Frequency Distributions
|
|
|
- Derick Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Frequency Distributions RAW DATA Raw data are collected data that have not been organized numerically. An example is the set of heights of 100 male students obtained from an alphabetical listing of university records. ARRAYS An array is an arrangement of raw numerical data in ascending or descending order of magnitude. The difference between the largest and smallest numbers is called the range of the data. For example, if the largest height of 100 male students is 74 inches (in) and the smallest height is 60 in, the range is in. FREQUECY DISTRIBUTIOS When summarizing large masses of raw data, it is often useful to distribute the data into classes, or categories, and to determine the number of individuals belonging to each class, called the class frequency. A tabular arrangement of data by classes together with the corresponding class frequencies is called a frequency distribution,orfrequency table. Table.1 is a frequency distribution of heights (recorded to the nearest inch) of 100 male students at XYZ University. Table.1 Heights of 100 male students at XYZ University Height (in) umber of Students Total 100!"#$%&'()*+*,--./*0111/*01../*010*3$*4(5*678%9:;<&==*!">#9?&5@/*A?7B*!=&7C*(5%5*D"%*)5%>@*"D*E@5B* 37
2 38 FREQUECY DISTRIBUTIOS [CHAP. The first class (or category), for example, consists of heights from 60 to 6 in and is indicated by the range symbol Since five students have heights belonging to this class, the corresponding class frequency is 5. Data organized and summarized as in the above frequency distribution are often called grouped data. Although the grouping process generally destroys much of the original detail of the data, an important advantage is gained in the clear overall picture that is obtained and in the vital relationships that are thereby made evident. CLASS ITERVALS AD CLASS LIMITS A symbol defining a class, such as 60 6 in Table.1, is called a class interval. The end numbers, 60 and 6, are called class limits; the smaller number (60) is the lower class limit, and the larger number (6) is the upper class limit. The terms class and class interval are often used interchangeably, although the class interval is actually a symbol for the class. A class interval that, at least theoretically, has either no upper class limit or no lower class limit indicated is called an open class interval. For example, referring to age groups of individuals, the class interval 65 years and over is an open class interval. CLASS BOUDARIES If heights are recorded to the nearest inch, the class interval 60 6 theoretically includes all measurements from to in. These numbers, indicated briefly by the exact numbers 59.5 and 6.5, are called class boundaries, or true class limits; the smaller number (59.5) is the lower class boundary, and the larger number (6.5) is the upper class boundary. In practice, the class boundaries are obtained by adding the upper limit of one class interval to the lower limit of the next-higher class interval and dividing by. Sometimes, class boundaries are used to symbolize classes. For example, the various classes in the first column of Table.1 could be indicated by , , etc. To avoid ambiguity in using such notation, class boundaries should not coincide with actual observations. Thus if an observation were 6.5, it would not be possible to decide whether it belonged to the class interval or THE SIZE, OR WIDTH, OF A CLASS ITERVAL The size, or width, of a class interval is the difference between the lower and upper class boundaries and is also referred to as the class width, class size, or class length. If all class intervals of a frequency distribution have equal widths, this common width is denoted by c. In such case c is equal to the difference between two successive lower class limits or two successive upper class limits. For the data of Table.1, for example, the class interval is c 6:5 59:5 65:5 6:5 3. THE CLASS MARK The class mark is the midpoint of the class interval and is obtained by adding the lower and upper class limits and dividing by. Thus the class mark of the interval 60 6 is ð60 þ 6Þ= 61. The class mark is also called the class midpoint. For purposes of further mathematical analysis, all observations belonging to a given class interval are assumed to coincide with the class mark. Thus all heights in the class interval 60 6 in are considered to be 61 in. GEERAL RULES FOR FORMIG FREQUECY DISTRIBUTIOS 1. Determine the largest and smallest numbers in the raw data and thus find the range (the difference between the largest and smallest numbers).
3 CHAP. ] FREQUECY DISTRIBUTIOS 39. Divide the range into a convenient number of class intervals having the same size. If this is not feasible, use class intervals of different sizes or open class intervals (see Problem.1). The number of class intervals is usually between 5 and 0, depending on the data. Class intervals are also chosen so that the class marks (or midpoints) coincide with the actually observed data. This tends to lessen the so-called grouping error involved in further mathematical analysis. However, the class boundaries should not coincide with the actually observed data. 3. Determine the number of observations falling into each class interval; that is, find the class frequencies. This is best done by using a tally, or score sheet (see Problem.8). HISTOGRAMS AD FREQUECY POLYGOS Histograms and frequency polygons are two graphic representations of frequency distributions. 1. A histogram or frequency histogram, consists of a set of rectangles having (a) bases on a horizontal axis (the X axis), with centers at the class marks and lengths equal to the class interval sizes, and (b) areas proportional to the class frequencies.. A frequency polygon is a line graph of the class frequencies plotted against class marks. It can be obtained by connecting the midpoints of the tops of the rectangles in the histogram. The histogram and frequency polygon corresponding to the frequency distribution of heights in Table.1 are shown in Figs. -1 and Frequency 0 10 Fig Height (in) A MIITAB histogram showing the class midpoints and frequencies. otice in Fig. - how the frequency polygon is tied down at the ends, that is, at 58 and 76. RELATIVE-FREQUECY DISTRIBUTIOS The relative frequency of a class is the frequency of the class divided by the total frequency of all classes and is generally expressed as a percentage. For example, the relative frequency of the class in Table.1 is 4=100 4%. The sum of the relative frequencies of all classes is clearly 1, or 100%. If the frequencies in Table.1 are replaced with the corresponding relative frequencies, the resulting table is called a relative-frequency distribution, percentage distribution, or relative-frequency table. Graphic representation of relative-frequency distributions can be obtained from the histogram or frequency polygon simply by changing the vertical scale from frequency to relative frequency, keeping exactly the same diagram. The resulting graphs are called relative-frequency histograms (or percentage histograms) and relative-frequency polygons (or percentage polygons), respectively.
