Test 1, Spring 2013 ( Solutions): Provided by Jeff Collins and Anil Patel. 1. Axioms for a finite AFFINE plane of order n.
|
|
|
- Alban Hines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 532, 736I: Modern Geometry Test 1, Spring 2013 ( Solutions): Provided by Jeff Collins and Anil Patel Part 1: 1. Axioms for a finite AFFINE plane of order n. AA1: There exist at least 4 points, no 3 of which are collinear. AA2: There exists at least 1 line with exactly n points on it. AA3: Given any 2 distinct points, there is exactly 1 line that passes through these points. AA4: Given any line l, and a point P not on l, there is exactly 1 line that does not intersect l and passes through P. 2. Model of a finite PROJECTIVE plane of order 3 ( see appendix) 3. Two points have been circled in a 7 x 7 array of points. Using the model for a finite affine plane of order 7, finish circling the points that belong to the same line as given points ( see appendix) 4. Consider the points ( 10,41) and ( 30,26) in a 59 x 59 array of points for our model of a finite affine plane of order 59. Find the equation of the line passing through these two points. Put your answer in the form y mx + k ( mod 59) where m and k are among the numbers 0,1,2,3,,58. ( 10,41) (30,26) m = = - 15 = m - 3 ( mod 59) Plugging in ( 10,41) (15)(4m) (15)( - 3) ( mod 59) 41 (14)(10) + k( mod 59) m - 45 ( mod 59) k ( mod 59) m = k ( mod 59) k = 19 So plugging in m and k, we get: y 14x + 19( mod 59)
2 5. Prove that in an affine plane of order n, for each line l, there are at least n - 1 lines parallel to l. (Using the theorem below, and the axioms for a finite affine plane stated in problem 1) Theorem: In an affine plane of order n, each line contains exactly n points. Note: The theorem is to be used in the proof below. The proof is establishing that there are at least n 1 lines parallel to l as stated above. Proof: Let l be an arbitrary line. By Axiom A 1, there is a point P₁ not on l. By From the provided theorem, line l has at least one point, say P₂, on it., Axiom A3, there is a line l ' passing through P₁ and P₂. Since P₁ is on l ' but not on l we have that l ' l. Axiom A3 implies that P₂ is the only, point on both l ' and l. By The provided theorem, l ' has exactly n points on it, two of which are P₁ and P₂. Let P₃,., Pn denote the remaining points on l '. For each j 2, Pj is not on l, so that Axiom A4 implies that there is a line l j passing through Pj and parallel to l. Each such l j is different from l ' since l ' intersects l and l j is parallel to l. It follows that the lines l j ( with j 2) are distinct by Axiom A3 ( since l ' is the unique line passing through any two of the Pj s ). Thus there are at least n 1 distinct lines parallel to l ( namely, the lines l j with j 2).
3 Part II Axiom 1. There exist 3 distinct non- collinear points. Axiom 2. There exist 3 distinct collinear points. Axiom 3. Given any 2 distinct points, there is exactly 1 line passing through them. 1. Justify that the axiomatic system is consistent ( see appendix) 2. Justify that the axiomatic system is not complete. ( see appendix) 3. Justify that the axiomatic system is independent. ( see appendix) 4. What is the dual of Axiom 2? Dual of Axiom 2: There exist 3 distinct lines that intersect at a point. 5. Prove that there are at least 4 distinct lines, using above given axiomatic system. Proof: By Axiom 2, there is a line l with at least 3 points on it. Call three such points P₁, P₂, and P₃. By Axiom 1, there is at least one point Q not on l. By Axiom 3, there is exactly one line l j passing through Q and Pj for each j Є {1, 2, 3}. Each l j is not equal to l because Q is on l j but not on l. Q Assume l i = l j for some i j with i and j in { 1,2,3}. Then Pi and Pj
4 are two distinct points on two distinct lines l i and l. This contradicts Axiom 3. Hence l₁, l₂, and l₃ are all different. Since we have shown l, l₁, l₂, and l₃ are all different, the proof is complete.
5
6
Hawraa Abbas Almurieb. Axiomatic Systems
 2 Axiomatic Systems 2.1. Introduction to Axiomatic Systems We need undefined terms for any axiomatic system to build the axioms upon them. Which are basic worlds or things for the system. 2.1.1 Definitions
2 Axiomatic Systems 2.1. Introduction to Axiomatic Systems We need undefined terms for any axiomatic system to build the axioms upon them. Which are basic worlds or things for the system. 2.1.1 Definitions
Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik
 Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik Prof. Dr. Dr. Jürgen Richter-Gebert, Bernhard Werner Projective Geometry SS 208 https://www-m0.ma.tum.de/bin/view/lehre/ss8/pgss8/webhome Solutions for
Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik Prof. Dr. Dr. Jürgen Richter-Gebert, Bernhard Werner Projective Geometry SS 208 https://www-m0.ma.tum.de/bin/view/lehre/ss8/pgss8/webhome Solutions for
Interpretations and Models. Chapter Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry
 Interpretations and Models Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry Axiomatic Systems in Mathematics The gold standard for rigor in an area of mathematics Not fully achieved in most areas
Interpretations and Models Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry Axiomatic Systems in Mathematics The gold standard for rigor in an area of mathematics Not fully achieved in most areas
Problem 3.1 (Building up geometry). For an axiomatically built-up geometry, six groups of axioms needed:
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe September 29, 2016 All3181\3181_fall16h3.tex Names: Homework has to be turned in this handout. For extra space, use the back pages, or put blank pages between. The homework can
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe September 29, 2016 All3181\3181_fall16h3.tex Names: Homework has to be turned in this handout. For extra space, use the back pages, or put blank pages between. The homework can
Lesson 19: The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables is a Line
 Lesson 19: The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables is a Line Classwork Exercises Theorem: The graph of a linear equation y = mx + b is a non-vertical line with slope m and passing through (0, b),
Lesson 19: The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables is a Line Classwork Exercises Theorem: The graph of a linear equation y = mx + b is a non-vertical line with slope m and passing through (0, b),
Synthetic Geometry. 1.1 Foundations 1.2 The axioms of projective geometry
 Synthetic Geometry 1.1 Foundations 1.2 The axioms of projective geometry Foundations Def: A geometry is a pair G = (Ω, I), where Ω is a set and I a relation on Ω that is symmetric and reflexive, i.e. 1.
