Vin Tutorial Alfred Sargezi
Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Code
 Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Code (Version 15) 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow
Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Code (Version 15) 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow
Synopsys Custom Designer Tutorial for a chip integra7on using the University of Utah Standard Cell Libraries In ON Semiconductor 0.
 Synopsys Custom Designer Tutorial for a chip integra7on using the University of Utah Standard Cell Libraries In ON Semiconductor 0.5u C5 CMOS Version 6.0 Overview This tutorial will take you through the
Synopsys Custom Designer Tutorial for a chip integra7on using the University of Utah Standard Cell Libraries In ON Semiconductor 0.5u C5 CMOS Version 6.0 Overview This tutorial will take you through the
Start Active-HDL. Create a new workspace TUTORIAL #1 CREATING AND SIMULATING SIMPLE SCHEMATICS
 Introduction to Active-HDL TUTORIAL #1 CREATING AND SIMULATING SIMPLE SCHEMATICS This tutorial will introduce the tools and techniques necessary to design a basic schematic. The goal of this tutorial is
Introduction to Active-HDL TUTORIAL #1 CREATING AND SIMULATING SIMPLE SCHEMATICS This tutorial will introduce the tools and techniques necessary to design a basic schematic. The goal of this tutorial is
Don t expect to be able to write and debug your code during the lab session.
 EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
Virtuoso Schematic Composer
 is a schematic design tool from Cadence. In this tutorial you will learn how to put electrical components, make wire connections, insert pins and check for connection error. Start Cadence Custom IC Design
is a schematic design tool from Cadence. In this tutorial you will learn how to put electrical components, make wire connections, insert pins and check for connection error. Start Cadence Custom IC Design
Hardware Verification Group. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, Canada. CAD Tool Tutorial.
 Digital Logic Synthesis and Equivalence Checking Tools Hardware Verification Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, Canada CAD Tool Tutorial May, 2010
Digital Logic Synthesis and Equivalence Checking Tools Hardware Verification Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, Canada CAD Tool Tutorial May, 2010
Tutorial II: Cadence Virtuoso ECE6133: Physical Design Automation of VLSI Systems Georgia Institute of Technology Prof.
 Tutorial II: Cadence Virtuoso ECE6133: Physical Design Automation of VLSI Systems Georgia Institute of Technology Prof. Sung Kyu Lim I. Setup for Cadence Virtuoso 1. Copy the following files into your
Tutorial II: Cadence Virtuoso ECE6133: Physical Design Automation of VLSI Systems Georgia Institute of Technology Prof. Sung Kyu Lim I. Setup for Cadence Virtuoso 1. Copy the following files into your
Quartus II Version 14.0 Tutorial Created September 10, 2014; Last Updated January 9, 2017
 Quartus II Version 14.0 Tutorial Created September 10, 2014; Last Updated January 9, 2017 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with
Quartus II Version 14.0 Tutorial Created September 10, 2014; Last Updated January 9, 2017 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with
The original document link is
 Tutorial:Analog Artist with HSPICE The original document link is http://www.eda.ncsu.edu/wiki/tutorial:analog_artist_with_hspice This tutorial will introduce you to the Cadence Environment: specifically
Tutorial:Analog Artist with HSPICE The original document link is http://www.eda.ncsu.edu/wiki/tutorial:analog_artist_with_hspice This tutorial will introduce you to the Cadence Environment: specifically
DOWNLOAD PDF CADENCE WAVEFORM CALCULATOR USER GUIDE
 Chapter 1 : CSE / Cadence Tutorial The Cadence Design Communities support Cadence users and technologists interacting to exchange ideas, news, technical information, and best practices to solve problems
Chapter 1 : CSE / Cadence Tutorial The Cadence Design Communities support Cadence users and technologists interacting to exchange ideas, news, technical information, and best practices to solve problems
An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design
 An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design Implementation of the first generation AsAP processor Zhiyi Yu and Tinoosh Mohsenin VCL Laboratory UC Davis Outline Overview of standard cellbased
An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design Implementation of the first generation AsAP processor Zhiyi Yu and Tinoosh Mohsenin VCL Laboratory UC Davis Outline Overview of standard cellbased
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits. Tutorial 2: Hierarchical Schematic and Simulation
 EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 2: Hierarchical Schematic and Simulation The objectives are to become familiar with Virtuoso schematic editor, learn how to create the symbol view of basic primitives,
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 2: Hierarchical Schematic and Simulation The objectives are to become familiar with Virtuoso schematic editor, learn how to create the symbol view of basic primitives,
Fall 2008: EE5323 VLSI Design I using Cadence
 1 of 23 9/17/2008 6:47 PM Fall 2008: EE5323 VLSI Design I using Cadence This tutorial has been adapted from EE5323 offered in Fall 2007. Thanks to Jie Gu, Prof. Chris Kim and Satish Sivaswamy of the University
1 of 23 9/17/2008 6:47 PM Fall 2008: EE5323 VLSI Design I using Cadence This tutorial has been adapted from EE5323 offered in Fall 2007. Thanks to Jie Gu, Prof. Chris Kim and Satish Sivaswamy of the University
