Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm
|
|
|
- Alison Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm Wesley Snyder, Ph.D. UWA, CSSE NCSU, ECE Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 1/2
2 The SKS Algorithm 2-d shape recognition algorithm which uses the philosophy of evidence accumulation. Invariant to translation, rotation, scale(zoom) and robust against partial occlusion. Highly parallel in nature which favours neural implementations. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 2/2
3 Model Building A digital contour i C = { i C 1, i C 2,... i C N }. Pick a set of reference points on the contour {i R j }, i R j i C, j = 1...J. (could use just one reference point if no occlusion) We use points of high curvature Others possible, such as inflection points[?]. Curvature is determined using Digital Straight Segments(DSS)[?],[?] which has been shown[?],[?] to be more reliable and accurate. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 3/2
4 Model Building At ( i R j ), use the Frenet Frame to establish a rotationally invariant reference coordinate system with respect to all the other points on the contour. Build the model with repect to each of these reference points. Figure 1: Feature Vectors Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 4/2
5 The model for a shape Let v jk = (r jk,θ jk,κ jk ) be the feature vector at an arbitrary point i C k with respect to the reference point i R j. The model for curve i with respect to the reference point i R j is given by: i M j (v) = N max k=1 exp( v v jk 2 2σ 2 ) (1) where σ will be determined later. ( i M j (v)): a function which estimates the presence of a feature(v) in the model. Can be precomputed. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 5/2
6 Matching Same philosophy as Hough transform evidence accumulation. To match shape 1 C which has L points, against shape 2 C, 1. Choose a particular reference point 1 R k 1 C, k = 1,...,K. 2. Compute the feature vectors to every other point in 1 C, and denote those vectors by v kl. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 6/2
7 Matching We have a collection of models, each referencing a curve and a reference point. Consider matching curve 1 C using reference point 1 R k to curve 2 C using reference point 2 R j, and compute 12 A kj = 1 L L l=1 2 M j (V kl ) (2) The best match between shapes 1 and 2 is then 12 A = max k,j A kj (3) Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 7/2
8 Computational Complexity The computational complexity of the algorithm as described above would seem high since it requires a search over all paris of reference points, but this is mitigated by the facts that there are very few reference points on any particular contour the search may be ordered by considering only pairs of reference points which are very similar Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 8/2
9 Test set with lots of straight lines Figure 2: Database of 12 tanks Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 9/2
10 Test Set with lots of examples Figure 3: The 31 randomly picked silhouettes from the SQUID database Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 10/2
11 Experimental Results If no occlusion, only one reference point required (CG is good) Figure 4: Two examples of matching contours. The one on the left exhibits a distinctive peak representing a good match. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 11/2
12 Contour Blur Figure 5: Left: The fish contour blurred by 2000 iterations of smoothing with unit variance Gaussian. Middle: The same contour after 6000 iterations Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 12/2
13 Invariance to Similarity Transforms We built models using all the tanks(rotated and scaled) and matched each tank contour with every model. 12 tanks and each tank has 6 rotated and scaled versions of itself, the total number of correct matches is Table below shows the retrieval results of the four algorithms. Algorithm Correct Retrievals(%) SKS Shape Context Hu Moments 77.6 CSS 75.1 Table 1: Invariance to Similarity Transforms Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 13/2
14 Generating Occluded Contours 31 fishes from the SQUID database, shown earlier. Partially occlude each fish by retaining 10-90% of the points. algorithm : Starting at point C 1, K points are chosen such that K/N = δ/100. Remove those K points. Move the starting point from 1 to 2, then 3, etc, generating a new occluded boundary with same percent occlusion. An example of this is shown in figure 6. The performance reported is the average of all the occlusions of that particular boundary. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 14/2
15 Occluded Contours (a) Original Contour (b) Contour at 40% occlusion (c) Same contour at 40% occlusion Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 15/2
16 Robustness to Occlusion Figure 7: Classification accuracy at various levels of occlusion. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 16/2
17 Content-based Image Retrieval (a) kk732 - Query shape. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 17/2
18 Content-based Image Retrieval (b) Top 5 matches in random order for the shape kk732 using CSS. (c) Top 5 matches in random order for the shape kk732 using Hu Moments. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 18/2
19 Content-based Image Retrieval Top 5 matches in random order for the shape kk732 using Shape Context. Top 5 matches in random order for the shape kk732 using the SKS algorithm. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 19/2
20 Conclusion Is the gestalt approach a good one? Belongie et al.: "Not all objects have distinguished key points (think of a circle for instance), and using key points alone sacrifices the shape information available in smooth portions of object contours". Srivastava: Among the papers that explicitly study shapes, a major limitation in many of them is the use of landmarks to define shapes. Shapes are often encoded by a coarse sampling of the objectsõ boundaries, and the outcome and accuracy of the ensuing shape analysis is heavily dependent on the choices made. In addition, it is usually difficult to automate the selection of these landmarks. A more fundamental approach is to represent the continuous boundaries as curves, and then study their shapes. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 20/2
21 Conclusion But, humans use key points Figure 8: A line drawing, without color or texture information, and consisting of only straight lines connecting salient points. Lecture 4, Part 2: The SKS Algorithm p. 21/2
CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2014) Problem Set 3
 CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2014) Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 18 th, 2015 (11:59pm) 1 Single Object Recognition Via SIFT (45 points) In his 2004 SIFT paper, David Lowe demonstrates impressive object recognition
CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2014) Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 18 th, 2015 (11:59pm) 1 Single Object Recognition Via SIFT (45 points) In his 2004 SIFT paper, David Lowe demonstrates impressive object recognition
HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V
 HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V HOUGH TRANSFORM The problem: Given a set of points in 2-D, find if a sub-set of these points, fall on a LINE. Hough Transform One powerful global method for detecting edges
HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V HOUGH TRANSFORM The problem: Given a set of points in 2-D, find if a sub-set of these points, fall on a LINE. Hough Transform One powerful global method for detecting edges
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS
 SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
Artifacts and Textured Region Detection
 Artifacts and Textured Region Detection 1 Vishal Bangard ECE 738 - Spring 2003 I. INTRODUCTION A lot of transformations, when applied to images, lead to the development of various artifacts in them. In
Artifacts and Textured Region Detection 1 Vishal Bangard ECE 738 - Spring 2003 I. INTRODUCTION A lot of transformations, when applied to images, lead to the development of various artifacts in them. In
Fitting. Lecture 8. Cristian Sminchisescu. Slide credits: K. Grauman, S. Seitz, S. Lazebnik, D. Forsyth, J. Ponce
 Fitting Lecture 8 Cristian Sminchisescu Slide credits: K. Grauman, S. Seitz, S. Lazebnik, D. Forsyth, J. Ponce Fitting We want to associate a model with observed features [Fig from Marszalek & Schmid,
Fitting Lecture 8 Cristian Sminchisescu Slide credits: K. Grauman, S. Seitz, S. Lazebnik, D. Forsyth, J. Ponce Fitting We want to associate a model with observed features [Fig from Marszalek & Schmid,
CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Perceptual Grouping Detecting Lines and Simple Curves
 CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Perceptual Grouping Detecting Lines and Simple Curves Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines Perceptual Grouping and Segmentation
CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Perceptual Grouping Detecting Lines and Simple Curves Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines Perceptual Grouping and Segmentation
An Efficient Single Chord-based Accumulation Technique (SCA) to Detect More Reliable Corners
 An Efficient Single Chord-based Accumulation Technique (SCA) to Detect More Reliable Corners Mohammad Asiful Hossain, Abdul Kawsar Tushar, and Shofiullah Babor Computer Science and Engineering Department,
An Efficient Single Chord-based Accumulation Technique (SCA) to Detect More Reliable Corners Mohammad Asiful Hossain, Abdul Kawsar Tushar, and Shofiullah Babor Computer Science and Engineering Department,
CS664 Lecture #21: SIFT, object recognition, dynamic programming
 CS664 Lecture #21: SIFT, object recognition, dynamic programming Some material taken from: Sebastian Thrun, Stanford http://cs223b.stanford.edu/ Yuri Boykov, Western Ontario David Lowe, UBC http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~lowe/keypoints/
CS664 Lecture #21: SIFT, object recognition, dynamic programming Some material taken from: Sebastian Thrun, Stanford http://cs223b.stanford.edu/ Yuri Boykov, Western Ontario David Lowe, UBC http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~lowe/keypoints/
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB
 Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 18 Feature extraction and representation What will we learn? What is feature extraction and why is it a critical step in most computer vision and
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 18 Feature extraction and representation What will we learn? What is feature extraction and why is it a critical step in most computer vision and
Estimating Human Pose in Images. Navraj Singh December 11, 2009
 Estimating Human Pose in Images Navraj Singh December 11, 2009 Introduction This project attempts to improve the performance of an existing method of estimating the pose of humans in still images. Tasks
Estimating Human Pose in Images Navraj Singh December 11, 2009 Introduction This project attempts to improve the performance of an existing method of estimating the pose of humans in still images. Tasks
Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation
 #1 Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Hough Transform Robust method to find a shape in an image Shape can be described in parametric form A voting
#1 Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Hough Transform Robust method to find a shape in an image Shape can be described in parametric form A voting
6.801/866. Segmentation and Line Fitting. T. Darrell
 6.801/866 Segmentation and Line Fitting T. Darrell Segmentation and Line Fitting Gestalt grouping Background subtraction K-Means Graph cuts Hough transform Iterative fitting (Next time: Probabilistic segmentation)
6.801/866 Segmentation and Line Fitting T. Darrell Segmentation and Line Fitting Gestalt grouping Background subtraction K-Means Graph cuts Hough transform Iterative fitting (Next time: Probabilistic segmentation)
Matching and Retrieval of Distorted and Occluded Shapes Using Dynamic Programming
 Matching and Retrieval of Distorted and Occluded Shapes Using Dynamic Programming Euripides G.M. Petrakis Aristeidis Diplaros Evangelos Milios April 10, 2002 Abstract We propose an approach for matching
Matching and Retrieval of Distorted and Occluded Shapes Using Dynamic Programming Euripides G.M. Petrakis Aristeidis Diplaros Evangelos Milios April 10, 2002 Abstract We propose an approach for matching
MPEG-7 Visual shape descriptors
 MPEG-7 Visual shape descriptors Miroslaw Bober presented by Peter Tylka Seminar on scientific soft skills 22.3.2012 Presentation Outline Presentation Outline Introduction to problem Shape spectrum - 3D
MPEG-7 Visual shape descriptors Miroslaw Bober presented by Peter Tylka Seminar on scientific soft skills 22.3.2012 Presentation Outline Presentation Outline Introduction to problem Shape spectrum - 3D
GENERALIZING THE HOUGH TRANSFORM TO DETECT ARBITRARY SHAPES. D. H. Ballard Pattern Recognition Vol. 13 No
 GENERALIZING THE HOUGH TRANSFORM TO DETECT ARBITRARY SHAPES D. H. Ballard Pattern Recognition Vol. 13 No. 2 1981 What is the generalized Hough (Huff) transform used for? Hough transform is a way of encoding
GENERALIZING THE HOUGH TRANSFORM TO DETECT ARBITRARY SHAPES D. H. Ballard Pattern Recognition Vol. 13 No. 2 1981 What is the generalized Hough (Huff) transform used for? Hough transform is a way of encoding
Binary Image Processing. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 5
 Binary Image Processing CSE 152 Lecture 5 Announcements Homework 2 is due Apr 25, 11:59 PM Reading: Szeliski, Chapter 3 Image processing, Section 3.3 More neighborhood operators Binary System Summary 1.
