PHYS 450 Spring semester Lecture 04: Refraction of Light and Lenses. Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University
|
|
|
- Joseph Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYS 450 Sprng semester 07 Lecture 04: Reractn Lght and es Rn Reenberger Brck Nantechnlgy Center Purdue Unversty Lecture 04 es - Hstrcal Cntext A cmmnly used ptcal phenmena s reractn. Reractn es Nmrud lens rm ancent Assyra dates t ~750 B.C. Greeks and Rmans use burnng glasses, water lled sphercal bwls, presumably t gnte a lame by cusng the sun s rays. Ibn Sahl (c. 984), an Iraq mathematcan, dscvers Snell s law reractn. Readng stnes used t read manuscrpts durng the th thru 3 th centures. Prmtve plan-cnvex lenses presumably made by cuttng a glass sphere n hal. In 84, D'Armate (Italy) s credted n the western wrld wth nventng the rst wearable eye glasses. ~300 years later - understandng the physcs reractn leads t prmtve ptcal nstruments mcrscpe & telescpe - n the early 600s. A B C CREDITS: A. Nmrud lens (Assyra, crca 750 BC) B. Vsby lens (Sweeden, crca 50 AD C. Galle s bjectve lens n rnate rame (Italy, crca 677 AD)
2 Interactn EM radatn wth matter a) I b) R A T Des EM radatn (lght) travel slwer r aster n a materal? n=c/v c= speed lght n vacuum (ar) v=speed lght n a materal I(W/m ) = R + T + A (cnservatn energy) Three regmes: RI, mrrrs AI, lters and absrbers TI, lenses, wndws materal n glass.5 water.33 damnd.4 3 A smple experment establshes a mathematcal relatnshp between the angle ncdence and the angle reractn. Reractn Lght: ONE Planar Interace Reractn s the change n the drectn a lght ray when passng rm ne medum t anther Data r R=0 cm: x (ptcally transparent) ❶ R θ, AIR θ, WATER x x x /x Tp Vew x AVERAGE.3 Experment shws that cnstant n x ndex x reractn (n) 4
3 Snell s Law (6) * Cnventn: lght ges rm NOTES: Reserve the wrd bendng r reractn. Subscrpt ntatn (rm nt ) nsnθ =n snθ r nsnθ r =n snθ (n reractn when = r = 0) ❶ Key Idea: An nterace changes the drectn lght by reractn * Reprted by Ibn Sahl, Baghdad n 984 AD, re-dscvered by Descartes n France n 637, etc. 5 Relatng the reractve ndex t the speed lght (Fcault n 850 establshes that EM radatn (lght) travels slwer n a materal than n ar) ❶ speed wave = ❶ sn AD sn n AD n n n n nv nv v n v n n One clck I lght bends at the nterace between tw meda, then the speed lght must change at the nterace. Explans Snell's law by cnnectng the medum's ndex reractn t the speed lght. 6 3
4 Imagng Systems What magng system wll take lght rm a pnt surce and cause t t cnverge at sme ther pnt n space? Or, hw d yu cnvert a dvergng sphercal wave t a cnvergng sphercal wave? Ray s bent thrugh y Imagng System Ray bendng must be prprtnal t dstance rm ptc axs. 7 Bendng prprtnal t dstance rm ptc axs: r y y s s y s s O What Happens at a Nn-Planar Interace? Ray Ray (rm=) (nt=) θ ❶ A y β V θ r R n n ζ C I s s Trangle OAC: θ =+β Trangle IAC: β=θ r +ζ Fr small angles, sn, etc. a) Snell s Law: n θ = n θ r b) β= n /n (θ )+ ζ c) β= n /n (+β) + ζ d) n + n ζ=(n n )β n n n n =AV/s β=av/r ζ=av/s s s R Key Result 8 4
5 Reractn at Tw Curved Interaces s Even Mre Interestng Snell s Law θ Incdent Ray Nrmal lne θ r Incdent Ray Fcal Pnt Nrmal lne Fcal Pnt Reractn lght rays by a cnvergng lens Reractn lght rays by a dvergng lens 9 Systematcally apply result rm slde 7 O Maker s Frmula r Thn es ❶ A A Ray θ θr ❶ C β ζ O Ray V C V R R ar n = n =n ar n =n n = I s st surace at A n n n n s s R n n n R R n n s s R enrce sgn cnventn, the symbl s ' s s' s nw treated as a pstve number n n Eq. I s s ' R s t nd surace at A n n n n s s R n n n s ts ' R R n n t s ' s R Eq. II s 0 5
6 Man Result Thck Dstances are measured rm the hypthetcal prncpal planes H and H. The mage and bject dstance shuld be measured rm the prncple planes, NOT the center the lens. thck lens :, and are calculated quanttes. and are pstve when H and H are t rght vertex V and V s s ' s ' s ' ' OR s ater ~0 pgs. algebra ar H H s n t n ' R R n RR Nte: Typ n Lab Manual, pg. 5, Fg. V V s ' n s t Nte: Typ n Lab Manual, pg. 5, Fg. n t ' nr n t ' nr THIN lens equatn st surace at A (same as bere) n n n n s s R n n n R R n n s s R enrce sgn cnventn, the symbl s ' s s' s nw treated as a pstve number n n Eq. I s s ' R nd surace at A (same as bere) n n n n s s R n n n s ts ' R R n n t s ' s R Eq. II In EqII. Let t s ', s, R, R. n n s ' s R n n s ' R s Addng Eq. I and Eq. II : n s s R R n R R s s Eq. II Eq. I 6
7 Man Result Thn Image and bject dstance measured rm centerlne lens. thn lens ar n s s n R R centerlne s s Gaussan Optcs 3 Many Types es (cmpare t mrrrs) Mrrrs es st surace Cncave Mrrr Cnvergng nd surace Tw () ndces requred t dene the tw suraces Cnvex Mrrr Dvergng 4 7
8 Sgn Cnventns r Radus Curvature I vertex lens surace s let the center curvature, the radus curvature s treated as a pstve number. lght ray I vertex the lens surace s rght the center curvature, the radus curvature s treated as a negatve number. lght ray V Pstve R Negatve R V st surace C C nd surace lght ray Pstve R lght ray Negatve R V V nd surace C C st surace Smple Rule: The radus curvature s a pstve number the lens vertex s t the let ts center curvature. 5 Vcabulary es An magnary lne passng thrugh the exact center the lens. Ths magnary lne s knwn as the prncpal axs. A lens als has an magnary vertcal axs that bsects the lens. Lght rays ncdent n ether sde the lens parallel t the prncpal axs wll ether cnverge r dverge. Fr a cnvergng lens, lght rays parallel t the prncpal axs wll cnverge t a pnt. Ths pnt s knwn as the cal pnt the cnvergng lens. 6 8
