ECE331 Homework 4. Due Monday, August 13, 2018 (via Moodle)
|
|
|
- Clyde McDowell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECE331 Homework 4 Due Monday, August 13, 2018 (via Moodle) 1. Below is a list of 32-bit memory address references, given as hexadecimal byte addresses. The memory accesses are all reads and they occur in the order given 0xA00, 0x864, 0x50234, 0xA00, 0xF0C, 0x50234, 0x63C, 0x128, 0x3C4, 0x34B4, 0x50234 a. For each of these references, identify the binary address, the tag, and the index given a direct-mapped cache with 16 one-word blocks. Also list if each reference is a hit or miss, assuming the cache is initially empty b. For each of these references, identify the binary address, the tag, and the index given a direct-mapped cache with 8 two-word blocks. Also list if each reference is a hit or miss, assuming the cache is initially empty c. For each of these references, identify the binary address, the tag, and the index given a two-way set-associative cache with 16 one-word blocks (Hint: there are 8 sets). Also list if each reference is a hit or miss, assuming the cache is initially empty. Use a LRU replacement strategy. d. Calculate the total number of bits required for the cache listed in (c). Include tag storage, dirty bit storage, valid bit storage, and the data storage
2 2. Given the following assumptions, fill out the table of data cache content on the next two pages based on memory access sequence shown in the following table. Cache is initially empty The data cache is a direct mapped cache The width of memory address is 8-bit and it is a byte address The cache block size is 4 bytes Write through strategy is used in this cache Memory Accesses # Access Size Access Type Byte Address in Binary 1 Byte Read Byte Read Byte Read Word Write Byte Read Word Write Word Read Byte Read Byte Read Byte Read
3 Data Cache Content Note: a.) For locations never accessed, leave the corresponding tag and data boxes blank. b.) Indicate the valid bit for each cache block. Use V for valid and I for invalid. c.) The block data should be given in the format of M [block address]. d.) Mark each access in order for up to 4 accesses. The first access should be the first one listed. Index V Tag Data
4 (b) What is the miss rate of the cache for the memory accesses in question (a)?
5 3. The following C program is run on a machine with a data cache that has two-word (8 bytes) blocks and the data capacity of the data cache is 128 bytes. Assume that only references to the array incur memory accesses and the cache is empty at the very beginning. Hint: a variable with int type contains four bytes and the MIPs uses byte addresses int i, c, array[128]; c = 0; for (i=0; i<128; i++) { c = c+array[i]; } (a) How many cache lines are there if the cache is direct mapped? Show your work. (b) How many sets are there if the cache is two-way associative? Which address bits are used for indexing the set in a 32-bit address? Please present the result in Addr[x:y] format (for example, Addr[8:5] means that bit 8 to bit 5 in the address are used for indexing). Show your work. (c) If a direct mapped cache is used, what is the expected miss rate after program execution. Show your work.
6 (d) If a two-way associative cache is used, what is the expected miss rate after program execution. Show your work. (e) If a four-way associative cache is used, what is the expected miss rate after execution the program. Show your work. 4. The diagram below illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache for 32-bit data words with 32-bit byte addresses
7 (a) What is the maximum number of words of data from the main memory that can be stored in the cache at any one time? (b) How many bits of the address are used to select which line of the cache is accessed? (c) How many bits wide is the tag field?
8 (d) Briefly explain the purpose of the one-bit V field associated with each cache line (e) Assume that location 0xCF120 was present in the cache. Using the row and column labels from the figure, in what location(s) could we find the data from that location? What would the value of the tag field have to be for the cache row in which the data appears? (f) Can data from location 0xF6768 and 0xF67F8 be present in the cache at the same time? What about the data from locations 0xB20738 and 0x2034? Explain? (g) When an access causes a cache miss, how many words need to be fetched from memory to fill the appropriate cache location?
