SYNTHESIS OF FINITE STATE MACHINES: LOGIC OPTIMIZATION
|
|
|
- Dennis Wilkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SYNTHESIS OF FINITE STATE MACHINES: LOGIC OPTIMIZATION
2 SYNTHESIS OF FINITE STATE MACHINES: LOGIC OPTIMIZATION Tiziano Villa University of California/Berkeley Timothy Kam Intel Corporation Robert K. Brayton University of California/Berkeley Alberto Sangiovanni-Vincentelli University of California/Berkeley ~. " SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, LLC
3 ISBN ISBN (ebook) DOI / Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data A C.I.P. Catalogue record for this book is available from the Library of Congress by Springer Science+Business Media New York Originally published by Kluwer Academic Publishers in 1997 Softcover reprint of the hardcover 1 st edition 1997 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, mechanical, photo-copying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permis sion of the publisher, Springer-Science+Business Media, LLC. Printed on acid-free paper.
4 To Alle mie scorte: Franco e Marta, Maria, Marta e Letizia; Professor and Mrs. Wai-Kee Kam, and Mrs. Kate Kam for unfailing love and support; Ruth for continuous support over many years; To Marcolino, whose laughters and joy of life are bringing so much happiness around him.
5 CONTENTS PREFACE xi Part I FROM SYMBOLIC TO LOGIC REPRESENTATIONS 1 1 INTRODUCTION Logic Synthesis of Sequential Behaviors The Encoding Problem: From Symbolic to Boolean Domain Overview of the Book 9 2 DEFINITIONS Sequential Functions and Their Representation Finite State Machines Taxonomy of Encoding Problems Behavior vs. Structure in Encoding Problems Boolean Algebras and Boolean Functions Discrete Functions as Boolean Functions Two-level Minimization of Multi-Valued Functions Multi-level Multi-Valued Functions Multi-Valued Relations Binary Decision Diagrams Hypercubes 37 3 COMPLEXITY ISSUES Computational Complexity Counting State Assignments 48 Vll
6 viiisvnthesis OF FINITE STATE MACHINES: LOGIC OPTIMIZATION 4 ENCODING FOR SYNTHESIS Algorithms for Optimal Encoding Combinational Encoding Problems State Assignment and FSM Decomposition State Assignment for Testability Sequential Optimization at the Gate Level 130 Part II CONSTRAINED ENCODING SYMBOLIC MINIMIZATION Introduction Encoding for Two-level Implementations A New Symbolic Minimization Algorithm Symbolic Reduction Symbolic Oring Ordering of Symbolic Minimization Symbolic Minimization by Example Experimental Results Conclusions ENCODING CONSTRAINTS Introduction Statement and Complexity of the Encoding Problems Definitions Abstraction of the Problem Input Constraint Satisfaction Input and Output Constraint Satisfaction Bounded Length Encoding Other Applications Results Conclusions 218 Part III GENERALIZED PRIME IMPLICANTS GENERALIZED PRIME IMPLICANTS Introduction 221
7 Contents ix 7.2 Definition of GPIs GPIs by Consensus Operation Encodeability of GPIs Sufficiency of GPIs GPIs by Computation of MV Primes A Procedure for Analysis of GPIs MINIMIZATION OF GPIS Reduction of GPI Minimization to Unate Covering Reduction of GPI Minimization to Binate Covering GPIs and Non-Determinism ENCODEABILITY OF GPIS Introduction Efficient Encodeability Check of GPIs Encoding of a Set of Encodeable GPIs Updating Sets and Raising Graphs Choice of a Branching Column Computation of a Lower Bound 295 Part IV IMPLICIT TECHNIQUES FOR ENCODING IMPLICIT FORMULATION OF UNATE COVERING Introduction Implicit Representations and Manipulations A Fully Implicit Unate Covering Solver Quantifier-Free Reduction of Unate Tables An Application to Encoding Dichotomies IMPLICIT MINIMIZATION OF GPIS Introduction Useful Relations Implicit Generation of GPIs and Minterms Implicit Selection of GPIs 328
8 xsvnthesis OF FINITE STATE MACHINES: LOGIC OPTIMIZATION 11.5 An Example of Implicit GPI Minimization 11.6 Verification of Correctness 11.7 Implementation Issues 11.8 Experiments 11.9 Conclusions Part V CONCL US IONS CONCLUSIONS REFERENCES INDEX
9 PREFACE This book is the second of a set of two monographs devoted to the synthesis of Finite State Machines (FSMs). The first volume addresses functional optimization, whereas this one addresses logic optimization. The result of functional optimization is a symbolic description of an FSM which represents a sequential function chosen from a collection of permissible candidates. Logic optimization is the body of techniques to convert a symbolic description of an FSM into an hardware implementation. The mapping of a given symbolic representation into a two-valued logic implementation is called state encoding (or state assignment) and it impacts heavily area, speed, testability and power consumption of the realized circuit. Here we present a quite extensive account of the subject matter, describing contributions due to the authors and to many other researchers. In the exposition we have emphasized modern approaches pursued since the 80s, but also the previous literature has been integrated into a comprehensive picture. The exposition is self-contained, but some familiarity with Boolean algebra and automata theory will be helpful. Key themes running throughout the book are the minimization of symbolic logic, the satisfaction of encoding constraints and the representation of combinatorial problems of FSM synthesis with binary decision diagrams (BDDs). The first part of the book introduces the relevant background, presents results previously scattered in the literature on the computational complexity of encoding problems, and finally surveys in depth old and new approaches to encoding in logic synthesis. Many recent techniques for encoding can be described as symbolic minimization, i.e., given a function, the generation of an optimal symbolic representation that is implement able in the two-valued domain, provided that some conditions on the binary codes of the states are satisfiable (encoding constraints). The second part of the book presents two main results about symbolic minimization: a new procedure to find minimal two-level symbolic covers, under face, domixi
10 xiisynthesis OF FINITE STATE MACHINES: LOGIC OPTIMIZATION nance and disjunctive constraints, and a unified frame to check encodeability of encoding constraints and find codes of minimum length that satisfy them. This frame has been used for various types of encoding constraints arising in problems that range from encoding for minimum multi-level representation to race-free encoding of asynchronous FSMs. Experiments for different applications are reported. The third part of the book introduces generalized prime implicants (GPIs), which are the counterpart, in symbolic minimization of two-level logic, to prime implicants in two-valued two-level minimization. GPIs enable the design of an exact procedure for two-level symbolic minimization, based on a covering step which is complicated by the need to guarantee encodeability of the final cover. We present a new efficient algorithm to verify encodeability of a selected cover. If a cover is not encodeable, it is shown how to augment it minimally until an encodeable superset of GPIs is determined. To handle encodeability we have extended the frame to satisfy encoding constraints presented in the second part. The covering problems generated in the minimization of GPIs tend to be very large. Recently large covering problems have been attacked successfully by representing the covering table with BDDs. In the fourth part of book we introduce such techniques and extend them to the case of the implicit minimization of GPIs, where also the encodeability and augmentation steps are performed implicitly. In all these years we benefited from close associations with various researchers operating in the field, especially our colleagues at the University of California at Berkeley. We owe gratitude to all of them. A special mention goes to Alex Saldanha with whom we developed the research presented in the second part of this volume. We acknowledge very helpful discussions with present or former colleagues in the Berkeley CAD group: Pranav Ashar, Mark Beardslee, Luca Carloni, Srinivas Devadas, Stephen Edwards, Eugene Goldberg, Sunil Khatri, Yuji Kukimoto, William Lam, Luciano Lavagno, Sharad Malik, Rick McGeer, Rajeev Murgai, Arlindo Oliveira, Tom Shiple, Gitanjali Swamy, Huey-Yih Wang and Yosinori Watanabe. Luciano Lavagno, Sharad Malik and Rajeev Murgai helped in countless ways through discussions and sharing material. Gitanjali Swamy and Rick McGeer contributed an efficient software package for the implicit computation of multivalued prime implicants. Huey-Yih Wang kindly shared some drawings from his dissertation. Stephen Edwards gave advice in matters of style and contributed a software package to visualize FSMs.
