ICS 51: Introduction to Computer Organization
|
|
|
- Milton Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ICS 51: Introduction to Computer Organization Sample problems for Quiz #4 ( Solution ) on Spring [Cache Design] Given a fully associative cache has 4 cache lines and each of them contains the following tag and block pairs. You job is to run a series of the load instructions on a simple processor which has 4 registers. This processor will also always replace the least recently used cache line to store a new item when the cache is full. At the initial state, the cache lines are ordered by the reversed order they are accessed, e.g. the cache line with tag 0 and block FA has been accessed most recently while the one with tag 6 and block has been accessed least recently. Assume the load instructions fetch data from a (8 x 8-bit) memory shown above, answer the following questions: a. How many cache hits and misses are for these instructions? 2 hits, 3 misses b. Assume a load with a cache hit needs 2 cycles, and a load with a cache miss needs 20 cycles. How many cycles are required to execute the above load instructions? 2 x x 20 = 64 cycles
2 2. [Cache Design] The target processor has a cache with 4 cache lines and a memory with 8 entries. You job is to run a series of the load instructions on this processor with 4 registers. Validity bit is 1 if the cache line is valid and 0 if it s invalid. This processor will also always replace the least recently used cache line (LRU) to store a new item when the cache is full. At the initial state, the least recently used cache line is denoted with LRU on the line next to the corresponding cache entry. At the beginning, the cache is partially filled and the registers are empty. Note: The LRU is the cache line that hasn t been used the longest, if a cache line is reused in a HIT, then it is recently used. a. For each instruction, show the changes in cache and the registers.
3 b. How many cache hits and misses are for these instructions? 2 Hits and 4 misses
4 3. [Cache/Memory Design] What is the final state of the memory after execution of following codes using the default value in the registers below? lw $R4, 5($R1) add $R1, $R2, $R3 sw $R1, 0($R3) add $R4, $R3, $R4 R1 R2 R3 R4 0xEF 0x02 0x12 0x34 Ans: 4. [ Instruction Set Architecture ] A simple processor was designed to support 100 instructions with the following instruction format. Assume all instructions are 16 bits. Each of them is performing an operation taking operands from two source registers and then storing the result to the destination register. Answer the following questions. a. How many bits are required to represent the opcodes? Ceil (log 2 100) = 7 b. How many bits are required to represent the operands? 16-7 = 9
5 c. How many bits are required to represent each operand? 9 / 3 = 3 d. What is the maximum number of registers does this processor have? 2 3 = 8 5. [ Instruction Set Architecture ] Given the memory values below and one target register R ( i.e. the result of each load is saved in the target register R), what values do the following instructions load in register R? Address Value Instruction Value of R Load immediate Load direct 20 Mem[20] = 40 Load indirect 20 Mem[mem[20]] = mem[40] = [ Instruction Set Architecture ] Assume a computer that has 32 8-bit registers, 128KB byte-addressable memory (meaning that each byte has a unique address) and can perform 130 distinct operations. Given the following register-memory instruction format: OP REG MEM (Hint: Note: OP stands for the code of the operation to be performed, REG stands for the index of the register to be used and MEM stands for the address of the 8-bit memory
6 words to be used.) How many bits are needed to properly express such an instruction? OP: ceil (log 2 (130)) = 8 REG: log 2 (32) = 5 MEM: log 2 (128KB) = log 2 (128 x 2 10 ) = log 2 (2 17 ) = 17 Total bits: = [ Instruction Set Architecture/ Addressing Modes] In ARM LC2K Assembly, determine the type of each of the following instructions in terms of addressing modes (direct, indirect, indexed, immediate) and instruction format (1,2,3-addressable, no address). Add R1, R2, R3 (R3 R1 + R2) Register direct, 3-addressable LW R1, R2, #100 (r2 mem[r1+100]) Indexed, 3-addressable J #1000 (unconditional jump to specified target address, i.e., #1000) Direct, 1-addressable JALR R1 (Unconditional jump to address in R1) Register Indirect, 1-addressable BEQ R1, R2, #1000 ( if R1=R2, goto to address #1000) Direct, 3-addressable
6.823 Computer System Architecture Datapath for DLX Problem Set #2
 6.823 Computer System Architecture Datapath for DLX Problem Set #2 Spring 2002 Students are allowed to collaborate in groups of up to 3 people. A group hands in only one copy of the solution to a problem
6.823 Computer System Architecture Datapath for DLX Problem Set #2 Spring 2002 Students are allowed to collaborate in groups of up to 3 people. A group hands in only one copy of the solution to a problem
The overall datapath for RT, lw,sw beq instrucution
 Designing The Main Control Unit: Remember the three instruction classes {R-type, Memory, Branch}: a) R-type : Op rs rt rd shamt funct 1.src 2.src dest. 31-26 25-21 20-16 15-11 10-6 5-0 a) Memory : Op rs
Designing The Main Control Unit: Remember the three instruction classes {R-type, Memory, Branch}: a) R-type : Op rs rt rd shamt funct 1.src 2.src dest. 31-26 25-21 20-16 15-11 10-6 5-0 a) Memory : Op rs
are Softw Instruction Set Architecture Microarchitecture are rdw
 Program, Application Software Programming Language Compiler/Interpreter Operating System Instruction Set Architecture Hardware Microarchitecture Digital Logic Devices (transistors, etc.) Solid-State Physics