Synthetic Geometry 1.1 Foundations 1.2 The axioms of projective geometry Foundations Def: A geometry is a pair G = (Ω, I), where Ω is a set and I a relation on Ω that is symmetric and reflexive, i.e. 1.
MAT 3271: Selected Solutions to the Assignment 6
 Chapter 2: Major Exercises MAT 3271: Selected Solutions to the Assignment 6 1. Since a projective plan is a model of incidence geometry, Incidence Axioms 1-3 and Propositions 2.1-2.5 (which follow logically
Chapter 2: Major Exercises MAT 3271: Selected Solutions to the Assignment 6 1. Since a projective plan is a model of incidence geometry, Incidence Axioms 1-3 and Propositions 2.1-2.5 (which follow logically
Math 102A Hw 3 P a (2 points)
 Math 102 Hw 3 P.93 12 a (2 points) If any pair of these lines are equal, the conclusion is immediate, so assume that we have three distinct lines such that l m and m n. Suppose, on the contrary, that l
Math 102 Hw 3 P.93 12 a (2 points) If any pair of these lines are equal, the conclusion is immediate, so assume that we have three distinct lines such that l m and m n. Suppose, on the contrary, that l
The clique number of a random graph in (,1 2) Let ( ) # -subgraphs in = 2 =: ( ) We will be interested in s.t. ( )~1. To gain some intuition note ( )
 The clique number of a random graph in (,1 2) Let () # -subgraphs in = 2 =:() We will be interested in s.t. ()~1. To gain some intuition note ()~ 2 =2 and so ~2log. Now let us work rigorously. () (+1)
The clique number of a random graph in (,1 2) Let () # -subgraphs in = 2 =:() We will be interested in s.t. ()~1. To gain some intuition note ()~ 2 =2 and so ~2log. Now let us work rigorously. () (+1)
Provide a drawing. Mark any line with three points in blue color.
 Math 3181 Name: Dr. Franz Rothe August 18, 2014 All3181\3181_fall14h1.tex Homework has to be turned in this handout. For extra space, use the back pages, or blank pages between. The homework can be done
Math 3181 Name: Dr. Franz Rothe August 18, 2014 All3181\3181_fall14h1.tex Homework has to be turned in this handout. For extra space, use the back pages, or blank pages between. The homework can be done
9.5 Equivalence Relations
 9.5 Equivalence Relations You know from your early study of fractions that each fraction has many equivalent forms. For example, 2, 2 4, 3 6, 2, 3 6, 5 30,... are all different ways to represent the same
9.5 Equivalence Relations You know from your early study of fractions that each fraction has many equivalent forms. For example, 2, 2 4, 3 6, 2, 3 6, 5 30,... are all different ways to represent the same
The clique number of a random graph in (,1 2) Let ( ) # -subgraphs in = 2 =: ( ) 2 ( ) ( )
 1 The clique number of a random graph in (,1 2) Let () # -subgraphs in = 2 =:() We will be interested in s.t. ()~1. To gain some intuition note ()~ 2 =2 and so ~2log. Now let us work rigorously. () (+1)
1 The clique number of a random graph in (,1 2) Let () # -subgraphs in = 2 =:() We will be interested in s.t. ()~1. To gain some intuition note ()~ 2 =2 and so ~2log. Now let us work rigorously. () (+1)
Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik
 Question 1. Incidence matrix with gaps Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik Prof. Dr. Dr. Jürgen Richter-Gebert, Bernhard Werner Projective Geometry SS 2016 www-m10.ma.tum.de/projektivegeometriess16
Question 1. Incidence matrix with gaps Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik Prof. Dr. Dr. Jürgen Richter-Gebert, Bernhard Werner Projective Geometry SS 2016 www-m10.ma.tum.de/projektivegeometriess16
CS-9645 Introduction to Computer Vision Techniques Winter 2019
 Table of Contents Projective Geometry... 1 Definitions...1 Axioms of Projective Geometry... Ideal Points...3 Geometric Interpretation... 3 Fundamental Transformations of Projective Geometry... 4 The D
Table of Contents Projective Geometry... 1 Definitions...1 Axioms of Projective Geometry... Ideal Points...3 Geometric Interpretation... 3 Fundamental Transformations of Projective Geometry... 4 The D
Final Exam 1:15-3:15 pm Thursday, December 13, 2018
 Final Exam 1:15-3:15 pm Thursday, December 13, 2018 Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided (or attach additional pages as needed). You are permitted to use pencils/pens, one cheat sheet
Final Exam 1:15-3:15 pm Thursday, December 13, 2018 Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided (or attach additional pages as needed). You are permitted to use pencils/pens, one cheat sheet
Lecture 15: The subspace topology, Closed sets
 Lecture 15: The subspace topology, Closed sets 1 The Subspace Topology Definition 1.1. Let (X, T) be a topological space with topology T. subset of X, the collection If Y is a T Y = {Y U U T} is a topology
Lecture 15: The subspace topology, Closed sets 1 The Subspace Topology Definition 1.1. Let (X, T) be a topological space with topology T. subset of X, the collection If Y is a T Y = {Y U U T} is a topology
A Communications Network???
