Slide 1. Advanced Cartography in ArcGIS. Robert Jensen Edie Punt. Technical Workshops
|
|
|
- Corey Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Slide 1 Technical Workshops Advanced Cartography in ArcGIS Robert Jensen Edie Punt
2 Slide 2 Overview Using representations to manage symbology Solving graphic conflicts Geoprocessing for cartography in ArcGIS 10 A good map communicates by: depicting data effectively reflecting the relative importance of features reducing distraction and conflict
3 Slide 3 Representation Symbology
4 Slide 4 Representation Symbology Representations are: A way to symbolize features to solve common cartographic challenges A storage model that stores symbols with data Part of a feature class, managed through a layer Common cartographic challenges previously required complex workarounds Storing symbols in the geodatabase makes that information available for re-use and sharing
5 Slide 5 Representation Symbology Representations symbolize features cartographically Representations follow a rule-based structure Red = dashes Blue = drop shadows Green = overpass Orange = rotation
6 Slide 6 Representation Symbology Representations can produce and draw dynamic geometry, which may differ from spatial geometry Rivers are drawn smoother than the underlying geometry
7 Slide 7 Representation Field Mapping Representations can be data-driven to tailor symbols to feature attribution Streets drawn with one symbol Casing and fill width from attributes When multiple rules share common aspects, it s a good idea to consider a single rule A single rule is easier to interact with and thus more efficient Attribute information controls the way symbols are drawn Establish field mapping for gray layer to Road Casing Establish field mapping for orange layer to Road Fill
8 Slide 8 Representation Symbology Representations can store and display multiple symbols for each feature The same data represented two ways Both versions are stored in the data, not in map documents or layers Allows for differing sets of symbology to be accessed from the same data source. A self contained solution.
9 Slide 9 Representation Rules Symbol layers Geometric effects, marker placement styles Representation rules are a set of properties that describes a unique symbol Stored as feature class attribute values A rule will always consist of at least one symbol layer but may consist of a combination of many types of symbol layers Symbol layers Marker Line Fill Geometric effects Dynamically alter display geometry Marker placement styles Place representation markers relative to input geometry
10 Slide 10 Marker Placement Styles Position representation markers - Along lines and polygon outlines - Within polygons - In relation to points Extensible: write your own The way in which a marker or multiple markers are positioned in relation to the supporting geometry of the feature This geometry could be a shape override or the result from a geometric effect
11 Slide 11 Geometric Effects Dynamically change geometry before symbol applied - Affect all symbol layers, or just one - Can convert geometry type Can work sequentially Extensible: write your own May be applied individually to symbol layers or globally to all symbol layers Chained effects work in sequence from the top down The order can create different results The geometric effects applied to one symbol layer have no influence on other symbol layers in the rule.
12 Slide 12 Chaining Geometric Effects Creates unique symbols Effects can be chained to themselves Dashes + Dashes Wave + Wave Note on first bullet: These symbols/patterns are not available with a single effect Chaining effects builds the complexity of the rules. Dash example Dashes 1: Red Line = 0.5 pt, dashes 4 4, half pattern, offset 0.25 Blue Line = 0.5pt, dashes 4 4, dashes 2 2 half pattern, offset Dashes 2: Red Line = 0.5 pt, dashes 4 4, half pattern, offset 0.25 Blue Line = 0.5pt, dashes 4 4, half pattern, dashes 2 2 half gap, offset Wave example Wave 1: 6 6, square Wave 2: 4 4, sinus
13 Slide 13 Representation Geometry Logic The geometry made by the last effect in the chain must match the geometry type of the symbol layer - Else a warning appears indicating a disconnect in geometry logic - The symbol layer doesn't have geometry to symbolize Geometric effects alter geometry and even, in some cases, geometry type, it is important to ensure that representation rules maintain geometric logic. Geometric effects operate sequentially. The output of one geometric effect becomes the input of the following one, so you can use a chain of geometric effects to achieve the appropriate geometry logic. Regardless of how the geometry is dynamically changed through the chain of geometric effects, the final output of the last effect must match the geometry type of the symbol layer. If a warning symbol appears on the heading of the symbol layer, there is a disconnect in the geometry logic. The symbol layer you just added doesn't have any geometry to symbolize. For example, adding a fill layer to a line representation rule would generate a warning because there is no polygon geometry to fill. To repair the logic, add a line-to-polygon geometric effect to either the fill layer or the global effects portion of the rule. However, the opposite scenario adding a line symbol layer to a polygon representation rule would not generate a warning, because the line symbol layer will symbolize the outlines of the polygon geometry.
14 Slide 14 Geometric Effects: Drop Shadows Simulate a 3-dimensional appearance Move effect Offset effect Method = Rounded Gradient pattern Color 1 = white Color 2 = black Intervals = 50 Percentage = 50 D -Demo script- Use Move and Offset on fill layers to show how polygons can have their location changed just like points are. Move: X offset = 0.5, Y offset = -0.5 Offset: Offset = 0.5, method = rounded Gradient: color 1 = 100% white, color 2 = 100% black, style = buffer, intervals = 50, percentage = 50, angle = 0 Bonus = create rounded corners for buildings: Offset = -0.5, Buffer = 0.5 Opposite order will create square corners again
15 Slide 15 Geometric Effects: Using Markers Offset: -3 Placement: Along outline Offset: -7 Placement: Along outline Offset: -10 Placement: Inside polygon The polygon shows a feature where the middle of the feature is the highest part. Use a representation symbol to emphasize this. Its representation has four symbol layers: a stroke layer symbolized with dark blue; and three marker layers, each a dark blue dot of a different size. Each marker layer has its own placement style and geometric effect. The desired cartographic effect is a depth perspective effect where the dots stand out more along the slopes at the edges of the feature. To make the feature look like a hill, change the marker sizes and placement styles for the inside and outside layers. a) The placement style on the smallest dot is "Inside polygon." These dots fill the polygon interior. They do not fill it to the edge because of the Offset curve effect with a - 10 value. For this marker layer, the polygon is shrunk by 10 points in all directions. b) The placement style on the medium dot is "Along outline." Without a geometric effect, this would cause one row of medium-sized dots to be placed along the polygon boundary. Because of the Offset curve and its negative value, the boundary is shifted seven points inward. c) The placement style on the big dot is also "Along outline," and the effect is the same as with the medium dot except that a different offset value is used.
16 Slide 16 Geometric Effects: Tapered Streams Organic, artistic look Use Wave and Tapered Polygon geometric effects Rivers drawn from line geometry Rivers drawn from dynamic polygon geometry D -Demo script- The first goal is to show a river dynamically changing width to give the impression that water is flowing downhill. The second goal is to give the river symbols a more natural look instead of the straight line geometry of the feature. Tributary rule: add a new fill layer (see warning) and move it below the stroke note that the fill layers attempts to draw something (might be OK for some features). Add Tapered Polygon effect (no warning), click apply to see poly draw. Move the fill layer above the stroke layer. Change To width to 2 - apply, change length to 45 apply, change color to Cretean Blue (3 rd from top/right) apply. Now add wave effect above taper, period = 12 apply, width = 4 apply, style = random apply. Note the difference between the fill and the stroke layers. Remove the stroke layer. click apply to finish with this rule. Body rule: Add the wave effect, period = 15, width = 5, style = sinus.