CS 433 Homework 5. Assigned on 11/7/2017 Due in class on 11/30/2017
 CS 433 Homework 5 Assigned on 11/7/2017 Due in class on 11/30/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
CS 433 Homework 5 Assigned on 11/7/2017 Due in class on 11/30/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
6.004 Tutorial Problems L14 Cache Implementation
 6.004 Tutorial Problems L14 Cache Implementation Cache Miss Types Compulsory Miss: Starting with an empty cache, a cache line is first referenced (invalid) Capacity Miss: The cache is not big enough to
6.004 Tutorial Problems L14 Cache Implementation Cache Miss Types Compulsory Miss: Starting with an empty cache, a cache line is first referenced (invalid) Capacity Miss: The cache is not big enough to
ELE 758 * DIGITAL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING * MIDTERM TEST * Circle the memory type based on electrically re-chargeable elements
 ELE 758 * DIGITAL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING * MIDTERM TEST * Student name: Date: Example 1 Section: Memory hierarchy (SRAM, DRAM) Question # 1.1 Circle the memory type based on electrically re-chargeable elements
ELE 758 * DIGITAL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING * MIDTERM TEST * Student name: Date: Example 1 Section: Memory hierarchy (SRAM, DRAM) Question # 1.1 Circle the memory type based on electrically re-chargeable elements
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering
 ECE 0 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #9 Spring 01 1. Given the following series of address references given as word addresses:,,, 1, 1, 1,, 8, 19,,,,, 7,, and. Assuming a direct-mapped
ECE 0 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #9 Spring 01 1. Given the following series of address references given as word addresses:,,, 1, 1, 1,, 8, 19,,,,, 7,, and. Assuming a direct-mapped
Project: Visual Cache Simulator Input: Real Addresses Outputs: 1. Number of Hits 2. Number of Misses 3. Hit Ratio 4. Visual Representation of Cache
 Project: Visual Cache Simulator Input: Real Addresses Outputs: 1. Number of Hits 2. Number of Misses 3. Hit Ratio 4. Visual Representation of Cache including 4.1. Index or Index Set 4.2. Tag 4.3. Cache
Project: Visual Cache Simulator Input: Real Addresses Outputs: 1. Number of Hits 2. Number of Misses 3. Hit Ratio 4. Visual Representation of Cache including 4.1. Index or Index Set 4.2. Tag 4.3. Cache
Virtual Memory Worksheet
 Virtual Memory Worksheet (v + p) bits in virtual address (m + p) bits in physical address 2 v number of virtual pages 2 m number of physical pages 2 p bytes per physical page 2 v+p bytes in virtual memory
Virtual Memory Worksheet (v + p) bits in virtual address (m + p) bits in physical address 2 v number of virtual pages 2 m number of physical pages 2 p bytes per physical page 2 v+p bytes in virtual memory
CAM Content Addressable Memory. For TAG look-up in a Fully-Associative Cache
 CAM Content Addressable Memory For TAG look-up in a Fully-Associative Cache 1 Tagin Fully Associative Cache Tag0 Data0 Tag1 Data1 Tag15 Data15 1 Tagin CAM Data RAM Tag0 Data0 Tag1 Data1 Tag15 Data15 Tag
CAM Content Addressable Memory For TAG look-up in a Fully-Associative Cache 1 Tagin Fully Associative Cache Tag0 Data0 Tag1 Data1 Tag15 Data15 1 Tagin CAM Data RAM Tag0 Data0 Tag1 Data1 Tag15 Data15 Tag
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
Figure 1: Organisation for 128KB Direct Mapped Cache with 16-word Block Size and Word Addressable
 Tutorial 12: Cache Problem 1: Direct Mapped Cache Consider a 128KB of data in a direct-mapped cache with 16 word blocks. Determine the size of the tag, index and offset fields if a 32-bit architecture
Tutorial 12: Cache Problem 1: Direct Mapped Cache Consider a 128KB of data in a direct-mapped cache with 16 word blocks. Determine the size of the tag, index and offset fields if a 32-bit architecture
ENCM 369 Winter 2016 Lab 11 for the Week of April 4
 page 1 of 13 ENCM 369 Winter 2016 Lab 11 for the Week of April 4 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary April 2016 Lab instructions and other documents for ENCM
page 1 of 13 ENCM 369 Winter 2016 Lab 11 for the Week of April 4 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary April 2016 Lab instructions and other documents for ENCM
ELEC3441: Computer Architecture Second Semester, Homework 3 (r1.1) SOLUTION. r1.1 Page 1 of 12
 Homework 3, Part ELEC3441: Computer Architecture Second Semester, 2015 16 Homework 3 (r1.1) r1.1 Page 1 of 12 A.1 Cache Access Part A: Problem Set Consider the following sequence of memory accesses to
Homework 3, Part ELEC3441: Computer Architecture Second Semester, 2015 16 Homework 3 (r1.1) r1.1 Page 1 of 12 A.1 Cache Access Part A: Problem Set Consider the following sequence of memory accesses to
Virtual Memory Overview
 Virtual Memory Overview Virtual address (VA): What your program uses Virtual Page Number Page Offset Physical address (PA): What actually determines where in memory to go Physical Page Number Page Offset
Virtual Memory Overview Virtual address (VA): What your program uses Virtual Page Number Page Offset Physical address (PA): What actually determines where in memory to go Physical Page Number Page Offset
Write only as much as necessary. Be brief!
 1 CIS371 Computer Organization and Design Midterm Exam Prof. Martin Thursday, March 15th, 2012 This exam is an individual-work exam. Write your answers on these pages. Additional pages may be attached
1 CIS371 Computer Organization and Design Midterm Exam Prof. Martin Thursday, March 15th, 2012 This exam is an individual-work exam. Write your answers on these pages. Additional pages may be attached
registers data 1 registers MEMORY ADDRESS on-chip cache off-chip cache main memory: real address space part of virtual addr. sp.
