Lecture 03. Fundamentals of Lidar Remote Sensing (1)
|
|
|
- Delphia Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 03. Fundamentals of Lidar Remote Sensing (1) q Introduction q History from searchlight to modern lidar q Various modern lidars q Determination of Altitude and Range q Summary and Questions 1
2 Introduction: Lidar q LIDAR is the acronym of Light Detection And Ranging -- laser radar in light frequency range or optical radar. q Although lidar and radar share similar detection principles, large differences exist in the physical processes, the treatment approaches, and the system hardware, due to the huge difference in the radiation frequencies used. q Lidar uses the concept of photons, while radar applies the concept of electromagnetic waves. q Lidar started in the pre-laser times in 1930s with searchlight beams, and then quickly evolved to modern lidars using nano-second laser pulses. q Lidar development has been and is strongly connected with progress in optical and electronic technology, especially laser technology. Lidar has always been both a source and beneficiary of technological innovations. 2
3 LIDAR History: Searchlight Modern Lidar Δz R = c Δt 2 z CW Light Receiver Pulsed Laser A Bistatic Configuration Monostatic Configuration CW searchlight ns laser pulse 3
4 History: Searchlight Lidar q Hulburt [1937] pioneered the aerosol measurements using the cw searchlight technique, who photographed the searchlight beam to 10 km. q Johnson [1939] followed a proposal of Tuve et al. [1935] and modulated the searchlight beam with a mechanical shutter rotating at 10 cycles per second. Scattering to a height of 34 km was measured with good agreement between theory and experiment above 8 km. q Elterman [1951, 1954, 1966] pushed the atmospheric study using searchlight to a high level and made practical devices. q The idea of using cw light source for lidar has reoccurred in modern time when certain cw lasers become available with high power options. 4
5 Lidar Started with Searchlight q Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) actually started with using the CW searchlights to measure stratospheric aerosols and molecular density in 1930s, well before the first (ruby) laser was invented in Atmospheric aerosol and density measurements using searchlight tech. I scatter n atmos Scattering light intensity is proportional to the atmosphere density in the aerosol free region CW Light Receiver 5
6 Searchlight Lidar θ T = 75! θ R = 0! 57! H T =1.39km H R = 2.76km d = 30.2km h = 2.76km 35.3km Transmitter (Projector) Angle fixed h = d tan(θ T ) tan(θ R ) + H T tan(θ R ) + H R tan(θ T ) tan(θ T ) + tan(θ R ) d h [Elterman, Applied Optics, 1966] Receiver (Collector) Angle scanning (3.1) 6
7 Photographing vs. Modulation -- DC detection vs. AC detection S 2 B B 2 I S2 I B2 SNR = I S2 I B2 SNR = A S2 A B2 >>1 S 1 B 1 I S1 I B1 Although night-sky may still have quite strong background (DC), its AC component at the modulation frequency is very small, while the searchlight is much stronger at the modulation frequency. Therefore, the AC detection of modulated searchlight dramatically improves the SNR, resulting in higher detection range. 7
8 Density measured by searchlight Elterman [1951] 8
9 CCD-Imaging Lidar with Similar Idea q Modern CCD-imaging lidar utilizes an similar idea as the searchlight lidar. q The bistatic lidar allows cw lasers to be used as the transmitter sources. 9
10 History: Modern Lidar q The first laser - a ruby laser was invented in 1960 by Schawlow and Townes [1958] (fundamental work) and Maiman [1960] (construction). q The first giant-pulse technique (Q-Switch) was invented by McClung and Hellwarth [1962]. q The first laser studies of the atmosphere were undertaken by Fiocco and Smullin [1963] for upper region and by Ligda [1963] for troposphere. q Following this, great strides were made both in the development of lidar technologies and instrumentation, and in the sophistication of their applications. q There are two major categories of lidar: one is to detect atmospheric properties (atmospheric lidars) and another is to detect non-atmosphere objects let s call them target lidars. 10
11 Modern Lidar: Atmosphere Lidar q The first application of lidar was the detection of atmospheric aerosols and density. Basically, it is to know whether there are aerosols/density in the regions and how much. However, the composition of atmosphere cannot be told, because only the scattering intensity was detected but nothing about the spectra. q An important advance in lidar was the recognition that the spectra of the detected radiation contained highly specific information related to the species, which could be used to determine the composition of the object region. q Furthermore, the utilization of Doppler effect and Boltzmann distribution lead to more sophisticated spectral analysis for wind and temperature measurements. 11
12 Lidar Observations of Cosmic Dust Catching Meteors during Leonid 1998 Profile on an Fe meteor trail measured by lidar [Chu et al., GRL, 2000b] Still a big debate on the daily mass input of meteor to the Earth : from 2 to 300 tonnes. 12
13 Modern Lidar Advancement q The broad selection of laser wavelengths became available and some lasers could be precisely tuned to specific frequencies. Highspectral-resolution filters became available along with modern data acquisition and processing technology. All these advancements enhanced the effective spectral analysis of the absorption features of objects and the returned radiation from objects. q This ability added a new dimension to remote sensing and made possible an extraordinary variety of applications, ranging from probing of the trace-constituent distribution as well as temperature and wind in the upper atmosphere (resonance fluorescence lidar), to lower atmosphere constituents (differential absorption lidar and Raman lidar), boundary layers, wind and temperature (coherent Doppler lidar and direction-detection lidar), to airborne chlorophyll mapping of the oceans to establish rich fishing areas and multiple species detection (fluorescence lidar, white light lidar, and optical comb lidar, in combination with spectroscopic analyzers). 13
14 Atmosphere Lidar 120 MSIS90 Temperature Altitude (km) Na Fluorescence Mesopause Stratopause Rayleigh Scattering Tropopause Temperature (K) Thermosphere Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere Resonant Fluorescence From Metal Atoms Rayleigh Scattering From Air Molecules Mie Scattering From Aerosols Range Determined From Time-of-Flight: R = c Δt / 2 14
15 Typical Atmosphere Lidar Profile 15
16 Modern Lidar: Target Lidar q Besides atmosphere, our environment includes many other things, like the solid earth, cryosphere, hydrosphere, and non-gas-phase objects on the earth, in the ocean, and in the air (e.g., plants, oil, buildings) etc. Study of our environment demands good measurement technologies and approaches for measurements in all sorts of occasions. Therefore, lidar technology for target (anything other than gas phase objects) detection is important and highly demanded. q Two main categories for target lidars: (1) lidars for ranging (laser range finder, laser altimeter) and (2) lidars for species identification (laser-induced-fluorescence lidar). q Lidar has two major functions: one is to identify species and measure their properties like density along with environmental conditions like temperature and wind, etc. along with their range distributions, and another is to determine the range/altitude very precisely. 16
