A Four-Terabit Single-Stage Packet Switch with Large. Round-Trip Time Support. F. Abel, C. Minkenberg, R. Luijten, M. Gusat, and I.
|
|
|
- Randolph Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Four-Terabit Single-Stage Packet Switch with Large Round-Trip Time Support F. Abel, C. Minkenberg, R. Luijten, M. Gusat, and I. Iliadis IBM Research, Zurich Research Laboratory, CH-8803 Ruschlikon, Switzerland
2 Motivation Merchant switch market Achieve coverage of wide application spectrum: MAN/WAN/SAN Can a versatile switch architecture be designed to achieve this? Requires: High performance for different protocols and QoS requirements Allows very little assumptions about traffic properties
3 Outline Current single-stage switch architectures Preferred architecture Physical implementation of a 4 Tb/s switch Simulated performance: 256 x 256 system Conclusions
4 Current Single-Stage Switch Architectures VOQ-Based Switch Architectures Centralized Scheduling Distributed Scheduling (full int. speedup) IQ (no speedup) CIOQ Crosspoint Queueing (lim. ext. speedup) Shared Buffer Distributed Shared Buffer Scheduler
5 Selection of the Preferred Architecture Initial focus on high-level architecture issues Equally significant aspects arise when actually building the system Physical system size Multi-rack packaging, interconnection, clocking and synchronization are required Power has become a tremendous challenge and a major design factor Typically required: 2 kw per rack, 150 W per card, 25 W per chip Switch fabric (SF) internal round trip (RT) has significantly increased Switch core (SC), line cards (LC) and VLSI chip packaging Significant consequences for system cost, power and practical implementation
6 Size of a Terabit-Class System 19" Rack 4 Shelves 16 x OC-192 / Shelf 30 m / 100 feet Line Cards 0-63 Line Cards Tb/s Switch Core Active + Backup Line Cards Line Cards
7 Switch-Fabric-Internal Round Trip (RT) RT = Number of cells in flight: RTtotal = RTcable + RTlogic Line Card Switch Core RTcable = cells in flight over backplanes and/or cables RTlogic = cells pipelined in arbiter and SerDes (Serializer/Deserializer) logic RT has become an important SF-internal issue because of: Increased physical system size Increased link speed rates SerDes-Tx SerDes-Rx SerDes circuits are now widely used to implement high-speed I/Os RT d SerDes-Rx SerDes-Tx Line rate OC-12 OC-48 OC-192 OC-768 Interconnect distance 1 m 1 m 6 m 30 m Interconnect type backplane backplane cable fiber Packet duration 512 ns 128 ns 32 ns 8 ns Round Trip << 1 cell ~ 1 cell 16 cells 64 cells Evolution of RT
8 Preferred Architecture (1/2) Combined input- and crosspoint- queued (CICQ) architecture Decoupling of the arrival and departure processes Distributed contention resolution over both inputs and outputs Close to ideal performance is achieved without speedup of the SC Memories are operated at the line rate ifi 1 VOQ 1,1 Buffered Crossbar (BC) VOQ 1,N IQS1 XP1,1 XP1,N efi 1 OQ1 XQS1 XQSN ifi N VOQ N,1 VOQ N,N IQSN XPN,1 XPN,N efi N OQN Switch Core (SC) Switch Fabric (SF)
9 Preferred Architecture: CICQ (2/2) Advantages: ifi 1 Performance and robust QoS of OQ switches A buffered crossbar is inherently free of buffer hogging A buffered SC enables hop-by-hop FC instead of end-to-end Reduced latency at low utilization VOQ 1,1 VOQ 1,N ifi N VOQ N,1 VOQ N,N IQS1 IQSN Buffered Crossbar (BC) XP1,1 XP1,N XQS1 XPN,1 XPN,N Switch Core (SC) Switch Fabric (SF) XQSN efi 1 OQ1 efi N OQN Distribution of OQs exhibits some of the fair queueing properties Fair bandwidth allocation (e.g. with a simple Round-Robin) Protection and isolation of the sources from each other
10 CICQ and CoS Support Selective queueing at each queueing point (ifi, SC, efi) Service scheduling in addition to contention resolution (IQS, XQS) Additional scheduler at the egress (EQS) ifi[1] VOQ 1,1 SC XP1,1 XPM XP1,N XPM VOQ 1,N IQS 1 efi[1] EQS1 ifi[n] XPN,1 VOQ N,1 XPM XQS1 XQSN XPN,N XPM VOQ N,N IQS N efi[n] EQSN
11 CICQ and Parallel Sliced Switching 64 x 64 Gb/s/port R ifi[i] VOQi,1 VOQi,N IQSi Hd D D.. D D R/k R/k R/k R/k M i e espex ispex ispex espex R D espex ispex ispex espex R D No. Master Chips No. Slave Chips 4 Tb/s 2 Tb/s 1 Tb/s x1 x1 x1 x30 x15 x8 R/k R/k No. Cards x8 x4 x2 D S S D S S S S
12 Crosspoint Buffer Dimensioning (1/2) Bandwidth (on the links) is becoming the scarce resource Hence Utilization must be maximized Link speedup should be avoided as much as possible Assuming a credit-based FC and a commun. channel with an RT of! cells! credits are required to keep link busy Do we also need! credits per XP? Traffic agnostic principle: The bandwidth of each flow can vary on an instantaneous basis Link utilization principle: Full utilization of the link bandwidth must be achieved in the absence of other flows To provide 100% throughout under any traffic condition: A minimum of! cells are required per XP to ensure that any input can transmit to any output at any instant and at full rate. (e.g. in the case of fully unbalanced traffic or in absence of output contention)
13 Crosspoint Buffer Dimensioning (2/2) RT evaluation RTcable = 2dR / SlightCsize j 30 cells (with R = 64 Gb/s, d = 30 m, Slight = 250 Mm/s (over the dielectric), Csize = 512 bits) RTlogic j 30 cells (estimated by design) RTtotal j 60 cells Buffer requirement (assuming RTtotal = 64 cells, Csize = 64 B) Per logical XP: XPMsize =! = (64 % 64) = 4 kb Total for the switch core: N 2 %! = 16 MB XPMsize=! = 64 cells provides: 100% throughput under contentionless traffic and d = 30 m / 100 feet 100% throughput under uniform traffic and d j 3 km / feet
14 VLSI Implementation CMOS 0.11-#m, Std. cell design, 2.5 Gb/s SerDes Slave chip 200 mm 2, 20 W, 750 SIOs Split master chip 225 mm 2, 28 W, 825 SIOs
15 Simulated Performance Parameters: 256 x 256 CICQ switch fabric 64 x 64 SC with 4 external ports (OC-192) per SC port (OC-768) 64/128 cells per XP partitioned into 4 areas of 16/32 cells Ingress and egress link RT = 64 cells (at the OC-768 level) Line card egress buffer = 4 x 256 cells CoS 8 classes of service (C0 is the highest, C7 is the lowest priority) Uniform distribution, i.e. 12.5% of offered traffic per class Strict priority scheduling throughout the system (ifi, SC, efi)