 Cache associativity Cache and performance 12 1 CMPE110 Spring 2005 A. Di Blas 110 Spring 2005 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Second Third Edition: 7.1 to 7.3
Cache associativity Cache and performance 12 1 CMPE110 Spring 2005 A. Di Blas 110 Spring 2005 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Second Third Edition: 7.1 to 7.3
6.004 Tutorial Problems L20 Virtual Memory
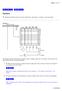
 6.004 Tutorial Problems L20 Virtual Memory Page Table (v + p) bits in virtual address (m + p) bits in physical address 2 v number of virtual pages 2 m number of physical pages 2 p bytes per physical page
6.004 Tutorial Problems L20 Virtual Memory Page Table (v + p) bits in virtual address (m + p) bits in physical address 2 v number of virtual pages 2 m number of physical pages 2 p bytes per physical page
Binghamton University. CS-220 Spring Cached Memory. Computer Systems Chapter
 Cached Memory Computer Systems Chapter 6.2-6.5 Cost Speed The Memory Hierarchy Capacity The Cache Concept CPU Registers Addresses Data Memory ALU Instructions The Cache Concept Memory CPU Registers Addresses
Cached Memory Computer Systems Chapter 6.2-6.5 Cost Speed The Memory Hierarchy Capacity The Cache Concept CPU Registers Addresses Data Memory ALU Instructions The Cache Concept Memory CPU Registers Addresses
Exercises 6 - Virtual vs. Physical Memory, Cache
 Questions 1. Consider a (very old!) computer with a hard disk of only 1 GB, main memory of 16 MB, and a cache with 512 blocks of 8 words each. Suppose the hard disk and main memory are partitioned into
Questions 1. Consider a (very old!) computer with a hard disk of only 1 GB, main memory of 16 MB, and a cache with 512 blocks of 8 words each. Suppose the hard disk and main memory are partitioned into
EE 3613: Computer Organization Homework #2
 EE 3613: Computer Organization Homework #2 Due Dates: (in-class) Hw #2A - Monday, September 24, 2018 Due Dates: (in-class) Hw #2B - Friday, September 21, 2018 by 11:59 PM Instructions: 1. The assignment
EE 3613: Computer Organization Homework #2 Due Dates: (in-class) Hw #2A - Monday, September 24, 2018 Due Dates: (in-class) Hw #2B - Friday, September 21, 2018 by 11:59 PM Instructions: 1. The assignment
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL
 The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Comp 411 Computer Organization Fall 2006 Solutions Problem Set #10 Problem 1. Cache accounting The diagram below illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Comp 411 Computer Organization Fall 2006 Solutions Problem Set #10 Problem 1. Cache accounting The diagram below illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache
Caches III. CSE 351 Autumn Instructor: Justin Hsia
 Caches III CSE 351 Autumn 2018 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Akshat Aggarwal An Wang Andrew Hu Brian Dai Britt Henderson James Shin Kevin Bi Kory Watson Riley Germundson Sophie Tian Teagan
Caches III CSE 351 Autumn 2018 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Akshat Aggarwal An Wang Andrew Hu Brian Dai Britt Henderson James Shin Kevin Bi Kory Watson Riley Germundson Sophie Tian Teagan
What is Cache Memory? EE 352 Unit 11. Motivation for Cache Memory. Memory Hierarchy. Cache Definitions Cache Address Mapping Cache Performance
 What is EE 352 Unit 11 Definitions Address Mapping Performance memory is a small, fast memory used to hold of data that the processor will likely need to access in the near future sits between the processor
What is EE 352 Unit 11 Definitions Address Mapping Performance memory is a small, fast memory used to hold of data that the processor will likely need to access in the near future sits between the processor
CSE 141 Spring 2016 Homework 5 PID: Name: 1. Consider the following matrix transpose code int i, j,k; double *A, *B, *C; A = (double
 CSE 141 Spring 2016 Homework 5 PID: Name: 1. Consider the following matrix transpose code int i, j,k; double *A, *B, *C; A = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*n*n); B = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*n*n);
CSE 141 Spring 2016 Homework 5 PID: Name: 1. Consider the following matrix transpose code int i, j,k; double *A, *B, *C; A = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*n*n); B = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*n*n);
Homework 3 (r1.1) Due: Part (A) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm Part (B) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm Part (C) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm
 Second Semester, 2015 16 Homework 3 (r1.1) Due: Part (A) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm Part (B) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm Part (C) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm Instruction: Submit your answers electronically through
Second Semester, 2015 16 Homework 3 (r1.1) Due: Part (A) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm Part (B) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm Part (C) -- Apr 29, 2016, 11:55pm Instruction: Submit your answers electronically through
6.004 Tutorial Problems L14 Cache Implementation
 6.004 Tutorial Problems L14 Cache Implementation Cache Miss Types Compulsory Miss: Starting with an empty cache, a cache line is first referenced (invalid) Capacity Miss: The cache is not big enough to
6.004 Tutorial Problems L14 Cache Implementation Cache Miss Types Compulsory Miss: Starting with an empty cache, a cache line is first referenced (invalid) Capacity Miss: The cache is not big enough to
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
ICS 51: Introduction to Computer Organization
 ICS 51: Introduction to Computer Organization Sample problems for Quiz #4 ( Solution ) on Spring 2018 1. [Cache Design] Given a fully associative cache has 4 cache lines and each of them contains the following
ICS 51: Introduction to Computer Organization Sample problems for Quiz #4 ( Solution ) on Spring 2018 1. [Cache Design] Given a fully associative cache has 4 cache lines and each of them contains the following
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering
 Print: First Name:............................. Last Name:............................. Student Number:............................................... University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and
Print: First Name:............................. Last Name:............................. Student Number:............................................... University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and
The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS 370 Introduction to Computer Architecture Midterm Exam 2 solutions April 5, 2011
 1. Performance Principles [5 pts] The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS 370 Introduction to Computer Architecture Midterm Exam 2 solutions April 5, 2011 For each of the following comparisons,
1. Performance Principles [5 pts] The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS 370 Introduction to Computer Architecture Midterm Exam 2 solutions April 5, 2011 For each of the following comparisons,
ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache
 Computer Architecture and Organization Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 28.1 Fundamental Questions
Computer Architecture and Organization Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 28.1 Fundamental Questions
CPE 631 Advanced Computer Systems Architecture: Homework #2
 CPE 631 Advanced Computer Systems Architecture: Homework #2 Issued: 02/01/2006 Due: 02/15/2006 Q#1. (30 points) Evaluate effectiveness of blocking optimization for matrix multiplication on SRx machines.
