Unsupervised learning: Clustering & Dimensionality reduction. Theo Knijnenburg Jorma de Ronde
|
|
|
- Molly Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unsupervised learning: Clustering & Dimensionality reduction Theo Knijnenburg Jorma de Ronde
2 Source of slides Marcel Reinders TU Delft Lodewyk Wessels NKI Bioalgorithms.info Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford Panos Pardalos - UFL
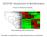
3 Unsupervised learning Find structure in unlabeled data
4 Unsupervised learning Find structure in unlabeled data samples features healthy labels disease
5 Unsupervised learning Find structure in unlabeled data samples features healthy labels disease
6 Clustering Group samples in unlabeled data samples features
7 Apples and pears
8 Clustering apples and pears Samples (apples and pears) features
9 Clustering apples and pears Weight Color Shape Gene expression Country of origin Sugar levels Taste Taste when fried Price Calories Water content Samples (apples and pears)
10 Classification (labeled data) Weight Color Shape Gene expression Country of origin Sugar levels Taste Taste when fried Price Calories Water content Samples (apples and pears) apples pears
11 Classification (labeled data) Weight Color Shape Gene expression Country of origin Sugar levels Taste Taste when fried Price Calories Water content Samples (apples and pears) r Not rotten rotten nr
12 Clustering apples and pears Weight Color Shape Gene expression Country of origin Sugar levels Taste Taste when fried Price Calories Water content Samples (apples and pears)
13 Clustering microarray data Samples (patients) Gene expression
14 Clustering microarray data Samples (patients) Gene expression w1 healthy Week 2 Week 1 disease w2
15 How many clusters?
16 Why do clustering? Group samples that are close to each other Reduce the amount of data Construct categories or taxonomies in an automated way Statistical and visual description of your data Generate hypotheses
17
18 Overview of clustering Distance measures Hierarchical clustering Clustering synthetic data Clustering less synthetic data K-means clustering
19 Unsupervised learning Clusters and distance measures
20 What makes a cluster a cluster? Intuitively: group objects together that are similar to eachother
21 Unsupervised clustering (loose) cluster definition: 1) Samples within cluster resemble each other (within variance, σ w (i)) 2) Clusters deviate from each other (between variance, σ B (i))
22 Unsupervised hierarchical clustering First step: Find the two samples that are closest to eachother (according to some measure of distance)
23 Unsupervised clustering We find objects 4 and 2 to be the closest to eachother, so they form the first cluster
24 Unsupervised clustering Next, we again look for the closest two objects, but we now consider objects 4 and 2 to 4 to be in the same cluster, so essentially one object The next two objects closest to eachother are objects 5 and 8
25 Unsupervised clustering Again, we look for the two objects closest to eachother. An object can also be a cluster, so we not only look at the distances between two single samples, but also between a sample and a cluster and between two clusters In this particular case object 3 and the cluster containing 4 and 2, ie c(4,2) are the closest two objects. C(4,2) and 3 now form a new cluster
26 Unsupervised clustering This process is repeated until a single, all-encompassing cluster is reached
27 Unsupervised clustering Finally, we have a hierarchical clustering of our data Since it is hierarchical, we need to set a cut-off if we want to look at clusters that do not contain all samples
28 Hierarchical clustering At each step of this simple hierarchical clustering algorithm we need to know: The distance between every two samples The distance between each sample and cluster The distance between every two clusters In which ways can we define these distance? We need to construct a distance matrix
29 Distance matrix A B C D A B C D 0 A B C+D A B C+D 0
30 Distance between samples
31 Distance matrices for different distance measures Euclidean Green Blue Yellow Red Green Blue Yellow Red Pearson correlation Green Blue Yellow Red Green Blue Yellow Red 0
32 Distance between clusters Single linkage: closest distance between two objects in two clusters Complete linkage: longest distance between two objects in two clusters Average linkage: distance between the averages of each cluster
33 Using different linkage measures can have a dramatic effect on cluster formation
34 How many clusters?
35 Assessing the robustness of a clustering Even when we use random data, we can generate a hierarchical clustering This clustering could even implicate some kind of structure in the data, whereas we know any apparent structure is derived from noisy data without any signal We need to assess the robustness of our clustering
36 Bootstrapping Say we set a cut-off and identify 2 clusters We can use bootstrapping to test the stability of these clusters by taking a random sample from our data (with replacement) Now, generate a new clustering with the bootstrapped data, and repeat x times Calculate for each iteration whether two objects cluster together
37 Bootstrap results for random data Yellow: clusters together often (ie in this case each object always clusters together with itself)
38 Data with structure Good support for nine clusters
39 How to select optimal number of clusters Many different methods exist Visually, you could solve this by checking at which point the dendrogram branch heights start to level off (ie high similarity between objects = low branches)
40 K-means Clustering
41 Algorithm k-means 1. Decide on a value for k. 2. Initialize the k cluster centers (randomly, if necessary). 3. Decide the class memberships of the N objects by assigning them to the nearest cluster center. 4. Re-estimate the k cluster centers, by assuming the memberships found above are correct. 5. If none of the N objects changed membership in the last iteration, exit. Otherwise goto 3.
