Robot Mapping. Graph-Based SLAM with Landmarks. Cyrill Stachniss
|
|
|
- Suzan Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Robot Mapping Graph-Based SLAM with Landmarks Cyrill Stachniss 1
2 Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15) Use a graph to represent the problem Every node in the graph corresponds to a pose of the robot during mapping Every edge between two nodes corresponds to a spatial constraint between them Graph-Based SLAM: Build the graph and find a node configuration that minimize the error introduced by the constraints 2
3 The Graph So far: Vertices for robot poses Edges for virtual observations (transformations) between robot poses Topic today: How to deal with landmarks 3
4 Landmark-Based SLAM 4
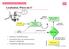
5 Real Landmark Map Example Image courtesy: E. Nebot 5
6 The Graph with Landmarks Feature Pose Constraint 6
7 The Graph with Landmarks Nodes can represent: Robot poses Landmark locations Edges can represent: Landmark observations Odometry measurements The minimization optimizes the landmark locations and robot poses Feature Pose Constraint 7
8 2D Landmarks Landmark is a (x,y)-point in the world Relative observation in 8
9 Landmarks Observation Expected observation (x-y sensor) robot landmark robot translation 9
10 Landmarks Observation Expected observation (x-y sensor) robot landmark robot translation Error function 10
11 Bearing Only Observations A landmark is still a 2D point The robot observe only the bearing (orientation towards the landmark) Observation function robot landmark robot-landmark robot angle orientation 11
12 Bearing Only Observations Observation function robot landmark robot-landmark robot angle orientation Error function 12
13 The Rank of the Matrix H What is the rank of for a 2D landmark-pose constraint? 13
14 The Rank of the Matrix H What is the rank of for a 2D landmark-pose constraint? The blocks of are a 2x3 matrices cannot have more than rank 2 14
15 The Rank of the Matrix H What is the rank of for a 2D landmark-pose constraint? The blocks of are a 2x3 matrices cannot have more than rank 2 What is the rank of for a bearing-only constraint? 15
16 The Rank of the Matrix H What is the rank of for a 2D landmark-pose constraint? The blocks of are a 2x3 matrices cannot have more than rank 2 What is the rank of for a bearing-only constraint? The blocks of are a 1x3 matrices has rank 1 16
17 Where is the Robot? Robot observes one landmark (x,y) Where can the robot be? The robot can be somewhere on a circle around the landmark It is a 1D solution space (constrained by the distance and the robot s orientation) 17
18 Where is the Robot? Robot observes one landmark (bearing-only) Where can the robot be? The robot can be anywhere in the x-y plane It is a 2D solution space (constrained by the robot s orientation) 18
19 Rank In landmark-based SLAM, the system can be under-determined The rank of is less or equal to the sum of the ranks of the constraints To determine a unique solution, the system must have full rank 19
20 Questions The rank of is less or equal to the sum of the ranks of the constraints To determine a unique solution, the system must have full rank Questions: How many 2D landmark observations are needed to resolve for a robot pose? How many bearing-only observations are needed to resolve for a robot pose? 20
21 Under-Determined Systems No guarantee for a full rank system Landmarks may be observed only once Robot might have no odometry We can still deal with these situations by adding a damping factor to Instead of solving, we solve (H + λ I) Δx = -b What is the effect of that? 21
22 (H + λ I) Δx = -b Damping factor for The damping factor makes the system positive definite It adds an additional constraints that drag the increments towards 0 What happens when? 22
23 Simplified Levenberg Marquardt Damping to regulate the convergence using backup/restore actions x: the initial guess while (! converged) λ = λ init <H,b> = buildlinearsystem(x); E = error(x) x old = x; Δx = solvesparse( (H + λ I) Δx = -b); x += Δx; If (E < error(x)){ x = x old ; λ *= 2; } else { λ /= 2; } 23
24 Summary Graph-Based SLAM for landmarks The rank of matters Levenberg Marquardt for optimization 24
Robot Mapping. Graph-Based SLAM with Landmarks. Cyrill Stachniss
 Robot Mapping Graph-Based SLAM with Landmarks Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15) Use a graph to represent the problem Every node in the graph corresponds to a pose of the robot during mapping
Robot Mapping Graph-Based SLAM with Landmarks Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15) Use a graph to represent the problem Every node in the graph corresponds to a pose of the robot during mapping
ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM. Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity. Cyrill Stachniss
 ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM?? 2 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous localization and mapping 3 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous
ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM?? 2 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous localization and mapping 3 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous
Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Graph-based SLAM using Least Squares. Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Kai Arras, Maren Bennewitz
 Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Graph-based SLAM using Least Squares Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Kai Arras, Maren Bennewitz SLAM Constraints connect the poses of the robot while it is moving
Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Graph-based SLAM using Least Squares Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Kai Arras, Maren Bennewitz SLAM Constraints connect the poses of the robot while it is moving
Robot Mapping. Least Squares Approach to SLAM. Cyrill Stachniss
 Robot Mapping Least Squares Approach to SLAM Cyrill Stachniss 1 Three Main SLAM Paradigms Kalman filter Particle filter Graphbased least squares approach to SLAM 2 Least Squares in General Approach for
Robot Mapping Least Squares Approach to SLAM Cyrill Stachniss 1 Three Main SLAM Paradigms Kalman filter Particle filter Graphbased least squares approach to SLAM 2 Least Squares in General Approach for
Graphbased. Kalman filter. Particle filter. Three Main SLAM Paradigms. Robot Mapping. Least Squares Approach to SLAM. Least Squares in General
 Robot Mapping Three Main SLAM Paradigms Least Squares Approach to SLAM Kalman filter Particle filter Graphbased Cyrill Stachniss least squares approach to SLAM 1 2 Least Squares in General! Approach for
Robot Mapping Three Main SLAM Paradigms Least Squares Approach to SLAM Kalman filter Particle filter Graphbased Cyrill Stachniss least squares approach to SLAM 1 2 Least Squares in General! Approach for