17 Slide 17 Representation Overrides Exceptions to the rule - Customize individual features - Made while editing Property overrides - Change any property of the rule Geometry overrides - Store alternate geometry
18 Slide 18 Representation Licensing Representations recognized by all ArcGIS products ArcView license: - View representations and properties ArcEditor license: - Create and edit representations - Some geoprocessing for representations ArcInfo license: - View, create, edit representations - All geoprocessing tools To use the representation geoprocessing tools, you must have an ArcInfo license. It s still useful to be aware of and understand representations if you re working with an ArcView license because although you can t create or edit them you will still be able to view them and their properties. Recognized by all ArcGIS products ArcView, ArcEditor, ArcInfo ArcGIS Server ArcGlobe, ArcScene ArcGIS Explorer ArcReader
19 Slide 19 Resolving Graphic Conflicts
20 Slide 20 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Features compete for map space - More prevalent as scale decreases - Retain representative character - Automate where possible Techniques to solve graphic conflicts: - Mask portions of features - Spread clustered features - Use contextual generalization Considerations: Some features must share the same map space Balance between showing elements and losing information Otherwise requires time consuming manual intervention Options to solve graphic conflicts: Mask only parts of a single feature Spread clustered point features apart for visible distinction Apply generalization techniques in a contextual fashion
21 Slide 21 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Vertical Coincidence Requirement: Symbolize vertical coincidence without altering the connectivity of associated data Solution: Create overpasses D GP tool automates a solution Find features where symbols intersect Build a mask at that location Create some bridges around those masks Use the masks to hide portions of a feature s symbol Masking at the feature level, instead of the layer level
22 Slide 22 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Symbol-level Masking Requirement: Show features clearly Solution: Hide parts of a feature D Introduced at Open Advanced Drawing Options Dialog Click Draw using.. check-box Choose a layer from list of Masking Layers Choose a layer from list of Masked Layer click apply Click Enable to check-box Click on the Masked Layer, then click in Level section which is now available Type 1, 3 (the comma is needed but spaces are optional) click enter Click apply to see result Click OK to close the dialog
23 Slide 23 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Disperse Markers tool Requirement: Display clustered markers clearly Solution: Spread markers apart with shape overrides D -Demo script- Open Disperse Markers tool Open help tab to learn about choice of patterns Choose input layer Choose 3 pts for the minimum spacing Choose ring for dispersal pattern Click OK to run tool Start editing and select features Open Representation properties dialog and see shape override button Click override button to remove it and see features returned to their original location
24 Slide 24 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Detect Graphic Conflicts tool Finds areas where symbology overlaps, even if geometry does not - Or find areas where symbology too close Compare two layers, or one layer to itself New at ArcGIS 10: use non-representation layers too The tool assesses conflicts among symbols, not geometry. The input layer and the conflict layer can be the same. Input layers can be symbolized with standard symbols or representation symbology. Input layers can include feature class annotation, including symbol substitution. Shapefile, coverage, and CAD layers are also acceptable inputs. The following inputs are not accepted by the tool: CAD, coverage, or VPF annotation, dimensions, charts, dot-density or proportional symbols, raster layers, network analyst layers, or 3D symbols. Use the Conflict Distance parameter to detect areas where input and conflict symbology is closer than a certain distance. The conflict calculation is based on a reference scale. Use the Line Connection Allowance parameter to disregard symbol overlaps where line ends meet. This is useful if you use line symbol end caps to ensure that lines connect visually, but you don't want each instance detected as a conflict.
25 Slide 25 Contextual Generalization with Geoprocessing Simplify data to display at smaller scales - Assess multiple layers contextually - Maintain representative pattern, density, and character - Resolve conflicts between symbolized features at scale Traditionally the generalization tools we have released focus on geometry only. They work on individual feature geometries, or small groups of features. They didn t consider symbology at all, and are useful for simplifying features, but not de-conflicting features. At 10 we released the next generation of generalization tools. These tools take into account that the: -Type of feature matters. Road networks are different from hydro networks, are different from pipeline networks -The relationships between layers matter. Moving Roads will affect how you need to move buildings. -The size of symbolized features at scale must be taken into account for de-conflicting features -Patterns need to be maintained. Road networks, building patterns -In a cartographic workflow it is often better modify the input layers, rather than creating new feature classes. Cartographic generalization takes place after the symbology has been applied and often after cartographic edits have taken place. For this reason the new tools will work with Representations. Generalization modifications can be written directly into the overrides without messing up the core geometry.
26 Slide 26 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Thin Road Network tool Removes less significant roads from display Retains representative pattern and connectivity Visibility controlled by attribute, easy to modify D Maintain pattern and density while retaining connectivity Keep significant roads only Balanced by road classification Retain specific features by locking Visibility controlled by attribute, easy to modify Level of 0 can be used in all the new tools as a lock. You can set up multiple visibility fields for multiple scales no overhead lots of different ways to view same feature class. This tool lowers the density of a displayed street network by eliminating smaller, less significant roads while maintaining the overall connectivity and character of the street network. The Thin Road Network tool eliminates road features from display to create a simplified arrangement of roads that maintains connectivity along with the representative pattern and density of the original arrangement. Flexibility is provided in that significant features can be forced to remain visible, and the visibility of any feature can be easily switched. No data is moved or deleted in the processing of this tool. Use a definition query to show the results zero = visible, one = invisible
27 Slide 27 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Merge Divided Roads tool Create a single highway feature from multiple lanes Create a single road from a boulevard Merge only equal-class roads together D This tool generates a line feature class whose features follow the course of divided road features to display a simpler network of single lines. The Merge Divided Roads tool creates a single road from a matched pair of paralleltrending, equal classification roads. This is particularly useful when data has been collected as separate lanes in a highway, or for multiple lane boulevards but should be depicted as a single feature at reduced scales. Pictures: 1 = original roads, 2 = thinned roads, 3 = merged roads at 10K, 4 = merged roads at 24K
28 Slide 28 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Resolve Road Conflicts tool Adjust roads to show visual separation - multi-lane highways, boulevards, dead-ends, roundabouts Less significant roads moved to accommodate more significant roads D Symbolized roads tend to coalesce at smaller scales Spread parallel-trending roads apart, Adjust roads to show visual separation multi-lane highways, boulevards, dead-ends, roundabouts Displacement can be saved as polygons visual check, or input for Propagate Displacement tool to maintain spatial relationships Enhance dead-end spacing This tool resolves symbol conflicts among roads by slightly displacing features while retaining connectivity and character of the road network. Input features are hierarchically categorized to ensure that less significant parts of the network are moved to accommodate more important features. The Resolve Road Conflicts tool separates roads that graphically conflict when symbolized at scale. Road classification is defined through attribution and used to dictate which features will remain in place (or move a relatively small amount) at the expense of others which must be moved and reshaped somewhat to accommodate them. This tool separates multiple highway lanes and boulevards, exaggerates roundabouts, and widens gaps between highways and exit ramps. The degree and direction of displacement can be stored in polygons which can be used to propagate this movement to spatially related features.
