N is Tarry's point. ABC. A B C is the fundamental triangle. Ma Ml, Me is the triangle formed by joining the middle points of the sides of
|
|
|
- Rosamund Riley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 104 CoLLiNEAR Sets of Three Points Connected With the Triangle. Robert J. A ley. By This paper does not claim to be either original or complete. It contains a fairly complete list of collinear sets connected with the triangle. All cases of collinearity connected with polygons of more than three sides have been omitted. The subject of collinearity is both interesting and fruitful. There are three well defined methods of proving the collinearity of three points. The classic one is the application of the theorem of Menelaus: "If I), E, F are points on the sides B C, C A, A B respectfully of AB (', such that B DXCEXA F = D CXE AXF B, then D, E, F are collinear." In many cases the data are insufficient for the u.se of this method. Another method of frequent use is to prove that the angle formed by the three points is a straight angle. The author has used another method, believed to be original with him, when the points in question are such that the ratios of their distances from the sides can be determined. This method is fully illustrated in " Contributions to the (Jeometry of the Triangle." Collinear prolilems fall into two very well marked classes. The first class is made up of those points which are definitely located with respect to the triangle. The second class is made up of those points which are located with reference to some auxiliary point. notation. In order to save time in the enunciation of propositions the following notation will be used : A B C is the fundamental triangle. Aj Bi C, is Brocard's first triangle. Ma Ml, Me is the triangle formed by joining the middle points of the sides of ABC. Mia Mil, Ml,- is the triangle formed by joining the middle points of the sides of A, B, C,. M is the centre of the circumcircle of AB C. M' is the point isotomic conjugate to M. G is the median point or Centroid of AB C. K is Grebe's point or the Symmedian point. D is the centre of perspective of AB C and Aj B, C,. D' is the {)oint isogonal conjugate to D. H is the Orthocentre. il and it^ are the two Brocard pcjints. N is Tarry's point.
2 . 105 Q is Nagel's point. (It is the point of concurrency of the three lines joining the vertices to the points of tangency of the three escribed circles.) Q^ is the isotomic conjugate of Q. O is the centre of the inscribed circle. S is the point of perspective of Ma Mb Me and Mia Mib Mic. S^ is the point isogonal conjugate to S. R is the point of concurrence of perpendiculars from A, B, C on the sides of Nagel's triangle. Mj is the centre of Nagel's circle. T is the point of concurrence of perpendiculars from A' B' C upon the respective sides of A''' B^^ 0,^' Z is Brocard's centre. Z^ is the point isogonal conjugate to Z., P is the point isotomic conjugate to O. P^ is the point isogonal conjugate to P. Qi is the point isogonal conjugate to Q'. F is the centre of Nine points circle. THEOREMS. The original sources of the theorems are known in only a very few cases. references simply indicate where the theorems may be found. (1.) M, H and G are collinear. The (Lachlan Modern Pure Geometry, p. 67.) (2.) K, G and the Symmedian point of Ma Mb Mo are collinear. (Ibid, p. 138.) (3.) Tangents to the circumcircle at the vertices of AB C form the triange P Q R; Ha, Hb, Ho are the feet of the altitudes of AB C; P Ha, QHb, RHo are concurrent in a point which is collinear with M and H, tibid, p. 138.) (4.) M, K and the orthocentre of its pedal triangle are collinear. (McClellan The Geometry of the Circle, p. 83.) (5) M and the orthocentre of its pedal triangle are equidistant from and collinear, with the centre of Taylor's Circle. (Ibid, p. 83.) (6.) Q, Q^ and P are collinear. (Aley Contributions to the Geometry of the Triangle, p. 8.) (7.) K, P^ and Qi are collinear. (Ibid, p. 13.)