CPE 631 Advanced Computer Systems Architecture: Homework #2 Issued: 02/01/2006 Due: 02/15/2006 Q#1. (30 points) Evaluate effectiveness of blocking optimization for matrix multiplication on SRx machines.
Prerequisite Quiz September 3, 2003 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Fall 2003 John Kubiatowicz Prerequisite Quiz September 3, 2003 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering This
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Fall 2003 John Kubiatowicz Prerequisite Quiz September 3, 2003 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering This
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Direct Mapped Cache Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Intel 8-core i7-5960x 3 GHz, 8-core, 20 MB of cache, 140
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Direct Mapped Cache Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Intel 8-core i7-5960x 3 GHz, 8-core, 20 MB of cache, 140
Problem 1 (logic design)
 Problem 1 (logic design) For this problem, you are to design and implement a sequential multiplexor that works as follows. On each clock cycle, interpret the current input as a selector from the most recent
Problem 1 (logic design) For this problem, you are to design and implement a sequential multiplexor that works as follows. On each clock cycle, interpret the current input as a selector from the most recent
Second Midterm Exam March 21, 2017 CS162 Operating Systems
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 2017 Ion Stoica Second Midterm Exam March 21, 2017 CS162 Operating Systems Your Name: SID AND 162 Login:
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 2017 Ion Stoica Second Midterm Exam March 21, 2017 CS162 Operating Systems Your Name: SID AND 162 Login:
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Introduction to Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Caches hold a subset of data from the main
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Introduction to Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Caches hold a subset of data from the main
ASSIGNMENT 9: CACHE MEMORY NAME. Assume we are building a cache for a memory system that s just 16 bytes big 4 address bits.
 . SSIGNMNT : H MMORY NM PROLM : -YT H OR -YT MMORY. ssume we are building a cache for a memory system that s just bytes big address bits. We will make a direct mapped cache that has four set, so there
. SSIGNMNT : H MMORY NM PROLM : -YT H OR -YT MMORY. ssume we are building a cache for a memory system that s just bytes big address bits. We will make a direct mapped cache that has four set, so there
Question F5: Caching [10 pts]
![Question F5: Caching [10 pts] Question F5: Caching [10 pts]](/thumbs/91/107229775.jpg) Question F5: Caching [ pts] SID: We have 6 KiB of RAM and two options for our cache. Both are two-way set associative with 256 B blocks, LRU replacement, and write-back policies. Cache A is size KiB and
Question F5: Caching [ pts] SID: We have 6 KiB of RAM and two options for our cache. Both are two-way set associative with 256 B blocks, LRU replacement, and write-back policies. Cache A is size KiB and
registers data 1 registers MEMORY ADDRESS on-chip cache off-chip cache main memory: real address space part of virtual addr. sp.
 13 1 CMPE110 Computer Architecture, Winter 2009 Andrea Di Blas 110 Winter 2009 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Cache associativity Cache and performance Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Third
13 1 CMPE110 Computer Architecture, Winter 2009 Andrea Di Blas 110 Winter 2009 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Cache associativity Cache and performance Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Third
1 /20 2 /18 3 /20 4 /18 5 /24
 M A S S A C H U S E T T S I N S T I T U T E O F T E C H N O L O G Y DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE 6.S084 Computation Structures Spring 2018 1 /20 2 /18 3 /20 4 /18 5 /24 Practice
M A S S A C H U S E T T S I N S T I T U T E O F T E C H N O L O G Y DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE 6.S084 Computation Structures Spring 2018 1 /20 2 /18 3 /20 4 /18 5 /24 Practice
Structure of Computer Systems
 222 Structure of Computer Systems Figure 4.64 shows how a page directory can be used to map linear addresses to 4-MB pages. The entries in the page directory point to page tables, and the entries in a
222 Structure of Computer Systems Figure 4.64 shows how a page directory can be used to map linear addresses to 4-MB pages. The entries in the page directory point to page tables, and the entries in a
CSE351: Memory, Data, & Addressing I
 CSE351: Memory, Data, & Addressing I CSE 351 Spring 2017 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis http://xkcd.com/138/
CSE351: Memory, Data, & Addressing I CSE 351 Spring 2017 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis http://xkcd.com/138/
Review: Computer Organization
 Review: Computer Organization Cache Chansu Yu Caches: The Basic Idea A smaller set of storage locations storing a subset of information from a larger set. Typically, SRAM for DRAM main memory: Processor
Review: Computer Organization Cache Chansu Yu Caches: The Basic Idea A smaller set of storage locations storing a subset of information from a larger set. Typically, SRAM for DRAM main memory: Processor
Question 6: Cache in While You Can (17 points, 26 Minutes)
 Question 6: Cache in While You Can (17 points, 26 Minutes) Consider a single 4KiB cache with 512B blocks and a write back policy. Assume a 32 bit address space. a) If the cache were direct mapped, # of
Question 6: Cache in While You Can (17 points, 26 Minutes) Consider a single 4KiB cache with 512B blocks and a write back policy. Assume a 32 bit address space. a) If the cache were direct mapped, # of
Memory Hierarchy. Mehran Rezaei
 Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
SLCD Technical Note TN-100. Programming the SLCD bitmap / macro flash memory in an embedded system
