Approximating Refraction Kenneth Hurley Please send me comments/questions/suggestions
|
|
|
- Kelley Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Approximating Refraction Kenneth Hurley Please send me comments/questions/suggestions Problem Statement Refraction is a phenomenon that simulates the bending of light rays through semi-transparent objects. Refraction can make a 3d graphics scene look much more realistic. Real world objects can both reflect and refract light waves to distort images seen through them. There are several properties defined with refraction, Snell's law and the critical angle. Snell's law states that for a light ray going from a less dense medium to a higher dense medium, the light ray will bend in one direction and going from a higher density medium to a lower density medium, it will bend in the other direction. These properties are known as the refraction index and it is a ratio of the speed of light through one medium divided by the speed of light through the other medium. Snell's Law Snell's law states that a light is traveling low index to a high index (e.g. air is a low index and glass is a high index), the light ray will be bent toward the normal. On the other hand if light is traveling from a high index to a low index (e.g. glass to air), the light will bend away from the normal. Here is a diagram of Snell's law. The purple line represents a light ray coming hitting a glass object and you can see that according to Snell's law that the light would bend towards the normal in this case (the red line). Mathematically speaking Snell's law is stated as: n1 * sin(α) = n2 * sin(β) where n1 and n2 are the index of refraction for each medium. If you reverse the sense of the light direction, you can see that if the light were the red line and the light were traveling from the glass to air, it would bend away from the normal of the surface. Snell also stated that the angles between the incident ray and the normal of the surface and the outgoing ray's angle in regards to that normal could be expressed in terms of a ratio. This ratio is specified as the speed of light through the medium as compared to the speed of light through a vacuum. If the speed of light through a vacuum is expressed as 1.0, all other mediums are expressed as a ratio of the speed of light compared to a vacuum. Here is a short list of refraction index of materials Page 1 of 6
2 Material Refraction Index Vacuum Air Alcohols Crown Glass Crystal Diamond Emerald Fused Quartz Heavy Flint Glass Glass Ice Quartz Ruby/Sapphire Salt Sugar Solution (80%) Sugar Solution (30%) Topaz Water Snell's law simply states that given an incident ray at an angle relative to the normal of a surface, that ray will change angle based on the refraction index, which is simply a ratio to reduce/increase the angle by after the ray passes from one medium to another. So if it is assumed that we are going from a vacuum (which is close to the refraction index of air) to water and we know the incident angle and refraction index, we can figure out what the outgoing angle should be. We can rewrite the equation as: sin(α) / n2 = sin(β) One other point is the fact that most rays enter a medium and leave a medium. For example a ray enters a sheet of glass and then exits the other side of that glass. In this diagram, the top purple line is the incident ray entering the glass, the red line is the ray refracted in the glass and the bottom purple line is the ray coming out of the glass. Page 2 of 6
3 As can be seen from the above diagram the light ray actually is parallel to the incoming light ray, but is just moved slightly towards the normal. On the other hand if the light ray strikes an object that is in water, then transmits to glass and out to air, then that object contributes to the bending of the light rays. The reason our technique works in the above example is that you can approximate the ray going into the glass and coming out of it by just using on ray as shown in the following diagram: The lines above are all the same as in the previous diagram, except for the yellow line. This line represents the refraction index that is actually used since we are just interested in the end point of the ray. How DirectX Calculates Reflection Vectors DirectX 7 documentation shows that the reflection vector for a vertex is calculated with the following formula: Page 3 of 6 R = 2(N E) N - E Since reflection is stated in terms of the refraction formula: R = -(α - 1)( (N E) N - E, where α = index of refraction and α = -1 for reflection, we can substitute the refraction equation back into each vertex and give that value to the hardware for indexing into the cube maps. How to Use Cube-Maps for the Effect You setup cube maps exactly the same as if you where going to reflect an object. Now instead of using the flags, D3DTSS_TCI_REFLECTIONVECTOR, you set the D3DTSS_TCI_PASSTHRU flag and calculate the equations for each vertex. The hardware will interpolate the texture coordinates across the cube map. The code sample actually doesn't do this, because this is the default state of Direct X. But if you wanted to set this up you would specify the following: SetTextureStageState( 0, D3DTSS_TEXCOORDINDEX, D3DTSS_TCI_PASSTHRU 0);