3 106 S', K and D are collinear. (Ibid, p. 15.) H, M^ and Dare collinear. (Ibid, p. 19.) Z', F and D are collinear. (Ibid, p. 24.) a, i2' and S are collinear. (Schwatt Geometric Treatment of Curves, p 7.) K, Z, M are all collinear. (Ibid, p. 3.) Z', H, and S are collinear. (Ibid, p. 13.) N, M, and I) are collinear. (Ibid, p. 17.) D, S and (i are collinear. (Ibid, p. 7.) Q, O and G are collinear. (Ibid, p. ;>G.) I)', H and N are collinear. (Ibid, p. 16.) Q, M and Z are collinear. (Ibid, p. 44.) R, O and Mj are collinear. Mc, Ml,- and S are collinear. (Ibid, p. 43.) (Casey Sequel, "Jth edition, p. 242.) K, M and the center of the triplicate ratio circle are collinear. (Richardson and Ramsey Modern Plane Geometry, p. 41.) N, M and the point of concurrence of lines through A, B, C parallel to the corresponding sides of Brocard's first triangle are collinear. (Lachlan Modern Pure Geometry, p. 81.) K, Ma and the middle point of altitude upon B C are collinear. (Richardson and Ramsey Modern Plane Geometry, p. 58.) H, G and F are collinear. (W. B. Smith Modern Synthetic Geometry, p. 141.) If A^ is the pole of B C with respect to the circumcircle of ABC, then A,, A and the Symmedian point are collinear. (Casey Sequel, 5th edition, p. 171.)
4 ) 107 (26.) The intersections of the anti-parallel chords D^ E, E^ F, F^ D with Lemoine's parallels D E\ E F^, F D^ respectively, are collinear. The D, E, F, D\ FJ, F', are the six points of intersection of Lemoine's circle with the sides of the triangle. (Ibid, p. 182.) (27.) If the line joining two corresponding points of directly similar figures Fi, F2, Fj described on the sides of the triangle AB C, pass through the centroid, the three corresponding points are collinear. (Ibid, p. 237.) (28.) If from Tarry's point _l_'s be drawn to the sides B C, C A, A B of the triangle, meeting the sides in (a, flj, a^) (/?, /3j, (32) (y, /i, y.^), the points a, p, }' are collinear, so also (a^, fi.^, y) and (f?,, P, Yi)- (Neiiberg.) (Ibid, p (29.) In any triangle AB C, O, ()^ are the centres of the inscribed circle and of the escribed circle opposite A; O O^ meets B C in D. Any straight line through D meets AB, AC respectively in b, c. O b, O' c intersect in P, O^b, O c in Q. P A Q is a straight line perpendicular to 0^ (Wolstenholme Math. Problems, p. 8, No. 79.) (30.) A triangle P Q R circumscribes a circle. A second triangle A B C is formed by taking points on the sides of this triangle such that A P, B Q, C R are concurrent. From the points A, B, C tangents A a, B b, C c are drawn to the circle. These tangents produced intersect the sides B C, C A, AB, in the three points a b c, which are collinear. (Catalan Geomdtrie Elementaire, p. 250.) (31.) The three internal and three external bisectors of the angles of a triangle meet the opposite sides in six points which lie three by three in four straight lines. (Richardson and Ramsey Modern Plane Geometry, p. 19.) (32.) If O be any point, then the external bisectors of the angles BO C, C O A, A O B meet the sides B C, C A, A B respectively in three collinear points. (Ibid, p. 52.) (83.) The external bisectors of the angles of a triangle meet the opposite sides in collinear points. (A special case of 31.) (Lachlan Modern Pure Geometry, p. 57.) (34.) Lines drawn through any point O perpendicular to the lines O A, O B, O C meet the sides of the triangle AB C in three collinear points. (Ibid, p. 59.)