 SLCD Technical Note TN-100 Programming the SLCD bitmap / macro flash memory in an embedded system December 3, 2004 Copyright Reach Technology Inc. 2004 All Rights Reserved Reach Technology, Inc. sales@reachtech.com
SLCD Technical Note TN-100 Programming the SLCD bitmap / macro flash memory in an embedded system December 3, 2004 Copyright Reach Technology Inc. 2004 All Rights Reserved Reach Technology, Inc. sales@reachtech.com
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 28: More Virtual Memory Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Virtual memory used to protect applications from
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 28: More Virtual Memory Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Virtual memory used to protect applications from
CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015
 CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015 Name: Rules and Hints The MIPS cheat sheet and datapath diagram are attached at the end of this exam for your reference. You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front
CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015 Name: Rules and Hints The MIPS cheat sheet and datapath diagram are attached at the end of this exam for your reference. You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front
Midterm #2 Solutions April 23, 1997
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Sp97 D.K. Jeong Midterm #2 Solutions
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Sp97 D.K. Jeong Midterm #2 Solutions
CS350 Midterm Spring 2012 Page 1
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO CS 350 MIDTERM :: SPRING 2012 Date: Monday, June 25, 2012 Time: 7:00 8:50 pm Instructor: Dave Tompkins Exam Type: Closed book Additional Materials Allowed: none Last Name: First
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO CS 350 MIDTERM :: SPRING 2012 Date: Monday, June 25, 2012 Time: 7:00 8:50 pm Instructor: Dave Tompkins Exam Type: Closed book Additional Materials Allowed: none Last Name: First
Memory Hierarchy & Caches Worksheet
 Memory Hierarchy & Caches Worksheet Keep the most often-used data in a small, fast SRAM (often local to CPU chip). The reason this strategy works: LOCALITY. Locality of reference: Access to address X at
Memory Hierarchy & Caches Worksheet Keep the most often-used data in a small, fast SRAM (often local to CPU chip). The reason this strategy works: LOCALITY. Locality of reference: Access to address X at
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned 9/17/2016 Problem Set #2 Due Tue, Oct 4 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/fa16 The problem sets are intended to help
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned 9/17/2016 Problem Set #2 Due Tue, Oct 4 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/fa16 The problem sets are intended to help
ECE260: Fundamentals of Computer Engineering
 Basics of Cache Memory James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy Cache Memory Cache
Basics of Cache Memory James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy Cache Memory Cache
ECE 3056: Architecture, Concurrency, and Energy of Computation. Sample Problem Set: Memory Systems
 ECE 356: Architecture, Concurrency, and Energy of Computation Sample Problem Set: Memory Systems TLB 1. Consider a processor system with 256 kbytes of memory, 64 Kbyte pages, and a 1 Mbyte virtual address
ECE 356: Architecture, Concurrency, and Energy of Computation Sample Problem Set: Memory Systems TLB 1. Consider a processor system with 256 kbytes of memory, 64 Kbyte pages, and a 1 Mbyte virtual address
CS 433 Homework 4. Assigned on 10/17/2017 Due in class on 11/7/ Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page.
 CS 433 Homework 4 Assigned on 10/17/2017 Due in class on 11/7/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
CS 433 Homework 4 Assigned on 10/17/2017 Due in class on 11/7/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
ECE 411 Exam 1 Practice Problems
 ECE 411 Exam 1 Practice Problems Topics Single-Cycle vs Multi-Cycle ISA Tradeoffs Performance Memory Hierarchy Caches (including interactions with VM) 1.) Suppose a single cycle design uses a clock period
ECE 411 Exam 1 Practice Problems Topics Single-Cycle vs Multi-Cycle ISA Tradeoffs Performance Memory Hierarchy Caches (including interactions with VM) 1.) Suppose a single cycle design uses a clock period
Last class. Caches. Direct mapped
 Memory Hierarchy II Last class Caches Direct mapped E=1 (One cache line per set) Each main memory address can be placed in exactly one place in the cache Conflict misses if two addresses map to same place
Memory Hierarchy II Last class Caches Direct mapped E=1 (One cache line per set) Each main memory address can be placed in exactly one place in the cache Conflict misses if two addresses map to same place
and data combined) is equal to 7% of the number of instructions. Miss Rate with Second- Level Cache, Direct- Mapped Speed
 5.3 By convention, a cache is named according to the amount of data it contains (i.e., a 4 KiB cache can hold 4 KiB of data); however, caches also require SRAM to store metadata such as tags and valid
5.3 By convention, a cache is named according to the amount of data it contains (i.e., a 4 KiB cache can hold 4 KiB of data); however, caches also require SRAM to store metadata such as tags and valid
Exam-2 Scope. 3. Shared memory architecture, distributed memory architecture, SMP, Distributed Shared Memory and Directory based coherence
 Exam-2 Scope 1. Memory Hierarchy Design (Cache, Virtual memory) Chapter-2 slides memory-basics.ppt Optimizations of Cache Performance Memory technology and optimizations Virtual memory 2. SIMD, MIMD, Vector,
Exam-2 Scope 1. Memory Hierarchy Design (Cache, Virtual memory) Chapter-2 slides memory-basics.ppt Optimizations of Cache Performance Memory technology and optimizations Virtual memory 2. SIMD, MIMD, Vector,
indicates problems that have been selected for discussion in section, time permitting.