4 106 THE STADARD DEVIATIO AD OTHER MEASURES OF DISPERSIO [CHAP The standard deviations of the two data sets given in Problem 4.1 were found using MIITAB and the results are shown below. Compare the answers with those obtained in Problem 4.9. MTB > print cl set MTB > print c set MTB > standard deviation cl Column Standard Deviation Standard deviation of set1 = 5.1 MTB > standard deviation c Column Standard Deviation Standard deviation of set = 4.14 SOLUTIO The MIITAB package uses the formula sffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi P ðx XÞ s 1 and therefore the standard deviations are not the same in Problems 4.9 and The panswers ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi in Problem 4.10 are obtainable from pffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi those in Problem 4.9 if we multiply those in Problem 4.9 by =ð 1Þ. Since 8 for both sets =ð 1Þ 1:069045, and for set 1, we have ð1:069045þð4:87þ 5:1, the standard deviation given by MIITAB. Similarly, ð1:069045þð3:87þ 4:14, the standard deviation given for set by MIITAB Find the standard deviation of the heights of the 100 male students at XYZ University (see Table.1). SOLUTIO From Problem 3.15, 3.0, or 3., X 67:45 in. The work can be arranged as in Table 4.. sffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi P rffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi f ðx XÞ 85:7500 p s ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi 8:575 :9 in 100 Table 4. Height (in) Class Mark (X) X X X 67:45 ðx XÞ Frequency ( f ) f ðx XÞ P f 100 P f ðx XÞ
5 CHAP. 4] THE STADARD DEVIATIO AD OTHER MEASURES OF DISPERSIO 107 COMPUTIG THE STADARD DEVIATIOS FROM GROUPED DATA 4.1 (a) Prove that sffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi P P X X s X X (b) Use the formula in part (a) to find the standard deviation of the set 1, 6, 7, 3, 15, 10, 18, 5. SOLUTIO (a) By definition, Then or sffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi P ðx XÞ s P ðx XÞ P ðx s XX þ X P Þ X X þ X P X X þ X X þ X X X X P X s P ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi P X X s X X ote that in the above summations we have used the abbreviated form, with X replacing X j and with P replacing P j1. Another method s ðx XÞ X X X þ X X X X þ X X X X þ X X X ðbþ Thus X ð1þ þð6þ þð7þ þð3þ þð15þ þð10þ þð18þ þð5þ 8 1 þ 6 þ 7 þ 3 þ 15 þ 10 þ 18 þ 5 X :5 p s X X ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi p :5 ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi 3:75 4: This method should be compared with that of Problem 4.9(a) Modify the formula of Problem 4.1(a) to allow for frequencies corresponding to the various values of X. SOLUTIO The appropriate modification is s P ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi P fx fx s X X As in Problem 4.1(a), this can be established by starting with sffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi P f ðx XÞ s
Chapter 2. Frequency distribution. Summarizing and Graphing Data
 Frequency distribution Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data Shows how data are partitioned among several categories (or classes) by listing the categories along with the number (frequency) of data values
Frequency distribution Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data Shows how data are partitioned among several categories (or classes) by listing the categories along with the number (frequency) of data values
Section 2-2 Frequency Distributions. Copyright 2010, 2007, 2004 Pearson Education, Inc
 Section 2-2 Frequency Distributions Copyright 2010, 2007, 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. 2.1-1 Frequency Distribution Frequency Distribution (or Frequency Table) It shows how a data set is partitioned among
Section 2-2 Frequency Distributions Copyright 2010, 2007, 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. 2.1-1 Frequency Distribution Frequency Distribution (or Frequency Table) It shows how a data set is partitioned among
Elementary Statistics. Organizing Raw Data
 Organizing Raw Data What is a Raw Data? Raw Data (sometimes called source data) is data that has not been processed for meaningful use. What is a Frequency Distribution Table? A Frequency Distribution
Organizing Raw Data What is a Raw Data? Raw Data (sometimes called source data) is data that has not been processed for meaningful use. What is a Frequency Distribution Table? A Frequency Distribution
Elementary Statistics
 1 Elementary Statistics Introduction Statistics is the collection of methods for planning experiments, obtaining data, and then organizing, summarizing, presenting, analyzing, interpreting, and drawing
1 Elementary Statistics Introduction Statistics is the collection of methods for planning experiments, obtaining data, and then organizing, summarizing, presenting, analyzing, interpreting, and drawing
Frequency Distributions
 Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Maths Class 9 Notes for Statistics
 1 P a g e Maths Class 9 Notes for Statistics BASIC TERMS Primary data : Data which collected for the first time by the statistical investigator or with the help of his workers is called primary data. Secondary
1 P a g e Maths Class 9 Notes for Statistics BASIC TERMS Primary data : Data which collected for the first time by the statistical investigator or with the help of his workers is called primary data. Secondary
Downloaded from
 UNIT 2 WHAT IS STATISTICS? Researchers deal with a large amount of data and have to draw dependable conclusions on the basis of data collected for the purpose. Statistics help the researchers in making
UNIT 2 WHAT IS STATISTICS? Researchers deal with a large amount of data and have to draw dependable conclusions on the basis of data collected for the purpose. Statistics help the researchers in making
This chapter will show how to organize data and then construct appropriate graphs to represent the data in a concise, easy-to-understand form.