42 5 K-means Clustering: Step 1 Algorithm: k-means, Distance Metric: Euclidean Distance 4 k k k 3
43 5 K-means Clustering: Step 2 Algorithm: k-means, Distance Metric: Euclidean Distance 4 k k k 3
44 5 K-means Clustering: Step 3 Algorithm: k-means, Distance Metric: Euclidean Distance 4 k k 2 k
45 5 K-means Clustering: Step 4 Algorithm: k-means, Distance Metric: Euclidean Distance 4 k k 2 k
46 5 K-means Clustering: Step 5 Algorithm: k-means, Distance Metric: Euclidean Distance expression in condition k 2 k expression in condition 1 k 1
47 How can we tell the right number of clusters? In general, this is a unsolved problem. However there are many approximate methods. In the next few slides we will see an example. For our example, we will use the familiar katydid/grasshopper dataset. 7 However, in this case we are imagining 6 that we do NOT know the class labels. We are only clustering on the X and Y axis 5 values
48 When k = 1, the objective function is
49 When k = 2, the objective function is
50 When k = 3, the objective function is
51 We can plot the objective function values for k equals 1 to 6 The abrupt change at k = 2, is highly suggestive of two clusters in the data. This technique for determining the number of clusters is known as knee finding or elbow finding. 1.00E E E+02 Objective Function 7.00E E E E E E E E+00 k Note that the results are not always as clear cut as in this toy example
10601 Machine Learning. Hierarchical clustering. Reading: Bishop: 9-9.2
 161 Machine Learning Hierarchical clustering Reading: Bishop: 9-9.2 Second half: Overview Clustering - Hierarchical, semi-supervised learning Graphical models - Bayesian networks, HMMs, Reasoning under
161 Machine Learning Hierarchical clustering Reading: Bishop: 9-9.2 Second half: Overview Clustering - Hierarchical, semi-supervised learning Graphical models - Bayesian networks, HMMs, Reasoning under
10701 Machine Learning. Clustering
 171 Machine Learning Clustering What is Clustering? Organizing data into clusters such that there is high intra-cluster similarity low inter-cluster similarity Informally, finding natural groupings among
171 Machine Learning Clustering What is Clustering? Organizing data into clusters such that there is high intra-cluster similarity low inter-cluster similarity Informally, finding natural groupings among
Network Traffic Measurements and Analysis
 DEIB - Politecnico di Milano Fall, 2017 Introduction Often, we have only a set of features x = x 1, x 2,, x n, but no associated response y. Therefore we are not interested in prediction nor classification,
DEIB - Politecnico di Milano Fall, 2017 Introduction Often, we have only a set of features x = x 1, x 2,, x n, but no associated response y. Therefore we are not interested in prediction nor classification,
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 15: Microarray clustering http://compbio.pbworks.com/f/wood2.gif Some slides were adapted from Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University of Central Florida) Microarray
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 15: Microarray clustering http://compbio.pbworks.com/f/wood2.gif Some slides were adapted from Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University of Central Florida) Microarray
Statistics 202: Data Mining. c Jonathan Taylor. Week 8 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes. December 2, / 1
 Week 8 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Part I Clustering 2 / 1 Clustering Clustering Goal: Finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group
Week 8 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Part I Clustering 2 / 1 Clustering Clustering Goal: Finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group
Distances, Clustering! Rafael Irizarry!
 Distances, Clustering! Rafael Irizarry! Heatmaps! Distance! Clustering organizes things that are close into groups! What does it mean for two genes to be close?! What does it mean for two samples to
Distances, Clustering! Rafael Irizarry! Heatmaps! Distance! Clustering organizes things that are close into groups! What does it mean for two genes to be close?! What does it mean for two samples to
Gene Clustering & Classification
 BINF, Introduction to Computational Biology Gene Clustering & Classification Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University Overview Introduction to Gene Clustering
BINF, Introduction to Computational Biology Gene Clustering & Classification Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University Overview Introduction to Gene Clustering
Clusteringon NGS data learning. Sarah, est ce que je dois mettre un nom de personnes ou des noms de personnes?
 Clusteringon NGS data learning Sarah, est ce que je dois mettre un nom de personnes ou des noms de personnes? To know about clustering There are two main methods: Classification = supervised method: Bring
Clusteringon NGS data learning Sarah, est ce que je dois mettre un nom de personnes ou des noms de personnes? To know about clustering There are two main methods: Classification = supervised method: Bring
Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis. Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan
 Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Unsupervised learning Finding centers of similarity using
Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Unsupervised learning Finding centers of similarity using
Dimension reduction : PCA and Clustering
 Dimension reduction : PCA and Clustering By Hanne Jarmer Slides by Christopher Workman Center for Biological Sequence Analysis DTU The DNA Array Analysis Pipeline Array design Probe design Question Experimental
Dimension reduction : PCA and Clustering By Hanne Jarmer Slides by Christopher Workman Center for Biological Sequence Analysis DTU The DNA Array Analysis Pipeline Array design Probe design Question Experimental
Classification. Vladimir Curic. Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University
 Classification Vladimir Curic Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline An overview on classification Basics of classification How to choose appropriate
Classification Vladimir Curic Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline An overview on classification Basics of classification How to choose appropriate
Clustering and Dimensionality Reduction
 Clustering and Dimensionality Reduction Some material on these is slides borrowed from Andrew Moore's excellent machine learning tutorials located at: Data Mining Automatically extracting meaning from
Clustering and Dimensionality Reduction Some material on these is slides borrowed from Andrew Moore's excellent machine learning tutorials located at: Data Mining Automatically extracting meaning from
Clustering, cont. Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein. Some slides adapted from Jacques van Helden
 Clustering, cont Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein Some slides adapted from Jacques van Helden Improving the search heuristic: Multiple starting points Simulated annealing Genetic algorithms
Clustering, cont Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein Some slides adapted from Jacques van Helden Improving the search heuristic: Multiple starting points Simulated annealing Genetic algorithms
11/2/2017 MIST.6060 Business Intelligence and Data Mining 1. Clustering. Two widely used distance metrics to measure the distance between two records
 11/2/2017 MIST.6060 Business Intelligence and Data Mining 1 An Example Clustering X 2 X 1 Objective of Clustering The objective of clustering is to group the data into clusters such that the records within
11/2/2017 MIST.6060 Business Intelligence and Data Mining 1 An Example Clustering X 2 X 1 Objective of Clustering The objective of clustering is to group the data into clusters such that the records within
Hard clustering. Each object is assigned to one and only one cluster. Hierarchical clustering is usually hard. Soft (fuzzy) clustering
 An unsupervised machine learning problem Grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other
An unsupervised machine learning problem Grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other
Measure of Distance. We wish to define the distance between two objects Distance metric between points:
 Measure of Distance We wish to define the distance between two objects Distance metric between points: Euclidean distance (EUC) Manhattan distance (MAN) Pearson sample correlation (COR) Angle distance
Measure of Distance We wish to define the distance between two objects Distance metric between points: Euclidean distance (EUC) Manhattan distance (MAN) Pearson sample correlation (COR) Angle distance
ECLT 5810 Clustering
 ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
Exploratory data analysis for microarrays
 Exploratory data analysis for microarrays Jörg Rahnenführer Computational Biology and Applied Algorithmics Max Planck Institute for Informatics D-66123 Saarbrücken Germany NGFN - Courses in Practical DNA
Exploratory data analysis for microarrays Jörg Rahnenführer Computational Biology and Applied Algorithmics Max Planck Institute for Informatics D-66123 Saarbrücken Germany NGFN - Courses in Practical DNA
Clustering Algorithms: Can anything be Concluded?
