NONUNIFORM FLOW AND PROFILES. Nonuniform flow varies in depth along the channel reach. Figure 1 Nonuniform Flow
|
|
|
- Avis Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nonuniorm Flow and Proiles Page 1 NONUNIFORM FLOW AND PROFILES Nonuniorm Flow Nonuniorm low varies in depth along the channel reach. Figure 1 Nonuniorm Flow Most lows are nonuniorm because Most channels are non-prismatic. Storm sewers are non-prismatic due to the presence o manholes and changes in pipe diameter, slope and direction. Flow may be nonuniorm in a prismatic channel due the inluence o a control, e.g., backwater created by a high tailwater depth or drawdown at a ree overall. Control A control is a channel eature, usually structural, where there is a unique (one-to-one) relationship between depth and discharge. A control regulates (controls) the state o low. Examples: Free overall at the end o a mild channel Weirs, Flumes (critical controls) Ininitely long prismatic channel (control reach) Subcritical low is controlled by downstream conditions. Supercritical low is controlled by upstream conditions. Channel Classiication Channel bed slopes are classiied hydraulically as mild, steep, critical, horizontal, and adverse. A channel bed slope may classiy as mild or one low rate and steep or another. The classiication is based on the relationship between the normal depth o low, y n, and the critical depth o low, y c, or a given lowrate. ECIV 36 Introduction to Water Resources Engineering
2 Nonuniorm Flow and Proiles Page The bed slope is called: Mild i y n >y c Steep i y c >y n Critical i y n y c Flow Proiles Depending on the relationship between y n and y c, there can be three zones where y(x) occurs. Figure Flow Proile Zones on a Mild Channel I y(x)>y n, then the low proile exists in Zone 1. In other words, the actual depth o low, y(x), is greater than y n and occurs in Zone 1. I y n >y(x)>y c, then the low proile exists in Zone. I y c >y(x), then the low proile exists in Zone 3. Flow proiles are identiied using a two-character label. The irst is an alpha character that identiies the type o channel slope (e.g., M or mild, S or steep). The second is a numeric character that identiies the zone (e.g., 1, or 3). For a hydraulically mild channel: I y(x)>y n, the proile exists in Zone 1, and is an M1 proile. I y n >y(x)>y c, the proile exists in Zone, and is an M proile. I y c >y(x), the proile exists in Zone 3, and is an M3 proile. Zone 1 low proiles are known as backwater proiles because the water "backs-up" due to a downstream control that restricts the outlow and orces the water to pond to a greater depth to "push" the low through/past the control. Zone proiles are known as drawdown or rontwater (HMI, et al., 004) curves. ECIV 36 Introduction to Water Resources Engineering
3 Nonuniorm Flow and Proiles Page 3 Figure 3 Mild Channel Proiles Figure 4 Steep Channel Proiles Flow Proile Analysis The change in depth in nonuniorm low is known as the low proile and is determined mathematically by low proile analysis. Calculations involve solving the energy equation at dierent points along the proile. Flow proile analysis is used in storm sewer design when determining the hydraulic grade line (FHWA, 1996). Theory Consider the deinition igure or nonuniorm low in an open channel (Figure 5). Applying energy conservation between sections 1 and gives EGL 1 EGL + h where EGL 1 is the total energy at section 1, EGL is the total energy at section, and h is energy lost to riction between 1 and. Rewrite the energy equation in terms o speciic energy E 1 + z1 E + z + h ECIV 36 Introduction to Water Resources Engineering
4 Nonuniorm Flow and Proiles Page 4 Figure 5 Deinition Figure The dierence in elevation heads is product o channel bed slope, S o, and reach length, Δx. z1 z So Δx and h is the product o riction slope, S, and reach length. h S Δ S is the slope o the energy grade line. Ater substitution, x ( S S ) x E - E1 o Δ Dividing both sides by Δx, we get E E 1 S 0 S Δx Because speciic energy is evaluated at both ends o a channel reach (Δx), convention is to evaluate the riction slope term at both ends o the reach to approximate the average riction slope over the reach. E E 1 S S o Δ x in which S 1 + S S where S 1 is the riction slope evaluated at 1 and S is the riction slope evaluated at. We use Manning's equation to approximate S. Simply substitute S or S o and solve or S. S Q n.1 A R n A Q R (English ) (SI) ECIV 36 Introduction to Water Resources Engineering
5 Nonuniorm Flow and Proiles Page 5 Solution Methods Most low proile analysis programs use numerical solution techniques. Two methods are commonly used: (1) Direct Step Method and () Standard Step Method. Direct Step Method Involves an explicit (direct) numerical solution o the energy equation. Applies only to prismatic channels. Involves solving or the position (xlocation) o user speciied y-values along the low proile. Rule-o-thumb: Given y, ind x. Standard Step Method Involves an iterative numerical solution o the energy equation. Applies to any channel: natural, prismatic, etc. Involves solving or the depth at user speciied x-locations. Rule-o-thumb: Given x, ind y. Direct Step Procedure: Determine the design lowrate, Q, channel geometry and dimensions, bed slope, and Manning's n-value. Determine normal depth, y n, and critical depth, y c, or the design low. Classiy the channel bed slope. Channel is mild i y n >y c, steep i y c >y n, etc. Determine the location o the control and the depth o low at the control. For example, i you are dealing with a hydraulically mild storm sewer with a ree overall at the outlet, the low will pass through critical depth at the outlet, meaning the control is at the outlet. Classiy the proile type, e.g., M1, M, S1, etc. For the example, the upstream proile is an M or drawdown curve. Knowing the proile type and the depth at the control, establish the range o values or the depth proile, y(x). For the example, y c <y(x)<y n. Create a worktable (Example Problem in Unit on Storm Sewer Design). Starting at the control, speciy several y-values over the range determined in the previous step. Use a small increment between successive y-values near the control. A larger increment can be used arther rom the control. Note: I the low is subcritical, the control is downstream, and the proile is evaluated in the upstream direction, starting at the control. I the low is supercritical, the control is upstream, and the proile is evaluated in the downstream direction, starting at the control. Solve the energy equation between successive y-values to determine the distance, Δx, between them. Sum Δx values to determine the distance o each point rom the control. Plot y(x) versus x. This is the desired low proile. Standard Step Procedure: Determine the design lowrate, Q. Determine the channel x-sectional geometry, slope and Manning's n-value. ECIV 36 Introduction to Water Resources Engineering