11 Preface xiii Ney Calazans, Giovanni De Micheli, Zafar Hasan, Bruce Holmer, Kurt Keutzer, David Johnson and Fabio Somenzi were kindly available to discuss technical questions and share literature. In particular we thank Kurt Keutzer for sending a draft of a paper on the computational complexity of problems in logic synthesis. But as usual the greatest source of sustenance have been our family members to whom we dedicate our work. The funding for this research was provided by DARPA, NSF, SRC and industrial grants from Bell Northern, Digital, Fujitsu, Intel, MICRO, Motorola, and we gratefully acknowledge it. We thank Carl Harris of Kluwer Academic Publishers for his patience and continuous encouragement to persevere in the task of writing the book(s).
Encoding Problems in Logic Synthesis
 Encoding Problems in Logic Synthesis by Tiziano Villa Laurea in Matematica (Università Statale di Milano, Italy), 1977 Mathematical Tripos, Part III, D.A.M.T.P., Cambridge University, U.K., 1982 M.S. (University
Encoding Problems in Logic Synthesis by Tiziano Villa Laurea in Matematica (Università Statale di Milano, Italy), 1977 Mathematical Tripos, Part III, D.A.M.T.P., Cambridge University, U.K., 1982 M.S. (University
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF REAL-TIME EMBEDDED SOFTWARE
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF REAL-TIME EMBEDDED SOFTWARE PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF REAL-TIME EMBEDDED SOFTWARE Yau-Tsun Steven Li Monterey Design Systems, Inc. Sharad Malik Princeton University ~. " SPRINGER
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF REAL-TIME EMBEDDED SOFTWARE PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF REAL-TIME EMBEDDED SOFTWARE Yau-Tsun Steven Li Monterey Design Systems, Inc. Sharad Malik Princeton University ~. " SPRINGER
LOGIC SYNTHESIS FOR FIELD-PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS
 LOGIC SYNTHESIS FOR FIELD-PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE VLSI, COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Consulting Editor Jonathan
LOGIC SYNTHESIS FOR FIELD-PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE VLSI, COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Consulting Editor Jonathan
SEQUENTIAL LOGIC TESTING AND VERIFICATION
 SEQUENTIAL LOGIC TESTING AND VERIFICATION THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE VLSI, COMPUTER ARCIllTECfURE AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Latest Titles Consulting Editor
SEQUENTIAL LOGIC TESTING AND VERIFICATION THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE VLSI, COMPUTER ARCIllTECfURE AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Latest Titles Consulting Editor
MULTIMEDIA DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
 MULTIMEDIA DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS AND APPLICATIONS Recently Published Titles: Consulting Editor Borko Furht Florida
MULTIMEDIA DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS AND APPLICATIONS Recently Published Titles: Consulting Editor Borko Furht Florida
ARCHITECTURE AND CAD FOR DEEP-SUBMICRON FPGAs
 ARCHITECTURE AND CAD FOR DEEP-SUBMICRON FPGAs THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE ARCHITECTURE AND CAD FOR DEEP-SUBMICRON FPGAs Vaughn Betz Jonathan Rose Alexander Marquardt
ARCHITECTURE AND CAD FOR DEEP-SUBMICRON FPGAs THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE ARCHITECTURE AND CAD FOR DEEP-SUBMICRON FPGAs Vaughn Betz Jonathan Rose Alexander Marquardt
LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND VERIFICATION ALGORITHMS. Gary D. Hachtel University of Colorado. Fabio Somenzi University of Colorado.
 LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND VERIFICATION ALGORITHMS by Gary D. Hachtel University of Colorado Fabio Somenzi University of Colorado Springer Contents I Introduction 1 1 Introduction 5 1.1 VLSI: Opportunity and
LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND VERIFICATION ALGORITHMS by Gary D. Hachtel University of Colorado Fabio Somenzi University of Colorado Springer Contents I Introduction 1 1 Introduction 5 1.1 VLSI: Opportunity and
Assign auniquecodeto each state to produce a. Given jsj states, needed at least dlog jsje state bits. (minimum width encoding), at most jsj state bits
 State Assignment The problem: Assign auniquecodeto each state to produce a logic level description. Given jsj states, needed at least dlog jsje state bits (minimum width encoding), at most jsj state bits
State Assignment The problem: Assign auniquecodeto each state to produce a logic level description. Given jsj states, needed at least dlog jsje state bits (minimum width encoding), at most jsj state bits
Don t Cares and Multi-Valued Logic Network Minimization
 Don t Cares and Multi-Valued Logic Network Minimization Yunian Jiang Robert K. Brayton Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley wiang,brayton @eecs.berkeley.edu
Don t Cares and Multi-Valued Logic Network Minimization Yunian Jiang Robert K. Brayton Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley wiang,brayton @eecs.berkeley.edu
Topological Structure and Analysis of Interconnection Networks
 Topological Structure and Analysis of Interconnection Networks Network Theory and Applications Volume 7 Managing Editors: Ding-Zhu Du, University of Minnesota, U.S.A. and Cauligi Raghavendra, University
Topological Structure and Analysis of Interconnection Networks Network Theory and Applications Volume 7 Managing Editors: Ding-Zhu Du, University of Minnesota, U.S.A. and Cauligi Raghavendra, University
Energy Efficient Microprocessor Design
 Energy Efficient Microprocessor Design Energy Efficient Microprocessor Design by Thomas D. Burd Robert W. Brodersen with Contributions Irom Trevor Pering Anthony Stratakos Berkeley Wireless Research Center
Energy Efficient Microprocessor Design Energy Efficient Microprocessor Design by Thomas D. Burd Robert W. Brodersen with Contributions Irom Trevor Pering Anthony Stratakos Berkeley Wireless Research Center
FUNCTIONAL DECOMPOSITION WITH APPLICATION TO FPGA SYNTHESIS
 FUNCTIONAL DECOMPOSITION WITH APPLICATION TO FPGA SYNTHESIS Functional Decomposition with Application to FPGA Synthesis by Christoph Scholl Institute of Computer Science, Albert-Ludwigs-University, Freiburg
FUNCTIONAL DECOMPOSITION WITH APPLICATION TO FPGA SYNTHESIS Functional Decomposition with Application to FPGA Synthesis by Christoph Scholl Institute of Computer Science, Albert-Ludwigs-University, Freiburg
Cofactoring-Based Upper Bound Computation for Covering Problems
 TR-CSE-98-06, UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST Cofactoring-Based Upper Bound Computation for Covering Problems Congguang Yang Maciej Ciesielski May 998 TR-CSE-98-06 Department of Electrical and Computer
TR-CSE-98-06, UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST Cofactoring-Based Upper Bound Computation for Covering Problems Congguang Yang Maciej Ciesielski May 998 TR-CSE-98-06 Department of Electrical and Computer
