Computer vision is the analysis of digital images by a computer for such applications as:
|
|
|
- Brice Campbell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction Computer vision is the analysis of digital images by a computer for such applications as: Industrial: part localization and inspection, robotics Medical: disease classification, screening, planning Military: autonomous vehicles, tank recognition Intelligence Gathering: face recognition, video analysis Security: video analysis Science: classification, measurement Document Processing: text recognition, diagram conversion 1
2 Medical Applications CT image of a patient s abdomen liver kidney kidney 2
3 Visible Man Slice Through Lung 3
4 3D Reconstruction of the Blood Vessel Tree 4
5 CBIR of Mouse Eye Images for Genetic Studies 5
6 Robotics 2D Gray-tone or Color Images Mars rover 3D Range Images What am I? 6
7 Image Databases: Images from my Ground-Truth collection. Retrieve all images that have trees. Retrieve all images that have buildings. Retrieve all images that have antelope. 7
8 Documents: 8
9 9
10 Surveillance: Object and Event Recognition in Aerial Videos Original Video Frame Color Regions Structure Regions 10
11 Digital Image Terminology: pixel (with value 94) its 3x3 neighborhood region of medium intensity resolution (7x7) binary image 0 s and 1 s gray-scale (or gray-tone) image 0 to 255 color image (R,G,B) at each pixel multi-spectral image multiple values per pixel range image depth value at each pixel labeled image result of processing and labeling 11
12 Goals of Image and Video Analysis Segment an image into useful regions Perform measurements on certain areas Determine what object(s) are in the scene Calculate the precise location(s) of objects Visually inspect a manufactured object Construct a 3D model of the imaged object Find interesting events in a video liver kidney spleen 12
13 The Three Stages of Computer Vision low-level image image mid-level image features high-level (the intelligent part) features analysis 13
14 Low-Level sharpening blurring 14
15 Low-Level Canny edge operator original image Mid-Level (Lines and Curves) edge image ORT line & circle extraction edge image data structure 15 circular arcs and line segments
16 Mid-level (Regions) K-means clustering (followed by connected component analysis) original color image regions of homogeneous color data structure 16
17 Low- to High-Level low-level edge image mid-level high-level consistent line clusters Building Recognition 17
18 Filtering Operations Use Masks Masks operate on a neighborhood of pixels. A mask of coefficients is centered on a pixel. The mask coefficients are multiplied by the pixel values in its neighborhood and the products are summed. The result (response) goes into the corresponding pixel position in the output image Input Image 1/9 1/9 1/9 1/9 1/9 1/9 1/9 1/9 1/9 3x3 Mask (mean filter) ** ** ** ** ** ** 39 ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** Output Image 18
19 Comparison: salt and pepper noise 19
20 Comparison: Gaussian noise 20
21 Lines and Arcs Segmentation In some image sets, lines, curves, and circular arcs are more useful than regions or helpful in addition to regions. Lines and arcs are often used in object recognition stereo matching document analysis 21
22 Edge Detection Basic idea: look for a neighborhood with strong signs of change. Problems: neighborhood size how to detect change 22
23 Differential Operators Differential operators attempt to approximate the gradient at a pixel via masks threshold the gradient to select the edge pixels 23
24 Example: Sobel Operator Sx = Sy = On a pixel of the image I let gx be the response to Sx let gy be the response to Sy Then the gradient is I = [gx gy] T 2 2 1/2 and g = (gx + gy ) is the gradient magnitude. θ = atan2(gy,gx) is the gradient direction. 24
25 Sobel Operator on the Blocks Image original image gradient thresholded magnitude gradient magnitude 25
26 Common Masks for Computing Gradient Sobel: Prewitt: Roberts Sx Sy 26
27 Canny Edge Detector Smooth the image with a Gaussian filter with spread σ. Compute gradient magnitude and direction at each pixel of the smoothed image. Zero out any pixel response the two neighboring pixels on either side of it, along the direction of the gradient. Track high-magnitude contours. Keep only pixels along these contours, so weak little segments go away. 27
28 Canny Examples Canny σ=1 Canny σ=4 Canny σ=1 Roberts 2X2 28
29 Canny on Kidney Image 29
30 Canny on the Blocks image 30
31 Canny Characteristics The Canny operator gives single-pixel-wide images with good continuation between adjacent pixels It is the most widely used edge operator today; no one has done better since it came out in the late 80s. Many implementations are available. It is very sensitive to its parameters, which need to be adjusted for different application domains. 31
32 Segmentation into Regions Instead of looking for 1D features like lines and curves, some processes look for regions. The regions must be homogeneous in some attribute such as gray-tone, color, texture,... Although region-growing was popular in the past, clustering the pixels into subsets has become the best methodology for finding regions. 32
33 K-Means Example 1 33
34 K-Means Example 2 34
35 K-Means Example 3 35
36 High-Level Computer Vision Detection of classes of objects (faces, motorbikes, trees, cheetahs) in images Recognition of specific objects such as George Bush or machine part #45732 Classification of images or parts of images for medical or scientific applications Recognition of events in surveillance videos Measurement of distances for robotics
37 High-level vision uses techniques from AI Graph-Matching: A*, Constraint Satisfaction, Branch and Bound Search, Simulated Annealing Learning Methodologies: Decision Trees, Neural Nets, SVMs, EM Classifier Probabilistic Reasoning, Belief Propagation, Graphical Models
38 Graph Matching for Object Recognition For each specific object, we have a geometric model. The geometric model leads to a symbolic model in terms of image features and their spatial relationships. An image is represented by all of its features and their spatial relationships. This leads to a graph matching problem.