6 Nonuniorm Flow and Proiles Page 6 I the channel is not prismatic, determine the cross-sectional geometry, dimensions and Manning's n-value at each cross-section where you desire the depth o low. Also, measure the distance o each x-section rom the control, and determine the bed slope between adjacent x-sections. Determine Δx between adjacent x-sections (known Δx values). Evaluate normal depth, y n, and critical depth, y c. I the channel is not prismatic, do this or each subreach, Δx. Classiy the channel bed slope. I the channel is not prismatic, to have one continuous proile type, all subreaches must have the same bed slope classiication; otherwise, multiple proiles exist. Determine the location and low depth at the control. Classiy the proile. Create a worktable. Starting at the control, choose a trial y value at the irst x-section rom the control. Solve the energy equation between the two x-sections to determine the distance, Δx, between them (predicted Δx). I the predicted Δx is suiciently close to the known Δx, the assumed y-value is good; otherwise, adjust the assumed y-value and repeat the process. Repeat the process or all sub-reaches. Plot y(x) versus x. This is the desired low proile. REFERENCES Federal Highway Administration (1996). Urban Drainage Design Manual, Hydraulic Engineering Circular No., Oice o Technology Applications, th Street SW, Washington, DC. Haestad Engineering Sta, Walski, T.M., Barnard, T.E., Durrans, S.R., and Meadows, M.E. (004). Computer Applications in Hydraulic Engineering, 6 th Edition, Haestad Press, Waterbury, CT, 375 p. ECIV 36 Introduction to Water Resources Engineering
GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW
 CVE 341 Water Resources Lecture Notes 5: (Chapter 14) GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW FLOW CLASSIFICATION Uniform (normal) flow: Depth is constant at every section along length of channel Non-uniform (varied) flow:
CVE 341 Water Resources Lecture Notes 5: (Chapter 14) GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW FLOW CLASSIFICATION Uniform (normal) flow: Depth is constant at every section along length of channel Non-uniform (varied) flow:
Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Rational Design
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA
 CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA CONTENTS 1. Flow Classification 2. Chezy s and Manning Equation 3. Specific Energy 4. Surface Water Profiles 5. Hydraulic Jump 6. HEC-RAS 7. HEC-HMS
CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA CONTENTS 1. Flow Classification 2. Chezy s and Manning Equation 3. Specific Energy 4. Surface Water Profiles 5. Hydraulic Jump 6. HEC-RAS 7. HEC-HMS
HEC-RAS. A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume)
 HEC-RAS A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume) HEC-RAS Hydraulic Engineering Center:River Analysis System 1-D step backwater model Utilizes energy equation to compute water surface elevation for
HEC-RAS A Tutorial (Model Development of a Small Flume) HEC-RAS Hydraulic Engineering Center:River Analysis System 1-D step backwater model Utilizes energy equation to compute water surface elevation for
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
Automating Hydraulic Analysis v 1.0.
 2011 Automating Hydraulic Analysis v 1.0. Basic tutorial and introduction Automating Hydraulic Analysis (AHYDRA) is a freeware application that automates some specific features of HEC RAS or other hydraulic
2011 Automating Hydraulic Analysis v 1.0. Basic tutorial and introduction Automating Hydraulic Analysis (AHYDRA) is a freeware application that automates some specific features of HEC RAS or other hydraulic
Peak Stormwater Engineering, LLC MEMORANDUM
 Peak Stormwater Engineering, LLC 922 Cypress Lane, Louisville, CO 80027 Tel: (720) 239-1151 Fax: (720) 239-1191 Email: drapp@peakstormwater.com MEMORANDUM Date: To: Holly Piza, UDFCD Ken MacKenzie, UDFCD
Peak Stormwater Engineering, LLC 922 Cypress Lane, Louisville, CO 80027 Tel: (720) 239-1151 Fax: (720) 239-1191 Email: drapp@peakstormwater.com MEMORANDUM Date: To: Holly Piza, UDFCD Ken MacKenzie, UDFCD
Required: 486DX-33, 8MB RAM, HDD w. 20 MB free, VGA, Win95. Recommended: Pentium 60, 16 MB RAM, SVGA, Win95 or NT
 Evaluation Form Evaluator Information Name: Jeff Hagan Date: Feb. 17, 2000 Software Information Title of Software: Purpose: Publisher: CulvertMaster Culvert Hydraulic Design Haestad Methods, Inc. Version:
Evaluation Form Evaluator Information Name: Jeff Hagan Date: Feb. 17, 2000 Software Information Title of Software: Purpose: Publisher: CulvertMaster Culvert Hydraulic Design Haestad Methods, Inc. Version:
Watershed Modeling Rational Method Interface. Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface Objectives Learn how to model urban areas using the Rational method, including how to compute rainfall intensity,
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface Objectives Learn how to model urban areas using the Rational method, including how to compute rainfall intensity,
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara. The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two
 41.4 Routing The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two problems, which may be considered jointly or seperately: 1. Determination of the outflow hydrograph from the
41.4 Routing The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two problems, which may be considered jointly or seperately: 1. Determination of the outflow hydrograph from the
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD Data Setup an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using CAD data with inlet and pipe information Objectives Learn to define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD Data Setup an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using CAD data with inlet and pipe information Objectives Learn to define
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW. An Introduction. -
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW An Introduction http://tsaad.utsi.edu - tsaad@utsi.edu OUTLINE General characteristics Surface Waves & Froude Number Effects Types of Channel flows The Hydraulic Jump Conclusion General
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW An Introduction http://tsaad.utsi.edu - tsaad@utsi.edu OUTLINE General characteristics Surface Waves & Froude Number Effects Types of Channel flows The Hydraulic Jump Conclusion General
Linear Routing: Floodrouting. HEC-RAS Introduction. Brays Bayou. Uniform Open Channel Flow. v = 1 n R2/3. S S.I. units
 Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
Prepared for CIVE 401 Hydraulic Engineering By Kennard Lai, Patrick Ndolo Goy & Dr. Pierre Julien Fall 2015
 Prepared for CIVE 401 Hydraulic Engineering By Kennard Lai, Patrick Ndolo Goy & Dr. Pierre Julien Fall 2015 Contents Introduction General Philosophy Overview of Capabilities Applications Computational
Prepared for CIVE 401 Hydraulic Engineering By Kennard Lai, Patrick Ndolo Goy & Dr. Pierre Julien Fall 2015 Contents Introduction General Philosophy Overview of Capabilities Applications Computational
The Graph of an Equation Graph the following by using a table of values and plotting points.