17 Laser Range Finder q Laser range finder belongs to the second type, mainly concerning about the range information. q The time-of-flight information from a lidar system can be used for laser rangefinding / laser altimetry from airborne or spaceborne platforms to measure the heights of surfaces with high resolution and accuracy. q Downward-pointing laser systems were operated in a mode where surface scattering and reflection represented the dominant form of interaction. q The reflected pulses from the solid surface (earth ground, ice sheet, vegetations, etc) dominant the return signals, which allow a determination of the time-of-flight with much higher resolution than the pulse duration time. 17
18 Laser Altimeter 18
19 Lidar for Hydrosphere 19
20 Laser Altimeter vs Radar Altimeter Lidar has much better resolution and precision. 20
21 Fluorescence Lidar q A notable advance was made with the realization that use of a short-wavelength laser could broaden the spectrum of applications, as a result of laser-induced fluorescence, and led to the development of a new form of remote sensor laser fluorosensor or fluorescence lidar. q The fluorescence signal could indicate the presence of high organic contamination and enable the dispersion of various kinds of effluent plumes to be remotely mapped. q Fluorescence lidar has also been used to detect insects and birds, as reported at the 25 th International Laser Radar Conference (ILRC) in St. Petersburg, Russia, at the 26 th ILRC in Porto Heli, Greece, and at the 27 th ILRC in New York, USA. q Using fluorescence lidar to detect organic materials in the environment is finding its applications in military and defense. 21
22 Scenarios for Fluorescence Lidar Aquatic monitoring Via folding mirror Vegetation Monitoring Airborne Fluorescence 22
23 Detection of Historic Monument 23
24 Determination of Altitude and Range q Searchlight lidar, cw laser lidar, and CCD-imaging lidar: determine altitude through the geometry calculation. h = d tan(θ T ) tan(θ R ) + H T tan(θ R ) + H R tan(θ T ) tan(θ T ) + tan(θ R ) (3.1) h Pseudo-random coding has been proposed for lidar employing cw laser, in analogy with radar technique, along with various ways of simulating pulses d 24
25 Range Determination from TOF (Distributed Scatters) q Modern atmosphere lidars: Due to the use of nanosecond pulse lasers, the range can be determined by the time-offlight through equation R = c Δt/2, where c is the light speed in the medium, Δt is the time-of-flight, and 2 for the round-trip of the photons traveled. q Because atmospheric scatters are distributed sources, i.e., scattered signals are continuous, the ultimate resolution of range determination is limited by the pulse duration time τ. q Ultimate resolution: ΔR = c τ/2 q For example, a 5-ns pulse gives 75 cm as the highest resolution for an atmospheric lidar. 25
26 More on TOF Range Determination q When scatters are continuously distributed, the ultimate resolution of range determination is limited by the pulse duration time τ: ΔR = c τ/2. q The distinct peak due to the strong reflection of light from surface or target, the range resolution can be significantly improved by digitizing the return pulse and compare shape. How to understand these statements? 115 (b) Fe Density at 8:54:26 (UT) on 11 August 2010 τ A pulse with long duration can be divided into many narrow pulses with sequentially delayed start times. Altitude (km) Fe Density (cm 3 ) Meteor Trail 26
27 LIDAR REMOTE SENSING PROF. XINZHAO CHU CU-BOULDER, SPRING 2016 More on TOF Range Determination A meteor head echo recorded by Arecibo 430-MHz radar with a 45 µs pulse (min ΔR = 6.75 km) 27
28 Range Determination from TOF (Hard Target or Distinct Peak) q Target lidar - laser altimeter: Distinct peak coming from the reflection of surfaces allows a more precise measurement of the time-of-flight through rising edge or peak comparison, thus enabling higher resolution than the pulse duration limitation. q For example, a laser altimeter using 5-ns pulse duration can have better than 5 cm resolution and accuracy. q Polarization lidar technique may help to further improve the time/range resolution under certain conditions. For example, in detection of a water body depth, if the water surface and bottom have different reflection properties, e.g., in terms of polarization, the detection of returned photons different properties (e.g., polarization) in two channels can help resolve the depth in a much finer scale. 28
29 Laser Altimeter and Ranging q For target lidar (e.g., laser altimeter), the distinct peak due to the strong reflection of light from surface or target, the range resolution can be significantly improved by digitizing the return pulse and compare shape. q The resolution is now determined by the resolution of the timer for recording pulses, instead of the pulse duration width. By computing the centroid, the resolution can be further improved. Altitude = Platform Base Altitude - Range ± Interference of aerosols and clouds 29
30 Summary (1) q LIDAR actually started with CW searchlight using geometry to determine altitude. The invention of lasers pushed lidar to a whole new level -- modern laser remote sensing. The time-of-flight of a short pulse is used to precisely determine range and altitude. q Modern lidars have various formats from numerous atmosphere lidars to target lidars. Here target lidars refer to lidars that detect non-atmosphere objects, including hydrospheric lidar, fluorescence lidar and laser rangefinder like laser altimeter. q Modern lidars utilize different approaches to determine altitude and range precisely: (1) Geometry for searchlight or most cw lidars; (2) Time of flight for ns pulse atmosphere lidar; (3) Time of flight and digitized pulse shape comparison for laser range finder and laser altimeter. (4) Multiple channels of time of flight to determine the difference in time of flight, e.g., for shallow-water hydrology lidar to determine depth. (5) Focusing and scanning laser beam longitudinally to determine the range for CW coherent Doppler lidar. 30
31 Summary (2) q Applications of spectroscopy knowledge and laser technology to lidar are the two main drivers that have significantly advanced the lidar field and are still driving the lidar innovation. You are encouraged to study fundamentals of spectroscopy. q This class will provide qualitative overview of all types of lidars, and in the same time focus on quantitative analysis of several key lidars, like resonance fluorescence lidar, wind lidar, laser altimeter, polarization lidar for aerosol/cloud detection, etc. How to understand these statements? How to derive the altitude from geometry? q When scatters are continuously distributed, the ultimate resolution of range determination is limited by the pulse duration time τ: ΔR = c τ/2. Related Reading Materials Chapter 1 of Laser Remote Sensing textbook Chapter 5. Sections 5.1 and Chapter 8. Sections 8.8 and 8.9 Chapter 9. Section
Lecture 24. Lidar Simulation
 Lecture 24. Lidar Simulation q Introduction q Lidar Modeling via Lidar Simulation & Error Analysis q Functions of Lidar Simulation and Error Analysis q How to Build up Lidar Simulation? q Range-resolved
Lecture 24. Lidar Simulation q Introduction q Lidar Modeling via Lidar Simulation & Error Analysis q Functions of Lidar Simulation and Error Analysis q How to Build up Lidar Simulation? q Range-resolved
Lecture 04. Fundamentals of Lidar Remote Sensing (2)
 Lecture 04. Fundamentals of Lidar Remote Sensing (2) Lidar Equation Introduction Physical Picture of Lidar Equation Fundamental Lidar Equation Different Forms of Lidar Equation Illustration of Lidar Equation
Lecture 04. Fundamentals of Lidar Remote Sensing (2) Lidar Equation Introduction Physical Picture of Lidar Equation Fundamental Lidar Equation Different Forms of Lidar Equation Illustration of Lidar Equation
Lecture 09. Lidar Simulation and Error Analysis Overview (1)
 Lecture 09. Lidar Simulation and Error Analysis Overview (1) Introduction Lidar Modeling via Lidar Simulation & Error Analysis Functions of Lidar Simulation and Error Analysis How to Build up Lidar Simulation?