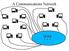 A Communications Network??? A Communications Network What are the desirable properties of the switching box? 1. Every two users must be connected at a switch. 2. Every switch must "look alike". 3. The
A Communications Network??? A Communications Network What are the desirable properties of the switching box? 1. Every two users must be connected at a switch. 2. Every switch must "look alike". 3. The
Chapter 8. Voronoi Diagrams. 8.1 Post Oce Problem
 Chapter 8 Voronoi Diagrams 8.1 Post Oce Problem Suppose there are n post oces p 1,... p n in a city. Someone who is located at a position q within the city would like to know which post oce is closest
Chapter 8 Voronoi Diagrams 8.1 Post Oce Problem Suppose there are n post oces p 1,... p n in a city. Someone who is located at a position q within the city would like to know which post oce is closest
Lecture 6: Faces, Facets
 IE 511: Integer Programming, Spring 2019 31 Jan, 2019 Lecturer: Karthik Chandrasekaran Lecture 6: Faces, Facets Scribe: Setareh Taki Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny
IE 511: Integer Programming, Spring 2019 31 Jan, 2019 Lecturer: Karthik Chandrasekaran Lecture 6: Faces, Facets Scribe: Setareh Taki Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny
3.4 Warm Up. Substitute the given values of m, x, and y into the equation y = mx + b and solve for b. 2. m = 2, x = 3, and y = 0
 3.4 Warm Up 1. Find the values of x and y. Substitute the given values of m, x, and y into the equation y = mx + b and solve for b. 2. m = 2, x = 3, and y = 0 3. m = -1, x = 5, and y = -4 3.3 Proofs with
3.4 Warm Up 1. Find the values of x and y. Substitute the given values of m, x, and y into the equation y = mx + b and solve for b. 2. m = 2, x = 3, and y = 0 3. m = -1, x = 5, and y = -4 3.3 Proofs with
Lesson 1 Introduction to Algebraic Geometry
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Algebraic Geometry I. What is Algebraic Geometry? Algebraic Geometry can be thought of as a (vast) generalization of linear algebra and algebra. Recall that, in linear algebra,
Lesson 1 Introduction to Algebraic Geometry I. What is Algebraic Geometry? Algebraic Geometry can be thought of as a (vast) generalization of linear algebra and algebra. Recall that, in linear algebra,
2 Solution of Homework
 Math 3181 Name: Dr. Franz Rothe February 6, 2014 All3181\3181_spr14h2.tex Homework has to be turned in this handout. The homework can be done in groups up to three due February 11/12 2 Solution of Homework
Math 3181 Name: Dr. Franz Rothe February 6, 2014 All3181\3181_spr14h2.tex Homework has to be turned in this handout. The homework can be done in groups up to three due February 11/12 2 Solution of Homework
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions. 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
Lecture-12: Closed Sets
 and Its Examples Properties of Lecture-12: Dr. Department of Mathematics Lovely Professional University Punjab, India October 18, 2014 Outline Introduction and Its Examples Properties of 1 Introduction
and Its Examples Properties of Lecture-12: Dr. Department of Mathematics Lovely Professional University Punjab, India October 18, 2014 Outline Introduction and Its Examples Properties of 1 Introduction
Math 302 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory. Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus)
 Math 30 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus) March 30, 009 Contents 1 The Integers 3 1.1 Axioms of Z...................................... 3 1.
Math 30 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus) March 30, 009 Contents 1 The Integers 3 1.1 Axioms of Z...................................... 3 1.
Topology Homework 3. Section Section 3.3. Samuel Otten
 Topology Homework 3 Section 3.1 - Section 3.3 Samuel Otten 3.1 (1) Proposition. The intersection of finitely many open sets is open and the union of finitely many closed sets is closed. Proof. Note that
Topology Homework 3 Section 3.1 - Section 3.3 Samuel Otten 3.1 (1) Proposition. The intersection of finitely many open sets is open and the union of finitely many closed sets is closed. Proof. Note that
An alternative way to generalise the pentagon
 An alternative way to generalise the pentagon joint work with John Bamberg, Alice Devillers and Klara Stokes Let P be a set whose elements are called points. Let L be a set of subsets of P, whose elements
An alternative way to generalise the pentagon joint work with John Bamberg, Alice Devillers and Klara Stokes Let P be a set whose elements are called points. Let L be a set of subsets of P, whose elements
TWO COORDINATIZATION THEOREMS FOR PROJECTIVE PLANES
 TWO COORDINATIZATION THEOREMS FOR PROJECTIVE PLANES HARRY ALTMAN A projective plane Π consists of a set of points Π p, a set of lines Π L, and a relation between them, denoted and read on, satisfying the
TWO COORDINATIZATION THEOREMS FOR PROJECTIVE PLANES HARRY ALTMAN A projective plane Π consists of a set of points Π p, a set of lines Π L, and a relation between them, denoted and read on, satisfying the
2 Geometry Solutions
 2 Geometry Solutions jacques@ucsd.edu Here is give problems and solutions in increasing order of difficulty. 2.1 Easier problems Problem 1. What is the minimum number of hyperplanar slices to make a d-dimensional
2 Geometry Solutions jacques@ucsd.edu Here is give problems and solutions in increasing order of difficulty. 2.1 Easier problems Problem 1. What is the minimum number of hyperplanar slices to make a d-dimensional
EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2
 EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2 eview In projective geometry, we regard figures as being the same if they can be made to appear the same as in the diagram below. In projective geometry: a projective point
EM225 Projective Geometry Part 2 eview In projective geometry, we regard figures as being the same if they can be made to appear the same as in the diagram below. In projective geometry: a projective point
EXTREME POINTS AND AFFINE EQUIVALENCE
 EXTREME POINTS AND AFFINE EQUIVALENCE The purpose of this note is to use the notions of extreme points and affine transformations which are studied in the file affine-convex.pdf to prove that certain standard
EXTREME POINTS AND AFFINE EQUIVALENCE The purpose of this note is to use the notions of extreme points and affine transformations which are studied in the file affine-convex.pdf to prove that certain standard
Math Introduction to Advanced Mathematics
 Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Number Theory Fall 2017 The following introductory guide to number theory is borrowed from Drew Shulman and is used in a couple of other Math 215 classes.
Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Number Theory Fall 2017 The following introductory guide to number theory is borrowed from Drew Shulman and is used in a couple of other Math 215 classes.
Definition 2 (Projective plane). A projective plane is a class of points, and a class of lines satisfying the axioms:
 Math 3181 Name: Dr. Franz Rothe January 30, 2014 All3181\3181_spr14h2.tex Homework has to be turned in this handout. The homework can be done in groups up to three due February 11/12 2 Homework 1 Definition
Math 3181 Name: Dr. Franz Rothe January 30, 2014 All3181\3181_spr14h2.tex Homework has to be turned in this handout. The homework can be done in groups up to three due February 11/12 2 Homework 1 Definition
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Geometry Indiana Standards Worktext Correlations
 Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Geometric transformations assign a point to a point, so it is a point valued function of points. Geometric transformation may destroy the equation
 Geometric transformations assign a point to a point, so it is a point valued function of points. Geometric transformation may destroy the equation and the type of an object. Even simple scaling turns a
Geometric transformations assign a point to a point, so it is a point valued function of points. Geometric transformation may destroy the equation and the type of an object. Even simple scaling turns a
TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT BERLIN WS2005 Fachbereich 3 - Mathematik Prof. Dr. U. Pinkall / Charles Gunn Abgabe:
 TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT BERLIN WS2005 Fachbereich 3 - Mathematik Prof. Dr. U. Pinkall / Charles Gunn Abgabe: 27.10.2005 1. Übung Geometrie I (Lines in P 2 (R), Separation, Desargues) 1. Aufgabe Line equations
TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT BERLIN WS2005 Fachbereich 3 - Mathematik Prof. Dr. U. Pinkall / Charles Gunn Abgabe: 27.10.2005 1. Übung Geometrie I (Lines in P 2 (R), Separation, Desargues) 1. Aufgabe Line equations
(1) Page #1 24 all. (2) Page #7-21 odd, all. (3) Page #8 20 Even, Page 35 # (4) Page #1 8 all #13 23 odd
 Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 1: Parallel Lines Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 25-26 #1 24 all (2) Page 33-34 #7-21 odd, 23 28 all (3) Page 33-34 #8 20 Even, Page 35 #40 44 (4) Page 60 61 #1 8 all #13
Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 1: Parallel Lines Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 25-26 #1 24 all (2) Page 33-34 #7-21 odd, 23 28 all (3) Page 33-34 #8 20 Even, Page 35 #40 44 (4) Page 60 61 #1 8 all #13
ON THE CONSTRUCTION OF ORTHOGONAL ARRAYS
 Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 31 (2002), 45 51 ON THE CONSTRUCTION OF ORTHOGONAL ARRAYS Hülya Bayrak and Aslıhan Alhan Received 04. 10. 2001 Abstract In this study, the geometric
Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 31 (2002), 45 51 ON THE CONSTRUCTION OF ORTHOGONAL ARRAYS Hülya Bayrak and Aslıhan Alhan Received 04. 10. 2001 Abstract In this study, the geometric
Lecture 19 Thursday, March 29. Examples of isomorphic, and non-isomorphic graphs will be given in class.
 CIS 160 - Spring 2018 (instructor Val Tannen) Lecture 19 Thursday, March 29 GRAPH THEORY Graph isomorphism Definition 19.1 Two graphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) and G 2 = (V 2, E 2 ) are isomorphic, write G 1 G
CIS 160 - Spring 2018 (instructor Val Tannen) Lecture 19 Thursday, March 29 GRAPH THEORY Graph isomorphism Definition 19.1 Two graphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) and G 2 = (V 2, E 2 ) are isomorphic, write G 1 G
Connected Components of Underlying Graphs of Halving Lines
 arxiv:1304.5658v1 [math.co] 20 Apr 2013 Connected Components of Underlying Graphs of Halving Lines Tanya Khovanova MIT November 5, 2018 Abstract Dai Yang MIT In this paper we discuss the connected components
arxiv:1304.5658v1 [math.co] 20 Apr 2013 Connected Components of Underlying Graphs of Halving Lines Tanya Khovanova MIT November 5, 2018 Abstract Dai Yang MIT In this paper we discuss the connected components
The statement implies that any three intersection points of two distinct planes lie on a line.
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe February 23, 2015 All3181\3181_spr15ts1.tex 1 Solution of Test Name: Problem 1.1. The second part of Hilbert s Proposition 1 states: Any two different planes have either no point
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe February 23, 2015 All3181\3181_spr15ts1.tex 1 Solution of Test Name: Problem 1.1. The second part of Hilbert s Proposition 1 states: Any two different planes have either no point
Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points.