Program, Application Software Programming Language Compiler/Interpreter Operating System Instruction Set Architecture Hardware Microarchitecture Digital Logic Devices (transistors, etc.) Solid-State Physics
Mark Redekopp and Gandhi Puvvada, All rights reserved. EE 357 Unit 15. Single-Cycle CPU Datapath and Control
 EE 37 Unit Single-Cycle CPU path and Control CPU Organization Scope We will build a CPU to implement our subset of the MIPS ISA Memory Reference Instructions: Load Word (LW) Store Word (SW) Arithmetic
EE 37 Unit Single-Cycle CPU path and Control CPU Organization Scope We will build a CPU to implement our subset of the MIPS ISA Memory Reference Instructions: Load Word (LW) Store Word (SW) Arithmetic
ECE 486/586. Computer Architecture. Lecture # 7
 ECE 486/586 Computer Architecture Lecture # 7 Spring 2015 Portland State University Lecture Topics Instruction Set Principles Instruction Encoding Role of Compilers The MIPS Architecture Reference: Appendix
ECE 486/586 Computer Architecture Lecture # 7 Spring 2015 Portland State University Lecture Topics Instruction Set Principles Instruction Encoding Role of Compilers The MIPS Architecture Reference: Appendix
Computer System Architecture Midterm Examination Spring 2002
 Computer System Architecture 6.823 Midterm Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 110 Minutes 1 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
Computer System Architecture 6.823 Midterm Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 110 Minutes 1 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
Comprehensive Exams COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE. Spring April 3, 2006
 Comprehensive Exams COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Spring 2006 April 3, 2006 ID Number 1 /15 2 /20 3 /20 4 /20 Total /75 Problem 1. ( 15 points) Logic Design: A three-input switching function is expressed as f(a,
Comprehensive Exams COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Spring 2006 April 3, 2006 ID Number 1 /15 2 /20 3 /20 4 /20 Total /75 Problem 1. ( 15 points) Logic Design: A three-input switching function is expressed as f(a,
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
Perfect Student CS 343 Final Exam May 19, 2011 Student ID: 9999 Exam ID: 9636 Instructions Use pencil, if you have one. For multiple choice
 Instructions Page 1 of 7 Use pencil, if you have one. For multiple choice questions, circle the letter of the one best choice unless the question specifically says to select all correct choices. There
Instructions Page 1 of 7 Use pencil, if you have one. For multiple choice questions, circle the letter of the one best choice unless the question specifically says to select all correct choices. There
CS 230 Practice Final Exam & Actual Take-home Question. Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts)
 Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts) 1. Assume that assembly code for the following variable definitions has already been generated (and initialization of A and length). int powerof2; /* powerof2
Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts) 1. Assume that assembly code for the following variable definitions has already been generated (and initialization of A and length). int powerof2; /* powerof2
Computer Architecture, IFE CS and T&CS, 4 th sem. Single-Cycle Architecture
 Single-Cycle Architecture Data flow Data flow is synchronized with clock (edge) in sequential systems Architecture Elements - assumptions Program (Instruction) memory: All instructions & buses are 32-bit
Single-Cycle Architecture Data flow Data flow is synchronized with clock (edge) in sequential systems Architecture Elements - assumptions Program (Instruction) memory: All instructions & buses are 32-bit
Multi-cycle Approach. Single cycle CPU. Multi-cycle CPU. Requires state elements to hold intermediate values. one clock cycle or instruction
 Multi-cycle Approach Single cycle CPU State element Combinational logic State element clock one clock cycle or instruction Multi-cycle CPU Requires state elements to hold intermediate values State Element
Multi-cycle Approach Single cycle CPU State element Combinational logic State element clock one clock cycle or instruction Multi-cycle CPU Requires state elements to hold intermediate values State Element
ECE331 Homework 4. Due Monday, August 13, 2018 (via Moodle)
 ECE331 Homework 4 Due Monday, August 13, 2018 (via Moodle) 1. Below is a list of 32-bit memory address references, given as hexadecimal byte addresses. The memory accesses are all reads and they occur
ECE331 Homework 4 Due Monday, August 13, 2018 (via Moodle) 1. Below is a list of 32-bit memory address references, given as hexadecimal byte addresses. The memory accesses are all reads and they occur
Instruction Set Architectures Part I: From C to MIPS. Readings:
 Instruction Set Architectures Part I: From C to MIPS Readings: 2.1-2.14 1 Goals for this Class Understand how CPUs run programs How do we express the computation the CPU? How does the CPU execute it? How
Instruction Set Architectures Part I: From C to MIPS Readings: 2.1-2.14 1 Goals for this Class Understand how CPUs run programs How do we express the computation the CPU? How does the CPU execute it? How
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10- CPU Microarchitecture. Processor Microarchitecture Introduction
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10- CPU Microarchitecture Feb 18, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec10-cpu Page 1 Processor Microarchitecture Introduction Microarchitecture: how to implement
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10- CPU Microarchitecture Feb 18, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec10-cpu Page 1 Processor Microarchitecture Introduction Microarchitecture: how to implement
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering
 ECE 0 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #9 Spring 01 1. Given the following series of address references given as word addresses:,,, 1, 1, 1,, 8, 19,,,,, 7,, and. Assuming a direct-mapped
ECE 0 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #9 Spring 01 1. Given the following series of address references given as word addresses:,,, 1, 1, 1,, 8, 19,,,,, 7,, and. Assuming a direct-mapped
Lecture 4: MIPS Instruction Set
 Lecture 4: MIPS Instruction Set No class on Tuesday Today s topic: MIPS instructions Code examples 1 Instruction Set Understanding the language of the hardware is key to understanding the hardware/software
Lecture 4: MIPS Instruction Set No class on Tuesday Today s topic: MIPS instructions Code examples 1 Instruction Set Understanding the language of the hardware is key to understanding the hardware/software
Processor (I) - datapath & control. Hwansoo Han
 Processor (I) - datapath & control Hwansoo Han Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count - Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time - Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two
Processor (I) - datapath & control Hwansoo Han Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count - Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time - Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Caches
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 More Caches 1 Prelim 2 stats High: 9 (out of 9) Mean: 7.2, Median: 73 Announcements Prelab 5(C) due tomorrow 2 Example: Direct Mapped (DM) Cache
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 More Caches 1 Prelim 2 stats High: 9 (out of 9) Mean: 7.2, Median: 73 Announcements Prelab 5(C) due tomorrow 2 Example: Direct Mapped (DM) Cache
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 2014
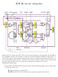 ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014
 CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014 Practice Assignment 5 Solutions Exercise 5-1: (Midterm Spring 2013) a. What are the values of the control signals (except ALUOp) for each of the following
CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014 Practice Assignment 5 Solutions Exercise 5-1: (Midterm Spring 2013) a. What are the values of the control signals (except ALUOp) for each of the following
Hardwired Control Unit Ch 14
 Hardwired Control Unit Ch 14 Micro-operations Controlling Execution Hardwired Control 1 What is Control (2) So far, we have shown what happens inside CPU execution of instructions opcodes, addressing modes,
Hardwired Control Unit Ch 14 Micro-operations Controlling Execution Hardwired Control 1 What is Control (2) So far, we have shown what happens inside CPU execution of instructions opcodes, addressing modes,
CPE 335 Computer Organization. Basic MIPS Architecture Part I
 CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part I Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s8/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part I Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s8/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
Assembler. Lecture 8 CS301
 Assembler Lecture 8 CS301 Discussion Given the following function header, int foo(int a, int b); what will be on the stack before any of the calculations in foo are performed? Assume foo() calls some other
Assembler Lecture 8 CS301 Discussion Given the following function header, int foo(int a, int b); what will be on the stack before any of the calculations in foo are performed? Assume foo() calls some other
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Pipelining. CSC Friday, November 6, 2015
 Pipelining CSC 211.01 Friday, November 6, 2015 Performance Issues Longest delay determines clock period Critical path: load instruction Instruction memory register file ALU data memory register file Not
Pipelining CSC 211.01 Friday, November 6, 2015 Performance Issues Longest delay determines clock period Critical path: load instruction Instruction memory register file ALU data memory register file Not
Programmable Machines
 Programmable Machines Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. Quiz 1: next week Covers L1-L8 Oct 11, 7:30-9:30PM Walker memorial 50-340 L09-1 6.004 So Far Using Combinational
Programmable Machines Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. Quiz 1: next week Covers L1-L8 Oct 11, 7:30-9:30PM Walker memorial 50-340 L09-1 6.004 So Far Using Combinational
Lecture 4: Instruction Set Architecture
 Lecture 4: Instruction Set Architecture ISA types, register usage, memory addressing, endian and alignment, quantitative evaluation Reading: Textbook (5 th edition) Appendix A Appendix B (4 th edition)
Lecture 4: Instruction Set Architecture ISA types, register usage, memory addressing, endian and alignment, quantitative evaluation Reading: Textbook (5 th edition) Appendix A Appendix B (4 th edition)
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Tajana Simunic Rosing Announcements and Outline Check webct grades, make sure everything is there and is correct Pick up graded d homework at
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Tajana Simunic Rosing Announcements and Outline Check webct grades, make sure everything is there and is correct Pick up graded d homework at
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 27: Midterm2 review Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Midterm 2 Review Midterm will cover Section 1.6: Processor
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 27: Midterm2 review Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Midterm 2 Review Midterm will cover Section 1.6: Processor
c. What are the machine cycle times (in nanoseconds) of the non-pipelined and the pipelined implementations?