Binary Image Processing CSE 152 Lecture 5 Announcements Homework 2 is due Apr 25, 11:59 PM Reading: Szeliski, Chapter 3 Image processing, Section 3.3 More neighborhood operators Binary System Summary 1.
Designing Applications that See Lecture 7: Object Recognition
 stanford hci group / cs377s Designing Applications that See Lecture 7: Object Recognition Dan Maynes-Aminzade 29 January 2008 Designing Applications that See http://cs377s.stanford.edu Reminders Pick up
stanford hci group / cs377s Designing Applications that See Lecture 7: Object Recognition Dan Maynes-Aminzade 29 January 2008 Designing Applications that See http://cs377s.stanford.edu Reminders Pick up
COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION
 VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
CoE4TN4 Image Processing
 CoE4TN4 Image Processing Chapter 11 Image Representation & Description Image Representation & Description After an image is segmented into regions, the regions are represented and described in a form suitable
CoE4TN4 Image Processing Chapter 11 Image Representation & Description Image Representation & Description After an image is segmented into regions, the regions are represented and described in a form suitable
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
Raghuraman Gopalan Center for Automation Research University of Maryland, College Park
 2D Shape Matching (and Object Recognition) Raghuraman Gopalan Center for Automation Research University of Maryland, College Park 1 Outline What is a shape? Part 1: Matching/ Recognition Shape contexts
2D Shape Matching (and Object Recognition) Raghuraman Gopalan Center for Automation Research University of Maryland, College Park 1 Outline What is a shape? Part 1: Matching/ Recognition Shape contexts
A NEW FEATURE BASED IMAGE REGISTRATION ALGORITHM INTRODUCTION
 A NEW FEATURE BASED IMAGE REGISTRATION ALGORITHM Karthik Krish Stuart Heinrich Wesley E. Snyder Halil Cakir Siamak Khorram North Carolina State University Raleigh, 27695 kkrish@ncsu.edu sbheinri@ncsu.edu
A NEW FEATURE BASED IMAGE REGISTRATION ALGORITHM Karthik Krish Stuart Heinrich Wesley E. Snyder Halil Cakir Siamak Khorram North Carolina State University Raleigh, 27695 kkrish@ncsu.edu sbheinri@ncsu.edu
Digital Image Processing Fundamentals
 Ioannis Pitas Digital Image Processing Fundamentals Chapter 7 Shape Description Answers to the Chapter Questions Thessaloniki 1998 Chapter 7: Shape description 7.1 Introduction 1. Why is invariance to
Ioannis Pitas Digital Image Processing Fundamentals Chapter 7 Shape Description Answers to the Chapter Questions Thessaloniki 1998 Chapter 7: Shape description 7.1 Introduction 1. Why is invariance to
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Part 9: Representation and Description AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapter 11 2011-05-17 Contents
Digital Image Processing Part 9: Representation and Description AASS Learning Systems Lab, Dep. Teknik Room T1209 (Fr, 11-12 o'clock) achim.lilienthal@oru.se Course Book Chapter 11 2011-05-17 Contents
Fitting. Fitting. Slides S. Lazebnik Harris Corners Pkwy, Charlotte, NC
 Fitting We ve learned how to detect edges, corners, blobs. Now what? We would like to form a higher-level, more compact representation of the features in the image by grouping multiple features according
Fitting We ve learned how to detect edges, corners, blobs. Now what? We would like to form a higher-level, more compact representation of the features in the image by grouping multiple features according
Report: Reducing the error rate of a Cat classifier
 Report: Reducing the error rate of a Cat classifier Raphael Sznitman 6 August, 2007 Abstract The following report discusses my work at the IDIAP from 06.2007 to 08.2007. This work had for objective to
Report: Reducing the error rate of a Cat classifier Raphael Sznitman 6 August, 2007 Abstract The following report discusses my work at the IDIAP from 06.2007 to 08.2007. This work had for objective to
A New Approach to Computation of Curvature Scale Space Image for Shape Similarity Retrieval
 A New Approach to Computation of Curvature Scale Space Image for Shape Similarity Retrieval Farzin Mokhtarian, Sadegh Abbasi and Josef Kittler Centre for Vision Speech and Signal Processing Department
A New Approach to Computation of Curvature Scale Space Image for Shape Similarity Retrieval Farzin Mokhtarian, Sadegh Abbasi and Josef Kittler Centre for Vision Speech and Signal Processing Department
Boundary descriptors. Representation REPRESENTATION & DESCRIPTION. Descriptors. Moore boundary tracking
 Representation REPRESENTATION & DESCRIPTION After image segmentation the resulting collection of regions is usually represented and described in a form suitable for higher level processing. Most important
Representation REPRESENTATION & DESCRIPTION After image segmentation the resulting collection of regions is usually represented and described in a form suitable for higher level processing. Most important
IRIS SEGMENTATION OF NON-IDEAL IMAGES
 IRIS SEGMENTATION OF NON-IDEAL IMAGES William S. Weld St. Lawrence University Computer Science Department Canton, NY 13617 Xiaojun Qi, Ph.D Utah State University Computer Science Department Logan, UT 84322