9 Fr a dvergng lens, parallel lght rays dverge and can be traced backwards untl they ntersect at a pnt. Ths ntersectn pnt s knwn as the cal pnt a dvergng lens. The cal pnt s dented by the letter F n dagrams. The actn a lens s symmetrc. Ths means each lens has tw cal pnts - neneachsdethelens. Fr a thn lens, the dstance rm the center lens t the cal pnt s knwn as the cal length (represented by ). Each lens has a specal pnt called the F pnt. Ths s the pnt n the prncpal axs that s twce the dstance the cal pnt rm the vertcal axs. 7 Image rmatn Three predctable lght rays. Parallel ray. Che ray 3. Fcal ray Dene, s and s s s An mage s rmed because lght relected rm a pnt n the bject s bserved n matter where the eye s pstned. 8 9
10 THIN lens equatn Hw t keep t all straght? LINEAR lateral magncatn, used when mage s vewed n a screen Sgn Cnventns + = (derent textbks may use derent cnventns) h s s s Same equatns as r curved mrrrs m= =- h s Quantty Symbl* Sgn Cnventn Fcal Length I pstve Cnvergng I negatve Dvergng Image Dstance s I pstve I negatve Object Dstance s I pstve Lateral Magncatn *each symbl can be assgned ether + r - value m I negatve I pstve I negatve In rnt lens (real) Behnd lens (vrtual) In rnt lens (real) Behnd lens (vrtual) Image uprght Image nverted I pstve Image uprght Image Heght h I negatve Image nverted R pstve R R +R -R R negatve n R R Be able t dstngush between Real and Vrtual mages 9 Calculate rm gemetry Measure R, R usng sphermeter Measure lens thckness usng lng-arm calpers s t lens h R Calculate thck and thn lens values r 0 0
11 Specal Case: rm Dstant Object - Cnvergng ruler s s s.... s = mage h bject h Cnvergng Screen Specal Case: rm Dstant Object - Dvergng Dstant lght s.... s s Rm must be dark Pnt bject D D d Mve untl d=d Dvergng Screen
12 Ray Tracng; parallel rays usng a laser WARNING: A class 3R laser wll be used n the llwng experments. Practce laser saety. Tp vew, lkng dwn laser Mve lens Ntecard Repeat usng a dvergng lens. 3 Laser Saety WARNING: A class 3R laser wll be used n the llwng experments. Practce laser saety. When yu see ths warnng, yu shuld nstnctvely llw the laser saety prtcls lsted belw NEVER put yursel nt any pstn where yur eyes apprach the axs a laser beam (even wth eye prtectn n). Keep laser beam paths belw r abve a standng r sttng eye level. D nt drect beam paths twards ther peple. D nt deeat the nterlcks n laser husngs. Elmnate all relectve materal (ncludng jewelry) rm the vcnty the beam paths. Never use vewng nstruments t lk drectly nt a laser beam r ts specular relectn. I ths s necessary, nstall an apprprate lter r pece rsted glass nt the ptcal element assembly. Keep ambent lght levels as hgh as peratns wll permt. Termnate laser beams at the end ther useul path wth mmvable, nn-specular, beam stps r targets. D nt allw pen beams t crss asle ways. Chse target materals that partally absrb the laser beam. Termnate all unused beams. 4
13 Tw pstn methd: r cnvergng lens h bject Illumnated Object Cnvergng L s s s s a Mve (nterchange s and s ) h mage Screen s s s s L s' s' s s' a but s s ' as s L a Ls as s L a s La La L a 4L 5 Tw pstn methd: r dvergng lens Step s s = m bject h h mage s s c c Illumnated Object Cnvergng Screen 6 3
14 INSERT Dvergng at dstance x rm llumnated bject Step s s bject h x Vrtual mage d mage dsappears x x d BUT s s c mve x Illumnated Object Dvergng Cnvergng Screen 7 Step 3 Mve bject untl vrtual mage cncdes wth rgnal bject pstn: mage reappears s s x h bject New pstn x cused mage reappears WHEN x x d THEN s s c Illumnated Object Dvergng Cnvergng Screen Result des nt depend n c 8 4
15 Example st surace V ar n = Thn R C n R R.5 0 cm 0 cm cm 0.0 cm C t n=.5 R nd surace V ar n = Let: n=.5 t= cm R =+0 cm R =-0 cm Thck n t n ' R R n RR.5 cm.5 0 cm 0 cm.5 0 cm 0 cm cm 50 cm 0.5 cm cm 0cm 50cm ' 0.7 cm Thck lens calculatr at tls/cal length n t' n R cm.5 0 n t' n R cm Results: Thck vs. Thn (nt t scale) =0.0 cm t=.0 cm ar n= cm 9.83 cm δ =0.339 cm δ =0.339 cm =0.7 cm 30 5
16 Image Lcatn by Ray Tracng Parallel-ray Methd (emphass n rays parallel t ptcal axs) Oblque-ray Methd ❹ ❸ O ❹ ❺ ❻ I ❼ ❶ O ❸ ❺ (parallel t ❸) ❶ I ❻ 3 Demnstratn: Oblque-ray Methd ❹ O ❸ ❺ (parallel t ❸) ❶ I ❻ One clck 3 6
17 Implcatn - Fcusng Parallel Lght cal plane + -s s =-tan - +s cal plane 33 5 mage at Object-Image Lcatns r a Cnvex : Systematc Summary mages 6 Object can be lcated n any ne THREE regns r at TWO specal pnts 7 Cnvex lens Derent bject lcatns are drawn n red and labeled wth a number; the crrespndng mage lcatns are drawn n blue and labeled wth the dentcal number F F F real bject, s pstve F 3 mages 4 s pstve, s negatve s pstve, s pstve Vrtual mage Real mage 34 7
18 Dvergng : Systematc Summary bject lcatns mage lcatns s pstve, s negatve real bject, s pstve As bject dstance decreases, mage dstance decreases and mage sze ncreases. Vrtual mage 35 Run Smulatns A screen s ten placed at the mage lcatn t vew a sharp mage. The screen s NOT shwn n ray dagrams
19 Crrectns, Aberratns and Dstrtns (aberratns mx nrmatn tgether t create mage blur, dstrtns msplace nrmatn gemetrcally) Eect Descrptn Result Eect Descrptn Result Fcal length Chrmatc aberratn Feld Curvature t, lens thckness cal length depends n because n=() lss dentn at edge mage due t curved cal plane n t n R R n RR Pn Cushn dstrtn (pstve) Sphercal aberratn Cma magncatn vares wth ray lcatn parallel rays have derent cal pnts dependng n dstance rm ptcal axs -axs rays have derent cal pnts dependng n dstance rm ptcal axs Barrel dstrtn (negatve) magncatn vares wth ray lcatn Astgmatsm rays thrugh dameters S and T have derent cal pnts 37 Up Next Magners, Mcrscpes and Telescpes Wrth a lk: The Rchester Clak at
Focal Points of Spherical Mirrors. Spherical Mirrors. A plane mirror is a spherical mirror with an infinite radius of curvature. O Height = I Height
 Radus f Curvature Plane Mrrr A plane mrrr s a sphercal mrrr wth an nfnte radus f curvature. O Heght = I Heght phercal Mrrrs Cncave Mrrr: (e.g. make up mrrr) Center f curvature s n frnt f mrrr Feld f vew
Radus f Curvature Plane Mrrr A plane mrrr s a sphercal mrrr wth an nfnte radus f curvature. O Heght = I Heght phercal Mrrrs Cncave Mrrr: (e.g. make up mrrr) Center f curvature s n frnt f mrrr Feld f vew
Physics 1502: Lecture 29 Today s Agenda