 Brown University School of Engineering ENGN 164 Design of Computing Systems Professor Sherief Reda Homework 07. 140 points. Due Date: Monday May 12th in B&H 349 1. [30 points] Consider the non-pipelined
Brown University School of Engineering ENGN 164 Design of Computing Systems Professor Sherief Reda Homework 07. 140 points. Due Date: Monday May 12th in B&H 349 1. [30 points] Consider the non-pipelined
Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University.
 Instructions: ti Language of the Computer Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Computer Hierarchy Levels Language understood
Instructions: ti Language of the Computer Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Computer Hierarchy Levels Language understood
Hardwired Control Unit Ch 16
 Hardwired Control Unit Ch 16 Micro-operations Controlling Execution Hardwired Control 1 What is Control (2) So far, we have shown what happens inside CPU execution of instructions opcodes, addressing modes,
Hardwired Control Unit Ch 16 Micro-operations Controlling Execution Hardwired Control 1 What is Control (2) So far, we have shown what happens inside CPU execution of instructions opcodes, addressing modes,
Instruction Set Architecture
 Computer Architecture Instruction Set Architecture Lynn Choi Korea University Machine Language Programming language High-level programming languages Procedural languages: C, PASCAL, FORTRAN Object-oriented
Computer Architecture Instruction Set Architecture Lynn Choi Korea University Machine Language Programming language High-level programming languages Procedural languages: C, PASCAL, FORTRAN Object-oriented
Programmable Machines
 Programmable Machines Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. Quiz 1: next week Covers L1-L8 Oct 11, 7:30-9:30PM Walker memorial 50-340 L09-1 6.004 So Far Using Combinational
Programmable Machines Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. Quiz 1: next week Covers L1-L8 Oct 11, 7:30-9:30PM Walker memorial 50-340 L09-1 6.004 So Far Using Combinational
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
Chapter 4. The Processor. Computer Architecture and IC Design Lab
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors CPI Clock Cycle Time Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors CPI Clock Cycle Time Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS
LECTURE 5. Single-Cycle Datapath and Control
 LECTURE 5 Single-Cycle Datapath and Control PROCESSORS In lecture 1, we reminded ourselves that the datapath and control are the two components that come together to be collectively known as the processor.
LECTURE 5 Single-Cycle Datapath and Control PROCESSORS In lecture 1, we reminded ourselves that the datapath and control are the two components that come together to be collectively known as the processor.
Review Questions. 1 The DRAM problem [5 points] Suggest a solution. 2 Big versus Little Endian Addressing [5 points]
![Review Questions. 1 The DRAM problem [5 points] Suggest a solution. 2 Big versus Little Endian Addressing [5 points] Review Questions. 1 The DRAM problem [5 points] Suggest a solution. 2 Big versus Little Endian Addressing [5 points]](/thumbs/80/81375776.jpg) Review Questions 1 The DRAM problem [5 points] Suggest a solution 2 Big versus Little Endian Addressing [5 points] Consider the 32-bit hexadecimal number 0x21d3ea7d. 1. What is the binary representation
Review Questions 1 The DRAM problem [5 points] Suggest a solution 2 Big versus Little Endian Addressing [5 points] Consider the 32-bit hexadecimal number 0x21d3ea7d. 1. What is the binary representation
Chapter 2. Instructions:
 Chapter 2 1 Instructions: Language of the Machine More primitive than higher level languages e.g., no sophisticated control flow Very restrictive e.g., MIPS Arithmetic Instructions We ll be working with
Chapter 2 1 Instructions: Language of the Machine More primitive than higher level languages e.g., no sophisticated control flow Very restrictive e.g., MIPS Arithmetic Instructions We ll be working with
Reminder: tutorials start next week!
