Computer Graphics. 2D Transforma5ons. Review Vertex Transforma5ons 2/3/15. adjust the zoom. posi+on the camera. posi+on the model
|
|
|
- Richard Horn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /3/5 Computer Graphics D Transforma5ons Review Verte Transforma5ons posi+on the model posi+on the camera adjust the zoom verte shader input verte shader output, transformed
2 /3/5 From Object to World Space Graphics Coordinate Sstems Right hand (or counterclockwise) coordinate sstem
3 /3/5 Object to World Transforma5ons D Transformations Required background reading: 3
4 /3/5 Translate (t, t) ʹ + t ʹ + t t p p t t T(t,t ) t Note: 3 rd dimension needed to encode transla+ons in matri Translate (t, t) OpenGL Implementa5on Verte shader: t t t p t p in vec3 vert; uniform mat4 model; gl_position model * vec4(vert, ); OpenGL: using namespace glm; mat4 tmat translate(mat4(.f), vec3(t,t,.f)); // Set the uniform model in the verte shader. Using tdogl: gprogram->setuniform("model", tmat); 4
5 /3/5 Transla5on of Objects How do en+re objects get translated? Individual ver+ces get translated The transforma+on applies to all ver+ces in the currentl bound verte arra object (VAO) " # % " # s s Scale (s, s) % ( ʹ, ʹ ) (, ) s s S(s,s ) fied point (pivot) 5
6 /3/5 6 Scale, then translate (note the order of calls in OpenGL): Actual transforma.on order should be read in reverse using namespace glm; mat4 tmat scale(mat4(.), vec3(s,s,.f)); OpenGL: Scale (s, s) OpenGL Implementation s s ( ), ( ) ʹ ʹ, pivot mat4 tmat(.f); tmat translate(tmat, vec3(.f,.f,.f)); tmat scale(tmat, vec3(.f,.f,.f)); Reflec5on as Scale Along X- ais Along Y- ais ʹ ʹ ʹ ʹ
7 /3/5 Rota5on cosθ sinθ sinθ + cosθ ( ʹ, ʹ ) θ (, ) cos θ sin θ -sin θ cos θ R(θ) pivot In D, rota+on is about the z- ais vec3(,,) Rota5on Pivot Default rota+on center is world origin (,) θ > : Rotate counterclockwise θ < : Rotate clockwise 7
8 /3/5 Rotation OpenGL Implementation cos θ sin θ -sin θ cos θ ( ʹ, ʹ ) θ (, ) OpenGL: pivot using namespace glm; mat4 tmat(.f); tmat rotate(tmat, radians(45.f), vec3(,,)); First scale, then rotate, then translate: mat4 tmat(.f); tmat translate(tmat, vec3(.f,.f,.f)); tmat rotate(tmat, radians(45.f), vec3(,,)); tmat scale(tmat, vec3(.f,.f,.f)); Rota5ng an En5re Object 8
9 /3/5 Arbitrar Rota5on Center Where is the rotation center here? Arbitrar Rota5on Center To rotate about arbitrar point P ( r, r ) b θ: Translate object b (- r, - r ) so that P is at origin Rotate the object b θ Translate object back b ( r, r ) In matri form: T( r, r) R( θ ) T( r, r) 9
10 /3/5 Arbitrar Rota5on Center T(r, r) r # # r # " % " # R(θ) cosθ sinθ sinθ cosθ % T( r, r) " r r # " cosθ sinθ r( cosθ) + r sinθ % sinθ cosθ r( cosθ) rsinθ # % Non- Commuta5ve Transforms Scale then Translate: (,) (,) Scale(,) (,) (,) Translate(3,) (3,) (5,3) Translate then Scale: (8,4) (,) Translate(3,) (4,) (3,) Scale(,) (6,) (,)
11 /3/5 Non- Commuta5ve Transforms Scale then Translate: p T ( S p ) TS p T(3,)*S(,) 3 3 Translate then Scale: p S ( T p ) ST p S(,)*T(3,) 3 6 Suppose we want Eample What are the transforma+ons?
12 /3/5 Composing Transforma5ons Matri mul+plica+on is not commuta+ve R( 9 ) T(,3) T(,3) R( 9 ) Rotation followed b translation Translation followed b rotation Hands- On Prac5ce D Transforma+on Applet at hdp:// _virtual_reconstruc+on/chapter5_trafo.html Handout distributed b instructor
13 /3/5 Hands- On Ac5vit Modif _tetures to scale and rotate our tetured image to produce this image: a) Update the verte shader to input a model matri into a uniform mat4 variable, and use it to transform the input verte (see lecture notes) b) Switch to the main program. Reset the verte coordinates in vertedata to represent a square, then focus on the Render func+on. c) Before drawing the image (with DrawArras), create the transforma+on matri and use it to set the model shader variable. The transforma+on is a uniform scale (b.5), follow b a counterclockwise 9 - rota+on. Recall that ou need to list these transforma+ons in reverse order (see notes) d) To be able to use matri opera+ons in our code, include <glm/gtc/ matri_transform.hpp> in our main program Hands- On Ac5vit Lets rotate our image over +me and for fun well also reposi+on it at the bodom- right side of the window: We will use the func+on glfwgettime, which returns the +me elapsed since GLFW has been ini+alized To rotate the image over +me, use a rota+on transforma+on similar to model rotate(model, (float)glfwgettime()*5.f, vec3(.f,.f,.f)); In addi+on to rota+on, scale and translate our image to appear similar to the one above. Pa careful aden+on to the order of transforma+ons Note that the model transforma+on matri gets recreated each +me the Render func+on is called (ever frame) 3
14 /3/5 Hands- On Ac5vit 3 Lets draw a second image with another call to gldrawarras, using transforma+ons onl: Add a second call to gldrawarras for the second image Before this second gldrawarras call, set the transforma+on matri to scale and posi+on the image at the top- lel of our window Readjust the transforma+on matri to scale this second image over +me, using the sin func+on for eample, the scale factor could be sin(glfwgettime()) note that sin will cause the object to invert as soon as the scale turns nega+ve Hands- On Ac5vit 4 Create a D image of our choice. You will need to tell the verte shader how to transform the verte data (b senng the model uniform) and draw it mul+ple +mes with gldrawarras You are free to choose our own design, or ou ma tr the birthda cake shown below. The teture images are available on the class website.. (,)
1/29/13. Computer Graphics. Transformations. Simple Transformations
 /29/3 Computer Graphics Transformations Simple Transformations /29/3 Contet 3D Coordinate Sstems Right hand (or counterclockwise) coordinate sstem Left hand coordinate sstem Not used in this class and
/29/3 Computer Graphics Transformations Simple Transformations /29/3 Contet 3D Coordinate Sstems Right hand (or counterclockwise) coordinate sstem Left hand coordinate sstem Not used in this class and
Computer Graphics. 2D transformations. Transforma3ons in computer graphics. Overview. Basic classes of geometric transforma3ons
 Transforma3ons in computer graphics omputer Graphics Transforma3ons leksandra Piurica Goal: introduce methodolog to hange coordinate sstem Move and deform objects Principle: transforma3ons are applied