 Page 1 of 17 Caches indicates problems that have been selected for discussion in section, time permitting. Problem 1. The diagram above illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache for a computer that uses
Page 1 of 17 Caches indicates problems that have been selected for discussion in section, time permitting. Problem 1. The diagram above illustrates a blocked, direct-mapped cache for a computer that uses
复旦大学软件学院 2017~2018 学年第一学期期中考试试卷
 复旦大学软件学院 2017~2018 学年第一学期期中考试试卷 1. Suppose that the target code of 400000 instructions run on a 50MHZ processor, and the program is composed of four instructions. According to the program tracking experiment
复旦大学软件学院 2017~2018 学年第一学期期中考试试卷 1. Suppose that the target code of 400000 instructions run on a 50MHZ processor, and the program is composed of four instructions. According to the program tracking experiment
Write only as much as necessary. Be brief!
 1 CIS371 Computer Organization and Design Final Exam Prof. Martin Wednesday, May 2nd, 2012 This exam is an individual-work exam. Write your answers on these pages. Additional pages may be attached (with
1 CIS371 Computer Organization and Design Final Exam Prof. Martin Wednesday, May 2nd, 2012 This exam is an individual-work exam. Write your answers on these pages. Additional pages may be attached (with
CSCI 2212: Intermediate Programming / C Chapter 15
 ... /34 CSCI 222: Intermediate Programming / C Chapter 5 Alice E. Fischer October 9 and 2, 25 ... 2/34 Outline Integer Representations Binary Integers Integer Types Bit Operations Applying Bit Operations
... /34 CSCI 222: Intermediate Programming / C Chapter 5 Alice E. Fischer October 9 and 2, 25 ... 2/34 Outline Integer Representations Binary Integers Integer Types Bit Operations Applying Bit Operations
Computer System Architecture Midterm Examination Spring 2002
 Computer System Architecture 6.823 Midterm Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 110 Minutes 1 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
Computer System Architecture 6.823 Midterm Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 110 Minutes 1 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
Computer Architecture: Optional Homework Set
 Computer Architecture: Optional Homework Set Black Board due date: Hard Copy due date: Monday April 27 th, at Midnight. Tuesday April 28 th, during Class. Exercise 1: (50 Points) Patterson and Hennessy
Computer Architecture: Optional Homework Set Black Board due date: Hard Copy due date: Monday April 27 th, at Midnight. Tuesday April 28 th, during Class. Exercise 1: (50 Points) Patterson and Hennessy
UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Final Exam
 Full Name: Student ID #: UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Final Exam March 20, 2013 2:30pm - 4:20pm Instructions: Write your full name and UW student ID number on the front of the exam. When the exam begins, make
Full Name: Student ID #: UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Final Exam March 20, 2013 2:30pm - 4:20pm Instructions: Write your full name and UW student ID number on the front of the exam. When the exam begins, make
Chapter 5A. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
MIPS) ( MUX
 Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
CS 4400 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam 2 Practice (Version 2)
 CS 4400 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam 2 Practice (Version 2) Name: Instructions You will have eighty minutes to complete the actual open-book, opennote exam. Electronic devices will be allowed only to consult
CS 4400 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam 2 Practice (Version 2) Name: Instructions You will have eighty minutes to complete the actual open-book, opennote exam. Electronic devices will be allowed only to consult
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2016 Instructors: Randy Katz, Bernhard Boser
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2016 Instructors: Randy Katz, Bernhard Boser 2016-12-16 L CS61C FINAL J After the
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Fall 2016 Instructors: Randy Katz, Bernhard Boser 2016-12-16 L CS61C FINAL J After the
Computer Architecture EE 4720 Final Examination
 Name Computer Architecture EE 4720 Final Examination 1 May 2017, 10:00 12:00 CDT Alias Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Exam Total (20 pts) (15 pts) (20 pts) (15 pts) (30 pts) (100 pts)
Name Computer Architecture EE 4720 Final Examination 1 May 2017, 10:00 12:00 CDT Alias Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Exam Total (20 pts) (15 pts) (20 pts) (15 pts) (30 pts) (100 pts)
Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng
 Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng Why memory hierarchy? CPU main memory lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3, $t2, $a1 addi $a0, $a0, 4 subi $a1, $a1, 1 bne $a1, LOOP lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3,
Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng Why memory hierarchy? CPU main memory lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3, $t2, $a1 addi $a0, $a0, 4 subi $a1, $a1, 1 bne $a1, LOOP lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3,
Changelog. Virtual Memory (2) exercise: 64-bit system. exercise: 64-bit system
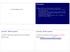 Changelog Virtual Memory (2) Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 21 November 2017: 1-level example: added final answer of memory value, not just location 21 November 2017: two-level
Changelog Virtual Memory (2) Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 21 November 2017: 1-level example: added final answer of memory value, not just location 21 November 2017: two-level
c. What are the machine cycle times (in nanoseconds) of the non-pipelined and the pipelined implementations?