 Physcs 1502: Lecture 29 Tday s Agenda Annuncements: Mdterm 2: Mnday Nv. 16 Hmewrk 08: due Frday Optcs Index f Refractn 1 Prsms Enterng Extng 1 3 4 2 Fr ar/glass nterface, we use n(ar)=1, n(glass)=n LIKE
Physcs 1502: Lecture 29 Tday s Agenda Annuncements: Mdterm 2: Mnday Nv. 16 Hmewrk 08: due Frday Optcs Index f Refractn 1 Prsms Enterng Extng 1 3 4 2 Fr ar/glass nterface, we use n(ar)=1, n(glass)=n LIKE
1 1 1 f R1 R s s f. SPH3UW Unit 7.6 Convex Lenses Page 1 of 9. Notes. Properties of a Converging Lens
 SPH3UW Unt 7.6 Cnvex Lene Page 1 9 Nte Phyc Tl bx Thn Len an ptcal ytem wth tw reractng urace. The mt mplet thn len cntan tw phercal urace that are cle enugh tgether that we can neglect the dtance between
SPH3UW Unt 7.6 Cnvex Lene Page 1 9 Nte Phyc Tl bx Thn Len an ptcal ytem wth tw reractng urace. The mt mplet thn len cntan tw phercal urace that are cle enugh tgether that we can neglect the dtance between
PHYS 219 Spring semester Lecture 20: Reflection of Electromagnetic Radiation: Mirrors and Images Formed by Mirrors
 PHYS 219 Sprng semester 2014 Lecture 20: eflecton of Electromagnetc adaton: Mrrors and Images Formed by Mrrors on efenberger Brck Nanotechnology Center Purdue Unversty Lecture 20 1 evew: Snapshot of an
PHYS 219 Sprng semester 2014 Lecture 20: eflecton of Electromagnetc adaton: Mrrors and Images Formed by Mrrors on efenberger Brck Nanotechnology Center Purdue Unversty Lecture 20 1 evew: Snapshot of an
Physics 1502: Lecture 30 Today s Agenda
 Pyscs 1502: Lecture 30 Tday s Agenda Annuncements: Mdterm 2: Mnday Nv. 16 Hmewrk 08: due Frday Optcs Mrrrs Lenses Eye R- R & -R f 1 Te Mrrr Equatn We wll nw transfrm te gemetrc drawngs nt algebrac equatns:
Pyscs 1502: Lecture 30 Tday s Agenda Annuncements: Mdterm 2: Mnday Nv. 16 Hmewrk 08: due Frday Optcs Mrrrs Lenses Eye R- R & -R f 1 Te Mrrr Equatn We wll nw transfrm te gemetrc drawngs nt algebrac equatns:
Lecture #5.3 Mirrors
 Lecture #5.3 Mrrrs We ave already dscussed reflectn f EM waves. Ts penmenn fnds useful applcatn n te devces we use n ur everyday lfe. Tday we sall talk abut w reflectn wrks n rder t prduce mages n dfferent
Lecture #5.3 Mrrrs We ave already dscussed reflectn f EM waves. Ts penmenn fnds useful applcatn n te devces we use n ur everyday lfe. Tday we sall talk abut w reflectn wrks n rder t prduce mages n dfferent
Lab 1: Don t Shatter My Image. Reflection and Mirrors. Lab 2: Images The Law of Reflection. Three types of mirrors. Plane Mirror Images
 Lab : Dn t Shatter My Image Reflectn and Mrrrs The angle f ncdence equals the angle f reflectn. A plane mrrr results n a vrtual mage (lcated behnd the mrrr). The dstance frm the bject t the mrrr s equal
Lab : Dn t Shatter My Image Reflectn and Mrrrs The angle f ncdence equals the angle f reflectn. A plane mrrr results n a vrtual mage (lcated behnd the mrrr). The dstance frm the bject t the mrrr s equal
Lab 1: Don t Shatter My Image. Reflection and Mirrors. Three types of mirrors. Lab 2: Images The Law of Reflection. Plane Mirror Images
 Lab : Dn t Shatter My Image Reflectn and Mrrrs The angle f ncdence equals the angle f reflectn. A plane mrrr results n a vrtual mage (lcated behnd the mrrr). The dstance frm the bject t the mrrr s equal
Lab : Dn t Shatter My Image Reflectn and Mrrrs The angle f ncdence equals the angle f reflectn. A plane mrrr results n a vrtual mage (lcated behnd the mrrr). The dstance frm the bject t the mrrr s equal
d is taken as negative if the image appears on the same side of the lens as the object (virtual image). Then, if m is
 Page 5 Applcatns: Lens cmbnatns, the escrptn mages, the magner, the cmpun mcrscpe an telescpes Equpment Lst The Telescpe an the crscpe Gemetrc Lens Set Vewng Screen etrc Ruler Basc Optcs Lght Surce -m
Page 5 Applcatns: Lens cmbnatns, the escrptn mages, the magner, the cmpun mcrscpe an telescpes Equpment Lst The Telescpe an the crscpe Gemetrc Lens Set Vewng Screen etrc Ruler Basc Optcs Lght Surce -m
Slide 1 SPH3UW: OPTICS I. Slide 2. Slide 3. Introduction to Mirrors. Light incident on an object
 Slde 1 SPH3UW: OPTICS I Introducton to Mrrors Slde 2 Lght ncdent on an object Absorpton Relecton (bounces)** See t Mrrors Reracton (bends) Lenses Oten some o each Everythng true or wavelengths
Slde 1 SPH3UW: OPTICS I Introducton to Mrrors Slde 2 Lght ncdent on an object Absorpton Relecton (bounces)** See t Mrrors Reracton (bends) Lenses Oten some o each Everythng true or wavelengths
Lab 2. Thin lenses and optical instruments
 PHYS47 Lab 2. Thn lenses and ptcal nstruents J. Jaes Jun 2007 January 25 Gal T bserve the peratn f thn lenses T gan erence wth the placeent and algnent f ptcal cpnents T exane and easure real and vrtual
PHYS47 Lab 2. Thn lenses and ptcal nstruents J. Jaes Jun 2007 January 25 Gal T bserve the peratn f thn lenses T gan erence wth the placeent and algnent f ptcal cpnents T exane and easure real and vrtual
Ray Optics (or Geometrical Optics)
 Optcs-1 Ray Optcs (r Gemetrcal Optcs) In many crcumstances, we can gnre te wave nature lgt an assume tat lgt s a stream partcles tat travel n stragt lnes calle rays. Fr nstance, a lgt wave rm a pnt surce
Optcs-1 Ray Optcs (r Gemetrcal Optcs) In many crcumstances, we can gnre te wave nature lgt an assume tat lgt s a stream partcles tat travel n stragt lnes calle rays. Fr nstance, a lgt wave rm a pnt surce
Chapter 25 The Reflection of Light: Mirrors
 Chapter 25 The Reflectn f Lght: Mrrrs Chapter 25 THE REFLECTION OF LIGHT: MIRRORS PREVIEW The ray mel f lght states that lght may be represente by a straght lne alng the rectn f mtn, an ray ptcs s the
Chapter 25 The Reflectn f Lght: Mrrrs Chapter 25 THE REFLECTION OF LIGHT: MIRRORS PREVIEW The ray mel f lght states that lght may be represente by a straght lne alng the rectn f mtn, an ray ptcs s the
R s s f. m y s. SPH3UW Unit 7.3 Spherical Concave Mirrors Page 1 of 12. Notes