Transforma3ons in computer graphics omputer Graphics Transforma3ons leksandra Piurica Goal: introduce methodolog to hange coordinate sstem Move and deform objects Principle: transforma3ons are applied
Today s class. Geometric objects and transformations. Informationsteknologi. Wednesday, November 7, 2007 Computer Graphics - Class 5 1
 Toda s class Geometric objects and transformations Wednesda, November 7, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 5 Vector operations Review of vector operations needed for working in computer graphics adding two
Toda s class Geometric objects and transformations Wednesda, November 7, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 5 Vector operations Review of vector operations needed for working in computer graphics adding two
4. Two Dimensional Transformations
 4. Two Dimensional Transformations CS362 Introduction to Computer Graphics Helena Wong, 2 In man applications, changes in orientations, sizes, and shapes are accomplished with geometric transformations
4. Two Dimensional Transformations CS362 Introduction to Computer Graphics Helena Wong, 2 In man applications, changes in orientations, sizes, and shapes are accomplished with geometric transformations
CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications
 CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics: Theor, Algorithms, and Applications Hong in State Universit of New York at Ston Brook (Ston Brook Universit) Ston Brook, New York 794-44 Tel: (63)632-845; Fa:
CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics: Theor, Algorithms, and Applications Hong in State Universit of New York at Ston Brook (Ston Brook Universit) Ston Brook, New York 794-44 Tel: (63)632-845; Fa:
Image Warping : Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall Some slides from Steve Seitz
 Image Warping http://www.jeffre-martin.com Some slides from Steve Seitz 5-463: Computational Photograph Aleei Efros, CMU, Fall 2 Image Transformations image filtering: change range of image g() T(f())
Image Warping http://www.jeffre-martin.com Some slides from Steve Seitz 5-463: Computational Photograph Aleei Efros, CMU, Fall 2 Image Transformations image filtering: change range of image g() T(f())
Image Warping. Some slides from Steve Seitz
 Image Warping http://www.jeffre-martin.com Some slides from Steve Seitz 5-463: Computational Photograph Aleei Efros, CMU, Fall 26 Image Warping image filtering: change range of image g() T(f()) f T f image
Image Warping http://www.jeffre-martin.com Some slides from Steve Seitz 5-463: Computational Photograph Aleei Efros, CMU, Fall 26 Image Warping image filtering: change range of image g() T(f()) f T f image
Two Dimensional Viewing
 Two Dimensional Viewing Dr. S.M. Malaek Assistant: M. Younesi Two Dimensional Viewing Basic Interactive Programming Basic Interactive Programming User controls contents, structure, and appearance of objects
Two Dimensional Viewing Dr. S.M. Malaek Assistant: M. Younesi Two Dimensional Viewing Basic Interactive Programming Basic Interactive Programming User controls contents, structure, and appearance of objects
CS F-07 Objects in 2D 1
 CS420-2010F-07 Objects in 2D 1 07-0: Representing Polgons We want to represent a simple polgon Triangle, rectangle, square, etc Assume for the moment our game onl uses these simple shapes No curves for
CS420-2010F-07 Objects in 2D 1 07-0: Representing Polgons We want to represent a simple polgon Triangle, rectangle, square, etc Assume for the moment our game onl uses these simple shapes No curves for
3D Coordinates & Transformations
 3D Coordinates & Transformations Prof. Aaron Lanterman (Based on slides b Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technolog 3D graphics rendering pipeline
3D Coordinates & Transformations Prof. Aaron Lanterman (Based on slides b Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technolog 3D graphics rendering pipeline
GLOBAL EDITION. Interactive Computer Graphics. A Top-Down Approach with WebGL SEVENTH EDITION. Edward Angel Dave Shreiner
 GLOBAL EDITION Interactive Computer Graphics A Top-Down Approach with WebGL SEVENTH EDITION Edward Angel Dave Shreiner This page is intentionall left blank. 4.10 Concatenation of Transformations 219 in
GLOBAL EDITION Interactive Computer Graphics A Top-Down Approach with WebGL SEVENTH EDITION Edward Angel Dave Shreiner This page is intentionall left blank. 4.10 Concatenation of Transformations 219 in
CS Computer Graphics: Transformations & The Synthetic Camera
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: Transformations The Snthetic Camera b Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Introduction to Transformations A transformation changes an objects Size
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: Transformations The Snthetic Camera b Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Introduction to Transformations A transformation changes an objects Size
Viewing. Cliff Lindsay, Ph.D. WPI
 Viewing Cliff Lindsa, Ph.D. WPI Building Virtual Camera Pipeline l Used To View Virtual Scene l First Half of Rendering Pipeline Related To Camera l Takes Geometr From ApplicaHon To RasteriaHon Stages
Viewing Cliff Lindsa, Ph.D. WPI Building Virtual Camera Pipeline l Used To View Virtual Scene l First Half of Rendering Pipeline Related To Camera l Takes Geometr From ApplicaHon To RasteriaHon Stages
Scene Graphs & Modeling Transformations COS 426
 Scene Graphs & Modeling Transformations COS 426 3D Object Representations Points Range image Point cloud Surfaces Polgonal mesh Subdivision Parametric Implicit Solids Voels BSP tree CSG Sweep High-level
Scene Graphs & Modeling Transformations COS 426 3D Object Representations Points Range image Point cloud Surfaces Polgonal mesh Subdivision Parametric Implicit Solids Voels BSP tree CSG Sweep High-level
1. We ll look at: Types of geometrical transformation. Vector and matrix representations
 Tob Howard COMP272 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 3: Transformations Tob.Howard@manchester.ac.uk Introduction We ll look at: Tpes of geometrical transformation Vector and matri representations
Tob Howard COMP272 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 3: Transformations Tob.Howard@manchester.ac.uk Introduction We ll look at: Tpes of geometrical transformation Vector and matri representations