 Brown University School of Engineering ENGN 164 Design of Computing Systems Professor Sherief Reda Homework 07. 140 points. Due Date: Monday May 12th in B&H 349 1. [30 points] Consider the non-pipelined
Brown University School of Engineering ENGN 164 Design of Computing Systems Professor Sherief Reda Homework 07. 140 points. Due Date: Monday May 12th in B&H 349 1. [30 points] Consider the non-pipelined
Full Name: CS Account:
 THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA CPSC 313: QUIZ 4 October 31, 2018 Full Name: CS Account: Signature: UBC Student #: Important notes about this examination 1. Write your 4 or 5 character CS account both
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA CPSC 313: QUIZ 4 October 31, 2018 Full Name: CS Account: Signature: UBC Student #: Important notes about this examination 1. Write your 4 or 5 character CS account both
UW CSE 351, Summer 2013 Final Exam
 Name Instructions: UW CSE 351, Summer 2013 Final Exam 9:40am - 10:40am, Friday, 23 August 2013 Make sure that your exam is not missing any of the 11 pages, then write your full name and UW student ID on
Name Instructions: UW CSE 351, Summer 2013 Final Exam 9:40am - 10:40am, Friday, 23 August 2013 Make sure that your exam is not missing any of the 11 pages, then write your full name and UW student ID on
We r e going to play Final (exam) Jeopardy! "Answers:" "Questions:" - 1 -
 . (0 pts) We re going to play Final (exam) Jeopardy! Associate the following answers with the appropriate question. (You are given the "answers": Pick the "question" that goes best with each "answer".)
. (0 pts) We re going to play Final (exam) Jeopardy! Associate the following answers with the appropriate question. (You are given the "answers": Pick the "question" that goes best with each "answer".)
Slide Set 9. for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 9 for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary March 2018 ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01
Slide Set 9 for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary March 2018 ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01
Cache Memory Mapping Techniques. Continue to read pp
 Cache Memory Mapping Techniques Continue to read pp. 289-305 Cache Memory Mapping Again cache memory is a small and fast memory between CPU and main memory A block of words have to be brought in and out
Cache Memory Mapping Techniques Continue to read pp. 289-305 Cache Memory Mapping Again cache memory is a small and fast memory between CPU and main memory A block of words have to be brought in and out
Direct Mapped Cache Hardware. Direct Mapped Cache. Direct Mapped Cache Performance. Direct Mapped Cache Performance. Miss Rate = 3/15 = 20%
 Direct Mapped Cache Direct Mapped Cache Hardware........................ mem[xff...fc] mem[xff...f8] mem[xff...f4] mem[xff...f] mem[xff...ec] mem[xff...e8] mem[xff...e4] mem[xff...e] 27 8-entry x (+27+)-bit
Direct Mapped Cache Direct Mapped Cache Hardware........................ mem[xff...fc] mem[xff...f8] mem[xff...f4] mem[xff...f] mem[xff...ec] mem[xff...e8] mem[xff...e4] mem[xff...e] 27 8-entry x (+27+)-bit
Caches II. CSE 351 Spring Instructor: Ruth Anderson
 Caches II CSE 35 Spring 27 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Office Hours Changes check calendar!!
Caches II CSE 35 Spring 27 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Office Hours Changes check calendar!!
ECE Lab 8. Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache. To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache.
 ECE 201 - Lab 8 Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache PURPOSE To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache. EQUIPMENT Simulation Software REQUIREMENTS Electronic copy of your
ECE 201 - Lab 8 Logic Design for a Direct-Mapped Cache PURPOSE To understand the function and design of a direct-mapped memory cache. EQUIPMENT Simulation Software REQUIREMENTS Electronic copy of your
CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017
![CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017](/thumbs/86/93964159.jpg) CS433 Homework 6 Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
CS433 Homework 6 Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
Next Generation Intelligent LCDs
 Next Generation Intelligent LCDs 2D Run-Length Encoding Application Note Version 1.0 Document Date: April 30, 2013 Copyright by demmel products gmbh 2004-2013 Unless otherwise noted, all materials contained
Next Generation Intelligent LCDs 2D Run-Length Encoding Application Note Version 1.0 Document Date: April 30, 2013 Copyright by demmel products gmbh 2004-2013 Unless otherwise noted, all materials contained
1 /15 2 /20 3 /20 4 /25 5 /20
 M A S S A C H U S E T T S I N S T I T U T E O F T E C H N O L O G Y DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE 6.S084 Computation Structures Spring 2018 1 /15 2 /20 3 /20 4 /25 5 /20 Quiz
M A S S A C H U S E T T S I N S T I T U T E O F T E C H N O L O G Y DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE 6.S084 Computation Structures Spring 2018 1 /15 2 /20 3 /20 4 /25 5 /20 Quiz
CS 251, Winter 2019, Assignment % of course mark
 CS 251, Winter 2019, Assignment 5.1.1 3% of course mark Due Wednesday, March 27th, 5:30PM Lates accepted until 1:00pm March 28th with a 15% penalty 1. (10 points) The code sequence below executes on a
CS 251, Winter 2019, Assignment 5.1.1 3% of course mark Due Wednesday, March 27th, 5:30PM Lates accepted until 1:00pm March 28th with a 15% penalty 1. (10 points) The code sequence below executes on a
Virtual Memory 1. Virtual Memory
 Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Problem 9. VM address translation. (9 points): The following problem concerns the way virtual addresses are translated into physical addresses.