Least Squares and SLAM Pose-SLAM
 Least Squares and SLAM Pose-SLAM Giorgio Grisetti Part of the material of this course is taken from the Robotics 2 lectures given by G.Grisetti, W.Burgard, C.Stachniss, K.Arras, D. Tipaldi and M.Bennewitz
Least Squares and SLAM Pose-SLAM Giorgio Grisetti Part of the material of this course is taken from the Robotics 2 lectures given by G.Grisetti, W.Burgard, C.Stachniss, K.Arras, D. Tipaldi and M.Bennewitz
Autonomous Mobile Robot Design
 Autonomous Mobile Robot Design Topic: EKF-based SLAM Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) These slides have partially relied on the course of C. Stachniss, Robot Mapping - WS 2013/14 Autonomous Robot Challenges Where
Autonomous Mobile Robot Design Topic: EKF-based SLAM Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) These slides have partially relied on the course of C. Stachniss, Robot Mapping - WS 2013/14 Autonomous Robot Challenges Where
Robot Mapping. SLAM Front-Ends. Cyrill Stachniss. Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1
 Robot Mapping SLAM Front-Ends Cyrill Stachniss Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1 Graph-Based SLAM Constraints connect the nodes through odometry and observations Robot pose Constraint 2 Graph-Based
Robot Mapping SLAM Front-Ends Cyrill Stachniss Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1 Graph-Based SLAM Constraints connect the nodes through odometry and observations Robot pose Constraint 2 Graph-Based
L15. POSE-GRAPH SLAM. NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms
 L15. POSE-GRAPH SLAM NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Today s Topic Nonlinear Least Squares Pose-Graph SLAM Incremental Smoothing and Mapping Feature-Based SLAM Filtering Problem: Motion Prediction
L15. POSE-GRAPH SLAM NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Today s Topic Nonlinear Least Squares Pose-Graph SLAM Incremental Smoothing and Mapping Feature-Based SLAM Filtering Problem: Motion Prediction
Humanoid Robotics. Least Squares. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Least Squares Maren Bennewitz Goal of This Lecture Introduction into least squares Use it yourself for odometry calibration, later in the lecture: camera and whole-body self-calibration
Humanoid Robotics Least Squares Maren Bennewitz Goal of This Lecture Introduction into least squares Use it yourself for odometry calibration, later in the lecture: camera and whole-body self-calibration
Robot Mapping. A Short Introduction to the Bayes Filter and Related Models. Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard
 Robot Mapping A Short Introduction to the Bayes Filter and Related Models Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Recursive
Robot Mapping A Short Introduction to the Bayes Filter and Related Models Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Recursive
g2o: A General Framework for Graph Optimization Rainer Kümmerle Giorgio Grisetti Hauke Strasdat Kurt Konolige Wolfram Burgard
 g2o: A General Framework for Graph Optimization Rainer Kümmerle Giorgio Grisetti Hauke Strasdat Kurt Konolige Wolfram Burgard Graph-Based SLAM Constraints connect the poses of the robot while it is moving
g2o: A General Framework for Graph Optimization Rainer Kümmerle Giorgio Grisetti Hauke Strasdat Kurt Konolige Wolfram Burgard Graph-Based SLAM Constraints connect the poses of the robot while it is moving
Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15) Robot Mapping. Hierarchical Pose-Graphs for Online Mapping. Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15) Graph-Based SLAM (Chap.
 Robot Mapping Hierarchical Pose-Graphs for Online Mapping Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15)! Constraints connect the poses of the robot while it is moving! Constraints are inherently uncertain Cyrill Stachniss
Robot Mapping Hierarchical Pose-Graphs for Online Mapping Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15)! Constraints connect the poses of the robot while it is moving! Constraints are inherently uncertain Cyrill Stachniss
L10. PARTICLE FILTERING CONTINUED. NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms
 L10. PARTICLE FILTERING CONTINUED NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Gaussian Filters The Kalman filter and its variants can only model (unimodal) Gaussian distributions Courtesy: K. Arras Motivation
L10. PARTICLE FILTERING CONTINUED NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Gaussian Filters The Kalman filter and its variants can only model (unimodal) Gaussian distributions Courtesy: K. Arras Motivation
SLAM with SIFT (aka Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping with Uncertainty using Scale-Invariant Visual Landmarks ) Se, Lowe, and Little
 SLAM with SIFT (aka Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping with Uncertainty using Scale-Invariant Visual Landmarks ) Se, Lowe, and Little + Presented by Matt Loper CS296-3: Robot Learning and Autonomy Brown
SLAM with SIFT (aka Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping with Uncertainty using Scale-Invariant Visual Landmarks ) Se, Lowe, and Little + Presented by Matt Loper CS296-3: Robot Learning and Autonomy Brown
Robot Mapping. Grid Maps. Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard
 Robot Mapping Grid Maps Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 Features vs. Volumetric Maps Courtesy: D. Hähnel Courtesy: E. Nebot 2 Features So far, we only used feature maps Natural choice for Kalman
Robot Mapping Grid Maps Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 Features vs. Volumetric Maps Courtesy: D. Hähnel Courtesy: E. Nebot 2 Features So far, we only used feature maps Natural choice for Kalman
L17. OCCUPANCY MAPS. NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms
 L17. OCCUPANCY MAPS NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Today s Topic Why Occupancy Maps? Bayes Binary Filters Log-odds Occupancy Maps Inverse sensor model Learning inverse sensor model ML map
L17. OCCUPANCY MAPS NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Today s Topic Why Occupancy Maps? Bayes Binary Filters Log-odds Occupancy Maps Inverse sensor model Learning inverse sensor model ML map
Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Landmark-based FastSLAM
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Landmark-based FastSLAM Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello Partial slide courtesy of Mike Montemerlo 1 The SLAM Problem
Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Landmark-based FastSLAM Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello Partial slide courtesy of Mike Montemerlo 1 The SLAM Problem
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering. ROB501H1 F: Computer Vision for Robotics. Midterm Examination.