Computer Graphics. P04 Transformations. Aleksandra Pizurica Ghent University
 Computer Graphics P4 Transformations Aleksandra Pizurica Ghent Universit Telecommunications and Information Processing Image Processing and Interpretation Group Transformations in computer graphics Goal:
Computer Graphics P4 Transformations Aleksandra Pizurica Ghent Universit Telecommunications and Information Processing Image Processing and Interpretation Group Transformations in computer graphics Goal:
3D graphics rendering pipeline (1) 3D graphics rendering pipeline (3) 3D graphics rendering pipeline (2) 8/29/11
 3D graphics rendering pipeline (1) Geometr Rasteriation 3D Coordinates & Transformations Prof. Aaron Lanterman (Based on slides b Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
3D graphics rendering pipeline (1) Geometr Rasteriation 3D Coordinates & Transformations Prof. Aaron Lanterman (Based on slides b Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Homogeneous Coordinates
 COMS W4172 3D Math 2 Steven Feiner Department of Computer Science Columbia Universit New York, NY 127 www.cs.columbia.edu/graphics/courses/csw4172 Februar 1, 218 1 Homogeneous Coordinates w X W Y X W Y
COMS W4172 3D Math 2 Steven Feiner Department of Computer Science Columbia Universit New York, NY 127 www.cs.columbia.edu/graphics/courses/csw4172 Februar 1, 218 1 Homogeneous Coordinates w X W Y X W Y
Image Warping. Many slides from Alyosha Efros + Steve Seitz. Photo by Sean Carroll
 Image Warping Man slides from Alosha Efros + Steve Seitz Photo b Sean Carroll Morphing Blend from one object to other with a series of local transformations Image Transformations image filtering: change
Image Warping Man slides from Alosha Efros + Steve Seitz Photo b Sean Carroll Morphing Blend from one object to other with a series of local transformations Image Transformations image filtering: change
3D Viewing and Projec5on. Taking Pictures with a Real Camera. Steps: Graphics does the same thing for rendering an image for 3D geometric objects
 3D Vieing and Projec5on Taking Pictures ith a Real Camera Steps: Iden5 interes5ng objects Rotate and translate the camera to desired viepoint Adjust camera seings such as ocal length Choose desired resolu5on
3D Vieing and Projec5on Taking Pictures ith a Real Camera Steps: Iden5 interes5ng objects Rotate and translate the camera to desired viepoint Adjust camera seings such as ocal length Choose desired resolu5on
Computer Graphics. Geometric Transformations
 Contents coordinate sstems scalar values, points, vectors, matrices right-handed and left-handed coordinate sstems mathematical foundations transformations mathematical descriptions of geometric changes,
Contents coordinate sstems scalar values, points, vectors, matrices right-handed and left-handed coordinate sstems mathematical foundations transformations mathematical descriptions of geometric changes,
CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications
 CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theor, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin State Universit of New York at Ston Brook (Ston Brook Universit) Ston Brook, New York 794--44 Tel: (63)632-845; Fa: (63)632-8334 qin@cs.sunsb.edu
CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theor, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin State Universit of New York at Ston Brook (Ston Brook Universit) Ston Brook, New York 794--44 Tel: (63)632-845; Fa: (63)632-8334 qin@cs.sunsb.edu
Computer Graphics. Geometric Transformations
 Computer Graphics Geometric Transformations Contents coordinate sstems scalar values, points, vectors, matrices right-handed and left-handed coordinate sstems mathematical foundations transformations mathematical
Computer Graphics Geometric Transformations Contents coordinate sstems scalar values, points, vectors, matrices right-handed and left-handed coordinate sstems mathematical foundations transformations mathematical
6. Modelview Transformations
 6. Modelview Transformations Transformation Basics Transformations map coordinates from one frame of reference to another through matri multiplications Basic transformation operations include: - translation
6. Modelview Transformations Transformation Basics Transformations map coordinates from one frame of reference to another through matri multiplications Basic transformation operations include: - translation
CS 335 Graphics and Multimedia. Geometric Warping
 CS 335 Graphics and Multimedia Geometric Warping Geometric Image Operations Eample transformations Straightforward methods and their problems The affine transformation Transformation algorithms: Forward
CS 335 Graphics and Multimedia Geometric Warping Geometric Image Operations Eample transformations Straightforward methods and their problems The affine transformation Transformation algorithms: Forward
What and Why Transformations?
 2D transformations What and Wh Transformations? What? : The geometrical changes of an object from a current state to modified state. Changing an object s position (translation), orientation (rotation)
2D transformations What and Wh Transformations? What? : The geometrical changes of an object from a current state to modified state. Changing an object s position (translation), orientation (rotation)
How is project #1 going?
 How is project # going? Last Lecture Edge Detection Filtering Pramid Toda Motion Deblur Image Transformation Removing Camera Shake from a Single Photograph Rob Fergus, Barun Singh, Aaron Hertzmann, Sam
How is project # going? Last Lecture Edge Detection Filtering Pramid Toda Motion Deblur Image Transformation Removing Camera Shake from a Single Photograph Rob Fergus, Barun Singh, Aaron Hertzmann, Sam
CAP5415-Computer Vision Lecture 8-Mo8on Models, Feature Tracking, and Alignment. Ulas Bagci
 CAP545-Computer Vision Lecture 8-Mo8on Models, Feature Tracking, and Alignment Ulas Bagci bagci@ucf.edu Readings Szeliski, R. Ch. 7 Bergen et al. ECCV 92, pp. 237-252. Shi, J. and Tomasi, C. CVPR 94, pp.593-6.
CAP545-Computer Vision Lecture 8-Mo8on Models, Feature Tracking, and Alignment Ulas Bagci bagci@ucf.edu Readings Szeliski, R. Ch. 7 Bergen et al. ECCV 92, pp. 237-252. Shi, J. and Tomasi, C. CVPR 94, pp.593-6.