IRIS SEGMENTATION OF NON-IDEAL IMAGES William S. Weld St. Lawrence University Computer Science Department Canton, NY 13617 Xiaojun Qi, Ph.D Utah State University Computer Science Department Logan, UT 84322
CRF Based Point Cloud Segmentation Jonathan Nation
 CRF Based Point Cloud Segmentation Jonathan Nation jsnation@stanford.edu 1. INTRODUCTION The goal of the project is to use the recently proposed fully connected conditional random field (CRF) model to
CRF Based Point Cloud Segmentation Jonathan Nation jsnation@stanford.edu 1. INTRODUCTION The goal of the project is to use the recently proposed fully connected conditional random field (CRF) model to
Lecture 14 Shape. ch. 9, sec. 1-8, of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder & Hairong Qi. Spring (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt)
 Lecture 14 Shape ch. 9, sec. 1-8, 12-14 of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder & Hairong Qi Spring 2018 16-725 (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt) Dr. John Galeotti The content of these slides by John Galeotti,
Lecture 14 Shape ch. 9, sec. 1-8, 12-14 of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder & Hairong Qi Spring 2018 16-725 (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt) Dr. John Galeotti The content of these slides by John Galeotti,
Edge and local feature detection - 2. Importance of edge detection in computer vision
 Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Region-based Segmentation
 Region-based Segmentation Image Segmentation Group similar components (such as, pixels in an image, image frames in a video) to obtain a compact representation. Applications: Finding tumors, veins, etc.
Region-based Segmentation Image Segmentation Group similar components (such as, pixels in an image, image frames in a video) to obtain a compact representation. Applications: Finding tumors, veins, etc.
Su et al. Shape Descriptors - III
 Su et al. Shape Descriptors - III Siddhartha Chaudhuri http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~cs749 Funkhouser; Feng, Liu, Gong Recap Global A shape descriptor is a set of numbers that describes a shape in a way that
Su et al. Shape Descriptors - III Siddhartha Chaudhuri http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~cs749 Funkhouser; Feng, Liu, Gong Recap Global A shape descriptor is a set of numbers that describes a shape in a way that
CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3
 CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3 Due: Nov. 13 th, 2012 (2:15pm) 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking (20 points) In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest
CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3 Due: Nov. 13 th, 2012 (2:15pm) 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking (20 points) In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest
Features Points. Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, Mestre (VE)
 Features Points Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, 30172 Mestre (VE) Finding Corners Edge detectors perform poorly at corners. Corners provide repeatable points for matching, so
Features Points Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, 30172 Mestre (VE) Finding Corners Edge detectors perform poorly at corners. Corners provide repeatable points for matching, so
10/03/11. Model Fitting. Computer Vision CS 143, Brown. James Hays. Slides from Silvio Savarese, Svetlana Lazebnik, and Derek Hoiem
 10/03/11 Model Fitting Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Slides from Silvio Savarese, Svetlana Lazebnik, and Derek Hoiem Fitting: find the parameters of a model that best fit the data Alignment:
10/03/11 Model Fitting Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Slides from Silvio Savarese, Svetlana Lazebnik, and Derek Hoiem Fitting: find the parameters of a model that best fit the data Alignment:
Lecture Notes (Reflection & Mirrors)
 Lecture Notes (Reflection & Mirrors) Intro: - plane mirrors are flat, smooth surfaces from which light is reflected by regular reflection - light rays are reflected with equal angles of incidence and reflection
Lecture Notes (Reflection & Mirrors) Intro: - plane mirrors are flat, smooth surfaces from which light is reflected by regular reflection - light rays are reflected with equal angles of incidence and reflection
One image is worth 1,000 words
 Image Databases Prof. Paolo Ciaccia http://www-db. db.deis.unibo.it/courses/si-ls/ 07_ImageDBs.pdf Sistemi Informativi LS One image is worth 1,000 words Undoubtedly, images are the most wide-spread MM
Image Databases Prof. Paolo Ciaccia http://www-db. db.deis.unibo.it/courses/si-ls/ 07_ImageDBs.pdf Sistemi Informativi LS One image is worth 1,000 words Undoubtedly, images are the most wide-spread MM
Lecture 15: Segmentation (Edge Based, Hough Transform)
 Lecture 15: Segmentation (Edge Based, Hough Transform) c Bryan S. Morse, Brigham Young University, 1998 000 Last modified on February 3, 000 at :00 PM Contents 15.1 Introduction..............................................
Lecture 15: Segmentation (Edge Based, Hough Transform) c Bryan S. Morse, Brigham Young University, 1998 000 Last modified on February 3, 000 at :00 PM Contents 15.1 Introduction..............................................