 Previous lecture recap! Metrics of computer architecture! Fundamental ways of improving performance: parallelism, locality, focus on the common case! Amdahl s Law: speedup proportional only to the affected
Previous lecture recap! Metrics of computer architecture! Fundamental ways of improving performance: parallelism, locality, focus on the common case! Amdahl s Law: speedup proportional only to the affected
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Datapath. Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Datapath Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa15 1 Components of a Computer Processor Control Enable? Read/Write
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Datapath Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa15 1 Components of a Computer Processor Control Enable? Read/Write
PIPELINING: HAZARDS. Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi. CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture. Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah
 PIPELINING: HAZARDS Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 1 submission deadline: Jan. 30 th This
PIPELINING: HAZARDS Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 1 submission deadline: Jan. 30 th This
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture
 Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2009 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture. Idea:
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2009 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture. Idea:
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9- CPU Microarchitecture. Watson: Jeopardy-playing Computer
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9- CPU Microarchitecture Feb 15, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec09-cpu Page 1 Watson: Jeopardy-playing Computer Watson is made up of a cluster of ninety IBM
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9- CPU Microarchitecture Feb 15, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec09-cpu Page 1 Watson: Jeopardy-playing Computer Watson is made up of a cluster of ninety IBM
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design. Computer Organization - Previously covered
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 6: MIPS Instructions II http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Computer Organization
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 6: MIPS Instructions II http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Computer Organization
Computer Systems Architecture
 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 12 Mahadevan Gomathisankaran March 4, 2010 03/04/2010 Lecture 12 CSCE 4610/5610 1 Discussion: Assignment 2 03/04/2010 Lecture 12 CSCE 4610/5610 2 Increasing Fetch
Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 12 Mahadevan Gomathisankaran March 4, 2010 03/04/2010 Lecture 12 CSCE 4610/5610 1 Discussion: Assignment 2 03/04/2010 Lecture 12 CSCE 4610/5610 2 Increasing Fetch
The Processor: Datapath & Control
 Orange Coast College Business Division Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture The Processor: Datapath & Control Processor Design Step 3 Assemble Datapath Meeting Requirements Build the
Orange Coast College Business Division Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture The Processor: Datapath & Control Processor Design Step 3 Assemble Datapath Meeting Requirements Build the
Instructions: Language of the Computer
 CS359: Computer Architecture Instructions: Language of the Computer Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 The Language a Computer Understands Word a computer understands: instruction
CS359: Computer Architecture Instructions: Language of the Computer Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 The Language a Computer Understands Word a computer understands: instruction
Computer Science and Engineering 331. Midterm Examination #1. Fall Name: Solutions S.S.#:
 Computer Science and Engineering 331 Midterm Examination #1 Fall 2000 Name: Solutions S.S.#: 1 41 2 13 3 18 4 28 Total 100 Instructions: This exam contains 4 questions. It is closed book and notes. Calculators
Computer Science and Engineering 331 Midterm Examination #1 Fall 2000 Name: Solutions S.S.#: 1 41 2 13 3 18 4 28 Total 100 Instructions: This exam contains 4 questions. It is closed book and notes. Calculators
CENG 5133 Computer Architecture Design Spring Sample Exam 2
 CENG 533 Computer Architecture Design Spring 24 Sample Exam 2. (6 pt) Determine the propagation delay and contamination delay of the following circuit using the gate delays given below. Gate t pd (ps)
CENG 533 Computer Architecture Design Spring 24 Sample Exam 2. (6 pt) Determine the propagation delay and contamination delay of the following circuit using the gate delays given below. Gate t pd (ps)
Computer Science 61C Spring Friedland and Weaver. The MIPS Datapath
 The MIPS Datapath 1 The Critical Path and Circuit Timing The critical path is the slowest path through the circuit For a synchronous circuit, the clock cycle must be longer than the critical path otherwise
The MIPS Datapath 1 The Critical Path and Circuit Timing The critical path is the slowest path through the circuit For a synchronous circuit, the clock cycle must be longer than the critical path otherwise
Levels of Programming. Registers
 Levels of Programming COSC 2021: Computer Organization Instructor: Dr. Amir Asif Department of Computer Science York University Handout # 3: MIPS Instruction Set I Topics: 1. Arithmetic Instructions 2.
Levels of Programming COSC 2021: Computer Organization Instructor: Dr. Amir Asif Department of Computer Science York University Handout # 3: MIPS Instruction Set I Topics: 1. Arithmetic Instructions 2.
Control Hazards - branching causes problems since the pipeline can be filled with the wrong instructions.
 Control Hazards - branching causes problems since the pipeline can be filled with the wrong instructions Stage Instruction Fetch Instruction Decode Execution / Effective addr Memory access Write-back Abbreviation
Control Hazards - branching causes problems since the pipeline can be filled with the wrong instructions Stage Instruction Fetch Instruction Decode Execution / Effective addr Memory access Write-back Abbreviation
The MIPS Instruction Set Architecture