 CHAPTER 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs Objectives Organize data using frequency distributions. Represent data in frequency distributions graphically using histograms, frequency polygons, and ogives.
CHAPTER 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs Objectives Organize data using frequency distributions. Represent data in frequency distributions graphically using histograms, frequency polygons, and ogives.
2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs
 2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs Frequency Distribution - way to display data that has many entries - table that shows classes or intervals of data entries and the number of entries in each
2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs Frequency Distribution - way to display data that has many entries - table that shows classes or intervals of data entries and the number of entries in each
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER STATISTICS 1 (The presentation of data) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 18.1 STATISTICS 1 (The presentation of data) by A.J.Hobson 18.1.1 Introduction 18.1.2 The tabulation of data 18.1.3 The graphical representation of data 18.1.4 Exercises 18.1.5
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 18.1 STATISTICS 1 (The presentation of data) by A.J.Hobson 18.1.1 Introduction 18.1.2 The tabulation of data 18.1.3 The graphical representation of data 18.1.4 Exercises 18.1.5
Chapter 5snow year.notebook March 15, 2018
 Chapter 5: Statistical Reasoning Section 5.1 Exploring Data Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median and Mode) attempt to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within a set of data
Chapter 5: Statistical Reasoning Section 5.1 Exploring Data Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median and Mode) attempt to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within a set of data
Graphical Presentation for Statistical Data (Relevant to AAT Examination Paper 4: Business Economics and Financial Mathematics) Introduction
 Graphical Presentation for Statistical Data (Relevant to AAT Examination Paper 4: Business Economics and Financial Mathematics) Y O Lam, SCOPE, City University of Hong Kong Introduction The most convenient
Graphical Presentation for Statistical Data (Relevant to AAT Examination Paper 4: Business Economics and Financial Mathematics) Y O Lam, SCOPE, City University of Hong Kong Introduction The most convenient
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers
 IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
Overview. Frequency Distributions. Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data. Descriptive Statistics. Inferential Statistics. Frequency Distribution
 Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data Slide 1 Overview Descriptive Statistics Slide 2 A) Overview B) Frequency Distributions C) Visualizing Data summarize or describe the important characteristics of a
Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data Slide 1 Overview Descriptive Statistics Slide 2 A) Overview B) Frequency Distributions C) Visualizing Data summarize or describe the important characteristics of a
Ms Nurazrin Jupri. Frequency Distributions
 Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I
 UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I Graphical Presentation of Data-I Structure 15.1 Introduction Objectives 15.2 Graphical Presentation 15.3 Types of Graphs Histogram Frequency Polygon Frequency Curve
UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I Graphical Presentation of Data-I Structure 15.1 Introduction Objectives 15.2 Graphical Presentation 15.3 Types of Graphs Histogram Frequency Polygon Frequency Curve
Chapter Two: Descriptive Methods 1/50
 Chapter Two: Descriptive Methods 1/50 2.1 Introduction 2/50 2.1 Introduction We previously said that descriptive statistics is made up of various techniques used to summarize the information contained
Chapter Two: Descriptive Methods 1/50 2.1 Introduction 2/50 2.1 Introduction We previously said that descriptive statistics is made up of various techniques used to summarize the information contained
Measures of Dispersion
 Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data
 Slide 1 Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Slide 2 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Visualizing Data 2-4 Measures of Center 2-5 Measures of Variation 2-6 Measures of Relative
Slide 1 Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Slide 2 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Visualizing Data 2-4 Measures of Center 2-5 Measures of Variation 2-6 Measures of Relative
MAT 142 College Mathematics. Module ST. Statistics. Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015
 MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
MATH 117 Statistical Methods for Management I Chapter Two
 Jubail University College MATH 117 Statistical Methods for Management I Chapter Two There are a wide variety of ways to summarize, organize, and present data: I. Tables 1. Distribution Table (Categorical
Jubail University College MATH 117 Statistical Methods for Management I Chapter Two There are a wide variety of ways to summarize, organize, and present data: I. Tables 1. Distribution Table (Categorical
Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data
 Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data Data recorded in the sequence in which they are collected and before they are processed or ranked are called raw data. Raw data is often difficult to make sense
Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data Data recorded in the sequence in which they are collected and before they are processed or ranked are called raw data. Raw data is often difficult to make sense
At the end of the chapter, you will learn to: Present data in textual form. Construct different types of table and graphs
 DATA PRESENTATION At the end of the chapter, you will learn to: Present data in textual form Construct different types of table and graphs Identify the characteristics of a good table and graph Identify
DATA PRESENTATION At the end of the chapter, you will learn to: Present data in textual form Construct different types of table and graphs Identify the characteristics of a good table and graph Identify
Measures of Central Tendency. A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set.