SOFTWARE FOR THE MINIMIZATION OF THE COMBINATIONAL LOGIC FUNCTIONS
 SOFTWARE FOR THE MINIMIZATION OF THE COMBINATIONAL LOGIC FUNCTIONS Rotar Dan Vasile Alecsandri University, Bacau, Romania Abstract An important component of the command and control circuit for the mechatronic
SOFTWARE FOR THE MINIMIZATION OF THE COMBINATIONAL LOGIC FUNCTIONS Rotar Dan Vasile Alecsandri University, Bacau, Romania Abstract An important component of the command and control circuit for the mechatronic
Software for The Minimization of The Combinational Logic Functions
 Software for The Minimization of The Combinational Logic Functions Rotar Dan Vasile Alecsandri University, Calea Marasesti 57, cod: 65, Bacau, Romania, drotar@ub.ro; drotarubro@yahoo.com ABSTRACT An important
Software for The Minimization of The Combinational Logic Functions Rotar Dan Vasile Alecsandri University, Calea Marasesti 57, cod: 65, Bacau, Romania, drotar@ub.ro; drotarubro@yahoo.com ABSTRACT An important
State assignment techniques short review
 State assignment techniques short review Aleksander Ślusarczyk The task of the (near)optimal FSM state encoding can be generally formulated as assignment of such binary vectors to the state symbols that
State assignment techniques short review Aleksander Ślusarczyk The task of the (near)optimal FSM state encoding can be generally formulated as assignment of such binary vectors to the state symbols that
SPECC: SPECIFICATION LANGUAGE AND METHODOLOGY
 SPECC: SPECIFICATION LANGUAGE AND METHODOLOGY SPECC: SPECIFICATION LANGUAGE AND METHODOLOGY Daniel D. Gajski Jianwen Zhu Rainer Dömer Andreas Gerstlauer Shuqing Zhao University of California, Irvine SPRINGER
SPECC: SPECIFICATION LANGUAGE AND METHODOLOGY SPECC: SPECIFICATION LANGUAGE AND METHODOLOGY Daniel D. Gajski Jianwen Zhu Rainer Dömer Andreas Gerstlauer Shuqing Zhao University of California, Irvine SPRINGER
RETARGETABLE CODE GENERATION FOR DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
 RETARGETABLE CODE GENERATION FOR DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS RETARGETABLE CODE GENERATION FOR DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS Rainer LEUPERS University of Dortmund Department of Computer Science Dortmund, Germany
RETARGETABLE CODE GENERATION FOR DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS RETARGETABLE CODE GENERATION FOR DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS Rainer LEUPERS University of Dortmund Department of Computer Science Dortmund, Germany
Design of Framework for Logic Synthesis Engine
 Design of Framework for Logic Synthesis Engine Tribikram Pradhan 1, Pramod Kumar 2, Anil N S 3, Amit Bakshi 4 1 School of Information technology and Engineering, VIT University, Vellore 632014, Tamilnadu,
Design of Framework for Logic Synthesis Engine Tribikram Pradhan 1, Pramod Kumar 2, Anil N S 3, Amit Bakshi 4 1 School of Information technology and Engineering, VIT University, Vellore 632014, Tamilnadu,
Heuristic Minimization of Boolean Relations Using Testing Techniques
 Heuristic Minimization of Boolean Relations Using Testing Techniques Abhijit Ghosh Srinivas Devadas A. Richard Newton Department of Electrical Engineering and Coniputer Sciences University of California,
Heuristic Minimization of Boolean Relations Using Testing Techniques Abhijit Ghosh Srinivas Devadas A. Richard Newton Department of Electrical Engineering and Coniputer Sciences University of California,
A Boolean Paradigm in Multi-Valued Logic Synthesis
 A Boolean Paradigm in Multi-Valued Logic Synthesis Abstract Alan Mishchenko Department of ECE Portland State University alanmi@ece.pd.edu Optimization algorithms used in binary multi-level logic synthesis,
A Boolean Paradigm in Multi-Valued Logic Synthesis Abstract Alan Mishchenko Department of ECE Portland State University alanmi@ece.pd.edu Optimization algorithms used in binary multi-level logic synthesis,
Multi-valued Logic Synthesis. Robert K Brayton Sunil P Khatri University of California Berkeley, CA brayton,
 Multi-valued Logic Synthesis Robert K Brayton Sunil P Khatri University of California Berkeley, CA 9470 brayton, linus @iceecsberkeleyedu Abstract We survey some of the methods used for manipulating, representing,
Multi-valued Logic Synthesis Robert K Brayton Sunil P Khatri University of California Berkeley, CA 9470 brayton, linus @iceecsberkeleyedu Abstract We survey some of the methods used for manipulating, representing,
Combinatorial Algorithms. Unate Covering Binate Covering Graph Coloring Maximum Clique
 Combinatorial Algorithms Unate Covering Binate Covering Graph Coloring Maximum Clique Example As an Example, let s consider the formula: F(x,y,z) = x y z + x yz + x yz + xyz + xy z The complete sum of
Combinatorial Algorithms Unate Covering Binate Covering Graph Coloring Maximum Clique Example As an Example, let s consider the formula: F(x,y,z) = x y z + x yz + x yz + xyz + xy z The complete sum of
THE VERILOG? HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE
 THE VERILOG? HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE THE VERILOGf HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE by Donald E. Thomas Carnegie Mellon University and Philip R. Moorby Cadence Design Systems, Inc. SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS
THE VERILOG? HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE THE VERILOGf HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE by Donald E. Thomas Carnegie Mellon University and Philip R. Moorby Cadence Design Systems, Inc. SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS
Giovanni De Micheli. Integrated Systems Centre EPF Lausanne
 Two-level Logic Synthesis and Optimization Giovanni De Micheli Integrated Systems Centre EPF Lausanne This presentation can be used for non-commercial purposes as long as this note and the copyright footers
Two-level Logic Synthesis and Optimization Giovanni De Micheli Integrated Systems Centre EPF Lausanne This presentation can be used for non-commercial purposes as long as this note and the copyright footers
Minimization of Multiple-Valued Functions in Post Algebra
 Minimization of Multiple-Valued Functions in Post Algebra Elena Dubrova Yunjian Jiang Robert Brayton Department of Electronics Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Royal Institute of Technology
Minimization of Multiple-Valued Functions in Post Algebra Elena Dubrova Yunjian Jiang Robert Brayton Department of Electronics Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Royal Institute of Technology
Algorithms for the Optimal State Assignment of Asynchronous State Machines
 Algorithms for the Optimal State Assignment of Asynchronous State Machines Robert M. Fuhrer Bill Lin Steven M. Nowick Dept. of Computer Science IMEC Laboratory Dept. of Computer Science Columbia University
Algorithms for the Optimal State Assignment of Asynchronous State Machines Robert M. Fuhrer Bill Lin Steven M. Nowick Dept. of Computer Science IMEC Laboratory Dept. of Computer Science Columbia University