 The MIPS Set Architecture CPS 14 Lecture 5 Today s Lecture Admin HW #1 is due HW #2 assigned Outline Review A specific ISA, we ll use it throughout semester, very similar to the NiosII ISA (we will use
The MIPS Set Architecture CPS 14 Lecture 5 Today s Lecture Admin HW #1 is due HW #2 assigned Outline Review A specific ISA, we ll use it throughout semester, very similar to the NiosII ISA (we will use
CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015
 CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015 Name: Rules and Hints The MIPS cheat sheet and datapath diagram are attached at the end of this exam for your reference. You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front
CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015 Name: Rules and Hints The MIPS cheat sheet and datapath diagram are attached at the end of this exam for your reference. You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front
Computer Architecture. The Language of the Machine
 Computer Architecture The Language of the Machine Instruction Sets Basic ISA Classes, Addressing, Format Administrative Matters Operations, Branching, Calling conventions Break Organization All computers
Computer Architecture The Language of the Machine Instruction Sets Basic ISA Classes, Addressing, Format Administrative Matters Operations, Branching, Calling conventions Break Organization All computers
Pipeline Overview. Dr. Jiang Li. Adapted from the slides provided by the authors. Jiang Li, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science
 Pipeline Overview Dr. Jiang Li Adapted from the slides provided by the authors Outline MIPS An ISA for Pipelining 5 stage pipelining Structural and Data Hazards Forwarding Branch Schemes Exceptions and
Pipeline Overview Dr. Jiang Li Adapted from the slides provided by the authors Outline MIPS An ISA for Pipelining 5 stage pipelining Structural and Data Hazards Forwarding Branch Schemes Exceptions and
Systems Architecture
 Systems Architecture Lecture 15: A Simple Implementation of MIPS Jeremy R. Johnson Anatole D. Ruslanov William M. Mongan Some or all figures from Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software
Systems Architecture Lecture 15: A Simple Implementation of MIPS Jeremy R. Johnson Anatole D. Ruslanov William M. Mongan Some or all figures from Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software
Lecture 2: The Instruction Set Architecture
 Lecture 2: The Instruction Set Architecture COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 2 Quiz 0 3 Quiz 0 CD 3 Miles of Music 4 Pits and Lands
Lecture 2: The Instruction Set Architecture COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 2 Quiz 0 3 Quiz 0 CD 3 Miles of Music 4 Pits and Lands
Pipelining: Overview. CPSC 252 Computer Organization Ellen Walker, Hiram College
 Pipelining: Overview CPSC 252 Computer Organization Ellen Walker, Hiram College Pipelining the Wash Divide into 4 steps: Wash, Dry, Fold, Put Away Perform the steps in parallel Wash 1 Wash 2, Dry 1 Wash
Pipelining: Overview CPSC 252 Computer Organization Ellen Walker, Hiram College Pipelining the Wash Divide into 4 steps: Wash, Dry, Fold, Put Away Perform the steps in parallel Wash 1 Wash 2, Dry 1 Wash
CS31001 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE. Debdeep Mukhopadhyay, CSE, IIT Kharagpur. Instructions and Addressing
 CS31001 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE Debdeep Mukhopadhyay, CSE, IIT Kharagpur Instructions and Addressing 1 ISA vs. Microarchitecture An ISA or Instruction Set Architecture describes the aspects
CS31001 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE Debdeep Mukhopadhyay, CSE, IIT Kharagpur Instructions and Addressing 1 ISA vs. Microarchitecture An ISA or Instruction Set Architecture describes the aspects
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
6.004 Tutorial Problems L22 Branch Prediction
 6.004 Tutorial Problems L22 Branch Prediction Branch target buffer (BTB): Direct-mapped cache (can also be set-associative) that stores the target address of jumps and taken branches. The BTB is searched
6.004 Tutorial Problems L22 Branch Prediction Branch target buffer (BTB): Direct-mapped cache (can also be set-associative) that stores the target address of jumps and taken branches. The BTB is searched
LECTURE 3: THE PROCESSOR
 LECTURE 3: THE PROCESSOR Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.4 Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU
LECTURE 3: THE PROCESSOR Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.4 Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)... the attributes of a [computing] system as seen by the programmer, i.e. the conceptual structure and functional behavior, as distinct from the organization of the data
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)... the attributes of a [computing] system as seen by the programmer, i.e. the conceptual structure and functional behavior, as distinct from the organization of the data
The University of Alabama in Huntsville Electrical & Computer Engineering Department CPE Test II November 14, 2000
 The University of Alabama in Huntsville Electrical & Computer Engineering Department CPE 513 01 Test II November 14, 2000 Name: 1. (5 points) For an eight-stage pipeline, how many cycles does it take to
The University of Alabama in Huntsville Electrical & Computer Engineering Department CPE 513 01 Test II November 14, 2000 Name: 1. (5 points) For an eight-stage pipeline, how many cycles does it take to
Lecture 10: Simple Data Path
 Lecture 10: Simple Data Path Course so far Performance comparisons Amdahl s law ISA function & principles What do bits mean? Computer math Today Take QUIZ 6 over P&H.1-, before 11:59pm today How do computers
Lecture 10: Simple Data Path Course so far Performance comparisons Amdahl s law ISA function & principles What do bits mean? Computer math Today Take QUIZ 6 over P&H.1-, before 11:59pm today How do computers
Chapter 2: Instructions:
 Chapter 2: Instructions: Language of the Computer Computer Architecture CS-3511-2 1 Instructions: To command a computer s hardware you must speak it s language The computer s language is called instruction
Chapter 2: Instructions: Language of the Computer Computer Architecture CS-3511-2 1 Instructions: To command a computer s hardware you must speak it s language The computer s language is called instruction
CS/CoE 1541 Mid Term Exam (Fall 2018).