16 Non-Uniform Traffic Non-uniform traffic: We adopt the distribution used by Rojas-Cessa et al. (HPSR 2001) where: $ i,j = $(w + (1-w)/N) if i = j, $(1-w)/N otherwise - N is the number of ports (256), $i,j is the traffic intensity from input i to output j - $ is the aggregate offered load (100%), w is the non-uniformity factor XPM = 68/72/80/ cells
17 Uniform Traffic Uniform traffic Uniformly distributed bursts over all 256 destinations Geometrically distributed bursts XPM = 64 cells / Bursts = 30 cells XPM = 128 cells / Bursts = 30 cells
18 Conclusions System design and implementation are equally important as performance considerations Impact of power, packaging, links, RT Traffic agnosticness requirement in OEM CoS support CICQ architecture is a viable solution Scalable Demonstrated sizing VLSI implementation of a single-stage 4 Tb/s switch Excellent performance
19 Contacts IBM Prizma research team IBM PowerPRS : Switch fabric products
Long Round-Trip Time Support with Shared-Memory Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch
 Long Round-Trip Time Support with Shared-Memory Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch Ziqian Dong and Roberto Rojas-Cessa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology
Long Round-Trip Time Support with Shared-Memory Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch Ziqian Dong and Roberto Rojas-Cessa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology
Shared-Memory Combined Input-Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch for Differentiated Services
 Shared-Memory Combined -Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch for Differentiated Services Ziqian Dong and Roberto Rojas-Cessa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology
Shared-Memory Combined -Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch for Differentiated Services Ziqian Dong and Roberto Rojas-Cessa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology
Shared-Memory Combined Input-Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch for Differentiated Services
 Shared-Memory Combined -Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch for Differentiated Services Ziqian Dong and Roberto Rojas-Cessa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology
Shared-Memory Combined -Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switch for Differentiated Services Ziqian Dong and Roberto Rojas-Cessa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology
Efficient Queuing Architecture for a Buffered Crossbar Switch
 Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUNICATIONS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 26-28, 2007 95 Efficient Queuing Architecture for a Buffered Crossbar Switch MICHAEL
Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUNICATIONS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 26-28, 2007 95 Efficient Queuing Architecture for a Buffered Crossbar Switch MICHAEL
A Four-Terabit Single-Stage Packet Switch with Large Round-Trip Time Support. F. Abel, C. Minkenberg, R. P. Luijten, M. Gusat, and I.
 RZ 343 (# 9369) 7//2 Electrical Engineering pages Research Report A Four-Terabit ingle-tage Packet witch with Large Round-Trip Time upport F. Abel, C. Minkenberg, R. P. Luijten, M. Gusat, and I. Iliadis
RZ 343 (# 9369) 7//2 Electrical Engineering pages Research Report A Four-Terabit ingle-tage Packet witch with Large Round-Trip Time upport F. Abel, C. Minkenberg, R. P. Luijten, M. Gusat, and I. Iliadis
IBM PowerPRS TM. A Scalable Switch Fabric to Multi- Terabit: Architecture and Challenges. July, Speaker: François Le Maut. IBM Microelectronics
 IBM PowerPRS TM A Scalable Switch Fabric to Multi- Terabit: Architecture and Challenges July, 2002 Speaker: François Le Maut IBM Microelectronics Outline Introduction General Architecture Flow Control
IBM PowerPRS TM A Scalable Switch Fabric to Multi- Terabit: Architecture and Challenges July, 2002 Speaker: François Le Maut IBM Microelectronics Outline Introduction General Architecture Flow Control
Throughput Analysis of Shared-Memory Crosspoint. Buffered Packet Switches
 Throughput Analysis of Shared-Memory Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switches Ziqian Dong and Roberto Rojas-Cessa Abstract This paper presents a theoretical throughput analysis of two buffered-crossbar switches,
Throughput Analysis of Shared-Memory Crosspoint Buffered Packet Switches Ziqian Dong and Roberto Rojas-Cessa Abstract This paper presents a theoretical throughput analysis of two buffered-crossbar switches,
6.2 Per-Flow Queueing and Flow Control
 6.2 Per-Flow Queueing and Flow Control Indiscriminate flow control causes local congestion (output contention) to adversely affect other, unrelated flows indiscriminate flow control causes phenomena analogous
6.2 Per-Flow Queueing and Flow Control Indiscriminate flow control causes local congestion (output contention) to adversely affect other, unrelated flows indiscriminate flow control causes phenomena analogous
A Partially Buffered Crossbar Packet Switching Architecture and its Scheduling
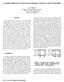 A Partially Buffered Crossbar Packet Switching Architecture and its Scheduling Lotfi Mhamdi Computer Engineering Laboratory TU Delft, The etherlands lotfi@ce.et.tudelft.nl Abstract The crossbar fabric
A Partially Buffered Crossbar Packet Switching Architecture and its Scheduling Lotfi Mhamdi Computer Engineering Laboratory TU Delft, The etherlands lotfi@ce.et.tudelft.nl Abstract The crossbar fabric
Packet Switch Architectures Part 2
 Packet Switch Architectures Part Adopted from: Sigcomm 99 Tutorial, by Nick McKeown and Balaji Prabhakar, Stanford University Slides used with permission from authors. 999-000. All rights reserved by authors.
Packet Switch Architectures Part Adopted from: Sigcomm 99 Tutorial, by Nick McKeown and Balaji Prabhakar, Stanford University Slides used with permission from authors. 999-000. All rights reserved by authors.