 Clustering Algorithms: Can anything be Concluded? Edward R. Dougherty, Seungchan Kim Texas A&M University Junior Barrera, Marcel Brun, Roberto Marcondes Universidade de Sao Paulo Yidong Chen, Michael Bittner,
Clustering Algorithms: Can anything be Concluded? Edward R. Dougherty, Seungchan Kim Texas A&M University Junior Barrera, Marcel Brun, Roberto Marcondes Universidade de Sao Paulo Yidong Chen, Michael Bittner,
Computing with large data sets
 Computing with large data sets Richard Bonneau, spring 2009 Lecture 8(week 5): clustering 1 clustering Clustering: a diverse methods for discovering groupings in unlabeled data Because these methods don
Computing with large data sets Richard Bonneau, spring 2009 Lecture 8(week 5): clustering 1 clustering Clustering: a diverse methods for discovering groupings in unlabeled data Because these methods don
UNSUPERVISED LEARNING IN R. Introduction to hierarchical clustering
 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING IN R Introduction to hierarchical clustering Hierarchical clustering Number of clusters is not known ahead of time Two kinds: bottom-up and top-down, this course bottom-up Hierarchical
UNSUPERVISED LEARNING IN R Introduction to hierarchical clustering Hierarchical clustering Number of clusters is not known ahead of time Two kinds: bottom-up and top-down, this course bottom-up Hierarchical
Clustering and Visualisation of Data
 Clustering and Visualisation of Data Hiroshi Shimodaira January-March 28 Cluster analysis aims to partition a data set into meaningful or useful groups, based on distances between data points. In some
Clustering and Visualisation of Data Hiroshi Shimodaira January-March 28 Cluster analysis aims to partition a data set into meaningful or useful groups, based on distances between data points. In some
Foundations of Machine Learning CentraleSupélec Fall Clustering Chloé-Agathe Azencot
 Foundations of Machine Learning CentraleSupélec Fall 2017 12. Clustering Chloé-Agathe Azencot Centre for Computational Biology, Mines ParisTech chloe-agathe.azencott@mines-paristech.fr Learning objectives
Foundations of Machine Learning CentraleSupélec Fall 2017 12. Clustering Chloé-Agathe Azencot Centre for Computational Biology, Mines ParisTech chloe-agathe.azencott@mines-paristech.fr Learning objectives
Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data
 Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data Seventh International Long Oligonucleotide Microarray Workshop Tucson, Arizona January 7-12, 2007 Dan Nettleton IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY 1 Clustering Group objects that
Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data Seventh International Long Oligonucleotide Microarray Workshop Tucson, Arizona January 7-12, 2007 Dan Nettleton IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY 1 Clustering Group objects that
Cluster Analysis. Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX April 2008 April 2010
 Cluster Analysis Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX 7575 April 008 April 010 Cluster Analysis, sometimes called data segmentation or customer segmentation,
Cluster Analysis Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX 7575 April 008 April 010 Cluster Analysis, sometimes called data segmentation or customer segmentation,
ECLT 5810 Clustering
 ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
High throughput Data Analysis 2. Cluster Analysis
 High throughput Data Analysis 2 Cluster Analysis Overview Why clustering? Hierarchical clustering K means clustering Issues with above two Other methods Quality of clustering results Introduction WHY DO
High throughput Data Analysis 2 Cluster Analysis Overview Why clustering? Hierarchical clustering K means clustering Issues with above two Other methods Quality of clustering results Introduction WHY DO
Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning
 Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning This slide set mainly uses the slides given in the following links: http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/ch8.pdf http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/dmslides/chap8_basic_cluster_analysis.pdf
Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning This slide set mainly uses the slides given in the following links: http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/ch8.pdf http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/dmslides/chap8_basic_cluster_analysis.pdf
Cluster Analysis: Agglomerate Hierarchical Clustering
 Cluster Analysis: Agglomerate Hierarchical Clustering Yonghee Lee Department of Statistics, The University of Seoul Oct 29, 2015 Contents 1 Cluster Analysis Introduction Distance matrix Agglomerative Hierarchical
Cluster Analysis: Agglomerate Hierarchical Clustering Yonghee Lee Department of Statistics, The University of Seoul Oct 29, 2015 Contents 1 Cluster Analysis Introduction Distance matrix Agglomerative Hierarchical
Multivariate analyses in ecology. Cluster (part 2) Ordination (part 1 & 2)