Lecture 09. Lidar Simulation and Error Analysis Overview (1) Introduction Lidar Modeling via Lidar Simulation & Error Analysis Functions of Lidar Simulation and Error Analysis How to Build up Lidar Simulation?
Lecture 13.1: Airborne Lidar Systems
 Lecture 13.1: Airborne Lidar Systems 1. Introduction v The main advantages of airborne lidar systems are that they expand the geographical range of studies beyond those possible by surface-based fixed
Lecture 13.1: Airborne Lidar Systems 1. Introduction v The main advantages of airborne lidar systems are that they expand the geographical range of studies beyond those possible by surface-based fixed
Lecture 05. First Example: A Real Lidar
 Lecture 05. First Example: A Real Lidar Brief review of lidar basics K Doppler lidar system architecture K lidar signal estimate from lidar equation Comparison of estimate to reality Summary Review of
Lecture 05. First Example: A Real Lidar Brief review of lidar basics K Doppler lidar system architecture K lidar signal estimate from lidar equation Comparison of estimate to reality Summary Review of
Claus Weitkamp Editor. Lidar. Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere. Foreword by Herbert Walther. With 162 Ulustrations.
 Claus Weitkamp Editor Lidar Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere Foreword by Herbert Walther With 162 Ulustrations 4Q Springer Contents Foreword Preface List of Contributors v vii xix
Claus Weitkamp Editor Lidar Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere Foreword by Herbert Walther With 162 Ulustrations 4Q Springer Contents Foreword Preface List of Contributors v vii xix
1.Rayleigh and Mie scattering. 2.Phase functions. 4.Single and multiple scattering
 5 November 2014 Outline 1.Rayleigh and Mie scattering 2.Phase functions 3.Extinction 4.Single and multiple scattering Luca Lelli luca@iup.physik.uni-bremen.de Room U2080 Phone 0421.218.62097 Scattering
5 November 2014 Outline 1.Rayleigh and Mie scattering 2.Phase functions 3.Extinction 4.Single and multiple scattering Luca Lelli luca@iup.physik.uni-bremen.de Room U2080 Phone 0421.218.62097 Scattering
Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR
 Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR ALS / LIDAR OUTLINE Laser remote sensing background Basic components of an ALS/LIDAR system Two distinct families of ALS systems Waveform Discrete Return
Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR ALS / LIDAR OUTLINE Laser remote sensing background Basic components of an ALS/LIDAR system Two distinct families of ALS systems Waveform Discrete Return
Lecture 13. Lidar Data Inversion
 Lecture 13. Lidar Data Inversion Review Doppler lidar architecture Daytime capability of Na Doppler lidar Introduction Common raw data format Basic ideas (clues) for data inversion Preprocess Main process
Lecture 13. Lidar Data Inversion Review Doppler lidar architecture Daytime capability of Na Doppler lidar Introduction Common raw data format Basic ideas (clues) for data inversion Preprocess Main process
GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2
 GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Data Quality Radiometric Distortion Radiometric Error Correction Relevant reading: Richards, sections 2.1 2.8; 2.10.1 2.10.3 Data Quality/Resolution Spatial
GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Data Quality Radiometric Distortion Radiometric Error Correction Relevant reading: Richards, sections 2.1 2.8; 2.10.1 2.10.3 Data Quality/Resolution Spatial
Using LiDAR for Classification and
 Using LiDAR for Classification and Recognition of Particulate Matter in the Atmosphere M. Elbakary, K. Iftekharuddin, and K. AFRIFA ECE Dept., Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA Outline Goals of the
Using LiDAR for Classification and Recognition of Particulate Matter in the Atmosphere M. Elbakary, K. Iftekharuddin, and K. AFRIFA ECE Dept., Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA Outline Goals of the
Lecture 14. Lidar Data Inversion and Sensitivity Analysis
 Lecture 14. Lidar Data Inversion and Sensitivity Analysis Data inversion process Nonlinearity of PMT and discriminator More considerations for Na Doppler lidar Definition of sensitivity Summary Office
Lecture 14. Lidar Data Inversion and Sensitivity Analysis Data inversion process Nonlinearity of PMT and discriminator More considerations for Na Doppler lidar Definition of sensitivity Summary Office
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Physics 4C Chapter 33: Electromagnetic Waves
 Physics 4C Chapter 33: Electromagnetic Waves Our greatest glory is not in never failing, but in rising up every time we fail. Ralph Waldo Emerson If you continue to do what you've always done, you'll continue
Physics 4C Chapter 33: Electromagnetic Waves Our greatest glory is not in never failing, but in rising up every time we fail. Ralph Waldo Emerson If you continue to do what you've always done, you'll continue
Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components.
 Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components. Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.A Hwk. Pts.: / 18 Unit 5.A Lab
Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components. Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.A Hwk. Pts.: / 18 Unit 5.A Lab
Option G 1: Refraction
 Name: Date: Option G 1: Refraction 1. The table below relates to the electromagnetic spectrum. Complete the table by stating the name of the region of the spectrum and the name of a possible source of
Name: Date: Option G 1: Refraction 1. The table below relates to the electromagnetic spectrum. Complete the table by stating the name of the region of the spectrum and the name of a possible source of
CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS
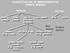 CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS PASSIVE ACTIVE DIGITAL CAMERA THERMAL (e.g. TIMS) VIDEO CAMERA MULTI- SPECTRAL SCANNERS VISIBLE & NIR MICROWAVE HYPERSPECTRAL (e.g. AVIRIS) SLAR Real Aperture
CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS PASSIVE ACTIVE DIGITAL CAMERA THERMAL (e.g. TIMS) VIDEO CAMERA MULTI- SPECTRAL SCANNERS VISIBLE & NIR MICROWAVE HYPERSPECTRAL (e.g. AVIRIS) SLAR Real Aperture
Development and Applications of an Interferometric Ground-Based SAR System
 Development and Applications of an Interferometric Ground-Based SAR System Tadashi Hamasaki (1), Zheng-Shu Zhou (2), Motoyuki Sato (2) (1) Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Tohoku University Aramaki
Development and Applications of an Interferometric Ground-Based SAR System Tadashi Hamasaki (1), Zheng-Shu Zhou (2), Motoyuki Sato (2) (1) Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Tohoku University Aramaki
Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1)
 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic sensors, infra-red sensors
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic sensors, infra-red sensors
Chapter 24. Geometric optics. Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24
 Chapter 24 Geometric optics Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24 A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted of tiny particles
Chapter 24 Geometric optics Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24 A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted of tiny particles
Basic Waves, Sound & Light Waves, and the E & M Spectrum
 Basic Waves, Sound & Light Waves, and the E & M Spectrum 1. What are the amplitude and wavelength of the wave shown below? A) amplitude = 0.10 m, wavelength = 0.30 m B) amplitude = 0.10 m, wavelength =
Basic Waves, Sound & Light Waves, and the E & M Spectrum 1. What are the amplitude and wavelength of the wave shown below? A) amplitude = 0.10 m, wavelength = 0.30 m B) amplitude = 0.10 m, wavelength =
Airborne LiDAR Data Acquisition for Forestry Applications. Mischa Hey WSI (Corvallis, OR)
 Airborne LiDAR Data Acquisition for Forestry Applications Mischa Hey WSI (Corvallis, OR) WSI Services Corvallis, OR Airborne Mapping: Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) Thermal Infrared Imagery 4-Band
Airborne LiDAR Data Acquisition for Forestry Applications Mischa Hey WSI (Corvallis, OR) WSI Services Corvallis, OR Airborne Mapping: Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) Thermal Infrared Imagery 4-Band
ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning
 1 ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning Petri Rönnholm Aalto University 2 Learning objectives To recognize applications of laser scanning To understand principles
1 ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning Petri Rönnholm Aalto University 2 Learning objectives To recognize applications of laser scanning To understand principles
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
LASERS FOR ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTATION
 LASERS FOR ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTATION CW Lasers (Broad and Narrow Spectrum) Nanosecond SLM Lasers Accessories ADVANTAGES One size One control interface One voltage (+5 VDC) One software Many wavelengths
LASERS FOR ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTATION CW Lasers (Broad and Narrow Spectrum) Nanosecond SLM Lasers Accessories ADVANTAGES One size One control interface One voltage (+5 VDC) One software Many wavelengths
Improvements to the SHDOM Radiative Transfer Modeling Package
 Improvements to the SHDOM Radiative Transfer Modeling Package K. F. Evans University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado W. J. Wiscombe National Aeronautics and Space Administration Goddard Space Flight Center
Improvements to the SHDOM Radiative Transfer Modeling Package K. F. Evans University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado W. J. Wiscombe National Aeronautics and Space Administration Goddard Space Flight Center
LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law
 Lectures Page 1 Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law Understand when the ray model of light is applicable. Be able to apply Snell's Law of Refraction to any system.
Lectures Page 1 Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law Understand when the ray model of light is applicable. Be able to apply Snell's Law of Refraction to any system.
10/5/09 1. d = 2. Range Sensors (time of flight) (2) Ultrasonic Sensor (time of flight, sound) (1) Ultrasonic Sensor (time of flight, sound) (2) 4.1.