4 Calculating refraction Below is the code for calculating the refraction: // eye vector (doesn't need to be normalized) FLOAT fenx = m_veyept.x - pvin->v.x; FLOAT feny = m_veyept.y - pvin->v.y; FLOAT fenz = m_veyept.z - pvin->v.z; FLOAT fndote = pvin->v.nx*fenx + pvin->v.ny*feny + pvin->v.nz*fenz; FLOAT fndotn = pvin->v.nx*pvin->v.nx + pvin->v.ny*pvin->v.ny + pvin->v.nz*pvin->v.nz; fndote *= 1.0f/gRefractIndex; // refracted vector pvin->v.tu = pvin->v.nx*fndote - fenx*fndotn; pvin->v.tv = pvin->v.ny*fndote - feny*fndotn; pvin->nz = pvin->v.nz*fndote - fenz*fndotn; Notice that above the calculation of 1.0f/gRefractIndex should be adjusted for minification/magnification that happens when a texture is being used that does not map to a 1-to-1 correspondence with the object being texture mapped. Suggested Methods Several papers including Paul Diefenbach's Thesis and early work by Paul Heckbert and Pat Hanahran, suggest using the planes that are refracting the image by use of a projection matrix that changes the angle of view. One problem that Paul Diefenbach notes is that using these techniques may not be possible on some hardware because moving the projection matrix, precludes the use of the Z-Buffer. This technique we have described does not suffer from this limitation as it uses cube-maps to render the scene first. The technique does not modify the projection matrix, so the Z-Buffer can be used with this technique. It also might be possible to use the projection matrix along with cube maps to automatically calculate out the values to be used in the cube map. I've looked into this a little, but I didn't see an obvious way to accomplish this. Enhancements Real world objects also reflect the environment. There is also a critical angle refraction that says when the angles falls between a certain point, the refraction turns into reflection. Another enhancement would be Fresnel effects. All of these effects can be achieved. For the reflection portion, you can alpha blend between the refraction effect and the reflection effect. Limitations With the current scheme there isn't an easy way to simulate placing a pencil in a glass of water. This technique also does not allow internal reflections. Page 4 of 6
5 Conclusion This effect is using an approximation to refraction. You can achieve real time frame rates using this technique and the end result is visually very good. Throughout this document you will noticed that I did this from the perspective of ray tracing, but you can also view this as ray casting from the eye point. Sample - Refraction Index 1.33 (Water) Page 5 of 6
6 Sample - Refraction Index ~= 1.5 (glass) Page 6 of 6
Refraction of Light. c = m / s. n = c v. The index of refraction is never less than 1. Some common indices of refraction are listed below.
 Refraction of Light The speed of light in a vacuum is c = 3.00 10 8 m / s In air, the speed is only slightly less. In other transparent materials, such as glass and water, the speed is always less than
Refraction of Light The speed of light in a vacuum is c = 3.00 10 8 m / s In air, the speed is only slightly less. In other transparent materials, such as glass and water, the speed is always less than
Reflection & refraction
 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Reflection & refraction Reflection revision Reflection is the bouncing of light rays off a surface Reflection from a mirror: Normal
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Reflection & refraction Reflection revision Reflection is the bouncing of light rays off a surface Reflection from a mirror: Normal
11.2 Refraction. December 10, Wednesday, 11 December, 13
 11.2 Refraction December 10, 2013. Refraction Light bends when it passes from one medium (material) to another this bending is called refraction this is because the speed of light changes The Speed of
11.2 Refraction December 10, 2013. Refraction Light bends when it passes from one medium (material) to another this bending is called refraction this is because the speed of light changes The Speed of
Geometrical optics: Refraction *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m40065 1 Geometrical optics: Refraction * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m40065 1 Geometrical optics: Refraction * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0
Textbook Reference: Glencoe Physics: Chapters 16-18
 Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Reflection and Refraction
 rev 05/2018 Equipment List and Refraction Qty Items Part Numbers 1 Light Source, Basic Optics OS-8517 1 Ray Optics Set OS-8516 2 White paper, sheet 1 Metric ruler 1 Protractor Introduction The purpose
rev 05/2018 Equipment List and Refraction Qty Items Part Numbers 1 Light Source, Basic Optics OS-8517 1 Ray Optics Set OS-8516 2 White paper, sheet 1 Metric ruler 1 Protractor Introduction The purpose
Investigation 21A: Refraction of light
 Investigation 21A: Refraction of light Essential question: How does light refract at a boundary? What is the index of refraction of water? Refraction may change the direction of light rays passing from