 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean the sum of all data values divided by the number of values in
Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean the sum of all data values divided by the number of values in
Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
 Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs Chapter 2 Outline Organization of Data Simple Frequency Distributions Grouped Frequency Distributions Graphs
Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs Chapter 2 Outline Organization of Data Simple Frequency Distributions Grouped Frequency Distributions Graphs
Raw Data. Statistics 1/8/2016. Relative Frequency Distribution. Frequency Distributions for Qualitative Data
 Statistics Raw Data Raw data is random and unranked data. Organizing Data Frequency distributions list all the categories and the numbers of elements that belong to each category Frequency Distributions
Statistics Raw Data Raw data is random and unranked data. Organizing Data Frequency distributions list all the categories and the numbers of elements that belong to each category Frequency Distributions
Part I, Chapters 4 & 5. Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures
 Part I, Chapters 4 & 5 Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures Descriptive Statistics 1 Are data points clumped? (order variable / exp. variable) Concentrated around one value? Concentrated
Part I, Chapters 4 & 5 Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures Descriptive Statistics 1 Are data points clumped? (order variable / exp. variable) Concentrated around one value? Concentrated
Measures of Central Tendency
 Page of 6 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean The sum of all data values divided by the number of
Page of 6 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean The sum of all data values divided by the number of
Univariate Statistics Summary
 Further Maths Univariate Statistics Summary Types of Data Data can be classified as categorical or numerical. Categorical data are observations or records that are arranged according to category. For example:
Further Maths Univariate Statistics Summary Types of Data Data can be classified as categorical or numerical. Categorical data are observations or records that are arranged according to category. For example:
Prepare a stem-and-leaf graph for the following data. In your final display, you should arrange the leaves for each stem in increasing order.
 Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
BUSINESS DECISION MAKING. Topic 1 Introduction to Statistical Thinking and Business Decision Making Process; Data Collection and Presentation
 BUSINESS DECISION MAKING Topic 1 Introduction to Statistical Thinking and Business Decision Making Process; Data Collection and Presentation (Chap 1 The Nature of Probability and Statistics) (Chap 2 Frequency
BUSINESS DECISION MAKING Topic 1 Introduction to Statistical Thinking and Business Decision Making Process; Data Collection and Presentation (Chap 1 The Nature of Probability and Statistics) (Chap 2 Frequency
Chapter 2: Descriptive Statistics
 Chapter 2: Descriptive Statistics Student Learning Outcomes By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Display data graphically and interpret graphs: stemplots, histograms and boxplots. Recognize,
Chapter 2: Descriptive Statistics Student Learning Outcomes By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Display data graphically and interpret graphs: stemplots, histograms and boxplots. Recognize,
+ Statistical Methods in
 + Statistical Methods in Practice STA/MTH 3379 + Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Discovering Statistics 2nd Edition
+ Statistical Methods in Practice STA/MTH 3379 + Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Discovering Statistics 2nd Edition
Averages and Variation
 Averages and Variation 3 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-1 Section 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency: Mode, Median, and Mean Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-2 Focus
Averages and Variation 3 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-1 Section 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency: Mode, Median, and Mean Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-2 Focus
Courtesy :
 STATISTICS The Nature of Statistics Introduction Statistics is the science of data Statistics is the science of conducting studies to collect, organize, summarize, analyze, and draw conclusions from data.
STATISTICS The Nature of Statistics Introduction Statistics is the science of data Statistics is the science of conducting studies to collect, organize, summarize, analyze, and draw conclusions from data.
Chapter 2 Organizing and Graphing Data. 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative Data
 Chapter 2 Organizing and Graphing Data 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative Data 2.2 Organizing and Graphing Quantitative Data 2.3 Stem-and-leaf Displays 2.4 Dotplots 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative
Chapter 2 Organizing and Graphing Data 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative Data 2.2 Organizing and Graphing Quantitative Data 2.3 Stem-and-leaf Displays 2.4 Dotplots 2.1 Organizing and Graphing Qualitative
2.3 Organizing Quantitative Data
 2.3 Organizing Quantitative Data This section will focus on ways to organize quantitative data into tables, charts, and graphs. Quantitative data is organized by dividing the observations into classes
2.3 Organizing Quantitative Data This section will focus on ways to organize quantitative data into tables, charts, and graphs. Quantitative data is organized by dividing the observations into classes
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA
 CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
Raw Data is data before it has been arranged in a useful manner or analyzed using statistical techniques.