 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Range Sensors (time of flight) (2) arge range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Range Sensors (time of flight) (2) arge range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic
Chapter 38. Diffraction Patterns and Polarization
 Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Modeling the Interaction of a Laser Target Detection Device with the Sea
 Modeling the Interaction of a Laser Target Detection Device with the Sea Gary Buzzard, Thales Missile Electronics Proximity Fuze Product Technical Manager Content Low Level & Embedded Threats TDD Sensor
Modeling the Interaction of a Laser Target Detection Device with the Sea Gary Buzzard, Thales Missile Electronics Proximity Fuze Product Technical Manager Content Low Level & Embedded Threats TDD Sensor
Sensor technology for mobile robots
 Laser application, vision application, sonar application and sensor fusion (6wasserf@informatik.uni-hamburg.de) Outline Introduction Mobile robots perception Definitions Sensor classification Sensor Performance
Laser application, vision application, sonar application and sensor fusion (6wasserf@informatik.uni-hamburg.de) Outline Introduction Mobile robots perception Definitions Sensor classification Sensor Performance
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer uses the interference of two reflected waves The third, beamsplitting, mirror is partially reflecting ( half silvered, except it s a thin Aluminum
Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer uses the interference of two reflected waves The third, beamsplitting, mirror is partially reflecting ( half silvered, except it s a thin Aluminum
PY212 Lecture 25. Prof. Tulika Bose 12/3/09. Interference and Diffraction. Fun Link: Diffraction with Ace Ventura
 PY212 Lecture 25 Interference and Diffraction Prof. Tulika Bose 12/3/09 Fun Link: Diffraction with Ace Ventura Summary from last time The wave theory of light is strengthened by the interference and diffraction
PY212 Lecture 25 Interference and Diffraction Prof. Tulika Bose 12/3/09 Fun Link: Diffraction with Ace Ventura Summary from last time The wave theory of light is strengthened by the interference and diffraction
A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere
 Spring Conference on Computer Graphics 00 A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere Jaroslav Sloup Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague
Spring Conference on Computer Graphics 00 A Survey of Modelling and Rendering of the Earth s Atmosphere Jaroslav Sloup Department of Computer Science and Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11. Reflection and refraction
 Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
LASERS FOR ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTATION
 CW Lasers Combiners Q-switch Lasers >20 s MM/SM/PM fiber Single-frequency options 405 nm to 660 nm 4 wavelengths Open beam or Fiber 1029 nm / 514.5 nm High pulse energy Single Longitudinal Mode LASERS
CW Lasers Combiners Q-switch Lasers >20 s MM/SM/PM fiber Single-frequency options 405 nm to 660 nm 4 wavelengths Open beam or Fiber 1029 nm / 514.5 nm High pulse energy Single Longitudinal Mode LASERS
Tutorial: Instantaneous Measurement of M 2 Beam Propagation Ratio in Real-Time
 Tutorial: Instantaneous Measurement of M 2 Beam Propagation Ratio in Real-Time By Allen M. Cary, Jeffrey L. Guttman, Razvan Chirita, Derrick W. Peterman, Photon Inc A new instrument design allows the M
Tutorial: Instantaneous Measurement of M 2 Beam Propagation Ratio in Real-Time By Allen M. Cary, Jeffrey L. Guttman, Razvan Chirita, Derrick W. Peterman, Photon Inc A new instrument design allows the M
Introduction to Diffraction Gratings
 Introduction to Diffraction Diffraction (Ruled and Holographic) Diffraction gratings can be divided into two basic categories: holographic and ruled. A ruled grating is produced by physically forming grooves
Introduction to Diffraction Diffraction (Ruled and Holographic) Diffraction gratings can be divided into two basic categories: holographic and ruled. A ruled grating is produced by physically forming grooves
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Light and Electromagnetic Waves. Honors Physics
 Light and Electromagnetic Waves Honors Physics Electromagnetic Waves EM waves are a result of accelerated charges and disturbances in electric and magnetic fields (Radio wave example here) As electrons
Light and Electromagnetic Waves Honors Physics Electromagnetic Waves EM waves are a result of accelerated charges and disturbances in electric and magnetic fields (Radio wave example here) As electrons
Design and Implementation of Data Models & Instrument Scheduling of Satellites in a Space Based Internet Emulation System
 Design and Implementation of Data Models & Instrument Scheduling of Satellites in a Space Based Internet Emulation System Karthik N Thyagarajan Masters Thesis Defense December 20, 2001 Defense Committee:
Design and Implementation of Data Models & Instrument Scheduling of Satellites in a Space Based Internet Emulation System Karthik N Thyagarajan Masters Thesis Defense December 20, 2001 Defense Committee:
The 4A/OP model: from NIR to TIR, new developments for time computing gain and validation results within the frame of international space missions
 ITSC-21, Darmstadt, Germany, November 29th-December 5th, 2017 session 2a Radiative Transfer The 4A/OP model: from NIR to TIR, new developments for time computing gain and validation results within the
ITSC-21, Darmstadt, Germany, November 29th-December 5th, 2017 session 2a Radiative Transfer The 4A/OP model: from NIR to TIR, new developments for time computing gain and validation results within the
Chapter 22. Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Chapter 22 Reflection and Refraction of Light Nature of Light Light has a dual nature. Particle Wave Wave characteristics will be discussed in this chapter. Reflection Refraction These characteristics
Chapter 22 Reflection and Refraction of Light Nature of Light Light has a dual nature. Particle Wave Wave characteristics will be discussed in this chapter. Reflection Refraction These characteristics
College Physics 150. Chapter 25 Interference and Diffraction
 College Physics 50 Chapter 5 Interference and Diffraction Constructive and Destructive Interference The Michelson Interferometer Thin Films Young s Double Slit Experiment Gratings Diffraction Resolution
College Physics 50 Chapter 5 Interference and Diffraction Constructive and Destructive Interference The Michelson Interferometer Thin Films Young s Double Slit Experiment Gratings Diffraction Resolution
THE USE OF TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING FOR MEASUREMENTS IN SHALLOW-WATER: CORRECTION OF THE 3D COORDINATES OF THE POINT CLOUD
 Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Published as: Deruyter, G., Vanhaelst, M., Stal, C., Glas, H., De Wulf, A. (2015). The use of terrestrial laser scanning for measurements in shallow-water: correction
Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Published as: Deruyter, G., Vanhaelst, M., Stal, C., Glas, H., De Wulf, A. (2015). The use of terrestrial laser scanning for measurements in shallow-water: correction
Solid-State Hybrid LiDAR for Autonomous Driving Product Description
 Solid-State Hybrid LiDAR for Autonomous Driving Product Description What is LiDAR Sensor Who is Using LiDARs How does LiDAR Work Hesai LiDAR Demo Features Terminologies Specifications What is LiDAR A LiDAR
Solid-State Hybrid LiDAR for Autonomous Driving Product Description What is LiDAR Sensor Who is Using LiDARs How does LiDAR Work Hesai LiDAR Demo Features Terminologies Specifications What is LiDAR A LiDAR
Midterm Review Exam. 1. The diagram below represents a transverse wave.