Investigation 21A: Refraction of light Essential question: How does light refract at a boundary? What is the index of refraction of water? Refraction may change the direction of light rays passing from
Regents Physics Lab #30R. Due Date. Refraction of Light
 Name Date Regents Physics Lab #0R Period Mrs. Nadworny Research Problem Materials Refraction of Light Due Date When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted. The
Name Date Regents Physics Lab #0R Period Mrs. Nadworny Research Problem Materials Refraction of Light Due Date When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted. The
Light. Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see
 Light Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see Facts About Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: REFLECTED ABSORBED REFRACTED
Light Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see Facts About Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: REFLECTED ABSORBED REFRACTED
CS 325 Computer Graphics
 CS 325 Computer Graphics 04 / 02 / 2012 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Illumination modelling Ambient, Diffuse, Specular Reflection Surface Rendering / Shading models Flat
CS 325 Computer Graphics 04 / 02 / 2012 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Illumination modelling Ambient, Diffuse, Specular Reflection Surface Rendering / Shading models Flat
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
PY106 Class31. Index of refraction. Refraction. Index of refraction. Sample values of n. Rays and wavefronts. index of refraction: n v.
 Refraction Index of refraction When an EM wave travels in a vacuum, its speed is: c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s. In any other medium, light generally travels at a slower speed. The speed of light v in a material
Refraction Index of refraction When an EM wave travels in a vacuum, its speed is: c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s. In any other medium, light generally travels at a slower speed. The speed of light v in a material
speed of light in vacuum = speed of light in the material
 Chapter 5 Let Us Entertain You Snell s law states that as light enters a substance such as acrylic (high index of refraction) from air (low index of refraction), the light bends toward the normal. When
Chapter 5 Let Us Entertain You Snell s law states that as light enters a substance such as acrylic (high index of refraction) from air (low index of refraction), the light bends toward the normal. When
Reflection and Refraction of Light
 PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
Purpose: To determine the index of refraction of glass, plastic and water.
 LAB 9 REFRACTION-THE BENDING OF LIGHT Purpose: To determine the index of refraction of glass, plastic and water. Materials: Common pins, glass block, plastic block, small semi-circular water container,
LAB 9 REFRACTION-THE BENDING OF LIGHT Purpose: To determine the index of refraction of glass, plastic and water. Materials: Common pins, glass block, plastic block, small semi-circular water container,
Physics 1C. Lecture 25B. "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton
 Physics 1C Lecture 25B "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton Refraction of Light When light passes from one medium to another, it is
Physics 1C Lecture 25B "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton Refraction of Light When light passes from one medium to another, it is
1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface?
 waves 6-2-04 Name 02-JUN-04 1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface? 1. 1 3. 3 2. 2 4. 4 2. In a vacuum, a monochromatic beam of light as a frequency of 6.3 X
waves 6-2-04 Name 02-JUN-04 1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface? 1. 1 3. 3 2. 2 4. 4 2. In a vacuum, a monochromatic beam of light as a frequency of 6.3 X
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction. Notes
 Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
Refraction: Snell's Law. October 26, 2010
 Refraction: Snell's Law October 26, 2010 When light passes from one medium into another, part of the incident light is reflected at the boundary The remainder passes into the new medium. Unless it is perpendicular,
Refraction: Snell's Law October 26, 2010 When light passes from one medium into another, part of the incident light is reflected at the boundary The remainder passes into the new medium. Unless it is perpendicular,
REFLECTION & REFRACTION
 REFLECTION & REFRACTION OBJECTIVE: To study and verify the laws of reflection and refraction using a plane mirror and a glass block. To see the virtual images that can be formed by the reflection and refraction
REFLECTION & REFRACTION OBJECTIVE: To study and verify the laws of reflection and refraction using a plane mirror and a glass block. To see the virtual images that can be formed by the reflection and refraction
Speed of Light in Glass
 Name Date Regents Physics Lab #R Period Mrs. Nadworny Research Problem Materials Speed of Light in Glass Due Date When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted.