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB
 Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Model Fitting, RANSAC. Jana Kosecka
 Model Fitting, RANSAC Jana Kosecka Fitting: Overview If we know which points belong to the line, how do we find the optimal line parameters? Least squares What if there are outliers? Robust fitting, RANSAC
Model Fitting, RANSAC Jana Kosecka Fitting: Overview If we know which points belong to the line, how do we find the optimal line parameters? Least squares What if there are outliers? Robust fitting, RANSAC
9 length of contour = no. of horizontal and vertical components + ( 2 no. of diagonal components) diameter of boundary B
 8. Boundary Descriptor 8.. Some Simple Descriptors length of contour : simplest descriptor - chain-coded curve 9 length of contour no. of horiontal and vertical components ( no. of diagonal components
8. Boundary Descriptor 8.. Some Simple Descriptors length of contour : simplest descriptor - chain-coded curve 9 length of contour no. of horiontal and vertical components ( no. of diagonal components
Lecture 6: Multimedia Information Retrieval Dr. Jian Zhang
 Lecture 6: Multimedia Information Retrieval Dr. Jian Zhang NICTA & CSE UNSW COMP9314 Advanced Database S1 2007 jzhang@cse.unsw.edu.au Reference Papers and Resources Papers: Colour spaces-perceptual, historical
Lecture 6: Multimedia Information Retrieval Dr. Jian Zhang NICTA & CSE UNSW COMP9314 Advanced Database S1 2007 jzhang@cse.unsw.edu.au Reference Papers and Resources Papers: Colour spaces-perceptual, historical
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 10 Segmentation 14/02/27 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 10 Segmentation 14/02/27 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
What is Computer Vision?
 Perceptual Grouping in Computer Vision Gérard Medioni University of Southern California What is Computer Vision? Computer Vision Attempt to emulate Human Visual System Perceive visual stimuli with cameras
Perceptual Grouping in Computer Vision Gérard Medioni University of Southern California What is Computer Vision? Computer Vision Attempt to emulate Human Visual System Perceive visual stimuli with cameras
Water-Filling: A Novel Way for Image Structural Feature Extraction
 Water-Filling: A Novel Way for Image Structural Feature Extraction Xiang Sean Zhou Yong Rui Thomas S. Huang Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign,
Water-Filling: A Novel Way for Image Structural Feature Extraction Xiang Sean Zhou Yong Rui Thomas S. Huang Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign,
Lecture 10: Image Descriptors and Representation
 I2200: Digital Image processing Lecture 10: Image Descriptors and Representation Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 15, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of
I2200: Digital Image processing Lecture 10: Image Descriptors and Representation Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 15, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University of
Partial Shape Matching using Transformation Parameter Similarity - Additional Material
 Volume xx (y), Number z, pp. 7 Partial Shape Matching using Transformation Parameter Similarity - Additional Material paper66. An Example for Local Contour Descriptors As mentioned in Section 4 of the
Volume xx (y), Number z, pp. 7 Partial Shape Matching using Transformation Parameter Similarity - Additional Material paper66. An Example for Local Contour Descriptors As mentioned in Section 4 of the
IOSR Journal of Electronics and communication Engineering (IOSR-JCE) ISSN: , ISBN: , PP:
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and communication Engineering (IOSR-JCE) ISSN: 2278-2834, ISBN: 2278-8735, PP: 48-53 www.iosrjournals.org SEGMENTATION OF VERTEBRAE FROM DIGITIZED X-RAY IMAGES Ashwini Shivdas
IOSR Journal of Electronics and communication Engineering (IOSR-JCE) ISSN: 2278-2834, ISBN: 2278-8735, PP: 48-53 www.iosrjournals.org SEGMENTATION OF VERTEBRAE FROM DIGITIZED X-RAY IMAGES Ashwini Shivdas
HISTOGRAMS OF ORIENTATIO N GRADIENTS
 HISTOGRAMS OF ORIENTATIO N GRADIENTS Histograms of Orientation Gradients Objective: object recognition Basic idea Local shape information often well described by the distribution of intensity gradients
HISTOGRAMS OF ORIENTATIO N GRADIENTS Histograms of Orientation Gradients Objective: object recognition Basic idea Local shape information often well described by the distribution of intensity gradients
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 1 / 45 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 45 Menu March 3, 2016 Topics: Hough
1 / 45 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 45 Menu March 3, 2016 Topics: Hough
Shape Descriptor using Polar Plot for Shape Recognition.
 Shape Descriptor using Polar Plot for Shape Recognition. Brijesh Pillai ECE Graduate Student, Clemson University bpillai@clemson.edu Abstract : This paper presents my work on computing shape models that
Shape Descriptor using Polar Plot for Shape Recognition. Brijesh Pillai ECE Graduate Student, Clemson University bpillai@clemson.edu Abstract : This paper presents my work on computing shape models that
AFFINE INVARIANT CURVE MATCHING USING NORMALIZATION AND CURVATURE SCALE-SPACE. V. Giannekou, P. Tzouveli, Y. Avrithis and S.
 AFFINE INVARIANT CURVE MATCHING USING NORMALIZATION AND CURVATURE SCALE-SPACE V. Giannekou, P. Tzouveli, Y. Avrithis and S.Kollias Image Video and Multimedia Systems Laboratory, School of Electrical and
AFFINE INVARIANT CURVE MATCHING USING NORMALIZATION AND CURVATURE SCALE-SPACE V. Giannekou, P. Tzouveli, Y. Avrithis and S.Kollias Image Video and Multimedia Systems Laboratory, School of Electrical and
Announcements. Edges. Last Lecture. Gradients: Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge Detection, Lines. Intro Computer Vision. CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Fitting: The Hough transform
 Fitting: The Hough transform Voting schemes Let each feature vote for all the models that are compatible with it Hopefully the noise features will not vote consistently for any single model Missing data
Fitting: The Hough transform Voting schemes Let each feature vote for all the models that are compatible with it Hopefully the noise features will not vote consistently for any single model Missing data
CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3
 CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 22 nd, 2011 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest through a sequence of images.
CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 22 nd, 2011 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest through a sequence of images.