29 Slide 29 Resolving Line Conflicts Comparing Resolve Road Conflicts tool and Merge Divided Roads tool Coalescing Displace Merge
30 Slide 30 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Propagate Displacement tool Conflict resolution may introduce spatial discrepancy - Adjust adjacent features to reestablish relationships Use displacement output from other tools - Merge Divided Roads tool - Resolve Road Conflicts tool D Propagate displacement to points, lines, polygons solid: entire feature moves as a block, i.e. building elastic: feature can be warped slightly to fit, i.e. forest auto: tool decides for each feature, based on geometry (default) This tool evaluates the displacement that was made to a road network and propagates the shift to nearby features to ensure that their original spatial relationships are retained. The Propagate Displacement tool preserves the spatial relationship between features by propagating the displacements made in conflict resolution to proximate features. Movement can be either solid, where the entire feature is translated to a new location, or elastic, where a large complex feature is reshaped proportionally to account for the positional changes. An automatic option allows the tool to make this choice dependent on the morphology of each feature.
31 Slide 31 Resolving Graphic Conflicts Resolve Building Conflicts tool Separate buildings from each other and from barriers - Retain relative density and pattern - Adjust visibility, size, and spacing, orientation D This tool resolves symbol conflicts among a collection of buildings with relation to one or more linear barriers. Minimum building size is enforced and placement in relation to barriers can be controlled. The Resolve Building Conflicts tool seeks to eliminate graphic conflicts between buildings and between buildings and specified barrier features through elimination and transformation when they are symbolized at scale. The characteristic pattern arrangement and density is preserved. Small buildings can be increased to a minimum size and multiple barrier layers can be considered simultaneously. Barriers typically include roads and streets, but can also include other layers like rail, hydrography, utilities, or administrative boundaries. Point and polygon building geometry can be assessed together. Buildings can be optionally oriented and positioned relative to the barrier features.
32 Slide 32 ESRI Mapping Center
33 Slide 33
Cartographic Techniques and Representations
 Cartographic Techniques and Representations NEARC 2007 ESRI Technical Session ESRI, Boston Overview of Presentation Labeling and Annotation Masking Layout Tips Cartographic Representations Labeling versus
Cartographic Techniques and Representations NEARC 2007 ESRI Technical Session ESRI, Boston Overview of Presentation Labeling and Annotation Masking Layout Tips Cartographic Representations Labeling versus
ArcGIS Multi-Scale and Generalization
 ArcGIS Multi-Scale and Generalization Paul Hardy 2014-12-04 Produce Many Information Products from One Database Production Workflows Authoritative Database Multi-scale Information products: Maps, Data,
ArcGIS Multi-Scale and Generalization Paul Hardy 2014-12-04 Produce Many Information Products from One Database Production Workflows Authoritative Database Multi-scale Information products: Maps, Data,
How to draw and create shapes
 Adobe Flash Professional Guide How to draw and create shapes You can add artwork to your Adobe Flash Professional documents in two ways: You can import images or draw original artwork in Flash by using
Adobe Flash Professional Guide How to draw and create shapes You can add artwork to your Adobe Flash Professional documents in two ways: You can import images or draw original artwork in Flash by using
In this exercise, you will convert labels into geodatabase annotation so you can edit the text features.
 Instructions: Use the provided data stored in a USB. For the report: 1. Start a new word document. 2. Follow an exercise step as given below. 3. Describe what you did in that step in the word document
Instructions: Use the provided data stored in a USB. For the report: 1. Start a new word document. 2. Follow an exercise step as given below. 3. Describe what you did in that step in the word document
From Data to Map in 30 Minutes. Aileen Buckley, PhD
 From Data to Map in 30 Minutes Aileen Buckley, PhD This session Crater Lake online map From NPS: https://www.nps.gov/carto/hfc/carto/media/crlamap1.pdf Download Crater Lake map packages here: ArcGIS Pro
From Data to Map in 30 Minutes Aileen Buckley, PhD This session Crater Lake online map From NPS: https://www.nps.gov/carto/hfc/carto/media/crlamap1.pdf Download Crater Lake map packages here: ArcGIS Pro
Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10
 Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10 Scenario In this exercise, imagine you are a GIS analyst working for Old Dominion University. Construction will begin shortly on renovation of the new
Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10 Scenario In this exercise, imagine you are a GIS analyst working for Old Dominion University. Construction will begin shortly on renovation of the new
A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE)
 A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE) Lesson overview In this interactive demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CC (2018 release), you ll get an overview of the main features of the application.
A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE) Lesson overview In this interactive demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CC (2018 release), you ll get an overview of the main features of the application.
THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT
 Vol. XIX, 2011, No. 1, 1 7, DOI: 10.2478/v10189-011-0001-4 V. DROPPOVÁ THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT Veronika Droppová email: veronika.droppova@gmail.com
Vol. XIX, 2011, No. 1, 1 7, DOI: 10.2478/v10189-011-0001-4 V. DROPPOVÁ THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT Veronika Droppová email: veronika.droppova@gmail.com
ArcGIS 9. Maplex Tutorial
 ArcGIS 9 Maplex Tutorial Copyright 004 006 ESRI All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of ESRI. This work is
ArcGIS 9 Maplex Tutorial Copyright 004 006 ESRI All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of ESRI. This work is
4. If you are prompted to enable hardware acceleration to improve performance, click
 Exercise 1a: Creating new points ArcGIS 10 Complexity: Beginner Data Requirement: ArcGIS Tutorial Data Setup About creating new points In this exercise, you will use an aerial photograph to create a new
Exercise 1a: Creating new points ArcGIS 10 Complexity: Beginner Data Requirement: ArcGIS Tutorial Data Setup About creating new points In this exercise, you will use an aerial photograph to create a new
Streamlining Editing Workflows. Amber Bethell
 Streamlining Editing Workflows Amber Bethell Workflow for solving geographic problems Ask a question Create or acquire data Validate and update data Analyze data Create cartographic product Act upon knowledge
Streamlining Editing Workflows Amber Bethell Workflow for solving geographic problems Ask a question Create or acquire data Validate and update data Analyze data Create cartographic product Act upon knowledge
ArcGIS Pro Editing. Jennifer Cadkin & Phil Sanchez
 ArcGIS Pro Editing Jennifer Cadkin & Phil Sanchez ArcGIS Pro Editing Overview Provides tools that allow you to maintain, update, and create new data - Modifying geometry, drawing new features - Entering
ArcGIS Pro Editing Jennifer Cadkin & Phil Sanchez ArcGIS Pro Editing Overview Provides tools that allow you to maintain, update, and create new data - Modifying geometry, drawing new features - Entering
What s New in Desktop 10.1
 What s New in Desktop 10.1 Damian Spangrud Esri Redlands Trip Down Memory Lane ArcGIS A Complete System for Geographic Information Cloud Web Online Mobile Enterprise Desktop Sharing Information sharing
What s New in Desktop 10.1 Damian Spangrud Esri Redlands Trip Down Memory Lane ArcGIS A Complete System for Geographic Information Cloud Web Online Mobile Enterprise Desktop Sharing Information sharing
Creating Great Labels Using Maplex
 Esri International User Conference San Diego, CA Technical Workshops July 11 15, 2011 Creating Great Labels Using Maplex Craig Williams Natalie Vines 2 Presentation Overview What are the types of text
Esri International User Conference San Diego, CA Technical Workshops July 11 15, 2011 Creating Great Labels Using Maplex Craig Williams Natalie Vines 2 Presentation Overview What are the types of text
Topology in the Geodatabase: An Introduction
 Topology in the Geodatabase: An Introduction Colin Zwicker Erik Hoel ESRI Super Secret Topology Laboratory, May 2016 Agenda ArcGIS Topology defined Validating a topology Editing a topology Geoprocessing
Topology in the Geodatabase: An Introduction Colin Zwicker Erik Hoel ESRI Super Secret Topology Laboratory, May 2016 Agenda ArcGIS Topology defined Validating a topology Editing a topology Geoprocessing
ArcView QuickStart Guide. Contents. The ArcView Screen. Elements of an ArcView Project. Creating an ArcView Project. Adding Themes to Views
 ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
TOPOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS, ACTIONS AND REFLEXES FOR GENERALIZATION BY OPTIMIZATION
 10 th ICA Workshop on Generalisation and Multiple Representation, 2-3 August 2007, Moscow TOPOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS, ACTIONS AND REFLEXES FOR GENERALIZATION BY OPTIMIZATION Jean-Luc Monnot, Paul Hardy, &
10 th ICA Workshop on Generalisation and Multiple Representation, 2-3 August 2007, Moscow TOPOLOGICAL CONSTRAINTS, ACTIONS AND REFLEXES FOR GENERALIZATION BY OPTIMIZATION Jean-Luc Monnot, Paul Hardy, &
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS
 Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
ArcGIS Pro Editing: An Introduction. Jennifer Cadkin & Phil Sanchez
 ArcGIS Pro Editing: An Introduction Jennifer Cadkin & Phil Sanchez See Us Here WORKSHOP ArcGIS Pro Editing: An Introduction LOCATION SDCC - Ballroom 20 D TIME FRAME Thursday 10:00 11:00 ArcGIS Pro: 3D
ArcGIS Pro Editing: An Introduction Jennifer Cadkin & Phil Sanchez See Us Here WORKSHOP ArcGIS Pro Editing: An Introduction LOCATION SDCC - Ballroom 20 D TIME FRAME Thursday 10:00 11:00 ArcGIS Pro: 3D
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Six: Labeling Map Features
 Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Six: Labeling Map Features In this activity, you will explore techniques for adding text to maps. As discussed in lecture, there are two aspects to using text
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Six: Labeling Map Features In this activity, you will explore techniques for adding text to maps. As discussed in lecture, there are two aspects to using text
13 Vectorizing. Overview
 13 Vectorizing Vectorizing tools are used to create vector data from scanned drawings or images. Combined with the display speed of Image Manager, these tools provide an efficient environment for data
13 Vectorizing Vectorizing tools are used to create vector data from scanned drawings or images. Combined with the display speed of Image Manager, these tools provide an efficient environment for data
Advanced Map Labeling using Maplex. Wendy Harrison & Samuel Troth
 Advanced Map Labeling using Maplex Wendy Harrison & Samuel Troth Presentation Overview We ll be using ArcGIS Pro Introduction - Different types of text in ArcGIS - role of the Maplex Label Engine labeling
Advanced Map Labeling using Maplex Wendy Harrison & Samuel Troth Presentation Overview We ll be using ArcGIS Pro Introduction - Different types of text in ArcGIS - role of the Maplex Label Engine labeling
Expression Design Lab Exercises
 Expression Design Lab Exercises Creating Images with Expression Design 2 Beaches Around the World (Part 1: Beaches Around the World Series) Information in this document, including URL and other Internet
Expression Design Lab Exercises Creating Images with Expression Design 2 Beaches Around the World (Part 1: Beaches Around the World Series) Information in this document, including URL and other Internet
Lecture 2 Map design. Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017
 Lecture 2 Map design Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
Lecture 2 Map design Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
ArcMap Editing Tips and Tricks. Sean Jones
 ArcMap Editing Tips and Tricks Sean Jones Overview Topics - Tuning your editing map - Creating features - Editing features and attributes - Aligning and editing coincident features - Addins Format - Software
ArcMap Editing Tips and Tricks Sean Jones Overview Topics - Tuning your editing map - Creating features - Editing features and attributes - Aligning and editing coincident features - Addins Format - Software
Exercise 1: An Overview of ArcMap and ArcCatalog
 Exercise 1: An Overview of ArcMap and ArcCatalog Introduction: ArcGIS is an integrated collection of GIS software products for building a complete GIS. ArcGIS enables users to deploy GIS functionality
Exercise 1: An Overview of ArcMap and ArcCatalog Introduction: ArcGIS is an integrated collection of GIS software products for building a complete GIS. ArcGIS enables users to deploy GIS functionality
Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial
 Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial Adobe InDesign CS6 is a page-layout software that takes print publishing and page design beyond current boundaries. InDesign is a desktop publishing program that incorporates
Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial Adobe InDesign CS6 is a page-layout software that takes print publishing and page design beyond current boundaries. InDesign is a desktop publishing program that incorporates
Excel 2013 Intermediate
 Instructor s Excel 2013 Tutorial 2 - Charts Excel 2013 Intermediate 103-124 Unit 2 - Charts Quick Links Chart Concepts Page EX197 EX199 EX200 Selecting Source Data Pages EX198 EX234 EX237 Creating a Chart
Instructor s Excel 2013 Tutorial 2 - Charts Excel 2013 Intermediate 103-124 Unit 2 - Charts Quick Links Chart Concepts Page EX197 EX199 EX200 Selecting Source Data Pages EX198 EX234 EX237 Creating a Chart
GIS Virtual Workshop: Buffering
 This workshop will teach the different methods of buffering data. They will include: Basic buffering of data Merging buffering zones Clipping the buffer Concentric rings around the object You will find
This workshop will teach the different methods of buffering data. They will include: Basic buffering of data Merging buffering zones Clipping the buffer Concentric rings around the object You will find
10.1 Overview. Section 10.1: Overview. Section 10.2: Procedure for Generating Prisms. Section 10.3: Prism Meshing Options
 Chapter 10. Generating Prisms This chapter describes the automatic and manual procedure for creating prisms in TGrid. It also discusses the solution to some common problems that you may face while creating
Chapter 10. Generating Prisms This chapter describes the automatic and manual procedure for creating prisms in TGrid. It also discusses the solution to some common problems that you may face while creating
Geographical Information Systems Institute. Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University. LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap
 Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Object modeling and geodatabases. GEOG 419: Advanced GIS
 Object modeling and geodatabases GEOG 419: Advanced GIS CAD Data Model 1960s and 1970s Geographic data stored as points, lines, and areas No attributes; each feature type stored on a different layer No
Object modeling and geodatabases GEOG 419: Advanced GIS CAD Data Model 1960s and 1970s Geographic data stored as points, lines, and areas No attributes; each feature type stored on a different layer No
Organizing Design Data
 Organizing Design Data Module Overview This module explains how to use the data in different files for reference purposes. Module Prerequisites Knowledge of MicroStation s interface Some knowledge about
Organizing Design Data Module Overview This module explains how to use the data in different files for reference purposes. Module Prerequisites Knowledge of MicroStation s interface Some knowledge about
OS OpenData masterclass 2013 Cartographic Design workshop
 OS OpenData masterclass 2013 Cartographic Design workshop 1 Quantum GIS Quantum GIS (QGIS) is a user-friendly Open Source Geographic Information System (GIS,) licensed under the GNU General Public License.