 Section 2.1 - Introduction Graphs are commonly used to organize, summarize, and analyze collections of data. Using a graph to visually present a data set makes it easy to comprehend and to describe the
Section 2.1 - Introduction Graphs are commonly used to organize, summarize, and analyze collections of data. Using a graph to visually present a data set makes it easy to comprehend and to describe the
ORGANIZING THE DATA IN A FREQUENCY TABLE
 ORGANIZING THE DATA IN A FREQUENCY TABLE Suppose the scores obtained by 5 students on a standardized test are as follows: 68, 55, 61, 55, 43, 59, 55, 58, 77, 6, 56, 53, 58, 7, 57, 62, 5, 69, 44, 63, 48,79,
ORGANIZING THE DATA IN A FREQUENCY TABLE Suppose the scores obtained by 5 students on a standardized test are as follows: 68, 55, 61, 55, 43, 59, 55, 58, 77, 6, 56, 53, 58, 7, 57, 62, 5, 69, 44, 63, 48,79,
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Slide 1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Slide 1 Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Histograms
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Slide 1 Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Histograms
Lesson 18-1 Lesson Lesson 18-1 Lesson Lesson 18-2 Lesson 18-2
 Topic 18 Set A Words survey data Topic 18 Set A Words Lesson 18-1 Lesson 18-1 sample line plot Lesson 18-1 Lesson 18-1 frequency table bar graph Lesson 18-2 Lesson 18-2 Instead of making 2-sided copies
Topic 18 Set A Words survey data Topic 18 Set A Words Lesson 18-1 Lesson 18-1 sample line plot Lesson 18-1 Lesson 18-1 frequency table bar graph Lesson 18-2 Lesson 18-2 Instead of making 2-sided copies
Chapter 2 - Frequency Distributions and Graphs
 1. Which of the following does not need to be done when constructing a frequency distribution? A) select the number of classes desired B) find the range C) make the class width an even number D) use classes
1. Which of the following does not need to be done when constructing a frequency distribution? A) select the number of classes desired B) find the range C) make the class width an even number D) use classes
STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES PART 2 - DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS CHAPTER 3 DESCRIPTIVE MEASURES
 STP 6 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES PART - DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS CHAPTER 3 DESCRIPTIVE MEASURES Chapter covered organizing data into tables, and summarizing data with graphical displays. We will now use
STP 6 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES PART - DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS CHAPTER 3 DESCRIPTIVE MEASURES Chapter covered organizing data into tables, and summarizing data with graphical displays. We will now use
STAT STATISTICAL METHODS. Statistics: The science of using data to make decisions and draw conclusions
 STAT 515 --- STATISTICAL METHODS Statistics: The science of using data to make decisions and draw conclusions Two branches: Descriptive Statistics: The collection and presentation (through graphical and
STAT 515 --- STATISTICAL METHODS Statistics: The science of using data to make decisions and draw conclusions Two branches: Descriptive Statistics: The collection and presentation (through graphical and
McGraw-Hill Ryerson. Data Management 12. Section 5.1 Continuous Random Variables. Continuous Random. Variables
 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Data Management 12 Section Continuous Random I am learning to distinguish between discrete variables and continuous variables work with sample values for situations that can take on
McGraw-Hill Ryerson Data Management 12 Section Continuous Random I am learning to distinguish between discrete variables and continuous variables work with sample values for situations that can take on
2.1 Objectives. Math Chapter 2. Chapter 2. Variable. Categorical Variable EXPLORING DATA WITH GRAPHS AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES
 EXPLORING DATA WITH GRAPHS AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES Chapter 2 2.1 Objectives 2.1 What Are the Types of Data? www.managementscientist.org 1. Know the definitions of a. Variable b. Categorical versus quantitative
EXPLORING DATA WITH GRAPHS AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES Chapter 2 2.1 Objectives 2.1 What Are the Types of Data? www.managementscientist.org 1. Know the definitions of a. Variable b. Categorical versus quantitative
- 1 - Class Intervals
 - 1 - Class Intervals To work with continuous numeric data and to represent it in some sort of a graph or a chart, you have to separate the data into class intervals that is, intervals of equal length.
- 1 - Class Intervals To work with continuous numeric data and to represent it in some sort of a graph or a chart, you have to separate the data into class intervals that is, intervals of equal length.
LESSON 3: CENTRAL TENDENCY
 LESSON 3: CENTRAL TENDENCY Outline Arithmetic mean, median and mode Ungrouped data Grouped data Percentiles, fractiles, and quartiles Ungrouped data Grouped data 1 MEAN Mean is defined as follows: Sum
LESSON 3: CENTRAL TENDENCY Outline Arithmetic mean, median and mode Ungrouped data Grouped data Percentiles, fractiles, and quartiles Ungrouped data Grouped data 1 MEAN Mean is defined as follows: Sum
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 2.1- #
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data 2-1 Review and Preview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Histograms
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data 2-1 Review and Preview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Histograms
Test Bank for Privitera, Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
 1. A simple frequency distribution A) can be used to summarize grouped data B) can be used to summarize ungrouped data C) summarizes the frequency of scores in a given category or range 2. To determine
1. A simple frequency distribution A) can be used to summarize grouped data B) can be used to summarize ungrouped data C) summarizes the frequency of scores in a given category or range 2. To determine
download instant at Summarizing Data: Listing and Grouping
 Ch. 2 download instant at www.easysemester.com Summarizing Data: Listing and Grouping 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Ch. 2 download instant at www.easysemester.com Summarizing Data: Listing and Grouping 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Chapter 2. Descriptive Statistics: Organizing, Displaying and Summarizing Data
 Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics: Organizing, Displaying and Summarizing Data Objectives Student should be able to Organize data Tabulate data into frequency/relative frequency tables Display data graphically
Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics: Organizing, Displaying and Summarizing Data Objectives Student should be able to Organize data Tabulate data into frequency/relative frequency tables Display data graphically
CHAPTER 7- STATISTICS
 CHAPTER 7- STATISTICS 7. MEASURE OF CETRAL TEDECY 7.. Ungrouped Data We have learned how to find mode, median and mean of ungrouped data in Form Three. So this is just a revision for us to remind on it.