WIRELESS ATM AND AD-HOC NETWORKS. Protocols and Architectures
 WIRELESS ATM AND AD-HOC NETWORKS Protocols and Architectures WIRELESS ATM AND AD-HOC NETWORKS Protocols and Architectures C-K Toh, Ph.D. University of Cambridge Cambridge, United Kingdom SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS
WIRELESS ATM AND AD-HOC NETWORKS Protocols and Architectures WIRELESS ATM AND AD-HOC NETWORKS Protocols and Architectures C-K Toh, Ph.D. University of Cambridge Cambridge, United Kingdom SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS
An Algorithm for Face-Constrained Encoding of Symbols Using Minimum Code Length
 An Algorithm for Face-Constrained Encoding of Symbols Using Minimum Code Length Manuel Martínez, María J. Avedillo, José M. Quintana and José L. Huertas Instituto de Microelectrónica de Sevilla - Centro
An Algorithm for Face-Constrained Encoding of Symbols Using Minimum Code Length Manuel Martínez, María J. Avedillo, José M. Quintana and José L. Huertas Instituto de Microelectrónica de Sevilla - Centro
MVSIS v1.1 Manual. Jie-Hong Jiang, Yunjian Jiang, Yinghua Li, Alan Mishchenko*, Subarna Sinha Tiziano Villa**, Robert Brayton
 MVSIS v1.1 Manual Jie-Hong Jiang, Yunjian Jiang, Yinghua Li, Alan Mishchenko*, Subarna Sinha Tiziano Villa**, Robert Brayton Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California,
MVSIS v1.1 Manual Jie-Hong Jiang, Yunjian Jiang, Yinghua Li, Alan Mishchenko*, Subarna Sinha Tiziano Villa**, Robert Brayton Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California,
VERILOG QUICKSTART. James M. Lee Cadence Design Systems, Inc. SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, LLC
 VERILOG QUICKSTART VERILOG QUICKSTART by James M. Lee Cadence Design Systems, Inc. ~. " SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, LLC ISBN 978-1-4613-7801-3 ISBN 978-1-4615-6113-2 (ebook) DOI 10.1007/978-1-4615-6113-2
VERILOG QUICKSTART VERILOG QUICKSTART by James M. Lee Cadence Design Systems, Inc. ~. " SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, LLC ISBN 978-1-4613-7801-3 ISBN 978-1-4615-6113-2 (ebook) DOI 10.1007/978-1-4615-6113-2
INTRUSION DETECTION IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS An Abstraction-Based Approach
 INTRUSION DETECTION IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS An Abstraction-Based Approach Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication ISBN 978-1-4613-5091-0 ISBN 978-1-4615-0467-2 (ebook) DOI 10.1007/978-1-4615-0467-2
INTRUSION DETECTION IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS An Abstraction-Based Approach Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication ISBN 978-1-4613-5091-0 ISBN 978-1-4615-0467-2 (ebook) DOI 10.1007/978-1-4615-0467-2
Fundamentals of Operating Systems. Fifth Edition
 Fundamentals of Operating Systems Fifth Edition Fundamentals of Operating Systems A.M. Lister University of Queensland R. D. Eager University of Kent at Canterbury Fifth Edition Springer Science+Business
Fundamentals of Operating Systems Fifth Edition Fundamentals of Operating Systems A.M. Lister University of Queensland R. D. Eager University of Kent at Canterbury Fifth Edition Springer Science+Business
Symbolic Hazard-Free Minimization and Encoding of Asynchronous Finite State Machines
 Symbolic Hazard-Free Minimization and Encoding of Asynchronous Finite State Machines Robert M. Fuhrer Bill Lin Steven M. Nowick Dept. of Computer Science IMEC Laboratory Dept. of Computer Science Columbia
Symbolic Hazard-Free Minimization and Encoding of Asynchronous Finite State Machines Robert M. Fuhrer Bill Lin Steven M. Nowick Dept. of Computer Science IMEC Laboratory Dept. of Computer Science Columbia
Hardware Acceleration of EDA Algorithms
 Hardware Acceleration of EDA Algorithms Kanupriya Gulati Sunil P. Khatri Hardware Acceleration of EDA Algorithms Custom ICs, FPGAs and GPUs 123 Kanupriya Gulati 109 Branchwood Trl Coppell TX 75019 USA
Hardware Acceleration of EDA Algorithms Kanupriya Gulati Sunil P. Khatri Hardware Acceleration of EDA Algorithms Custom ICs, FPGAs and GPUs 123 Kanupriya Gulati 109 Branchwood Trl Coppell TX 75019 USA
Computer-Aided Design in Magnetics
 Computer-Aided Design in Magnetics D. A. Lowther P. P. Silvester Computer-Aided Design in Magnetics With 84 illustrations Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo D. A. Lowther Associate Professor
Computer-Aided Design in Magnetics D. A. Lowther P. P. Silvester Computer-Aided Design in Magnetics With 84 illustrations Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo D. A. Lowther Associate Professor
A Structured Programming Approach to Data
 A Structured Programming Approach to Data Derek Coleman A Structured Programming Approach to Data Springer-Verlag New York Derek Coleman Department of Computation Institute of Science Technology University
A Structured Programming Approach to Data Derek Coleman A Structured Programming Approach to Data Springer-Verlag New York Derek Coleman Department of Computation Institute of Science Technology University
LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND VERIFICATION ALGORITHMS
 LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND VERIFICATION ALGORITHMS LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND VERIFICATION ALGORITHMS by Gary D. Hachtel University of Colorado Fabio Somenzi University of Colorado KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS NEW YORK,
LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND VERIFICATION ALGORITHMS LOGIC SYNTHESIS AND VERIFICATION ALGORITHMS by Gary D. Hachtel University of Colorado Fabio Somenzi University of Colorado KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS NEW YORK,
FINITE FIELDS FOR COMPUTER SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS
 FINITE FIELDS FOR COMPUTER SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE INFORMATION THEORY Consulting Editor Robert G. Gallager FINITE FIELDS FOR COMPUTER
FINITE FIELDS FOR COMPUTER SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE INFORMATION THEORY Consulting Editor Robert G. Gallager FINITE FIELDS FOR COMPUTER
TECHNICAL TRANSLATION
 TECHNICAL TRANSLATION Technical Translation Usability Strategies for Translating Technical Documentation JODY BYRNE University of Sheffield, UK A C.I.P. Catalogue record for this book is available from
TECHNICAL TRANSLATION Technical Translation Usability Strategies for Translating Technical Documentation JODY BYRNE University of Sheffield, UK A C.I.P. Catalogue record for this book is available from
INTRUSION DETECTION AND CORRELATION. Challenges and Solutions
 INTRUSION DETECTION AND CORRELATION Challenges and Solutions Advances in Information Security Sushil Jajodia Consulting editor Center for Secure Information Systems George Mason University Fairfax, VA
INTRUSION DETECTION AND CORRELATION Challenges and Solutions Advances in Information Security Sushil Jajodia Consulting editor Center for Secure Information Systems George Mason University Fairfax, VA