OS OpenData masterclass 2013 Cartographic Design workshop 1 Quantum GIS Quantum GIS (QGIS) is a user-friendly Open Source Geographic Information System (GIS,) licensed under the GNU General Public License.
Schematics in ArcMap Tutorial
 Schematics in ArcMap Tutorial Copyright 1995-2010 Esri All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introducing Schematics in ArcMap Tutorial........................ 3 Exercise 1: Getting familiar with Schematics
Schematics in ArcMap Tutorial Copyright 1995-2010 Esri All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introducing Schematics in ArcMap Tutorial........................ 3 Exercise 1: Getting familiar with Schematics
layers in a raster model
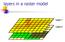 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
Adding Objects Creating Shapes Adding. Text Printing and Exporting Getting Started Creating a. Creating Shapes Adding Text Printing and Exporting
 Getting Started Creating a Workspace Pages, Masters and Guides Adding Objects Creating Shapes Adding Text Printing and Exporting Getting Started Creating a Workspace Pages, Masters and Guides Adding Objects
Getting Started Creating a Workspace Pages, Masters and Guides Adding Objects Creating Shapes Adding Text Printing and Exporting Getting Started Creating a Workspace Pages, Masters and Guides Adding Objects
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8
 LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
Topology in the Geodatabase an Introduction. Erik Hoel Doug Morgenthaler
 Topology in the Geodatabase an Introduction Erik Hoel Doug Morgenthaler ESRI Super Secret Topology Laboratory, May 2012 Agenda ArcGIS Topology defined Validating a topology Editing a topology Geoprocessing
Topology in the Geodatabase an Introduction Erik Hoel Doug Morgenthaler ESRI Super Secret Topology Laboratory, May 2012 Agenda ArcGIS Topology defined Validating a topology Editing a topology Geoprocessing
User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015
 User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015 - 2 / 112 - V1.1 Variegator... 7 Variegator Features... 7 1. Variable elements... 7 2. Static elements... 7 3. Element Manipulation... 7 4. Document Formats... 7 5.
User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015 - 2 / 112 - V1.1 Variegator... 7 Variegator Features... 7 1. Variable elements... 7 2. Static elements... 7 3. Element Manipulation... 7 4. Document Formats... 7 5.
Introduction to GIS 2011
 Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
GIS OPERATION MANUAL
 GIS OPERATION MANUAL 1. Computer System Description Hardware Make Compaq Presario 5004 CPU AMD Athlon 1.1 Ghz Main Memory 640MB CD-ROM 52 X CD-RW 8 X HD 57GB Monitor 19 inch Video Adapter 16 Mb Nvidia
GIS OPERATION MANUAL 1. Computer System Description Hardware Make Compaq Presario 5004 CPU AMD Athlon 1.1 Ghz Main Memory 640MB CD-ROM 52 X CD-RW 8 X HD 57GB Monitor 19 inch Video Adapter 16 Mb Nvidia
Session 3: Cartography in ArcGIS. Mapping population data
 Exercise 3: Cartography in ArcGIS Mapping population data Background GIS is well known for its ability to produce high quality maps. ArcGIS provides useful tools that allow you to do this. It is important
Exercise 3: Cartography in ArcGIS Mapping population data Background GIS is well known for its ability to produce high quality maps. ArcGIS provides useful tools that allow you to do this. It is important
Information Technology and Media Services. Office Excel. Charts
 Information Technology and Media Services Office 2010 Excel Charts August 2014 Information Technology and Media Services CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 CHART TYPES... 3 CHOOSING A CHART... 4 CREATING A COLUMN
Information Technology and Media Services Office 2010 Excel Charts August 2014 Information Technology and Media Services CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 CHART TYPES... 3 CHOOSING A CHART... 4 CREATING A COLUMN
Visualization with ArcGlobe. Brady Hoak
 Visualization with ArcGlobe Brady Hoak Contents What is ArcGlobe? 3D Mapping and ArcGlobe Displaying data in ArcGlobe ArcGlobe tools Tips for constructing ArcGlobe documents New at ArcGIS 9.3 ArcGIS integration
Visualization with ArcGlobe Brady Hoak Contents What is ArcGlobe? 3D Mapping and ArcGlobe Displaying data in ArcGlobe ArcGlobe tools Tips for constructing ArcGlobe documents New at ArcGIS 9.3 ArcGIS integration
for ArcSketch Version 1.1 ArcSketch is a sample extension to ArcGIS. It works with ArcGIS 9.1
 ArcSketch User Guide for ArcSketch Version 1.1 ArcSketch is a sample extension to ArcGIS. It works with ArcGIS 9.1 ArcSketch allows the user to quickly create, or sketch, features in ArcMap using easy-to-use
ArcSketch User Guide for ArcSketch Version 1.1 ArcSketch is a sample extension to ArcGIS. It works with ArcGIS 9.1 ArcSketch allows the user to quickly create, or sketch, features in ArcMap using easy-to-use
Step by Step GIS. Section 1
 Step by Step GIS Section 1 Contact the web page given below for the data required to do the exercises (http://www.pasda.psu.edu/default.asp) Before beginning the tutorials please visit the Preparation
Step by Step GIS Section 1 Contact the web page given below for the data required to do the exercises (http://www.pasda.psu.edu/default.asp) Before beginning the tutorials please visit the Preparation
3D Programming. 3D Programming Concepts. Outline. 3D Concepts. 3D Concepts -- Coordinate Systems. 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models
 3D Programming Concepts Outline 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models 3D Programming CS 4390 3D Computer 1 2 3D Concepts 3D Model is a 3D simulation of an object. Coordinate Systems 3D Models 3D Shapes 3D Concepts
3D Programming Concepts Outline 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models 3D Programming CS 4390 3D Computer 1 2 3D Concepts 3D Model is a 3D simulation of an object. Coordinate Systems 3D Models 3D Shapes 3D Concepts
Microsoft Word
 OBJECTS: Shapes (part 1) Shapes and the Drawing Tools Basic shapes can be used to graphically represent information or categories. The NOTE: Please read the Objects (add-on) document before continuing.