39 Model-based Recognition as Graph Matching Let U = the set of model features. Let R be a relation expressing their spatial relationships. Let L = the set of image features. Let S be a relation expressing their spatial relationships. The ideal solution would be a subgraph isomorphism f: U-> L satisfying if (u 1, u 2,..., u n ) ε R, then (f(u 1 ),f(u 2 ),...,f(u n )) ε S
40 House Example 2D model 2D image P L RP and RL are connection relations. f(s1)=sj f(s2)=sa f(s3)=sb f(s4)=sn f(s5)=si f(s6)=sk f(s7)=sg f(s8) = Sl f(s9)=sd f(s10)=sf f(s11)=sh
41 But this is too simplistic The model specifies all the features of the object that may appear in the image. Some of them don t appear at all, due to occlusion or failures at low or mid level. Some of them are broken and not recognized. Some of them are distorted. Relationships don t all hold.
42 TRIBORS: view class matching of polyhedral objects edges from image model overlayed improved location A view-class is a typical 2D view of a 3D object. Each object had 4-5 view classes (hand selected). The representation of a view class for matching included: - triplets of line segments visible in that class - the probability of detectability of each triplet The first version of this program used iterative-deepening A* search.
43 RIO: Relational Indexing for Object Recognition RIO worked with more complex parts that could have - planar surfaces - cylindrical surfaces - threads
44 Object Representation in RIO 3D objects are represented by a 3D mesh and set of 2D view classes. Each view class is represented by an attributed graph whose nodes are features and whose attributed edges are relationships. For purposes of indexing, attributed graphs are stored as sets of 2-graphs, graphs with 2 nodes and 2 relationships. ellipse share an arc coaxial arc cluster
45 RIO Features ellipses coaxials coaxials-multi parallel lines junctions triples close and far L V Y Z U
46 RIO Relationships share one arc share one line share two lines coaxial close at extremal points bounding box encloses / enclosed by
47 Hexnut Object How are 1, 2, and 3 related? What other features and relationships can you find?
48 Graph and 2-Graph Representations 1 coaxialsmulti encloses encloses encloses 2 ellipse e e e c 3 parallel lines coaxial RDF!
49 Relational Indexing for Recognition Preprocessing (off-line) Phase for each model view Mi in the database encode each 2-graph of Mi to produce an index store Mi and associated information in the indexed bin of a hash table H
50 Matching (on-line) phase 1. Construct a relational (2-graph) description D for the scene 2. For each 2-graph G of D encode it, producing an index to access the hash table H cast a vote for each Mi in the associated bin 3. Select the Mi s with high votes as possible hypotheses 4. Verify or disprove via alignment, using the 3D meshes
51 The Voting Process
52 RIO Verifications incorrect hypothesis 1. The matched features of the hypothesized object are used to determine its pose. 2. The 3D mesh of the object is used to project all its features onto the image. 3. A verification procedure checks how well the object features line up with edges on the image.
53 Use of classifiers is big in computer vision today. 2 Examples: Rowley s Face Detection using neural nets Yi s image classification using EM
54 Object Detection: Rowley s Face Finder 1. convert to gray scale 2. normalize for lighting 3. histogram equalization 4. apply neural net(s) trained on 16K images What data is fed to the classifier? 32 x 32 windows in a pyramid structure
55 Object Class Recognition using Images of Abstract Regions Yi Li, Jeff A. Bilmes, and Linda G. Shapiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington
56 Problem Statement Given: Some images and their corresponding descriptions {trees, grass, cherry trees} {cheetah, trunk} {mountains, sky} {beach, sky, trees, water} To solve: What object classes are present in new images????
57 Image Features for Object Recognition Color Texture Structure Context
58 Abstract Regions Original Images Color Regions Texture Regions Line Clusters
59 Abstract Regions Multiple segmentations whose regions are not labeled; a list of labels is provided for each training image. image labels {sky, building} various different segmentations region attributes from several different types of regions
60 Model Initial Estimation Estimate the initial model of an object using all the region features from all images that contain the object Tree Sky
61 EM Classifier: the Idea Initial Model for trees Final Model for trees EM Initial Model for sky Final Model for sky
62 A Better Approach to Combining Phase 1: Different Feature Types Treat each type of abstract region separately For abstract region type a and for object class o, use the EM algorithm to construct clusters that are multivariate Gaussians over the features for type a regions.
63 Aggregate Scores for Color Components beach beach not beach
64 Phase 2 Learning Let C i be row i of the training matrix. Each such row is a feature vector for the color features of regions of image I i that relates them to the Phase 1 components. Now we can use a second-stage classifier to learn P(o I i ) for each object class o and image I i.
65 Multiple Feature Case We calculate separate Gaussian mixture models for each different features type: Color: Texture: Structure: C i T i S i and any more features we have (motion).