 Problem 9. VM address translation. (9 points): The following problem concerns the way virtual addresses are translated into physical addresses. The memory is byte addressable. Memory accesses are to 1-byte
Problem 9. VM address translation. (9 points): The following problem concerns the way virtual addresses are translated into physical addresses. The memory is byte addressable. Memory accesses are to 1-byte
CS 251, Winter 2018, Assignment % of course mark
 CS 251, Winter 2018, Assignment 5.0.4 3% of course mark Due Wednesday, March 21st, 4:30PM Lates accepted until 10:00am March 22nd with a 15% penalty 1. (10 points) The code sequence below executes on a
CS 251, Winter 2018, Assignment 5.0.4 3% of course mark Due Wednesday, March 21st, 4:30PM Lates accepted until 10:00am March 22nd with a 15% penalty 1. (10 points) The code sequence below executes on a
Memory, Data, & Addressing I
 Memory, Data, & Addressing I CSE 351 Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Lucas Wotton Michael Zhang Parker DeWilde Ryan Wong Sam Gehman Sam Wolfson Savanna Yee Vinny Palaniappan http://xkcd.com/953/
Memory, Data, & Addressing I CSE 351 Autumn 2017 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Lucas Wotton Michael Zhang Parker DeWilde Ryan Wong Sam Gehman Sam Wolfson Savanna Yee Vinny Palaniappan http://xkcd.com/953/
Virtual Memory 1. Virtual Memory
 Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 2014
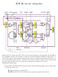 ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
CPSC 3300 Spring 2016 Final Exam Version A No Calculators
 CPSC 3300 Spring 2016 Final Exam Version A No Calculators Name: 1. Find the execution time of a program that executes 8 billion instructions on a processor with an average CPI of 2 and a clock frequency
CPSC 3300 Spring 2016 Final Exam Version A No Calculators Name: 1. Find the execution time of a program that executes 8 billion instructions on a processor with an average CPI of 2 and a clock frequency
Cache and Virtual Memory Simulations
 Cache and Virtual Memory Simulations Does it really matter if you pull a USB out before it safely ejects? Data structure: Cache struct Cache { }; Set *sets; int set_count; int line_count; int block_size;
Cache and Virtual Memory Simulations Does it really matter if you pull a USB out before it safely ejects? Data structure: Cache struct Cache { }; Set *sets; int set_count; int line_count; int block_size;
Associative. Associative. Number of Bits Group or Set Tag
 1. A memory system has 16 Mbytes of address space, 256 cache lines, and 16 bytes per cache line. Complete the address bit count table below for the three types of cache memory systems. Direct-Mapped 2-way
1. A memory system has 16 Mbytes of address space, 256 cache lines, and 16 bytes per cache line. Complete the address bit count table below for the three types of cache memory systems. Direct-Mapped 2-way
ISA Instruction Operation
 This exam has 6 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have three hours to complete this exam.
This exam has 6 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have three hours to complete this exam.
Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam
 Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam NAME: STUDENT NUMBER 1. Consider a computer system with 64Kbytes main memory and 256bytes cache. If we assume the cache line size is
Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam NAME: STUDENT NUMBER 1. Consider a computer system with 64Kbytes main memory and 256bytes cache. If we assume the cache line size is
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Part I: Pen & Paper Exercises, Cache
 Fall Term 2016 SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING AND COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Assignment 11: Caches & Virtual Memory Assigned on: 8th Dec 2016 Due by: 15th Dec 2016 Part I: Pen & Paper Exercises, Cache Question 1 The following
Fall Term 2016 SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING AND COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Assignment 11: Caches & Virtual Memory Assigned on: 8th Dec 2016 Due by: 15th Dec 2016 Part I: Pen & Paper Exercises, Cache Question 1 The following
Translation Buffers (TLB s)
 Translation Buffers (TLB s) To perform virtual to physical address translation we need to look-up a page table Since page table is in memory, need to access memory Much too time consuming; 20 cycles or
Translation Buffers (TLB s) To perform virtual to physical address translation we need to look-up a page table Since page table is in memory, need to access memory Much too time consuming; 20 cycles or
Virtual Memory (2) 1
 Virtual Memory (2) 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 21 November 2017: 1-level example: added final answer of memory value, not just location 21 November 2017: two-level
Virtual Memory (2) 1 Changelog 1 Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 21 November 2017: 1-level example: added final answer of memory value, not just location 21 November 2017: two-level