OBJECTS: Shapes (part 1) Shapes and the Drawing Tools Basic shapes can be used to graphically represent information or categories. The NOTE: Please read the Objects (add-on) document before continuing.
Adobe Flash CS4 Part 1: Introduction to Flash
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Flash CS4 Part 1: Introduction to Flash Fall 2010, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Downloading the Data Files...3
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Flash CS4 Part 1: Introduction to Flash Fall 2010, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Downloading the Data Files...3
CHAPTER 11. Learn to use GEOPAK Automated Superelevation dialog box and Autoshape Builder to apply superelevation to a roadway.
 CHAPTER 11 Superelevation 11.1 Introduction Objectives Project Manager Learn to use GEOPAK Automated Superelevation dialog box and Autoshape Builder to apply superelevation to a roadway. Calculate Superelevation
CHAPTER 11 Superelevation 11.1 Introduction Objectives Project Manager Learn to use GEOPAK Automated Superelevation dialog box and Autoshape Builder to apply superelevation to a roadway. Calculate Superelevation
12 APPLYING EFFECTS. Lesson overview
 12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects, such as Pathfinder, Scribble, and Drop Shadow. Use Warp effects to distort type. Create three-dimensional
12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects, such as Pathfinder, Scribble, and Drop Shadow. Use Warp effects to distort type. Create three-dimensional
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling
 Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
1. Start ArcMap by going to the Start menu > All Programs > ArcGIS > ArcMap.
 Learning ArcGIS: Introduction to ArcMap 10.1 The Map Document Feature Manipulation Navigating ArcMap Map Documents, Layers, and Features Shapes, Location, and Attribute Data Symbology Zoom, Pan and Map
Learning ArcGIS: Introduction to ArcMap 10.1 The Map Document Feature Manipulation Navigating ArcMap Map Documents, Layers, and Features Shapes, Location, and Attribute Data Symbology Zoom, Pan and Map
Sample Chapters. To learn more about this book, visit the detail page at: go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=192147
 Sample Chapters Copyright 2010 by Online Training Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved. To learn more about this book, visit the detail page at: go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=192147 Chapter at a Glance
Sample Chapters Copyright 2010 by Online Training Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved. To learn more about this book, visit the detail page at: go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=192147 Chapter at a Glance
Adobe Illustrator. Always NAME your project file. It should be specific to you and the project you are working on.
 Adobe Illustrator This packet will serve as a basic introduction to Adobe Illustrator and some of the tools it has to offer. It is recommended that anyone looking to become more familiar with the program
Adobe Illustrator This packet will serve as a basic introduction to Adobe Illustrator and some of the tools it has to offer. It is recommended that anyone looking to become more familiar with the program
Using Flash Animation Basics
 Using Flash Contents Using Flash... 1 Animation Basics... 1 Exercise 1. Creating a Symbol... 2 Exercise 2. Working with Layers... 4 Exercise 3. Using the Timeline... 6 Exercise 4. Previewing an animation...
Using Flash Contents Using Flash... 1 Animation Basics... 1 Exercise 1. Creating a Symbol... 2 Exercise 2. Working with Layers... 4 Exercise 3. Using the Timeline... 6 Exercise 4. Previewing an animation...
Key Terms. Symbology. Categorical attributes. Style. Layer file
 Key Terms Symbology Categorical attributes Style Layer file Review Questions POP-RANGE is a string field of the Cities feature class with the following entries: 0-9,999, 10,000-49,999, 50,000-99,000 This
Key Terms Symbology Categorical attributes Style Layer file Review Questions POP-RANGE is a string field of the Cities feature class with the following entries: 0-9,999, 10,000-49,999, 50,000-99,000 This
This group is dedicated to Modeler tools for Layout s FiberFX hair and fur system. For the Layout interface and controls see FiberFX
 Fiber FX Click here to expand Table of Contents... FiberFX Strand Modeler Global Controls Fiber Tab Guides Tab Random Tab Gravity Tab Tools1 Tab Tools2 Tab Options Tab Strand Tool Strand Maker This group
Fiber FX Click here to expand Table of Contents... FiberFX Strand Modeler Global Controls Fiber Tab Guides Tab Random Tab Gravity Tab Tools1 Tab Tools2 Tab Options Tab Strand Tool Strand Maker This group
Work with Shapes. Concepts CHAPTER. Concepts, page 3-1 Procedures, page 3-5
 3 CHAPTER Revised: November 15, 2011 Concepts, page 3-1, page 3-5 Concepts The Shapes Tool is Versatile, page 3-2 Guidelines for Shapes, page 3-2 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?, page
3 CHAPTER Revised: November 15, 2011 Concepts, page 3-1, page 3-5 Concepts The Shapes Tool is Versatile, page 3-2 Guidelines for Shapes, page 3-2 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?, page
Excel Core Certification
 Microsoft Office Specialist 2010 Microsoft Excel Core Certification 2010 Lesson 6: Working with Charts Lesson Objectives This lesson introduces you to working with charts. You will look at how to create
Microsoft Office Specialist 2010 Microsoft Excel Core Certification 2010 Lesson 6: Working with Charts Lesson Objectives This lesson introduces you to working with charts. You will look at how to create
Exercise 1: Getting to know ArcGIS
 The Scenario You are working for the California Visitor s Commission. You have been asked to prepare a map of California for several dignitaries from out of the country. Your map will need to include enough
The Scenario You are working for the California Visitor s Commission. You have been asked to prepare a map of California for several dignitaries from out of the country. Your map will need to include enough
Illustrator Charts. Advanced options
 Illustrator Charts Advanced options Setting up labels Labels are words or numbers that describe two things: the sets of data you want to compare, and the categories across which you want to compare them.
Illustrator Charts Advanced options Setting up labels Labels are words or numbers that describe two things: the sets of data you want to compare, and the categories across which you want to compare them.