Editing and Transformation
 Lecture 5 Editing and Transformation Modeling Model can be produced b the combination of entities that have been edited. D: circle, arc, line, ellipse 3D: primitive bodies, etrusion and revolved of a profile
Lecture 5 Editing and Transformation Modeling Model can be produced b the combination of entities that have been edited. D: circle, arc, line, ellipse 3D: primitive bodies, etrusion and revolved of a profile
Ligh%ng in OpenGL. The Phong Illumina%on Model. Vector Background
 Ligh%ng in OpenGL The Phong Illumina%on Model Vector Background 1 Vector Dot Product The dot product of two vectors is a number:! x $ # 1 v 1 = # y 1 # " z 1 %! x $ # 2 v 2 = # y 2 # " z 2 % In GLSL you
Ligh%ng in OpenGL The Phong Illumina%on Model Vector Background 1 Vector Dot Product The dot product of two vectors is a number:! x $ # 1 v 1 = # y 1 # " z 1 %! x $ # 2 v 2 = # y 2 # " z 2 % In GLSL you
CS559: Computer Graphics
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 8: 3D Transforms Li Zhang Spring 28 Most Slides from Stephen Chenne Finish Color space Toda 3D Transforms and Coordinate sstem Reading: Shirle ch 6 RGB and HSV Green(,,)
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 8: 3D Transforms Li Zhang Spring 28 Most Slides from Stephen Chenne Finish Color space Toda 3D Transforms and Coordinate sstem Reading: Shirle ch 6 RGB and HSV Green(,,)
Math 26: Fall (part 1) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pythagorean Identity)
 Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Modeling Transformations
 Modeling Transformations Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 5 FvDFH Ch. 5 Announcement Assignment 2 has been posted: Due: 10/24 ASAP: Download the code and make sure it compiles» On windows: just build
Modeling Transformations Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 5 FvDFH Ch. 5 Announcement Assignment 2 has been posted: Due: 10/24 ASAP: Download the code and make sure it compiles» On windows: just build
Modeling Transformations
 Modeling Transformations Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 5 FvDFH Ch. 5 Overview Ra-Tracing so far Modeling transformations Ra Tracing Image RaTrace(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int heigh,
Modeling Transformations Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 5 FvDFH Ch. 5 Overview Ra-Tracing so far Modeling transformations Ra Tracing Image RaTrace(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int heigh,
Interactive Computer Graphics. Warping and morphing. Warping and Morphing. Warping and Morphing. Lecture 14+15: Warping and Morphing. What is.
 Interactive Computer Graphics Warping and morphing Lecture 14+15: Warping and Morphing Lecture 14: Warping and Morphing: Slide 1 Lecture 14: Warping and Morphing: Slide 2 Warping and Morphing What is Warping
Interactive Computer Graphics Warping and morphing Lecture 14+15: Warping and Morphing Lecture 14: Warping and Morphing: Slide 1 Lecture 14: Warping and Morphing: Slide 2 Warping and Morphing What is Warping
2D transformations and homogeneous coordinates
 2D transformations and homogeneous coordinates Dr Nicolas Holzschuch Universit of Cape Ton e-mail: holzschu@cs.uct.ac.za Map of the lecture Transformations in 2D: vector/matri notation eample: translation,
2D transformations and homogeneous coordinates Dr Nicolas Holzschuch Universit of Cape Ton e-mail: holzschu@cs.uct.ac.za Map of the lecture Transformations in 2D: vector/matri notation eample: translation,
Image Warping. Some slides from Steve Seitz
 Image Warping http://www.jeffre-martin.com Some slides from Steve Seitz 5-463: Computational Photograph Aleei Efros, CMU, Spring 2 Image Transformations image filtering: change range of image g() = T(f())
Image Warping http://www.jeffre-martin.com Some slides from Steve Seitz 5-463: Computational Photograph Aleei Efros, CMU, Spring 2 Image Transformations image filtering: change range of image g() = T(f())
Warping, Morphing and Mosaics
 Computational Photograph and Video: Warping, Morphing and Mosaics Prof. Marc Pollefes Dr. Gabriel Brostow Toda s schedule Last week s recap Warping Morphing Mosaics Toda s schedule Last week s recap Warping
Computational Photograph and Video: Warping, Morphing and Mosaics Prof. Marc Pollefes Dr. Gabriel Brostow Toda s schedule Last week s recap Warping Morphing Mosaics Toda s schedule Last week s recap Warping
Modeling Transformations Revisited
 Modeling Transformations Revisited Basic 3D Transformations Translation Scale Shear Rotation 3D Transformations Same idea as 2D transformations o Homogeneous coordinates: (,,z,w) o 44 transformation matrices
Modeling Transformations Revisited Basic 3D Transformations Translation Scale Shear Rotation 3D Transformations Same idea as 2D transformations o Homogeneous coordinates: (,,z,w) o 44 transformation matrices
What does OpenGL do?
 Theor behind Geometrical Transform What does OpenGL do? So the user specifies a lot of information Ee Center Up Near, far, UP EE Left, right top, bottom, etc. f b CENTER left right top bottom What does
Theor behind Geometrical Transform What does OpenGL do? So the user specifies a lot of information Ee Center Up Near, far, UP EE Left, right top, bottom, etc. f b CENTER left right top bottom What does
PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9)
 PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9) Name Date Directions: You may NOT use Right Triangle Trigonometry for any of these problems! Use your unit circle knowledge to solve these problems.
PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9) Name Date Directions: You may NOT use Right Triangle Trigonometry for any of these problems! Use your unit circle knowledge to solve these problems.
CSCI-4530/6530 Advanced Computer Graphics
 Luo Jr. CSCI-453/653 Advanced Computer Graphics http://www.cs.rpi.edu/~cutler/classes/advancedgraphics/s7/ Barb Cutler cutler@cs.rpi.edu MRC 33A Piar Animation Studios, 986 Topics for the Semester Meshes
Luo Jr. CSCI-453/653 Advanced Computer Graphics http://www.cs.rpi.edu/~cutler/classes/advancedgraphics/s7/ Barb Cutler cutler@cs.rpi.edu MRC 33A Piar Animation Studios, 986 Topics for the Semester Meshes
Transformations II. Arbitrary 3D Rotation. What is its inverse? What is its transpose? Can we constructively elucidate this relationship?