 Multivariate analyses in ecology Cluster (part 2) Ordination (part 1 & 2) 1 Exercise 9B - solut 2 Exercise 9B - solut 3 Exercise 9B - solut 4 Exercise 9B - solut 5 Multivariate analyses in ecology Cluster
Multivariate analyses in ecology Cluster (part 2) Ordination (part 1 & 2) 1 Exercise 9B - solut 2 Exercise 9B - solut 3 Exercise 9B - solut 4 Exercise 9B - solut 5 Multivariate analyses in ecology Cluster
Lecture 10: Semantic Segmentation and Clustering
 Lecture 10: Semantic Segmentation and Clustering Vineet Kosaraju, Davy Ragland, Adrien Truong, Effie Nehoran, Maneekwan Toyungyernsub Department of Computer Science Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
Lecture 10: Semantic Segmentation and Clustering Vineet Kosaraju, Davy Ragland, Adrien Truong, Effie Nehoran, Maneekwan Toyungyernsub Department of Computer Science Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
Lecture 25: Review I
 Lecture 25: Review I Reading: Up to chapter 5 in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis Jonathan Taylor 1 / 18 Unsupervised learning In unsupervised learning, all the variables are on equal standing,
Lecture 25: Review I Reading: Up to chapter 5 in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis Jonathan Taylor 1 / 18 Unsupervised learning In unsupervised learning, all the variables are on equal standing,
Chapter 6: Cluster Analysis
 Chapter 6: Cluster Analysis The major goal of cluster analysis is to separate individual observations, or items, into groups, or clusters, on the basis of the values for the q variables measured on each
Chapter 6: Cluster Analysis The major goal of cluster analysis is to separate individual observations, or items, into groups, or clusters, on the basis of the values for the q variables measured on each
Data Science and Statistics in Research: unlocking the power of your data Session 3.4: Clustering
 Data Science and Statistics in Research: unlocking the power of your data Session 3.4: Clustering 1/ 1 OUTLINE 2/ 1 Overview 3/ 1 CLUSTERING Clustering is a statistical technique which creates groupings
Data Science and Statistics in Research: unlocking the power of your data Session 3.4: Clustering 1/ 1 OUTLINE 2/ 1 Overview 3/ 1 CLUSTERING Clustering is a statistical technique which creates groupings
Lecture 27: Review. Reading: All chapters in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis. December 6, 2017
 Lecture 27: Review Reading: All chapters in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis December 6, 2017 1 / 16 Final exam: Announcements Tuesday, December 12, 8:30-11:30 am, in the following rooms: Last
Lecture 27: Review Reading: All chapters in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis December 6, 2017 1 / 16 Final exam: Announcements Tuesday, December 12, 8:30-11:30 am, in the following rooms: Last
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING
 CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10. Cluster
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10. Cluster
BBS654 Data Mining. Pinar Duygulu. Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler
 BBS654 Data Mining Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler 1 Classification Classification systems: Supervised learning Make a rational prediction given evidence There are several methods for
BBS654 Data Mining Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler 1 Classification Classification systems: Supervised learning Make a rational prediction given evidence There are several methods for
CHAPTER 5 CLUSTER VALIDATION TECHNIQUES
 120 CHAPTER 5 CLUSTER VALIDATION TECHNIQUES 5.1 INTRODUCTION Prediction of correct number of clusters is a fundamental problem in unsupervised classification techniques. Many clustering techniques require
120 CHAPTER 5 CLUSTER VALIDATION TECHNIQUES 5.1 INTRODUCTION Prediction of correct number of clusters is a fundamental problem in unsupervised classification techniques. Many clustering techniques require
Analyzing Genomic Data with NOJAH
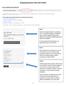 Analyzing Genomic Data with NOJAH TAB A) GENOME WIDE ANALYSIS Step 1: Select the example dataset or upload your own. Two example datasets are available. Genome-Wide TCGA-BRCA Expression datasets and CoMMpass
Analyzing Genomic Data with NOJAH TAB A) GENOME WIDE ANALYSIS Step 1: Select the example dataset or upload your own. Two example datasets are available. Genome-Wide TCGA-BRCA Expression datasets and CoMMpass
STATS306B STATS306B. Clustering. Jonathan Taylor Department of Statistics Stanford University. June 3, 2010
 STATS306B Jonathan Taylor Department of Statistics Stanford University June 3, 2010 Spring 2010 Outline K-means, K-medoids, EM algorithm choosing number of clusters: Gap test hierarchical clustering spectral
STATS306B Jonathan Taylor Department of Statistics Stanford University June 3, 2010 Spring 2010 Outline K-means, K-medoids, EM algorithm choosing number of clusters: Gap test hierarchical clustering spectral
VIDAEXPERT: DATA ANALYSIS Here is the Statistics button.