L E S S O N 2 Background
 Flight, Naperville Central High School, Naperville, Ill. No hard hat needed in the InDesign work area Once you learn the concepts of good page design, and you learn how to use InDesign, you are limited
Flight, Naperville Central High School, Naperville, Ill. No hard hat needed in the InDesign work area Once you learn the concepts of good page design, and you learn how to use InDesign, you are limited
12 APPLYING EFFECTS. Lesson overview
 12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects like Pathfinder, Distort & Transform, Offset Path, and Drop Shadow effects. Use Warp effects
12 APPLYING EFFECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Use various effects like Pathfinder, Distort & Transform, Offset Path, and Drop Shadow effects. Use Warp effects
Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 2: Vector Graphic Effects
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 2: Vector Graphic Effects Summer 2011, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading the
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 2: Vector Graphic Effects Summer 2011, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading the
Computer Graphics. Attributes of Graphics Primitives. Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1
 Computer Graphics Chapter 4 Attributes of Graphics Primitives Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1 Outline OpenGL State Variables Point Attributes t Line Attributes Fill-Area Attributes Scan-Line
Computer Graphics Chapter 4 Attributes of Graphics Primitives Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1 Outline OpenGL State Variables Point Attributes t Line Attributes Fill-Area Attributes Scan-Line
Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models
 Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
v Data Visualization SMS 12.3 Tutorial Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data.
 v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data. Prerequisites None Requirements GIS Module Map Module Time 30 60 minutes Page 1 of 16 Aquaveo 2017 1 Introduction...
v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data. Prerequisites None Requirements GIS Module Map Module Time 30 60 minutes Page 1 of 16 Aquaveo 2017 1 Introduction...
SETTINGS AND WORKSPACE
 ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR Adobe Illustrator is a program used to create vector illustrations / graphics (.ai/.eps/.svg). These graphics will then be used for logos, banners, infographics, flyers... in print and
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR Adobe Illustrator is a program used to create vector illustrations / graphics (.ai/.eps/.svg). These graphics will then be used for logos, banners, infographics, flyers... in print and
GstarCAD Complete Features Guide
 GstarCAD 2017 Complete Features Guide Table of Contents Core Performance Improvement... 3 Block Data Sharing Process... 3 Hatch Boundary Search Improvement... 4 New and Enhanced Functionalities... 5 Table...
GstarCAD 2017 Complete Features Guide Table of Contents Core Performance Improvement... 3 Block Data Sharing Process... 3 Hatch Boundary Search Improvement... 4 New and Enhanced Functionalities... 5 Table...
Office Excel. Charts
 Office 2007 Excel Charts October 2007 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 Bold text... 2 CHART TYPES... 3 CHOOSING A CHART... 4 CREATING A COLUMN CHART... 5 FORMATTING A COLUMN CHART... 8 Changing the chart style...
Office 2007 Excel Charts October 2007 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 Bold text... 2 CHART TYPES... 3 CHOOSING A CHART... 4 CREATING A COLUMN CHART... 5 FORMATTING A COLUMN CHART... 8 Changing the chart style...
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Two: Map Design Issues in ArcMap
 Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Two: Map Design Issues in ArcMap This activity provides an introduction to the map design process. It takes you through a typical sequence from the initial decision
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Two: Map Design Issues in ArcMap This activity provides an introduction to the map design process. It takes you through a typical sequence from the initial decision
By Colin Childs, ESRI Education Services. Catalog
 s resolve many traditional raster management issues By Colin Childs, ESRI Education Services Source images ArcGIS 10 introduces Catalog Mosaicked images Sources, mosaic methods, and functions are used
s resolve many traditional raster management issues By Colin Childs, ESRI Education Services Source images ArcGIS 10 introduces Catalog Mosaicked images Sources, mosaic methods, and functions are used
Selective Space Structures Manual
 Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Drawing shapes and lines
 Fine F Fi i Handmade H d d Ch Chocolates l Hours Mon Sat 10am 6pm In this demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CS6, you will be introduced to new and exciting application features, like gradients on a stroke
Fine F Fi i Handmade H d d Ch Chocolates l Hours Mon Sat 10am 6pm In this demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CS6, you will be introduced to new and exciting application features, like gradients on a stroke
MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3
 MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3 Shapes: (Insert Tab Shapes) Example: Select on the rounded rectangle Then use the mouse to position the upper left corner and produce the size by dragging out
MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3 Shapes: (Insert Tab Shapes) Example: Select on the rounded rectangle Then use the mouse to position the upper left corner and produce the size by dragging out
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Initial Analysis of Natural and Anthropogenic Adjustments in the Lower Mississippi River since 1880
 Richard Knox CE 394K Fall 2011 Initial Analysis of Natural and Anthropogenic Adjustments in the Lower Mississippi River since 1880 Objective: The objective of this term project is to use ArcGIS to evaluate
Richard Knox CE 394K Fall 2011 Initial Analysis of Natural and Anthropogenic Adjustments in the Lower Mississippi River since 1880 Objective: The objective of this term project is to use ArcGIS to evaluate
Annotation/Labeling Workshop. Tim Rankin Pat Dolan
 Annotation/Labeling Workshop Tim Rankin Pat Dolan Agenda 8:00am - Introductions 8:05am - Goals of the Workshop 8:15am Labeling 8:45am Annotation Part I 9:15am Break 9:25am Annotation Part II 9:50am Questions
Annotation/Labeling Workshop Tim Rankin Pat Dolan Agenda 8:00am - Introductions 8:05am - Goals of the Workshop 8:15am Labeling 8:45am Annotation Part I 9:15am Break 9:25am Annotation Part II 9:50am Questions
3 Polygonal Modeling. Getting Started with Maya 103
 3 Polygonal Modeling In Maya, modeling refers to the process of creating virtual 3D surfaces for the characters and objects in the Maya scene. Surfaces play an important role in the overall Maya workflow
3 Polygonal Modeling In Maya, modeling refers to the process of creating virtual 3D surfaces for the characters and objects in the Maya scene. Surfaces play an important role in the overall Maya workflow
MAPLOGIC CORPORATION. GIS Software Solutions. Getting Started. With MapLogic Layout Manager
 MAPLOGIC CORPORATION GIS Software Solutions Getting Started With MapLogic Layout Manager Getting Started with MapLogic Layout Manager 2011 MapLogic Corporation All Rights Reserved 330 West Canton Ave.,
MAPLOGIC CORPORATION GIS Software Solutions Getting Started With MapLogic Layout Manager Getting Started with MapLogic Layout Manager 2011 MapLogic Corporation All Rights Reserved 330 West Canton Ave.,
Photoshop / Editing paths
 Photoshop / Editing paths Path segments, components, and points Select a path Adjust path segments Add or delete anchor points Convert between smooth points and corner points Adjust path components Path