CSE 123A Computer Networks
 CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 8: IP Router Design Many portions courtesy Nick McKeown Overview Router basics Interconnection architecture Input Queuing Output Queuing Virtual output Queuing
CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 8: IP Router Design Many portions courtesy Nick McKeown Overview Router basics Interconnection architecture Input Queuing Output Queuing Virtual output Queuing
Providing Flow Based Performance Guarantees for Buffered Crossbar Switches
 Providing Flow Based Performance Guarantees for Buffered Crossbar Switches Deng Pan Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Florida International University Miami, Florida 33174, USA pand@fiu.edu Yuanyuan
Providing Flow Based Performance Guarantees for Buffered Crossbar Switches Deng Pan Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Florida International University Miami, Florida 33174, USA pand@fiu.edu Yuanyuan
Sample Routers and Switches. High Capacity Router Cisco CRS-1 up to 46 Tb/s thruput. Routers in a Network. Router Design
 outer Design outers in a Network Overview of Generic outer Architecture Input-d Switches (outers) IP Look-up Algorithms Packet Classification Algorithms Sample outers and Switches Cisco 46 outer up to
outer Design outers in a Network Overview of Generic outer Architecture Input-d Switches (outers) IP Look-up Algorithms Packet Classification Algorithms Sample outers and Switches Cisco 46 outer up to
Efficient Multicast Support in Buffered Crossbars using Networks on Chip
 Efficient Multicast Support in Buffered Crossbars using etworks on Chip Iria Varela Senin Lotfi Mhamdi Kees Goossens, Computer Engineering, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The etherlands XP Semiconductors,
Efficient Multicast Support in Buffered Crossbars using etworks on Chip Iria Varela Senin Lotfi Mhamdi Kees Goossens, Computer Engineering, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The etherlands XP Semiconductors,
Packet Switching Queuing Architecture: A Study
 Packet Switching Queuing Architecture: A Study Shikhar Bahl 1, Rishabh Rai 2, Peeyush Chandra 3, Akash Garg 4 M.Tech, Department of ECE, Ajay Kumar Garg Engineering College, Ghaziabad, U.P., India 1,2,3
Packet Switching Queuing Architecture: A Study Shikhar Bahl 1, Rishabh Rai 2, Peeyush Chandra 3, Akash Garg 4 M.Tech, Department of ECE, Ajay Kumar Garg Engineering College, Ghaziabad, U.P., India 1,2,3
Lecture 16: Router Design
 Lecture 16: Router Design CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Eample courtesy Mike Freedman Lecture 16 Overview End-to-end lookup and forwarding example Router internals Buffering Scheduling 2 Example:
Lecture 16: Router Design CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Eample courtesy Mike Freedman Lecture 16 Overview End-to-end lookup and forwarding example Router internals Buffering Scheduling 2 Example:
Scalable Schedulers for High-Performance Switches
 Scalable Schedulers for High-Performance Switches Chuanjun Li and S Q Zheng Mei Yang Department of Computer Science Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas Columbus State University
Scalable Schedulers for High-Performance Switches Chuanjun Li and S Q Zheng Mei Yang Department of Computer Science Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas Columbus State University
Scheduling in Switches with Small Internal Buffers
 cheduling in witches with mall Internal Buffers ikos Chrysos and Manolis Katevenis Inst. of Computer cience (IC), Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH) - member of HiPEAC FORTH-IC, Vassilika
cheduling in witches with mall Internal Buffers ikos Chrysos and Manolis Katevenis Inst. of Computer cience (IC), Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH) - member of HiPEAC FORTH-IC, Vassilika
Variable-Size Multipacket Segments in Buffered Crossbar (CICQ) Architectures
 Variable-Size Multipacket Segments in Buffered Crossbar (CICQ) Architectures Manolis Katevenis and Georgios Passas Institute of Computer Science (ICS), Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH)
Variable-Size Multipacket Segments in Buffered Crossbar (CICQ) Architectures Manolis Katevenis and Georgios Passas Institute of Computer Science (ICS), Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH)
Matching Schemes with Captured-Frame Eligibility for Input-Queued Packet Switches
 Matching Schemes with Captured-Frame Eligibility for -Queued Packet Switches Roberto Rojas-Cessa and Chuan-bi Lin Abstract Virtual output queues (VOQs) are widely used by input-queued (IQ) switches to
Matching Schemes with Captured-Frame Eligibility for -Queued Packet Switches Roberto Rojas-Cessa and Chuan-bi Lin Abstract Virtual output queues (VOQs) are widely used by input-queued (IQ) switches to
Int. J. Advanced Networking and Applications 1194 Volume: 03; Issue: 03; Pages: (2011)
 Int J Advanced Networking and Applications 1194 ISA-Independent Scheduling Algorithm for Buffered Crossbar Switch Dr Kannan Balasubramanian Department of Computer Science, Mepco Schlenk Engineering College,
Int J Advanced Networking and Applications 1194 ISA-Independent Scheduling Algorithm for Buffered Crossbar Switch Dr Kannan Balasubramanian Department of Computer Science, Mepco Schlenk Engineering College,
EE 122: Router Design
 Routers EE 22: Router Design Kevin Lai September 25, 2002.. A router consists - A set of input interfaces at which packets arrive - A set of output interfaces from which packets depart - Some form of interconnect
Routers EE 22: Router Design Kevin Lai September 25, 2002.. A router consists - A set of input interfaces at which packets arrive - A set of output interfaces from which packets depart - Some form of interconnect
Internet-Router Buffered Crossbars Based on Networks on Chip
 Internet-Router Buffered Crossbars Based on etworks on Chip Kees Goossens,2 Lotfi Mhamdi 2 Iria Varela Senín 2 XP Semiconductors, Eindhoven, The etherlands 2 Computer Engineering, Delft University of Technology,
Internet-Router Buffered Crossbars Based on etworks on Chip Kees Goossens,2 Lotfi Mhamdi 2 Iria Varela Senín 2 XP Semiconductors, Eindhoven, The etherlands 2 Computer Engineering, Delft University of Technology,
Packetisation in Optical Packet Switch Fabrics using adaptive timeout values
 Packetisation in Optical Packet Switch Fabrics using adaptive timeout values Brian B. Mortensen COM DTU Technical University of Denmark DK-28 Kgs. Lyngby Email: bbm@com.dtu.dk Abstract Hybrid electro-optical
Packetisation in Optical Packet Switch Fabrics using adaptive timeout values Brian B. Mortensen COM DTU Technical University of Denmark DK-28 Kgs. Lyngby Email: bbm@com.dtu.dk Abstract Hybrid electro-optical
Configuring Fabric Congestion Control and QoS
 CHAPTER 1 Fibre Channel Congestion Control (FCC) is a Cisco proprietary flow control mechanism that alleviates congestion on Fibre Channel networks. Quality of service () offers the following advantages:
CHAPTER 1 Fibre Channel Congestion Control (FCC) is a Cisco proprietary flow control mechanism that alleviates congestion on Fibre Channel networks. Quality of service () offers the following advantages:
Crossbar - example. Crossbar. Crossbar. Combination: Time-space switching. Simple space-division switch Crosspoints can be turned on or off
 Crossbar Crossbar - example Simple space-division switch Crosspoints can be turned on or off i n p u t s sessions: (,) (,) (,) (,) outputs Crossbar Advantages: simple to implement simple control flexible
Crossbar Crossbar - example Simple space-division switch Crosspoints can be turned on or off i n p u t s sessions: (,) (,) (,) (,) outputs Crossbar Advantages: simple to implement simple control flexible
Network layer (addendum) Slides adapted from material by Nick McKeown and Kevin Lai
 Network layer (addendum) Slides adapted from material by Nick McKeown and Kevin Lai Routers.. A router consists - A set of input interfaces at which packets arrive - A set of output interfaces from which
Network layer (addendum) Slides adapted from material by Nick McKeown and Kevin Lai Routers.. A router consists - A set of input interfaces at which packets arrive - A set of output interfaces from which
4. Time-Space Switching and the family of Input Queueing Architectures
 4. Time-Space Switching and the family of Input Queueing Architectures 4.1 Intro: Time-Space Sw.; Input Q ing w/o VOQ s 4.2 Input Queueing with VOQ s: Crossbar Scheduling 4.3 Adv.Topics: Pipelined, Packet,
4. Time-Space Switching and the family of Input Queueing Architectures 4.1 Intro: Time-Space Sw.; Input Q ing w/o VOQ s 4.2 Input Queueing with VOQ s: Crossbar Scheduling 4.3 Adv.Topics: Pipelined, Packet,
Ting Wu, Chi-Ying Tsui, Mounir Hamdi Hong Kong University of Science & Technology Hong Kong SAR, China
 CMOS Crossbar Ting Wu, Chi-Ying Tsui, Mounir Hamdi Hong Kong University of Science & Technology Hong Kong SAR, China OUTLINE Motivations Problems of Designing Large Crossbar Our Approach - Pipelined MUX
CMOS Crossbar Ting Wu, Chi-Ying Tsui, Mounir Hamdi Hong Kong University of Science & Technology Hong Kong SAR, China OUTLINE Motivations Problems of Designing Large Crossbar Our Approach - Pipelined MUX
A 400Gbps Multi-Core Network Processor
 A 400Gbps Multi-Core Network Processor James Markevitch, Srinivasa Malladi Cisco Systems August 22, 2017 Legal THE INFORMATION HEREIN IS PROVIDED ON AN AS IS BASIS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS,
A 400Gbps Multi-Core Network Processor James Markevitch, Srinivasa Malladi Cisco Systems August 22, 2017 Legal THE INFORMATION HEREIN IS PROVIDED ON AN AS IS BASIS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS,
Topics for Today. Network Layer. Readings. Introduction Addressing Address Resolution. Sections 5.1,
 Topics for Today Network Layer Introduction Addressing Address Resolution Readings Sections 5.1, 5.6.1-5.6.2 1 Network Layer: Introduction A network-wide concern! Transport layer Between two end hosts
Topics for Today Network Layer Introduction Addressing Address Resolution Readings Sections 5.1, 5.6.1-5.6.2 1 Network Layer: Introduction A network-wide concern! Transport layer Between two end hosts
Themes. The Network 1. Energy in the DC: ~15% network? Energy by Technology
 Themes The Network 1 Low Power Computing David Andersen Carnegie Mellon University Last two classes: Saving power by running more slowly and sleeping more. This time: Network intro; saving power by architecting
Themes The Network 1 Low Power Computing David Andersen Carnegie Mellon University Last two classes: Saving power by running more slowly and sleeping more. This time: Network intro; saving power by architecting
EECS 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Switch and Router Architectures. Today s Lecture
 EECS : Introduction to Computer Networks Switch and Router Architectures Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley,
EECS : Introduction to Computer Networks Switch and Router Architectures Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley,
Challenges for Future Interconnection Networks Hot Interconnects Panel August 24, Dennis Abts Sr. Principal Engineer
 Challenges for Future Interconnection Networks Hot Interconnects Panel August 24, 2006 Sr. Principal Engineer Panel Questions How do we build scalable networks that balance power, reliability and performance
Challenges for Future Interconnection Networks Hot Interconnects Panel August 24, 2006 Sr. Principal Engineer Panel Questions How do we build scalable networks that balance power, reliability and performance
Multi-gigabit Switching and Routing
 Multi-gigabit Switching and Routing Gignet 97 Europe: June 12, 1997. Nick McKeown Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science nickm@ee.stanford.edu http://ee.stanford.edu/~nickm
Multi-gigabit Switching and Routing Gignet 97 Europe: June 12, 1997. Nick McKeown Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science nickm@ee.stanford.edu http://ee.stanford.edu/~nickm
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 6,000 20M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 6,000 20M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
Router Architectures
 Router Architectures Venkat Padmanabhan Microsoft Research 13 April 2001 Venkat Padmanabhan 1 Outline Router architecture overview 50 Gbps multi-gigabit router (Partridge et al.) Technology trends Venkat
Router Architectures Venkat Padmanabhan Microsoft Research 13 April 2001 Venkat Padmanabhan 1 Outline Router architecture overview 50 Gbps multi-gigabit router (Partridge et al.) Technology trends Venkat
Scaling routers: Where do we go from here?
 Scaling routers: Where do we go from here? HPSR, Kobe, Japan May 28 th, 2002 Nick McKeown Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Stanford University nickm@stanford.edu www.stanford.edu/~nickm
Scaling routers: Where do we go from here? HPSR, Kobe, Japan May 28 th, 2002 Nick McKeown Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Stanford University nickm@stanford.edu www.stanford.edu/~nickm
Efficient Throughput-Guarantees for Latency-Sensitive Networks-On-Chip
 ASP-DAC 2010 20 Jan 2010 Session 6C Efficient Throughput-Guarantees for Latency-Sensitive Networks-On-Chip Jonas Diemer, Rolf Ernst TU Braunschweig, Germany diemer@ida.ing.tu-bs.de Michael Kauschke Intel,
ASP-DAC 2010 20 Jan 2010 Session 6C Efficient Throughput-Guarantees for Latency-Sensitive Networks-On-Chip Jonas Diemer, Rolf Ernst TU Braunschweig, Germany diemer@ida.ing.tu-bs.de Michael Kauschke Intel,
Packet Scheduling in Data Centers. Lecture 17, Computer Networks (198:552)
 Packet Scheduling in Data Centers Lecture 17, Computer Networks (198:552) Datacenter transport Goal: Complete flows quickly / meet deadlines Short flows (e.g., query, coordination) Large flows (e.g., data
Packet Scheduling in Data Centers Lecture 17, Computer Networks (198:552) Datacenter transport Goal: Complete flows quickly / meet deadlines Short flows (e.g., query, coordination) Large flows (e.g., data
Network Interface Architecture and Prototyping for Chip and Cluster Multiprocessors