5 ; 108 (35.) If any line cuts the sides of a triangle in X, Y, Z ; the isogonal conjugates of A X, B Y, C Z respectively will meet the opposite sides in couinear points. (Ibid, p. 59.) (36.) If a line cut the sides in X, Y, Z; the isotoraic points of X, Y, Z with respect to the sides will be collinear, (Ibid, p. 59.) (37.) If from any jioint P on the circumcircle of the triangle AB C, P L, P M, P N be drawn perpendicular to P A, P B, P C, meeting B C, C A, AB, in L, M, N, then these points L, M, N are collinear with'circnmcentre. (Ibid, p. 67.) (38.) If P L, P M, P N be _L's drawn from a point P on the circumcircle to the sides B C, C A, AB respectively, and if PI, Pm, Pn be drawn meeting the sides in 1, m, n and making the angles L PI, M Pm, N Pn equal when measured in the same sense, then the points 1, m, n are collinear. (Ibid, p. 68.) (39.) If X Y Z and X' Y' Z' are any two transversals of the triangle AP. C: Y Z'; Z X', X Y'^' cut the sides B C, C A, AB in collinear points. (Ibid, p. 60.) (40.) If X Y Z and X' Y' Z' be any two transversals of the triangle AB C, and and if Y Z', \' Z meet in P, Z X', Z> X meet in Q, X Y', X' Y in R, then A P, B Q, C R cut the sides B C, C.\, AB in collinear points. (Ibid, p. 61.) (41.) If the lines AO, BO, CO cut the sides of the triangle AB C in X, Y, Z and if the points X*, Y', 7J be the harmonic conjugate points of X, Y. Z with respect to B, C; C, A; and A, B, respectively, then X', Y', Z' are collinear. (Ibid, p. 61.) (42.) If the inscribed circle touch the sides in X, Y, Z, then the lines Y Z, Z X, X Y cut the sides B C, C A, AB in three collinear points. (Ibid, p. 62.) (43.) The feet of perpendiculars from H and G upon A G and A H respectively are collinear with K. (Ibid, p. 147.) (44.) If three triangles AB C, A, B, C,, and A, B. C, have a common axis of perspective, their centres of perspective when taken two and two, are collinear. (McClellan Geometry of the Circle, p. 122.)
6 ' 109 (45.) AB C is a triangle inscribed in and in perspective with A' B' C; the tangents from A B C to the incircle of A^ B^ C meet the opposite sides in three couinear points, X, Y, Z (B C in X, etc.). (Ibid, p. 128.) (46.) If three pairs of tangents drawn from the vertices of a triangle to any circle, meet the opposite sides X, X', Y, Y\ Z, Z', and if X, Y, Z are collinear, so also are X', Y', Z^. (Ibid, p. 128.) (47.) If X Y Z is a transversal and if X\ Y^ Z^ are the harmonic conjugates of X, Y, Z, then Y\ Z\ X; Z' Xi, Y; X^, Yi, Z are collinear. X X\ Y Y\ Z 7J are collinear. Also the middle points of (Ibid, p ) (48.) If L is an axis of symmetry to the congruent triangles ABC and A' B^ C and O is any point on L, A' O, B' O, C^ O cut the sides B C, C A, AB in three collinear points. (Depuis Modern Synthetic Geometry, p. 204.) (49.) Two triangles which have their vertices connecting concurrently, have their corresponding sides intersecting collinearly. (Desargue's Theorem.) (Ibid, p. 204.) (50.) A\ B,i Ci are points on sides of AB C such that AA^, BBi, C C^ are concurrent, then AB, A^ B' ; B C, B^ C, C A, C* A^ meet in three points Z, X, Y which are collinear. (Ibid, p. 205.) (51.) If P be any point, AB C a triangle and A^ B^ C^ its polar reciprocal with respect to a polar centre O, the perpendiculars from O on the joins P A, P B, and P C intersect the sides of A^ B^ C^ collinearly. (Ibid, p ) (52.) If the three vertices of a triangle be reflected with respect to any line, the three lines connecting the reflexions with any point on the line intersect collinearly with the opposite sides. (Townsend Modern Geometry, p. 180.) (53.) When three of the six tangents to a circle from three vertices of a triangle intersect collinearly with the opposite sides, the remaining three also intersect collinearly with the opposite sides. (Ibid, p. 180.)