 Midterm Review Exam Name: 1. The diagram below represents a transverse wave. 4. The graph below represents the displacement of a particle in a medium over a period of time. The wavelength of the wave is
Midterm Review Exam Name: 1. The diagram below represents a transverse wave. 4. The graph below represents the displacement of a particle in a medium over a period of time. The wavelength of the wave is
Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2. Sources of light
 We are here Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2 Some history of technology How vision works What is light Wavelength and Frequency: c = f λ Scientific notation and metric units Electromagnetic spectrum Transmission
We are here Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2 Some history of technology How vision works What is light Wavelength and Frequency: c = f λ Scientific notation and metric units Electromagnetic spectrum Transmission
Course Outline (1) #6 Data Acquisition for Built Environment. Fumio YAMAZAKI
 AT09.98 Applied GIS and Remote Sensing for Disaster Mitigation #6 Data Acquisition for Built Environment 9 October, 2002 Fumio YAMAZAKI yamazaki@ait.ac.th http://www.star.ait.ac.th/~yamazaki/ Course Outline
AT09.98 Applied GIS and Remote Sensing for Disaster Mitigation #6 Data Acquisition for Built Environment 9 October, 2002 Fumio YAMAZAKI yamazaki@ait.ac.th http://www.star.ait.ac.th/~yamazaki/ Course Outline
PGx01 series. High Peak Power. Available models
 Picosecond Lasers Nanosecond Lasers Nanosecond Tunable Lasers High Energy Lasers Ultrafast Fiber Lasers Other Ekspla Products PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Travelling Wave Optical Parametric Generators (TWOPG) are
Picosecond Lasers Nanosecond Lasers Nanosecond Tunable Lasers High Energy Lasers Ultrafast Fiber Lasers Other Ekspla Products PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Travelling Wave Optical Parametric Generators (TWOPG) are
Polarization of Light
 From http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/optics/lightandcolor/polarization.html by Mortimer Abramowitz, Shannon Neaves and Michael Davidson and http://technology.niagarac.on.ca/courses/tech238g/lasers.html by
From http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/optics/lightandcolor/polarization.html by Mortimer Abramowitz, Shannon Neaves and Michael Davidson and http://technology.niagarac.on.ca/courses/tech238g/lasers.html by
A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean
 1 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean LONG-TERM GOALS Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
1 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean LONG-TERM GOALS Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering
Retrieval of optical and microphysical properties of ocean constituents using polarimetric remote sensing
 Retrieval of optical and microphysical properties of ocean constituents using polarimetric remote sensing Presented by: Amir Ibrahim Optical Remote Sensing Laboratory, The City College of the City University
Retrieval of optical and microphysical properties of ocean constituents using polarimetric remote sensing Presented by: Amir Ibrahim Optical Remote Sensing Laboratory, The City College of the City University
LASERS FOR ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTATION
 LASERS FOR ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTATION CW Lasers (Broad and Narrow Spectrum) Nanosecond SLM Lasers Accessories ADVANTAGES One size One control interface One voltage (+5 VDC) One software Many wavelengths
LASERS FOR ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTATION CW Lasers (Broad and Narrow Spectrum) Nanosecond SLM Lasers Accessories ADVANTAGES One size One control interface One voltage (+5 VDC) One software Many wavelengths
Diffraction. Single-slit diffraction. Diffraction by a circular aperture. Chapter 38. In the forward direction, the intensity is maximal.
 Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Doppler Global Velocimetry: A Potential Velocity Measurement Method for General Aviation Applications
 Doppler Global Velocimetry: A Potential Velocity Measurement Method for General Aviation Applications L. Scott Miller The Wichita State University Wichita, Kansas and James F. Meyers, and Jimmy W. Usry
Doppler Global Velocimetry: A Potential Velocity Measurement Method for General Aviation Applications L. Scott Miller The Wichita State University Wichita, Kansas and James F. Meyers, and Jimmy W. Usry
Lab2: Single Photon Interference
 Lab2: Single Photon Interference Xiaoshu Chen* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester, NY, 14623 ABSTRACT The wave-particle duality of light was verified by multi and single photon
Lab2: Single Photon Interference Xiaoshu Chen* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester, NY, 14623 ABSTRACT The wave-particle duality of light was verified by multi and single photon
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
Towards a robust model of planetary thermal profiles
 Towards a robust model of planetary thermal profiles RT Equation: General Solution: RT Equation: General Solution: Extinction coefficient Emission coefficient How would you express the Source function
Towards a robust model of planetary thermal profiles RT Equation: General Solution: RT Equation: General Solution: Extinction coefficient Emission coefficient How would you express the Source function
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3. Chapter 20. Classic and Modern Optics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
1. Particle Scattering. Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes
 1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3*
 PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
Infrared Scene Simulation for Chemical Standoff Detection System Evaluation
 Infrared Scene Simulation for Chemical Standoff Detection System Evaluation Peter Mantica, Chris Lietzke, Jer Zimmermann ITT Industries, Advanced Engineering and Sciences Division Fort Wayne, Indiana Fran
Infrared Scene Simulation for Chemical Standoff Detection System Evaluation Peter Mantica, Chris Lietzke, Jer Zimmermann ITT Industries, Advanced Engineering and Sciences Division Fort Wayne, Indiana Fran
Navigation for Future Space Exploration Missions Based on Imaging LiDAR Technologies. Alexandre Pollini Amsterdam,
 Navigation for Future Space Exploration Missions Based on Imaging LiDAR Technologies Alexandre Pollini Amsterdam, 12.11.2013 Presentation outline The needs: missions scenario Current benchmark in space
Navigation for Future Space Exploration Missions Based on Imaging LiDAR Technologies Alexandre Pollini Amsterdam, 12.11.2013 Presentation outline The needs: missions scenario Current benchmark in space
DELIVERABLE 2 SPECIALIZED NOVEL SOFTWARE FOR THE ACQUISITION AND ANALYSIS OF 6 DIFFERENT LIDAR SIGNALS IN REAL TIME
 DELIVERABLE 2 SPECIALIZED NOVEL SOFTWARE FOR THE ACQUISITION AND ANALYSIS OF 6 DIFFERENT LIDAR SIGNALS IN REAL TIME Project Title : Development of a 6-wavelength LIDAR system for the retrieval of the microphysical