 University of Crete School of Sciences & Engineering Computer Science Department Master Thesis by Michael Papamichael Network Interface Architecture and Prototyping for Chip and Cluster Multiprocessors
University of Crete School of Sciences & Engineering Computer Science Department Master Thesis by Michael Papamichael Network Interface Architecture and Prototyping for Chip and Cluster Multiprocessors
Generic Architecture. EECS 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Switch and Router Architectures. Shared Memory (1 st Generation) Today s Lecture
 Generic Architecture EECS : Introduction to Computer Networks Switch and Router Architectures Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California,
Generic Architecture EECS : Introduction to Computer Networks Switch and Router Architectures Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California,
The GLIMPS Terabit Packet Switching Engine
 February 2002 The GLIMPS Terabit Packet Switching Engine I. Elhanany, O. Beeri Terabit Packet Switching Challenges The ever-growing demand for additional bandwidth reflects on the increasing capacity requirements
February 2002 The GLIMPS Terabit Packet Switching Engine I. Elhanany, O. Beeri Terabit Packet Switching Challenges The ever-growing demand for additional bandwidth reflects on the increasing capacity requirements
Routers: Forwarding EECS 122: Lecture 13
 Input Port Functions Routers: Forwarding EECS 22: Lecture 3 epartment of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Physical layer: bit-level reception ata link layer:
Input Port Functions Routers: Forwarding EECS 22: Lecture 3 epartment of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Physical layer: bit-level reception ata link layer:
Introduction: Two motivating examples for the analytical approach
 Introduction: Two motivating examples for the analytical approach Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. D. Manjunath Outline
Introduction: Two motivating examples for the analytical approach Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. D. Manjunath Outline
Routers with a Single Stage of Buffering * Sigcomm Paper Number: 342, Total Pages: 14
 Routers with a Single Stage of Buffering * Sigcomm Paper Number: 342, Total Pages: 14 Abstract -- Most high performance routers today use combined input and output queueing (CIOQ). The CIOQ router is also
Routers with a Single Stage of Buffering * Sigcomm Paper Number: 342, Total Pages: 14 Abstract -- Most high performance routers today use combined input and output queueing (CIOQ). The CIOQ router is also
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction In a packet-switched network, packets are buffered when they cannot be processed or transmitted at the rate they arrive. There are three main reasons that a router, with generic
Chapter 1 Introduction In a packet-switched network, packets are buffered when they cannot be processed or transmitted at the rate they arrive. There are three main reasons that a router, with generic
ECE 697J Advanced Topics in Computer Networks
 ECE 697J Advanced Topics in Computer Networks Switching Fabrics 10/02/03 Tilman Wolf 1 Router Data Path Last class: Single CPU is not fast enough for processing packets Multiple advanced processors in
ECE 697J Advanced Topics in Computer Networks Switching Fabrics 10/02/03 Tilman Wolf 1 Router Data Path Last class: Single CPU is not fast enough for processing packets Multiple advanced processors in
Efficient Switches with QoS Support for Clusters
 Efficient Switches with QoS Support for Clusters Alejandro Martínez, Francisco J. Alfaro,JoséL.Sánchez,José Duato 2 DSI - Univ. of Castilla-La Mancha 2 DISCA - Tech. Univ. of Valencia 27 - Albacete, Spain
Efficient Switches with QoS Support for Clusters Alejandro Martínez, Francisco J. Alfaro,JoséL.Sánchez,José Duato 2 DSI - Univ. of Castilla-La Mancha 2 DISCA - Tech. Univ. of Valencia 27 - Albacete, Spain
Scaling Internet Routers Using Optics Producing a 100TB/s Router. Ashley Green and Brad Rosen February 16, 2004
 Scaling Internet Routers Using Optics Producing a 100TB/s Router Ashley Green and Brad Rosen February 16, 2004 Presentation Outline Motivation Avi s Black Box Black Box: Load Balance Switch Conclusion
Scaling Internet Routers Using Optics Producing a 100TB/s Router Ashley Green and Brad Rosen February 16, 2004 Presentation Outline Motivation Avi s Black Box Black Box: Load Balance Switch Conclusion
Buffer Sizing in a Combined Input Output Queued (CIOQ) Switch
 Buffer Sizing in a Combined Input Output Queued (CIOQ) Switch Neda Beheshti, Nick Mckeown Stanford University Abstract In all internet routers buffers are needed to hold packets during times of congestion.
Buffer Sizing in a Combined Input Output Queued (CIOQ) Switch Neda Beheshti, Nick Mckeown Stanford University Abstract In all internet routers buffers are needed to hold packets during times of congestion.
PCRRD: A Pipeline-Based Concurrent Round-Robin Dispatching Scheme for Clos-Network Switches
 : A Pipeline-Based Concurrent Round-Robin Dispatching Scheme for Clos-Network Switches Eiji Oki, Roberto Rojas-Cessa, and H. Jonathan Chao Abstract This paper proposes a pipeline-based concurrent round-robin
: A Pipeline-Based Concurrent Round-Robin Dispatching Scheme for Clos-Network Switches Eiji Oki, Roberto Rojas-Cessa, and H. Jonathan Chao Abstract This paper proposes a pipeline-based concurrent round-robin
Toward a Reliable Data Transport Architecture for Optical Burst-Switched Networks
 Toward a Reliable Data Transport Architecture for Optical Burst-Switched Networks Dr. Vinod Vokkarane Assistant Professor, Computer and Information Science Co-Director, Advanced Computer Networks Lab University
Toward a Reliable Data Transport Architecture for Optical Burst-Switched Networks Dr. Vinod Vokkarane Assistant Professor, Computer and Information Science Co-Director, Advanced Computer Networks Lab University
Swizzle Switch: A Self-Arbitrating High-Radix Crossbar for NoC Systems
 1 Swizzle Switch: A Self-Arbitrating High-Radix Crossbar for NoC Systems Ronald Dreslinski, Korey Sewell, Thomas Manville, Sudhir Satpathy, Nathaniel Pinckney, Geoff Blake, Michael Cieslak, Reetuparna
1 Swizzle Switch: A Self-Arbitrating High-Radix Crossbar for NoC Systems Ronald Dreslinski, Korey Sewell, Thomas Manville, Sudhir Satpathy, Nathaniel Pinckney, Geoff Blake, Michael Cieslak, Reetuparna
1 Architectures of Internet Switches and Routers
 1 Architectures of Internet Switches and Routers Xin Li, Lotfi Mhamdi, Jing Liu, Konghong Pun, and Mounir Hamdi The Hong-Kong University of Science & Technology. {lixin,lotfi,liujing, konghong,hamdi}@cs.ust.hk
1 Architectures of Internet Switches and Routers Xin Li, Lotfi Mhamdi, Jing Liu, Konghong Pun, and Mounir Hamdi The Hong-Kong University of Science & Technology. {lixin,lotfi,liujing, konghong,hamdi}@cs.ust.hk
IV. PACKET SWITCH ARCHITECTURES
 IV. PACKET SWITCH ARCHITECTURES (a) General Concept - as packet arrives at switch, destination (and possibly source) field in packet header is used as index into routing tables specifying next switch in