7 A meet 110 (54.) If from the middle points of the sides of the triangle ABC, tangents be drawn to the corresponding Neuberg circles, the points of contact lie on two right lines through the centroid of A B C. (Casey Sequel, p. 241.) (55.) If P is a Simson's point for A B C, and O any other point on the circumcircle of A B C, then the projections of O upon the Simson's lines of O with respect to the triangles P A C, P B C, P C A, A B C are collinear. (Lachlan Modern Pure Geometry, p. 69.) (56.) When three lines through the vertices of a triangle are concurrent, the six bisectors of the three angles they determine intersect the corresponding sides of the triangle at six points, every three of which on different sides are collinear if an odd number is external. (Ibid, p. 181.) (57.) When three points on the sides of a triangle are collinear, the six bisections of the three segments they determine connect with the corresponding vertices of the triangle by six lines, every three of which through different vertices are couinearly intersecttant with the oi)posite sides if an odd number is external. (Ibid, p. 182.) (58.) A, Ml,, and K', the intersection of the Symmedian through A and the tangent to circumcircle at C, are collinear. (Schwatt Geometric Treatment of Curves, p. 4.) (59.) If M X and F Y are parallel radii, in the same direction, in circumcircle and Feuerbach circle, then X, Y, and H are collinear. (Ibid, p. 21.) (60.) If Y'l is tlu- other extremity of the diameter F Y, then Y,, G, and X are collinear. (Ibid, p. 21.) (61.) If P, a point on the circumcircle of ABC l)e joineil witii H',H'',H"\ (62. 1 the respective intersections of the produced altitudes with circumcircle, and if the points of intersection of P H, P H ", P II " i with B C, C A, AB l)e U, V, W respectively, then U, V, W are collinear. (Ibid, p. 23.) O, B O, C O meet the circumcircle in A', B', ('' ; perpendiculars from M upon the sides B C, C A, AB meet Nagel's circle in A", B' >, C" ; the corresponding sides of A' B' C^ and A'' B' ' C collinear points. (Ibid, p. 40.) ' in three
8 Ill (63.) The feet of the perpendiculars on the sides of a triangle.from any point in the circumference of the circumcircle are collinear. (Simson's line.) (6-1.) If two triangles are in perspective the intersections of the corresponding sides are collinear. A difterent statement of 49. (Mulcahy Modern Geometry, p. 28.) (65.) The perpendiculars to the bisectors of the angles of a triangle at their middle points meet the sides opposite those angles in three points which are collinear. (G. DeLong Champs.) (Mackay, Euclid, p. 356.) I, Ij, 1^, I3 are the centres of the inscribed and three escribed circles of the triangle ABC. D, E, F; Di, E,, Fj ; D E^, F,; D3 ; E3 ; F3 : are the feet of the perpendiculars from these centres upon the respective sides. N, P, Q are the feet of the bisectors of the angles A, B, C. (66.) A B, D E, B. Ej concur at Qj. B C, E F, E3 F, concur at Nj. C A, F D, Fi D3 concur at Pj. Qi, Nj, and Pj are collinear. (67.) A B, Di E2, D3 E3 concur at Q,. B C, E.^ F3, El Fi concur at N.. C A, F3 Di, F, D, concur at P^. Q,) ^2, and P, are collinear. (68.) A B, N P, Ii I2 concur at Q3. B C, P Q, I2 I3 concur at N3. C A, Q N, I3 Ij concur at P3. Q3 N3 and P3 are collinear. {66, 67, 68 Stephen Watson in Lady's and Gentleman's Diary for 1867, p, 72. Mackay, Euclid, p. 357.) (69.) Ma, the middle point of Q O and the middle point of Q A are collinear. (Mackay, Euclid, p. 363.) (70.) The six lines joining two and two the centres of the four circles touching the sides of the triangle ABC, pass each through a vertex of the triangle. (Mackay, Euclid, p. 252.) (71.) Ma, O, and the middle of the line drawn from the vertex to the point of inscribed contact on the base are collinear. A similar property holds for the escribed centres. Indiana University, December 18, (Mackay, Euclid, p. 360.)