DELIVERABLE 2 SPECIALIZED NOVEL SOFTWARE FOR THE ACQUISITION AND ANALYSIS OF 6 DIFFERENT LIDAR SIGNALS IN REAL TIME Project Title : Development of a 6-wavelength LIDAR system for the retrieval of the microphysical
AUTOMOTIVE ENVIRONMENT SENSORS
 AUTOMOTIVE ENVIRONMENT SENSORS Lecture 3. LIDARs Dr. Szilárd Aradi BME KÖZLEKEDÉSMÉRNÖKI ÉS JÁRMŰMÉRNÖKI KAR 32708-2/2017/INTFIN SZÁMÚ EMMI ÁLTAL TÁMOGATOTT TANANYAG LIDAR intro Light Detection and Ranging
AUTOMOTIVE ENVIRONMENT SENSORS Lecture 3. LIDARs Dr. Szilárd Aradi BME KÖZLEKEDÉSMÉRNÖKI ÉS JÁRMŰMÉRNÖKI KAR 32708-2/2017/INTFIN SZÁMÚ EMMI ÁLTAL TÁMOGATOTT TANANYAG LIDAR intro Light Detection and Ranging
SIMULATED LIDAR WAVEFORMS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF LIGHT PROPAGATION THROUGH A TREE CANOPY
 SIMULATED LIDAR WAVEFORMS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF LIGHT PROPAGATION THROUGH A TREE CANOPY Angela M. Kim and Richard C. Olsen Remote Sensing Center Naval Postgraduate School 1 University Circle Monterey, CA
SIMULATED LIDAR WAVEFORMS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF LIGHT PROPAGATION THROUGH A TREE CANOPY Angela M. Kim and Richard C. Olsen Remote Sensing Center Naval Postgraduate School 1 University Circle Monterey, CA
Chapter 37. Wave Optics
 Chapter 37 Wave Optics Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics. Sometimes called physical optics These phenomena include:
Chapter 37 Wave Optics Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics. Sometimes called physical optics These phenomena include:
Hyperspectral Remote Sensing
 Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Multi-spectral: Several comparatively wide spectral bands Hyperspectral: Many (could be hundreds) very narrow spectral bands GEOG 4110/5100 30 AVIRIS: Airborne Visible/Infrared
Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Multi-spectral: Several comparatively wide spectral bands Hyperspectral: Many (could be hundreds) very narrow spectral bands GEOG 4110/5100 30 AVIRIS: Airborne Visible/Infrared
Understanding the Propagation of Light
 [ Assignment View ] [ Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 33. The Nature and Propagation of Light Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, January 17, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after
[ Assignment View ] [ Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 33. The Nature and Propagation of Light Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, January 17, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after
UV Remote Sensing of Volcanic Ash
 UV Remote Sensing of Volcanic Ash Kai Yang University of Maryland College Park WMO Inter-comparison of Satellite-based Volcanic Ash Retrieval Algorithms Workshop June 26 July 2, 2015, Madison, Wisconsin
UV Remote Sensing of Volcanic Ash Kai Yang University of Maryland College Park WMO Inter-comparison of Satellite-based Volcanic Ash Retrieval Algorithms Workshop June 26 July 2, 2015, Madison, Wisconsin
Light and Sound. Wave Behavior and Interactions
 Light and Sound Wave Behavior and Interactions How do light/sound waves interact with matter? WORD Definition Example Picture REFLECTED REFRACTED is the change in direction of a wave when it changes speed
Light and Sound Wave Behavior and Interactions How do light/sound waves interact with matter? WORD Definition Example Picture REFLECTED REFRACTED is the change in direction of a wave when it changes speed
LECTURE 14 PHASORS & GRATINGS. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 14 PHASORS & GRATINGS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 14 2 Reading chapter 33-5 & 33-8 Phasors n Addition of two harmonic waves n Interference pattern from multiple sources n Single slit diffraction
LECTURE 14 PHASORS & GRATINGS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 14 2 Reading chapter 33-5 & 33-8 Phasors n Addition of two harmonic waves n Interference pattern from multiple sources n Single slit diffraction
Learning Objectives LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING. Sensing. Blacksburg, VA July 24 th 30 th, 2010 LiDAR: Mapping the world in 3-D Page 1
 LiDAR: Mapping the world in 3-D Val Thomas Department of Forest Resources & Environmental Conservation July 29, 2010 Learning Objectives Part 1: Lidar theory What is lidar? How does lidar work? What are
LiDAR: Mapping the world in 3-D Val Thomas Department of Forest Resources & Environmental Conservation July 29, 2010 Learning Objectives Part 1: Lidar theory What is lidar? How does lidar work? What are
Rietveld refinements collection strategies!
 Rietveld refinements collection strategies! Luca Lutterotti! Department of Materials Engineering and Industrial Technologies! University of Trento - Italy! Quality of the experiment! A good refinement,
Rietveld refinements collection strategies! Luca Lutterotti! Department of Materials Engineering and Industrial Technologies! University of Trento - Italy! Quality of the experiment! A good refinement,
Physics 11 - Waves Extra Practice Questions
 Physics - Waves xtra Practice Questions. Wave motion in a medium transfers ) energy, only ) mass, only. both mass and energy. neither mass nor energy. single vibratory disturbance that moves from point
Physics - Waves xtra Practice Questions. Wave motion in a medium transfers ) energy, only ) mass, only. both mass and energy. neither mass nor energy. single vibratory disturbance that moves from point
Class 11 Introduction to Surface BRDF and Atmospheric Scattering. Class 12/13 - Measurements of Surface BRDF and Atmospheric Scattering
 University of Maryland Baltimore County - UMBC Phys650 - Special Topics in Experimental Atmospheric Physics (Spring 2009) J. V. Martins and M. H. Tabacniks http://userpages.umbc.edu/~martins/phys650/ Class
University of Maryland Baltimore County - UMBC Phys650 - Special Topics in Experimental Atmospheric Physics (Spring 2009) J. V. Martins and M. H. Tabacniks http://userpages.umbc.edu/~martins/phys650/ Class
Optical Scattering. Analysis. Measurement and SPIE PRESS. John C. Stover THIRD EDITION. Bellingham, Washington USA
 Optical Scattering Measurement and Analysis THIRD EDITION John C. Stover SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Contents Preface to the First Edition xiii Preface to the Second Edition xv Acknowledgments
Optical Scattering Measurement and Analysis THIRD EDITION John C. Stover SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Contents Preface to the First Edition xiii Preface to the Second Edition xv Acknowledgments
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
Chapter 37. Interference of Light Waves
 Chapter 37 Interference of Light Waves Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics These phenomena include: Interference Diffraction
Chapter 37 Interference of Light Waves Wave Optics Wave optics is a study concerned with phenomena that cannot be adequately explained by geometric (ray) optics These phenomena include: Interference Diffraction