 CS/CoE 1541 Mid Term Exam (Fall 2018). Name: Question 1: (6+3+3+4+4=20 points) For this question, refer to the following pipeline architecture. a) Consider the execution of the following code (5 instructions)
CS/CoE 1541 Mid Term Exam (Fall 2018). Name: Question 1: (6+3+3+4+4=20 points) For this question, refer to the following pipeline architecture. a) Consider the execution of the following code (5 instructions)
Cache Memory Mapping Techniques. Continue to read pp
 Cache Memory Mapping Techniques Continue to read pp. 289-305 Cache Memory Mapping Again cache memory is a small and fast memory between CPU and main memory A block of words have to be brought in and out
Cache Memory Mapping Techniques Continue to read pp. 289-305 Cache Memory Mapping Again cache memory is a small and fast memory between CPU and main memory A block of words have to be brought in and out
CPSC 3300 Spring 2016 Final Exam Version A No Calculators
 CPSC 3300 Spring 2016 Final Exam Version A No Calculators Name: 1. Find the execution time of a program that executes 8 billion instructions on a processor with an average CPI of 2 and a clock frequency
CPSC 3300 Spring 2016 Final Exam Version A No Calculators Name: 1. Find the execution time of a program that executes 8 billion instructions on a processor with an average CPI of 2 and a clock frequency
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H ) Next: continued. Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23)
 Lecture Topics Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H 4.1-4.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Exam #1 (Wednesday, 2/15) 2 1 Exam #1 Wednesday, 2/15 (3:00-4:20
Lecture Topics Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H 4.1-4.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Exam #1 (Wednesday, 2/15) 2 1 Exam #1 Wednesday, 2/15 (3:00-4:20
MIPS Pipelining. Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing. Wednesday 8 October 14
 MIPS Pipelining Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Wednesday 8 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition, 2011, MK
MIPS Pipelining Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Wednesday 8 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition, 2011, MK
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 14: One Cycle MIPs Datapath Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB R-Format Instructions Read two register operands Perform
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 14: One Cycle MIPs Datapath Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB R-Format Instructions Read two register operands Perform
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control
 ELEC 52/62 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 217 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849
ELEC 52/62 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 217 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849
Final Exam Spring 2017
 COE 3 / ICS 233 Computer Organization Final Exam Spring 27 Friday, May 9, 27 7:3 AM Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
COE 3 / ICS 233 Computer Organization Final Exam Spring 27 Friday, May 9, 27 7:3 AM Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
Control MIPS unconditional branch instruction (i.e., jump)
 Control Instruction that potentially changes the flow of program execution MIPS conditional branch instructions bne $s4, $s3, LABEL goto LABEL if $s4!= $s3 beq $s4, $s3, LABEL goto LABEL if $s4 == $s3
Control Instruction that potentially changes the flow of program execution MIPS conditional branch instructions bne $s4, $s3, LABEL goto LABEL if $s4!= $s3 beq $s4, $s3, LABEL goto LABEL if $s4 == $s3
Concocting an Instruction Set
 Concocting an Instruction Set Nerd Chef at work. move flour,bowl add milk,bowl add egg,bowl move bowl,mixer rotate mixer... Read: Chapter 2.1-2.7 L03 Instruction Set 1 A General-Purpose Computer The von
Concocting an Instruction Set Nerd Chef at work. move flour,bowl add milk,bowl add egg,bowl move bowl,mixer rotate mixer... Read: Chapter 2.1-2.7 L03 Instruction Set 1 A General-Purpose Computer The von
ECE 15B Computer Organization Spring 2011
 ECE 15B Computer Organization Spring 2011 Dmitri Strukov Partially adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th edition, Patterson and Hennessy, Agenda Instruction formats Addressing modes Advanced
ECE 15B Computer Organization Spring 2011 Dmitri Strukov Partially adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th edition, Patterson and Hennessy, Agenda Instruction formats Addressing modes Advanced
EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver. Lecture 13 EE141
 EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver Lecture 13 Project Introduction You will design and optimize a RISC-V processor Phase 1: Design
EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver Lecture 13 Project Introduction You will design and optimize a RISC-V processor Phase 1: Design
EN2910A: Advanced Computer Architecture Topic 02: Review of classical concepts
 EN2910A: Advanced Computer Architecture Topic 02: Review of classical concepts Prof. Sherief Reda School of Engineering Brown University S. Reda EN2910A FALL'15 1 Classical concepts (prerequisite) 1. Instruction
EN2910A: Advanced Computer Architecture Topic 02: Review of classical concepts Prof. Sherief Reda School of Engineering Brown University S. Reda EN2910A FALL'15 1 Classical concepts (prerequisite) 1. Instruction
RISC Design: Multi-Cycle Implementation
 RISC Design: Multi-Cycle Implementation Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
RISC Design: Multi-Cycle Implementation Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface. 5 th. Edition. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination
 THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination May 23, 2014 Name: Email: Student ID: Lab Section Number: Instructions: 1. This
THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination May 23, 2014 Name: Email: Student ID: Lab Section Number: Instructions: 1. This
Computer Architecture. Lecture 2 : Instructions
 Computer Architecture Lecture 2 : Instructions 1 Components of a Computer Hierarchical Layers of Program Code 3 Instruction Set The repertoire of instructions of a computer 2.1 Intr roduction Different
Computer Architecture Lecture 2 : Instructions 1 Components of a Computer Hierarchical Layers of Program Code 3 Instruction Set The repertoire of instructions of a computer 2.1 Intr roduction Different
Chapter 4. Instruction Execution. Introduction. CPU Overview. Multiplexers. Chapter 4 The Processor 1. The Processor.