Name Date Regents Physics Lab #R Period Mrs. Nadworny Research Problem Materials Speed of Light in Glass Due Date When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted.
Geometric Optics. The Law of Reflection. Physics Waves & Oscillations 3/20/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
Unit 9 Light & Optics
 Unit 9 Light & Optics 1 A quick review of the properties of light. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation Light travels as transverse waves having wavelength and frequency. fλ=c The velocity of EMR
Unit 9 Light & Optics 1 A quick review of the properties of light. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation Light travels as transverse waves having wavelength and frequency. fλ=c The velocity of EMR
ACTIVITY A FIRST LOOK AT REFRACTION OBJECTIVE To observe optical refraction and theorize the mechanism for the observation.
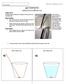 Name (printed) ACTIVITY A FIRST LOOK AT REFRACTION OBJECTIVE To observe optical refraction and theorize the mechanism for the observation. PROCEDURE 1. Start with no water in the cup and orient your line
Name (printed) ACTIVITY A FIRST LOOK AT REFRACTION OBJECTIVE To observe optical refraction and theorize the mechanism for the observation. PROCEDURE 1. Start with no water in the cup and orient your line
Index of refraction n
 Refraction 1 Refraction Cause 2 Index of refraction n In texbook n values Diamond Flint Glass Crown Glass Fused quartz Ice Benzene Ethyl Alcohol Water Carbon Dioxide Air Others corn oil glycerol Lucite
Refraction 1 Refraction Cause 2 Index of refraction n In texbook n values Diamond Flint Glass Crown Glass Fused quartz Ice Benzene Ethyl Alcohol Water Carbon Dioxide Air Others corn oil glycerol Lucite
Rules for Deviation of Light Rays During Refraction
 REFLECTION OF LIGHT Refraction of light is the phenomenon due to which a ray of light deviates from its path, at the surface of separation of two media, when the ray of light is travelling from one optical
REFLECTION OF LIGHT Refraction of light is the phenomenon due to which a ray of light deviates from its path, at the surface of separation of two media, when the ray of light is travelling from one optical
Ray tracing. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1
 Ray tracing Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1 From last time Hidden surface removal Painter s algorithm Clipping algorithms Area subdivision BSP trees Z-Buffer
Ray tracing Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 3/19/07 1 From last time Hidden surface removal Painter s algorithm Clipping algorithms Area subdivision BSP trees Z-Buffer
CHAP: REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACES
 CHAP: REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACES Ex : 4A Q: 1 The change in the direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is called refraction
CHAP: REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACES Ex : 4A Q: 1 The change in the direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is called refraction
Refraction of Light. Research Problem. Materials. Procedure. Due Date. Glass Block Protractor Ruler PENCIL 4 Pins Cardboard
 Name SI Physics Period Date Lab #0(90 pts) Mrs. Nadworny Due Date Research Problem Materials Refraction of Light When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted. The
Name SI Physics Period Date Lab #0(90 pts) Mrs. Nadworny Due Date Research Problem Materials Refraction of Light When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted. The
Light. Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction
 Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Photons with particle-like nature
Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Photons with particle-like nature
Reflection and Refraction. Chapter 29
 Reflection and Refraction Chapter 29 Reflection When a wave reaches a boundary between two media, some or all of the wave bounces back into the first medium. Reflection The angle of incidence is equal
Reflection and Refraction Chapter 29 Reflection When a wave reaches a boundary between two media, some or all of the wave bounces back into the first medium. Reflection The angle of incidence is equal
Waves-Refraction. 5. A change in the speed of a wave as it enters a new medium produces a change in 1. frequency 2. period 3. wavelength 4.