IV. PACKET SWITCH ARCHITECTURES (a) General Concept - as packet arrives at switch, destination (and possibly source) field in packet header is used as index into routing tables specifying next switch in
Routers: Forwarding EECS 122: Lecture 13
 Routers: Forwarding EECS 122: Lecture 13 epartment of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Router Architecture Overview Two key router functions: run routing algorithms/protocol
Routers: Forwarding EECS 122: Lecture 13 epartment of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Router Architecture Overview Two key router functions: run routing algorithms/protocol
Stability of CIOQ Switches with Finite Buffers and Non-Negligible Round-Trip Time
 Stability of CIOQ Switches with Finite Buffers and on-egligible Round-Trip Time M. Gusat, F. Abel, F. Gramsamer, R. Luijten, C. Minkenberg, and M. Verhappen IBM Research, Zurich Research Laboratory, 8803
Stability of CIOQ Switches with Finite Buffers and on-egligible Round-Trip Time M. Gusat, F. Abel, F. Gramsamer, R. Luijten, C. Minkenberg, and M. Verhappen IBM Research, Zurich Research Laboratory, 8803
Configuring Fabric Congestion Control and QoS
 Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com. 47 CHAPTER Configuring Fabric Congestion Control and QoS Fibre Channel Congestion Control (FCC) is a Cisco proprietary flow control mechanism that
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com. 47 CHAPTER Configuring Fabric Congestion Control and QoS Fibre Channel Congestion Control (FCC) is a Cisco proprietary flow control mechanism that
1 Introduction
 Published in IET Communications Received on 17th September 2009 Revised on 3rd February 2010 ISSN 1751-8628 Multicast and quality of service provisioning in parallel shared memory switches B. Matthews
Published in IET Communications Received on 17th September 2009 Revised on 3rd February 2010 ISSN 1751-8628 Multicast and quality of service provisioning in parallel shared memory switches B. Matthews
PARALLEL ALGORITHMS FOR IP SWITCHERS/ROUTERS
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND INFORMATION ENGINEERING FINAL YEAR PROJECT. PROJECT NO. 60 PARALLEL ALGORITHMS FOR IP SWITCHERS/ROUTERS OMARI JAPHETH N. F17/2157/2004 SUPERVISOR:
THE UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND INFORMATION ENGINEERING FINAL YEAR PROJECT. PROJECT NO. 60 PARALLEL ALGORITHMS FOR IP SWITCHERS/ROUTERS OMARI JAPHETH N. F17/2157/2004 SUPERVISOR:
Optical Packet Switching
 Optical Packet Switching DEISNet Gruppo Reti di Telecomunicazioni http://deisnet.deis.unibo.it WDM Optical Network Legacy Networks Edge Systems WDM Links λ 1 λ 2 λ 3 λ 4 Core Nodes 2 1 Wavelength Routing
Optical Packet Switching DEISNet Gruppo Reti di Telecomunicazioni http://deisnet.deis.unibo.it WDM Optical Network Legacy Networks Edge Systems WDM Links λ 1 λ 2 λ 3 λ 4 Core Nodes 2 1 Wavelength Routing
EE382C Lecture 1. Bill Dally 3/29/11. EE 382C - S11 - Lecture 1 1
 EE382C Lecture 1 Bill Dally 3/29/11 EE 382C - S11 - Lecture 1 1 Logistics Handouts Course policy sheet Course schedule Assignments Homework Research Paper Project Midterm EE 382C - S11 - Lecture 1 2 What
EE382C Lecture 1 Bill Dally 3/29/11 EE 382C - S11 - Lecture 1 1 Logistics Handouts Course policy sheet Course schedule Assignments Homework Research Paper Project Midterm EE 382C - S11 - Lecture 1 2 What
GUARANTEED END-TO-END LATENCY THROUGH ETHERNET
 GUARANTEED END-TO-END LATENCY THROUGH ETHERNET Øyvind Holmeide, OnTime Networks AS, Oslo, Norway oeyvind@ontimenet.com Markus Schmitz, OnTime Networks LLC, Texas, USA markus@ontimenet.com Abstract: Latency
GUARANTEED END-TO-END LATENCY THROUGH ETHERNET Øyvind Holmeide, OnTime Networks AS, Oslo, Norway oeyvind@ontimenet.com Markus Schmitz, OnTime Networks LLC, Texas, USA markus@ontimenet.com Abstract: Latency
Network Support for Multimedia
 Network Support for Multimedia Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Network Support for Multimedia 2/33 make the best of best effort use application-level techniques use CDNs
Network Support for Multimedia Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Network Support for Multimedia 2/33 make the best of best effort use application-level techniques use CDNs
048866: Packet Switch Architectures
 048866: Packet Switch Architectures Output-Queued Switches Deterministic Queueing Analysis Fairness and Delay Guarantees Dr. Isaac Keslassy Electrical Engineering, Technion isaac@ee.technion.ac.il http://comnet.technion.ac.il/~isaac/
048866: Packet Switch Architectures Output-Queued Switches Deterministic Queueing Analysis Fairness and Delay Guarantees Dr. Isaac Keslassy Electrical Engineering, Technion isaac@ee.technion.ac.il http://comnet.technion.ac.il/~isaac/
The Arbitration Problem
 HighPerform Switchingand TelecomCenterWorkshop:Sep outing ance t4, 97. EE84Y: Packet Switch Architectures Part II Load-balanced Switches ick McKeown Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,
HighPerform Switchingand TelecomCenterWorkshop:Sep outing ance t4, 97. EE84Y: Packet Switch Architectures Part II Load-balanced Switches ick McKeown Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,
PCI Express: Evolution, Deployment and Challenges
 PCI Express: Evolution, Deployment and Challenges Nick Ma 马明辉 Field Applications Engineer, PLX Freescale Technology Forum, Beijing Track: Enabling Technologies Freescale Technology Forum, Beijing - November
PCI Express: Evolution, Deployment and Challenges Nick Ma 马明辉 Field Applications Engineer, PLX Freescale Technology Forum, Beijing Track: Enabling Technologies Freescale Technology Forum, Beijing - November
4A0-107 Q&As. Alcatel-Lucent Quality of Service. Pass Alcatel-Lucent 4A0-107 Exam with 100% Guarantee
 4A0-107 Q&As Alcatel-Lucent Quality of Service Pass Alcatel-Lucent 4A0-107 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee 100% Money Back
4A0-107 Q&As Alcatel-Lucent Quality of Service Pass Alcatel-Lucent 4A0-107 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee 100% Money Back
SoC Design Lecture 13: NoC (Network-on-Chip) Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology
 SoC Design Lecture 13: NoC (Network-on-Chip) Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Outline SoC Interconnect NoC Introduction NoC layers Typical NoC Router NoC Issues Switching
SoC Design Lecture 13: NoC (Network-on-Chip) Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Outline SoC Interconnect NoC Introduction NoC layers Typical NoC Router NoC Issues Switching
Dynamic Scheduling Algorithm for input-queued crossbar switches
 Dynamic Scheduling Algorithm for input-queued crossbar switches Mihir V. Shah, Mehul C. Patel, Dinesh J. Sharma, Ajay I. Trivedi Abstract Crossbars are main components of communication switches used to
Dynamic Scheduling Algorithm for input-queued crossbar switches Mihir V. Shah, Mehul C. Patel, Dinesh J. Sharma, Ajay I. Trivedi Abstract Crossbars are main components of communication switches used to
Switching/Flow Control Overview. Interconnection Networks: Flow Control and Microarchitecture. Packets. Switching.