 Calculus Preparation - Section 1 Graphs and Models Success in math as well as Calculus is to use a multiple perspective -- graphical, analytical, and numerical. Thanks to Rene Descartes we can represent
Calculus Preparation - Section 1 Graphs and Models Success in math as well as Calculus is to use a multiple perspective -- graphical, analytical, and numerical. Thanks to Rene Descartes we can represent
Classwork 5 Using HEC-RAS for computing water surface profiles
 Classwork 5 Using HEC-RAS for computing water surface profiles (in collaboration with Dr. Ing. Luca Milanesi) Why classwork 5? This lecture will give us the possibility to make our first acquaintance with
Classwork 5 Using HEC-RAS for computing water surface profiles (in collaboration with Dr. Ing. Luca Milanesi) Why classwork 5? This lecture will give us the possibility to make our first acquaintance with
Gavin Fields Senior Water Resources Engineer XP Solutions
 Hydraulics 101 Gavin Fields Senior Water Resources Engineer XP Solutions Hydraulics 101 Introduction Structures Hydraulic Model Building Q&A XP Solutions Software for modeling wastewater, stormwater, and
Hydraulics 101 Gavin Fields Senior Water Resources Engineer XP Solutions Hydraulics 101 Introduction Structures Hydraulic Model Building Q&A XP Solutions Software for modeling wastewater, stormwater, and
Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2
 Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2 H.1 Ditch Design... 2 H.1.1 Introduction... 2 H.1.2 Link/Ditch Configuration... 2 H.2 Lab 19: Ditch Design... 3 H.2.1 Introduction...
Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2 H.1 Ditch Design... 2 H.1.1 Introduction... 2 H.1.2 Link/Ditch Configuration... 2 H.2 Lab 19: Ditch Design... 3 H.2.1 Introduction...
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define a basic MODRAT model using
Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files
 WMS 10.1 Tutorial v. 10.1 Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files Set up an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using common file types such
WMS 10.1 Tutorial v. 10.1 Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files Set up an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using common file types such
FLOODPLAIN MODELING MANUAL. HEC-RAS Procedures for HEC-2 Modelers
 FLOODPLAIN MODELING MANUAL HEC-RAS Procedures for HEC-2 Modelers Federal Emergency Management Agency Mitigation Directorate 500 C Street, SW Washington, DC 20472 April 2002 Floodplain Modeling Manual HEC-RAS
FLOODPLAIN MODELING MANUAL HEC-RAS Procedures for HEC-2 Modelers Federal Emergency Management Agency Mitigation Directorate 500 C Street, SW Washington, DC 20472 April 2002 Floodplain Modeling Manual HEC-RAS
Culvert Studio User's Guide
 Culvert Studio User's Guide 2 Culvert Studio Table of Contents Foreword 0 Part I Introduction 5 1 Installing... and Activating 6 2 Getting... Updates 7 3 About... This Guide 7 Part II Overview 9 1 The
Culvert Studio User's Guide 2 Culvert Studio Table of Contents Foreword 0 Part I Introduction 5 1 Installing... and Activating 6 2 Getting... Updates 7 3 About... This Guide 7 Part II Overview 9 1 The
Introducion to Hydrologic Engineering Centers River Analysis System (HEC- RAS) Neena Isaac Scientist D CWPRS, Pune -24
 Introducion to Hydrologic Engineering Centers River Analysis System (HEC- RAS) Neena Isaac Scientist D CWPRS, Pune -24 One dimensional river models (1-D models) Assumptions Flow is one dimensional Streamline
Introducion to Hydrologic Engineering Centers River Analysis System (HEC- RAS) Neena Isaac Scientist D CWPRS, Pune -24 One dimensional river models (1-D models) Assumptions Flow is one dimensional Streamline
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1. Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations:
 ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1 Assignment 1 Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations: Examiner: Jahangir Alam Due Date: 27 Apr 2017 Weighting: 1% Objectives
ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1 Assignment 1 Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations: Examiner: Jahangir Alam Due Date: 27 Apr 2017 Weighting: 1% Objectives
This loads a preset standard set of data appropriate for Malaysian modeling projects.
 XP Software On-Site Detention (OSD) Example Step 1 Open xpswmm2010 program Or from Start menu select Programs XPS - then select xpswmm2010 Select Create From Template Save file, e.g. Filename.xp The program
XP Software On-Site Detention (OSD) Example Step 1 Open xpswmm2010 program Or from Start menu select Programs XPS - then select xpswmm2010 Select Create From Template Save file, e.g. Filename.xp The program
Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining
v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining
UTILITY REPORT FOR THORNTON SELF STORAGE THORNTON, COLORADO
 UTILITY REPORT FOR THORNTON SELF STORAGE THORNTON, COLORADO Prepared by: Bowman Consulting 63 Park Point Dr. Suite 1 Golden, CO 841 (33)-81-29 June 29, 215 Revised August 14, 215 CERTIFICATE SHEET DCB
UTILITY REPORT FOR THORNTON SELF STORAGE THORNTON, COLORADO Prepared by: Bowman Consulting 63 Park Point Dr. Suite 1 Golden, CO 841 (33)-81-29 June 29, 215 Revised August 14, 215 CERTIFICATE SHEET DCB
H y d r o C A D. Owner's Manual
 H y d r o C A D Stormwater Modeling System Version 8 Owner's Manual Copyright 2006 HydroCAD Software Solutions LLC. All rights reserved. HydroCAD is a registered trademark of HydroCAD Software Solutions
H y d r o C A D Stormwater Modeling System Version 8 Owner's Manual Copyright 2006 HydroCAD Software Solutions LLC. All rights reserved. HydroCAD is a registered trademark of HydroCAD Software Solutions
HY-8 User Manual (v7.5) HY-8 Culvert Analysis Program
 HY-8 User Manual (v7.5) HY-8 Culvert Analysis Program HY-8 User Manual 2 1. Introduction... 6 Introduction...6 Getting Started...7 Differences from DOS HY-8...9 Limitations...10 Vena Contracta...13 2.