CHAPTER 7- STATISTICS 7. MEASURE OF CETRAL TEDECY 7.. Ungrouped Data We have learned how to find mode, median and mean of ungrouped data in Form Three. So this is just a revision for us to remind on it.
MATH1635, Statistics (2)
 MATH1635, Statistics (2) Chapter 2 Histograms and Frequency Distributions I. A Histogram is a form of bar graph in which: A. The width of a bar is designated by an interval or ratio data value and thus
MATH1635, Statistics (2) Chapter 2 Histograms and Frequency Distributions I. A Histogram is a form of bar graph in which: A. The width of a bar is designated by an interval or ratio data value and thus
1.2. Pictorial and Tabular Methods in Descriptive Statistics
 1.2. Pictorial and Tabular Methods in Descriptive Statistics Section Objectives. 1. Stem-and-Leaf displays. 2. Dotplots. 3. Histogram. Types of histogram shapes. Common notation. Sample size n : the number
1.2. Pictorial and Tabular Methods in Descriptive Statistics Section Objectives. 1. Stem-and-Leaf displays. 2. Dotplots. 3. Histogram. Types of histogram shapes. Common notation. Sample size n : the number
4.2 and 4.6 filled in notes.notebook. December 08, Integration. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 4.2 Area Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Use sigma notation to write and evaluate a sum. Understand the concept
4 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 4.2 Area Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Use sigma notation to write and evaluate a sum. Understand the concept
Chapter 2. Frequency Distributions and Graphs. Bluman, Chapter 2
 Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs 1 Chapter 2 Overview Introduction 2-1 Organizing Data 2-2 Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Ogives 2-3 Other Types of Graphs 2 Chapter 2 Objectives 1. Organize
Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs 1 Chapter 2 Overview Introduction 2-1 Organizing Data 2-2 Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Ogives 2-3 Other Types of Graphs 2 Chapter 2 Objectives 1. Organize
Describing Data: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic Presentation
 Describing Data: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic Presentation Chapter 2 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. GOALS 1. Organize
Describing Data: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic Presentation Chapter 2 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. GOALS 1. Organize
Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Graphing Utilities; Introduction to Graphing Equations
 Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Graphing Utilities; Introduction to Graphing Equations origin (x, y) Ordered pair (x-coordinate, y-coordinate) (abscissa, ordinate) x axis Rectangular or
Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Graphing Utilities; Introduction to Graphing Equations origin (x, y) Ordered pair (x-coordinate, y-coordinate) (abscissa, ordinate) x axis Rectangular or
B. Graphing Representation of Data
 B Graphing Representation of Data The second way of displaying data is by use of graphs Although such visual aids are even easier to read than tables, they often do not give the same detail It is essential
B Graphing Representation of Data The second way of displaying data is by use of graphs Although such visual aids are even easier to read than tables, they often do not give the same detail It is essential
Rectangle Sums
 Rectangle Sums --208 You can approximate the area under a curve using rectangles. To do this, divide the base interval into pieces subintervals). Then on each subinterval, build a rectangle that goes up
Rectangle Sums --208 You can approximate the area under a curve using rectangles. To do this, divide the base interval into pieces subintervals). Then on each subinterval, build a rectangle that goes up
BIOL Gradation of a histogram (a) into the normal curve (b)
 (التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
(التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
ENGI 4421 Probability and Statistics Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 1 Descriptive Statistics
 ENGI 44 Probability ad Statistics Faculty of Egieerig ad Applied Sciece Problem Set Descriptive Statistics. If, i the set of values {,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 } a error causes the value 5 to be replaced by 50,
ENGI 44 Probability ad Statistics Faculty of Egieerig ad Applied Sciece Problem Set Descriptive Statistics. If, i the set of values {,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 } a error causes the value 5 to be replaced by 50,
Distributions of random variables
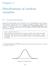 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Use of GeoGebra in teaching about central tendency and spread variability
 CREAT. MATH. INFORM. 21 (2012), No. 1, 57-64 Online version at http://creative-mathematics.ubm.ro/ Print Edition: ISSN 1584-286X Online Edition: ISSN 1843-441X Use of GeoGebra in teaching about central
CREAT. MATH. INFORM. 21 (2012), No. 1, 57-64 Online version at http://creative-mathematics.ubm.ro/ Print Edition: ISSN 1584-286X Online Edition: ISSN 1843-441X Use of GeoGebra in teaching about central
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution. Measures of center and spread. Features of the normal distribution
 Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES. Chapter 2
 EXPLORING DATA WITH GRAPHS AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES Chapter 2 2.1 What Are the Types of Data? 2.1 Objectives www.managementscientist.org 1. Know the definitions of a. Variable b. Categorical versus quantitative
EXPLORING DATA WITH GRAPHS AND NUMERICAL SUMMARIES Chapter 2 2.1 What Are the Types of Data? 2.1 Objectives www.managementscientist.org 1. Know the definitions of a. Variable b. Categorical versus quantitative
Notice that the height of each rectangle is and the width of each rectangle is.