Scale Invariant Feature Transform
 Why do we care about matching features? Scale Invariant Feature Transform Camera calibration Stereo Tracking/SFM Image moiaicing Object/activity Recognition Objection representation and recognition Automatic
Why do we care about matching features? Scale Invariant Feature Transform Camera calibration Stereo Tracking/SFM Image moiaicing Object/activity Recognition Objection representation and recognition Automatic
Computer Vision Lecture 6
 Course Outline Computer Vision Lecture 6 Segmentation Image Processing Basics Structure Extraction Segmentation Segmentation as Clustering Graph-theoretic Segmentation 12.11.2015 Recognition Global Representations
Course Outline Computer Vision Lecture 6 Segmentation Image Processing Basics Structure Extraction Segmentation Segmentation as Clustering Graph-theoretic Segmentation 12.11.2015 Recognition Global Representations
A Comparative Study of Curvature Scale Space and Fourier Descriptors for Shape-based Image Retrieval
 A Comparative Study of Curvature Scale Space and Fourier Descriptors for Shape-based Image Retrieval Dengsheng Zhang (contact author) and Guojun Lu Gippsland School of Computing and Information Technology
A Comparative Study of Curvature Scale Space and Fourier Descriptors for Shape-based Image Retrieval Dengsheng Zhang (contact author) and Guojun Lu Gippsland School of Computing and Information Technology
2: Image Display and Digital Images. EE547 Computer Vision: Lecture Slides. 2: Digital Images. 1. Introduction: EE547 Computer Vision
 EE547 Computer Vision: Lecture Slides Anthony P. Reeves November 24, 1998 Lecture 2: Image Display and Digital Images 2: Image Display and Digital Images Image Display: - True Color, Grey, Pseudo Color,
EE547 Computer Vision: Lecture Slides Anthony P. Reeves November 24, 1998 Lecture 2: Image Display and Digital Images 2: Image Display and Digital Images Image Display: - True Color, Grey, Pseudo Color,
Announcements. Binary Image Processing. Binary System Summary. Histogram-based Segmentation. How do we select a Threshold?
 Announcements Binary Image Processing Homework is due Apr 24, :59 PM Homework 2 will be assigned this week Reading: Chapter 3 Image processing CSE 52 Lecture 8 Binary System Summary. Acquire images and
Announcements Binary Image Processing Homework is due Apr 24, :59 PM Homework 2 will be assigned this week Reading: Chapter 3 Image processing CSE 52 Lecture 8 Binary System Summary. Acquire images and
Lecture 8: Fitting. Tuesday, Sept 25
 Lecture 8: Fitting Tuesday, Sept 25 Announcements, schedule Grad student extensions Due end of term Data sets, suggestions Reminder: Midterm Tuesday 10/9 Problem set 2 out Thursday, due 10/11 Outline Review
Lecture 8: Fitting Tuesday, Sept 25 Announcements, schedule Grad student extensions Due end of term Data sets, suggestions Reminder: Midterm Tuesday 10/9 Problem set 2 out Thursday, due 10/11 Outline Review
Chapter 11 Representation & Description
 Chain Codes Chain codes are used to represent a boundary by a connected sequence of straight-line segments of specified length and direction. The direction of each segment is coded by using a numbering
Chain Codes Chain codes are used to represent a boundary by a connected sequence of straight-line segments of specified length and direction. The direction of each segment is coded by using a numbering
Image Segmentation Techniques for Object-Based Coding
 Image Techniques for Object-Based Coding Junaid Ahmed, Joseph Bosworth, and Scott T. Acton The Oklahoma Imaging Laboratory School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Oklahoma State University {ajunaid,bosworj,sacton}@okstate.edu
Image Techniques for Object-Based Coding Junaid Ahmed, Joseph Bosworth, and Scott T. Acton The Oklahoma Imaging Laboratory School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Oklahoma State University {ajunaid,bosworj,sacton}@okstate.edu
Fractals and the Chaos Game
 Math: Outside the box! Fractals and the Chaos Game Monday February 23, 2009 3:30-4:20 IRMACS theatre, ASB 10900 Randall Pyke Senior Lecturer Department of Mathematics, SFU A Game. Is this a random walk?
Math: Outside the box! Fractals and the Chaos Game Monday February 23, 2009 3:30-4:20 IRMACS theatre, ASB 10900 Randall Pyke Senior Lecturer Department of Mathematics, SFU A Game. Is this a random walk?