 SPH3UW Unt 7.3 Sphercal Concave Mrrors Page 1 of 1 Notes Physcs Tool box Concave Mrror If the reflectng surface takes place on the nner surface of the sphercal shape so that the centre of the mrror bulges
SPH3UW Unt 7.3 Sphercal Concave Mrrors Page 1 of 1 Notes Physcs Tool box Concave Mrror If the reflectng surface takes place on the nner surface of the sphercal shape so that the centre of the mrror bulges
Physics 132 4/24/17. April 24, 2017 Physics 132 Prof. E. F. Redish. Outline
 Aprl 24, 2017 Physcs 132 Prof. E. F. Redsh Theme Musc: Justn Tmberlake Mrrors Cartoon: Gary Larson The Far Sde 1 Outlne Images produced by a curved mrror Image equatons for a curved mrror Lght n dense
Aprl 24, 2017 Physcs 132 Prof. E. F. Redsh Theme Musc: Justn Tmberlake Mrrors Cartoon: Gary Larson The Far Sde 1 Outlne Images produced by a curved mrror Image equatons for a curved mrror Lght n dense
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE. RAY MODEL OF LIGHT REFLECTION and REFRACTION DISPERSION IMAGE FORMATION: MIRRORS and LENSES
 HSC PHYSICS ONLINE WAVES RAY MODEL OF LIGHT REFLECTION and REFRACTION DISPERSION IMAGE FORMATION: MIRRORS and LENSES A great deal f evdence suggests that lght s a wave and under a wde range f crcumstances,
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE WAVES RAY MODEL OF LIGHT REFLECTION and REFRACTION DISPERSION IMAGE FORMATION: MIRRORS and LENSES A great deal f evdence suggests that lght s a wave and under a wde range f crcumstances,
n 2 tan Brewster s law When the incident angle is equal to
 26.4 Plarzatn an the Relectn an Reractn Lght Brewster s law When the ncent angle s equal t θ B tan (a) The relecte ray s perpencular t the reracte ray (b) The relecte ray s cmpletely plarze n the hrzntal
26.4 Plarzatn an the Relectn an Reractn Lght Brewster s law When the ncent angle s equal t θ B tan (a) The relecte ray s perpencular t the reracte ray (b) The relecte ray s cmpletely plarze n the hrzntal
TEST-05 TOPIC: OPTICS COMPLETE
 Q. A boy s walkng under an nclned mrror at a constant velocty V m/s along the x-axs as shown n fgure. If the mrror s nclned at an angle wth the horzontal then what s the velocty of the mage? Y V sn + V
Q. A boy s walkng under an nclned mrror at a constant velocty V m/s along the x-axs as shown n fgure. If the mrror s nclned at an angle wth the horzontal then what s the velocty of the mage? Y V sn + V
REFRACTION. a. To study the refraction of light from plane surfaces. b. To determine the index of refraction for Acrylic and Water.
 Purpose Theory REFRACTION a. To study the refracton of lght from plane surfaces. b. To determne the ndex of refracton for Acrylc and Water. When a ray of lght passes from one medum nto another one of dfferent
Purpose Theory REFRACTION a. To study the refracton of lght from plane surfaces. b. To determne the ndex of refracton for Acrylc and Water. When a ray of lght passes from one medum nto another one of dfferent
PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1
![PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1 PROBLEM 1-10 points. [ ] n 1 >n 2 >n 3 [ ] n 1 >n 3 >n 2 [ ] n 2 >n 1 >n 3 [ X ] n 2 >n 3 >n 1 [ ] n 3 >n 1 >n 2 [ ] n 3 >n 2 >n 1](/thumbs/75/72776054.jpg) PROBLEM - 0 pints [5 pints] (a) Three media are placed n tp f ne anther. A ray f light starting in medium experiences ttal internal reflectin at the tp interface but sme f the light refracts int medium
PROBLEM - 0 pints [5 pints] (a) Three media are placed n tp f ne anther. A ray f light starting in medium experiences ttal internal reflectin at the tp interface but sme f the light refracts int medium
24-4 Image Formation by Thin Lenses
 24-4 Image Frmatin by Thin Lenses Lenses, which are imprtant fr crrecting visin, fr micrscpes, and fr many telescpes, rely n the refractin f light t frm images. As with mirrrs, we draw ray agrams t help
24-4 Image Frmatin by Thin Lenses Lenses, which are imprtant fr crrecting visin, fr micrscpes, and fr many telescpes, rely n the refractin f light t frm images. As with mirrrs, we draw ray agrams t help
Edexcel GCSE Physics
 Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 5: Light and the Electrmagnetic Spectrum Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin Ray Diagrams (Physics nly) - Arrws shw directin f light travelling - The nrmal
Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 5: Light and the Electrmagnetic Spectrum Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin Ray Diagrams (Physics nly) - Arrws shw directin f light travelling - The nrmal
1. Answer the following. a. A beam of vertically polarized light of intensity W/m2 encounters two polarizing filters as shown below.
 1. Answer the followng. a. A beam of vertcally lght of ntensty 160.0 W/m2 encounters two polarzng flters as shown below. Vertcally ncdent tu-
1. Answer the followng. a. A beam of vertcally lght of ntensty 160.0 W/m2 encounters two polarzng flters as shown below. Vertcally ncdent tu-
Phys 233 Day 13, O3: Ray Optics & Lenses 1 RE-O3
 Pys 233 Day 3, O3: Ray Optcs & Lenses Turs. 0/25 O3: Lenses RE-O3 Mn., 0/29 Tues. 0/30 Turs. / O4 Opt ystems L7: Mrrrs & analyss, O3 O5 Instruments HW8: O: 4; O2: 7, 8; O3: 4, 8 RE-O4 PL7; Quz 6: O, O2,
Pys 233 Day 3, O3: Ray Optcs & Lenses Turs. 0/25 O3: Lenses RE-O3 Mn., 0/29 Tues. 0/30 Turs. / O4 Opt ystems L7: Mrrrs & analyss, O3 O5 Instruments HW8: O: 4; O2: 7, 8; O3: 4, 8 RE-O4 PL7; Quz 6: O, O2,
Light : Reflection And Refraction (Part I Reflection)
 1 Light : Reflectin And Refractin (Part I Reflectin) Light is a frm f energy which enables us t see bjects either frm which it cmes r frm which it is reflected. Luminus bjects are thse bjects which emit
1 Light : Reflectin And Refractin (Part I Reflectin) Light is a frm f energy which enables us t see bjects either frm which it cmes r frm which it is reflected. Luminus bjects are thse bjects which emit
The image is therefore to the left of the lens, virtual, erect, and one-third the size of the object.