OPTIMISTA: State Minimization of Asynchronous FSMs for Optimum Output Logic
 OPTIMISTA: State Minimization of Asynchronous FSMs for Optimum Output Logic Robert M. Fuhrer Steven M. Nowick Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027 {rmf,nowick}@cs.columbia.edu
OPTIMISTA: State Minimization of Asynchronous FSMs for Optimum Output Logic Robert M. Fuhrer Steven M. Nowick Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027 {rmf,nowick}@cs.columbia.edu
Algorithm Collections for Digital Signal Processing Applications Using Matlab
 Algorithm Collections for Digital Signal Processing Applications Using Matlab Algorithm Collections for Digital Signal Processing Applications Using Matlab E.S. Gopi National Institute of Technology, Tiruchi,
Algorithm Collections for Digital Signal Processing Applications Using Matlab Algorithm Collections for Digital Signal Processing Applications Using Matlab E.S. Gopi National Institute of Technology, Tiruchi,
OPTIMIST: State Minimization for Optimal 2-Level Logic Implementation
 OPTIMIST: State Minimization for Optimal 2-Level Logic Implementation Robert M. Fuhrer Steven M. Nowick Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027 Abstract We present a novel
OPTIMIST: State Minimization for Optimal 2-Level Logic Implementation Robert M. Fuhrer Steven M. Nowick Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027 Abstract We present a novel
Computational Geometry on Surfaces
 Computational Geometry on Surfaces Computational Geometry on Surfaces Performing Computational Geometry on the Cylinder, the Sphere, the Torus, and the Cone by Clara I. Grima Department 0/ Applied Mathematics
Computational Geometry on Surfaces Computational Geometry on Surfaces Performing Computational Geometry on the Cylinder, the Sphere, the Torus, and the Cone by Clara I. Grima Department 0/ Applied Mathematics
Chunjie Duan Brock J. LaMeres Sunil P. Khatri. On and Off-Chip Crosstalk Avoidance in VLSI Design
 Chunjie Duan Brock J. LaMeres Sunil P. Khatri On and Off-Chip Crosstalk Avoidance in VLSI Design 123 On and Off-Chip Crosstalk Avoidance in VLSI Design Chunjie Duan Brock J. LaMeres Sunil P. Khatri On
Chunjie Duan Brock J. LaMeres Sunil P. Khatri On and Off-Chip Crosstalk Avoidance in VLSI Design 123 On and Off-Chip Crosstalk Avoidance in VLSI Design Chunjie Duan Brock J. LaMeres Sunil P. Khatri On
SEPP: a New Compact Three-Level Logic Form
 SEPP: a New Compact Three-Level Logic Form Valentina Ciriani Department of Information Technologies Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy valentina.ciriani@unimi.it Anna Bernasconi Department of Computer
SEPP: a New Compact Three-Level Logic Form Valentina Ciriani Department of Information Technologies Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy valentina.ciriani@unimi.it Anna Bernasconi Department of Computer
SIS: A System for Sequential Circuit Synthesis
 SIS: A System for Sequential Circuit Synthesis Electronics Research Laboratory Memorandum No. UCB/ERL M92/41 Ellen M. Sentovich Kanwar Jit Singh Luciano Lavagno Cho Moon Rajeev Murgai Alexander Saldanha
SIS: A System for Sequential Circuit Synthesis Electronics Research Laboratory Memorandum No. UCB/ERL M92/41 Ellen M. Sentovich Kanwar Jit Singh Luciano Lavagno Cho Moon Rajeev Murgai Alexander Saldanha
Philip Andrew Simpson. FPGA Design. Best Practices for Team-based Reuse. Second Edition
 FPGA Design Philip Andrew Simpson FPGA Design Best Practices for Team-based Reuse Second Edition Philip Andrew Simpson San Jose, CA, USA ISBN 978-3-319-17923-0 DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-17924-7 ISBN 978-3-319-17924-7
FPGA Design Philip Andrew Simpson FPGA Design Best Practices for Team-based Reuse Second Edition Philip Andrew Simpson San Jose, CA, USA ISBN 978-3-319-17923-0 DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-17924-7 ISBN 978-3-319-17924-7
INVERSE PROBLEMS IN GROUNDWATER MODELING
 INVERSE PROBLEMS IN GROUNDWATER MODELING Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous Media Series Editor: Jacob Bear, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel Volume 6 The titles published
INVERSE PROBLEMS IN GROUNDWATER MODELING Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous Media Series Editor: Jacob Bear, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel Volume 6 The titles published
Yves Nievergelt. Wavelets Made Easy. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
 Wavelets Made Easy Yves Nievergelt Wavelets Made Easy Springer Science+Business Media, LLC Yves Nievergelt Department of Mathematics Eastem Washington University Cheney, WA 99004-2431 USA Library of Congress
Wavelets Made Easy Yves Nievergelt Wavelets Made Easy Springer Science+Business Media, LLC Yves Nievergelt Department of Mathematics Eastem Washington University Cheney, WA 99004-2431 USA Library of Congress
Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 303
 Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 303 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs303/ Teacher: Robert Dick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 Outline 1. Finite state machines
Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 303 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs303/ Teacher: Robert Dick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 Outline 1. Finite state machines
MINING VERY LARGE DATABASES WITH PARALLEL PROCESSING
 MINING VERY LARGE DATABASES WITH PARALLEL PROCESSING The Kluwer International Series on ADVANCES IN DATABASE SYSTEMS Series Editor Ahmed K. Elmagarmid Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47907 Other books
MINING VERY LARGE DATABASES WITH PARALLEL PROCESSING The Kluwer International Series on ADVANCES IN DATABASE SYSTEMS Series Editor Ahmed K. Elmagarmid Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47907 Other books
Using Synthesis Techniques in SAT Solvers
 1. Introduction Using Synthesis Techniques in SAT Solvers Rolf Drechsler Institute of Computer Science University of Bremen 28359 Bremen, Germany drechsle@informatik.uni-bremen.de Abstract In many application
1. Introduction Using Synthesis Techniques in SAT Solvers Rolf Drechsler Institute of Computer Science University of Bremen 28359 Bremen, Germany drechsle@informatik.uni-bremen.de Abstract In many application
Unit 4: Formal Verification
 Course contents Unit 4: Formal Verification Logic synthesis basics Binary-decision diagram (BDD) Verification Logic optimization Technology mapping Readings Chapter 11 Unit 4 1 Logic Synthesis & Verification
Course contents Unit 4: Formal Verification Logic synthesis basics Binary-decision diagram (BDD) Verification Logic optimization Technology mapping Readings Chapter 11 Unit 4 1 Logic Synthesis & Verification
A Recursive Paradigm To Solve Boolean Relations
 A Recursive Paradigm To Solve Boolean Relations David Bañeres Univ. Politècnica de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain Jordi Cortadella Univ. Politècnica de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain Mike Kishinevsky Strategic