Photoshop / Editing paths Path segments, components, and points Select a path Adjust path segments Add or delete anchor points Convert between smooth points and corner points Adjust path components Path
Web-Friendly Sites. Planning & Design 1
 Planning & Design 1 This tutorial presents useful tips and tricks to help you achieve a more Web-friendly design and make your sites more efficient. The following topics are discussed: How Z-order and
Planning & Design 1 This tutorial presents useful tips and tricks to help you achieve a more Web-friendly design and make your sites more efficient. The following topics are discussed: How Z-order and
GIS LAB 8. Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation
 GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
Nye funktioner i ArcGIS Pro - ArcGIS Pro 2.1
 Nye funktioner i ArcGIS Pro - ArcGIS Pro 2.1 Paulina Karkauskaite GIS Konsulent Paulinak@geoinfo.dk Tlf: +45 53 39 59 16 Niklas Gregersen Presales GIS Konsulent Niklasg@geoinfo.dk Tlf: +45 53 39 59 28
Nye funktioner i ArcGIS Pro - ArcGIS Pro 2.1 Paulina Karkauskaite GIS Konsulent Paulinak@geoinfo.dk Tlf: +45 53 39 59 16 Niklas Gregersen Presales GIS Konsulent Niklasg@geoinfo.dk Tlf: +45 53 39 59 28
Desktop Studio: Charts. Version: 7.3
 Desktop Studio: Charts Version: 7.3 Copyright 2015 Intellicus Technologies This document and its content is copyrighted material of Intellicus Technologies. The content may not be copied or derived from,
Desktop Studio: Charts Version: 7.3 Copyright 2015 Intellicus Technologies This document and its content is copyrighted material of Intellicus Technologies. The content may not be copied or derived from,
Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007
 Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007 A chart is a pictorial representation of the data you enter in a worksheet. Often, a chart can be a more descriptive way of representing your data. As a result, those
Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007 A chart is a pictorial representation of the data you enter in a worksheet. Often, a chart can be a more descriptive way of representing your data. As a result, those
GENERALIZATIONS Cartographic Design & Principles Winter 2017
 GENERALIZATIONS Cartographic Design & Principles Winter 2017 The earth is infinitely complex maps are models that require some level of generalization Methods of Generalization Selection Dimension Simplification
GENERALIZATIONS Cartographic Design & Principles Winter 2017 The earth is infinitely complex maps are models that require some level of generalization Methods of Generalization Selection Dimension Simplification
Integrating CAD Data with ArcGIS
 Integrating CAD Data with ArcGIS Agenda An Overview of CAD Drawings CAD Data Structure in ArcGIS Visualization Georeferencing Data Conversion ArcGIS for AutoCAD Q & A CAD Drawings - Overview Widely used
Integrating CAD Data with ArcGIS Agenda An Overview of CAD Drawings CAD Data Structure in ArcGIS Visualization Georeferencing Data Conversion ArcGIS for AutoCAD Q & A CAD Drawings - Overview Widely used
Press the Plus + key to zoom in. Press the Minus - key to zoom out. Scroll the mouse wheel away from you to zoom in; towards you to zoom out.
 Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects
 9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects You can alter the look of an object without changing its structure using appearance attributes fills, strokes, effects, transparency, blending modes,
9 Using Appearance Attributes, Styles, and Effects You can alter the look of an object without changing its structure using appearance attributes fills, strokes, effects, transparency, blending modes,
PUG List. Raster Analysis 3D Analysis Geoprocessing. Steve Kopp
 PUG List Raster Analysis 3D Analysis Geoprocessing Steve Kopp Contour Polygons Spatial Analyst - color-filled contours. Similar to thematic classification, where blue = -1000 to zero, and red = 0 to +1000,
PUG List Raster Analysis 3D Analysis Geoprocessing Steve Kopp Contour Polygons Spatial Analyst - color-filled contours. Similar to thematic classification, where blue = -1000 to zero, and red = 0 to +1000,
Controlling the Drawing Display
 Controlling the Drawing Display In This Chapter 8 AutoCAD provides many ways to display views of your drawing. As you edit your drawing, you can control the drawing display and move quickly to different
Controlling the Drawing Display In This Chapter 8 AutoCAD provides many ways to display views of your drawing. As you edit your drawing, you can control the drawing display and move quickly to different
Data Visualization SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM. 1 Introduction. 2 Data sets. 3 Open the Geometry and Solution Files
 SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM Data Visualization 1 Introduction It is useful to view the geospatial data utilized as input and generated as solutions in the process of numerical analysis. It is also helpful
SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM Data Visualization 1 Introduction It is useful to view the geospatial data utilized as input and generated as solutions in the process of numerical analysis. It is also helpful
Computer Graphics. Chapter 4 Attributes of Graphics Primitives. Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1
 Computer Graphics Chapter 4 Attributes of Graphics Primitives Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1 Outline OpenGL State Variables Point Attributes Line Attributes Fill-Area Attributes Scan-Line
Computer Graphics Chapter 4 Attributes of Graphics Primitives Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1 Outline OpenGL State Variables Point Attributes Line Attributes Fill-Area Attributes Scan-Line
CHAPTER 4: MICROSOFT OFFICE: EXCEL 2010
 CHAPTER 4: MICROSOFT OFFICE: EXCEL 2010 Quick Summary A workbook an Excel document that stores data contains one or more pages called a worksheet. A worksheet or spreadsheet is stored in a workbook, and
CHAPTER 4: MICROSOFT OFFICE: EXCEL 2010 Quick Summary A workbook an Excel document that stores data contains one or more pages called a worksheet. A worksheet or spreadsheet is stored in a workbook, and
animation, and what interface elements the Flash editor contains to help you create and control your animation.
 e r ch02.fm Page 43 Wednesday, November 15, 2000 8:52 AM c h a p t 2 Animating the Page IN THIS CHAPTER Timelines and Frames Movement Tweening Shape Tweening Fading Recap Advanced Projects You have totally
e r ch02.fm Page 43 Wednesday, November 15, 2000 8:52 AM c h a p t 2 Animating the Page IN THIS CHAPTER Timelines and Frames Movement Tweening Shape Tweening Fading Recap Advanced Projects You have totally
Getting Started. Extruding Features. Convert to feature class
 http://gmv.cast.uark.edu A Method Store for Advanced Survey and Modeling Technologies Mon, 01 Apr 2013 03:29:18 +0000 en-us hourly 1 http://wordpress.org/?v=3.5.1 http://gmv.cast.uark.edu/modeling/software-visualization/sketchup/workflow-sketchup/arcscene-tosketchup-to-arcscene/
http://gmv.cast.uark.edu A Method Store for Advanced Survey and Modeling Technologies Mon, 01 Apr 2013 03:29:18 +0000 en-us hourly 1 http://wordpress.org/?v=3.5.1 http://gmv.cast.uark.edu/modeling/software-visualization/sketchup/workflow-sketchup/arcscene-tosketchup-to-arcscene/
Solo 4.6 Release Notes
 June9, 2017 (Updated to include Solo 4.6.4 changes) Solo 4.6 Release Notes This release contains a number of new features, as well as enhancements to the user interface and overall performance. Together
June9, 2017 (Updated to include Solo 4.6.4 changes) Solo 4.6 Release Notes This release contains a number of new features, as well as enhancements to the user interface and overall performance. Together