 1. In which way does blue light change as it travels from diamond into crown glass? 1. Its frequency decreases. 2. Its frequency increases. 3. Its speed decreases. 4. Its speed increases. Base your answers
1. In which way does blue light change as it travels from diamond into crown glass? 1. Its frequency decreases. 2. Its frequency increases. 3. Its speed decreases. 4. Its speed increases. Base your answers
Lecture 14: Refraction
 Lecture 14: Refraction We know from experience that there are several transparent substances through which light can travel air, water, and glass are three examples When light passes from one such medium
Lecture 14: Refraction We know from experience that there are several transparent substances through which light can travel air, water, and glass are three examples When light passes from one such medium
Chapter 5 Mirror and Lenses
 Chapter 5 Mirror and Lenses Name: 5.1 Ray Model of Light Another model for light is that it is made up of tiny particles called. Photons travel in perfect, lines from a light source This model helps us
Chapter 5 Mirror and Lenses Name: 5.1 Ray Model of Light Another model for light is that it is made up of tiny particles called. Photons travel in perfect, lines from a light source This model helps us
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Refraction of Light. light ray. rectangular plastic slab. normal rectangular slab
 Refraction of Light light ray light box single slit rectangular plastic slab What is the light path for a ray aligned with the normal? What is the light path for rays not aligned with the normal? light
Refraction of Light light ray light box single slit rectangular plastic slab What is the light path for a ray aligned with the normal? What is the light path for rays not aligned with the normal? light
The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses 5/3/2018. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Not so for refraction.
 The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses Unit 11 These are not photographs, but rather computer generated graphics based on the artist s understanding of the index of refraction. The angle of incidence
The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses Unit 11 These are not photographs, but rather computer generated graphics based on the artist s understanding of the index of refraction. The angle of incidence
Hot Sync. Materials Needed Today
 Chapter 11 Lesson 2 Materials Needed Today Please take these materials out of your backpack. Pencil Blank sheet of paper for a lab! Hot Sync Thursday 3/27/14 After learning how light acts. Write a new
Chapter 11 Lesson 2 Materials Needed Today Please take these materials out of your backpack. Pencil Blank sheet of paper for a lab! Hot Sync Thursday 3/27/14 After learning how light acts. Write a new
16/05/2016. Book page 110 and 112 Syllabus 3.18, Snell s Law. cgrahamphysics.com 2016
 16/05/2016 Snell s Law cgrahamphysics.com 2016 Book page 110 and 112 Syllabus 3.18, 3.19 Match the words to the objects absorbs transmits emits diffracts disperses refracts reflects Fibre optics Totally
16/05/2016 Snell s Law cgrahamphysics.com 2016 Book page 110 and 112 Syllabus 3.18, 3.19 Match the words to the objects absorbs transmits emits diffracts disperses refracts reflects Fibre optics Totally
Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend...
 SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
1. What is the law of reflection?
 Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
Name: Skill Sheet 7.A The Law of Reflection The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. For example, how would
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
PHY 1160C Homework Chapter 23: Reflection and Refraction of Light Ch 23: 8, 10, 14, 20, 26, 28, 33,38, 43, 45, 52
 PHY 1160C Homework Chapter 3: Reflection and Refraction of Light Ch 3: 8, 10, 14, 0, 6, 8, 33,38, 43, 45, 5 3.8 What is the speed of light in water (n = 1.33)? n = c/v v = c/n v = (3.00 x 10 8 m/s)/(1.33)
PHY 1160C Homework Chapter 3: Reflection and Refraction of Light Ch 3: 8, 10, 14, 0, 6, 8, 33,38, 43, 45, 5 3.8 What is the speed of light in water (n = 1.33)? n = c/v v = c/n v = (3.00 x 10 8 m/s)/(1.33)
Physics Experiment 13
 Fig. 13-1 Equipment This side of the mirror is gray. Place this side on the baseline. You can see your reflection on this side of the mirror. Fig. 13-2 Mirror Placement: The "Plexi-Ray Kit" contains a
Fig. 13-1 Equipment This side of the mirror is gray. Place this side on the baseline. You can see your reflection on this side of the mirror. Fig. 13-2 Mirror Placement: The "Plexi-Ray Kit" contains a
Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018
 Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Theoretical foundations Ray Tracing from the Ground Up Chapters 13-15 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF
Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Theoretical foundations Ray Tracing from the Ground Up Chapters 13-15 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics
 Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION PHYSICS - GRADE: VIII REFRACTION OF LIGHT
 L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS - GRADE: VIII REFRACTION OF LIGHT REFRACTION When light travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, it bends from
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS - GRADE: VIII REFRACTION OF LIGHT REFRACTION When light travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, it bends from
Reflections. I feel pretty, oh so pretty
 Reflections I feel pretty, oh so pretty Objectives By the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Draw an accurate reflective angle Determine the focal length of a spherical mirror Light Review Light
Reflections I feel pretty, oh so pretty Objectives By the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Draw an accurate reflective angle Determine the focal length of a spherical mirror Light Review Light
The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses 4/26/2016. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Not so for refraction.