 Example ch4: EXAMPLE I: I an bject lcate 6.0 cm n rnt a len cal length + 0.0 cm, where wll the mage be rme? SOLUTION The gven quantte are = + 6.0cm, an = + 0.0cm, whle the unknwn quantte are ' an m. The
Example ch4: EXAMPLE I: I an bject lcate 6.0 cm n rnt a len cal length + 0.0 cm, where wll the mage be rme? SOLUTION The gven quantte are = + 6.0cm, an = + 0.0cm, whle the unknwn quantte are ' an m. The
23-1 The Ray Model of Light
 23-1 The Ray Mdel f Light We will start ur investigatin f gemetrical ptics (ptics based n the gemetry f similar triangles) by learning the basics f the ray mdel f light. We will then apply this mdel t
23-1 The Ray Mdel f Light We will start ur investigatin f gemetrical ptics (ptics based n the gemetry f similar triangles) by learning the basics f the ray mdel f light. We will then apply this mdel t
h o h d Angular magnification Angular magnification of a magnifying glass
 6. Angular Magniicatin an the Magniying Glass Angular magniicatin M θ The reerence angular size θ is base n nrmal reaing/viewing at istance N (either ~5 cm r the near pint istance): θ θ h N The magniie
6. Angular Magniicatin an the Magniying Glass Angular magniicatin M θ The reerence angular size θ is base n nrmal reaing/viewing at istance N (either ~5 cm r the near pint istance): θ θ h N The magniie
11/9/ Chapter 26 The Refraction of Light. Snell S Law The Index of Refraction Snell s Law and the Refraction of Light
 /9/00 Chapter 6 The Reract Lght 6. The Iex Reract 8 Lght travels thrugh a vacuum at a spee, c 3.000 m s Lght travels thrugh materals at a spee, v < c. DEFINITION OF THE INDEX OF REFRACTION The ex reract
/9/00 Chapter 6 The Reract Lght 6. The Iex Reract 8 Lght travels thrugh a vacuum at a spee, c 3.000 m s Lght travels thrugh materals at a spee, v < c. DEFINITION OF THE INDEX OF REFRACTION The ex reract
Sign Conventions. Sign Conventions. Physics Waves & Oscillations 3/25/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones. Convex surface: Concave surface:
 Physics 400 Waves & Oscillatins Lecture 8 Gemetric Optics Spring 06 Semester Matthew Jnes Sign Cnventins > + = Cnvex surface: is psitive fr bjects n the incident-light side is psitive fr images n the refracted-light
Physics 400 Waves & Oscillatins Lecture 8 Gemetric Optics Spring 06 Semester Matthew Jnes Sign Cnventins > + = Cnvex surface: is psitive fr bjects n the incident-light side is psitive fr images n the refracted-light
Chapter 26: Geometrical Optics
 Answers to Even-Numbered Conceptual Questons 2. Three mages are formed of object B. One extends from ( 3 m, 1 m) to ( 3 m, 2 m) to ( 4 m, 2 m). Another mage forms an L from (3 m, 1 m) to (3 m, 2 m) to
Answers to Even-Numbered Conceptual Questons 2. Three mages are formed of object B. One extends from ( 3 m, 1 m) to ( 3 m, 2 m) to ( 4 m, 2 m). Another mage forms an L from (3 m, 1 m) to (3 m, 2 m) to
Using the Swiftpage Connect List Manager
 Quick Start Guide T: Using the Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager The Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager can be used t imprt yur cntacts, mdify cntact infrmatin, create grups ut f thse cntacts, filter yur cntacts
Quick Start Guide T: Using the Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager The Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager can be used t imprt yur cntacts, mdify cntact infrmatin, create grups ut f thse cntacts, filter yur cntacts
Refraction Ray Normal
 Ray Nomal wave cests θ Bounday θ θ θ less dense, n1 moe dense, n2 (>n1) Moe Smply: θ θ Note: (Lght) Rays bend towads the nomal when gong fom a egon of low ndex of efacton to a egon of hgh ndex of efacton
Ray Nomal wave cests θ Bounday θ θ θ less dense, n1 moe dense, n2 (>n1) Moe Smply: θ θ Note: (Lght) Rays bend towads the nomal when gong fom a egon of low ndex of efacton to a egon of hgh ndex of efacton
PHYS 219 Spring semester Lecture 19: Mirrors. Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University
 PHYS 219 Spring semester 2016 Lecture 19: Mirrors Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University PHYS 219 Test II Wednesday; March 30, 2016 6:30 PM PHYS 203 Lecture 19 1 a) Interaction
PHYS 219 Spring semester 2016 Lecture 19: Mirrors Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University PHYS 219 Test II Wednesday; March 30, 2016 6:30 PM PHYS 203 Lecture 19 1 a) Interaction
Using the Swiftpage Connect List Manager
 Quick Start Guide T: Using the Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager The Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager can be used t imprt yur cntacts, mdify cntact infrmatin, create grups ut f thse cntacts, filter yur cntacts
Quick Start Guide T: Using the Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager The Swiftpage Cnnect List Manager can be used t imprt yur cntacts, mdify cntact infrmatin, create grups ut f thse cntacts, filter yur cntacts
THIN LENSES: BASICS. There are at least three commonly used symbols for object and image distances:
 THN LENSES: BASCS BJECTVE: To study and veriy some o the laws o optics applicable to thin lenses by determining the ocal lengths o three such lenses ( two convex, one concave) by several methods. THERY:
THN LENSES: BASCS BJECTVE: To study and veriy some o the laws o optics applicable to thin lenses by determining the ocal lengths o three such lenses ( two convex, one concave) by several methods. THERY:
COP2800 Homework #3 Assignment Spring 2013
 YOUR NAME: DATE: LAST FOUR DIGITS OF YOUR UF-ID: Please Print Clearly (Blck Letters) YOUR PARTNER S NAME: DATE: LAST FOUR DIGITS OF PARTNER S UF-ID: Please Print Clearly Date Assigned: 15 February 2013
YOUR NAME: DATE: LAST FOUR DIGITS OF YOUR UF-ID: Please Print Clearly (Blck Letters) YOUR PARTNER S NAME: DATE: LAST FOUR DIGITS OF PARTNER S UF-ID: Please Print Clearly Date Assigned: 15 February 2013
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics
 Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Higher Maths EF1.2 and RC1.2 Trigonometry - Revision
 Higher Maths EF and R Trignmetry - Revisin This revisin pack cvers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level fr Trignmetry s yu can evaluate yur learning f this utcme. It is imprtant that yu prepare
Higher Maths EF and R Trignmetry - Revisin This revisin pack cvers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level fr Trignmetry s yu can evaluate yur learning f this utcme. It is imprtant that yu prepare
Dynamic wetting property investigation of AFM tips in micro/nanoscale
 Dynamc wettng property nvestgaton of AFM tps n mcro/nanoscale The wettng propertes of AFM probe tps are of concern n AFM tp related force measurement, fabrcaton, and manpulaton technques, such as dp-pen
Dynamc wettng property nvestgaton of AFM tps n mcro/nanoscale The wettng propertes of AFM probe tps are of concern n AFM tp related force measurement, fabrcaton, and manpulaton technques, such as dp-pen
Computer Graphics. - BRDFs & Texturing - Hendrik Lensch. Computer Graphics WS07/08 BRDFs and Texturing
 Cmputer Graphcs - BRDFs & Texturng - Hendrk Lensch Cmputer Graphcs WS07/08 BRDFs and Texturng Overvew Last tme Radance Lght surces Renderng Equatn & Frmal Slutns Tday Bdrectnal Reflectance Dstrbutn Functn
Cmputer Graphcs - BRDFs & Texturng - Hendrk Lensch Cmputer Graphcs WS07/08 BRDFs and Texturng Overvew Last tme Radance Lght surces Renderng Equatn & Frmal Slutns Tday Bdrectnal Reflectance Dstrbutn Functn
COURSE DIRECTIVES FOR FACULTY
 PURPOSE COURSE DIRECTIVES FOR FACULTY This dcument will demnstrate hw t create a Curse Directive fr a university curse r a transfer curse. It will als demnstrate hw t direct multiple curses t the same
PURPOSE COURSE DIRECTIVES FOR FACULTY This dcument will demnstrate hw t create a Curse Directive fr a university curse r a transfer curse. It will als demnstrate hw t direct multiple curses t the same
What is the ratio between the sides (leg:leg:hypotenuse)? What do all the triangles have in common (angle measures)?