 Here is the Statistics button. After creating dataset you can analyze it in different ways. First, you can calculate statistics. Open Statistics dialog, Common tabsheet, click Calculate. Min, Max: minimal
Here is the Statistics button. After creating dataset you can analyze it in different ways. First, you can calculate statistics. Open Statistics dialog, Common tabsheet, click Calculate. Min, Max: minimal
Clustering. CS294 Practical Machine Learning Junming Yin 10/09/06
 Clustering CS294 Practical Machine Learning Junming Yin 10/09/06 Outline Introduction Unsupervised learning What is clustering? Application Dissimilarity (similarity) of objects Clustering algorithm K-means,
Clustering CS294 Practical Machine Learning Junming Yin 10/09/06 Outline Introduction Unsupervised learning What is clustering? Application Dissimilarity (similarity) of objects Clustering algorithm K-means,
What is clustering. Organizing data into clusters such that there is high intra- cluster similarity low inter- cluster similarity
 Clustering What is clustering Organizing data into clusters such that there is high intra- cluster similarity low inter- cluster similarity Informally, finding natural groupings among objects. High dimensional
Clustering What is clustering Organizing data into clusters such that there is high intra- cluster similarity low inter- cluster similarity Informally, finding natural groupings among objects. High dimensional
May 1, CODY, Error Backpropagation, Bischop 5.3, and Support Vector Machines (SVM) Bishop Ch 7. May 3, Class HW SVM, PCA, and K-means, Bishop Ch
 May 1, CODY, Error Backpropagation, Bischop 5.3, and Support Vector Machines (SVM) Bishop Ch 7. May 3, Class HW SVM, PCA, and K-means, Bishop Ch 12.1, 9.1 May 8, CODY Machine Learning for finding oil,
May 1, CODY, Error Backpropagation, Bischop 5.3, and Support Vector Machines (SVM) Bishop Ch 7. May 3, Class HW SVM, PCA, and K-means, Bishop Ch 12.1, 9.1 May 8, CODY Machine Learning for finding oil,
Case-Based Reasoning. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Nearest-Neighbor Classification. Parametric / Non-parametric.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
GS Analysis of Microarray Data
 GS01 0163 Analysis of Microarray Data Keith Baggerly and Bradley Broom Department of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center kabagg@mdanderson.org bmbroom@mdanderson.org 19
GS01 0163 Analysis of Microarray Data Keith Baggerly and Bradley Broom Department of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center kabagg@mdanderson.org bmbroom@mdanderson.org 19
K-Nearest Neighbors. Jia-Bin Huang. Virginia Tech Spring 2019 ECE-5424G / CS-5824
 K-Nearest Neighbors Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Check out review materials Probability Linear algebra Python and NumPy Start your HW 0 On your Local machine:
K-Nearest Neighbors Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Check out review materials Probability Linear algebra Python and NumPy Start your HW 0 On your Local machine:
DATA MINING LECTURE 7. Hierarchical Clustering, DBSCAN The EM Algorithm
 DATA MINING LECTURE 7 Hierarchical Clustering, DBSCAN The EM Algorithm CLUSTERING What is a Clustering? In general a grouping of objects such that the objects in a group (cluster) are similar (or related)
DATA MINING LECTURE 7 Hierarchical Clustering, DBSCAN The EM Algorithm CLUSTERING What is a Clustering? In general a grouping of objects such that the objects in a group (cluster) are similar (or related)
Statistical Methods for Data Mining
 Statistical Methods for Data Mining Kuangnan Fang Xiamen University Email: xmufkn@xmu.edu.cn Unsupervised Learning Unsupervised vs Supervised Learning: Most of this course focuses on supervised learning
Statistical Methods for Data Mining Kuangnan Fang Xiamen University Email: xmufkn@xmu.edu.cn Unsupervised Learning Unsupervised vs Supervised Learning: Most of this course focuses on supervised learning
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Clustering (1): Basics. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Clustering (1): Basics Kalev Kask Unsupervised learning Supervised learning Predict target value ( y ) given features ( x ) Unsupervised learning Understand patterns of
Machine Learning and Data Mining Clustering (1): Basics Kalev Kask Unsupervised learning Supervised learning Predict target value ( y ) given features ( x ) Unsupervised learning Understand patterns of
Cluster Analysis. Mu-Chun Su. Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Central University 2003/3/11 1
 Cluster Analysis Mu-Chun Su Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Central University 2003/3/11 1 Introduction Cluster analysis is the formal study of algorithms and methods
Cluster Analysis Mu-Chun Su Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Central University 2003/3/11 1 Introduction Cluster analysis is the formal study of algorithms and methods
CSE 40171: Artificial Intelligence. Learning from Data: Unsupervised Learning
 CSE 40171: Artificial Intelligence Learning from Data: Unsupervised Learning 32 Homework #6 has been released. It is due at 11:59PM on 11/7. 33 CSE Seminar: 11/1 Amy Reibman Purdue University 3:30pm DBART
CSE 40171: Artificial Intelligence Learning from Data: Unsupervised Learning 32 Homework #6 has been released. It is due at 11:59PM on 11/7. 33 CSE Seminar: 11/1 Amy Reibman Purdue University 3:30pm DBART
Clustering. Robert M. Haralick. Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York
 Clustering Robert M. Haralick Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York Outline K-means 1 K-means 2 3 4 5 Clustering K-means The purpose of clustering is to determine the similarity
Clustering Robert M. Haralick Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York Outline K-means 1 K-means 2 3 4 5 Clustering K-means The purpose of clustering is to determine the similarity
CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2010
 CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2010 Lecture 16: Machine Learning Topics 12/7/2010 Luke Zettlemoyer Most slides over the course adapted from Dan Klein. 1 Announcements Syllabus revised Machine
CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2010 Lecture 16: Machine Learning Topics 12/7/2010 Luke Zettlemoyer Most slides over the course adapted from Dan Klein. 1 Announcements Syllabus revised Machine
ECS 234: Data Analysis: Clustering ECS 234
 : Data Analysis: Clustering What is Clustering? Given n objects, assign them to groups (clusters) based on their similarity Unsupervised Machine Learning Class Discovery Difficult, and maybe ill-posed
: Data Analysis: Clustering What is Clustering? Given n objects, assign them to groups (clusters) based on their similarity Unsupervised Machine Learning Class Discovery Difficult, and maybe ill-posed
R/BioC Exercises & Answers: Unsupervised methods
 R/BioC Exercises & Answers: Unsupervised methods Perry Moerland April 20, 2010 Z Information on how to log on to a PC in the exercise room and the UNIX server can be found here: http://bioinformaticslaboratory.nl/twiki/bin/view/biolab/educationbioinformaticsii.
R/BioC Exercises & Answers: Unsupervised methods Perry Moerland April 20, 2010 Z Information on how to log on to a PC in the exercise room and the UNIX server can be found here: http://bioinformaticslaboratory.nl/twiki/bin/view/biolab/educationbioinformaticsii.