 The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses These are not photographs, but rather computer generated graphics based on the artist s understanding of the index of refraction. The angle of incidence
The path of light is bent. Refraction and Lenses These are not photographs, but rather computer generated graphics based on the artist s understanding of the index of refraction. The angle of incidence
GEOMETRIC OPTICS. LENSES refract light, so we need to know how light bends when entering and exiting a lens and how that interaction forms an image.
 I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
Lighting and Shading
 Lighting and Shading Today: Local Illumination Solving the rendering equation is too expensive First do local illumination Then hack in reflections and shadows Local Shading: Notation light intensity in,
Lighting and Shading Today: Local Illumination Solving the rendering equation is too expensive First do local illumination Then hack in reflections and shadows Local Shading: Notation light intensity in,
FLAP P6.2 Rays and geometrical optics COPYRIGHT 1998 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY S570 V1.1
 F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In
F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3
 PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3 The speed of light is in a vacuum. it travels 299 972 458 m/s. (rounded to m/s). Speed of light is given the symbol comes from the word meaning. How far do you think light
PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3 The speed of light is in a vacuum. it travels 299 972 458 m/s. (rounded to m/s). Speed of light is given the symbol comes from the word meaning. How far do you think light
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing. Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19
 Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall October 9/10/11 Angles and Light
 Facult of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2018 - October 9/10/11 Angles and Light Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Toda we will be learning about angles.
Facult of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2018 - October 9/10/11 Angles and Light Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Toda we will be learning about angles.
Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them:
 Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them: physics transparent convex mirror real image optics translucent refraction virtual image
Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them: physics transparent convex mirror real image optics translucent refraction virtual image
Refraction Ch. 29 in your text book
 Refraction Ch. 29 in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: 1) Identify incident and refracted angles 2) Explain what the index of refraction tells about a material 3) Calculate the index
Refraction Ch. 29 in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: 1) Identify incident and refracted angles 2) Explain what the index of refraction tells about a material 3) Calculate the index
Light. Reflection of light. Types of reflection
 Light Reflection of light Reflection is when light bounces off an object. If the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the
Light Reflection of light Reflection is when light bounces off an object. If the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the
Refraction of Light Finding the Index of Refraction and the Critical Angle
 Finding the Index of Refraction and the Critical Angle OBJECTIVE Students will verify the law of refraction for light passing from water into air. Measurements of the angle of incidence and the angle of
Finding the Index of Refraction and the Critical Angle OBJECTIVE Students will verify the law of refraction for light passing from water into air. Measurements of the angle of incidence and the angle of
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11. Reflection and refraction
 Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Recap: Refraction. Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium. (n 2 > n 1 ) n 2
 Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics
 PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Exam 2 is scheduled on Tuesday, March 26 @ 8 10 PM In Physics 114 It will cover four Chapters 21, 22, 23, and 24. Start reviewing lecture
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Exam 2 is scheduled on Tuesday, March 26 @ 8 10 PM In Physics 114 It will cover four Chapters 21, 22, 23, and 24. Start reviewing lecture
TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions
 TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 14 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away, the
TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 14 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away, the
The Ray model of Light. Reflection. Class 18
 The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law
 Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law Learning Goal: Students will be able to calculate the angle of reflection of a bent light wave. Take out your notes from yesterday as we learn about Snell s Law.
Today s Topic: Refraction / Snell s Law Learning Goal: Students will be able to calculate the angle of reflection of a bent light wave. Take out your notes from yesterday as we learn about Snell s Law.