66 Now we concatenate the matrix rows from the different region types to obtain a multifeature-type training matrix and train a neural net classifier to classify images. color texture structure everything C 1 + C C 1 - C T 1 + T T 1 - T S 1 + S S 1 - S C + 1 T + 1 S + 1 C + 2 T + 2 S C - 1 T - 1 S - 1 C - 2 T - 2 S
67 Groundtruth Data Set: Top Results Asian city Cannon beach Italy park
68 Groundtruth Data Set: Top Results sky spring flowers tree water
69 Groundtruth Data Set: Annotation Samples tree(97.3), bush(91.6), spring flowers(90.3), flower(84.4), park(84.3), sidewalk(67.5), grass(52.5), pole(34.1) sky(99.8), Columbia gorge(98.8), lantern(94.2), street(89.2), house(85.8), bridge(80.8), car(80.5), hill(78.3), boat(73.1), pole(72.3), water(64.3), mountain(63.8), building(9.5) sky(95.1), Iran(89.3), house(88.6), building(80.1), boat(71.7), bridge(67.0), water(13.5), tree(7.7) Italy(99.9), grass(98.5), sky(93.8), rock(88.8), boat(80.1), water(77.1), Iran(64.2), stone(63.9), bridge(59.6), European(56.3), sidewalk(51.1), house(5.3)
High-Level Computer Vision
 High-Level Computer Vision Detection of classes of objects (faces, motorbikes, trees, cheetahs) in images Recognition of specific objects such as George Bush or machine part #45732 Classification of images
High-Level Computer Vision Detection of classes of objects (faces, motorbikes, trees, cheetahs) in images Recognition of specific objects such as George Bush or machine part #45732 Classification of images
Computer vision is the analysis of digital images by a computer for such applications as:
 Introduction Computer vision is the analysis of digital images by a computer for such applications as: Industrial: part localization and inspection, robotics Medical: disease classification, screening,
Introduction Computer vision is the analysis of digital images by a computer for such applications as: Industrial: part localization and inspection, robotics Medical: disease classification, screening,
Object Recognition I. Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576
 Object Recognition I Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576 1 Low- to High-Level low-level edge image mid-level high-level consistent line clusters Building Recognition 2 High-Level Computer Vision Detection of classes
Object Recognition I Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576 1 Low- to High-Level low-level edge image mid-level high-level consistent line clusters Building Recognition 2 High-Level Computer Vision Detection of classes
COMPUTER VISION Introduction
 COMPUTER VISION Introduction Computer vision is the analysis of digital images by a computer for such applications as: Industrial: part localization and inspection, robotics Medical: disease classification,
COMPUTER VISION Introduction Computer vision is the analysis of digital images by a computer for such applications as: Industrial: part localization and inspection, robotics Medical: disease classification,
3D Models and Matching
 3D Models and Matching representations for 3D object models particular matching techniques alignment-based systems appearance-based systems GC model of a screwdriver 1 3D Models Many different representations
3D Models and Matching representations for 3D object models particular matching techniques alignment-based systems appearance-based systems GC model of a screwdriver 1 3D Models Many different representations
CSE 455: Computer Vision Winter 2007
 CSE 455: Computer Vision Winter 2007 Instructor: Professor Linda Shapiro (shapiro@cs) Additional Instructor: Dr. Matthew Brown (brown@microsoft.com) TAs: Masa Kobashi (mkbsh@cs) Peter Davis (pediddle@cs)
CSE 455: Computer Vision Winter 2007 Instructor: Professor Linda Shapiro (shapiro@cs) Additional Instructor: Dr. Matthew Brown (brown@microsoft.com) TAs: Masa Kobashi (mkbsh@cs) Peter Davis (pediddle@cs)
Object Class Recognition using Images of Abstract Regions
 Object Class Recognition using Images of Abstract Regions Yi Li, Jeff A. Bilmes, and Linda G. Shapiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington
Object Class Recognition using Images of Abstract Regions Yi Li, Jeff A. Bilmes, and Linda G. Shapiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington
3D Models and Matching
 3D Models and Matching representations for 3D object models particular matching techniques alignment-based systems appearance-based systems GC model of a screwdriver 1 3D Models Many different representations
3D Models and Matching representations for 3D object models particular matching techniques alignment-based systems appearance-based systems GC model of a screwdriver 1 3D Models Many different representations
Example 1: Regions. Image Segmentation. Example 3: Lines and Circular Arcs. Example 2: Straight Lines. Region Segmentation: Segmentation Criteria
 Image Segmentation Image segmentation is the operation of partitioning an image into a collection of connected sets of pixels. 1. into regions, which usually cover the image Example 1: Regions. into linear
Image Segmentation Image segmentation is the operation of partitioning an image into a collection of connected sets of pixels. 1. into regions, which usually cover the image Example 1: Regions. into linear
Example 2: Straight Lines. Image Segmentation. Example 3: Lines and Circular Arcs. Example 1: Regions
 Image Segmentation Image segmentation is the operation of partitioning an image into a collection of connected sets of pixels. 1. into regions, which usually cover the image Example : Straight Lines. into
Image Segmentation Image segmentation is the operation of partitioning an image into a collection of connected sets of pixels. 1. into regions, which usually cover the image Example : Straight Lines. into
Specific Object Recognition: Matching in 2D
 Specific Object Recognition: Matching in 2D engine model Is there an engine in the image? If so, where is it located? image containing an instance of the model Alignment Use a geometric feature-based model
Specific Object Recognition: Matching in 2D engine model Is there an engine in the image? If so, where is it located? image containing an instance of the model Alignment Use a geometric feature-based model
A Generative/Discriminative Learning Algorithm for Image Classification
 A Generative/Discriminative Learning Algorithm for Image Classification Y Li, L G Shapiro, and J Bilmes Department of Computer Science and Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering University of
A Generative/Discriminative Learning Algorithm for Image Classification Y Li, L G Shapiro, and J Bilmes Department of Computer Science and Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering University of
Edge Detection. EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro
 Edge Detection EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) 2 Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity illumination discontinuity Edges are caused
Edge Detection EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) 2 Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity illumination discontinuity Edges are caused
Edges and Lines Readings: Chapter 10: better edge detectors line finding circle finding
 Edges and Lines Readings: Chapter 10: 10.2.3-10.3 better edge detectors line finding circle finding 1 Lines and Arcs Segmentation In some image sets, lines, curves, and circular arcs are more useful than
Edges and Lines Readings: Chapter 10: 10.2.3-10.3 better edge detectors line finding circle finding 1 Lines and Arcs Segmentation In some image sets, lines, curves, and circular arcs are more useful than
Filtering and Enhancing Images
 KECE471 Computer Vision Filtering and Enhancing Images Chang-Su Kim Chapter 5, Computer Vision by Shapiro and Stockman Note: Some figures and contents in the lecture notes of Dr. Stockman are used partly.