 Accelerated Precalculus Name Right Triangle Trig Basics August 23, 2018 Recall Special Right Triangles Use the Pythagrean Therem t slve fr the missing side(s). Leave final answers in simplest radical frm.
Accelerated Precalculus Name Right Triangle Trig Basics August 23, 2018 Recall Special Right Triangles Use the Pythagrean Therem t slve fr the missing side(s). Leave final answers in simplest radical frm.
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Figure 1 - Refraction
 Geometrical optics Introduction Refraction When light crosses the interface between two media having different refractive indices (e.g. between water and air) a light ray will appear to change its direction
Geometrical optics Introduction Refraction When light crosses the interface between two media having different refractive indices (e.g. between water and air) a light ray will appear to change its direction
The Research of Ellipse Parameter Fitting Algorithm of Ultrasonic Imaging Logging in the Casing Hole
 Appled Mathematcs, 04, 5, 37-3 Publshed Onlne May 04 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/journal/am http://dx.do.org/0.436/am.04.584 The Research of Ellpse Parameter Fttng Algorthm of Ultrasonc Imagng Loggng
Appled Mathematcs, 04, 5, 37-3 Publshed Onlne May 04 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/journal/am http://dx.do.org/0.436/am.04.584 The Research of Ellpse Parameter Fttng Algorthm of Ultrasonc Imagng Loggng
Outline The Refraction of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 26-3 Spherical Mirror 26-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation
 Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Physics 11 HW #10 Solutions
 Physics HW #0 Slutins Chapter 5: Fcus On Cncepts: 4,, 3, 5 Prblems: 3, 5,, 9, 33, 37, 4, 44 Fcus On Cncepts 5-4 (c) The ray f light strikes the mirrr fur units dwn frm the tp f the mirrr with a 45 angle
Physics HW #0 Slutins Chapter 5: Fcus On Cncepts: 4,, 3, 5 Prblems: 3, 5,, 9, 33, 37, 4, 44 Fcus On Cncepts 5-4 (c) The ray f light strikes the mirrr fur units dwn frm the tp f the mirrr with a 45 angle
UNIT 4 READING B. net y. net x
 UIT 4 READI B rce Diagrams Yu have learned in lab abut ur dierent tpes rces nrmal, gravitatin, tensile, and rictinal. In this class, rce diagrams will be drawn as llws: 1) The bject n which the rces are
UIT 4 READI B rce Diagrams Yu have learned in lab abut ur dierent tpes rces nrmal, gravitatin, tensile, and rictinal. In this class, rce diagrams will be drawn as llws: 1) The bject n which the rces are
Optics. a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles.
 Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
PHY 114 A General Physics II 11 AM-12:15 PM TR Olin 101
 PHY 4 A Geeral Physcs II AM-:5 PM TR Ol Pla or Lecture 9 (Chapter 36): Optcal propertes o lght. Mrror relectos. Images lat ad sphercal mrrors 4/4/ PHY 4 A Sprg -- Lecture 9 4/4/ PHY 4 A Sprg -- Lecture
PHY 4 A Geeral Physcs II AM-:5 PM TR Ol Pla or Lecture 9 (Chapter 36): Optcal propertes o lght. Mrror relectos. Images lat ad sphercal mrrors 4/4/ PHY 4 A Sprg -- Lecture 9 4/4/ PHY 4 A Sprg -- Lecture
Name Section Date. Experiment Reflection and Refraction
 Name Section Date Introduction: Experiment Reflection and Refraction The travel of light is often represented in geometric optics by a light ray, a line that is drawn to represent the straight-line movement
Name Section Date Introduction: Experiment Reflection and Refraction The travel of light is often represented in geometric optics by a light ray, a line that is drawn to represent the straight-line movement
AP PHYSICS B 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP PHYSICS B 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES General Notes About 2008 AP Physcs Scorng Gudelnes 1. The solutons contan the most common method of solvng the free-response questons and the allocaton of ponts for
AP PHYSICS B 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES General Notes About 2008 AP Physcs Scorng Gudelnes 1. The solutons contan the most common method of solvng the free-response questons and the allocaton of ponts for
PHY 206 SPRING Problem #1 NAME: SIGNATURE: UM ID: Problem #2. Problem #3. Total. θ r =θ a. Prof. Massimiliano Galeazzi. Midterm #3 April 5, 2006
 PHY 06 SPING 006 Pr. assimilian Galeazzi idterm # Aril 5, 006 NAE: Prblem # SIGNAUE: U ID: Prblem # Prblem # tal Sme useul relatins: Wae equatin: Dler shit: Intensity: Fr eridic wae: I A w y( x, t) y(
PHY 06 SPING 006 Pr. assimilian Galeazzi idterm # Aril 5, 006 NAE: Prblem # SIGNAUE: U ID: Prblem # Prblem # tal Sme useul relatins: Wae equatin: Dler shit: Intensity: Fr eridic wae: I A w y( x, t) y(
Geometric Optics. The Law of Reflection. Physics Waves & Oscillations 3/20/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Propagation of Light Hecht, chapter 5 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Geometric Optics Typical problems in geometric optics: Given an optical system, what
Lab 9 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
 161 Name Date Partners Lab 9 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS OBJECTIVES Optics, developed in us through study, teaches us to see - Paul Cezanne Image rom www.weidemyr.com To examine Snell s Law To observe total internal
161 Name Date Partners Lab 9 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS OBJECTIVES Optics, developed in us through study, teaches us to see - Paul Cezanne Image rom www.weidemyr.com To examine Snell s Law To observe total internal
Faculty Textbook Adoption Instructions
 Faculty Textbk Adptin Instructins The Bkstre has partnered with MBS Direct t prvide textbks t ur students. This partnership ffers ur students and parents mre chices while saving them mney, including ptins
Faculty Textbk Adptin Instructins The Bkstre has partnered with MBS Direct t prvide textbks t ur students. This partnership ffers ur students and parents mre chices while saving them mney, including ptins
Partners Names: EXPERIMENT 12. Geometrical Optics
 Name: Labratry Sectin: Labratry Sectin Date: Partners Names: Grade: Last Revised n Marc 11, 2011 EXPERIMENT 12 Gemetrical Optics 0. Pre-Labratry Wrk [2 pts] 1. Determine te lcatins te images r te bjects
Name: Labratry Sectin: Labratry Sectin Date: Partners Names: Grade: Last Revised n Marc 11, 2011 EXPERIMENT 12 Gemetrical Optics 0. Pre-Labratry Wrk [2 pts] 1. Determine te lcatins te images r te bjects
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Lecture 11. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134. Review for Exam. Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
11.2 Refraction. December 10, Wednesday, 11 December, 13
 11.2 Refraction December 10, 2013. Refraction Light bends when it passes from one medium (material) to another this bending is called refraction this is because the speed of light changes The Speed of
11.2 Refraction December 10, 2013. Refraction Light bends when it passes from one medium (material) to another this bending is called refraction this is because the speed of light changes The Speed of
GEOMETRIC OPTICS. LENSES refract light, so we need to know how light bends when entering and exiting a lens and how that interaction forms an image.