 Math 1410 Worksheet #40: Section 6.3 Name: In some cases, computing the volume of a solid of revolution with cross-sections can be difficult or even impossible. Is there another way to compute volumes
Math 1410 Worksheet #40: Section 6.3 Name: In some cases, computing the volume of a solid of revolution with cross-sections can be difficult or even impossible. Is there another way to compute volumes
The basic arrangement of numeric data is called an ARRAY. Array is the derived data from fundamental data Example :- To store marks of 50 student
 Organizing data Learning Outcome 1. make an array 2. divide the array into class intervals 3. describe the characteristics of a table 4. construct a frequency distribution table 5. constructing a composite
Organizing data Learning Outcome 1. make an array 2. divide the array into class intervals 3. describe the characteristics of a table 4. construct a frequency distribution table 5. constructing a composite
Chapter 2: Frequency Distributions
 Chapter 2: Frequency Distributions Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction to Frequency Distributions 2.2 Frequency Distribution Tables Obtaining ΣX from a Frequency Distribution Table Proportions and Percentages
Chapter 2: Frequency Distributions Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction to Frequency Distributions 2.2 Frequency Distribution Tables Obtaining ΣX from a Frequency Distribution Table Proportions and Percentages
STATISTICS Chapter (1) Introduction
 REFERENCES: 1. Calculus and analytic geometry By Thomas / FINNEY sixth Edition. 2. Advanced engineering mathematics By C.Ray Wylie fifth edition Lovis C. Barrett 3. Mathematical Methods for science students
REFERENCES: 1. Calculus and analytic geometry By Thomas / FINNEY sixth Edition. 2. Advanced engineering mathematics By C.Ray Wylie fifth edition Lovis C. Barrett 3. Mathematical Methods for science students
Density Curve (p52) Density curve is a curve that - is always on or above the horizontal axis.
 1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
TYPES OF NUMBER P1 P2 P3 Learning Objective Understand place value in large numbers Add and subtract large numbers (up to 3 digits) Multiply and
 TYPES OF NUMBER P1 P2 P3 Understand place value in large numbers Add and subtract large numbers (up to 3 digits) Multiply and divide large numbers (up to 3 by 2) Understand positive and negative integers
TYPES OF NUMBER P1 P2 P3 Understand place value in large numbers Add and subtract large numbers (up to 3 digits) Multiply and divide large numbers (up to 3 by 2) Understand positive and negative integers
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Statistical Methods. Instructor: Lingsong Zhang. Any questions, ask me during the office hour, or me, I will answer promptly.
 Statistical Methods Instructor: Lingsong Zhang 1 Issues before Class Statistical Methods Lingsong Zhang Office: Math 544 Email: lingsong@purdue.edu Phone: 765-494-7913 Office Hour: Monday 1:00 pm - 2:00
Statistical Methods Instructor: Lingsong Zhang 1 Issues before Class Statistical Methods Lingsong Zhang Office: Math 544 Email: lingsong@purdue.edu Phone: 765-494-7913 Office Hour: Monday 1:00 pm - 2:00
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
CHAPTER 3: Data Description
 CHAPTER 3: Data Description You ve tabulated and made pretty pictures. Now what numbers do you use to summarize your data? Ch3: Data Description Santorico Page 68 You ll find a link on our website to a
CHAPTER 3: Data Description You ve tabulated and made pretty pictures. Now what numbers do you use to summarize your data? Ch3: Data Description Santorico Page 68 You ll find a link on our website to a
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Frequency Distributions and Graphs
 //05 C H A P T E R T W O s and s and Outline CHAPTER - Organizing Data - Histograms, Polygons, and - Other Types of -4 Paired Data and Scatter Plots Learning Objectives Organize data using a frequency
//05 C H A P T E R T W O s and s and Outline CHAPTER - Organizing Data - Histograms, Polygons, and - Other Types of -4 Paired Data and Scatter Plots Learning Objectives Organize data using a frequency
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
IQR = number. summary: largest. = 2. Upper half: Q3 =
 Step by step box plot Height in centimeters of players on the 003 Women s Worldd Cup soccer team. 157 1611 163 163 164 165 165 165 168 168 168 170 170 170 171 173 173 175 180 180 Determine the 5 number
Step by step box plot Height in centimeters of players on the 003 Women s Worldd Cup soccer team. 157 1611 163 163 164 165 165 165 168 168 168 170 170 170 171 173 173 175 180 180 Determine the 5 number
Section 2-2. Histograms, frequency polygons and ogives. Friday, January 25, 13
 Section 2-2 Histograms, frequency polygons and ogives 1 Histograms 2 Histograms The histogram is a graph that displays the data by using contiguous vertical bars of various heights to represent the frequencies
Section 2-2 Histograms, frequency polygons and ogives 1 Histograms 2 Histograms The histogram is a graph that displays the data by using contiguous vertical bars of various heights to represent the frequencies
Round each observation to the nearest tenth of a cent and draw a stem and leaf plot.
 Warm Up Round each observation to the nearest tenth of a cent and draw a stem and leaf plot. 1. Constructing Frequency Polygons 2. Create Cumulative Frequency and Cumulative Relative Frequency Tables 3.
Warm Up Round each observation to the nearest tenth of a cent and draw a stem and leaf plot. 1. Constructing Frequency Polygons 2. Create Cumulative Frequency and Cumulative Relative Frequency Tables 3.