Clustering. CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring Soleymani
 Clustering CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 Soleymani Outline Clustering Definition Clustering main approaches Partitional (flat) Hierarchical Clustering validation
Clustering CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 Soleymani Outline Clustering Definition Clustering main approaches Partitional (flat) Hierarchical Clustering validation
Redefining and Enhancing K-means Algorithm
 Redefining and Enhancing K-means Algorithm Nimrat Kaur Sidhu 1, Rajneet kaur 2 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science Engineering, SGGSWU, Fatehgarh Sahib, Punjab, India 1 Assistant Professor,
Redefining and Enhancing K-means Algorithm Nimrat Kaur Sidhu 1, Rajneet kaur 2 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science Engineering, SGGSWU, Fatehgarh Sahib, Punjab, India 1 Assistant Professor,
INF 4300 Classification III Anne Solberg The agenda today:
 INF 4300 Classification III Anne Solberg 28.10.15 The agenda today: More on estimating classifier accuracy Curse of dimensionality and simple feature selection knn-classification K-means clustering 28.10.15
INF 4300 Classification III Anne Solberg 28.10.15 The agenda today: More on estimating classifier accuracy Curse of dimensionality and simple feature selection knn-classification K-means clustering 28.10.15
Statistical Analysis of Metabolomics Data. Xiuxia Du Department of Bioinformatics & Genomics University of North Carolina at Charlotte
 Statistical Analysis of Metabolomics Data Xiuxia Du Department of Bioinformatics & Genomics University of North Carolina at Charlotte Outline Introduction Data pre-treatment 1. Normalization 2. Centering,
Statistical Analysis of Metabolomics Data Xiuxia Du Department of Bioinformatics & Genomics University of North Carolina at Charlotte Outline Introduction Data pre-treatment 1. Normalization 2. Centering,
What to come. There will be a few more topics we will cover on supervised learning
 Summary so far Supervised learning learn to predict Continuous target regression; Categorical target classification Linear Regression Classification Discriminative models Perceptron (linear) Logistic regression
Summary so far Supervised learning learn to predict Continuous target regression; Categorical target classification Linear Regression Classification Discriminative models Perceptron (linear) Logistic regression
Multivariate Analysis
 Multivariate Analysis Cluster Analysis Prof. Dr. Anselmo E de Oliveira anselmo.quimica.ufg.br anselmo.disciplinas@gmail.com Unsupervised Learning Cluster Analysis Natural grouping Patterns in the data
Multivariate Analysis Cluster Analysis Prof. Dr. Anselmo E de Oliveira anselmo.quimica.ufg.br anselmo.disciplinas@gmail.com Unsupervised Learning Cluster Analysis Natural grouping Patterns in the data
University of Florida CISE department Gator Engineering. Clustering Part 2
 Clustering Part 2 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Partitional Clustering Original Points A Partitional Clustering Hierarchical
Clustering Part 2 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Partitional Clustering Original Points A Partitional Clustering Hierarchical
Unsupervised learning, Clustering CS434
 Unsupervised learning, Clustering CS434 Unsupervised learning and pattern discovery So far, our data has been in this form: We will be looking at unlabeled data: x 11,x 21, x 31,, x 1 m x 12,x 22, x 32,,
Unsupervised learning, Clustering CS434 Unsupervised learning and pattern discovery So far, our data has been in this form: We will be looking at unlabeled data: x 11,x 21, x 31,, x 1 m x 12,x 22, x 32,,
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING
 CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University 09/25/2017 Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10.
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University 09/25/2017 Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10.
Introduc)on to Machine Learning: Clustering Algorithms How to Analyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013
 Introduc)on to Machine Learning: Clustering Algorithms 02-223 How to Analyze Your Own Genome Fall 203 Organizing data into clusters such that there is high intra- cluster similarity low inter- cluster
Introduc)on to Machine Learning: Clustering Algorithms 02-223 How to Analyze Your Own Genome Fall 203 Organizing data into clusters such that there is high intra- cluster similarity low inter- cluster
Statistics 202: Data Mining. c Jonathan Taylor. Clustering Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes.
 Clustering Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Clustering Clustering Goal: Finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group will be similar (or
Clustering Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Clustering Clustering Goal: Finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group will be similar (or
Contents. ! Data sets. ! Distance and similarity metrics. ! K-means clustering. ! Hierarchical clustering. ! Evaluation of clustering results
 Statistical Analysis of Microarray Data Contents Data sets Distance and similarity metrics K-means clustering Hierarchical clustering Evaluation of clustering results Clustering Jacques van Helden Jacques.van.Helden@ulb.ac.be
Statistical Analysis of Microarray Data Contents Data sets Distance and similarity metrics K-means clustering Hierarchical clustering Evaluation of clustering results Clustering Jacques van Helden Jacques.van.Helden@ulb.ac.be
Introduction to Machine Learning. Xiaojin Zhu
 Introduction to Machine Learning Xiaojin Zhu jerryzhu@cs.wisc.edu Read Chapter 1 of this book: Xiaojin Zhu and Andrew B. Goldberg. Introduction to Semi- Supervised Learning. http://www.morganclaypool.com/doi/abs/10.2200/s00196ed1v01y200906aim006
Introduction to Machine Learning Xiaojin Zhu jerryzhu@cs.wisc.edu Read Chapter 1 of this book: Xiaojin Zhu and Andrew B. Goldberg. Introduction to Semi- Supervised Learning. http://www.morganclaypool.com/doi/abs/10.2200/s00196ed1v01y200906aim006
Clustering Jacques van Helden
 Statistical Analysis of Microarray Data Clustering Jacques van Helden Jacques.van.Helden@ulb.ac.be Contents Data sets Distance and similarity metrics K-means clustering Hierarchical clustering Evaluation
Statistical Analysis of Microarray Data Clustering Jacques van Helden Jacques.van.Helden@ulb.ac.be Contents Data sets Distance and similarity metrics K-means clustering Hierarchical clustering Evaluation
A top down approach for determining the load profiles of consumers. Nimai
 A top down approach for determining the load profiles of consumers Nimai INTRODUCTION Load profiles represent a useful tool in the retail power market, where, in general, small consumers do not have the
A top down approach for determining the load profiles of consumers Nimai INTRODUCTION Load profiles represent a useful tool in the retail power market, where, in general, small consumers do not have the
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Clustering. (adapted from) Prof. Alexander Ihler
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Clustering (adapted from) Prof. Alexander Ihler Overview What is clustering and its applications? Distance between two clusters. Hierarchical Agglomerative clustering.