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)
 Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) http://code.google.com/creative/radiohead/ Types of aerial sensors passive active 1 Active sensors for mapping terrain Radar transmits microwaves in pulses determines
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) http://code.google.com/creative/radiohead/ Types of aerial sensors passive active 1 Active sensors for mapping terrain Radar transmits microwaves in pulses determines
High Spectral Resolution Infrared Radiance Modeling Using Optimal Spectral Sampling (OSS) Method
 High Spectral Resolution Infrared Radiance Modeling Using Optimal Spectral Sampling (OSS) Method J.-L. Moncet, G. Uymin and H. Snell 1 Parameteriation of radiative transfer equation is necessary for operational
High Spectral Resolution Infrared Radiance Modeling Using Optimal Spectral Sampling (OSS) Method J.-L. Moncet, G. Uymin and H. Snell 1 Parameteriation of radiative transfer equation is necessary for operational
Instructional Sequence for Electromagnetic Waves & Technology
 Grade Level: 7 Content and Performance Expectations Essential Question Disciplinary Core Ideas Cross Cutting Concepts Performance Expectation for Assessment Instructional Sequence for Electromagnetic Waves
Grade Level: 7 Content and Performance Expectations Essential Question Disciplinary Core Ideas Cross Cutting Concepts Performance Expectation for Assessment Instructional Sequence for Electromagnetic Waves
NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1223-7027 NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS Bogdan Stefaniţă CALIN 1, Liliana PREDA 2 We have successfully designed a
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1223-7027 NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS Bogdan Stefaniţă CALIN 1, Liliana PREDA 2 We have successfully designed a
Diffraction Diffraction occurs when light waves is passed by an aperture/edge Huygen's Principal: each point on wavefront acts as source of another
 Diffraction Diffraction occurs when light waves is passed by an aperture/edge Huygen's Principal: each point on wavefront acts as source of another circular wave Consider light from point source at infinity
Diffraction Diffraction occurs when light waves is passed by an aperture/edge Huygen's Principal: each point on wavefront acts as source of another circular wave Consider light from point source at infinity
MODULE 3. FACTORS AFFECTING 3D LASER SCANNING
 MODULE 3. FACTORS AFFECTING 3D LASER SCANNING Learning Outcomes: This module discusses factors affecting 3D laser scanner performance. Students should be able to explain the impact of various factors on
MODULE 3. FACTORS AFFECTING 3D LASER SCANNING Learning Outcomes: This module discusses factors affecting 3D laser scanner performance. Students should be able to explain the impact of various factors on
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
12/7/2012. Biomolecular structure. Diffraction, X-ray crystallography, light- and electron microscopy. CD spectroscopy, mass spectrometry
 phase difference at a given distance constructive/destructive interference Biomolecular structure. Diffraction, X-ray crystallography, light- and electron microscopy. CD spectroscopy, mass spectrometry
phase difference at a given distance constructive/destructive interference Biomolecular structure. Diffraction, X-ray crystallography, light- and electron microscopy. CD spectroscopy, mass spectrometry
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
TRiCAM APPLICATIONS KEY FEATURES. Time Resolved intensified CAMera. TRiCAM 13001A01 31/10/2013
 TRiCAM Time Resolved intensified CAMera The TRiCAM is a compact Intensified CCD camera for scientific and industrial applications that require 1) lowlight level imaging, 2) ultra-short exposures through
TRiCAM Time Resolved intensified CAMera The TRiCAM is a compact Intensified CCD camera for scientific and industrial applications that require 1) lowlight level imaging, 2) ultra-short exposures through
Particle Image Velocimetry for Fluid Dynamics Measurements
 Particle Image Velocimetry for Fluid Dynamics Measurements Lyes KADEM, Ph.D; Eng kadem@encs.concordia.ca Laboratory for Cardiovascular Fluid Dynamics MIE Concordia University Presentation - A bit of history
Particle Image Velocimetry for Fluid Dynamics Measurements Lyes KADEM, Ph.D; Eng kadem@encs.concordia.ca Laboratory for Cardiovascular Fluid Dynamics MIE Concordia University Presentation - A bit of history
Spectroscopic equipment. Multispectral Imaging
 Spectroscopic equipment Multispectral Imaging Basic spectroscopic arrangement Source Sample Analyzer Detector Sun Lamps Lasers LEDs Synchrotron Plants Forests Tissue Cells Flames Chemical compounds etc.
Spectroscopic equipment Multispectral Imaging Basic spectroscopic arrangement Source Sample Analyzer Detector Sun Lamps Lasers LEDs Synchrotron Plants Forests Tissue Cells Flames Chemical compounds etc.
Workhorse ADCP Multi- Directional Wave Gauge Primer
 Acoustic Doppler Solutions Workhorse ADCP Multi- Directional Wave Gauge Primer Brandon Strong October, 2000 Principles of ADCP Wave Measurement The basic principle behind wave the measurement, is that
Acoustic Doppler Solutions Workhorse ADCP Multi- Directional Wave Gauge Primer Brandon Strong October, 2000 Principles of ADCP Wave Measurement The basic principle behind wave the measurement, is that
Chapter 15. Light Waves
 Chapter 15 Light Waves Chapter 15 is finished, but is not in camera-ready format. All diagrams are missing, but here are some excerpts from the text with omissions indicated by... After 15.1, read 15.2
Chapter 15 Light Waves Chapter 15 is finished, but is not in camera-ready format. All diagrams are missing, but here are some excerpts from the text with omissions indicated by... After 15.1, read 15.2
1. Polarization effects in optical spectra of photonic crystals
 Speech for JASS 05. April 2005. Samusev A. 1. Polarization effects in optical spectra of photonic crystals Good afternoon. I would like to introduce myself. My name is Anton Samusev. I m a student of Saint
Speech for JASS 05. April 2005. Samusev A. 1. Polarization effects in optical spectra of photonic crystals Good afternoon. I would like to introduce myself. My name is Anton Samusev. I m a student of Saint
A Surrogate Time Series Model for the Kp Geomagnetic Index
 AEROSPACE REPORT NO. TOR-2013-00515 A Surrogate Time Series Model for the Kp Geomagnetic Index August 20, 2013 T. Paul O Brien Space Science Applications Laboratory Physical Sciences Laboratories Prepared
AEROSPACE REPORT NO. TOR-2013-00515 A Surrogate Time Series Model for the Kp Geomagnetic Index August 20, 2013 T. Paul O Brien Space Science Applications Laboratory Physical Sciences Laboratories Prepared
Reflection and Refraction of Light
 PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods
 TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, October 20 th, 2017 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, October 20 th, 2017 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