 Utah School of Computing Fall 25 Transformations II CS46 Computer Graphics From Rich Riesenfeld Fall 25 Arbitrar 3D Rotation What is its inverse? What is its transpose? Can we constructivel elucidate this
Utah School of Computing Fall 25 Transformations II CS46 Computer Graphics From Rich Riesenfeld Fall 25 Arbitrar 3D Rotation What is its inverse? What is its transpose? Can we constructivel elucidate this
High Dimensional Rendering in OpenGL
 High Dimensional Rendering in OpenGL Josh McCo December, 2003 Description of Project Adding high dimensional rendering capabilit to the OpenGL graphics programming environment is the goal of this project
High Dimensional Rendering in OpenGL Josh McCo December, 2003 Description of Project Adding high dimensional rendering capabilit to the OpenGL graphics programming environment is the goal of this project
CSCI-4530/6530 Advanced Computer Graphics
 Luo Jr. CSCI-45/65 Advanced Computer Graphics http://www.cs.rpi.edu/~cutler/classes/advancedgraphics/s9/ Barb Cutler cutler@cs.rpi.edu MRC 9A Piar Animation Studios, 986 Topics for the Semester Mesh Simplification
Luo Jr. CSCI-45/65 Advanced Computer Graphics http://www.cs.rpi.edu/~cutler/classes/advancedgraphics/s9/ Barb Cutler cutler@cs.rpi.edu MRC 9A Piar Animation Studios, 986 Topics for the Semester Mesh Simplification
Introduction to Homogeneous Transformations & Robot Kinematics
 Introduction to Homogeneous Transformations & Robot Kinematics Jennifer Ka Rowan Universit Computer Science Department. Drawing Dimensional Frames in 2 Dimensions We will be working in -D coordinates,
Introduction to Homogeneous Transformations & Robot Kinematics Jennifer Ka Rowan Universit Computer Science Department. Drawing Dimensional Frames in 2 Dimensions We will be working in -D coordinates,
Quiz #2 Review. Transformations & Matrices. Quiz #2 Review. Quiz #2 Review. Example: Change the time on y the clock. Example: Move clock hands
 Quiz #2 Review Transformations & Matrices Introduction to Computer Graphics Dot Product a. b a b cos θ a b + a y b y + a z b z a. b a T b thus b [a a y a z ] b y b z a b + a y b y + a z b z Quiz #2 Review
Quiz #2 Review Transformations & Matrices Introduction to Computer Graphics Dot Product a. b a b cos θ a b + a y b y + a z b z a. b a T b thus b [a a y a z ] b y b z a b + a y b y + a z b z Quiz #2 Review
[ ] [ ] Orthogonal Transformation of Cartesian Coordinates in 2D & 3D. φ = cos 1 1/ φ = tan 1 [ 2 /1]
![[ ] [ ] Orthogonal Transformation of Cartesian Coordinates in 2D & 3D. φ = cos 1 1/ φ = tan 1 [ 2 /1] [ ] [ ] Orthogonal Transformation of Cartesian Coordinates in 2D & 3D. φ = cos 1 1/ φ = tan 1 [ 2 /1]](/thumbs/84/89383711.jpg) Orthogonal Transformation of Cartesian Coordinates in 2D & 3D A vector is specified b its coordinates, so it is defined relative to a reference frame. The same vector will have different coordinates in
Orthogonal Transformation of Cartesian Coordinates in 2D & 3D A vector is specified b its coordinates, so it is defined relative to a reference frame. The same vector will have different coordinates in
Image Metamorphosis By Affine Transformations
 Image Metamorphosis B Affine Transformations Tim Mers and Peter Spiegel December 16, 2005 Abstract Among the man was to manipulate an image is a technique known as morphing. Image morphing is a special
Image Metamorphosis B Affine Transformations Tim Mers and Peter Spiegel December 16, 2005 Abstract Among the man was to manipulate an image is a technique known as morphing. Image morphing is a special
Supplementary Material: The Rotation Matrix
 Supplementary Material: The Rotation Matrix Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland January 16, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) The Rotation Matrix January
Supplementary Material: The Rotation Matrix Computer Science 4766/6778 Department of Computer Science Memorial University of Newfoundland January 16, 2014 COMP 4766/6778 (MUN) The Rotation Matrix January
Modeling Transformations
 Transformations Transformations Specif transformations for objects o Allos definitions of objects in on coordinate sstems o Allos use of object definition multiple times in a scene Adam Finkelstein Princeton
Transformations Transformations Specif transformations for objects o Allos definitions of objects in on coordinate sstems o Allos use of object definition multiple times in a scene Adam Finkelstein Princeton
Image Warping CSE399b, Spring 07 Computer Vision
 Image Warping CSE399b, Spring 7 Computer Vision http://maps.a9.com http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~mbrown/autostitch/autostitch.html http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~mbrown/autostitch/autostitch.html Autostiching on A9.com
Image Warping CSE399b, Spring 7 Computer Vision http://maps.a9.com http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~mbrown/autostitch/autostitch.html http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~mbrown/autostitch/autostitch.html Autostiching on A9.com
Modeling Transformations
 Modeling Transformations Thomas Funkhouser Princeton Universit CS 426, Fall 2 Modeling Transformations Specif transformations for objects Allos definitions of objects in on coordinate sstems Allos use
Modeling Transformations Thomas Funkhouser Princeton Universit CS 426, Fall 2 Modeling Transformations Specif transformations for objects Allos definitions of objects in on coordinate sstems Allos use
General Purpose Computation (CAD/CAM/CAE) on the GPU (a.k.a. Topics in Manufacturing)
 ME 29-R: General Purpose Computation (CAD/CAM/CAE) on the GPU (a.k.a. Topics in Manufacturing) Sara McMains Spring 29 lecture 2 Toda s GPU eample: moldabilit feedback Two-part mold [The Complete Sculptor
ME 29-R: General Purpose Computation (CAD/CAM/CAE) on the GPU (a.k.a. Topics in Manufacturing) Sara McMains Spring 29 lecture 2 Toda s GPU eample: moldabilit feedback Two-part mold [The Complete Sculptor
(x, y) (ρ, θ) ρ θ. Polar Coordinates. Cartesian Coordinates
 Coordinate Sstems Point Representation in two dimensions Cartesian Coordinates: (; ) Polar Coordinates: (; ) (, ) ρ θ (ρ, θ) Cartesian Coordinates Polar Coordinates p = CPS1, 9: Computer Graphics D Geometric
Coordinate Sstems Point Representation in two dimensions Cartesian Coordinates: (; ) Polar Coordinates: (; ) (, ) ρ θ (ρ, θ) Cartesian Coordinates Polar Coordinates p = CPS1, 9: Computer Graphics D Geometric
Modeling Transformations
 שיעור 3 גרפיקה ממוחשבת תשס"ח ב ליאור שפירא Modeling Transformations Heavil based on: Thomas Funkhouser Princeton Universit CS 426, Fall 2 Modeling Transformations Specif transformations for objects Allows
שיעור 3 גרפיקה ממוחשבת תשס"ח ב ליאור שפירא Modeling Transformations Heavil based on: Thomas Funkhouser Princeton Universit CS 426, Fall 2 Modeling Transformations Specif transformations for objects Allows
To Do. Course Outline. Course Outline. Goals. Motivation. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lecture 3: Transformations 1