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_spr13t1.tex 1 Solution of Test I Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points. Definition
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_spr13t1.tex 1 Solution of Test I Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points. Definition
Laguerre Planes: A Basic Introduction
 Laguerre Planes: A Basic Introduction Tam Knox Spring 2009 1 1 Introduction Like a projective plane, a Laguerre plane is a type of incidence structure, defined in terms of sets of elements and an incidence
Laguerre Planes: A Basic Introduction Tam Knox Spring 2009 1 1 Introduction Like a projective plane, a Laguerre plane is a type of incidence structure, defined in terms of sets of elements and an incidence
Lattice Polygon s and Pick s Theorem From Dana Paquin and Tom Davis 1 Warm-Up to Ponder
 Lattice Polygon s and Pick s Theorem From Dana Paquin and Tom Davis http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles/pick.pdf 1 Warm-Up to Ponder 1. Is it possible to draw an equilateral triangle on graph paper so
Lattice Polygon s and Pick s Theorem From Dana Paquin and Tom Davis http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles/pick.pdf 1 Warm-Up to Ponder 1. Is it possible to draw an equilateral triangle on graph paper so
CSE101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Ragesh Jaiswal, CSE, UCSD
 Recap. Growth rates: Arrange the following functions in ascending order of growth rate: n 2 log n n log n 2 log n n/ log n n n Introduction Algorithm: A step-by-step way of solving a problem. Design of
Recap. Growth rates: Arrange the following functions in ascending order of growth rate: n 2 log n n log n 2 log n n/ log n n n Introduction Algorithm: A step-by-step way of solving a problem. Design of
Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4. Harper Langston New York University
 Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4 Harper Langston New York University Sequences Sequence is a set of (usually infinite number of) ordered elements: a 1, a 2,, a n, Each individual element a k is called a
Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4 Harper Langston New York University Sequences Sequence is a set of (usually infinite number of) ordered elements: a 1, a 2,, a n, Each individual element a k is called a
Chapter 4 Concepts from Geometry
 Chapter 4 Concepts from Geometry An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2014 Wei-Ta Chu 1 Line Segments The line segment between two points and in R n is the set of points on the straight line joining
Chapter 4 Concepts from Geometry An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2014 Wei-Ta Chu 1 Line Segments The line segment between two points and in R n is the set of points on the straight line joining
Topics in geometry Exam 1 Solutions 7/8/4
 Topics in geometry Exam 1 Solutions 7/8/4 Question 1 Consider the following axioms for a geometry: There are exactly five points. There are exactly five lines. Each point lies on exactly three lines. Each
Topics in geometry Exam 1 Solutions 7/8/4 Question 1 Consider the following axioms for a geometry: There are exactly five points. There are exactly five lines. Each point lies on exactly three lines. Each
Lemma (x, y, z) is a Pythagorean triple iff (y, x, z) is a Pythagorean triple.
 Chapter Pythagorean Triples.1 Introduction. The Pythagorean triples have been known since the time of Euclid and can be found in the third century work Arithmetica by Diophantus [9]. An ancient Babylonian
Chapter Pythagorean Triples.1 Introduction. The Pythagorean triples have been known since the time of Euclid and can be found in the third century work Arithmetica by Diophantus [9]. An ancient Babylonian
ON SWELL COLORED COMPLETE GRAPHS
 Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXIII, (1994), pp. 303 308 303 ON SWELL COLORED COMPLETE GRAPHS C. WARD and S. SZABÓ Abstract. An edge-colored graph is said to be swell-colored if each triangle contains
Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXIII, (1994), pp. 303 308 303 ON SWELL COLORED COMPLETE GRAPHS C. WARD and S. SZABÓ Abstract. An edge-colored graph is said to be swell-colored if each triangle contains
Math 485, Graph Theory: Homework #3
 Math 485, Graph Theory: Homework #3 Stephen G Simpson Due Monday, October 26, 2009 The assignment consists of Exercises 2129, 2135, 2137, 2218, 238, 2310, 2313, 2314, 2315 in the West textbook, plus the
Math 485, Graph Theory: Homework #3 Stephen G Simpson Due Monday, October 26, 2009 The assignment consists of Exercises 2129, 2135, 2137, 2218, 238, 2310, 2313, 2314, 2315 in the West textbook, plus the
4 Basis, Subbasis, Subspace
 4 Basis, Subbasis, Subspace Our main goal in this chapter is to develop some tools that make it easier to construct examples of topological spaces. By Definition 3.12 in order to define a topology on a
4 Basis, Subbasis, Subspace Our main goal in this chapter is to develop some tools that make it easier to construct examples of topological spaces. By Definition 3.12 in order to define a topology on a
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Conic Duality. yyye
 Conic Linear Optimization and Appl. MS&E314 Lecture Note #02 1 Conic Duality Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/
Conic Linear Optimization and Appl. MS&E314 Lecture Note #02 1 Conic Duality Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/
Geometry Definitions, Postulates, and Theorems. Chapter 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Section 3.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles.
 Geometry Definitions, Postulates, and Theorems Chapter : Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Section.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Standards: Prepare for 7.0 Students prove and use theorems involving
Geometry Definitions, Postulates, and Theorems Chapter : Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Section.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Standards: Prepare for 7.0 Students prove and use theorems involving
It All Depends on How You Slice It: An Introduction to Hyperplane Arrangements
 It All Depends on How You Slice It: An Introduction to Hyperplane Arrangements Paul Renteln California State University San Bernardino and Caltech April, 2008 Outline Hyperplane Arrangements Counting Regions
It All Depends on How You Slice It: An Introduction to Hyperplane Arrangements Paul Renteln California State University San Bernardino and Caltech April, 2008 Outline Hyperplane Arrangements Counting Regions
1 Elementary number theory
 Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Spring 2019 1 Elementary number theory We assume the existence of the natural numbers and the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...} Z = {..., 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...},
Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Spring 2019 1 Elementary number theory We assume the existence of the natural numbers and the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...} Z = {..., 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...},
2009 HMMT Team Round. Writing proofs. Misha Lavrov. ARML Practice 3/2/2014
 Writing proofs Misha Lavrov ARML Practice 3/2/2014 Warm-up / Review 1 (From my research) If x n = 2 1 x n 1 for n 2, solve for x n in terms of x 1. (For a more concrete problem, set x 1 = 2.) 2 (From this
Writing proofs Misha Lavrov ARML Practice 3/2/2014 Warm-up / Review 1 (From my research) If x n = 2 1 x n 1 for n 2, solve for x n in terms of x 1. (For a more concrete problem, set x 1 = 2.) 2 (From this
ON THE EMPTY CONVEX PARTITION OF A FINITE SET IN THE PLANE**
 Chin. Ann. of Math. 23B:(2002),87-9. ON THE EMPTY CONVEX PARTITION OF A FINITE SET IN THE PLANE** XU Changqing* DING Ren* Abstract The authors discuss the partition of a finite set of points in the plane
Chin. Ann. of Math. 23B:(2002),87-9. ON THE EMPTY CONVEX PARTITION OF A FINITE SET IN THE PLANE** XU Changqing* DING Ren* Abstract The authors discuss the partition of a finite set of points in the plane
Final Test in MAT 410: Introduction to Topology Answers to the Test Questions
 Final Test in MAT 410: Introduction to Topology Answers to the Test Questions Stefan Kohl Question 1: Give the definition of a topological space. (3 credits) A topological space (X, τ) is a pair consisting
Final Test in MAT 410: Introduction to Topology Answers to the Test Questions Stefan Kohl Question 1: Give the definition of a topological space. (3 credits) A topological space (X, τ) is a pair consisting
A point is pictured by a dot. While a dot must have some size, the point it represents has no size. Points are named by capital letters..