HY-8 User Manual (v7.5) HY-8 Culvert Analysis Program HY-8 User Manual 2 1. Introduction... 6 Introduction...6 Getting Started...7 Differences from DOS HY-8...9 Limitations...10 Vena Contracta...13 2.
Efficiency and Accuracy of Importing HEC RAS Datafiles into PCSWMM and SWMM5
 5 Efficiency and Accuracy of Importing HEC RAS Datafiles into PCSWMM and SWMM5 Karen Finney, Rob James, William James and Tiehong Xiao An advantage of USEPA s SWMM5 is its capability to dynamically model
5 Efficiency and Accuracy of Importing HEC RAS Datafiles into PCSWMM and SWMM5 Karen Finney, Rob James, William James and Tiehong Xiao An advantage of USEPA s SWMM5 is its capability to dynamically model
Introduction to Bentley PondPack
 Introduction to Bentley PondPack CE 365K Hydraulic Engineering Design Prepared by Cassandra Fagan and David Maidment Spring 2015 Contents Goals of the Tutorial... 1 Procedure... 1 (1) Opening Bentley PondPack...
Introduction to Bentley PondPack CE 365K Hydraulic Engineering Design Prepared by Cassandra Fagan and David Maidment Spring 2015 Contents Goals of the Tutorial... 1 Procedure... 1 (1) Opening Bentley PondPack...
Concavity. Notice the location of the tangents to each type of curve.
 Concavity We ve seen how knowing where a unction is increasing and decreasing gives a us a good sense o the shape o its graph We can reine that sense o shape by determining which way the unction bends
Concavity We ve seen how knowing where a unction is increasing and decreasing gives a us a good sense o the shape o its graph We can reine that sense o shape by determining which way the unction bends
Tree-Dimensional numerical study of flows in complex CSOs for their instrumentation
 Wasserbaukolloquium 2006 Strömungssimulation im Wasserbau Dresdner Wasserbauliche Mitteilungen Heft 32 353 Tree-Dimensional numerical study of flows in complex CSOs for their instrumentation Vazquez, J.
Wasserbaukolloquium 2006 Strömungssimulation im Wasserbau Dresdner Wasserbauliche Mitteilungen Heft 32 353 Tree-Dimensional numerical study of flows in complex CSOs for their instrumentation Vazquez, J.
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
Hydraulic Calculations Relating to the Flooding and Draining. of the Roman Colosseum for Naumachiae. Research Report
 Hydraulic Calculations Relating to the Flooding and Draining of the Roman Colosseum for Naumachiae Research Report Edinburgh Research Archive (www.era.lib.ed.ac.uk) By Martin Crapper PhD C Eng MICE MCIWEM
Hydraulic Calculations Relating to the Flooding and Draining of the Roman Colosseum for Naumachiae Research Report Edinburgh Research Archive (www.era.lib.ed.ac.uk) By Martin Crapper PhD C Eng MICE MCIWEM
The HEC-RAS Model Refresher
 The HEC-RAS Model Refresher Minmin Shu P.E. Transportation Review Unit Water Resources Division Michigan Department of Environmental Quality 12-6-2018 What Does the HEC-RAS Mean RAS----River Analysis System
The HEC-RAS Model Refresher Minmin Shu P.E. Transportation Review Unit Water Resources Division Michigan Department of Environmental Quality 12-6-2018 What Does the HEC-RAS Mean RAS----River Analysis System
HEC-22 Inlets in INFOSWMM and H2OMAP SWMM v12
 HEC-22 Inlets in INFOSWMM and H2OMAP SWMM v12 Table of Contents How the Inlet and Overland Junctions are Defined 3 Why Would You Use the HEC-22 Inlets Option? 4 Types of Inlets 5 Nodes in InfoSWMM and
HEC-22 Inlets in INFOSWMM and H2OMAP SWMM v12 Table of Contents How the Inlet and Overland Junctions are Defined 3 Why Would You Use the HEC-22 Inlets Option? 4 Types of Inlets 5 Nodes in InfoSWMM and
HY-8 Quick Start Guide. What s in this Quick Start Document. Technical Methods. HY-8 Quick Start
 HY-8 Quick Start Guide This Quick Start guide is intended to provide essential information for installing and running the updated version 7.1 of the HY-8 culvert hydraulic analysis and design program (HY-8
HY-8 Quick Start Guide This Quick Start guide is intended to provide essential information for installing and running the updated version 7.1 of the HY-8 culvert hydraulic analysis and design program (HY-8
Improved understanding of combined sewer systems using the Illinois Conveyance Analysis Program (ICAP)
 Improved understanding of combined sewer systems using the Illinois Conveyance Analysis Program (ICAP) Nils Oberg 1*, Arthur R. Schmidt 1, Blake J. Landry 1, Arturo S. Leon 1,2, Andrew R. Waratuke 1, José
Improved understanding of combined sewer systems using the Illinois Conveyance Analysis Program (ICAP) Nils Oberg 1*, Arthur R. Schmidt 1, Blake J. Landry 1, Arturo S. Leon 1,2, Andrew R. Waratuke 1, José
Benefits of 2D Modeling for Urban Stormwater Master Planning Niles, Illinois
 Benefits of 2D Modeling for Urban Stormwater Master Planning Niles, Illinois Patrick Lach, P.E., CFM, Hey and Associates, Inc. Steve Vinezeano, ICMA CM, LEED AP Assistant Village Manager Three Geographic