A Recursive Paradigm To Solve Boolean Relations David Bañeres Univ. Politècnica de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain Jordi Cortadella Univ. Politècnica de Catalunya Barcelona, Spain Mike Kishinevsky Strategic
COPAS: A New Algorithm for the Partial Input Encoding Problem
 VLSI Design, 2002 Vol. 14 (2), pp. 171 181 COPAS: A New Algorithm for the Partial Input Encoding Problem MANUEL MARTÍNEZ, MARÍA J. AVEDILLO*, JOSÉ M. QUINTANA and JOSÉ L. HUERTAS Instituto de Microelectrónica
VLSI Design, 2002 Vol. 14 (2), pp. 171 181 COPAS: A New Algorithm for the Partial Input Encoding Problem MANUEL MARTÍNEZ, MARÍA J. AVEDILLO*, JOSÉ M. QUINTANA and JOSÉ L. HUERTAS Instituto de Microelectrónica
Logic Synthesis & Optimization Lectures 4, 5 Boolean Algebra - Basics
 Logic Synthesis & Optimization Lectures 4, 5 Boolean Algebra - Basics 1 Instructor: Priyank Kalla Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Email: kalla@ece.utah.edu
Logic Synthesis & Optimization Lectures 4, 5 Boolean Algebra - Basics 1 Instructor: Priyank Kalla Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Email: kalla@ece.utah.edu
TIME-CONSTRAINED TRANSACTION MANAGEMENT. Real-Time Constraints in Database Transaction Systems
 TIME-CONSTRAINED TRANSACTION MANAGEMENT Real-Time Constraints in Database Transaction Systems The Kluwer International Series on ADV ANCES IN DATABASE SYSTEMS Other books in the Series: Series Editor Ahmed
TIME-CONSTRAINED TRANSACTION MANAGEMENT Real-Time Constraints in Database Transaction Systems The Kluwer International Series on ADV ANCES IN DATABASE SYSTEMS Other books in the Series: Series Editor Ahmed
A Parallel Branching Program Machine for Emulation of Sequential Circuits
 A Parallel Branching Program Machine for Emulation of Sequential Circuits Hiroki Nakahara 1, Tsutomu Sasao 1 Munehiro Matsuura 1, and Yoshifumi Kawamura 2 1 Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan 2 Renesas
A Parallel Branching Program Machine for Emulation of Sequential Circuits Hiroki Nakahara 1, Tsutomu Sasao 1 Munehiro Matsuura 1, and Yoshifumi Kawamura 2 1 Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan 2 Renesas
HIGH-LEVEL SYNTHESIS FOR REAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
 HIGH-LEVEL SYNTHESIS FOR REAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE VLSI, COMPUTER ARCHITECfURE AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Latest Titles
HIGH-LEVEL SYNTHESIS FOR REAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE VLSI, COMPUTER ARCHITECfURE AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Latest Titles
Enhancing the Performance of Multi-Cycle Path Analysis in an Industrial Setting
 Enhancing the Performance of Multi-Cycle Path Analysis in an Industrial Setting Hiroyuki Higuchi Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. / Kyushu University e-mail: higuchi@labs.fujitsu.com Yusuke Matsunaga Kyushu University
Enhancing the Performance of Multi-Cycle Path Analysis in an Industrial Setting Hiroyuki Higuchi Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. / Kyushu University e-mail: higuchi@labs.fujitsu.com Yusuke Matsunaga Kyushu University
Using Integer Equations for High Level Formal Verification Property Checking
 Using Integer Equations for High Level Formal Verification Property Checking Bijan Alizadeh Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Tehran 4399 Tehran, Iran bijan@cad.ece.ut.ac.ir Mohammad R.
Using Integer Equations for High Level Formal Verification Property Checking Bijan Alizadeh Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Tehran 4399 Tehran, Iran bijan@cad.ece.ut.ac.ir Mohammad R.
Fault-Tolerant Parallel and Distributed Systems
 Fault-Tolerant Parallel and Distributed Systems Fault-Tolerant Parallel and Distributed Systems by DIMITER R. AVRESKY Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University Boston, MA and
Fault-Tolerant Parallel and Distributed Systems Fault-Tolerant Parallel and Distributed Systems by DIMITER R. AVRESKY Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University Boston, MA and
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS The State of the Art
 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS The State of the Art IFIP The International Federation for Information Processing lfip was founded in 1960 under the auspices of UNESCO, following the First World Computer Congress
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS The State of the Art IFIP The International Federation for Information Processing lfip was founded in 1960 under the auspices of UNESCO, following the First World Computer Congress
Whitestein Series in software Agent Technologies. About whitestein Technologies
 Whitestein Series in software Agent Technologies Series Editors: Marius Walliser Stefan Brantschen Monique Calisti Thomas Hempfling This series reports new developments in agent-based software technologies
Whitestein Series in software Agent Technologies Series Editors: Marius Walliser Stefan Brantschen Monique Calisti Thomas Hempfling This series reports new developments in agent-based software technologies
Application of Binary Decision Diagram in digital circuit analysis.
 Application of Binary Decision Diagram in digital circuit analysis. Jyoti Kukreja University of Southern California For Dr. James Ellison Abstract: Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) are one of the biggest
Application of Binary Decision Diagram in digital circuit analysis. Jyoti Kukreja University of Southern California For Dr. James Ellison Abstract: Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) are one of the biggest
History: Combinational Logic! single FSM! Hierarchy. Facilities for managing networks of FSMs MISII. Facilities for handling latches
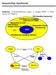 Sequential Synthesis History: Combinational Logic! single FSM! Hierarchy of FSM's. Sequential Circuit Optimization (single machine) SIS Facilities for managing networks of FSMs MISII Facilities for handling
Sequential Synthesis History: Combinational Logic! single FSM! Hierarchy of FSM's. Sequential Circuit Optimization (single machine) SIS Facilities for managing networks of FSMs MISII Facilities for handling
Fundamentals of Operating Systems
 Fundamentals of Operating Systems Macmillan Computer Science Series Consulting Editor Professor F. H. Sumner, University of Manchester S. T. Allworth, Introduction to Real-time Software Design Ian O. Angell,
Fundamentals of Operating Systems Macmillan Computer Science Series Consulting Editor Professor F. H. Sumner, University of Manchester S. T. Allworth, Introduction to Real-time Software Design Ian O. Angell,
Loop Tiling for Parallelism
 Loop Tiling for Parallelism THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE LOOP TILING FOR PARALLELISM JINGLING XUE School of Computer Science and Engineering The University of New