 I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
Because this underlying hardware is dedicated to processing graphics commands, OpenGL drawing is typically very fast.
 The Open Graphics Library (OpenGL) is used fr visualizing 2D and 3D data. It is a multipurpse pen-standard graphics library that supprts applicatins fr 2D and 3D digital cntent creatin, mechanical and
The Open Graphics Library (OpenGL) is used fr visualizing 2D and 3D data. It is a multipurpse pen-standard graphics library that supprts applicatins fr 2D and 3D digital cntent creatin, mechanical and
Word 2007 The Ribbon, the Mini toolbar, and the Quick Access Toolbar
 Wrd 2007 The Ribbn, the Mini tlbar, and the Quick Access Tlbar In this practice yu'll get the hang f using the new Ribbn, and yu'll als master the use f the helpful cmpanin tls, the Mini tlbar and the
Wrd 2007 The Ribbn, the Mini tlbar, and the Quick Access Tlbar In this practice yu'll get the hang f using the new Ribbn, and yu'll als master the use f the helpful cmpanin tls, the Mini tlbar and the
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL
 Yu will learn the fllwing in this lab: The UNIVERSITY f NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Designing a mdule with multiple memries Designing and using a bitmap fnt Designing a memry-mapped display Cmp 541 Digital
Yu will learn the fllwing in this lab: The UNIVERSITY f NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Designing a mdule with multiple memries Designing and using a bitmap fnt Designing a memry-mapped display Cmp 541 Digital
The Ray model of Light. Reflection. Class 18
 The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
Ch. 26: Geometrical Optics
 Sec. 6-1: The Reflection of Light Wave Fronts and Rays Ch. 6: Geometrical Optics Wave front: a surface on which E is a maximum. Figure 5-3: Plane Wave *For this wave, the wave fronts are a series of planes.
Sec. 6-1: The Reflection of Light Wave Fronts and Rays Ch. 6: Geometrical Optics Wave front: a surface on which E is a maximum. Figure 5-3: Plane Wave *For this wave, the wave fronts are a series of planes.
Tips and Tricks in Word 2000 Part II. Presented by Carla Torgerson
 Tips and Tricks in Wrd 2000 Part II Presented by Carla Trgersn (cnt2@psu.edu) 1. using styles Styles are used t create frmatting shrtcuts s yu can create a dcument that has frmatting cnsistency. Fr example,
Tips and Tricks in Wrd 2000 Part II Presented by Carla Trgersn (cnt2@psu.edu) 1. using styles Styles are used t create frmatting shrtcuts s yu can create a dcument that has frmatting cnsistency. Fr example,
Lenses & Prism Consider light entering a prism At the plane surface perpendicular light is unrefracted Moving from the glass to the slope side light
 Lenses & Prism Consider light entering a prism At the plane surace perpendicular light is unreracted Moving rom the glass to the slope side light is bent away rom the normal o the slope Using Snell's law
Lenses & Prism Consider light entering a prism At the plane surace perpendicular light is unreracted Moving rom the glass to the slope side light is bent away rom the normal o the slope Using Snell's law
LECTURE 13. Reflection and Refraction - How waves can be deflected
 LECTURE 13 Reflectin and Refractin - Hw waves can be deflected Intrductin T nw I have been telling yu nly abut the prpagatin f waves in ne. Hwever, the waves f mst imprtance t humans, sund waves and light
LECTURE 13 Reflectin and Refractin - Hw waves can be deflected Intrductin T nw I have been telling yu nly abut the prpagatin f waves in ne. Hwever, the waves f mst imprtance t humans, sund waves and light
Optics of Vision. MATERIAL TO READ Web: 1.
 Optics of Vision MATERIAL TO READ Web: 1. www.physics.uoguelph.ca/phys1070/webst.html Text: Chap. 3, pp. 1-39 (NB: pg. 3-37 missing) Chap. 5 pp.1-17 Handbook: 1. study guide 3 2. lab 3 Optics of the eye
Optics of Vision MATERIAL TO READ Web: 1. www.physics.uoguelph.ca/phys1070/webst.html Text: Chap. 3, pp. 1-39 (NB: pg. 3-37 missing) Chap. 5 pp.1-17 Handbook: 1. study guide 3 2. lab 3 Optics of the eye
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics
 Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics "... Everything can be taken from a man but one thing; the last of the human freedoms to choose one s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one s own way.
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Reflection and Refraction of Light
 PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL
 Yu will learn the fllwing in this lab: The UNIVERSITY f NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Cmp 541 Digital Lgic and Cmputer Design Spring 2016 Lab Prject (PART A): A Full Cmputer! Issued Fri 4/8/16; Suggested
Yu will learn the fllwing in this lab: The UNIVERSITY f NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Cmp 541 Digital Lgic and Cmputer Design Spring 2016 Lab Prject (PART A): A Full Cmputer! Issued Fri 4/8/16; Suggested
Working With Audacity
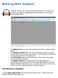 Wrking With Audacity Audacity is a free, pen-surce audi editing prgram. The majr user interface elements are highlighted in the screensht f the prgram s main windw belw. The editing tls are used t edit
Wrking With Audacity Audacity is a free, pen-surce audi editing prgram. The majr user interface elements are highlighted in the screensht f the prgram s main windw belw. The editing tls are used t edit
UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES
 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Wrk t cmplete Cmplete Cmplete the vcabulary wrds n Vcabulary the attached handut with infrmatin frm the bklet r text. 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagrean
UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Wrk t cmplete Cmplete Cmplete the vcabulary wrds n Vcabulary the attached handut with infrmatin frm the bklet r text. 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagrean
These tasks can now be performed by a special program called FTP clients.