Matching and Recognition in 3D. Based on slides by Tom Funkhouser and Misha Kazhdan
 Matching and Recognition in 3D Based on slides by Tom Funkhouser and Misha Kazhdan From 2D to 3D: Some Things Easier No occlusion (but sometimes missing data instead) Segmenting objects often simpler From
Matching and Recognition in 3D Based on slides by Tom Funkhouser and Misha Kazhdan From 2D to 3D: Some Things Easier No occlusion (but sometimes missing data instead) Segmenting objects often simpler From
Planar Symmetry Detection by Random Sampling and Voting Process
 Planar Symmetry Detection by Random Sampling and Voting Process Atsushi Imiya, Tomoki Ueno, and Iris Fermin Dept. of IIS, Chiba University, 1-33, Yayo-cho, Inage-ku, Chiba, 263-8522, Japan imiya@ics.tj.chiba-u.ac.jp
Planar Symmetry Detection by Random Sampling and Voting Process Atsushi Imiya, Tomoki Ueno, and Iris Fermin Dept. of IIS, Chiba University, 1-33, Yayo-cho, Inage-ku, Chiba, 263-8522, Japan imiya@ics.tj.chiba-u.ac.jp
Image Processing. Image Features
 Image Processing Image Features Preliminaries 2 What are Image Features? Anything. What they are used for? Some statements about image fragments (patches) recognition Search for similar patches matching
Image Processing Image Features Preliminaries 2 What are Image Features? Anything. What they are used for? Some statements about image fragments (patches) recognition Search for similar patches matching
Feature Extraction and Image Processing, 2 nd Edition. Contents. Preface
 , 2 nd Edition Preface ix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 Human and Computer Vision 1 1.3 The Human Vision System 3 1.3.1 The Eye 4 1.3.2 The Neural System 7 1.3.3 Processing 7 1.4 Computer Vision
, 2 nd Edition Preface ix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 Human and Computer Vision 1 1.3 The Human Vision System 3 1.3.1 The Eye 4 1.3.2 The Neural System 7 1.3.3 Processing 7 1.4 Computer Vision
A System for Historic Document Image Indexing and Retrieval Based on XML Database Conforming to MPEG7 Standard
 A System for Historic Document Image Indexing and Retrieval Based on XML Database Conforming to MPEG7 Standard Wafa Maghrebi *, Anis Borchani *, Mohamed A. Khabou +, Adel M. Alimi * * REsearch Group on
A System for Historic Document Image Indexing and Retrieval Based on XML Database Conforming to MPEG7 Standard Wafa Maghrebi *, Anis Borchani *, Mohamed A. Khabou +, Adel M. Alimi * * REsearch Group on
Computer Vision Lecture 6
 Computer Vision Lecture 6 Segmentation 12.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Image Processing Basics Structure Extraction Segmentation
Computer Vision Lecture 6 Segmentation 12.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Image Processing Basics Structure Extraction Segmentation
Lecture 8 Object Descriptors
 Lecture 8 Object Descriptors Azadeh Fakhrzadeh Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University 2 Reading instructions Chapter 11.1 11.4 in G-W Azadeh Fakhrzadeh
Lecture 8 Object Descriptors Azadeh Fakhrzadeh Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University 2 Reading instructions Chapter 11.1 11.4 in G-W Azadeh Fakhrzadeh
Multi-Scale Free-Form Surface Description
 Multi-Scale Free-Form Surface Description Farzin Mokhtarian, Nasser Khalili and Peter Yuen Centre for Vision Speech and Signal Processing Dept. of Electronic and Electrical Engineering University of Surrey,
Multi-Scale Free-Form Surface Description Farzin Mokhtarian, Nasser Khalili and Peter Yuen Centre for Vision Speech and Signal Processing Dept. of Electronic and Electrical Engineering University of Surrey,
Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking
 Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science
 Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science Lecture 16: Models of Object Recognition Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk February 23, 2010 Frank Keller Computational
Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science Lecture 16: Models of Object Recognition Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk February 23, 2010 Frank Keller Computational
A Survey of Light Source Detection Methods
 A Survey of Light Source Detection Methods Nathan Funk University of Alberta Mini-Project for CMPUT 603 November 30, 2003 Abstract This paper provides an overview of the most prominent techniques for light
A Survey of Light Source Detection Methods Nathan Funk University of Alberta Mini-Project for CMPUT 603 November 30, 2003 Abstract This paper provides an overview of the most prominent techniques for light
EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm
 EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm Group 1: Mina A. Makar Stanford University mamakar@stanford.edu Abstract In this report, we investigate the application of the Scale-Invariant
EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm Group 1: Mina A. Makar Stanford University mamakar@stanford.edu Abstract In this report, we investigate the application of the Scale-Invariant
TA Section 7 Problem Set 3. SIFT (Lowe 2004) Shape Context (Belongie et al. 2002) Voxel Coloring (Seitz and Dyer 1999)
 TA Section 7 Problem Set 3 SIFT (Lowe 2004) Shape Context (Belongie et al. 2002) Voxel Coloring (Seitz and Dyer 1999) Sam Corbett-Davies TA Section 7 02-13-2014 Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant
TA Section 7 Problem Set 3 SIFT (Lowe 2004) Shape Context (Belongie et al. 2002) Voxel Coloring (Seitz and Dyer 1999) Sam Corbett-Davies TA Section 7 02-13-2014 Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant
Shape recognition with edge-based features
 Shape recognition with edge-based features K. Mikolajczyk A. Zisserman C. Schmid Dept. of Engineering Science Dept. of Engineering Science INRIA Rhône-Alpes Oxford, OX1 3PJ Oxford, OX1 3PJ 38330 Montbonnot
Shape recognition with edge-based features K. Mikolajczyk A. Zisserman C. Schmid Dept. of Engineering Science Dept. of Engineering Science INRIA Rhône-Alpes Oxford, OX1 3PJ Oxford, OX1 3PJ 38330 Montbonnot
Case-Based Reasoning. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Nearest-Neighbor Classification. Parametric / Non-parametric.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 09 130219 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Feature Descriptors Feature Matching Feature
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 09 130219 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Feature Descriptors Feature Matching Feature
Affine Matching of Planar Sets