Machine Learning and Data Mining Clustering (adapted from) Prof. Alexander Ihler Overview What is clustering and its applications? Distance between two clusters. Hierarchical Agglomerative clustering.
Cluster Analysis. Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University
 Cluster Analysis Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University Cluster analysis Cluster analysis groups data objects based only on the attributes in the data. The main objective is that The objects within a group
Cluster Analysis Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University Cluster analysis Cluster analysis groups data objects based only on the attributes in the data. The main objective is that The objects within a group
Cluster analysis. Agnieszka Nowak - Brzezinska
 Cluster analysis Agnieszka Nowak - Brzezinska Outline of lecture What is cluster analysis? Clustering algorithms Measures of Cluster Validity What is Cluster Analysis? Finding groups of objects such that
Cluster analysis Agnieszka Nowak - Brzezinska Outline of lecture What is cluster analysis? Clustering algorithms Measures of Cluster Validity What is Cluster Analysis? Finding groups of objects such that
Unsupervised learning in Vision
 Chapter 7 Unsupervised learning in Vision The fields of Computer Vision and Machine Learning complement each other in a very natural way: the aim of the former is to extract useful information from visual
Chapter 7 Unsupervised learning in Vision The fields of Computer Vision and Machine Learning complement each other in a very natural way: the aim of the former is to extract useful information from visual
K Nearest Neighbor Wrap Up K- Means Clustering. Slides adapted from Prof. Carpuat
 K Nearest Neighbor Wrap Up K- Means Clustering Slides adapted from Prof. Carpuat K Nearest Neighbor classification Classification is based on Test instance with Training Data K: number of neighbors that
K Nearest Neighbor Wrap Up K- Means Clustering Slides adapted from Prof. Carpuat K Nearest Neighbor classification Classification is based on Test instance with Training Data K: number of neighbors that
Exploratory Data Analysis using Self-Organizing Maps. Madhumanti Ray
 Exploratory Data Analysis using Self-Organizing Maps Madhumanti Ray Content Introduction Data Analysis methods Self-Organizing Maps Conclusion Visualization of high-dimensional data items Exploratory data
Exploratory Data Analysis using Self-Organizing Maps Madhumanti Ray Content Introduction Data Analysis methods Self-Organizing Maps Conclusion Visualization of high-dimensional data items Exploratory data
What is Unsupervised Learning?
 Clustering What is Unsupervised Learning? Unlike in supervised learning, in unsupervised learning, there are no labels We simply a search for patterns in the data Examples Clustering Density Estimation
Clustering What is Unsupervised Learning? Unlike in supervised learning, in unsupervised learning, there are no labels We simply a search for patterns in the data Examples Clustering Density Estimation
Unsupervised Learning
 Outline Unsupervised Learning Basic concepts K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Which clustering algorithm to use? NN Supervised learning vs. unsupervised
Outline Unsupervised Learning Basic concepts K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Which clustering algorithm to use? NN Supervised learning vs. unsupervised
Supervised and Unsupervised Learning (II)
 Supervised and Unsupervised Learning (II) Yong Zheng Center for Web Intelligence DePaul University, Chicago IPD 346 - Data Science for Business Program DePaul University, Chicago, USA Intro: Supervised
Supervised and Unsupervised Learning (II) Yong Zheng Center for Web Intelligence DePaul University, Chicago IPD 346 - Data Science for Business Program DePaul University, Chicago, USA Intro: Supervised
MSA220 - Statistical Learning for Big Data
 MSA220 - Statistical Learning for Big Data Lecture 13 Rebecka Jörnsten Mathematical Sciences University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology Clustering Explorative analysis - finding groups
MSA220 - Statistical Learning for Big Data Lecture 13 Rebecka Jörnsten Mathematical Sciences University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology Clustering Explorative analysis - finding groups
Machine Learning (BSMC-GA 4439) Wenke Liu
 Machine Learning (BSMC-GA 4439) Wenke Liu 01-25-2018 Outline Background Defining proximity Clustering methods Determining number of clusters Other approaches Cluster analysis as unsupervised Learning Unsupervised
Machine Learning (BSMC-GA 4439) Wenke Liu 01-25-2018 Outline Background Defining proximity Clustering methods Determining number of clusters Other approaches Cluster analysis as unsupervised Learning Unsupervised
Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning
 Clustering Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning So far we have assumed that the training samples used to design the classifier were labeled by their class membership (supervised learning) We assume now
Clustering Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning So far we have assumed that the training samples used to design the classifier were labeled by their class membership (supervised learning) We assume now
Clustering analysis of gene expression data
 Clustering analysis of gene expression data Chapter 11 in Jonathan Pevsner, Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics, 3 rd edition (Chapter 9 in 2 nd edition) Human T cell expression data The matrix contains
Clustering analysis of gene expression data Chapter 11 in Jonathan Pevsner, Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics, 3 rd edition (Chapter 9 in 2 nd edition) Human T cell expression data The matrix contains
Kernels and Clustering
 Kernels and Clustering Robert Platt Northeastern University All slides in this file are adapted from CS188 UC Berkeley Case-Based Learning Non-Separable Data Case-Based Reasoning Classification from similarity
Kernels and Clustering Robert Platt Northeastern University All slides in this file are adapted from CS188 UC Berkeley Case-Based Learning Non-Separable Data Case-Based Reasoning Classification from similarity
An Introduction to Cluster Analysis. Zhaoxia Yu Department of Statistics Vice Chair of Undergraduate Affairs