 Chapter 1 Points, Lines & Planes s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess that you might already be pretty familiar with many
Chapter 1 Points, Lines & Planes s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess that you might already be pretty familiar with many
CSE331 Introduction to Algorithms Lecture 15 Minimum Spanning Trees
 CSE1 Introduction to Algorithms Lecture 1 Minimum Spanning Trees Antoine Vigneron antoine@unist.ac.kr Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology July 11, 201 Antoine Vigneron (UNIST) CSE1 Lecture
CSE1 Introduction to Algorithms Lecture 1 Minimum Spanning Trees Antoine Vigneron antoine@unist.ac.kr Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology July 11, 201 Antoine Vigneron (UNIST) CSE1 Lecture
The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 9 (2005), No. 1, 31 36. The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex Ma lgorzata Buba-Brzozowa Department of Mathematics and Information Sciences,
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 9 (2005), No. 1, 31 36. The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex Ma lgorzata Buba-Brzozowa Department of Mathematics and Information Sciences,
Lecture 5: More Examples/Applications of Quasirandom Graphs
 Random and Quasirandom Graphs Instructor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 5: More Examples/Applications of Quasirandom Graphs Week 4 Mathcamp 2012 In our last class, we saw that the Paley graphs were an example
Random and Quasirandom Graphs Instructor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 5: More Examples/Applications of Quasirandom Graphs Week 4 Mathcamp 2012 In our last class, we saw that the Paley graphs were an example
CS473-Algorithms I. Lecture 13-A. Graphs. Cevdet Aykanat - Bilkent University Computer Engineering Department
 CS473-Algorithms I Lecture 3-A Graphs Graphs A directed graph (or digraph) G is a pair (V, E), where V is a finite set, and E is a binary relation on V The set V: Vertex set of G The set E: Edge set of
CS473-Algorithms I Lecture 3-A Graphs Graphs A directed graph (or digraph) G is a pair (V, E), where V is a finite set, and E is a binary relation on V The set V: Vertex set of G The set E: Edge set of
Problem Set 3. MATH 778C, Spring 2009, Austin Mohr (with John Boozer) April 15, 2009
 Problem Set 3 MATH 778C, Spring 2009, Austin Mohr (with John Boozer) April 15, 2009 1. Show directly that P 1 (s) P 1 (t) for all t s. Proof. Given G, let H s be a subgraph of G on s vertices such that
Problem Set 3 MATH 778C, Spring 2009, Austin Mohr (with John Boozer) April 15, 2009 1. Show directly that P 1 (s) P 1 (t) for all t s. Proof. Given G, let H s be a subgraph of G on s vertices such that
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 5.2. GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 5.2 GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) by A.J.Hobson 5.2.1 Preamble 5.2.2 Standard equations of a straight line 5.2.3 Perpendicular straight lines 5.2.4 Change of origin UNIT 5.2
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 5.2 GEOMETRY 2 (The straight line) by A.J.Hobson 5.2.1 Preamble 5.2.2 Standard equations of a straight line 5.2.3 Perpendicular straight lines 5.2.4 Change of origin UNIT 5.2
Functions. How is this definition written in symbolic logic notation?
 functions 1 Functions Def. Let A and B be sets. A function f from A to B is an assignment of exactly one element of B to each element of A. We write f(a) = b if b is the unique element of B assigned by
functions 1 Functions Def. Let A and B be sets. A function f from A to B is an assignment of exactly one element of B to each element of A. We write f(a) = b if b is the unique element of B assigned by
One motivation for developing axiomatic systems is to determine precisely which properties
 1 Axiomatic Systems 1.1 Features of Axiomatic Systems One motivation for developing axiomatic systems is to determine precisely which properties of certain objects can be deduced from which other properties.
1 Axiomatic Systems 1.1 Features of Axiomatic Systems One motivation for developing axiomatic systems is to determine precisely which properties of certain objects can be deduced from which other properties.
CHAPTER 8. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 CHAPTER 8 RELATIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 8.3 Equivalence Relations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Relation Induced by a Partition 3 The Relation
CHAPTER 8 RELATIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 8.3 Equivalence Relations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Relation Induced by a Partition 3 The Relation
1 Solution of Homework I
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_spr13h1.tex 1 Solution of Homework I 10 Problem 1.1. As far as two-dimensional geometry is concerned, Hilbert s Proposition 1 reduces to one simple statement:
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_spr13h1.tex 1 Solution of Homework I 10 Problem 1.1. As far as two-dimensional geometry is concerned, Hilbert s Proposition 1 reduces to one simple statement:
GLOBAL GEOMETRY OF POLYGONS. I: THE THEOREM OF FABRICIUS-BJERRE
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 45, Number 2, August, 1974 GLOBAL GEOMETRY OF POLYGONS. I: THE THEOREM OF FABRICIUS-BJERRE THOMAS F.BANCHOFF ABSTRACT. Deformation methods provide
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 45, Number 2, August, 1974 GLOBAL GEOMETRY OF POLYGONS. I: THE THEOREM OF FABRICIUS-BJERRE THOMAS F.BANCHOFF ABSTRACT. Deformation methods provide
Solutions to the Test. Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written?
 Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Pearson Mathematics Geometry
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY. 1. Definitions
 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY D. JAKOBSON 1. Definitions A graph G consists of vertices {v 1, v 2,..., v n } and edges {e 1, e 2,..., e m } connecting pairs of vertices. An edge e = (uv) is incident with
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY D. JAKOBSON 1. Definitions A graph G consists of vertices {v 1, v 2,..., v n } and edges {e 1, e 2,..., e m } connecting pairs of vertices. An edge e = (uv) is incident with
On the number of distinct directions of planes determined by n points in R 3
 On the number of distinct directions of planes determined by n points in R 3 Rom Pinchasi August 27, 2007 Abstract We show that any set of n points in R 3, that is not contained in a plane, determines
On the number of distinct directions of planes determined by n points in R 3 Rom Pinchasi August 27, 2007 Abstract We show that any set of n points in R 3, that is not contained in a plane, determines
Formalising the Foundations of Geometry
 Formalising the March 27, 2015 Formalising Mathematics Why formalise? Because some proofs are too hard to verify by inspection (Kepler conjecture, Four-Colour Theorem, ABC conjecture) We need to contribute
Formalising the March 27, 2015 Formalising Mathematics Why formalise? Because some proofs are too hard to verify by inspection (Kepler conjecture, Four-Colour Theorem, ABC conjecture) We need to contribute
Solution to Graded Problem Set 4
 Graph Theory Applications EPFL, Spring 2014 Solution to Graded Problem Set 4 Date: 13.03.2014 Due by 18:00 20.03.2014 Problem 1. Let V be the set of vertices, x be the number of leaves in the tree and
Graph Theory Applications EPFL, Spring 2014 Solution to Graded Problem Set 4 Date: 13.03.2014 Due by 18:00 20.03.2014 Problem 1. Let V be the set of vertices, x be the number of leaves in the tree and
Homotopy type of the complement. complex lines arrangements
 On the homotopy type of the complement of complex lines arrangements Department of Geometry-Topology Institute of Mathematics, VAST, Hanoi Singapore December 15, 2008 Introduction Let A be an l-arrangement,
On the homotopy type of the complement of complex lines arrangements Department of Geometry-Topology Institute of Mathematics, VAST, Hanoi Singapore December 15, 2008 Introduction Let A be an l-arrangement,
On the Minimum Number of Convex Quadrilaterals in Point Sets of Given Numbers of Points
 On the Minimum Number of Convex Quadrilaterals in Point Sets of Given Numbers of Points Hu Yuzhong Chen Luping Zhu Hui Ling Xiaofeng (Supervisor) Abstract Consider the following problem. Given n, k N,
On the Minimum Number of Convex Quadrilaterals in Point Sets of Given Numbers of Points Hu Yuzhong Chen Luping Zhu Hui Ling Xiaofeng (Supervisor) Abstract Consider the following problem. Given n, k N,
Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term I) 5. InTroduCTIon To EuClId s GEoMETry. l Euclid s five postulates are : ANIL TUTORIALS
 Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term I) 5. InTroduCTIon To EuClId s GEoMETry IMporTAnT TErMs, definitions And results l In geometry, we take a point, a line and a plane as undefined terms. l An axiom
Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term I) 5. InTroduCTIon To EuClId s GEoMETry IMporTAnT TErMs, definitions And results l In geometry, we take a point, a line and a plane as undefined terms. l An axiom
What makes geometry Euclidean or Non-Euclidean?
 What makes geometry Euclidean or Non-Euclidean? I-1. Each two distinct points determine a line I-2. Three noncollinear points determine a plane The 5 Axioms of I-3. If two points lie in a plane, then any
What makes geometry Euclidean or Non-Euclidean? I-1. Each two distinct points determine a line I-2. Three noncollinear points determine a plane The 5 Axioms of I-3. If two points lie in a plane, then any
3D Computer Vision II. Reminder Projective Geometry, Transformations
 3D Computer Vision II Reminder Projective Geometry, Transformations Nassir Navab" based on a course given at UNC by Marc Pollefeys & the book Multiple View Geometry by Hartley & Zisserman" October 21,
3D Computer Vision II Reminder Projective Geometry, Transformations Nassir Navab" based on a course given at UNC by Marc Pollefeys & the book Multiple View Geometry by Hartley & Zisserman" October 21,
2-5 Postulates and Paragraph Proofs
 Determine whether each statement is always, sometimes, or never true. Explain your reasoning. 7. The intersection of three planes is a line. If three planes intersect, then their intersection may be a
Determine whether each statement is always, sometimes, or never true. Explain your reasoning. 7. The intersection of three planes is a line. If three planes intersect, then their intersection may be a
A Short Introduction to Projective Geometry
 A Short Introduction to Projective Geometry Vector Spaces over Finite Fields We are interested only in vector spaces of finite dimension. To avoid a notational difficulty that will become apparent later,
A Short Introduction to Projective Geometry Vector Spaces over Finite Fields We are interested only in vector spaces of finite dimension. To avoid a notational difficulty that will become apparent later,
Projective geometry and the extended Euclidean plane
 Chapter 2 Projective geometry and the extended Euclidean plane Math 4520, Fall 2017 As we can see from Hilbert s treatment, a completely worked out axiom system for geometry in the plane is quite complicated.
Chapter 2 Projective geometry and the extended Euclidean plane Math 4520, Fall 2017 As we can see from Hilbert s treatment, a completely worked out axiom system for geometry in the plane is quite complicated.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers.
 Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. 2-5 Objectives You will learn to: Identify and use basic postulates about points, lines, and planes. Write paragraph proofs. Vocabulary
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. 2-5 Objectives You will learn to: Identify and use basic postulates about points, lines, and planes. Write paragraph proofs. Vocabulary
Betweenness and the Crossbar Theorem. Lemma: Let A, B, and C be distinct points. If A*B*C, then neither A*C*B nor B*A*C.
 Betweenness and the Crossbar Theorem Lemma: Let A, B, and C be distinct points. If A*B*C, then neither A*C*B nor B*A*C. Suppose that both A*B*C and A*C*B. Thus AB+BC =AC, and AC +CB = AB. From this we
Betweenness and the Crossbar Theorem Lemma: Let A, B, and C be distinct points. If A*B*C, then neither A*C*B nor B*A*C. Suppose that both A*B*C and A*C*B. Thus AB+BC =AC, and AC +CB = AB. From this we
Figure 1: Two polygonal loops
 Math 1410: The Polygonal Jordan Curve Theorem: The purpose of these notes is to prove the polygonal Jordan Curve Theorem, which says that the complement of an embedded polygonal loop in the plane has exactly
Math 1410: The Polygonal Jordan Curve Theorem: The purpose of these notes is to prove the polygonal Jordan Curve Theorem, which says that the complement of an embedded polygonal loop in the plane has exactly
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 11 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY POINTS TO REMEMBER Distance between points P(x 1 ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ x x y y z z 1 1 1 (i) The coordinates of point
For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 11 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY POINTS TO REMEMBER Distance between points P(x 1 ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ x x y y z z 1 1 1 (i) The coordinates of point
Pantographic polygons
 203 Pantographic polygons John Miller and Emanuel Strzelecki Abstract Necessary and sufficient conditions are given for a polygon to be pantographic. The property is held by all regular polygons and by
203 Pantographic polygons John Miller and Emanuel Strzelecki Abstract Necessary and sufficient conditions are given for a polygon to be pantographic. The property is held by all regular polygons and by
Michael Greenberg. September 13, 2004
 Finite Geometries for Those with a Finite Patience for Mathematics Michael Greenberg September 13, 2004 1 Introduction 1.1 Objective When my friends ask me what I ve been studying this past summer and
Finite Geometries for Those with a Finite Patience for Mathematics Michael Greenberg September 13, 2004 1 Introduction 1.1 Objective When my friends ask me what I ve been studying this past summer and
The set consisting of all natural numbers that are in A and are in B is the set f1; 3; 5g;
 Chapter 5 Set Theory 5.1 Sets and Operations on Sets Preview Activity 1 (Set Operations) Before beginning this section, it would be a good idea to review sets and set notation, including the roster method
Chapter 5 Set Theory 5.1 Sets and Operations on Sets Preview Activity 1 (Set Operations) Before beginning this section, it would be a good idea to review sets and set notation, including the roster method
Pick s Theorem and Lattice Point Geometry
 Pick s Theorem and Lattice Point Geometry 1 Lattice Polygon Area Calculations Lattice points are points with integer coordinates in the x, y-plane. A lattice line segment is a line segment that has 2 distinct
Pick s Theorem and Lattice Point Geometry 1 Lattice Polygon Area Calculations Lattice points are points with integer coordinates in the x, y-plane. A lattice line segment is a line segment that has 2 distinct
Robot Vision: Projective Geometry
 Robot Vision: Projective Geometry Ass.Prof. Friedrich Fraundorfer SS 2018 1 Learning goals Understand homogeneous coordinates Understand points, line, plane parameters and interpret them geometrically
Robot Vision: Projective Geometry Ass.Prof. Friedrich Fraundorfer SS 2018 1 Learning goals Understand homogeneous coordinates Understand points, line, plane parameters and interpret them geometrically
Algebra of Sets (Mathematics & Logic A)
 Algebra of Sets (Mathematics & Logic A) RWK/MRQ October 28, 2002 Note. These notes are adapted (with thanks) from notes given last year by my colleague Dr Martyn Quick. Please feel free to ask me (not
Algebra of Sets (Mathematics & Logic A) RWK/MRQ October 28, 2002 Note. These notes are adapted (with thanks) from notes given last year by my colleague Dr Martyn Quick. Please feel free to ask me (not
2 and 6 4 and 8 1 and 5 3 and 7
 Geo Ch 3 Angles formed by Lines Parallel lines are two coplanar lines that do not intersect. Skew lines are that are not coplanar and do not intersect. Transversal is a line that two or more lines at different
Geo Ch 3 Angles formed by Lines Parallel lines are two coplanar lines that do not intersect. Skew lines are that are not coplanar and do not intersect. Transversal is a line that two or more lines at different
Lesson 19: The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables Is a Line
 The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables Is a Line Classwork Exercises THEOREM: The graph of a linear equation yy = mmmm + bb is a non-vertical line with slope mm and passing through (0, bb), where
The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables Is a Line Classwork Exercises THEOREM: The graph of a linear equation yy = mmmm + bb is a non-vertical line with slope mm and passing through (0, bb), where
Crossing Families. Abstract
 Crossing Families Boris Aronov 1, Paul Erdős 2, Wayne Goddard 3, Daniel J. Kleitman 3, Michael Klugerman 3, János Pach 2,4, Leonard J. Schulman 3 Abstract Given a set of points in the plane, a crossing
Crossing Families Boris Aronov 1, Paul Erdős 2, Wayne Goddard 3, Daniel J. Kleitman 3, Michael Klugerman 3, János Pach 2,4, Leonard J. Schulman 3 Abstract Given a set of points in the plane, a crossing
Review of Sets. Review. Philippe B. Laval. Current Semester. Kennesaw State University. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Sets Current Semester 1 / 16
 Review of Sets Review Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Current Semester Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Sets Current Semester 1 / 16 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Definitions, Notations and Examples 3 Special
Review of Sets Review Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Current Semester Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Sets Current Semester 1 / 16 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Definitions, Notations and Examples 3 Special