Benefits of 2D Modeling for Urban Stormwater Master Planning Niles, Illinois Patrick Lach, P.E., CFM, Hey and Associates, Inc. Steve Vinezeano, ICMA CM, LEED AP Assistant Village Manager Three Geographic
Section 3 Laying Out Structures
 Mastering Storm&Sanitary Section 3 Laying Out Structures Section Goals: How to Set Drainage Options When to Set Structure Settings Using Preference Sets Laying Out Ditch Inlets Laying Out a connecting
Mastering Storm&Sanitary Section 3 Laying Out Structures Section Goals: How to Set Drainage Options When to Set Structure Settings Using Preference Sets Laying Out Ditch Inlets Laying Out a connecting
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS
 INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS HEC- RAS stands for Hydrologic Engineering Center s River Analysis System By U.S. Army Corps of Engineers One dimensional analysis of : 1. Steady flow 2. Unsteady flow 3. Sediment
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS HEC- RAS stands for Hydrologic Engineering Center s River Analysis System By U.S. Army Corps of Engineers One dimensional analysis of : 1. Steady flow 2. Unsteady flow 3. Sediment
SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions Objectives Learn techniques for using various additional boundary conditions with the Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions Objectives Learn techniques for using various additional boundary conditions with the Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional
Improving the Senior Level Hydraulic Engineering Design Course (CE 474) By Means of Computer Assisted Instruction
 Improving the Senior Level Hydraulic Engineering Design Course (CE 474) By Means of Computer Assisted Instruction Rolando Bravo 1 Abstract- This paper presents the development of spreadsheet software at
Improving the Senior Level Hydraulic Engineering Design Course (CE 474) By Means of Computer Assisted Instruction Rolando Bravo 1 Abstract- This paper presents the development of spreadsheet software at
PRACTICAL UNIT 1 exercise task
 Practical Unit 1 1 1 PRACTICAL UNIT 1 exercise task Developing a hydraulic model with HEC RAS using schematic river geometry data In the course of practical unit 1 we prepare the input for the execution
Practical Unit 1 1 1 PRACTICAL UNIT 1 exercise task Developing a hydraulic model with HEC RAS using schematic river geometry data In the course of practical unit 1 we prepare the input for the execution
PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design
 PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design A Hello World Example Prepared by Dr. Robert Pitt and Jason Kirby, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Alabama August 20, 2002 Introduction
PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design A Hello World Example Prepared by Dr. Robert Pitt and Jason Kirby, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Alabama August 20, 2002 Introduction
HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes
 HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes A new version of HEC-RAS (3.0) has been released with significant new features over the previous version (2.21). Version 3.0 includes unsteady flow routing capabilities,
HEC-RAS 3.0 January, 2001 Release Notes A new version of HEC-RAS (3.0) has been released with significant new features over the previous version (2.21). Version 3.0 includes unsteady flow routing capabilities,
Introduction to MIKE FLOOD
 Introduction to MIKE FLOOD HYDROEUROPE, Sophia-Antipolis, February 2011 Julie Landrein, DHI Denmark Introduction to MIKE FLOOD - Introduction to MIKE FLOOD - 1D Modelling: MIKE 11, MIKE URBAN - 2D Modelling:
Introduction to MIKE FLOOD HYDROEUROPE, Sophia-Antipolis, February 2011 Julie Landrein, DHI Denmark Introduction to MIKE FLOOD - Introduction to MIKE FLOOD - 1D Modelling: MIKE 11, MIKE URBAN - 2D Modelling:
Multi-Stage Outlet Structures
 Methods in Stormwater Management Using HydroCAD Multi-Stage Outlet Structures H09 Multi-Stage Outlet Structures.pdf 1 Topics 1. Multi-State Outlet Structures Definition 2. Orifice and Weir Equations 3.
Methods in Stormwater Management Using HydroCAD Multi-Stage Outlet Structures H09 Multi-Stage Outlet Structures.pdf 1 Topics 1. Multi-State Outlet Structures Definition 2. Orifice and Weir Equations 3.
Questions and Answers
 Autodesk Storm and Sanitary Analysis Extension 2011 Questions and Answers Design stormwater and wastewater systems more effectively with integrated analysis. Contents 1. GENERAL PRODUCT INFORMATION...
Autodesk Storm and Sanitary Analysis Extension 2011 Questions and Answers Design stormwater and wastewater systems more effectively with integrated analysis. Contents 1. GENERAL PRODUCT INFORMATION...
Rapid Floodplain Delineation. Presented by: Leo R. Kreymborg 1, P.E. David T. Williams 2, Ph.D., P.E. Iwan H. Thomas 3, E.I.T.