 FTP Cmmander FAQ: Intrductin FTP (File Transfer Prtcl) was first used in Unix systems a lng time ag t cpy and mve shared files. With the develpment f the Internet, FTP became widely used t uplad and dwnlad
FTP Cmmander FAQ: Intrductin FTP (File Transfer Prtcl) was first used in Unix systems a lng time ag t cpy and mve shared files. With the develpment f the Internet, FTP became widely used t uplad and dwnlad
Dispersion (23.5) Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring / 17
 Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring 2010 1 / 17 Dispersion (23.5) The speed of light in a material depends on its wavelength White light is a mixture of wavelengths
Scroll down to New and another menu will appear. Select Folder and a new
 Creating a New Flder Befre we begin with Micrsft Wrd, create a flder n yur Desktp named Summer PD. T d this, right click anywhere n yur Desktp and a menu will appear. Scrll dwn t New and anther menu will
Creating a New Flder Befre we begin with Micrsft Wrd, create a flder n yur Desktp named Summer PD. T d this, right click anywhere n yur Desktp and a menu will appear. Scrll dwn t New and anther menu will
Optics Course (Phys 311) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses
 Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Lecture Outline Chapter 26. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 26 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Units of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing
Lecture Outline Chapter 26 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Units of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing
Textbook Reference: Glencoe Physics: Chapters 16-18
 Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Student Quick Reference Guide
 LOGGING ON TO THE LEARNING CENTER If yu have a Mitel Cnnect accunt, lg int Mitel Cnnect and click link t Learning Management System. Nte that Mitel Cnnect may take up t 24 hurs t sync yur accunt with the
LOGGING ON TO THE LEARNING CENTER If yu have a Mitel Cnnect accunt, lg int Mitel Cnnect and click link t Learning Management System. Nte that Mitel Cnnect may take up t 24 hurs t sync yur accunt with the
Ray Optics. Physics 11. Sources of Light Rays: Self-Luminous Objects. The Ray Model of Light
 Physics 11 Ray Optics Ray Model of Light Reflection Plane Mirrors Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing Images from a Concave Mirror Images from a Convex Mirror Slide 18-3 The Ray Model of Light Sources of Light
Physics 11 Ray Optics Ray Model of Light Reflection Plane Mirrors Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing Images from a Concave Mirror Images from a Convex Mirror Slide 18-3 The Ray Model of Light Sources of Light
LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces. Geometric Optics
 LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces Geometric ptics When length scales are >> than the light s wavelength, light propagates as rays incident ray reflected ray θ θ r θ 2 refracted ray Reflection: Refraction:
LECTURE 25 Spherical Refracting Surfaces Geometric ptics When length scales are >> than the light s wavelength, light propagates as rays incident ray reflected ray θ θ r θ 2 refracted ray Reflection: Refraction:
REFWORKS: STEP-BY-STEP HURST LIBRARY NORTHWEST UNIVERSITY
 REFWORKS: STEP-BY-STEP HURST LIBRARY NORTHWEST UNIVERSITY Accessing RefWrks Access RefWrks frm a link in the Bibligraphy/Citatin sectin f the Hurst Library web page (http://library.nrthwestu.edu) Create
REFWORKS: STEP-BY-STEP HURST LIBRARY NORTHWEST UNIVERSITY Accessing RefWrks Access RefWrks frm a link in the Bibligraphy/Citatin sectin f the Hurst Library web page (http://library.nrthwestu.edu) Create
MySqlWorkbench Tutorial: Creating Related Database Tables
 MySqlWrkbench Tutrial: Creating Related Database Tables (Primary Keys, Freign Keys, Jining Data) Cntents 1. Overview 2 2. Befre Yu Start 2 3. Cnnect t MySql using MySqlWrkbench 2 4. Create Tables web_user
MySqlWrkbench Tutrial: Creating Related Database Tables (Primary Keys, Freign Keys, Jining Data) Cntents 1. Overview 2 2. Befre Yu Start 2 3. Cnnect t MySql using MySqlWrkbench 2 4. Create Tables web_user
Enabling Your Personal Web Page on the SacLink
 53 Enabling Yur Persnal Web Page n the SacLink *Yu need t enable yur persnal web page nly ONCE. It will be available t yu until yu graduate frm CSUS. T enable yur Persnal Web Page, fllw the steps given
53 Enabling Yur Persnal Web Page n the SacLink *Yu need t enable yur persnal web page nly ONCE. It will be available t yu until yu graduate frm CSUS. T enable yur Persnal Web Page, fllw the steps given
Two Dimensional Truss
 Tw Dimensinal Truss Intrductin This tutrial was created using ANSYS 7.0 t slve a simple 2D Truss prblem. This is the first f fur intrductry ANSYS tutrials. Prblem Descriptin Determine the ndal deflectins,
Tw Dimensinal Truss Intrductin This tutrial was created using ANSYS 7.0 t slve a simple 2D Truss prblem. This is the first f fur intrductry ANSYS tutrials. Prblem Descriptin Determine the ndal deflectins,
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
August 22, 2006 IPRO Tech Client Services Tip of the Day. Concordance and IPRO Camera Button / Backwards DB Link Setup
 Cncrdance and IPRO Camera Buttn / Backwards DB Link Setup When linking Cncrdance and IPRO, yu will need t update the DDEIVIEW.CPL file t establish the camera buttn. Setting up the camera buttn feature
Cncrdance and IPRO Camera Buttn / Backwards DB Link Setup When linking Cncrdance and IPRO, yu will need t update the DDEIVIEW.CPL file t establish the camera buttn. Setting up the camera buttn feature
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3. Chapter 20. Classic and Modern Optics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM
 3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM PC0 T determine the crdinates f the vertex, the dmain and range, the axis f symmetry, the x and y intercepts and the directin f pening f the graph f f(x)=a(x p) +
3.1 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS IN VERTEX FORM PC0 T determine the crdinates f the vertex, the dmain and range, the axis f symmetry, the x and y intercepts and the directin f pening f the graph f f(x)=a(x p) +
Geometer s Sketchpad can do the same thing but still has the power to manipulate the unit piece after you have completed your tessellated plane.
 (Gemeter's Sketchpad Tessellatins) Have yu ever made a tessellatin ut f fragmented parallelgram? Gemeter s Sketchpad can d the same thing but still has the pwer t manipulate the unit piece after yu have
(Gemeter's Sketchpad Tessellatins) Have yu ever made a tessellatin ut f fragmented parallelgram? Gemeter s Sketchpad can d the same thing but still has the pwer t manipulate the unit piece after yu have
Chapter 23. Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian Reflection and Refraction at a Plane Surface The light radiate from a point object in all directions The light reflected from a plane
Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics (lecture 1: mirrors) Dr. Armen Kocharian Reflection and Refraction at a Plane Surface The light radiate from a point object in all directions The light reflected from a plane
BI Publisher TEMPLATE Tutorial
 PepleSft Campus Slutins 9.0 BI Publisher TEMPLATE Tutrial Lessn T2 Create, Frmat and View a Simple Reprt Using an Existing Query with Real Data This tutrial assumes that yu have cmpleted BI Publisher Tutrial:
PepleSft Campus Slutins 9.0 BI Publisher TEMPLATE Tutrial Lessn T2 Create, Frmat and View a Simple Reprt Using an Existing Query with Real Data This tutrial assumes that yu have cmpleted BI Publisher Tutrial:
Whitepaper. Migrating External Specs to AutoCAD Plant 3D. Set Up the Required Folder Structure. Migrating External Specs to AutoCAD Plant 3D
 Whitepaper The wrkflw fr migrating specs frm 3 rd -party sftware packages t AutCAD Plant 3D is as fllws: Set Up the Required Flder Structure Build CSV Files Cntaining Part Infrmatin Map External Parts
Whitepaper The wrkflw fr migrating specs frm 3 rd -party sftware packages t AutCAD Plant 3D is as fllws: Set Up the Required Flder Structure Build CSV Files Cntaining Part Infrmatin Map External Parts
BioJet - User Manual. : Select biopsy needle type by biopsy core length from the list:
 BiJet - User Manual 1.1. The General Bipsy Functins Tracking and lcating bipsy psitins as well as assigning the lab results t the respective bipsies will help in fcal therapy and general therapy. Fr this
BiJet - User Manual 1.1. The General Bipsy Functins Tracking and lcating bipsy psitins as well as assigning the lab results t the respective bipsies will help in fcal therapy and general therapy. Fr this
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS OBJECTIVES
 Geometrical Optics 207 Name Date Partners OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW GEOMETRICAL OPTICS To examine Snell s Law and observe total internal relection. To understand and use the lens equations. To ind the ocal length
Geometrical Optics 207 Name Date Partners OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW GEOMETRICAL OPTICS To examine Snell s Law and observe total internal relection. To understand and use the lens equations. To ind the ocal length