KECE471 Computer Vision Filtering and Enhancing Images Chang-Su Kim Chapter 5, Computer Vision by Shapiro and Stockman Note: Some figures and contents in the lecture notes of Dr. Stockman are used partly.
Edges and Lines Readings: Chapter 10: better edge detectors line finding circle finding
 Edges and Lines Readings: Chapter 10: 10.2.3-10.3 better edge detectors line finding circle finding 1 Lines and Arcs Segmentation In some image sets, lines, curves, and circular arcs are more useful than
Edges and Lines Readings: Chapter 10: 10.2.3-10.3 better edge detectors line finding circle finding 1 Lines and Arcs Segmentation In some image sets, lines, curves, and circular arcs are more useful than
Image Processing. Bilkent University. CS554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu
 Image Processing CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Today Image Formation Point and Blob Processing Binary Image Processing Readings: Gonzalez & Woods, Ch. 3 Slides are adapted from
Image Processing CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Today Image Formation Point and Blob Processing Binary Image Processing Readings: Gonzalez & Woods, Ch. 3 Slides are adapted from
Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR)
 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) Searching a large database for images that match a query: What kinds of databases? What kinds of queries? What constitutes a match?
Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) Searching a large database for images that match a query: What kinds of databases? What kinds of queries? What constitutes a match?
Image Segmentation and Registration
 Image Segmentation and Registration Dr. Christine Tanner (tanner@vision.ee.ethz.ch) Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zürich Dr. Verena Kaynig, Machine Learning Laboratory, ETH Zürich Outline Segmentation
Image Segmentation and Registration Dr. Christine Tanner (tanner@vision.ee.ethz.ch) Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zürich Dr. Verena Kaynig, Machine Learning Laboratory, ETH Zürich Outline Segmentation
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 23: Applications. Linda Shapiro Spring 2016
 CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 23: Applications Linda Shapiro Spring 2016 Announcements Spring 2016 CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms 2 Other Data Structures and Algorithms Quadtrees:
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 23: Applications Linda Shapiro Spring 2016 Announcements Spring 2016 CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms 2 Other Data Structures and Algorithms Quadtrees:
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Skin and Face Detection
 Skin and Face Detection Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576 1 What s Coming 1. Review of Bakic flesh detector 2. Fleck and Forsyth flesh detector 3. Details of Rowley face detector 4. Review of the basic AdaBoost
Skin and Face Detection Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576 1 What s Coming 1. Review of Bakic flesh detector 2. Fleck and Forsyth flesh detector 3. Details of Rowley face detector 4. Review of the basic AdaBoost
Local Feature Detectors
 Local Feature Detectors Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Slides adapted from Cordelia Schmid and David Lowe, CVPR 2003 Tutorial, Matthew Brown,
Local Feature Detectors Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Slides adapted from Cordelia Schmid and David Lowe, CVPR 2003 Tutorial, Matthew Brown,
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
Edge Detection Lecture 03 Computer Vision
 Edge Detection Lecture 3 Computer Vision Suggested readings Chapter 5 Linda G. Shapiro and George Stockman, Computer Vision, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall,. Chapter David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Edge Detection Lecture 3 Computer Vision Suggested readings Chapter 5 Linda G. Shapiro and George Stockman, Computer Vision, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall,. Chapter David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu. Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy
 BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy Image matching Image matching is a fundamental aspect of many problems in computer vision. Object or scene recognition Solving
BSB663 Image Processing Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Selim Aksoy Image matching Image matching is a fundamental aspect of many problems in computer vision. Object or scene recognition Solving
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images. Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009
 Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
CS 4495 Computer Vision. Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges. Aaron Bobick. School of Interactive Computing. Templates/Edges
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
Dietrich Paulus Joachim Hornegger. Pattern Recognition of Images and Speech in C++
 Dietrich Paulus Joachim Hornegger Pattern Recognition of Images and Speech in C++ To Dorothea, Belinda, and Dominik In the text we use the following names which are protected, trademarks owned by a company
Dietrich Paulus Joachim Hornegger Pattern Recognition of Images and Speech in C++ To Dorothea, Belinda, and Dominik In the text we use the following names which are protected, trademarks owned by a company
Ulrik Söderström 16 Feb Image Processing. Segmentation
 Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 10 Segmentation 14/02/27 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 10 Segmentation 14/02/27 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION
 VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
Babu Madhav Institute of Information Technology Years Integrated M.Sc.(IT)(Semester - 7)
 5 Years Integrated M.Sc.(IT)(Semester - 7) 060010707 Digital Image Processing UNIT 1 Introduction to Image Processing Q: 1 Answer in short. 1. What is digital image? 1. Define pixel or picture element?