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE
 CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Cevians, Symmedians, and Excircles. Cevian. Cevian Triangle & Circle 10/5/2011. MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16
 Cevians, Symmedians, and MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian A D C 05-Oct-2011
Cevians, Symmedians, and MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian A D C 05-Oct-2011
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle
 Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
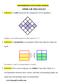 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA
 GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
 1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
EUCLID S GEOMETRY. Raymond Hoobler. January 27, 2008
 EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
 CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
ME 111: Engineering Drawing. Geometric Constructions
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence
 Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles
 Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
with slopes m 1 and m 2 ), if and only if its coordinates satisfy the equation y y 0 = 0 and Ax + By + C 2
 CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
S56 (5.3) Higher Straight Line.notebook June 22, 2015
 Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Circumference of a Circle
 Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units
 Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, Glossary
 TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, 2003 2004 Glossary Absolute value The size of a number with its + or sign removed. The absolute value of 3.2 is 3.2, the absolute value of +4.6 is 4.6. We write this: 3.2 = 3.2
TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, 2003 2004 Glossary Absolute value The size of a number with its + or sign removed. The absolute value of 3.2 is 3.2, the absolute value of +4.6 is 4.6. We write this: 3.2 = 3.2
Midpoint of a Line Segment Pg. 78 # 1, 3, 4-6, 8, 18. Classifying Figures on a Cartesian Plane Quiz ( )
 UNIT 2 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework Feb. 22 Feb. 23 Feb. 24 Feb. 27 Feb. 28 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.1-2.3 2.1-2.3 Mar. 1 2.6 2.4 Mar. 2 2.7 2.5 Mar. 3 2.8 2.6 Mar. 6 2.9 2.7 Mar.
UNIT 2 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework Feb. 22 Feb. 23 Feb. 24 Feb. 27 Feb. 28 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.1-2.3 2.1-2.3 Mar. 1 2.6 2.4 Mar. 2 2.7 2.5 Mar. 3 2.8 2.6 Mar. 6 2.9 2.7 Mar.
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined
 MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: a b 1.
 ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
Solutions to the Test. Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written?
 Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Killingly Public Schools. Grades Draft Sept. 2002
 Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Geometry Indiana Standards Worktext Correlations
 Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry
 The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry Paul Yiu Abstract. The notion of homogeneous barycentric coordinates provides a powerful tool of analysing problems in plane
The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry Paul Yiu Abstract. The notion of homogeneous barycentric coordinates provides a powerful tool of analysing problems in plane
Investigating Properties of Kites
 Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry: Traditional Pathway
 GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
Plane Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2011
 lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
Pearson Mathematics Geometry
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
Euclidean geometry deals mainly with points and straight lines. Its basic transformation is
 1. Inversion 1.1 Introduction Euclidean geometry deals mainly with points and straight lines. Its basic transformation is the reflection, which leaves fixed all the points on one line and interchanges
1. Inversion 1.1 Introduction Euclidean geometry deals mainly with points and straight lines. Its basic transformation is the reflection, which leaves fixed all the points on one line and interchanges
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with
 Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS
 EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Systems of Spheres connected with the Tetrahedron.
 108 Systems of Spheres connected with the Tetrahedron. By J. A THIRD, M.A. [References in square brackets are to my paper on Systems of Circles analogous to Tucker Circles.] 1. If A a and B 3 (Fig. 17),
108 Systems of Spheres connected with the Tetrahedron. By J. A THIRD, M.A. [References in square brackets are to my paper on Systems of Circles analogous to Tucker Circles.] 1. If A a and B 3 (Fig. 17),
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 7. Some triangle centers. 7.1 The Euler line Inferior and superior triangles
 hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
Exterior Region Interior Region
 Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
Perimeter. Area. Surface Area. Volume. Circle (circumference) C = 2πr. Square. Rectangle. Triangle. Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh
 Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Centres of a Triangle. Teacher Notes
 Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric Activities
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Point A location in geometry. A point has no dimensions without any length, width, or depth. This is represented by a dot and is usually labelled.
 Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Chapter 6. Sir Migo Mendoza
 Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
CLASSICAL THEOREMS IN PLANE GEOMETRY. September 2007 BC 1 AC 1 CA 1 BA 1 = 1.
 SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK
 Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Theorems & Postulates Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Problem 3.1 (Building up geometry). For an axiomatically built-up geometry, six groups of axioms needed:
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe September 29, 2016 All3181\3181_fall16h3.tex Names: Homework has to be turned in this handout. For extra space, use the back pages, or put blank pages between. The homework can
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe September 29, 2016 All3181\3181_fall16h3.tex Names: Homework has to be turned in this handout. For extra space, use the back pages, or put blank pages between. The homework can
arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013](/thumbs/74/70304288.jpg) Solution of Sondow s problem: a synthetic proof of the tangency property of the parbelos Emmanuel Tsukerman arxiv:1210.5580v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 Abstract In a recent paper titled The parbelos, a parabolic
Solution of Sondow s problem: a synthetic proof of the tangency property of the parbelos Emmanuel Tsukerman arxiv:1210.5580v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 Abstract In a recent paper titled The parbelos, a parabolic
Honors Geometry Pacing Guide Honors Geometry Pacing First Nine Weeks
 Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Grade IX. Mathematics Geometry Notes. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
Grade IX Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen The distance of a point from the y - axis is called its x -coordinate, or abscissa, and the distance of the point from the x -axis is called its y-coordinate,
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Course Number: Course Title: Geometry
 Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
added to equal quantities, their sum is equal. Same holds for congruence.
 Mr. Cheung s Geometry Cheat Sheet Theorem List Version 6.0 Updated 3/14/14 (The following is to be used as a guideline. The rest you need to look up on your own, but hopefully this will help. The original
Mr. Cheung s Geometry Cheat Sheet Theorem List Version 6.0 Updated 3/14/14 (The following is to be used as a guideline. The rest you need to look up on your own, but hopefully this will help. The original
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source:
 Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Figure 1. The centroid and the symmedian point of a triangle
 ISOGONAL TRANSFORMATIONS REVISITED WITH GEOGEBRA Péter KÖRTESI, Associate Professor Ph.D., University of Miskolc, Miskolc, Hungary Abstract: The symmedian lines and the symmedian point of a given triangle
ISOGONAL TRANSFORMATIONS REVISITED WITH GEOGEBRA Péter KÖRTESI, Associate Professor Ph.D., University of Miskolc, Miskolc, Hungary Abstract: The symmedian lines and the symmedian point of a given triangle
Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology Program of Studies TJ Math 1
 Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited
 230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
CONSTRUCTIONS Introduction Division of a Line Segment
 216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
Angles. An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex.
 Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method. Goals:
 Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method Goals: Construct an inscribed hexagon and dodecagon. Construct a circumscribed hexagon
Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method Goals: Construct an inscribed hexagon and dodecagon. Construct a circumscribed hexagon
CIRCLE. Circle is a collection of all points in a plane which are equidistant from a fixed point.
 CIRCLE Circle is a collection of all points in a plane which are equidistant from a fixed point. The fixed point is called as the centre and the constant distance is called as the radius. Parts of a Circle
CIRCLE Circle is a collection of all points in a plane which are equidistant from a fixed point. The fixed point is called as the centre and the constant distance is called as the radius. Parts of a Circle
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
VOCABULARY. Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8. WORD IMAGE DEFINITION An angle with measure between 0 and A triangle with three acute angles.
 Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
a) 1/3 area of triangle ABC b) 3.6 c) 3 d) e) Euclid s fifth postulate is equivalent to: Given a line and a point not on that line
 1. Given is a right triangle with AD a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse, find the length of AD given AB = 6, BC = 10 and AC = 8. B D A C a) 7.5 b) 6.5 c) 4.8 d) e) 2. Using the figure
1. Given is a right triangle with AD a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse, find the length of AD given AB = 6, BC = 10 and AC = 8. B D A C a) 7.5 b) 6.5 c) 4.8 d) e) 2. Using the figure
CURRICULUM GUIDE. Honors Geometry
 CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Geometry This level of Geometry is approached at an accelerated pace. Topics of postulates, theorems and proofs are discussed both traditionally and with a discovery approach. The
CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Geometry This level of Geometry is approached at an accelerated pace. Topics of postulates, theorems and proofs are discussed both traditionally and with a discovery approach. The
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry
 8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
Appendix. Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 Appendix Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics The correlation shows how the activities in Exploring Geometry with The Geometer s Sketchpad
Appendix Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics The correlation shows how the activities in Exploring Geometry with The Geometer s Sketchpad
Period: Date Lesson 13: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means
 : Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of
: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of
Mathematics High School Geometry
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Unit 1 Unit 1 A M. M.Sigley, Baker MS. Unit 1 Unit 1. 3 M.Sigley, Baker MS
 A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
IX GEOMETRICAL OLYMPIAD IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHARYGIN.