 Switching/Flow Control Overview Interconnection Networks: Flow Control and Microarchitecture Topology: determines connectivity of network Routing: determines paths through network Flow Control: determine
Switching/Flow Control Overview Interconnection Networks: Flow Control and Microarchitecture Topology: determines connectivity of network Routing: determines paths through network Flow Control: determine
Scheduling. Scheduling algorithms. Scheduling. Output buffered architecture. QoS scheduling algorithms. QoS-capable router
 Scheduling algorithms Scheduling Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Scheduling: choose a packet to transmit over a link among all
Scheduling algorithms Scheduling Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Scheduling: choose a packet to transmit over a link among all
The RM9150 and the Fast Device Bus High Speed Interconnect
 The RM9150 and the Fast Device High Speed Interconnect John R. Kinsel Principal Engineer www.pmc -sierra.com 1 August 2004 Agenda CPU-based SOC Design Challenges Fast Device (FDB) Overview Generic Device
The RM9150 and the Fast Device High Speed Interconnect John R. Kinsel Principal Engineer www.pmc -sierra.com 1 August 2004 Agenda CPU-based SOC Design Challenges Fast Device (FDB) Overview Generic Device
Quality-of-Service for a High-Radix Switch
 Quality-of-Service for a High-Radix Switch Nilmini Abeyratne, Supreet Jeloka, Yiping Kang, David Blaauw, Ronald G. Dreslinski, Reetuparna Das, and Trevor Mudge University of Michigan 51 st DAC 06/05/2014
Quality-of-Service for a High-Radix Switch Nilmini Abeyratne, Supreet Jeloka, Yiping Kang, David Blaauw, Ronald G. Dreslinski, Reetuparna Das, and Trevor Mudge University of Michigan 51 st DAC 06/05/2014
The Network Layer and Routers
 The Network Layer and Routers Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/18 Network Layer deliver packets from sending host to receiving host must be on every host, router in
The Network Layer and Routers Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/18 Network Layer deliver packets from sending host to receiving host must be on every host, router in
Pi-PIFO: A Scalable Pipelined PIFO Memory Management Architecture
 Pi-PIFO: A Scalable Pipelined PIFO Memory Management Architecture Steven Young, Student Member, IEEE, Itamar Arel, Senior Member, IEEE, Ortal Arazi, Member, IEEE Networking Research Group Electrical Engineering
Pi-PIFO: A Scalable Pipelined PIFO Memory Management Architecture Steven Young, Student Member, IEEE, Itamar Arel, Senior Member, IEEE, Ortal Arazi, Member, IEEE Networking Research Group Electrical Engineering
Routers with a Single Stage of Buffering *
 Routers with a Single Stage of Buffering * Sundar Iyer, Rui Zhang, Nick McKeown Computer Systems Laboratory, Stanford University, Ph: (650)-725 9077, Fax: (650)-725 6949 Stanford, CA 94305-9030 {sundaes,
Routers with a Single Stage of Buffering * Sundar Iyer, Rui Zhang, Nick McKeown Computer Systems Laboratory, Stanford University, Ph: (650)-725 9077, Fax: (650)-725 6949 Stanford, CA 94305-9030 {sundaes,
Configuring Queuing and Flow Control
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Queues, page 1 Information About Flow Control, page 3 Configuring Queuing, page 4 Configuring Flow Control, page 7 Verifying the Queue and
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Queues, page 1 Information About Flow Control, page 3 Configuring Queuing, page 4 Configuring Flow Control, page 7 Verifying the Queue and
Variable Packet Size Buffered Crossbar (CICQ) Switches
 Variable Packet Size uffered Crossbar (CICQ) Switches Manolis Katevenis, Georgios Passas, Dimitrios Simos, Ioannis Papaefstathiou and Nikos Chrysos y Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research
Variable Packet Size uffered Crossbar (CICQ) Switches Manolis Katevenis, Georgios Passas, Dimitrios Simos, Ioannis Papaefstathiou and Nikos Chrysos y Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research
EECS 598: Integrating Emerging Technologies with Computer Architecture. Lecture 12: On-Chip Interconnects
 1 EECS 598: Integrating Emerging Technologies with Computer Architecture Lecture 12: On-Chip Interconnects Instructor: Ron Dreslinski Winter 216 1 1 Announcements Upcoming lecture schedule Today: On-chip
1 EECS 598: Integrating Emerging Technologies with Computer Architecture Lecture 12: On-Chip Interconnects Instructor: Ron Dreslinski Winter 216 1 1 Announcements Upcoming lecture schedule Today: On-chip
FM4000. A Scalable, Low-latency 10 GigE Switch for High-performance Data Centers
 A Scalable, Low-latency 10 GigE Switch for High-performance Data Centers Uri Cummings Rebecca Collins Virat Agarwal Dan Daly Fabrizio Petrini Michael Perrone Davide Pasetto Hot Interconnects 17 (Aug 2009)
A Scalable, Low-latency 10 GigE Switch for High-performance Data Centers Uri Cummings Rebecca Collins Virat Agarwal Dan Daly Fabrizio Petrini Michael Perrone Davide Pasetto Hot Interconnects 17 (Aug 2009)
K-Selector-Based Dispatching Algorithm for Clos-Network Switches
 K-Selector-Based Dispatching Algorithm for Clos-Network Switches Mei Yang, Mayauna McCullough, Yingtao Jiang, and Jun Zheng Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Nevada Las Vegas,
K-Selector-Based Dispatching Algorithm for Clos-Network Switches Mei Yang, Mayauna McCullough, Yingtao Jiang, and Jun Zheng Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Nevada Las Vegas,
Switch Fabric. Switch Fabric Overview
 This chapter describes the Cisco CRS Carrier Routing System 16-Slot Line Card Chassis switch fabric. It includes the following sections: Overview, on page 1 Operation, on page 2 Card Description, on page
This chapter describes the Cisco CRS Carrier Routing System 16-Slot Line Card Chassis switch fabric. It includes the following sections: Overview, on page 1 Operation, on page 2 Card Description, on page
A Pipelined Memory Management Algorithm for Distributed Shared Memory Switches
 A Pipelined Memory Management Algorithm for Distributed Shared Memory Switches Xike Li, Student Member, IEEE, Itamar Elhanany, Senior Member, IEEE* Abstract The distributed shared memory (DSM) packet switching
A Pipelined Memory Management Algorithm for Distributed Shared Memory Switches Xike Li, Student Member, IEEE, Itamar Elhanany, Senior Member, IEEE* Abstract The distributed shared memory (DSM) packet switching
Quality of Service (QoS)
 Quality of Service (QoS) The Internet was originally designed for best-effort service without guarantee of predictable performance. Best-effort service is often sufficient for a traffic that is not sensitive
Quality of Service (QoS) The Internet was originally designed for best-effort service without guarantee of predictable performance. Best-effort service is often sufficient for a traffic that is not sensitive
Design and Evaluation of a Parallel-Polled Virtual Output Queued Switch *