 COMPUTER VISION AND IMAGE UNDERSTANDING Vol. 70, No. 1, April, pp. 1 22, 1998 ARTICLE NO. IV970623 Affine Matching of Planar Sets Kenji Nagao Multimedia Systems Research Laboratory, Matsushita Electric
COMPUTER VISION AND IMAGE UNDERSTANDING Vol. 70, No. 1, April, pp. 1 22, 1998 ARTICLE NO. IV970623 Affine Matching of Planar Sets Kenji Nagao Multimedia Systems Research Laboratory, Matsushita Electric
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Affine-invariant shape matching and recognition under partial occlusion
 Title Affine-invariant shape matching and recognition under partial occlusion Author(s) Mai, F; Chang, CQ; Hung, YS Citation The 17th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2010), Hong
Title Affine-invariant shape matching and recognition under partial occlusion Author(s) Mai, F; Chang, CQ; Hung, YS Citation The 17th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2010), Hong
Solution: filter the image, then subsample F 1 F 2. subsample blur subsample. blur
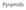 Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Automatic Image Alignment (feature-based)
 Automatic Image Alignment (feature-based) Mike Nese with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2006 Today s lecture Feature
Automatic Image Alignment (feature-based) Mike Nese with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2006 Today s lecture Feature
Fitting: The Hough transform
 Fitting: The Hough transform Voting schemes Let each feature vote for all the models that are compatible with it Hopefully the noise features will not vote consistently for any single model Missing data
Fitting: The Hough transform Voting schemes Let each feature vote for all the models that are compatible with it Hopefully the noise features will not vote consistently for any single model Missing data
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF IMAGE EDGE DETECTION ALGORITHMS
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF IMAGE EDGE DETECTION ALGORITHMS Shubham Saini 1, Bhavesh Kasliwal 2, Shraey Bhatia 3 1 Student, School of Computing Science and Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, India,
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF IMAGE EDGE DETECTION ALGORITHMS Shubham Saini 1, Bhavesh Kasliwal 2, Shraey Bhatia 3 1 Student, School of Computing Science and Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, India,
Model Fitting: The Hough transform II
 Model Fitting: The Hough transform II Guido Gerig, CS6640 Image Processing, Utah Theory: See handwritten notes GG: HT-notes-GG-II.pdf Credits: S. Narasimhan, CMU, Spring 2006 15-385,-685, Link Svetlana
Model Fitting: The Hough transform II Guido Gerig, CS6640 Image Processing, Utah Theory: See handwritten notes GG: HT-notes-GG-II.pdf Credits: S. Narasimhan, CMU, Spring 2006 15-385,-685, Link Svetlana
VC 11/12 T14 Visual Feature Extraction
 VC 11/12 T14 Visual Feature Extraction Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Feature Vectors Colour Texture
VC 11/12 T14 Visual Feature Extraction Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Feature Vectors Colour Texture
COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION
 VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington T V ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington T V ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
3D Object Recognition using Multiclass SVM-KNN
 3D Object Recognition using Multiclass SVM-KNN R. Muralidharan, C. Chandradekar April 29, 2014 Presented by: Tasadduk Chowdhury Problem We address the problem of recognizing 3D objects based on various
3D Object Recognition using Multiclass SVM-KNN R. Muralidharan, C. Chandradekar April 29, 2014 Presented by: Tasadduk Chowdhury Problem We address the problem of recognizing 3D objects based on various
A New Algorithm for Shape Detection
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 19, Issue 3, Ver. I (May.-June. 2017), PP 71-76 www.iosrjournals.org A New Algorithm for Shape Detection Hewa
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 19, Issue 3, Ver. I (May.-June. 2017), PP 71-76 www.iosrjournals.org A New Algorithm for Shape Detection Hewa
CSE 152 Lecture 7. Intro Computer Vision
 Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 7 Binary Tracking for Robot Control Binary System Summary 1. Acquire images and binarize (tresholding, color labels, etc.). 2. Possibly clean up image using
Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 7 Binary Tracking for Robot Control Binary System Summary 1. Acquire images and binarize (tresholding, color labels, etc.). 2. Possibly clean up image using
Active contour: a parallel genetic algorithm approach
 id-1 Active contour: a parallel genetic algorithm approach Florence Kussener 1 1 MathWorks, 2 rue de Paris 92196 Meudon Cedex, France Florence.Kussener@mathworks.fr Abstract This paper presents an algorithm
id-1 Active contour: a parallel genetic algorithm approach Florence Kussener 1 1 MathWorks, 2 rue de Paris 92196 Meudon Cedex, France Florence.Kussener@mathworks.fr Abstract This paper presents an algorithm
Distributed Algorithms. Image and Video Processing
 Chapter 5 Object Recognition Distributed Algorithms for Motivation Requirements Overview Object recognition via Colors Shapes (outlines) Textures Movements Summary 2 1 Why object recognition? Character
Chapter 5 Object Recognition Distributed Algorithms for Motivation Requirements Overview Object recognition via Colors Shapes (outlines) Textures Movements Summary 2 1 Why object recognition? Character
Schedule for Rest of Semester
 Schedule for Rest of Semester Date Lecture Topic 11/20 24 Texture 11/27 25 Review of Statistics & Linear Algebra, Eigenvectors 11/29 26 Eigenvector expansions, Pattern Recognition 12/4 27 Cameras & calibration
Schedule for Rest of Semester Date Lecture Topic 11/20 24 Texture 11/27 25 Review of Statistics & Linear Algebra, Eigenvectors 11/29 26 Eigenvector expansions, Pattern Recognition 12/4 27 Cameras & calibration
Signature Based Document Retrieval using GHT of Background Information
 2012 International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition Signature Based Document Retrieval using GHT of Background Information Partha Pratim Roy Souvik Bhowmick Umapada Pal Jean Yves Ramel
2012 International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition Signature Based Document Retrieval using GHT of Background Information Partha Pratim Roy Souvik Bhowmick Umapada Pal Jean Yves Ramel