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering ROB501H1 F: Computer Vision for Robotics October 26, 2016 Student Name: Student Number: Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. The value
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering ROB501H1 F: Computer Vision for Robotics October 26, 2016 Student Name: Student Number: Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. The value
Experimental Analysis of Dynamic Covariance Scaling for Robust Map Optimization Under Bad Initial Estimates
 Experimental Analysis of Dynamic Covariance Scaling for Robust Map Optimization Under Bad Initial Estimates Pratik Agarwal Giorgio Grisetti Gian Diego Tipaldi Luciano Spinello Wolfram Burgard Cyrill Stachniss
Experimental Analysis of Dynamic Covariance Scaling for Robust Map Optimization Under Bad Initial Estimates Pratik Agarwal Giorgio Grisetti Gian Diego Tipaldi Luciano Spinello Wolfram Burgard Cyrill Stachniss
L12. EKF-SLAM: PART II. NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms
 L12. EKF-SLAM: PART II NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Today s Lecture Feature-based EKF-SLAM Review Data Association Configuration Space Incremental ML (i.e., Nearest Neighbor) Joint Compatibility
L12. EKF-SLAM: PART II NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Today s Lecture Feature-based EKF-SLAM Review Data Association Configuration Space Incremental ML (i.e., Nearest Neighbor) Joint Compatibility
ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter
 ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Siwei Guo: s9guo@eng.ucsd.edu
ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Siwei Guo: s9guo@eng.ucsd.edu
Robot Mapping. TORO Gradient Descent for SLAM. Cyrill Stachniss
 Robot Mapping TORO Gradient Descent for SLAM Cyrill Stachniss 1 Stochastic Gradient Descent Minimize the error individually for each constraint (decomposition of the problem into sub-problems) Solve one
Robot Mapping TORO Gradient Descent for SLAM Cyrill Stachniss 1 Stochastic Gradient Descent Minimize the error individually for each constraint (decomposition of the problem into sub-problems) Solve one
ME 456: Probabilistic Robotics
 ME 456: Probabilistic Robotics Week 5, Lecture 2 SLAM Reading: Chapters 10,13 HW 2 due Oct 30, 11:59 PM Introduction In state esemaeon and Bayes filter lectures, we showed how to find robot s pose based
ME 456: Probabilistic Robotics Week 5, Lecture 2 SLAM Reading: Chapters 10,13 HW 2 due Oct 30, 11:59 PM Introduction In state esemaeon and Bayes filter lectures, we showed how to find robot s pose based
Robot Mapping. Hierarchical Pose-Graphs for Online Mapping. Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard
 Robot Mapping Hierarchical Pose-Graphs for Online Mapping Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 Graph-Based SLAM Measurements connect the poses of the robot while it is moving Measurements are inherently
Robot Mapping Hierarchical Pose-Graphs for Online Mapping Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 Graph-Based SLAM Measurements connect the poses of the robot while it is moving Measurements are inherently
From Least-Squares to ICP
 From Least-Squares to ICP Giorgio Grisetti grisetti@dis.uniroma1.it Dept of Computer Control and Management Engineering Sapienza University of Rome Special thanks to Ulrich Wollath for reporting errors
From Least-Squares to ICP Giorgio Grisetti grisetti@dis.uniroma1.it Dept of Computer Control and Management Engineering Sapienza University of Rome Special thanks to Ulrich Wollath for reporting errors
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Visual Bearing-Only Simultaneous Localization and Mapping with Improved Feature Matching
 Visual Bearing-Only Simultaneous Localization and Mapping with Improved Feature Matching Hauke Strasdat, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, and Wolfram Burgard Computer Science Institute, University of
Visual Bearing-Only Simultaneous Localization and Mapping with Improved Feature Matching Hauke Strasdat, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, and Wolfram Burgard Computer Science Institute, University of
Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview
 Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview Arun Das 05/09/2017 Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous Vehicles Lab Introduction What s in a name? Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous
Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview Arun Das 05/09/2017 Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous Vehicles Lab Introduction What s in a name? Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous
Particle Filter in Brief. Robot Mapping. FastSLAM Feature-based SLAM with Particle Filters. Particle Representation. Particle Filter Algorithm
 Robot Mapping FastSLAM Feature-based SLAM with Particle Filters Cyrill Stachniss Particle Filter in Brief! Non-parametric, recursive Bayes filter! Posterior is represented by a set of weighted samples!
Robot Mapping FastSLAM Feature-based SLAM with Particle Filters Cyrill Stachniss Particle Filter in Brief! Non-parametric, recursive Bayes filter! Posterior is represented by a set of weighted samples!