 An Introduction to Cluster Analysis Zhaoxia Yu Department of Statistics Vice Chair of Undergraduate Affairs zhaoxia@ics.uci.edu 1 What can you say about the figure? signal C 0.0 0.5 1.0 1500 subjects Two
An Introduction to Cluster Analysis Zhaoxia Yu Department of Statistics Vice Chair of Undergraduate Affairs zhaoxia@ics.uci.edu 1 What can you say about the figure? signal C 0.0 0.5 1.0 1500 subjects Two
9/29/13. Outline Data mining tasks. Clustering algorithms. Applications of clustering in biology
 9/9/ I9 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Clustering algorithms Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Outline Data mining tasks Predictive tasks vs descriptive tasks Example
9/9/ I9 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Clustering algorithms Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Outline Data mining tasks Predictive tasks vs descriptive tasks Example
Unsupervised Learning
 Unsupervised Learning A review of clustering and other exploratory data analysis methods HST.951J: Medical Decision Support Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.951J: Medical Decision
Unsupervised Learning A review of clustering and other exploratory data analysis methods HST.951J: Medical Decision Support Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.951J: Medical Decision
Introduction to Supervised Learning
 Introduction to Supervised Learning Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 February 17, 2014 Abstract This document introduces the
Introduction to Supervised Learning Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 February 17, 2014 Abstract This document introduces the
How do microarrays work
 Lecture 3 (continued) Alvis Brazma European Bioinformatics Institute How do microarrays work condition mrna cdna hybridise to microarray condition Sample RNA extract labelled acid acid acid nucleic acid
Lecture 3 (continued) Alvis Brazma European Bioinformatics Institute How do microarrays work condition mrna cdna hybridise to microarray condition Sample RNA extract labelled acid acid acid nucleic acid
Hierarchical clustering
 Hierarchical clustering Rebecca C. Steorts, Duke University STA 325, Chapter 10 ISL 1 / 63 Agenda K-means versus Hierarchical clustering Agglomerative vs divisive clustering Dendogram (tree) Hierarchical
Hierarchical clustering Rebecca C. Steorts, Duke University STA 325, Chapter 10 ISL 1 / 63 Agenda K-means versus Hierarchical clustering Agglomerative vs divisive clustering Dendogram (tree) Hierarchical
5/15/16. Computational Methods for Data Analysis. Massimo Poesio UNSUPERVISED LEARNING. Clustering. Unsupervised learning introduction
 Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio UNSUPERVISED LEARNING Clustering Unsupervised learning introduction 1 Supervised learning Training set: Unsupervised learning Training set: 2 Clustering
Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio UNSUPERVISED LEARNING Clustering Unsupervised learning introduction 1 Supervised learning Training set: Unsupervised learning Training set: 2 Clustering
Machine Learning in Biology
 Università degli studi di Padova Machine Learning in Biology Luca Silvestrin (Dottorando, XXIII ciclo) Supervised learning Contents Class-conditional probability density Linear and quadratic discriminant
Università degli studi di Padova Machine Learning in Biology Luca Silvestrin (Dottorando, XXIII ciclo) Supervised learning Contents Class-conditional probability density Linear and quadratic discriminant
Supervised vs unsupervised clustering
 Classification Supervised vs unsupervised clustering Cluster analysis: Classes are not known a- priori. Classification: Classes are defined a-priori Sometimes called supervised clustering Extract useful
Classification Supervised vs unsupervised clustering Cluster analysis: Classes are not known a- priori. Classification: Classes are defined a-priori Sometimes called supervised clustering Extract useful
CSE 255 Lecture 6. Data Mining and Predictive Analytics. Community Detection
 CSE 255 Lecture 6 Data Mining and Predictive Analytics Community Detection Dimensionality reduction Goal: take high-dimensional data, and describe it compactly using a small number of dimensions Assumption:
CSE 255 Lecture 6 Data Mining and Predictive Analytics Community Detection Dimensionality reduction Goal: take high-dimensional data, and describe it compactly using a small number of dimensions Assumption:
4. Cluster Analysis. Francesc J. Ferri. Dept. d Informàtica. Universitat de València. Febrer F.J. Ferri (Univ. València) AIRF 2/ / 1
 Anàlisi d Imatges i Reconeixement de Formes Image Analysis and Pattern Recognition:. Cluster Analysis Francesc J. Ferri Dept. d Informàtica. Universitat de València Febrer 8 F.J. Ferri (Univ. València)
Anàlisi d Imatges i Reconeixement de Formes Image Analysis and Pattern Recognition:. Cluster Analysis Francesc J. Ferri Dept. d Informàtica. Universitat de València Febrer 8 F.J. Ferri (Univ. València)
10. Clustering. Introduction to Bioinformatics Jarkko Salojärvi. Based on lecture slides by Samuel Kaski
 10. Clustering Introduction to Bioinformatics 30.9.2008 Jarkko Salojärvi Based on lecture slides by Samuel Kaski Definition of a cluster Typically either 1. A group of mutually similar samples, or 2. A
10. Clustering Introduction to Bioinformatics 30.9.2008 Jarkko Salojärvi Based on lecture slides by Samuel Kaski Definition of a cluster Typically either 1. A group of mutually similar samples, or 2. A
Unsupervised Learning
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.951J: Medical Decision Support, Fall 2005 Instructors: Professor Lucila Ohno-Machado and Professor Staal Vinterbo 6.873/HST.951 Medical Decision
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.951J: Medical Decision Support, Fall 2005 Instructors: Professor Lucila Ohno-Machado and Professor Staal Vinterbo 6.873/HST.951 Medical Decision
HIERARCHICAL clustering analysis (or HCA) is an
 A Data-Driven Approach to Estimating the Number of Clusters in Hierarchical Clustering* Antoine E. Zambelli arxiv:1608.04700v1 [q-bio.qm] 16 Aug 2016 Abstract We propose two new methods for estimating
A Data-Driven Approach to Estimating the Number of Clusters in Hierarchical Clustering* Antoine E. Zambelli arxiv:1608.04700v1 [q-bio.qm] 16 Aug 2016 Abstract We propose two new methods for estimating