 IX GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN. THE ORRESPONDENE ROUND. SOLUTIONS. 1. (N.Moskvitin) Let be an isosceles triangle with =. Point E lies on side, and ED is the perpendicular from E to. It is
IX GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN. THE ORRESPONDENE ROUND. SOLUTIONS. 1. (N.Moskvitin) Let be an isosceles triangle with =. Point E lies on side, and ED is the perpendicular from E to. It is
G.CO.2 G.CO.3 G.CO.4 G.CO.5 G.CO.6
 Standard G.CO.1 G.CO.2 G.CO.3 G.CO.4 G.CO.5 G.CO.6 Jackson County Core Curriculum Collaborative (JC4) Geometry Learning Targets in Student Friendly Language I can define the following terms precisely in
Standard G.CO.1 G.CO.2 G.CO.3 G.CO.4 G.CO.5 G.CO.6 Jackson County Core Curriculum Collaborative (JC4) Geometry Learning Targets in Student Friendly Language I can define the following terms precisely in
correlated to the Utah 2007 Secondary Math Core Curriculum Geometry
 correlated to the Utah 2007 Secondary Math Core Curriculum Geometry McDougal Littell Geometry: Concepts and Skills 2005 correlated to the Utah 2007 Secondary Math Core Curriculum Geometry The main goal
correlated to the Utah 2007 Secondary Math Core Curriculum Geometry McDougal Littell Geometry: Concepts and Skills 2005 correlated to the Utah 2007 Secondary Math Core Curriculum Geometry The main goal
Course: Geometry PAP Prosper ISD Course Map Grade Level: Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block Days. Unit Title
 Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
terms, postulates, and notation segment and angle measurement basic constructions
 SEPTEMBER 2008 OCTOBER 2008 geometry terms, postulates, and notation understand how to calculate segment and angle measurements understand how to do basic constructions with a compass and straight edge
SEPTEMBER 2008 OCTOBER 2008 geometry terms, postulates, and notation understand how to calculate segment and angle measurements understand how to do basic constructions with a compass and straight edge
University of Sioux Falls. MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry
 University of Sioux Falls MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry Concepts addressed: Geometry Texts Cited: Hvidsten, Michael, Exploring Geometry, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2004. Kay, David, College Geometry: A
University of Sioux Falls MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry Concepts addressed: Geometry Texts Cited: Hvidsten, Michael, Exploring Geometry, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2004. Kay, David, College Geometry: A
TEACHER: Nelson/Ryalls/Ragan COURSE _Geometry I & II Curriculum Map
 SEPTEMBER understand how to apply geometry terms, postulates, and notation understand how to calculate segment and angle measurements understand how to do basic constructions with a compass and straight
SEPTEMBER understand how to apply geometry terms, postulates, and notation understand how to calculate segment and angle measurements understand how to do basic constructions with a compass and straight
ALLEGHANY COUNTY SCHOOLS CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE/COURSE: Geometry GRADING PERIOD: 1 Year Course Time SEMESTER 1: 1 ST SIX WEEKS Pre-Test, Class Meetings, Homeroom Chapter 1 12 days Lines and Angles Point Line AB Ray AB Segment AB Plane ABC Opposite
GRADE/COURSE: Geometry GRADING PERIOD: 1 Year Course Time SEMESTER 1: 1 ST SIX WEEKS Pre-Test, Class Meetings, Homeroom Chapter 1 12 days Lines and Angles Point Line AB Ray AB Segment AB Plane ABC Opposite
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) FORUM GEOM ISSN Pseudo-Incircles. Stanley Rabinowitz
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 107 115. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Pseudo-Incircles Stanley Rabinowitz bstract. This paper generalizes properties of mixtilinear incircles. Let (S) be any circle in
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 107 115. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Pseudo-Incircles Stanley Rabinowitz bstract. This paper generalizes properties of mixtilinear incircles. Let (S) be any circle in
If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of 4 Congruence
 Postulates Through any two points there is exactly one line. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those
Postulates Through any two points there is exactly one line. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those
7. 2 More Things Under. Construction. A Develop Understanding Task
 7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
Modeling with Geometry
 Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
0811ge. Geometry Regents Exam
 0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