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor The Processor - Introduction
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor The Processor - Introduction
CENG 3420 Lecture 06: Datapath
 CENG 342 Lecture 6: Datapath Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk CENG342 L6. Spring 27 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified to contain only: memory-reference
CENG 342 Lecture 6: Datapath Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk CENG342 L6. Spring 27 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified to contain only: memory-reference
ECE170 Computer Architecture. Single Cycle Control. Review: 3b: Add & Subtract. Review: 3e: Store Operations. Review: 3d: Load Operations
 ECE7 Computer Architecture Single Cycle Control Review: 3a: Overview of the Fetch Unit The common operations Fetch the : mem[] Update the program counter: Sequential Code: < + Branch and Jump: < something
ECE7 Computer Architecture Single Cycle Control Review: 3a: Overview of the Fetch Unit The common operations Fetch the : mem[] Update the program counter: Sequential Code: < + Branch and Jump: < something
ELEC / Computer Architecture and Design Fall 2013 Instruction Set Architecture (Chapter 2)
 ELEC 5200-001/6200-001 Computer Architecture and Design Fall 2013 Instruction Set Architecture (Chapter 2) Victor P. Nelson, Professor & Asst. Chair Vishwani D. Agrawal, James J. Danaher Professor Department
ELEC 5200-001/6200-001 Computer Architecture and Design Fall 2013 Instruction Set Architecture (Chapter 2) Victor P. Nelson, Professor & Asst. Chair Vishwani D. Agrawal, James J. Danaher Professor Department
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition The Processor - Introduction
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition The Processor - Introduction
EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture
 EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture 5 Instruction Set Architecture I Dr Hashim Ali Fall 2018 Department of Computer Science and Engineering HITEC University Taxila!1 Instruction Set Architecture
EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture 5 Instruction Set Architecture I Dr Hashim Ali Fall 2018 Department of Computer Science and Engineering HITEC University Taxila!1 Instruction Set Architecture
Solution : mov R0, mov R3,0 mov R4,31 movu R2,0x0001 mov R5,0 andu R1,R0,0xffff
 Q4. Write an ARM assembly program that checks if a 32-bit number is a palindrome. Assume that the input is available in r 3. The program should set r 4 to 1 if it is a palindrome, otherwise r 4 should
Q4. Write an ARM assembly program that checks if a 32-bit number is a palindrome. Assume that the input is available in r 3. The program should set r 4 to 1 if it is a palindrome, otherwise r 4 should
Processor. Han Wang CS3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H Chapter , 4.1 4
 Processor Han Wang CS3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H Chapter 2.16 20, 4.1 4 Announcements Project 1 Available Design Document due in one week. Final Design due in three weeks.
Processor Han Wang CS3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H Chapter 2.16 20, 4.1 4 Announcements Project 1 Available Design Document due in one week. Final Design due in three weeks.
Microprogrammed Control Approach
 Microprogrammed Control Approach Considering the FSM for our MIPS subset has 10 states, the complete MIPS instruction set, which contains more than 100 instructions, and considering that these instructions
Microprogrammed Control Approach Considering the FSM for our MIPS subset has 10 states, the complete MIPS instruction set, which contains more than 100 instructions, and considering that these instructions
Chapter 4 The Processor 1. Chapter 4A. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor 1 Chapter 4A The Processor Chapter 4 The Processor 2 Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware
Chapter 4 The Processor 1 Chapter 4A The Processor Chapter 4 The Processor 2 Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware
ECE 313 Computer Organization FINAL EXAM December 14, This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours.
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours. Problems 1-5 refer to the following: We wish to add a new R-Format instruction to the MIPS Instruction Set Architecture called l_inc (load and increment).
This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours. Problems 1-5 refer to the following: We wish to add a new R-Format instruction to the MIPS Instruction Set Architecture called l_inc (load and increment).
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture
 Computer Science 220 Assembly Language & Comp. Architecture Siena College Fall 2011 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture.
Computer Science 220 Assembly Language & Comp. Architecture Siena College Fall 2011 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture.
Pipelined Processors. Ideal Pipelining. Example: FP Multiplier. 55:132/22C:160 Spring Jon Kuhl 1
 55:3/C:60 Spring 00 Pipelined Design Motivation: Increase processor throughput with modest increase in hardware. Bandwidth or Throughput = Performance Pipelined Processors Chapter Bandwidth (BW) = no.
55:3/C:60 Spring 00 Pipelined Design Motivation: Increase processor throughput with modest increase in hardware. Bandwidth or Throughput = Performance Pipelined Processors Chapter Bandwidth (BW) = no.