Final project: 45% of the grade, 10% presentation, 35% write-up. Presentations: in lecture Dec 1 and schedule:
 Announcements PS2: due Friday 23:59pm. Final project: 45% of the grade, 10% presentation, 35% write-up Presentations: in lecture Dec 1 and 3 --- schedule: CS 287: Advanced Robotics Fall 2009 Lecture 24:
Announcements PS2: due Friday 23:59pm. Final project: 45% of the grade, 10% presentation, 35% write-up Presentations: in lecture Dec 1 and 3 --- schedule: CS 287: Advanced Robotics Fall 2009 Lecture 24:
Today MAPS AND MAPPING. Features. process of creating maps. More likely features are things that can be extracted from images:
 MAPS AND MAPPING Features In the first class we said that navigation begins with what the robot can see. There are several forms this might take, but it will depend on: What sensors the robot has What
MAPS AND MAPPING Features In the first class we said that navigation begins with what the robot can see. There are several forms this might take, but it will depend on: What sensors the robot has What
Announcements. Recap Landmark based SLAM. Types of SLAM-Problems. Occupancy Grid Maps. Grid-based SLAM. Page 1. CS 287: Advanced Robotics Fall 2009
 Announcements PS2: due Friday 23:59pm. Final project: 45% of the grade, 10% presentation, 35% write-up Presentations: in lecture Dec 1 and 3 --- schedule: CS 287: Advanced Robotics Fall 2009 Lecture 24:
Announcements PS2: due Friday 23:59pm. Final project: 45% of the grade, 10% presentation, 35% write-up Presentations: in lecture Dec 1 and 3 --- schedule: CS 287: Advanced Robotics Fall 2009 Lecture 24:
Humanoid Robotics. Monte Carlo Localization. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Monte Carlo Localization Maren Bennewitz 1 Basis Probability Rules (1) If x and y are independent: Bayes rule: Often written as: The denominator is a normalizing constant that ensures
Humanoid Robotics Monte Carlo Localization Maren Bennewitz 1 Basis Probability Rules (1) If x and y are independent: Bayes rule: Often written as: The denominator is a normalizing constant that ensures
360 Full View Spherical Mosaic
 360 Full View Spherical Mosaic Huang Wenfan Huang Yehui Rong Nan U017865B U017844X U018274R Objective Full spherical mosaic 360 x 180. All images are taken with camera mounted on a tripod. Registration
360 Full View Spherical Mosaic Huang Wenfan Huang Yehui Rong Nan U017865B U017844X U018274R Objective Full spherical mosaic 360 x 180. All images are taken with camera mounted on a tripod. Registration
Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Grid-based FastSLAM. Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Grid-based FastSLAM Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello 1 The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization
Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Grid-based FastSLAM Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello 1 The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization
IROS 05 Tutorial. MCL: Global Localization (Sonar) Monte-Carlo Localization. Particle Filters. Rao-Blackwellized Particle Filters and Loop Closing
 IROS 05 Tutorial SLAM - Getting it Working in Real World Applications Rao-Blackwellized Particle Filters and Loop Closing Cyrill Stachniss and Wolfram Burgard University of Freiburg, Dept. of Computer
IROS 05 Tutorial SLAM - Getting it Working in Real World Applications Rao-Blackwellized Particle Filters and Loop Closing Cyrill Stachniss and Wolfram Burgard University of Freiburg, Dept. of Computer
First scan matching algorithms. Alberto Quattrini Li University of South Carolina
 First scan matching algorithms Alberto Quattrini Li 2015-10-22 University of South Carolina Robot mapping through scan-matching Framework for consistent registration of multiple frames of measurements
First scan matching algorithms Alberto Quattrini Li 2015-10-22 University of South Carolina Robot mapping through scan-matching Framework for consistent registration of multiple frames of measurements
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision
 CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 10 Class 2: Visual Odometry November 2nd, 2017 Today Visual Odometry Intro Algorithm SLAM Visual Odometry Input Output Images, Video Camera trajectory, motion
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 10 Class 2: Visual Odometry November 2nd, 2017 Today Visual Odometry Intro Algorithm SLAM Visual Odometry Input Output Images, Video Camera trajectory, motion
Probabilistic Robotics
 Probabilistic Robotics FastSLAM Sebastian Thrun (abridged and adapted by Rodrigo Ventura in Oct-2008) The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization and mapping The task of building a map while
Probabilistic Robotics FastSLAM Sebastian Thrun (abridged and adapted by Rodrigo Ventura in Oct-2008) The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization and mapping The task of building a map while
Practical Course WS 2010 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
 Practical Course WS 2010 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Cyrill Stachniss University of Freiburg, Germany Topics of this Course SLAM - simultaneous localization and mapping What does the world look
Practical Course WS 2010 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Cyrill Stachniss University of Freiburg, Germany Topics of this Course SLAM - simultaneous localization and mapping What does the world look
(W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202)
 2016 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Schedule of Events Week Date Lecture (W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202) 1 27-Jul Introduction 2 Representing Position
2016 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Schedule of Events Week Date Lecture (W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202) 1 27-Jul Introduction 2 Representing Position
Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization
 Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization Cyrill Stachniss and Luciano Spinello 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Bayes Filter
Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization Cyrill Stachniss and Luciano Spinello 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Bayes Filter
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)
 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Lecture 16 April 8, 2013 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time series of
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Lecture 16 April 8, 2013 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time series of
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
 Sebastian Lembcke SLAM 1 / 29 MIN Faculty Department of Informatics Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Visual Loop-Closure Detection University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural
Sebastian Lembcke SLAM 1 / 29 MIN Faculty Department of Informatics Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Visual Loop-Closure Detection University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural
Lecture 20: The Spatial Semantic Hierarchy. What is a Map?