 Design and Evaluation of a Parallel-Polled Virtual Output Queued Switch * K. J. Christensen Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Florida Tampa, FL 3360 Abstract - Input-buffered
Design and Evaluation of a Parallel-Polled Virtual Output Queued Switch * K. J. Christensen Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Florida Tampa, FL 3360 Abstract - Input-buffered
Cisco Series Internet Router Architecture: Packet Switching
 Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router Architecture: Packet Switching Document ID: 47320 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Packet Switching:
Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router Architecture: Packet Switching Document ID: 47320 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Packet Switching:
Understanding Cisco Express Forwarding
 Understanding Cisco Express Forwarding Document ID: 47321 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Overview CEF Operations Updating the GRP's Routing Tables Packet Forwarding
Understanding Cisco Express Forwarding Document ID: 47321 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Overview CEF Operations Updating the GRP's Routing Tables Packet Forwarding
PUSHING THE LIMITS, A PERSPECTIVE ON ROUTER ARCHITECTURE CHALLENGES
 PUSHING THE LIMITS, A PERSPECTIVE ON ROUTER ARCHITECTURE CHALLENGES Greg Hankins APRICOT 2012 2012 Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. 2012/02/28 Lookup Capacity and Forwarding
PUSHING THE LIMITS, A PERSPECTIVE ON ROUTER ARCHITECTURE CHALLENGES Greg Hankins APRICOT 2012 2012 Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. 2012/02/28 Lookup Capacity and Forwarding
Cisco Nexus 9500 Series Switches Buffer and Queuing Architecture
 White Paper Cisco Nexus 9500 Series Switches Buffer and Queuing Architecture White Paper December 2014 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
White Paper Cisco Nexus 9500 Series Switches Buffer and Queuing Architecture White Paper December 2014 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Integrated Scheduling and Buffer Management Scheme for Input Queued Switches under Extreme Traffic Conditions
 Integrated Scheduling and Buffer Management Scheme for Input Queued Switches under Extreme Traffic Conditions Anuj Kumar, Rabi N. Mahapatra Texas A&M University, College Station, U.S.A Email: {anujk, rabi}@cs.tamu.edu
Integrated Scheduling and Buffer Management Scheme for Input Queued Switches under Extreme Traffic Conditions Anuj Kumar, Rabi N. Mahapatra Texas A&M University, College Station, U.S.A Email: {anujk, rabi}@cs.tamu.edu
PEX8764, PCI Express Gen3 Switch, 64 Lanes, 16 Ports
 Highlights PEX8764 General Features o 64-lane, 16-port PCIe Gen3 switch Integrated 8.0 GT/s SerDes o 35 x 35mm 2, 1156-ball FCBGA package o Typical Power: 1. Watts PEX8764 Key Features o Standards Compliant
Highlights PEX8764 General Features o 64-lane, 16-port PCIe Gen3 switch Integrated 8.0 GT/s SerDes o 35 x 35mm 2, 1156-ball FCBGA package o Typical Power: 1. Watts PEX8764 Key Features o Standards Compliant
Module 17: "Interconnection Networks" Lecture 37: "Introduction to Routers" Interconnection Networks. Fundamentals. Latency and bandwidth
 Interconnection Networks Fundamentals Latency and bandwidth Router architecture Coherence protocol and routing [From Chapter 10 of Culler, Singh, Gupta] file:///e /parallel_com_arch/lecture37/37_1.htm[6/13/2012
Interconnection Networks Fundamentals Latency and bandwidth Router architecture Coherence protocol and routing [From Chapter 10 of Culler, Singh, Gupta] file:///e /parallel_com_arch/lecture37/37_1.htm[6/13/2012
DESIGN OF EFFICIENT ROUTING ALGORITHM FOR CONGESTION CONTROL IN NOC
 DESIGN OF EFFICIENT ROUTING ALGORITHM FOR CONGESTION CONTROL IN NOC 1 Pawar Ruchira Pradeep M. E, E&TC Signal Processing, Dr. D Y Patil School of engineering, Ambi, Pune Email: 1 ruchira4391@gmail.com
DESIGN OF EFFICIENT ROUTING ALGORITHM FOR CONGESTION CONTROL IN NOC 1 Pawar Ruchira Pradeep M. E, E&TC Signal Processing, Dr. D Y Patil School of engineering, Ambi, Pune Email: 1 ruchira4391@gmail.com
SwitchX Virtual Protocol Interconnect (VPI) Switch Architecture
 SwitchX Virtual Protocol Interconnect (VPI) Switch Architecture 2012 MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES 1 SwitchX - Virtual Protocol Interconnect Solutions Server / Compute Switch / Gateway Virtual Protocol Interconnect
SwitchX Virtual Protocol Interconnect (VPI) Switch Architecture 2012 MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES 1 SwitchX - Virtual Protocol Interconnect Solutions Server / Compute Switch / Gateway Virtual Protocol Interconnect
TOC: Switching & Forwarding
 TOC: Switching & Forwarding Why? Switching Techniques Switch Characteristics Switch Examples Switch Architectures Summary TOC Switching Why? Direct vs. Switched Networks: n links Single link Direct Network
TOC: Switching & Forwarding Why? Switching Techniques Switch Characteristics Switch Examples Switch Architectures Summary TOC Switching Why? Direct vs. Switched Networks: n links Single link Direct Network
Scheduling in Non-Blocking Buffered Three-Stage Switching Fabrics
 cheduling in Non-Blocking Buffered Three-tage witching Fabrics Nikos Chrysos and Manolis Katevenis Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH), member of HiPEAC Abstract Three-stage non-blocking
cheduling in Non-Blocking Buffered Three-tage witching Fabrics Nikos Chrysos and Manolis Katevenis Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH), member of HiPEAC Abstract Three-stage non-blocking
THE CAPACITY demand of the early generations of
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 55, NO. 3, MARCH 2007 605 Resequencing Worst-Case Analysis for Parallel Buffered Packet Switches Ilias Iliadis, Senior Member, IEEE, and Wolfgang E. Denzel Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 55, NO. 3, MARCH 2007 605 Resequencing Worst-Case Analysis for Parallel Buffered Packet Switches Ilias Iliadis, Senior Member, IEEE, and Wolfgang E. Denzel Abstract
Exam HP0-Y43 Implementing HP Network Infrastructure Solutions Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 62 ]
![Exam HP0-Y43 Implementing HP Network Infrastructure Solutions Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 62 ] Exam HP0-Y43 Implementing HP Network Infrastructure Solutions Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 62 ]](/thumbs/92/109899386.jpg) s@lm@n HP Exam HP0-Y43 Implementing HP Network Infrastructure Solutions Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 62 ] Question No : 1 A customer requires an HP FlexCampus solution with a core that scales to 40/100G.
s@lm@n HP Exam HP0-Y43 Implementing HP Network Infrastructure Solutions Version: 10.0 [ Total Questions: 62 ] Question No : 1 A customer requires an HP FlexCampus solution with a core that scales to 40/100G.