 Fondations of Compter Graphics (Fall 212) CS 184, Lectre 3: Transformations 1 http://inst.eecs.berkele.ed/~cs184 Sbmit HW b To Do Start looking at HW 1 (simple, bt need to think) Ais-angle rotation and
Fondations of Compter Graphics (Fall 212) CS 184, Lectre 3: Transformations 1 http://inst.eecs.berkele.ed/~cs184 Sbmit HW b To Do Start looking at HW 1 (simple, bt need to think) Ais-angle rotation and
Determining the 2d transformation that brings one image into alignment (registers it) with another. And
 Last two lectures: Representing an image as a weighted combination of other images. Toda: A different kind of coordinate sstem change. Solving the biggest problem in using eigenfaces? Toda Recognition
Last two lectures: Representing an image as a weighted combination of other images. Toda: A different kind of coordinate sstem change. Solving the biggest problem in using eigenfaces? Toda Recognition
Honors Advanced Math More on Determinants, Transformations and Systems 14 May 2013
 Honors Advanced Math Name: More on Determinants, Transformations and Sstems 14 Ma 013 Directions: The following problems are designed to help develop connections between determinants, sstems of equations
Honors Advanced Math Name: More on Determinants, Transformations and Sstems 14 Ma 013 Directions: The following problems are designed to help develop connections between determinants, sstems of equations
GRAPHING QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN STANDARD FORM
 FOM 11 T7 GRAPHING QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN STANDARD FORM 1 1 GRAPHING QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN STANDARD FORM I) THE STANDARD FORM OF A QUADRATIC FUNCTION (PARABOLA) IS = a +b +c. To graph a quadratic function
FOM 11 T7 GRAPHING QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN STANDARD FORM 1 1 GRAPHING QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN STANDARD FORM I) THE STANDARD FORM OF A QUADRATIC FUNCTION (PARABOLA) IS = a +b +c. To graph a quadratic function
3D Geometry and Camera Calibration
 3D Geometr and Camera Calibration 3D Coordinate Sstems Right-handed vs. left-handed 2D Coordinate Sstems ais up vs. ais down Origin at center vs. corner Will often write (u, v) for image coordinates v
3D Geometr and Camera Calibration 3D Coordinate Sstems Right-handed vs. left-handed 2D Coordinate Sstems ais up vs. ais down Origin at center vs. corner Will often write (u, v) for image coordinates v
GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING
 GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING 2D and 3D 1/44 2D TRANSFORMATIONS HOMOGENIZED Transformation Scaling Rotation Translation Matrix s x s y cosθ sinθ sinθ cosθ 1 dx 1 dy These 3 transformations are
GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING 2D and 3D 1/44 2D TRANSFORMATIONS HOMOGENIZED Transformation Scaling Rotation Translation Matrix s x s y cosθ sinθ sinθ cosθ 1 dx 1 dy These 3 transformations are
Introduction to Homogeneous Transformations & Robot Kinematics
 Introduction to Homogeneous Transformations & Robot Kinematics Jennifer Ka, Rowan Universit Computer Science Department Januar 25. Drawing Dimensional Frames in 2 Dimensions We will be working in -D coordinates,
Introduction to Homogeneous Transformations & Robot Kinematics Jennifer Ka, Rowan Universit Computer Science Department Januar 25. Drawing Dimensional Frames in 2 Dimensions We will be working in -D coordinates,
13.2. General Angles and Radian Measure. What you should learn
 Page 1 of 1. General Angles and Radian Measure What ou should learn GOAL 1 Measure angles in standard position using degree measure and radian measure. GOAL Calculate arc lengths and areas of sectors,
Page 1 of 1. General Angles and Radian Measure What ou should learn GOAL 1 Measure angles in standard position using degree measure and radian measure. GOAL Calculate arc lengths and areas of sectors,
Network Coding: Theory and Applica7ons
 Network Coding: Theory and Applica7ons PhD Course Part IV Tuesday 9.15-12.15 18.6.213 Muriel Médard (MIT), Frank H. P. Fitzek (AAU), Daniel E. Lucani (AAU), Morten V. Pedersen (AAU) Plan Hello World! Intra
Network Coding: Theory and Applica7ons PhD Course Part IV Tuesday 9.15-12.15 18.6.213 Muriel Médard (MIT), Frank H. P. Fitzek (AAU), Daniel E. Lucani (AAU), Morten V. Pedersen (AAU) Plan Hello World! Intra
We can conclude that if f is differentiable in an interval containing a, then. f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f (a)(x a).
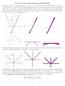 = sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
= sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
BUMP MAPPING. Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos Prof. João A. Madeiras Pereira MEIC-A/IST
 UMP MAPPIG Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos Prof. João A. Madeiras Pereira MEIC-A/IS Eamples Shading Generating ormal Map ase teture (RG) Height map (Gre scale) ormal map (normal encoded RG) Displacement
UMP MAPPIG Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos Prof. João A. Madeiras Pereira MEIC-A/IS Eamples Shading Generating ormal Map ase teture (RG) Height map (Gre scale) ormal map (normal encoded RG) Displacement
Image Warping (Szeliski Sec 2.1.2)
 Image Warping (Szeliski Sec 2..2) http://www.jeffre-martin.com CS94: Image Manipulation & Computational Photograph Aleei Efros, UC Berkele, Fall 7 Some slides from Steve Seitz Image Transformations image
Image Warping (Szeliski Sec 2..2) http://www.jeffre-martin.com CS94: Image Manipulation & Computational Photograph Aleei Efros, UC Berkele, Fall 7 Some slides from Steve Seitz Image Transformations image
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Matrix Transformations. Affine Transformations
 Matri ransformations Basic Graphics ransforms ranslation Scaling Rotation Reflection Shear All Can be Epressed As Linear Functions of the Original Coordinates : A + B + C D + E + F ' A ' D 1 B E C F 1
Matri ransformations Basic Graphics ransforms ranslation Scaling Rotation Reflection Shear All Can be Epressed As Linear Functions of the Original Coordinates : A + B + C D + E + F ' A ' D 1 B E C F 1
10. ROTATIONS (I) I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Uses of rota=on in geolog (and engineering) B Concepts behind rota=on C Appendi (Geometr on a Sphere for Plate Tectonics) 10/5/15 GG303 1 II Uses of rota=on in geolog (and engineering)
I Main Topics A Uses of rota=on in geolog (and engineering) B Concepts behind rota=on C Appendi (Geometr on a Sphere for Plate Tectonics) 10/5/15 GG303 1 II Uses of rota=on in geolog (and engineering)
CS 157: Assignment 6
 CS 7: Assignment Douglas R. Lanman 8 Ma Problem : Evaluating Conve Polgons This write-up presents several simple algorithms for determining whether a given set of twodimensional points defines a conve
CS 7: Assignment Douglas R. Lanman 8 Ma Problem : Evaluating Conve Polgons This write-up presents several simple algorithms for determining whether a given set of twodimensional points defines a conve
STRAND I: Geometry and Trigonometry. UNIT 37 Further Transformations: Student Text Contents. Section Reflections. 37.