 Lecture 20: The Spatial Semantic Hierarchy CS 344R/393R: Robotics Benjamin Kuipers What is a Map? A map is a model of an environment that helps an agent plan and take action. A topological map is useful
Lecture 20: The Spatial Semantic Hierarchy CS 344R/393R: Robotics Benjamin Kuipers What is a Map? A map is a model of an environment that helps an agent plan and take action. A topological map is useful
Robotic Perception and Action: Vehicle SLAM Assignment
 Robotic Perception and Action: Vehicle SLAM Assignment Mariolino De Cecco Mariolino De Cecco, Mattia Tavernini 1 CONTENTS Vehicle SLAM Assignment Contents Assignment Scenario 3 Odometry Localization...........................................
Robotic Perception and Action: Vehicle SLAM Assignment Mariolino De Cecco Mariolino De Cecco, Mattia Tavernini 1 CONTENTS Vehicle SLAM Assignment Contents Assignment Scenario 3 Odometry Localization...........................................
CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment. Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018
 CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018 Lecture Overview Dense Feature Correspondences Bundle Adjustment in Structure-from-Motion Image Matching Algorithm
CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018 Lecture Overview Dense Feature Correspondences Bundle Adjustment in Structure-from-Motion Image Matching Algorithm
Simultaneous Localization
 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed
Introduction to Mobile Robotics. SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping The SLAM Problem SLAM is the process by which a robot builds a map of the environment and, at the same time, uses this map to
Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping The SLAM Problem SLAM is the process by which a robot builds a map of the environment and, at the same time, uses this map to
Colorado School of Mines. Computer Vision. Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science.
 Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Bundle Adjustment 2 Example Application A vehicle needs to map its environment that it is moving
Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Bundle Adjustment 2 Example Application A vehicle needs to map its environment that it is moving
Mobile Robotics. Mathematics, Models, and Methods. HI Cambridge. Alonzo Kelly. Carnegie Mellon University UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Evaluation of Pose Only SLAM
 The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Evaluation of Pose Only SLAM Gibson Hu, Shoudong Huang and Gamini Dissanayake Abstract In
The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Evaluation of Pose Only SLAM Gibson Hu, Shoudong Huang and Gamini Dissanayake Abstract In
Localization, Where am I?
 5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
Dynamic Covariance Scaling for Robust Map Optimization
 Dynamic Covariance Scaling for Robust Map Optimization Gian Diego Tipaldi Luciano Spinello Cyrill Stachniss Wolfram Burgard Simulated Stereo (bad initial estimate) Manhattan35 (1 outliers) Sphere25 (1
Dynamic Covariance Scaling for Robust Map Optimization Gian Diego Tipaldi Luciano Spinello Cyrill Stachniss Wolfram Burgard Simulated Stereo (bad initial estimate) Manhattan35 (1 outliers) Sphere25 (1
Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3
 Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3 Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland January 28, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) Kinematics of
Unit 2: Locomotion Kinematics of Wheeled Robots: Part 3 Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland January 28, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) Kinematics of
Hartley - Zisserman reading club. Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: Presented by Daniel Fontijne
 Hartley - Zisserman reading club Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Iterative estimation methods Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: A Flexible New Technique for Camera Calibration Presented by Daniel Fontijne
Hartley - Zisserman reading club Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Iterative estimation methods Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: A Flexible New Technique for Camera Calibration Presented by Daniel Fontijne
TORO - Efficient Constraint Network Optimization for SLAM
 TORO - Efficient Constraint Network Optimization for SLAM Cyrill Stachniss Joint work with Giorgio Grisetti and Wolfram Burgard Special thanks to and partial slide courtesy of: Diego Tipaldi, Edwin Olson,
TORO - Efficient Constraint Network Optimization for SLAM Cyrill Stachniss Joint work with Giorgio Grisetti and Wolfram Burgard Special thanks to and partial slide courtesy of: Diego Tipaldi, Edwin Olson,
Rigid Body Transformations
 F1/10 th Racing Rigid Body Transformations (Or How Different sensors see the same world) By, Paritosh Kelkar Mapping the surroundings Specify destination and generate path to goal The colored cells represent
F1/10 th Racing Rigid Body Transformations (Or How Different sensors see the same world) By, Paritosh Kelkar Mapping the surroundings Specify destination and generate path to goal The colored cells represent
Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects
 Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
g 2 o: A General Framework for Graph Optimization
 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Shanghai International Conference Center May 9-13, 2011, Shanghai, China g 2 o: A General Framework for Graph Optimization Rainer Kümmerle
2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Shanghai International Conference Center May 9-13, 2011, Shanghai, China g 2 o: A General Framework for Graph Optimization Rainer Kümmerle
Robot Mapping. A Short Introduction to Homogeneous Coordinates. Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard
 Robot Mapping A Short Introduction to Homogeneous Coordinates Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 Motivation Cameras generate a projected image of the world Euclidian geometry is suboptimal to describe
Robot Mapping A Short Introduction to Homogeneous Coordinates Gian Diego Tipaldi, Wolfram Burgard 1 Motivation Cameras generate a projected image of the world Euclidian geometry is suboptimal to describe
Probabilistic Robotics. FastSLAM
 Probabilistic Robotics FastSLAM The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization and mapping The task of building a map while estimating the pose of the robot relative to this map Why is SLAM
Probabilistic Robotics FastSLAM The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization and mapping The task of building a map while estimating the pose of the robot relative to this map Why is SLAM
Overview. Animation is a big topic We will concentrate on character animation as is used in many games today. humans, animals, monsters, robots, etc.