 007 ASCE Rapid Floodplain Delineation Presented by: Leo R. Kreymborg 1, P.E. David T. Williams, Ph.D., P.E. Iwan H. Thomas 3, E.I.T. 1 Project Manager, PBS&J, 975 Sky Park Court, Suite 00, San Diego, CA
007 ASCE Rapid Floodplain Delineation Presented by: Leo R. Kreymborg 1, P.E. David T. Williams, Ph.D., P.E. Iwan H. Thomas 3, E.I.T. 1 Project Manager, PBS&J, 975 Sky Park Court, Suite 00, San Diego, CA
THE NWS SIMPLIFIED DAM-BREAK FLOOD FORECASTING MODEL
 THE NWS SIMPLIFIED DAM-BREAK FLOOD FORECASTING MODEL by Jonathan N. Wetmore and Danny L. Fread 1 (Revised 12/18/91) by Danny L. Fread, Janice M. Lewis 2, and Stephen M. Wiele 2 SYNOPSIS The National Weather
THE NWS SIMPLIFIED DAM-BREAK FLOOD FORECASTING MODEL by Jonathan N. Wetmore and Danny L. Fread 1 (Revised 12/18/91) by Danny L. Fread, Janice M. Lewis 2, and Stephen M. Wiele 2 SYNOPSIS The National Weather
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Efficiency and performances
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Efficiency and performances
iric Software Changing River Science River2D Tutorials
 iric Software Changing River Science River2D Tutorials iric Software Changing River Science Confluence of the Colorado River, Blue River and Indian Creek, Colorado, USA 1 TUTORIAL 1: RIVER2D STEADY SOLUTION
iric Software Changing River Science River2D Tutorials iric Software Changing River Science Confluence of the Colorado River, Blue River and Indian Creek, Colorado, USA 1 TUTORIAL 1: RIVER2D STEADY SOLUTION
Canal design by dynamic programming, computer programme CANDY G. Radovic Energoprojekt-Hidronizenjering, Bui. Lenjina 12, Belgrade, Yugoslavia
 Canal design by dynamic programming, computer programme CANDY G. Radovic Energoprojekt-Hidronizenjering, Bui. Lenjina 12, 11 000 Belgrade, Yugoslavia Abstract The problem considered in this technical note
Canal design by dynamic programming, computer programme CANDY G. Radovic Energoprojekt-Hidronizenjering, Bui. Lenjina 12, 11 000 Belgrade, Yugoslavia Abstract The problem considered in this technical note
Urban Floodplain modeling- Application of Two-Dimensional Analyses to Refine Results
 Urban Floodplain modeling- Application of Two-Dimensional Analyses to Refine Results Prabharanjani Madduri, P.E., CFM Mathini Sreetharan, Ph.D., P.E., CFM Hydraulic modeling of urban areas and issues Modeling
Urban Floodplain modeling- Application of Two-Dimensional Analyses to Refine Results Prabharanjani Madduri, P.E., CFM Mathini Sreetharan, Ph.D., P.E., CFM Hydraulic modeling of urban areas and issues Modeling
v Prerequisite Tutorials GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow GSSHA WMS Basics Creating Feature Objects and Mapping their Attributes to the 2D Grid
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
TECHNICAL PROBLEM The author's work, software application "BALBYKAN", solves the problem of hydraulic
 1 SOFTWARE APPLICATION "BALBYKAN" FOR HYDRAULIC CALCULATION, ENGINEERING DESIGN, AND SIMULATION OF SEWERAGE SYSTEMS AUTHOR: Pavle Babac, Civil Engineer, MSc ABSTRACT The author's work, software application
1 SOFTWARE APPLICATION "BALBYKAN" FOR HYDRAULIC CALCULATION, ENGINEERING DESIGN, AND SIMULATION OF SEWERAGE SYSTEMS AUTHOR: Pavle Babac, Civil Engineer, MSc ABSTRACT The author's work, software application
Wave load formulae for prediction of wave-induced forces on a slender pile within pile groups
 Wave load ormulae or prediction o wave-induced orces on a slender pile within pile groups Lisham Bonakdar 1 *, Hocine Oumeraci 1 and Amir Etemad-Shahidi 2 1 Leichtweiss-Institute or Hydraulic Engineering
Wave load ormulae or prediction o wave-induced orces on a slender pile within pile groups Lisham Bonakdar 1 *, Hocine Oumeraci 1 and Amir Etemad-Shahidi 2 1 Leichtweiss-Institute or Hydraulic Engineering
Flood Inundation Mapping using HEC-RAS
 Flood Inundation Mapping using HEC-RAS Goodell, C. 1 ; Warren, C. 2 WEST Consultants, 2601 25 th St SE, Suite 450, Salem, OR 97302. Abstract Flood inundation mapping is an important tool for municipal
Flood Inundation Mapping using HEC-RAS Goodell, C. 1 ; Warren, C. 2 WEST Consultants, 2601 25 th St SE, Suite 450, Salem, OR 97302. Abstract Flood inundation mapping is an important tool for municipal
Aalborg Universitet. Numerical 3-D Modelling of Overflows Larsen, Torben; Nielsen, L.; Jensen, B.; Christensen, E. D.
 Aalborg Universitet Numerical 3-D Modelling of Overflows Larsen, Torben; Nielsen, L.; Jensen, B.; Christensen, E. D. Published in: Confernce Proceedings : 11th International Conference on Urban Drainage
Aalborg Universitet Numerical 3-D Modelling of Overflows Larsen, Torben; Nielsen, L.; Jensen, B.; Christensen, E. D. Published in: Confernce Proceedings : 11th International Conference on Urban Drainage
Open Channel Flow. Course paper: Water level calculation with HEC-RAS
 Course paper: Water level calculation with HEC-RAS Prof. Dr.-Ing. Tobias Bleninger Graduate Program for Water Resources and Environmental Engineering (PPGERHA) Universidade Federal do Paraná - UFPR Centro
Course paper: Water level calculation with HEC-RAS Prof. Dr.-Ing. Tobias Bleninger Graduate Program for Water Resources and Environmental Engineering (PPGERHA) Universidade Federal do Paraná - UFPR Centro
WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model Objectives Learn how to add hydraulic channel routing to your GSSHA model and how to define channel properties. Learn how
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model Objectives Learn how to add hydraulic channel routing to your GSSHA model and how to define channel properties. Learn how
Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD
 Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD Workshop Overview In this workshop you will use StormCAD to analyze an existing storm sewer system. You will add a parking
Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD Workshop Overview In this workshop you will use StormCAD to analyze an existing storm sewer system. You will add a parking
Day 1. HEC-RAS 1-D Training. Rob Keller and Mark Forest. Break (9:45 am to 10:00 am) Lunch (12:00 pm to 1:00 pm)
 Day 1 HEC-RAS 1-D Training Rob Keller and Mark Forest Introductions and Course Objectives (8:00 am to 8:15 am) Introductions: Class and Content Module 1 Open Channel Hydraulics (8:15 am to 9:45 am) Lecture
Day 1 HEC-RAS 1-D Training Rob Keller and Mark Forest Introductions and Course Objectives (8:00 am to 8:15 am) Introductions: Class and Content Module 1 Open Channel Hydraulics (8:15 am to 9:45 am) Lecture