 MEP Jamaica: STRN I UNIT 7 Further Transformations: Student Tet ontents STRN I: Geometr and Trigonometr Unit 7 Further Transformations Student Tet ontents Section 7. Reflections 7. Rotations 7. Translations
MEP Jamaica: STRN I UNIT 7 Further Transformations: Student Tet ontents STRN I: Geometr and Trigonometr Unit 7 Further Transformations Student Tet ontents Section 7. Reflections 7. Rotations 7. Translations
Lecture 4: Viewing. Topics:
 Lecture 4: Viewing Topics: 1. Classical viewing 2. Positioning the camera 3. Perspective and orthogonal projections 4. Perspective and orthogonal projections in OpenGL 5. Perspective and orthogonal projection
Lecture 4: Viewing Topics: 1. Classical viewing 2. Positioning the camera 3. Perspective and orthogonal projections 4. Perspective and orthogonal projections in OpenGL 5. Perspective and orthogonal projection
Sample Problems for Quiz # 3
 EE 1301 UMN Introduction to Computing Sstems Spring 2013 Sample Problems for Quiz # 3 1. Implementing XOR with AND gates Recall that the Eclusive-OR (XOR) function is 1 if an odd number of the inputs are
EE 1301 UMN Introduction to Computing Sstems Spring 2013 Sample Problems for Quiz # 3 1. Implementing XOR with AND gates Recall that the Eclusive-OR (XOR) function is 1 if an odd number of the inputs are
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective Department of Computing and Information Systems The Lecture outline Introduction Rotation about artibrary axis
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective Department of Computing and Information Systems The Lecture outline Introduction Rotation about artibrary axis
Polar Coordinates
 Polar Coordinates 7-7-2 Polar coordinates are an alternative to rectangular coordinates for referring to points in the plane. A point in the plane has polar coordinates r,θ). r is roughly) the distance
Polar Coordinates 7-7-2 Polar coordinates are an alternative to rectangular coordinates for referring to points in the plane. A point in the plane has polar coordinates r,θ). r is roughly) the distance
is a plane curve and the equations are parametric equations for the curve, with parameter t.
 MATH 2412 Sections 6.3, 6.4, and 6.5 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates. Plane Curves and Parametric Equations Suppose t is contained in some interval I of the real numbers, and = f( t), = gt (
MATH 2412 Sections 6.3, 6.4, and 6.5 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates. Plane Curves and Parametric Equations Suppose t is contained in some interval I of the real numbers, and = f( t), = gt (
Computer Graphics. Geometric. Transformations. by Brian Wyvill University of Calgary. Lecture 2 Geometric. Transformations. Lecture 2 Geometric
 Lecture 2 Geometric Transformations Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Geometric Transformations b Brian Wvill Universit of Calgar ENEL/CPSC. Lecture 2 Geometric Transformations Lecture 2 Geometric Transformations
Lecture 2 Geometric Transformations Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Geometric Transformations b Brian Wvill Universit of Calgar ENEL/CPSC. Lecture 2 Geometric Transformations Lecture 2 Geometric Transformations
2D Transformations. 7 February 2017 Week 5-2D Transformations 1
 2D Transformations 7 Februar 27 Week 5-2D Transformations Matri math Is there a difference between possible representations? a c b e d f ae bf ce df a c b d e f ae cf be df a b c d e f ae bf ce df 7 Februar
2D Transformations 7 Februar 27 Week 5-2D Transformations Matri math Is there a difference between possible representations? a c b e d f ae bf ce df a c b d e f ae cf be df a b c d e f ae bf ce df 7 Februar
Name: [20 points] Consider the following OpenGL commands:
![Name: [20 points] Consider the following OpenGL commands: Name: [20 points] Consider the following OpenGL commands:](/thumbs/80/82290206.jpg) Name: 2 1. [20 points] Consider the following OpenGL commands: glmatrimode(gl MODELVIEW); glloadidentit(); glrotatef( 90.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0 ); gltranslatef( 2.0, 0.0, 0.0 ); glscalef( 2.0, 1.0, 1.0 ); What
Name: 2 1. [20 points] Consider the following OpenGL commands: glmatrimode(gl MODELVIEW); glloadidentit(); glrotatef( 90.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0 ); gltranslatef( 2.0, 0.0, 0.0 ); glscalef( 2.0, 1.0, 1.0 ); What
CMSC 425: Lecture 10 Basics of Skeletal Animation and Kinematics
 : Lecture Basics of Skeletal Animation and Kinematics Reading: Chapt of Gregor, Game Engine Architecture. The material on kinematics is a simplification of similar concepts developed in the field of robotics,
: Lecture Basics of Skeletal Animation and Kinematics Reading: Chapt of Gregor, Game Engine Architecture. The material on kinematics is a simplification of similar concepts developed in the field of robotics,
Uses of Transformations. 2D transformations Homogeneous coordinates. Transformations. Transformations. Transformations. Transformations and matrices
 Uses of Transformations 2D transformations Homogeneous coordinates odeling: position and resie parts of a comple model; Viewing: define and position the virtual camera Animation: define how objects move/change
Uses of Transformations 2D transformations Homogeneous coordinates odeling: position and resie parts of a comple model; Viewing: define and position the virtual camera Animation: define how objects move/change
Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D
 Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D In today s lecture we are going to have a look at: Transformations in 3-D How do transformations in 3-D work? Contents 3-D homogeneous coordinates and matrix based transformations
Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D In today s lecture we are going to have a look at: Transformations in 3-D How do transformations in 3-D work? Contents 3-D homogeneous coordinates and matrix based transformations
2D Image Transforms Computer Vision (Kris Kitani) Carnegie Mellon University
 2D Image Transforms 16-385 Computer Vision (Kris Kitani) Carnegie Mellon University Extract features from an image what do we do next? Feature matching (object recognition, 3D reconstruction, augmented
2D Image Transforms 16-385 Computer Vision (Kris Kitani) Carnegie Mellon University Extract features from an image what do we do next? Feature matching (object recognition, 3D reconstruction, augmented
Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates
 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates. A flat plate is in the shape of the region in the first quadrant ling between the circles + and +. The densit of the plate at point, is + kilograms per square meter
Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates. A flat plate is in the shape of the region in the first quadrant ling between the circles + and +. The densit of the plate at point, is + kilograms per square meter
Transforming Coordinates
 # Transforming Coordinates The drawing window in man computer geometr programs is a coordinate grid. You make designs b specifing the endpoints of line segments. When ou transform a design, the coordinates
# Transforming Coordinates The drawing window in man computer geometr programs is a coordinate grid. You make designs b specifing the endpoints of line segments. When ou transform a design, the coordinates
3D Computer Vision II. Reminder Projective Geometry, Transformations. Nassir Navab. October 27, 2009
 3D Computer Vision II Reminder Projective Geometr, Transformations Nassir Navab based on a course given at UNC b Marc Pollefes & the book Multiple View Geometr b Hartle & Zisserman October 27, 29 2D Transformations
3D Computer Vision II Reminder Projective Geometr, Transformations Nassir Navab based on a course given at UNC b Marc Pollefes & the book Multiple View Geometr b Hartle & Zisserman October 27, 29 2D Transformations
CS 450: COMPUTER GRAPHICS 2D TRANSFORMATIONS SPRING 2016 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE
 CS 45: COMUTER GRAHICS 2D TRANSFORMATIONS SRING 26 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE INTRODUCTION Now that we hae some linear algebra under our resectie belts, we can start ug it in grahics! So far, for each rimitie,
CS 45: COMUTER GRAHICS 2D TRANSFORMATIONS SRING 26 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE INTRODUCTION Now that we hae some linear algebra under our resectie belts, we can start ug it in grahics! So far, for each rimitie,
To Do. Demo (Projection Tutorial) Motivation. What we ve seen so far. Outline. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lecture 5: Viewing
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 0) CS 84, Lecture 5: Viewing http://inst.eecs.berkele.edu/~cs84 To Do Questions/concerns about assignment? Remember it is due Sep. Ask me or TAs re problems Motivation
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 0) CS 84, Lecture 5: Viewing http://inst.eecs.berkele.edu/~cs84 To Do Questions/concerns about assignment? Remember it is due Sep. Ask me or TAs re problems Motivation
CS770/870 Spring 2017 Transformations
 CS770/870 Spring 2017 Transformations Coordinate sstems 2D Transformations Homogeneous coordinates Matrices, vectors, points Coordinate Sstems Coordinate sstems used in graphics Screen coordinates: the
CS770/870 Spring 2017 Transformations Coordinate sstems 2D Transformations Homogeneous coordinates Matrices, vectors, points Coordinate Sstems Coordinate sstems used in graphics Screen coordinates: the
Image Warping. Computational Photography Derek Hoiem, University of Illinois 09/28/17. Photo by Sean Carroll
 Image Warping 9/28/7 Man slides from Alosha Efros + Steve Seitz Computational Photograph Derek Hoiem, Universit of Illinois Photo b Sean Carroll Reminder: Proj 2 due monda Much more difficult than project
Image Warping 9/28/7 Man slides from Alosha Efros + Steve Seitz Computational Photograph Derek Hoiem, Universit of Illinois Photo b Sean Carroll Reminder: Proj 2 due monda Much more difficult than project
It s Not Complex Just Its Solutions Are Complex!
 It s Not Comple Just Its Solutions Are Comple! Solving Quadratics with Comple Solutions 15.5 Learning Goals In this lesson, ou will: Calculate comple roots of quadratic equations and comple zeros of quadratic
It s Not Comple Just Its Solutions Are Comple! Solving Quadratics with Comple Solutions 15.5 Learning Goals In this lesson, ou will: Calculate comple roots of quadratic equations and comple zeros of quadratic
Graphics Programming. Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2. Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University
 Graphics Programming Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2 Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University Graphics programming Typically deals with How to define a 3D scene with a
Graphics Programming Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2 Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University Graphics programming Typically deals with How to define a 3D scene with a
IMGD The Game Development Process: 3D Modeling and Transformations
 IMGD - The Game Development Process: 3D Modeling and Transformations b Robert W. Lindeman (gogo@wpi.edu Kent Quirk (kent_quirk@cognito.com (with lots of input from Mark Clapool! Overview of 3D Modeling
IMGD - The Game Development Process: 3D Modeling and Transformations b Robert W. Lindeman (gogo@wpi.edu Kent Quirk (kent_quirk@cognito.com (with lots of input from Mark Clapool! Overview of 3D Modeling
To Do. Motivation. Demo (Projection Tutorial) What we ve seen so far. Computer Graphics. Summary: The Whole Viewing Pipeline
 Computer Graphics CSE 67 [Win 9], Lecture 5: Viewing Ravi Ramamoorthi http://viscomp.ucsd.edu/classes/cse67/wi9 To Do Questions/concerns about assignment? Remember it is due tomorrow! (Jan 6). Ask me or
Computer Graphics CSE 67 [Win 9], Lecture 5: Viewing Ravi Ramamoorthi http://viscomp.ucsd.edu/classes/cse67/wi9 To Do Questions/concerns about assignment? Remember it is due tomorrow! (Jan 6). Ask me or
GPU-Accelerated Iterated Function Systems. Simon Green, NVIDIA Corporation
 GPU-Accelerated Iterated Function Sstems Simon Green NVIDIA Corporation Iterated Function Sstems Fractal Conceived b John Hutchinson 1981 Popularized b Michael Barnsle Fractals Everwhere 1998 Consists
GPU-Accelerated Iterated Function Sstems Simon Green NVIDIA Corporation Iterated Function Sstems Fractal Conceived b John Hutchinson 1981 Popularized b Michael Barnsle Fractals Everwhere 1998 Consists
For example, could you make the XNA func8ons yourself?
 1 For example, could you make the XNA func8ons yourself? For the second assignment you need to know about the en8re process of using the graphics hardware. You will use shaders which play a vital role
1 For example, could you make the XNA func8ons yourself? For the second assignment you need to know about the en8re process of using the graphics hardware. You will use shaders which play a vital role
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6. ) is graphed below:
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES
 Mathematics SKE, Strand J UNIT J Further Transformations: Tet STRND J: TRNSFORMTIONS, VETORS and MTRIES J Further Transformations Tet ontents Section J.1 Translations * J. ombined Transformations Mathematics
Mathematics SKE, Strand J UNIT J Further Transformations: Tet STRND J: TRNSFORMTIONS, VETORS and MTRIES J Further Transformations Tet ontents Section J.1 Translations * J. ombined Transformations Mathematics