 ANIMATION Overview Animation is a big topic We will concentrate on character animation as is used in many games today humans, animals, monsters, robots, etc. Character Representation A character is represented
ANIMATION Overview Animation is a big topic We will concentrate on character animation as is used in many games today humans, animals, monsters, robots, etc. Character Representation A character is represented
Multiview Stereo COSC450. Lecture 8
 Multiview Stereo COSC450 Lecture 8 Stereo Vision So Far Stereo and epipolar geometry Fundamental matrix captures geometry 8-point algorithm Essential matrix with calibrated cameras 5-point algorithm Intersect
Multiview Stereo COSC450 Lecture 8 Stereo Vision So Far Stereo and epipolar geometry Fundamental matrix captures geometry 8-point algorithm Essential matrix with calibrated cameras 5-point algorithm Intersect
Perspective projection and Transformations
 Perspective projection and Transformations The pinhole camera The pinhole camera P = (X,,) p = (x,y) O λ = 0 Q λ = O λ = 1 Q λ = P =-1 Q λ X = 0 + λ X 0, 0 + λ 0, 0 + λ 0 = (λx, λ, λ) The pinhole camera
Perspective projection and Transformations The pinhole camera The pinhole camera P = (X,,) p = (x,y) O λ = 0 Q λ = O λ = 1 Q λ = P =-1 Q λ X = 0 + λ X 0, 0 + λ 0, 0 + λ 0 = (λx, λ, λ) The pinhole camera
Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features
 Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Presented by Adam Bickett
Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Presented by Adam Bickett
BBR Progress Report 006: Autonomous 2-D Mapping of a Building Floor
 BBR Progress Report 006: Autonomous 2-D Mapping of a Building Floor Andy Sayler & Constantin Berzan November 30, 2010 Abstract In the past two weeks, we implemented and tested landmark extraction based
BBR Progress Report 006: Autonomous 2-D Mapping of a Building Floor Andy Sayler & Constantin Berzan November 30, 2010 Abstract In the past two weeks, we implemented and tested landmark extraction based
Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM. Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology
 Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology Content Introduction to Problem (s) Localization A few basic equations Dead Reckoning
Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology Content Introduction to Problem (s) Localization A few basic equations Dead Reckoning
Announcements. Hough Transform [ Patented 1962 ] Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting. Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class
![Announcements. Hough Transform [ Patented 1962 ] Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting. Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class Announcements. Hough Transform [ Patented 1962 ] Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting. Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class](/thumbs/85/92905127.jpg) Announcements Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 11a What is region like if: 1. λ 1 = 0?
Announcements Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 11a What is region like if: 1. λ 1 = 0?
Computer Vision I - Algorithms and Applications: Multi-View 3D reconstruction
 Computer Vision I - Algorithms and Applications: Multi-View 3D reconstruction Carsten Rother 09/12/2013 Computer Vision I: Multi-View 3D reconstruction Roadmap this lecture Computer Vision I: Multi-View
Computer Vision I - Algorithms and Applications: Multi-View 3D reconstruction Carsten Rother 09/12/2013 Computer Vision I: Multi-View 3D reconstruction Roadmap this lecture Computer Vision I: Multi-View
Particle Filters. CSE-571 Probabilistic Robotics. Dependencies. Particle Filter Algorithm. Fast-SLAM Mapping
 CSE-571 Probabilistic Robotics Fast-SLAM Mapping Particle Filters Represent belief by random samples Estimation of non-gaussian, nonlinear processes Sampling Importance Resampling (SIR) principle Draw
CSE-571 Probabilistic Robotics Fast-SLAM Mapping Particle Filters Represent belief by random samples Estimation of non-gaussian, nonlinear processes Sampling Importance Resampling (SIR) principle Draw
Localization and Map Building
 Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Humanoid Robotics. Projective Geometry, Homogeneous Coordinates. (brief introduction) Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Projective Geometry, Homogeneous Coordinates (brief introduction) Maren Bennewitz Motivation Cameras generate a projected image of the 3D world In Euclidian geometry, the math for describing
Humanoid Robotics Projective Geometry, Homogeneous Coordinates (brief introduction) Maren Bennewitz Motivation Cameras generate a projected image of the 3D world In Euclidian geometry, the math for describing
DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING
 Inženýrská MECHANIKA, roč. 15, 2008, č. 5, s. 337 344 337 DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Jiří Krejsa, Stanislav Věchet* The paper presents Potential-Based
Inženýrská MECHANIKA, roč. 15, 2008, č. 5, s. 337 344 337 DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Jiří Krejsa, Stanislav Věchet* The paper presents Potential-Based
Computational Geometry TOPICS Preliminaries Point in a Polygon Polygon Construction Convex Hulls
 Computational Geometry TOPICS Preliminaries Point in a Polygon Polygon Construction Convex Hulls CSE5311 Kumar 1 Geometric Algorithms Geometric Algorithms find applications in such areas as Computer Graphics
Computational Geometry TOPICS Preliminaries Point in a Polygon Polygon Construction Convex Hulls CSE5311 Kumar 1 Geometric Algorithms Geometric Algorithms find applications in such areas as Computer Graphics