5 Years Integrated M.Sc.(IT)(Semester - 7) 060010707 Digital Image Processing UNIT 1 Introduction to Image Processing Q: 1 Answer in short. 1. What is digital image? 1. Define pixel or picture element?
Line, edge, blob and corner detection
 Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Segmentation and Grouping
 Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester. CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester
 Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester Charles Stewart Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic
Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester Charles Stewart Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic
Feature Descriptors. CS 510 Lecture #21 April 29 th, 2013
 Feature Descriptors CS 510 Lecture #21 April 29 th, 2013 Programming Assignment #4 Due two weeks from today Any questions? How is it going? Where are we? We have two umbrella schemes for object recognition
Feature Descriptors CS 510 Lecture #21 April 29 th, 2013 Programming Assignment #4 Due two weeks from today Any questions? How is it going? Where are we? We have two umbrella schemes for object recognition
Edge and local feature detection - 2. Importance of edge detection in computer vision
 Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
5. Feature Extraction from Images
 5. Feature Extraction from Images Aim of this Chapter: Learn the Basic Feature Extraction Methods for Images Main features: Color Texture Edges Wie funktioniert ein Mustererkennungssystem Test Data x i
5. Feature Extraction from Images Aim of this Chapter: Learn the Basic Feature Extraction Methods for Images Main features: Color Texture Edges Wie funktioniert ein Mustererkennungssystem Test Data x i
Local Image preprocessing (cont d)
 Local Image preprocessing (cont d) 1 Outline - Edge detectors - Corner detectors - Reading: textbook 5.3.1-5.3.5 and 5.3.10 2 What are edges? Edges correspond to relevant features in the image. An edge
Local Image preprocessing (cont d) 1 Outline - Edge detectors - Corner detectors - Reading: textbook 5.3.1-5.3.5 and 5.3.10 2 What are edges? Edges correspond to relevant features in the image. An edge
EE 701 ROBOT VISION. Segmentation
 EE 701 ROBOT VISION Regions and Image Segmentation Histogram-based Segmentation Automatic Thresholding K-means Clustering Spatial Coherence Merging and Splitting Graph Theoretic Segmentation Region Growing
EE 701 ROBOT VISION Regions and Image Segmentation Histogram-based Segmentation Automatic Thresholding K-means Clustering Spatial Coherence Merging and Splitting Graph Theoretic Segmentation Region Growing
Lecture 6: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
#1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
Lecture 4: Image Processing
 Lecture 4: Image Processing Definitions Many graphics techniques that operate only on images Image processing: operations that take images as input, produce images as output In its most general form, an
Lecture 4: Image Processing Definitions Many graphics techniques that operate only on images Image processing: operations that take images as input, produce images as output In its most general form, an
Image Segmentation. Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah. Slides borrowed from Ross Whitaker
 Image Segmentation Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Slides borrowed from Ross Whitaker Segmentation Semantic Segmentation Indoor layout estimation What is Segmentation? Partitioning
Image Segmentation Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Slides borrowed from Ross Whitaker Segmentation Semantic Segmentation Indoor layout estimation What is Segmentation? Partitioning
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Noise Model. Important Noise Probability Density Functions (Cont.) Important Noise Probability Density Functions
 Others -- Noise Removal Techniques -- Edge Detection Techniques -- Geometric Operations -- Color Image Processing -- Color Spaces Xiaojun Qi Noise Model The principal sources of noise in digital images
Others -- Noise Removal Techniques -- Edge Detection Techniques -- Geometric Operations -- Color Image Processing -- Color Spaces Xiaojun Qi Noise Model The principal sources of noise in digital images
Digital Image Processing (CS/ECE 545) Lecture 5: Edge Detection (Part 2) & Corner Detection
 Digital Image Processing (CS/ECE 545) Lecture 5: Edge Detection (Part 2) & Corner Detection Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: Edge Detection Image processing
Digital Image Processing (CS/ECE 545) Lecture 5: Edge Detection (Part 2) & Corner Detection Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: Edge Detection Image processing
convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
Filtering Images. Contents
 Image Processing and Data Visualization with MATLAB Filtering Images Hansrudi Noser June 8-9, 010 UZH, Multimedia and Robotics Summer School Noise Smoothing Filters Sigmoid Filters Gradient Filters Contents
Image Processing and Data Visualization with MATLAB Filtering Images Hansrudi Noser June 8-9, 010 UZH, Multimedia and Robotics Summer School Noise Smoothing Filters Sigmoid Filters Gradient Filters Contents
CHAPTER 3 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN
 CHAPTER 3 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN CHAPTER 3: IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN Principal objective: to process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original image
CHAPTER 3 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN CHAPTER 3: IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN Principal objective: to process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original image
Deformable Part Models
 CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Deformable Part Models Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 9, 2016 Today: Object category detection Window-based approaches: Last time: Viola-Jones
CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Deformable Part Models Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 9, 2016 Today: Object category detection Window-based approaches: Last time: Viola-Jones
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement - Filtering
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement - Filtering Derivative Derivative is defined as a rate of change. Discrete Derivative Finite Distance Example Derivatives in 2-dimension Derivatives of Images
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement - Filtering Derivative Derivative is defined as a rate of change. Discrete Derivative Finite Distance Example Derivatives in 2-dimension Derivatives of Images
Image Segmentation. Ross Whitaker SCI Institute, School of Computing University of Utah
 Image Segmentation Ross Whitaker SCI Institute, School of Computing University of Utah What is Segmentation? Partitioning images/volumes into meaningful pieces Partitioning problem Labels Isolating a specific
Image Segmentation Ross Whitaker SCI Institute, School of Computing University of Utah What is Segmentation? Partitioning images/volumes into meaningful pieces Partitioning problem Labels Isolating a specific
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS
 SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
Content-Based Image Retrieval Readings: Chapter 8:
 Content-Based Image Retrieval Readings: Chapter 8: 8.1-8.4 Queries Commercial Systems Retrieval Features Indexing in the FIDS System Lead-in to Object Recognition 1 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR)
Content-Based Image Retrieval Readings: Chapter 8: 8.1-8.4 Queries Commercial Systems Retrieval Features Indexing in the FIDS System Lead-in to Object Recognition 1 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR)
Knowledge-Based Organ Identification from CT Images. Masahara Kobashi and Linda Shapiro Best-Paper Prize in Pattern Recognition Vol. 28, No.