Loop Tiling for Parallelism THE KLUWER INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE LOOP TILING FOR PARALLELISM JINGLING XUE School of Computer Science and Engineering The University of New
Lazy Group Sifting for Efficient Symbolic State Traversal of FSMs
 Lazy Group Sifting for Efficient Symbolic State Traversal of FSMs Hiroyuki Higuchi Fabio Somenzi Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. University of Colorado Kawasaki, Japan Boulder, CO Abstract This paper proposes
Lazy Group Sifting for Efficient Symbolic State Traversal of FSMs Hiroyuki Higuchi Fabio Somenzi Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. University of Colorado Kawasaki, Japan Boulder, CO Abstract This paper proposes
SpringerBriefs in Computer Science
 SpringerBriefs in Computer Science Series Editors Stan Zdonik Peng Ning Shashi Shekhar Jonathan Katz Xindong Wu Lakhmi C. Jain David Padua Xuemin (Sherman) Shen Borko Furht V.S. Subrahmanian Martial Hebert
SpringerBriefs in Computer Science Series Editors Stan Zdonik Peng Ning Shashi Shekhar Jonathan Katz Xindong Wu Lakhmi C. Jain David Padua Xuemin (Sherman) Shen Borko Furht V.S. Subrahmanian Martial Hebert
ESOP CIRCUIT MINIMIZATION BASED ON THE FUNCTION ON-SET. Likai Chai
 ESOP CIRCUIT MINIMIZATION BASED ON THE FUNCTION ON-SET By Likai Chai A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Mississippi State University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master
ESOP CIRCUIT MINIMIZATION BASED ON THE FUNCTION ON-SET By Likai Chai A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Mississippi State University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master
ON AN OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUE USING BINARY DECISION DIAGRAM
 ON AN OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUE USING BINARY DECISION DIAGRAM Debajit Sensarma # 1, Subhashis Banerjee #1, Krishnendu Basuli #1,Saptarshi Naskar #2, Samar Sen Sarma #3 #1 West Bengal State University, West
ON AN OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUE USING BINARY DECISION DIAGRAM Debajit Sensarma # 1, Subhashis Banerjee #1, Krishnendu Basuli #1,Saptarshi Naskar #2, Samar Sen Sarma #3 #1 West Bengal State University, West
Modeling and Simulation in Scilab/Scicos with ScicosLab 4.4
 Modeling and Simulation in Scilab/Scicos with ScicosLab 4.4 Stephen L. Campbell, Jean-Philippe Chancelier and Ramine Nikoukhah Modeling and Simulation in Scilab/Scicos with ScicosLab 4.4 Second Edition
Modeling and Simulation in Scilab/Scicos with ScicosLab 4.4 Stephen L. Campbell, Jean-Philippe Chancelier and Ramine Nikoukhah Modeling and Simulation in Scilab/Scicos with ScicosLab 4.4 Second Edition
Synthia: Synthesis of Interacting Automata Targeting LUT-Based FPGAs
 Synthia: Synthesis of Interacting Automata Targeting LUT-Based FPGAs George A. Constantinides 1, Peter Y. K. Cheung 1, and Wayne Luk 2 1 Electrical and Electronic Engineering Dept., Imperial College, London,
Synthia: Synthesis of Interacting Automata Targeting LUT-Based FPGAs George A. Constantinides 1, Peter Y. K. Cheung 1, and Wayne Luk 2 1 Electrical and Electronic Engineering Dept., Imperial College, London,
Jinkun Liu Xinhua Wang. Advanced Sliding Mode Control for Mechanical Systems. Design, Analysis and MATLAB Simulation
 Jinkun Liu Xinhua Wang Advanced Sliding Mode Control for Mechanical Systems Design, Analysis and MATLAB Simulation Jinkun Liu Xinhua Wang Advanced Sliding Mode Control for Mechanical Systems Design, Analysis
Jinkun Liu Xinhua Wang Advanced Sliding Mode Control for Mechanical Systems Design, Analysis and MATLAB Simulation Jinkun Liu Xinhua Wang Advanced Sliding Mode Control for Mechanical Systems Design, Analysis
Algorithms for Discrete Fourier Transform and Convolution
 Algorithms for Discrete Fourier Transform and Convolution Second Edition Springer Science+Business Media, LLC Signal Processing and Digital Filtering Synthetic Aperture Radar J.P. Fitch Multiplicative
Algorithms for Discrete Fourier Transform and Convolution Second Edition Springer Science+Business Media, LLC Signal Processing and Digital Filtering Synthetic Aperture Radar J.P. Fitch Multiplicative
Using Genetic Algorithm with Non-identical Population for Minimizing Boolean Functions
 World Applied Programming, Vol (2), No (1), January 2012. 12-17 ISSN: 2222-2510 2011 WAP journal. www.waprogramming.com Using Genetic Algorithm with Non-identical Population for Minimizing Boolean Functions
World Applied Programming, Vol (2), No (1), January 2012. 12-17 ISSN: 2222-2510 2011 WAP journal. www.waprogramming.com Using Genetic Algorithm with Non-identical Population for Minimizing Boolean Functions
Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 303
 Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 303 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs303/ Teacher: Robert Dick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 Outline 1. 2. 2 Robert Dick
Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 303 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs303/ Teacher: Robert Dick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 Outline 1. 2. 2 Robert Dick
On the Relation between SAT and BDDs for Equivalence Checking
 On the Relation between SAT and BDDs for Equivalence Checking Sherief Reda 1 Rolf Drechsler 2 Alex Orailoglu 1 1 Computer Science & Engineering Department University of California, San Diego La Jolla,
On the Relation between SAT and BDDs for Equivalence Checking Sherief Reda 1 Rolf Drechsler 2 Alex Orailoglu 1 1 Computer Science & Engineering Department University of California, San Diego La Jolla,
By: Chaitanya Settaluri Devendra Kalia
 By: Chaitanya Settaluri Devendra Kalia What is an embedded system? An embedded system Uses a controller to perform some function Is not perceived as a computer Software is used for features and flexibility
By: Chaitanya Settaluri Devendra Kalia What is an embedded system? An embedded system Uses a controller to perform some function Is not perceived as a computer Software is used for features and flexibility
An Introduction to Zero-Suppressed Binary Decision Diagrams
 An Introduction to Zero-Suppressed Binary Decision Diagrams Alan Mishchenko Berkeley Verification and Synthesis Research Center Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of
An Introduction to Zero-Suppressed Binary Decision Diagrams Alan Mishchenko Berkeley Verification and Synthesis Research Center Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of
Graphics Programming in c++
 Graphics Programming in c++ Springer London Berlin Heidelberg New York Barcelona Budapest Hong Kong Milan Paris Santa Clara Singapore Tokyo Mark Walmsley Graphics Programming in c++ Writing Graphics Applications
Graphics Programming in c++ Springer London Berlin Heidelberg New York Barcelona Budapest Hong Kong Milan Paris Santa Clara Singapore Tokyo Mark Walmsley Graphics Programming in c++ Writing Graphics Applications
1 Construct implication chart, one square for each combination of states. 2 Square labeled S i, S j, if outputs differ than square gets X (0).
 Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 33 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs33/ FSM design overview Teacher: Robert Dick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 State diagram
Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 33 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs33/ FSM design overview Teacher: Robert Dick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 State diagram
Stock Message Boards
 Stock Message Boards This page intentionally left blank Stock Message Boards A Quantitative Approach to Measuring Investor Sentiment Ying Zhang STOCK MESSAGE BOARDS Copyright Ying Zhang, 2014. Softcover
Stock Message Boards This page intentionally left blank Stock Message Boards A Quantitative Approach to Measuring Investor Sentiment Ying Zhang STOCK MESSAGE BOARDS Copyright Ying Zhang, 2014. Softcover
Boolean Factoring with Multi-Objective Goals
 Boolean Factoring with Multi-Objective Goals Mayler G. A. Martins 1, Leomar Rosa Jr. 1, Anders B. Rasmussen 2, Renato P. Ribas 1 and Andre I. Reis 1 1 PGMICRO - Instituto de Informática UFRGS / 2 Nangate
Boolean Factoring with Multi-Objective Goals Mayler G. A. Martins 1, Leomar Rosa Jr. 1, Anders B. Rasmussen 2, Renato P. Ribas 1 and Andre I. Reis 1 1 PGMICRO - Instituto de Informática UFRGS / 2 Nangate
Mobile Phone Security and Forensics
 Mobile Phone Security and Forensics Iosif I. Androulidakis Mobile Phone Security and Forensics A Practical Approach Second Edition Iosif I. Androulidakis Pedini Ioannina Greece ISBN 978-3-319-29741-5
Mobile Phone Security and Forensics Iosif I. Androulidakis Mobile Phone Security and Forensics A Practical Approach Second Edition Iosif I. Androulidakis Pedini Ioannina Greece ISBN 978-3-319-29741-5
EECS 219C: Formal Methods Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) Sanjit A. Seshia EECS, UC Berkeley
 EECS 219C: Formal Methods Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) Sanjit A. Seshia EECS, UC Berkeley Boolean Function Representations Syntactic: e.g.: CNF, DNF (SOP), Circuit Semantic: e.g.: Truth table, Binary
EECS 219C: Formal Methods Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) Sanjit A. Seshia EECS, UC Berkeley Boolean Function Representations Syntactic: e.g.: CNF, DNF (SOP), Circuit Semantic: e.g.: Truth table, Binary
VLSI System Design Part II : Logic Synthesis (1) Oct Feb.2007
 VLSI System Design Part II : Logic Synthesis (1) Oct.2006 - Feb.2007 Lecturer : Tsuyoshi Isshiki Dept. Communications and Integrated Systems, Tokyo Institute of Technology isshiki@vlsi.ss.titech.ac.jp
VLSI System Design Part II : Logic Synthesis (1) Oct.2006 - Feb.2007 Lecturer : Tsuyoshi Isshiki Dept. Communications and Integrated Systems, Tokyo Institute of Technology isshiki@vlsi.ss.titech.ac.jp
FUZZY DATABASES Principles and Applications
 FUZZY DATABASES Principles and Applications INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN INTELLIGENT TECHNOLOGIES Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. Hans-Jiirgen Zimmermann, Editor European Laboratory for Intelligent Techniques Engineering
FUZZY DATABASES Principles and Applications INTERNATIONAL SERIES IN INTELLIGENT TECHNOLOGIES Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. Hans-Jiirgen Zimmermann, Editor European Laboratory for Intelligent Techniques Engineering
Binary Decision Diagrams and Symbolic Model Checking
 Binary Decision Diagrams and Symbolic Model Checking Randy Bryant Ed Clarke Ken McMillan Allen Emerson CMU CMU Cadence U Texas http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bryant Binary Decision Diagrams Restricted Form of
Binary Decision Diagrams and Symbolic Model Checking Randy Bryant Ed Clarke Ken McMillan Allen Emerson CMU CMU Cadence U Texas http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bryant Binary Decision Diagrams Restricted Form of
This content has been downloaded from IOPscience. Please scroll down to see the full text.
 This content has been downloaded from IOPscience. Please scroll down to see the full text. Download details: IP Address: 148.251.232.83 This content was downloaded on 22/11/2018 at 08:50 Please note that
This content has been downloaded from IOPscience. Please scroll down to see the full text. Download details: IP Address: 148.251.232.83 This content was downloaded on 22/11/2018 at 08:50 Please note that
Software Implementation of Break-Up Algorithm for Logic Minimization
 vol. 2, no. 6. 2, pp. 141-145, 2017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.24999/ijoaem/02060034 Software Implementation of Break-Up Algorithm for Logic Minimization Koustuvmoni Bharadwaj and Sahadev Roy Abstract In
vol. 2, no. 6. 2, pp. 141-145, 2017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.24999/ijoaem/02060034 Software Implementation of Break-Up Algorithm for Logic Minimization Koustuvmoni Bharadwaj and Sahadev Roy Abstract In
What Can Boolean Networks Learn?
 What Can Boolean Networks Learn? Arlindo L. Oliveira Alberto Sangiovanni-Vincentelli Dept. of EECS, UC Berkeley, Berkeley CA 94720 June 26, 1992 Abstract We study the generalization abilities of networks
What Can Boolean Networks Learn? Arlindo L. Oliveira Alberto Sangiovanni-Vincentelli Dept. of EECS, UC Berkeley, Berkeley CA 94720 June 26, 1992 Abstract We study the generalization abilities of networks
1/28/2013. Synthesis. The Y-diagram Revisited. Structural Behavioral. More abstract designs Physical. CAD for VLSI 2
 Synthesis The Y-diagram Revisited Structural Behavioral More abstract designs Physical CAD for VLSI 2 1 Structural Synthesis Behavioral Physical CAD for VLSI 3 Structural Processor Memory Bus Behavioral
Synthesis The Y-diagram Revisited Structural Behavioral More abstract designs Physical CAD for VLSI 2 1 Structural Synthesis Behavioral Physical CAD for VLSI 3 Structural Processor Memory Bus Behavioral
Hierarchical Functional Timing Analysis
 Abstract Hierarchical Functional Timing Analysis Yuji Kukimoto Robert K. Brayton Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley, CA 9470 fkukimoto,braytong@eecs.berkeley.edu
Abstract Hierarchical Functional Timing Analysis Yuji Kukimoto Robert K. Brayton Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley, CA 9470 fkukimoto,braytong@eecs.berkeley.edu
DISSEMINATING SECURITY UPDATES AT INTERNET SCALE
 DISSEMINATING SECURITY UPDATES AT INTERNET SCALE Advances in Information Security Sushil Jajodia Consulting editor Center for Secure Information Systems George Mason University Fairfax, VA 22030-4444 email:
DISSEMINATING SECURITY UPDATES AT INTERNET SCALE Advances in Information Security Sushil Jajodia Consulting editor Center for Secure Information Systems George Mason University Fairfax, VA 22030-4444 email:
ACTUAL-DELAY CIRCUITS ON FPGA: TRADING-OFF LUTS FOR SPEED. Evangelia Kassapaki, Pavlos M. Mattheakis and Christos P. Sotiriou
 ACTUAL-DELAY CIRCUITS ON FPGA: TRADING-OFF LUTS FOR SPEED Evangelia Kassapaki, Pavlos M. Mattheakis and Christos P. Sotiriou Institute of Computer Science, FORTH, Crete, Greece. email: kassapak@ics.forth.gr,
ACTUAL-DELAY CIRCUITS ON FPGA: TRADING-OFF LUTS FOR SPEED Evangelia Kassapaki, Pavlos M. Mattheakis and Christos P. Sotiriou Institute of Computer Science, FORTH, Crete, Greece. email: kassapak@ics.forth.gr,
Functional Programming in R
 Functional Programming in R Advanced Statistical Programming for Data Science, Analysis and Finance Thomas Mailund Functional Programming in R: Advanced Statistical Programming for Data Science, Analysis
Functional Programming in R Advanced Statistical Programming for Data Science, Analysis and Finance Thomas Mailund Functional Programming in R: Advanced Statistical Programming for Data Science, Analysis