Probabilistic Robotics
 Probabilistic Robotics Bayes Filter Implementations Discrete filters, Particle filters Piecewise Constant Representation of belief 2 Discrete Bayes Filter Algorithm 1. Algorithm Discrete_Bayes_filter(
Probabilistic Robotics Bayes Filter Implementations Discrete filters, Particle filters Piecewise Constant Representation of belief 2 Discrete Bayes Filter Algorithm 1. Algorithm Discrete_Bayes_filter(
Probabilistic Robotics Course. Multi-Point Registration
 Probabilistic Robotics Course Multi-Point Registration Giorgio Grisetti grisetti@dis.uniroma1.it Dept of Computer Control and Management Engineering Sapienza University of Rome Problem Definition The environment
Probabilistic Robotics Course Multi-Point Registration Giorgio Grisetti grisetti@dis.uniroma1.it Dept of Computer Control and Management Engineering Sapienza University of Rome Problem Definition The environment
Epipolar Geometry Prof. D. Stricker. With slides from A. Zisserman, S. Lazebnik, Seitz
 Epipolar Geometry Prof. D. Stricker With slides from A. Zisserman, S. Lazebnik, Seitz 1 Outline 1. Short introduction: points and lines 2. Two views geometry: Epipolar geometry Relation point/line in two
Epipolar Geometry Prof. D. Stricker With slides from A. Zisserman, S. Lazebnik, Seitz 1 Outline 1. Short introduction: points and lines 2. Two views geometry: Epipolar geometry Relation point/line in two
LOAM: LiDAR Odometry and Mapping in Real Time
 LOAM: LiDAR Odometry and Mapping in Real Time Aayush Dwivedi (14006), Akshay Sharma (14062), Mandeep Singh (14363) Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur 1 Abstract This project deals with online simultaneous
LOAM: LiDAR Odometry and Mapping in Real Time Aayush Dwivedi (14006), Akshay Sharma (14062), Mandeep Singh (14363) Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur 1 Abstract This project deals with online simultaneous
EKF Localization and EKF SLAM incorporating prior information
 EKF Localization and EKF SLAM incorporating prior information Final Report ME- Samuel Castaneda ID: 113155 1. Abstract In the context of mobile robotics, before any motion planning or navigation algorithm
EKF Localization and EKF SLAM incorporating prior information Final Report ME- Samuel Castaneda ID: 113155 1. Abstract In the context of mobile robotics, before any motion planning or navigation algorithm
Robot Programming with Lisp
 7. Coordinate Transformations, TF, ActionLib Institute for Artificial University of Bremen Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 2 Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 3 Poses in 3D
7. Coordinate Transformations, TF, ActionLib Institute for Artificial University of Bremen Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 2 Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 3 Poses in 3D
COS429: COMPUTER VISON CAMERAS AND PROJECTIONS (2 lectures)
 COS429: COMPUTER VISON CMERS ND PROJECTIONS (2 lectures) Pinhole cameras Camera with lenses Sensing nalytical Euclidean geometry The intrinsic parameters of a camera The extrinsic parameters of a camera
COS429: COMPUTER VISON CMERS ND PROJECTIONS (2 lectures) Pinhole cameras Camera with lenses Sensing nalytical Euclidean geometry The intrinsic parameters of a camera The extrinsic parameters of a camera
3D Scanning. Lecture courtesy of Szymon Rusinkiewicz Princeton University
 3D Scanning Lecture courtesy of Szymon Rusinkiewicz Princeton University Computer Graphics Pipeline 3D Scanning Shape Motion Rendering Lighting and Reflectance Human time = expensive Sensors = cheap Computer
3D Scanning Lecture courtesy of Szymon Rusinkiewicz Princeton University Computer Graphics Pipeline 3D Scanning Shape Motion Rendering Lighting and Reflectance Human time = expensive Sensors = cheap Computer
CVPR 2014 Visual SLAM Tutorial Efficient Inference
 CVPR 2014 Visual SLAM Tutorial Efficient Inference kaess@cmu.edu The Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University The Mapping Problem (t=0) Robot Landmark Measurement Onboard sensors: Wheel odometry Inertial
CVPR 2014 Visual SLAM Tutorial Efficient Inference kaess@cmu.edu The Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University The Mapping Problem (t=0) Robot Landmark Measurement Onboard sensors: Wheel odometry Inertial
Bundle Adjustment. Frank Dellaert CVPR 2014 Visual SLAM Tutorial
 Bundle Adjustment Frank Dellaert CVPR 2014 Visual SLAM Tutorial Mo@va@on VO: just two frames - > R,t using 5- pt or 3- pt Can we do bener? SFM, SLAM - > VSLAM Later: integrate IMU, other sensors Objec@ve
Bundle Adjustment Frank Dellaert CVPR 2014 Visual SLAM Tutorial Mo@va@on VO: just two frames - > R,t using 5- pt or 3- pt Can we do bener? SFM, SLAM - > VSLAM Later: integrate IMU, other sensors Objec@ve
User Activity Recognition Based on Kalman Filtering Approach
 User Activity Recognition Based on Kalman Filtering Approach EEC 592, Prosthesis Design and Control Final Project Report Gholamreza Khademi khademi.gh@gmail.com December 2, 214 Abstract Different control
User Activity Recognition Based on Kalman Filtering Approach EEC 592, Prosthesis Design and Control Final Project Report Gholamreza Khademi khademi.gh@gmail.com December 2, 214 Abstract Different control
Topological Mapping. Discrete Bayes Filter
 Topological Mapping Discrete Bayes Filter Vision Based Localization Given a image(s) acquired by moving camera determine the robot s location and pose? Towards localization without odometry What can be
Topological Mapping Discrete Bayes Filter Vision Based Localization Given a image(s) acquired by moving camera determine the robot s location and pose? Towards localization without odometry What can be