 Knowledge-Based Organ Identification from CT Images Masahara Kobashi and Linda Shapiro Best-Paper Prize in Pattern Recognition Vol. 28, No. 4 1995 1 Motivation The extraction of structure from CT volumes
Knowledge-Based Organ Identification from CT Images Masahara Kobashi and Linda Shapiro Best-Paper Prize in Pattern Recognition Vol. 28, No. 4 1995 1 Motivation The extraction of structure from CT volumes
Bus Detection and recognition for visually impaired people
 Bus Detection and recognition for visually impaired people Hangrong Pan, Chucai Yi, and Yingli Tian The City College of New York The Graduate Center The City University of New York MAP4VIP Outline Motivation
Bus Detection and recognition for visually impaired people Hangrong Pan, Chucai Yi, and Yingli Tian The City College of New York The Graduate Center The City University of New York MAP4VIP Outline Motivation
Edges and Binary Images
 CS 699: Intro to Computer Vision Edges and Binary Images Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 5, 205 Plan for today Edge detection Binary image analysis Homework Due on 9/22, :59pm
CS 699: Intro to Computer Vision Edges and Binary Images Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 5, 205 Plan for today Edge detection Binary image analysis Homework Due on 9/22, :59pm
Image Processing
 Image Processing 159.731 Canny Edge Detection Report Syed Irfanullah, Azeezullah 00297844 Danh Anh Huynh 02136047 1 Canny Edge Detection INTRODUCTION Edges Edges characterize boundaries and are therefore
Image Processing 159.731 Canny Edge Detection Report Syed Irfanullah, Azeezullah 00297844 Danh Anh Huynh 02136047 1 Canny Edge Detection INTRODUCTION Edges Edges characterize boundaries and are therefore
Classification of objects from Video Data (Group 30)
 Classification of objects from Video Data (Group 30) Sheallika Singh 12665 Vibhuti Mahajan 12792 Aahitagni Mukherjee 12001 M Arvind 12385 1 Motivation Video surveillance has been employed for a long time
Classification of objects from Video Data (Group 30) Sheallika Singh 12665 Vibhuti Mahajan 12792 Aahitagni Mukherjee 12001 M Arvind 12385 1 Motivation Video surveillance has been employed for a long time
Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors
 #1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
#1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
Content-Based Image Retrieval Readings: Chapter 8:
 Content-Based Image Retrieval Readings: Chapter 8: 8.1-8.4 Queries Commercial Systems Retrieval Features Indexing in the FIDS System Lead-in to Object Recognition 1 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR)
Content-Based Image Retrieval Readings: Chapter 8: 8.1-8.4 Queries Commercial Systems Retrieval Features Indexing in the FIDS System Lead-in to Object Recognition 1 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR)
Category vs. instance recognition
 Category vs. instance recognition Category: Find all the people Find all the buildings Often within a single image Often sliding window Instance: Is this face James? Find this specific famous building
Category vs. instance recognition Category: Find all the people Find all the buildings Often within a single image Often sliding window Instance: Is this face James? Find this specific famous building
Texture. Texture is a description of the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image or a selected region of an image.
 Texture Texture is a description of the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image or a selected region of an image. Structural approach: a set of texels in some regular or repeated pattern
Texture Texture is a description of the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image or a selected region of an image. Structural approach: a set of texels in some regular or repeated pattern
COSC160: Detection and Classification. Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor
 COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
Perception. Autonomous Mobile Robots. Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction from laser scans. Autonomous Systems Lab. Zürich.
 Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
6.801/866. Segmentation and Line Fitting. T. Darrell
 6.801/866 Segmentation and Line Fitting T. Darrell Segmentation and Line Fitting Gestalt grouping Background subtraction K-Means Graph cuts Hough transform Iterative fitting (Next time: Probabilistic segmentation)
6.801/866 Segmentation and Line Fitting T. Darrell Segmentation and Line Fitting Gestalt grouping Background subtraction K-Means Graph cuts Hough transform Iterative fitting (Next time: Probabilistic segmentation)
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies"
 ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
Final Review CMSC 733 Fall 2014
 Final Review CMSC 733 Fall 2014 We have covered a lot of material in this course. One way to organize this material is around a set of key equations and algorithms. You should be familiar with all of these,
Final Review CMSC 733 Fall 2014 We have covered a lot of material in this course. One way to organize this material is around a set of key equations and algorithms. You should be familiar with all of these,
Image features. Image Features
 Image features Image features, such as edges and interest points, provide rich information on the image content. They correspond to local regions in the image and are fundamental in many applications in
Image features Image features, such as edges and interest points, provide rich information on the image content. They correspond to local regions in the image and are fundamental in many applications in
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis. A. Criminisi
 Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Image Processing, Analysis and Machine Vision
 Image Processing, Analysis and Machine Vision Milan Sonka PhD University of Iowa Iowa City, USA Vaclav Hlavac PhD Czech Technical University Prague, Czech Republic and Roger Boyle DPhil, MBCS, CEng University
Image Processing, Analysis and Machine Vision Milan Sonka PhD University of Iowa Iowa City, USA Vaclav Hlavac PhD Czech Technical University Prague, Czech Republic and Roger Boyle DPhil, MBCS, CEng University
Introduction to Medical Imaging (5XSA0) Module 5
 Introduction to Medical Imaging (5XSA0) Module 5 Segmentation Jungong Han, Dirk Farin, Sveta Zinger ( s.zinger@tue.nl ) 1 Outline Introduction Color Segmentation region-growing region-merging watershed
Introduction to Medical Imaging (5XSA0) Module 5 Segmentation Jungong Han, Dirk Farin, Sveta Zinger ( s.zinger@tue.nl ) 1 Outline Introduction Color Segmentation region-growing region-merging watershed
CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision
 CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision Sources for online computer vision tutorials and demos - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/hipr and Computer Vision resources online - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/cvonline Vision
CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision Sources for online computer vision tutorials and demos - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/hipr and Computer Vision resources online - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/cvonline Vision
Content-Based Image Retrieval. Queries Commercial Systems Retrieval Features Indexing in the FIDS System Lead-in to Object Recognition
 Content-Based Image Retrieval Queries Commercial Systems Retrieval Features Indexing in the FIDS System Lead-in to Object Recognition 1 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) Searching a large database for
Content-Based Image Retrieval Queries Commercial Systems Retrieval Features Indexing in the FIDS System Lead-in to Object Recognition 1 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) Searching a large database for
Detection III: Analyzing and Debugging Detection Methods
 CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Detection III: Analyzing and Debugging Detection Methods Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 17, 2015 Today Review: Deformable part models How can
CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Detection III: Analyzing and Debugging Detection Methods Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 17, 2015 Today Review: Deformable part models How can
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB
 Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests. Daniel Munoz Februrary 9, 2009
 Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests Daniel Munoz 16-721 Februrary 9, 2009 Papers [shotton-eccv-06] J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi, TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context
Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests Daniel Munoz 16-721 Februrary 9, 2009 Papers [shotton-eccv-06] J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi, TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context
Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing. The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) ECE 497: Introduction to Mobile Robotics -Visual Sensors
 Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) Bring your laptop and robot everyday DO NOT unplug the network cables from the desktop computers or the walls Tuesday s Quiz is on Visual
Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) Bring your laptop and robot everyday DO NOT unplug the network cables from the desktop computers or the walls Tuesday s Quiz is on Visual
Image Processing. Traitement d images. Yuliya Tarabalka Tel.
 Traitement d images Yuliya Tarabalka yuliya.tarabalka@hyperinet.eu yuliya.tarabalka@gipsa-lab.grenoble-inp.fr Tel. 04 76 82 62 68 Noise reduction Image restoration Restoration attempts to reconstruct an
Traitement d images Yuliya Tarabalka yuliya.tarabalka@hyperinet.eu yuliya.tarabalka@gipsa-lab.grenoble-inp.fr Tel. 04 76 82 62 68 Noise reduction Image restoration Restoration attempts to reconstruct an
Binocular Stereo Vision. System 6 Introduction Is there a Wedge in this 3D scene?
 System 6 Introduction Is there a Wedge in this 3D scene? Binocular Stereo Vision Data a stereo pair of images! Given two 2D images of an object, how can we reconstruct 3D awareness of it? AV: 3D recognition
System 6 Introduction Is there a Wedge in this 3D scene? Binocular Stereo Vision Data a stereo pair of images! Given two 2D images of an object, how can we reconstruct 3D awareness of it? AV: 3D recognition
EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 4: Corners, Interest Points, Hough Transform
 EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 4: Corners, Interest Points, Hough Transform The goal of this fourth lab is to ˆ Learn how to detect corners, and use them in a tracking application ˆ Learn how to describe
EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 4: Corners, Interest Points, Hough Transform The goal of this fourth lab is to ˆ Learn how to detect corners, and use them in a tracking application ˆ Learn how to describe
Boundaries and Sketches
 Boundaries and Sketches Szeliski 4.2 Computer Vision James Hays Many slides from Michael Maire, Jitendra Malek Today s lecture Segmentation vs Boundary Detection Why boundaries / Grouping? Recap: Canny
Boundaries and Sketches Szeliski 4.2 Computer Vision James Hays Many slides from Michael Maire, Jitendra Malek Today s lecture Segmentation vs Boundary Detection Why boundaries / Grouping? Recap: Canny
Computer Science Faculty, Bandar Lampung University, Bandar Lampung, Indonesia