Another Look at the Safety Effects of Horizontal Curvature on Rural Two-Lane Highways
 1 2 Another Look at the Safety Effects of Horizontal Curvature on Rural Two-Lane Highways 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
1 2 Another Look at the Safety Effects of Horizontal Curvature on Rural Two-Lane Highways 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
Floodplain Engineering
 Floodplain Engineering by David E. Fantina, PE Introduction: This course presents a discussion of the modeling procedure for flood profiling. The most commonly used software for flood profiling is the
Floodplain Engineering by David E. Fantina, PE Introduction: This course presents a discussion of the modeling procedure for flood profiling. The most commonly used software for flood profiling is the
v SMS Tutorials SRH-2D Prerequisites Requirements SRH-2D Model Map Module Mesh Module Data files Time
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation using SMS version 11.2 or later. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation using SMS version 11.2 or later. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial
ITU - Telecommunication Standardization Sector. G.fast: Far-end crosstalk in twisted pair cabling; measurements and modelling ABSTRACT
 ITU - Telecommunication Standardization Sector STUDY GROUP 15 Temporary Document 11RV-22 Original: English Richmond, VA. - 3-1 Nov. 211 Question: 4/15 SOURCE 1 : TNO TITLE: G.ast: Far-end crosstalk in
ITU - Telecommunication Standardization Sector STUDY GROUP 15 Temporary Document 11RV-22 Original: English Richmond, VA. - 3-1 Nov. 211 Question: 4/15 SOURCE 1 : TNO TITLE: G.ast: Far-end crosstalk in
Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk SSA
 Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk Josh Kehs, P.E. Autodesk, Inc. CI4541 Learning Objectives At the end of this class, you will be able to: Model
Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk Josh Kehs, P.E. Autodesk, Inc. CI4541 Learning Objectives At the end of this class, you will be able to: Model
Section 4: Pond Storage
 Section 4: Pond Storage Defining and calculating pond storage 55 Minutes Press Space, PageDown, or Click to advance. Press PageUp to reverse. Esc to exit. Right-Click for other options. Pond Storage Introduction
Section 4: Pond Storage Defining and calculating pond storage 55 Minutes Press Space, PageDown, or Click to advance. Press PageUp to reverse. Esc to exit. Right-Click for other options. Pond Storage Introduction
Using a Projected Subgradient Method to Solve a Constrained Optimization Problem for Separating an Arbitrary Set of Points into Uniform Segments
 Using a Projected Subgradient Method to Solve a Constrained Optimization Problem or Separating an Arbitrary Set o Points into Uniorm Segments Michael Johnson May 31, 2011 1 Background Inormation The Airborne
Using a Projected Subgradient Method to Solve a Constrained Optimization Problem or Separating an Arbitrary Set o Points into Uniorm Segments Michael Johnson May 31, 2011 1 Background Inormation The Airborne
Comparison of 1D and 2D Surface Water Models for Solid Waste Facilities. Garth R. Bowers, P.E., Carl E. Bueter, P.E., Larry Henk
 Comparison of 1D and 2D Surface Water Models for Solid Waste Facilities Garth R. Bowers, P.E., Carl E. Bueter, P.E., Larry Henk Introduction Importance of Accurate Floodplain Delineation Required by Federal
Comparison of 1D and 2D Surface Water Models for Solid Waste Facilities Garth R. Bowers, P.E., Carl E. Bueter, P.E., Larry Henk Introduction Importance of Accurate Floodplain Delineation Required by Federal
Chapter 16. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents BANK FAILURE CALCULATIONS IN HEC-6T...16-1 Introduction...16-1 Approach...16-2 Conceptual Model...16-3 Theoretical Development...16-4 Two Foot Test...16-6 Mass Conservation...16-6 Command
Table of Contents BANK FAILURE CALCULATIONS IN HEC-6T...16-1 Introduction...16-1 Approach...16-2 Conceptual Model...16-3 Theoretical Development...16-4 Two Foot Test...16-6 Mass Conservation...16-6 Command
Skill Sets Chapter 5 Functions
 Skill Sets Chapter 5 Functions No. Skills Examples o questions involving the skills. Sketch the graph o the (Lecture Notes Example (b)) unction according to the g : x x x, domain. x, x - Students tend
Skill Sets Chapter 5 Functions No. Skills Examples o questions involving the skills. Sketch the graph o the (Lecture Notes Example (b)) unction according to the g : x x x, domain. x, x - Students tend
A Proposed Approach for Solving Rough Bi-Level. Programming Problems by Genetic Algorithm
 Int J Contemp Math Sciences, Vol 6, 0, no 0, 45 465 A Proposed Approach or Solving Rough Bi-Level Programming Problems by Genetic Algorithm M S Osman Department o Basic Science, Higher Technological Institute
Int J Contemp Math Sciences, Vol 6, 0, no 0, 45 465 A Proposed Approach or Solving Rough Bi-Level Programming Problems by Genetic Algorithm M S Osman Department o Basic Science, Higher Technological Institute
A parabolic curve that is applied to make a smooth and safe transition between two grades on a roadway or a highway.
 A parabolic curve that is applied to make a smooth and safe transition between two grades on a roadway or a highway. VPC: Vertical Point of Curvature VPI: Vertical Point of Intersection VPT: Vertical Point
A parabolic curve that is applied to make a smooth and safe transition between two grades on a roadway or a highway. VPC: Vertical Point of Curvature VPI: Vertical Point of Intersection VPT: Vertical Point
River Analysis System HEC-RAS
 Hydrologic Engineering Center River Analysis System HEC-RAS Release Notes Version 4.0.0 March 2008 Approved for Public Release Distribution Unlimited 1 Introduction Version 4.0.0 of the River Analysis
Hydrologic Engineering Center River Analysis System HEC-RAS Release Notes Version 4.0.0 March 2008 Approved for Public Release Distribution Unlimited 1 Introduction Version 4.0.0 of the River Analysis
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering. Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner Exercise Topic: Getting started with HEC RAS Objective: Create
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner Exercise Topic: Getting started with HEC RAS Objective: Create
MEMORANDUM. Corona Subdivision XP Storm Evaluation. Date: March 5, Curt Bates, City of Petaluma. David S. Smith, P.E., WEST Consultants, Inc.