Homework #1. Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical modeling, Projections
 Computer Graphics Instructor: rian Curless CSEP 557 Winter 213 Homework #1 Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical modeling, Projections Assigned: Tuesday, January 22 nd Due: Tuesday,
Computer Graphics Instructor: rian Curless CSEP 557 Winter 213 Homework #1 Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical modeling, Projections Assigned: Tuesday, January 22 nd Due: Tuesday,
CS6200 Information Retreival. The WebGraph. July 13, 2015
 CS6200 Information Retreival The WebGraph The WebGraph July 13, 2015 1 Web Graph: pages and links The WebGraph describes the directed links between pages of the World Wide Web. A directed edge connects
CS6200 Information Retreival The WebGraph The WebGraph July 13, 2015 1 Web Graph: pages and links The WebGraph describes the directed links between pages of the World Wide Web. A directed edge connects
Graph-Based SLAM and Open Source Tools. Giorgio Grisetti
 Graph-Based SLAM and Open Source Tools Giorgio Grisetti SLAM SLAM= Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Estimate: the map of the environment the trajectory of a moving device using a sequence of sensor
Graph-Based SLAM and Open Source Tools Giorgio Grisetti SLAM SLAM= Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Estimate: the map of the environment the trajectory of a moving device using a sequence of sensor
Camera Calibration. COS 429 Princeton University
 Camera Calibration COS 429 Princeton University Point Correspondences What can you figure out from point correspondences? Noah Snavely Point Correspondences X 1 X 4 X 3 X 2 X 5 X 6 X 7 p 1,1 p 1,2 p 1,3
Camera Calibration COS 429 Princeton University Point Correspondences What can you figure out from point correspondences? Noah Snavely Point Correspondences X 1 X 4 X 3 X 2 X 5 X 6 X 7 p 1,1 p 1,2 p 1,3
EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 3
 EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 3 Welcome Dr. Ahmad Kamal Nasir Today s Objectives Motion Models Velocity based model (Dead-Reckoning) Odometry based model (Wheel Encoders) Sensor Models Beam model of range
EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 3 Welcome Dr. Ahmad Kamal Nasir Today s Objectives Motion Models Velocity based model (Dead-Reckoning) Odometry based model (Wheel Encoders) Sensor Models Beam model of range
Dealing with Scale. Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech
 Dealing with Scale Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech Stephan.Weiss@ieee.org (c) 2013. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Outline Why care about size? The IMU as scale provider: The
Dealing with Scale Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech Stephan.Weiss@ieee.org (c) 2013. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Outline Why care about size? The IMU as scale provider: The
Rational Trigonometry Applied to Robotics
 Robot Kinematic Modeling using Rational Trigonometry 6 de Novembro de 2007 Overview Overview 1 Overview 2 3 The Fixed Frames Model for Robot Kinematics 4 Conclusions 4 Perspectives and Future Work 5 Q&A
Robot Kinematic Modeling using Rational Trigonometry 6 de Novembro de 2007 Overview Overview 1 Overview 2 3 The Fixed Frames Model for Robot Kinematics 4 Conclusions 4 Perspectives and Future Work 5 Q&A
Appendix C Mathcad Tutorial
 Appendix C Mathcad Tutorial The following tutorial was extracted from Mathcad ver. 11. (with permission). The areas covered include fundamental math operations (Figs. C.1-C.16), plotting (Figs. C.17-C.18),
Appendix C Mathcad Tutorial The following tutorial was extracted from Mathcad ver. 11. (with permission). The areas covered include fundamental math operations (Figs. C.1-C.16), plotting (Figs. C.17-C.18),
Robot Localization based on Geo-referenced Images and G raphic Methods
 Robot Localization based on Geo-referenced Images and G raphic Methods Sid Ahmed Berrabah Mechanical Department, Royal Military School, Belgium, sidahmed.berrabah@rma.ac.be Janusz Bedkowski, Łukasz Lubasiński,
Robot Localization based on Geo-referenced Images and G raphic Methods Sid Ahmed Berrabah Mechanical Department, Royal Military School, Belgium, sidahmed.berrabah@rma.ac.be Janusz Bedkowski, Łukasz Lubasiński,
Humanoid Robotics. Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning Maren Bennewitz 1 Motivation Plan a sequence of configurations (vector of joint angle values) that let the robot move from its current
Humanoid Robotics Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning Maren Bennewitz 1 Motivation Plan a sequence of configurations (vector of joint angle values) that let the robot move from its current
Survey: Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM) Ronja Güldenring Master Informatics Project Intellgient Robotics University of Hamburg
 Survey: Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM) Ronja Güldenring Master Informatics Project Intellgient Robotics University of Hamburg Introduction EKF-SLAM FastSLAM Loop Closure 01.06.17 Ronja Güldenring
Survey: Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM) Ronja Güldenring Master Informatics Project Intellgient Robotics University of Hamburg Introduction EKF-SLAM FastSLAM Loop Closure 01.06.17 Ronja Güldenring
Humanoid Robotics. Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning Maren Bennewitz 1 Motivation Planning for object manipulation Whole-body motion to reach a desired goal configuration Generate a sequence
Humanoid Robotics Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning Maren Bennewitz 1 Motivation Planning for object manipulation Whole-body motion to reach a desired goal configuration Generate a sequence