 Application Object Detection Using Histogram of Oriented Gradient For Artificial Intelegence System Module of Nao Robot (Control System Laboratory (LSKK) Bandung Institute of Technology) A K Saputra 1.,
Application Object Detection Using Histogram of Oriented Gradient For Artificial Intelegence System Module of Nao Robot (Control System Laboratory (LSKK) Bandung Institute of Technology) A K Saputra 1.,
Previously. Part-based and local feature models for generic object recognition. Bag-of-words model 4/20/2011
 Previously Part-based and local feature models for generic object recognition Wed, April 20 UT-Austin Discriminative classifiers Boosting Nearest neighbors Support vector machines Useful for object recognition
Previously Part-based and local feature models for generic object recognition Wed, April 20 UT-Austin Discriminative classifiers Boosting Nearest neighbors Support vector machines Useful for object recognition
JNTUWORLD. 4. Prove that the average value of laplacian of the equation 2 h = ((r2 σ 2 )/σ 4 ))exp( r 2 /2σ 2 ) is zero. [16]
![JNTUWORLD. 4. Prove that the average value of laplacian of the equation 2 h = ((r2 σ 2 )/σ 4 ))exp( r 2 /2σ 2 ) is zero. [16] JNTUWORLD. 4. Prove that the average value of laplacian of the equation 2 h = ((r2 σ 2 )/σ 4 ))exp( r 2 /2σ 2 ) is zero. [16]](/thumbs/78/78591353.jpg) Code No: 07A70401 R07 Set No. 2 1. (a) What are the basic properties of frequency domain with respect to the image processing. (b) Define the terms: i. Impulse function of strength a ii. Impulse function
Code No: 07A70401 R07 Set No. 2 1. (a) What are the basic properties of frequency domain with respect to the image processing. (b) Define the terms: i. Impulse function of strength a ii. Impulse function
AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors
 AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors 1 Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors: Motivation 2 Step 1: Detect local features should be invariant to scale and rotation, or perspective
AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors 1 Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors: Motivation 2 Step 1: Detect local features should be invariant to scale and rotation, or perspective
VC 11/12 T14 Visual Feature Extraction
 VC 11/12 T14 Visual Feature Extraction Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Feature Vectors Colour Texture
VC 11/12 T14 Visual Feature Extraction Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Feature Vectors Colour Texture
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong)
 Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Announcements. Hough Transform [ Patented 1962 ] Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting. Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class
![Announcements. Hough Transform [ Patented 1962 ] Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting. Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class Announcements. Hough Transform [ Patented 1962 ] Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting. Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class](/thumbs/85/92905127.jpg) Announcements Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 11a What is region like if: 1. λ 1 = 0?
Announcements Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 5 in class Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 11a What is region like if: 1. λ 1 = 0?
Why study Computer Vision?
 Why study Computer Vision? Images and movies are everywhere Fast-growing collection of useful applications building representations of the 3D world from pictures automated surveillance (who s doing what)
Why study Computer Vision? Images and movies are everywhere Fast-growing collection of useful applications building representations of the 3D world from pictures automated surveillance (who s doing what)
Filtering and Edge Detection. Computer Vision I. CSE252A Lecture 10. Announcement
 Filtering and Edge Detection CSE252A Lecture 10 Announcement HW1graded, will be released later today HW2 assigned, due Wed. Nov. 7 1 Image formation: Color Channel k " $ $ # $ I r I g I b % " ' $ ' = (
Filtering and Edge Detection CSE252A Lecture 10 Announcement HW1graded, will be released later today HW2 assigned, due Wed. Nov. 7 1 Image formation: Color Channel k " $ $ # $ I r I g I b % " ' $ ' = (
Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching
 Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching Lecture 08 Computer Vision Material Citations Dr George Stockman Professor Emeritus, Michigan State University Dr David Lowe Professor, University of British
Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching Lecture 08 Computer Vision Material Citations Dr George Stockman Professor Emeritus, Michigan State University Dr David Lowe Professor, University of British
Image Features: Local Descriptors. Sanja Fidler CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 1/ 58
 Image Features: Local Descriptors Sanja Fidler CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 1/ 58 [Source: K. Grauman] Sanja Fidler CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 2/ 58 Local Features Detection: Identify
Image Features: Local Descriptors Sanja Fidler CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 1/ 58 [Source: K. Grauman] Sanja Fidler CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 2/ 58 Local Features Detection: Identify
Human detection using histogram of oriented gradients. Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah
 Human detection using histogram of oriented gradients Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Reference Navneet Dalal and Bill Triggs, Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection,
Human detection using histogram of oriented gradients Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Reference Navneet Dalal and Bill Triggs, Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection,
Solution: filter the image, then subsample F 1 F 2. subsample blur subsample. blur
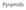 Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
CAP 6412 Advanced Computer Vision
 CAP 6412 Advanced Computer Vision http://www.cs.ucf.edu/~bgong/cap6412.html Boqing Gong April 21st, 2016 Today Administrivia Free parameters in an approach, model, or algorithm? Egocentric videos by Aisha
CAP 6412 Advanced Computer Vision http://www.cs.ucf.edu/~bgong/cap6412.html Boqing Gong April 21st, 2016 Today Administrivia Free parameters in an approach, model, or algorithm? Egocentric videos by Aisha
Texture. Frequency Descriptors. Frequency Descriptors. Frequency Descriptors. Frequency Descriptors. Frequency Descriptors
 Texture The most fundamental question is: How can we measure texture, i.e., how can we quantitatively distinguish between different textures? Of course it is not enough to look at the intensity of individual
Texture The most fundamental question is: How can we measure texture, i.e., how can we quantitatively distinguish between different textures? Of course it is not enough to look at the intensity of individual
Other Linear Filters CS 211A
 Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
6. Object Identification L AK S H M O U. E D U
 6. Object Identification L AK S H M AN @ O U. E D U Objects Information extracted from spatial grids often need to be associated with objects not just an individual pixel Group of pixels that form a real-world
6. Object Identification L AK S H M AN @ O U. E D U Objects Information extracted from spatial grids often need to be associated with objects not just an individual pixel Group of pixels that form a real-world