 MEMORANDUM Project: Corona Subdivision XP Storm Evaluation Subject: Results Summary Date: March 5, 2013 To: Curt Bates, City of Petaluma No. C056132 EXP. 12/31/14 From: David S. Smith, P.E., WEST Consultants,
MEMORANDUM Project: Corona Subdivision XP Storm Evaluation Subject: Results Summary Date: March 5, 2013 To: Curt Bates, City of Petaluma No. C056132 EXP. 12/31/14 From: David S. Smith, P.E., WEST Consultants,
Building a new model in wspg2010
 Building a new model in wspg2010 The Water Surface Profile Gradient 2010 (wspg2010 by XP Software) model is a hydraulic analysis system that computes and plots uniform and non-uniform steady flow water
Building a new model in wspg2010 The Water Surface Profile Gradient 2010 (wspg2010 by XP Software) model is a hydraulic analysis system that computes and plots uniform and non-uniform steady flow water
This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional (SRH-2D) simulation. Requirements
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
Comparing HEC-RAS v5.0 2-D Results with Verification Datasets
 Comparing HEC-RAS v5.0 2-D Results with Verification Datasets Tom Molls 1, Gary Brunner 2, & Alejandro Sanchez 2 1. David Ford Consulting Engineers, Inc., Sacramento, CA 2. USACE Hydrologic Engineering
Comparing HEC-RAS v5.0 2-D Results with Verification Datasets Tom Molls 1, Gary Brunner 2, & Alejandro Sanchez 2 1. David Ford Consulting Engineers, Inc., Sacramento, CA 2. USACE Hydrologic Engineering
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1P - Designing with a Pond Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1P - Designing with a Pond Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
Watershed Modeling With DEMs: The Rest of the Story
 Watershed Modeling With DEMs: The Rest of the Story Lesson 7 7-1 DEM Delineation: The Rest of the Story DEM Fill for some cases when merging DEMs Delineate Basins Wizard Smoothing boundaries Representing
Watershed Modeling With DEMs: The Rest of the Story Lesson 7 7-1 DEM Delineation: The Rest of the Story DEM Fill for some cases when merging DEMs Delineate Basins Wizard Smoothing boundaries Representing
Cross Sections, Profiles, and Rating Curves. Viewing Results From The River System Schematic. Viewing Data Contained in an HEC-DSS File
 C H A P T E R 9 Viewing Results After the model has finished the steady or unsteady flow computations the user can begin to view the output. Output is available in a graphical and tabular format. The current
C H A P T E R 9 Viewing Results After the model has finished the steady or unsteady flow computations the user can begin to view the output. Output is available in a graphical and tabular format. The current
1-2. Composition of Functions. OBJECTIVES Perform operations with functions. Find composite functions. Iterate functions using real numbers.
 - OBJECTIVES Perorm operations with unctions. Find composite unctions. Iterate unctions using real numbers. Composition o Functions BUSINESS Each year, thousands o people visit Yellowstone National Park
- OBJECTIVES Perorm operations with unctions. Find composite unctions. Iterate unctions using real numbers. Composition o Functions BUSINESS Each year, thousands o people visit Yellowstone National Park
Use of measured and interpolated crosssections
 Use of measured and interpolated crosssections in hydraulic river modelling Y. Chen/, R. Crowded & R. A. Falconer^ ^ Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, University ofbradford, Bradford, West
Use of measured and interpolated crosssections in hydraulic river modelling Y. Chen/, R. Crowded & R. A. Falconer^ ^ Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, University ofbradford, Bradford, West
Conic Sections. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Conic Sections MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department o Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction The conic sections include the parabola, the ellipse, and the hyperbola. y y y x x x Parabola A
Conic Sections MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department o Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction The conic sections include the parabola, the ellipse, and the hyperbola. y y y x x x Parabola A
General Applications
 Chapter General Applications The general analysis modules can be used to calculate section properties, wind pressures on buildings and evaluate drainage systems of building roofs. General Applications
Chapter General Applications The general analysis modules can be used to calculate section properties, wind pressures on buildings and evaluate drainage systems of building roofs. General Applications
NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE
 NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE Jungseok Ho 1, Hong Koo Yeo 2, Julie Coonrod 3, and Won-Sik Ahn 4 1 Research Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering,
NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE Jungseok Ho 1, Hong Koo Yeo 2, Julie Coonrod 3, and Won-Sik Ahn 4 1 Research Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering,
Practice Workbook. QuickStart using Subsurface Utility Engineering
 Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand selfstudy. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or in
Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand selfstudy. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or in
Writing and Graphing Linear Equations. Linear equations can be used to represent relationships.
 Writing and Graphing Linear Equations Linear equations can be used to represent relationships. Linear equation An equation whose solutions form a straight line on a coordinate plane. Collinear Points that
Writing and Graphing Linear Equations Linear equations can be used to represent relationships. Linear equation An equation whose solutions form a straight line on a coordinate plane. Collinear Points that
Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D.
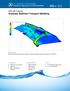 SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial SRH-2D SRH-2D Sediment Transport
SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial SRH-2D SRH-2D Sediment Transport
Appendix E. HEC-RAS and HEC-Ecosystem Functions Models
 Appendix E HEC-RAS and HEC-Ecosystem Functions Models 1 Appendix E: Modeled Reaches for the Connecticut River Watershed application of HEC-RAS Separate from the report for the Decision Support System of
Appendix E HEC-RAS and HEC-Ecosystem Functions Models 1 Appendix E: Modeled Reaches for the Connecticut River Watershed application of HEC-RAS Separate from the report for the Decision Support System of