Physics. Bending Light ID: 8878
 Bending Light ID: 8878 By Peter Fox Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore the refraction of a single light ray. They begin by exploring light traveling from a less
Bending Light ID: 8878 By Peter Fox Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore the refraction of a single light ray. They begin by exploring light traveling from a less
Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction
 Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction OBJECTIVE To study the imaging properties of a plane mirror. To prove the law of reflection from the previous imaging study. To study the refraction
Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction OBJECTIVE To study the imaging properties of a plane mirror. To prove the law of reflection from the previous imaging study. To study the refraction
Refracon. Refracon The spoon in the glass photo can be translated into a ray diagram.
 The of Light Learning Goals: to understand why light refracts when travelling through different media to calculate the index of refraction to use the index of refraction to calculate the speed of light
The of Light Learning Goals: to understand why light refracts when travelling through different media to calculate the index of refraction to use the index of refraction to calculate the speed of light
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23)
 Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law
 Home Lab Week 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Activity 7-1: Snell s Law Objective: Verify Snell s law Materials Included: Laser pointer Cylindrical
Home Lab Week 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Home Lab 7 Refraction, Ray Tracing, and Snell s Law Activity 7-1: Snell s Law Objective: Verify Snell s law Materials Included: Laser pointer Cylindrical
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring Lab #7: Reflection & Refraction
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #7: Reflection & Refraction Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, March 26/28/29/30, 2018 Background Light
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #7: Reflection & Refraction Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, March 26/28/29/30, 2018 Background Light
(Equation 24.1: Index of refraction) We can make sense of what happens in Figure 24.1
 24-1 Refraction To understand what happens when light passes from one medium to another, we again use a model that involves rays and wave fronts, as we did with reflection. Let s begin by creating a short
24-1 Refraction To understand what happens when light passes from one medium to another, we again use a model that involves rays and wave fronts, as we did with reflection. Let s begin by creating a short
SNC2D PHYSICS 5/20/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Total Internal Reflection (TIR) (P ) Total Internal Reflection (TIR)
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L (P.442-443) Sometimes, such as in the case of fibre optics or laser light travelling from water into air, the light does not pass from one medium to another but
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L (P.442-443) Sometimes, such as in the case of fibre optics or laser light travelling from water into air, the light does not pass from one medium to another but
Reflection and Refraction
 Reflection and Refraction 1) Students will be able to state the law of reflection. 2) Students will be able to describe refraction and use Snell's law. 1 Teachers' notes Subject Topic Title Grade(s) Cross
Reflection and Refraction 1) Students will be able to state the law of reflection. 2) Students will be able to describe refraction and use Snell's law. 1 Teachers' notes Subject Topic Title Grade(s) Cross
Lecture Ray Model of Light. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org
 Lecture 1201 Ray Model of Light Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Reflection of Light A ray of light, the incident ray, travels in a medium. When it encounters a boundary with a second medium, part
Lecture 1201 Ray Model of Light Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Reflection of Light A ray of light, the incident ray, travels in a medium. When it encounters a boundary with a second medium, part
M = h' h = #i. n = c v
 Name: Physics Chapter 14 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: c = 3 "10 8 m s 1 i + 1 o = 1 f M = h' h =
Name: Physics Chapter 14 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: c = 3 "10 8 m s 1 i + 1 o = 1 f M = h' h =
Light and Lenses Notes
 Light and Lenses Notes Refraction The change in speed and direction of a wave Due to change in medium Must cross boundary at an angle other than 90 o, otherwise no change in direction I R (unlike reflection)
Light and Lenses Notes Refraction The change in speed and direction of a wave Due to change in medium Must cross boundary at an angle other than 90 o, otherwise no change in direction I R (unlike reflection)
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
So far, we have considered only local models of illumination; they only account for incident light coming directly from the light sources.
 11 11.1 Basics So far, we have considered only local models of illumination; they only account for incident light coming directly from the light sources. Global models include incident light that arrives
11 11.1 Basics So far, we have considered only local models of illumination; they only account for incident light coming directly from the light sources. Global models include incident light that arrives
TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry 25 Questions
 TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 13 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away,
TEAMS National Competition Middle School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 13 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away,
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 Level Physics: Waves Total Internal Reflection - Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 970 replaced AS 9054. In 9054, from 004 to 0, there was an Evidence column with the
Level Physics: Waves Total Internal Reflection - Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 970 replaced AS 9054. In 9054, from 004 to 0, there was an Evidence column with the
Outline The Refraction of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 26-3 Spherical Mirror 26-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation
 Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Physics 10. Lecture 28A. "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?