No. of blue jelly beans No. of bags
 Math 167 Ch5 Review 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 5 EXPLORING DATA DISTRIBUTIONS A sample of jelly bean bags is chosen and the number of blue jelly beans in each bag is counted. The results are shown in
Math 167 Ch5 Review 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 5 EXPLORING DATA DISTRIBUTIONS A sample of jelly bean bags is chosen and the number of blue jelly beans in each bag is counted. The results are shown in
End-of-Module Assessment Task
 Name Date 1. The juice box pictured below is 4 inches high, 3 inches long, and 2 inches wide. a. In the grid above, the distance between grid lines represents one inch. Use the grid paper to sketch the
Name Date 1. The juice box pictured below is 4 inches high, 3 inches long, and 2 inches wide. a. In the grid above, the distance between grid lines represents one inch. Use the grid paper to sketch the
Common Core Vocabulary and Representations
 Vocabulary Description Representation 2-Column Table A two-column table shows the relationship between two values. 5 Group Columns 5 group columns represent 5 more or 5 less. a ten represented as a 5-group
Vocabulary Description Representation 2-Column Table A two-column table shows the relationship between two values. 5 Group Columns 5 group columns represent 5 more or 5 less. a ten represented as a 5-group
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 0580 MATHEMATICS
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 03 series 0580 MATHEMATICS 0580/4 Paper 4 (Extended),
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 03 series 0580 MATHEMATICS 0580/4 Paper 4 (Extended),
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data
 Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data 3.1 Graphs for Quantitative Data (LABEL GRAPHS) August 25, 2014 Histogram (p. 44) - Graph that uses bars to represent different frequencies or relative
Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data 3.1 Graphs for Quantitative Data (LABEL GRAPHS) August 25, 2014 Histogram (p. 44) - Graph that uses bars to represent different frequencies or relative
Decimals should be spoken digit by digit eg 0.34 is Zero (or nought) point three four (NOT thirty four).
 Numeracy Essentials Section 1 Number Skills Reading and writing numbers All numbers should be written correctly. Most pupils are able to read, write and say numbers up to a thousand, but often have difficulty
Numeracy Essentials Section 1 Number Skills Reading and writing numbers All numbers should be written correctly. Most pupils are able to read, write and say numbers up to a thousand, but often have difficulty
Chapter 2: Graphical Summaries of Data 2.1 Graphical Summaries for Qualitative Data. Frequency: Frequency distribution:
 Chapter 2: Graphical Summaries of Data 2.1 Graphical Summaries for Qualitative Data Frequency: Frequency distribution: Example 2.1 The following are survey results from Fall 2014 Statistics class regarding
Chapter 2: Graphical Summaries of Data 2.1 Graphical Summaries for Qualitative Data Frequency: Frequency distribution: Example 2.1 The following are survey results from Fall 2014 Statistics class regarding
Expression and Equations
 7 CHAPTER Expression and Equations Basic Concepts In algebra, letters are used as variables. A variable can assume values of numbers. Numbers are called constants. Math Note: In some cases, a letter may
7 CHAPTER Expression and Equations Basic Concepts In algebra, letters are used as variables. A variable can assume values of numbers. Numbers are called constants. Math Note: In some cases, a letter may
Chapter 2: Understanding Data Distributions with Tables and Graphs
 Test Bank Chapter 2: Understanding Data with Tables and Graphs Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following would best depict nominal level data? a. pie chart b. line graph c. histogram d. polygon Ans: A
Test Bank Chapter 2: Understanding Data with Tables and Graphs Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following would best depict nominal level data? a. pie chart b. line graph c. histogram d. polygon Ans: A
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Intermediate Statistics
 Gait Learig Guides Itermediate Statistics Data processig & display, Cetral tedecy Author: Raghu M.D. STATISTICS DATA PROCESSING AND DISPLAY Statistics is the study of data or umerical facts of differet
Gait Learig Guides Itermediate Statistics Data processig & display, Cetral tedecy Author: Raghu M.D. STATISTICS DATA PROCESSING AND DISPLAY Statistics is the study of data or umerical facts of differet
15 Wyner Statistics Fall 2013
 15 Wyner Statistics Fall 2013 CHAPTER THREE: CENTRAL TENDENCY AND VARIATION Summary, Terms, and Objectives The two most important aspects of a numerical data set are its central tendencies and its variation.
15 Wyner Statistics Fall 2013 CHAPTER THREE: CENTRAL TENDENCY AND VARIATION Summary, Terms, and Objectives The two most important aspects of a numerical data set are its central tendencies and its variation.
Table of Contents (As covered from textbook)
 Table of Contents (As covered from textbook) Ch 1 Data and Decisions Ch 2 Displaying and Describing Categorical Data Ch 3 Displaying and Describing Quantitative Data Ch 4 Correlation and Linear Regression
Table of Contents (As covered from textbook) Ch 1 Data and Decisions Ch 2 Displaying and Describing Categorical Data Ch 3 Displaying and Describing Quantitative Data Ch 4 Correlation and Linear Regression
STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES
 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES PART 2 - DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS CHAPTER 2 ORGANIZING DATA Descriptive Statistics - include methods for organizing and summarizing information clearly and effectively. - classify
ELEMENTARY STATISTICS NOTES PART 2 - DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS CHAPTER 2 ORGANIZING DATA Descriptive Statistics - include methods for organizing and summarizing information clearly and effectively. - classify
Learning Objectives. Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution. Continuous Random Variable
 Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