 Physics 10 Lecture 28A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright The Nature of Light From now on we will have to treat light as
Physics 10 Lecture 28A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright The Nature of Light From now on we will have to treat light as
Date. Refraction. What do you think is happening in the above photo and why? Key words Reflection Reflected Ray Incident Ray Normal Refraction Convex
 Refraction Date Key words Reflection Reflected Ray Incident Ray Normal Refraction Convex What do you think is happening in the above photo and why? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o08jgkut7e8 Refraction
Refraction Date Key words Reflection Reflected Ray Incident Ray Normal Refraction Convex What do you think is happening in the above photo and why? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o08jgkut7e8 Refraction
Real Time Reflections Han-Wei Shen
 Real Time Reflections Han-Wei Shen Reflections One of the most noticeable effect of inter-object lighting Direct calculation of the physics (ray tracing) is too expensive Our focus is to capture the most
Real Time Reflections Han-Wei Shen Reflections One of the most noticeable effect of inter-object lighting Direct calculation of the physics (ray tracing) is too expensive Our focus is to capture the most
LIGHT. Descartes particle theory, however, could not be used to explain diffraction of light.
 1 LIGHT Theories of Light In the 17 th century Descartes, a French scientist, formulated two opposing theories to explain the nature of light. These two theories are the particle theory and the wave theory.
1 LIGHT Theories of Light In the 17 th century Descartes, a French scientist, formulated two opposing theories to explain the nature of light. These two theories are the particle theory and the wave theory.
Computer Graphics. Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring
 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring Today Environment Mapping Introduction Cubic mapping Sphere mapping refractive mapping Mirroring Introduction reflection first stencil buffer
Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring Today Environment Mapping Introduction Cubic mapping Sphere mapping refractive mapping Mirroring Introduction reflection first stencil buffer
4. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year. How far does light travel in one year? 9.46 x m
 hapter 6 Light, Mirrors, and Lenses Practice Problems Name: Section 1: Speed, Distance, and Time (v = d/t) 1. In communicating with an automatic space station, radio signals travelling at the speed of
hapter 6 Light, Mirrors, and Lenses Practice Problems Name: Section 1: Speed, Distance, and Time (v = d/t) 1. In communicating with an automatic space station, radio signals travelling at the speed of
Physics 1C. Lecture 22A. "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton
 Physics 1C Lecture 22A "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton The Nature of Light An interesting question developed as to the nature of
Physics 1C Lecture 22A "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton The Nature of Light An interesting question developed as to the nature of
Chapter 23 Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Reflection and Refraction C O L O R S White light contains all colors. White objects reflect all colors. Black objects absorb all colors. Green objects absorb all colors but reflect green. Red,
Chapter 23 Reflection and Refraction C O L O R S White light contains all colors. White objects reflect all colors. Black objects absorb all colors. Green objects absorb all colors but reflect green. Red,
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction
 Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
CS354 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing. Qixing Huang Januray 24th 2017
 CS354 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Qixing Huang Januray 24th 2017 Graphics Pipeline Elements of rendering Object Light Material Camera Geometric optics Modern theories of light treat it as both a wave
CS354 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Qixing Huang Januray 24th 2017 Graphics Pipeline Elements of rendering Object Light Material Camera Geometric optics Modern theories of light treat it as both a wave
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007
 Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Introduction: The Nature of Light
 O1 Introduction: The Nature of Light Introduction Optical elements and systems Basic properties O1.1 Overview Generally Geometrical Optics is considered a less abstract subject than Waves or Physical Optics
O1 Introduction: The Nature of Light Introduction Optical elements and systems Basic properties O1.1 Overview Generally Geometrical Optics is considered a less abstract subject than Waves or Physical Optics
Plane mirror. Norrnal. Nome. Take Home - Reflection ondrefroction
 Take Home - Reflection ondrefroction Nome ') A ray of monochromatic light traveling in air is.incident on a plane minor at an angle of 30'o, as shown in the diagram below. Plane mirror The angle of reflection
Take Home - Reflection ondrefroction Nome ') A ray of monochromatic light traveling in air is.incident on a plane minor at an angle of 30'o, as shown in the diagram below. Plane mirror The angle of reflection
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
